Adherence to Intranasal Corticosteroids in Patients with Severe Asthma and Nasal Polyposis: Pharmacological and Clinical Factors Involved
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Adherence to Intranasal Corticosteroids
3.3. Pharmacological Variables and Adherence
3.4. Adherence to Inhaled Therapies and Use of Biologics
3.5. Adherence to Intranasal Corticosteroids Among Patients on Biological Therapy
3.6. Adherence and Endoscopic Sinus Surgery
3.7. Spirometry and Asthma Control
4. Discussion
Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SA | Severe asthma |
| NP | Nasal polyposis |
| INC | Intranasal corticosteroids |
| MPR | Medication possession ratio |
| CRS | Chronic rhinosinusitis |
| CRSwNP | Chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis |
| IQR | Interquartile ranges |
| ESS | Endoscopic sinus surgery |
| ACT | Asthma Control Test |
References
- Klossek, J.M.; Neukirch, F.; Pribil, C.; Jankowski, R.; Serrano, E.; Chanal, I.; El Hasnaoui, A. Prevalence of nasal polyposis in France: A cross-sectional, case-control study. Allergy 2005, 60, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, W.W.; Peters, A.T.; Hirsch, A.G.; Nordberg, C.M.; Schwartz, B.S.; Mercer, D.G.; Mahdavinia, M.; Grammer, L.C.; Hulse, K.E.; Kern, R.C.; et al. Clinical characteristics of patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps, asthma, and aspirin exacerbated respiratory disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2017, 5, 1061–1070.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stjärne, P.; Blomgren, K.; Cayé-Thomasen, P.; Salo, S.; Søderstrøm, T. The efficacy and safety of once-daily mometasone furoate nasal spray in nasal polyposis: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Acta Otolaryngol. 2006, 126, 606–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Small, C.B.; Hernandez, J.; Reyes, A.; Schenkel, E.; Damiano, A.; Stryszak, P.; Staudinger, H.; Danzig, M. Efficacy and safety of mometasone furoate nasal spray in nasal polyposis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2005, 116, 1275–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, L.Y.; Head, K.; Hopkins, C.; Philpott, C.; Burton, M.J.; Schilder, A.G.M. Different types of intranasal steroids for chronic rhinosinusitis. Cochr. Database Syst. Rev. 2016, 4, CD011993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Veen, J.; Seys, S.F.; Timmermans, M.; Levie, P.; Jorissen, M.; Fokkens, W.J.; Hellings, P.W. Real-life study showing uncontrolled rhinosinusitis after sinus surgery in a tertiary referral centre. Allergy 2017, 72, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rimmer, J.; Fokkens, W.; Chong, L.Y.; Hopkins, C. Surgical versus medical interventions for chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Cochr. Database Syst. Rev. 2014, 2014, CD006991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, R.M.; Dinnie, K.; Smith, T.L. When do the risks of repeated courses of corticosteroids exceed the risks of surgery? Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2014, 4, 871–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vashishta, R.; Soler, Z.M.; Nguyen, S.A.; Schlosser, R.J. A systematic review and meta-analysis of asthma outcomes following endoscopic sinus surgery for chronic rhinosinusitis. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2013, 3, 788–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gevaert, P.; Calus, L.; van Zele, T.; Blomme, K.; de Ruyck, N.; Bauters, W.; Hellings, P.; Brusselle, G.; De Bacquer, D.; van Cauwenberge, P.; et al. Omalizumab is effective in allergic and nonallergic patients with nasal polyps and asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 131, 110–116.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gevaert, P.; Omachi, T.A.; Corren, J.; Mullol, J.; Han, J.; Lee, S.E.; Kaufman, D.; Ligueros-Saylan, M.; Howard, M.; Zhu, R.; et al. Efficacy and safety of omalizumab in nasal polyposis: 2 randomized phase 3 trials. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 146, 595–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachert, C.; Sousa, A.R.; Lund, V.J.; Scadding, G.K.; Gevaert, P.; Nasser, S.; Durham, S.R.; Cornet, M.E.; Kariyawasam, H.H.; Gilbert, J.; et al. Reduced need for surgery in severe nasal polyposis with mepolizumab: Randomized trial. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 140, 1024–1031.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gevaert, P.; van Bruaene, N.; Cattaert, T.; van Steen, K.; van Zele, T.; Acke, F.; De Ruyck, N.; Blomme, K.; Sousa, A.R.; Marshall, R.P.; et al. Mepolizumab, a humanized anti-IL-5 mAb, as a treatment option for severe nasal polyposis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 128, 989–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachert, C.; Hellings, P.W.; Mullol, J.; Hamilos, D.L.; Gevaert, P.; Naclerio, R.M.; Joish, V.N.; Chao, J.; Mannent, L.P.; Amin, N.; et al. Dupilumab improves health-related quality of life in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis. Allergy 2020, 75, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachert, C.; Mannent, L.; Naclerio, R.M.; Mullol, J.; Ferguson, B.J.; Gevaert, P.; Hellings, P.; Jiao, L.; Wang, L.; Evans, R.R.; et al. Effect of Subcutaneous Dupilumab on Nasal Polyp Burden in Patients with Chronic Sinusitis and Nasal Polyposis: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2016, 315, 469–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachert, C.; Han, J.K.; Desrosiers, M.; Hellings, P.W.; Amin, N.; Lee, S.E.; Mullol, J.; Greos, L.S.; Bosso, J.V.; Laidlaw, T.M.; et al. Efficacy and safety of dupilumab in patients with severe chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (LIBERTY NP SINUS-24 and LIBERTY NP SINUS-52): Results from two multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group phase 3 trials. Lancet 2019, 394, 1638–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipworth, B.J.; Han, J.K.; Desrosiers, M.; Hopkins, C.; Lee, S.E.; Mullol, J.; Pfaar, O.; Li, T.; Chen, C.; Almqvist, G.; et al. Tezepelumab in Adults with Severe Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps. N. Engl. J. Med. 2025, 392, 1178–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudmik, L.; Xu, Y.; Liu, M.; Bird, C.; Kukec, E.; Quan, H. Utilization Patterns of Topical Intranasal Steroid Therapy for Chronic Rhinosinusitis: A Canadian Population-Based Analysis. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2016, 142, 1056–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, K.M.; Hoehle, L.P.; Caradonna, D.S.; Gray, S.T.; Sedaghat, A.R. Intranasal corticosteroids and saline: Usage and adherence in chronic rhinosinusitis patients. Laryngoscope 2020, 130, 852–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philpott, C.; Erskine, S.; Smith, R.; Hopkins, C.; Kara, N.; Farboud, A.; Salam, M.; Robertson, A.; Almeyda, R.; Kumar, B.; et al. Current use of baseline medical treatment in chronic rhinosinusitis: Data from the National Chronic Rhinosinusitis Epidemiology Study (CRES). Clin. Otolaryngol. 2018, 43, 509–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega-Martin, L.; Betancor, D.; Barroso, B.; Valverde-Monge, M.; Santillan, J.; Villacampa, J.M.; Sastre, J. Where Has All The Nasal Polyposis Gone? J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2021, 31, 500–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valverde-Monge, M.; Barroso, B.; Ortega-Martin, L.; Betancor, D.; Santillan, J.; Villacampa, J.M.; Sastre, J. Exploring Adherence to Treatment in Nasal Polyposis. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2022, 32, 299–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norelli, F.; Schiappoli, M.; Senna, G.; Pinter, P.; Olivieri, B.; Ottaviano, G.; De Corso, E.; Caminati, M. Adherence to Intranasal Steroids in Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyposis Prior to and during Biologic Therapy: A Neglected Matter. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Global Initiative for Asthma. Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention (2021 Update) [Internet]; GINA: Fontana, WI, USA, 2021; Available online: https://ginasthma.org/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/GINA-2024-Strategy-Report-24_05_22_WMS.pdf (accessed on 19 December 2024).
- GEMA 5.4. Spanish Guideline on the Management of Asthma [Internet]. Available online: http://www.gemasma.com (accessed on 21 June 2024).
- Granda, P.; Villamañán, E.; Carpio, C.; Laorden, D.; Sobrino, C.; Herrero, A.; Quirce, S.; Álvarez-Sala, R. Adherence to inhalers in patients with severe asthma treated with anti-interleukin-5 biologics. Farm. Hosp. 2022, 46, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Plaza, V.; Lopez-Vina, A.; Entrenas, L.M.; Fernandez-Rodriguez, C.; Melero, C.; Perez Llano, L.; Gutiérrez-Pereyra, F.; Tarragona, E.; Palomino, R.; Cosio, B.G. Differences in adherence and non-adherence behaviour patterns to inhaler devices between COPD and asthma patients. COPD J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2016, 13, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourdin, A.; Halimi, L.; Vachier, I.; Paganin, F.; Lamouroux, A.; Gouitaa, M.; Vairon, E.; Godard, P.; Chanez, P. Adherence in severe asthma. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2012, 42, 1566–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alobid, I.; Colás, C.; Castillo, J.A.; Arismendi, E.; Del Cuvillo, A.; Gómez-Outes, A.; Sastre, J.; Mullol, J.; POLINA group. Spanish Consensus on the Management of Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps (POLIposis NAsal/POLINA 2.0). J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2023, 33, 317–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laorden, D.; Hernández, I.; Domínguez-Ortega, J.; Romero, D.; Álvarez-Sala, R.; Quirce, S. A real-life cohort of mepolizumab treatment in severe eosinophilic asthma. Eur. Ann. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2024, 56, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillo Vizuete, J.A.; Sastre, J.; Del Cuvillo Bernal, A.; Picado, C.; Martínez Moragón, E.; Ignacio García, J.M.; Serrano, C.C.; Gutiérrez, F.J.Á.; Miret, J.M. Asthma, rhinitis, and nasal polyp multimorbidities. Arch. Bronconeumol. (Engl. Ed.) 2019, 55, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, E.; Wechsler, M.E.; Tran, T.N.; Heaney, L.G.; Jones, R.C.; Menzies-Gow, A.N.; Busby, J.; Jackson, D.J.; Pfeffer, P.E.; Rhee, C.K.; et al. Characterization of Severe Asthma Worldwide: Data From the International Severe Asthma Registry. Chest 2020, 157, 790–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bridgeman, M.B. Overcoming barriers to intranasal corticosteroid use in patients with uncontrolled allergic rhinitis. Integr. Pharm. Res. Pract. 2017, 6, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manjit Singh, P.K.; Krishnan, E.K.; Mat Lazim, N.; Yaacob, N.M.; Abdullah, B. Medication Adherence to Intranasal Corticosteroids in Allergic Rhinitis Patients with Comorbid Medical Conditions. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venditti, V.; Bleve, E.; Morano, S.; Filardi, T. Gender-Related Factors in Medication Adherence for Metabolic and Cardiovascular Health. Metabolites 2023, 13, 1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biffi, A.; Rea, F.; Iannaccone, T.; Filippelli, A.; Mancia, G.; Corrao, G. Sex differences in the adherence of antihypertensive drugs: A systematic review with meta-analyses. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e036418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rolnick, S.J.; Pawloski, P.A.; Hedblom, B.D.; Asche, S.E.; Bruzek, R.J. Patient characteristics associated with medication adherence. Clin. Med. Res. 2013, 11, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, E.S.; Braunwald, E.; Morrow, D.A.; Giugliano, R.P.; Antman, E.M.; Gibson, C.M.; Scirica, B.M.; Bohula, E.A.; Wiviott, S.D.; Bhatt, D.L.; et al. Sex, Permanent Drug Discontinuation, and Study Retention in Clinical Trials: Insights From the TIMI trials. Circulation 2021, 143, 685–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, B.; Dilley, M.; Anterasian, C. Biologic Therapies for Allergic Rhinitis and Nasal Polyposis. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2021, 21, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fokkens, W.J.; Viskens, A.S.; Backer, V.; Conti, D.; De Corso, E.; Gevaert, P.; Scadding, G.K.; Wagemann, M.; Bernal-Sprekelsen, M.; Chaker, A.; et al. EPOS/EUFOREA update on indication and evaluation of Biologics in Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps 2023. Rhinology 2023, 61, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristic | N = 86 |
|---|---|
| Median age | 63 (IQR 57−71) |
| Female | 60 (69.8%) |
| Comorbidity associated with severe asthma | N = 65/86 (75.6%) |
| Gastroesophageal reflux | 17 (37.8%) |
| Allergic rhinitis | 16 (35.6%) |
| Bronchiectasis | 15 (33.3%) |
| Aspirin-Exacerbated Respiratory Disease | 9 (20.0%) |
| Anxiety/Depression | 5 (11.1%) |
| Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis | 3 (6.7%) |
| Characteristic | Acceptable Adherence to INC (>50%) | Poor Adherence to INC (<50%) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | |||
| Females | 23 (57.5) | 37 (80.4) | 0.038 |
| Males | 17 (42.5) | 9 (19.6) | |
| Asthma-related comorbidities | |||
| Gastroesophageal reflux | 9 (39.1) | 8 (36.4) | 1.000 |
| Allergic rhinitis | 9 (39.1) | 7 (31.8) | 0.841 |
| Bronchiectasis | 10 (43.5) | 5 (22.7) | 0.246 |
| Aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease | 9 (20) | 3 (13.6) | 0.502 |
| Anxiety/depression | 4 (11.1) | 1 (4.5) | 0.370 |
| Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis | 1 (4.3) | 2 (9.1) | 0.968 |
| Corticosteroid | Acceptable adherence to INC (>50%) | Poor adherence to INC (<50%) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal corticosteroid | 40 | 46 | 0.285 |
| Fluticasone | 23 (26.7) | 24 (27.9) | |
| Mometasone | 16 (18.6) | 20 (23.2) | |
| Triamcinolona | - | 1 (2.2) | |
| Mometasona + olopatadine | 1 (2.5) | - | |
| Concomitant systemic corticosteroids | |||
| Long-term systemic corticosteroids | 6 (85.7) | 1 (14.3) | 0.027 |
| Short courses of systemic corticosteroids | 3 (21.4) | 11 (78.6) | 0.006 |
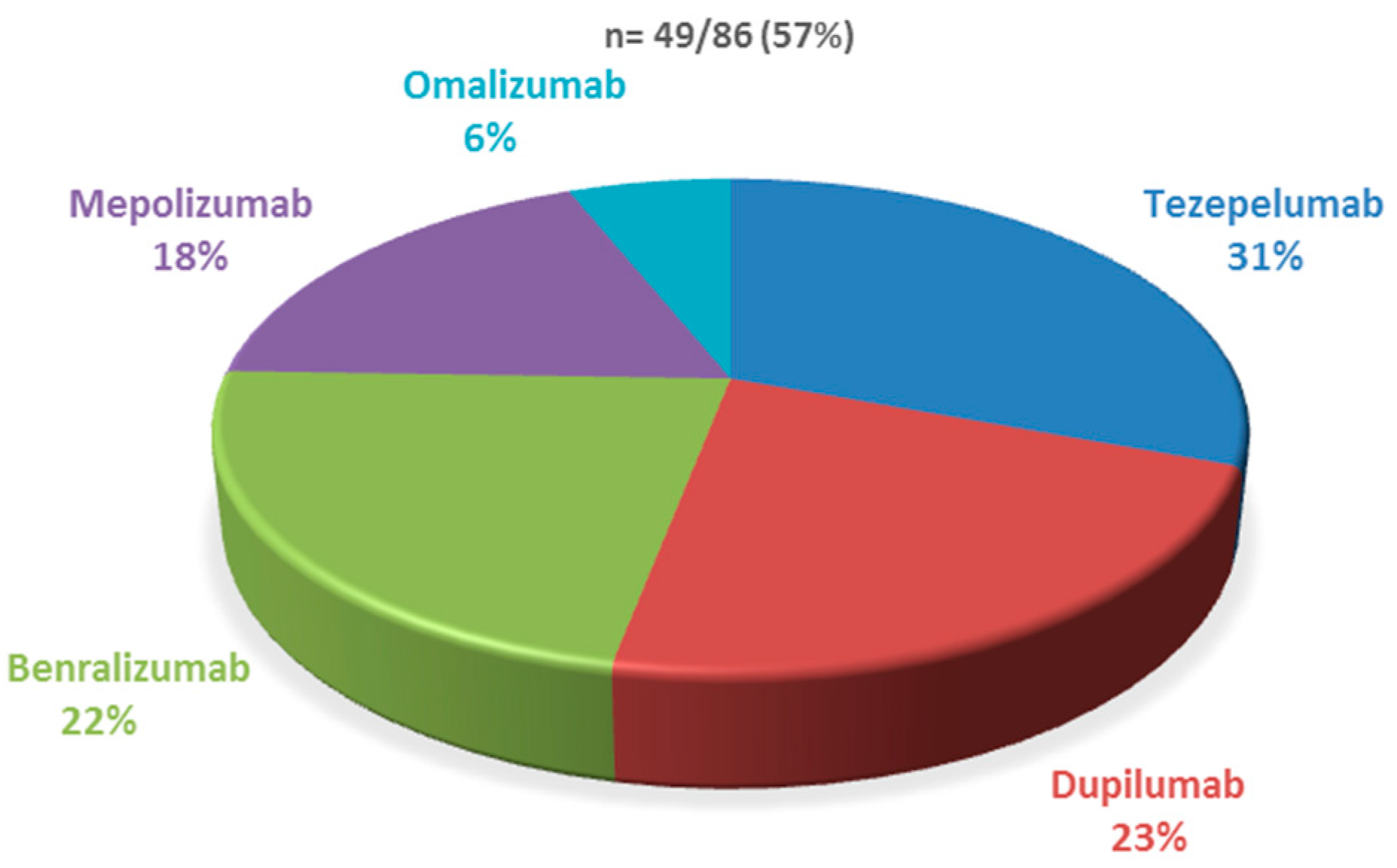
| Biologic Therapy | Acceptable Adherence to INC (>50%) | Poor adherence to INC (<50%) |
|---|---|---|
| Dupilumab | 7 (29.2) | 4 (16) |
| Tezepelumab | 8 (33.3) | 7 (28) |
| Benralizumab | 5 (20.8) | 6 (24) |
| Mepolizumab | 4 (16.7) | 5 (20) |
| Omalizumab | - | 3 (12) |
| Acceptable Adherence to INC (>50%) N = 40 | Poor Adherence to INC (<50%) N = 46 | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of endoscopic sinus surgery | 2.00 [1.00, 3.25] | 0.50 [0.00, 1.75] | 0.042 |
| Respiratory Outcomes | Acceptable Adherence to INC (>50%) | Poor Adherence to INC (<50%) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| FEV 1 pre-biologic % (median(IQR)) | 79.00 [66.00, 91.75] | 77.00 [72.00, 88.00] | 0.704 |
| FEV 1 mL pre (median(IQR)) | 2,01 [1.537, 2.895] | 2095 [1.852, 3.307] | 0.978 |
| FVC pre-biologic % (median(IQR)) | 88.50 [77.00, 105.50] | 93.00 [87.50, 105.00] | 0.244 |
| FVC ml pre (median(IQR)) | 3.005 [2.435, 4.145] | 2800 [2.640, 3.790] | 1.000 |
| FEV 1/FVC pre-biologic % (median(IQR)) | 72.02 [64.61, 79.32] | 67.87 [60.94, 76.94] | 0.109 |
| FENO pre-biologic % (median(IQR)) | 36.00 [18.50, 57.90] | 24.00 [10.82, 45.63] | 0.242 |
| FEV 1 post-biologic % (median(IQR)) | 83.00 [77.00, 94.00] | 78.00 [65.75, 92.00] | 0.464 |
| FEV 1 mL post (median(IQR)) | 2030 [1960, 3140] | 2330 [1.960, 2.615] | 0.808 |
| FVC post-biologic % (median(IQR)) | 114.00 [99.00, 115.00] | 98.00 [88.75, 104.25] | 0.092 |
| FVC ml post (median(IQR)) | 3780 [3.290, 4.100] | 3110 [2.820, 3.805] | 0.465 |
| FEV 1/FVC post-biologic % (median(IQR)) | 62.00 [60.28, 66.25] | 66.22 [61.81, 71.35] | 0.558 |
| FENO post-biologic % (median(IQR)) | 37.00 [20.00, 51.00] | 24.50 [15.50, 30.00] | 0.380 |
| ACT pre-biologic % (median(IQR)) | 18.00 [10.00, 20.00] | 20.00 [17.00, 21.00] | 0.130 |
| ACT post-biologic % (median(IQR)) | 20.00 [16.50, 22.00] | 21.00 [18.75, 24.00] | 0.400 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Villamañán, E.; Laorden, D.; Ibáñez, M.E.; De las Vecillas, L.; Carpio, C.; Alfonso, C.; Domínguez-Ortega, J.; Romero, D.; Quirce, S.; Álvarez-Sala, R., on behalf of Asma Grave HULP Study Group. Adherence to Intranasal Corticosteroids in Patients with Severe Asthma and Nasal Polyposis: Pharmacological and Clinical Factors Involved. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 5070. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14145070
Villamañán E, Laorden D, Ibáñez ME, De las Vecillas L, Carpio C, Alfonso C, Domínguez-Ortega J, Romero D, Quirce S, Álvarez-Sala R on behalf of Asma Grave HULP Study Group. Adherence to Intranasal Corticosteroids in Patients with Severe Asthma and Nasal Polyposis: Pharmacological and Clinical Factors Involved. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(14):5070. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14145070
Chicago/Turabian StyleVillamañán, Elena, Daniel Laorden, María Enriqueta Ibáñez, Leticia De las Vecillas, Carlos Carpio, Carolina Alfonso, Javier Domínguez-Ortega, David Romero, Santiago Quirce, and Rodolfo Álvarez-Sala on behalf of Asma Grave HULP Study Group. 2025. "Adherence to Intranasal Corticosteroids in Patients with Severe Asthma and Nasal Polyposis: Pharmacological and Clinical Factors Involved" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 14: 5070. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14145070
APA StyleVillamañán, E., Laorden, D., Ibáñez, M. E., De las Vecillas, L., Carpio, C., Alfonso, C., Domínguez-Ortega, J., Romero, D., Quirce, S., & Álvarez-Sala, R., on behalf of Asma Grave HULP Study Group. (2025). Adherence to Intranasal Corticosteroids in Patients with Severe Asthma and Nasal Polyposis: Pharmacological and Clinical Factors Involved. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(14), 5070. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14145070






