Surgical Management Strategies for Pericardial Effusion—A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Data Extraction
2.3. Assessment of Risk of Bias
2.4. Pericardial Effusion Surgical Drainage Techniques
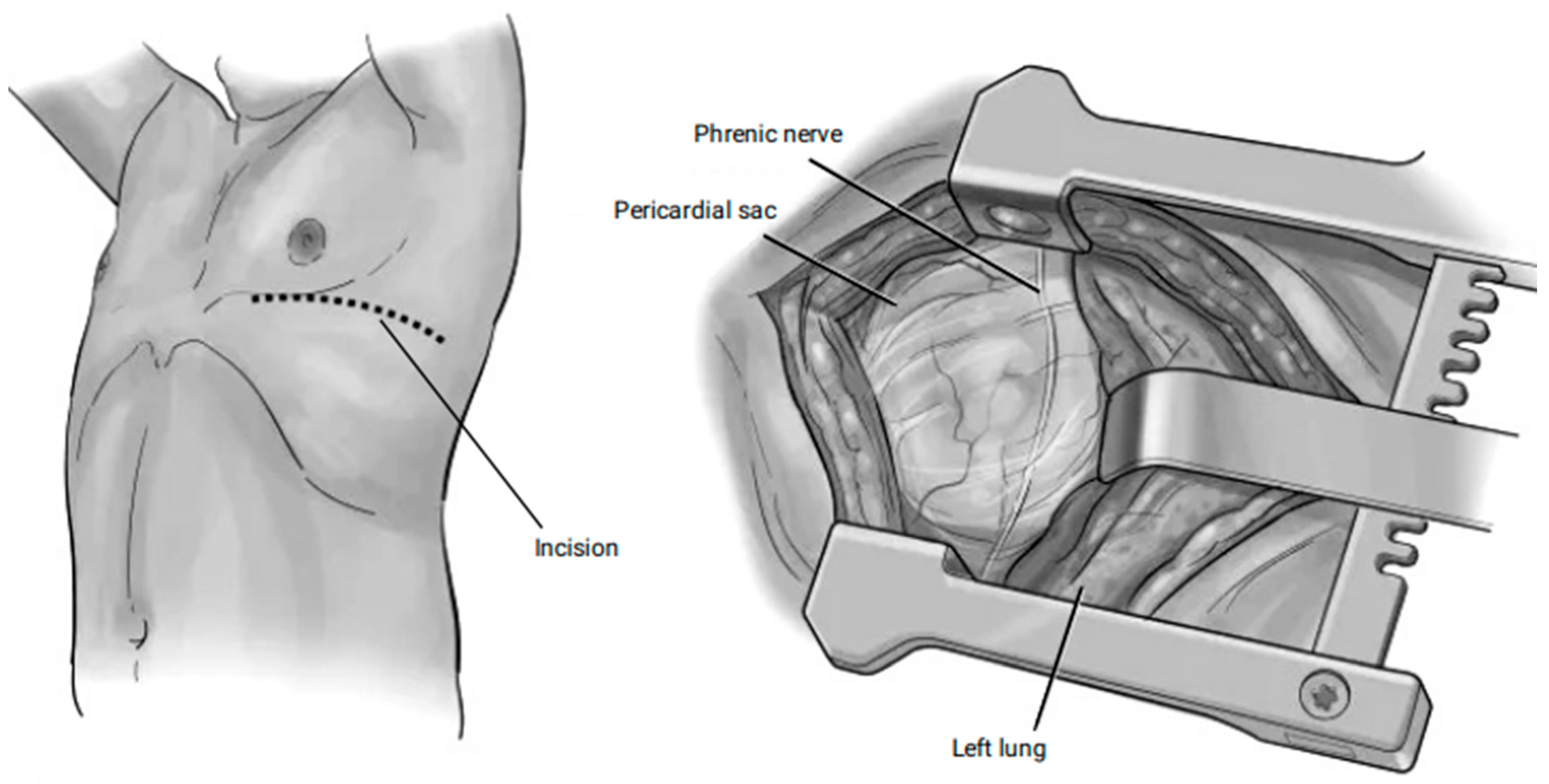
2.4.1. The Subxiphoid Pericardial Window
2.4.2. Anterior and Lateral Thoracotomy
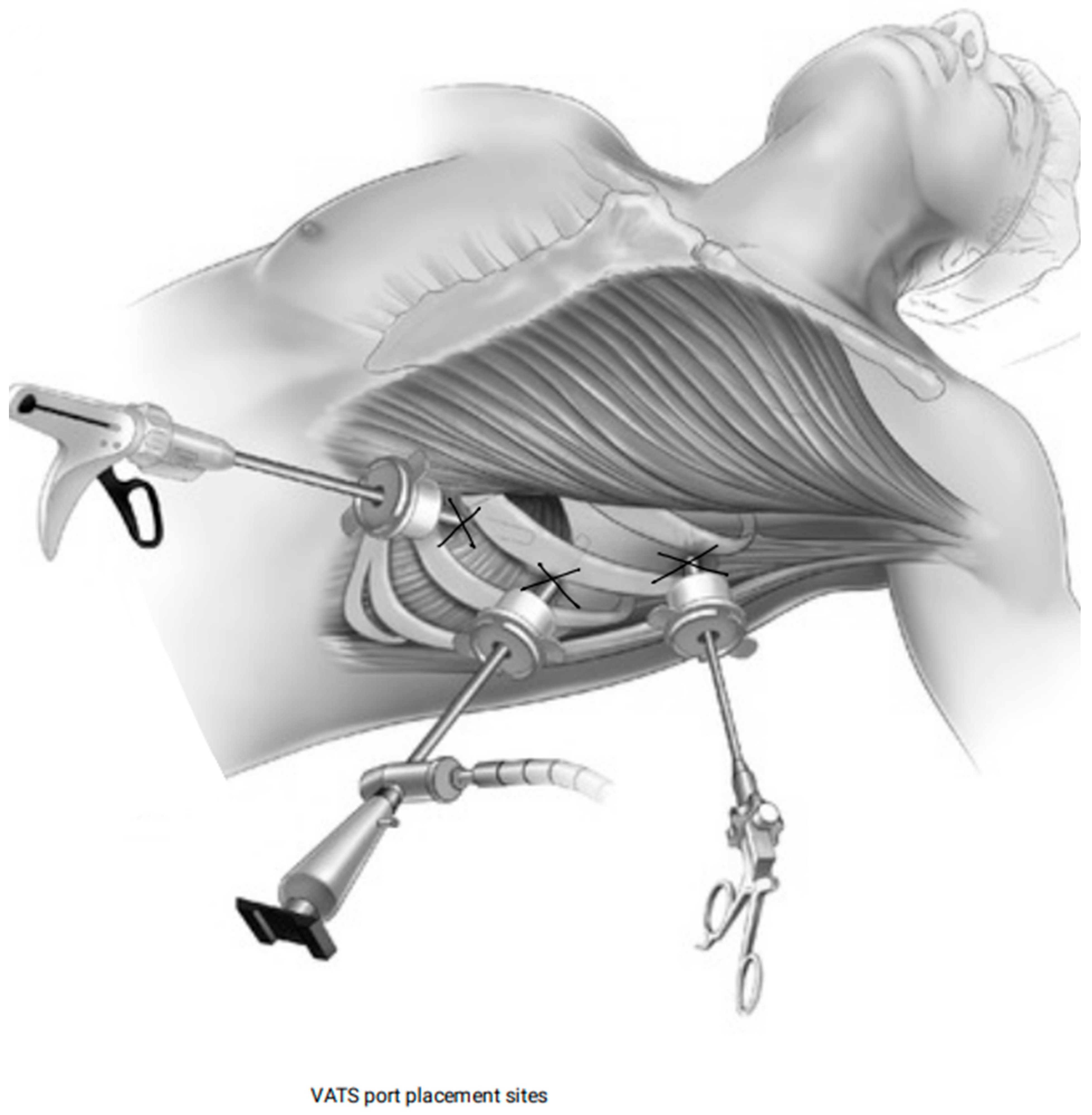
2.4.3. VATS
2.4.4. Median Sternotomy
3. Results
3.1. Study and Patient Characteristics
3.2. Etiology of Pericardial Effusion
3.3. Intervention Type
3.4. Outcomes by Type of Intervention
3.5. Subxiphoid Pericardial Window
3.5.1. Intra-Operative Complications
3.5.2. Post-Operative (30-Day) Outcomes
3.5.3. Chest Tube Drainage Amount and Duration of Stay
3.5.4. Mortality
3.6. Anterior or Lateral Thoracotomy Approach
3.6.1. Intra-Operative Complications
3.6.2. Post-Operative (30-Day Outcomes)
3.6.3. Chest Tube Drainage Amount and Duration of Stay
3.6.4. Mortality
3.7. VATS Pericardial Window
3.7.1. Intra-Operative Complications
3.7.2. Post-Operative (30-Day Outcomes)
3.7.3. Chest Tube Drainage Amount and Duration of Stay
3.7.4. Mortality

4. Discussion
4.1. Etiology and Outcomes
4.2. Procedure Selection Based on Etiology
4.3. Management of Recurrent Effusions and Preventative Strategies
4.4. Complications, Length of Hospital Stay, and Mortality Variations
4.5. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| VATS | Video-Assisted Thoracoscopic Surgery (VATS) |
| HIV | Human Immunodeficiency Virus |
| PRISMA | Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses |
| ESC | European Society of Cardiology |
References
- Adler, Y.; Charron, P.; Imazio, M.; Badano, L.; Barón-Esquivias, G.; Bogaert, J.; Brucato, A.; Gueret, P.; Klingel, K.; Lionis, C.; et al. 2015 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of pericardial diseases. Eur. Heart J. 2015, 36, 2921–2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayosi, B.M.; Wiysonge, C.S.; Ntsekhe, M.; Gumedze, F.; Volmink, J.A.; Maartens, G.; Aje, A.; Thomas, B.M.; Thomas, K.M.; Awotedu, A.A.; et al. Mortality in patients treated for tuberculous pericarditis in sub-Saharan Africa. S. Afr. Med. J. Suid-Afr. Tydskr. Vir. Geneeskd. 2008, 98, 36–40. [Google Scholar]
- Vakamudi, S.; Ho, N.; Cremer, P.C. Pericardial Effusions: Causes, Diagnosis, and Management. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2017, 59, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imazio, M.; Adler, Y. Management of pericardial effusion. Eur. Heart J. 2013, 34, 1186–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamani, N.; Abbasi, A.; Almas, T.; Mookadam, F.; Unzek, S. Diagnosis, treatment, and management of pericardial effusion-review. Ann. Med. Surg. 2022, 80, 104142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, N.A.; Hennecken, C.; Van Den Eynde, J.; Doulamis, I.P.; Avgerinos, D.V.; Kampaktsis, P.N. Pericardiectomy and Pericardial Window for the Treatment of Pericardial Disease in the Contemporary Era. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2022, 24, 1619–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palatianos, G.M.; Thurer, R.J.; Pompeo, M.Q.; Kaiser, G.A. Clinical Experience with Subxiphoid Drainage of Pericardial Effusions. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 1989, 48, 381–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trigt, P.V.; Douglas, J.; Smith, P.K.; Campbell, P.T.; Wall, T.C.; Kenney, R.T.; Oʼconnor, C.M.; Sheikh, K.H.; Corey, G.R. A Prospective Trial of Subxiphoid Pericardiotomy in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Large Pericardial Effusion A Follow-Up Report. Ann. Surg. 1993, 218, 777–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moores, D.W.O.; Allen, K.B.; Faber, L.P.; Dziuban, S.W.; Gillman, D.J.; Warren, W.H.; Ilves, R.; Lininger, L. Subxiphoid pericardial drainage for pericardial tamponade. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 1995, 109, 546–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarigül, A.; Farsak, B.; Ateş, M.Ş.; Demircin, M.; Paşaoğlu, İ. Subxiphoid Approach for Treatment of Pericardial Effusion. Asian Cardiovasc. Thorac. Ann. 1999, 7, 297–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becit, N.; Özyazicioğlu, A.; Ceviz, M.; Karakelleoğlu, Ş.; Karapolat, S.; Koçak, H. Clinical Experience with Subxiphoid Pericardiostomy in the Management of Pericardial Effusions: A Study of 240 Cases. J. Int. Med. Res. 2003, 31, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daugirdas, J.T.; Leehey, D.J.; Popli, S.; McCray, G.M.; Gandhi, V.C.; Pifarré, R.; Ing, T.S. Subxiphoid pericardiostomy for hemodialysis-associated pericardial effusion. Arch. Intern. Med. 1986, 146, 1113–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosios, T.; Theakos, N.; Angouras, D.; Asimacopoulos, P. Risk factors affecting the survival of patients with pericardial effusion submitted to subxiphoid pericardiostomy. Chest 2003, 124, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porte, H.L.; Janecki-Delebecq, T.J.; Finzi, L.; Métois, D.G.; Millaire, A.; Wurtz, A.J. Pericardoscopy for primary management of pericardial effusion in cancer patients. Eur. J. Cardio-Thorac. Surg. 1999, 16, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wall, T.C.; Campbell, P.T.; O’Connor, C.M.; Van Trigt, P.; Kenney, R.T.; Sheikh, K.H.; Kisslo, J.A.; Corey, G.R. Diagnosis and management (by subxiphoid pericardiotomy) of large pericardial effusions causing cardiac tamponade. Am. J. Cardiol. 1992, 69, 1075–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, P.; Sorensen, C.; Andersen, H. Surgical treatment of large pericardial effusions Etiology and long-term survival. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 1991, 5, 430–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, S.; Celik, M.; Aydemir, B.; Tanrıkulu, H.; Okay, T.; Tanrikulu, N. Surgical properties and survival of a pericardial window via left minithoracotomy for benign and malignant pericardial tamponade in cancer patients. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2012, 10, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çardak, M.E.; Külahçioglu, S.; Erdem, E. Awake uniportal video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery for the management of pericardial effusion. J. Minimal Access Surg. 2023, 19, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georghiou, G.P.; Stamler, A.; Sharoni, E.; Fichman-Horn, S.; Berman, M.; Vidne, B.A.; Saute, M. Video-assisted thoracoscopic pericardial window for diagnosis and management of pericardial effusions. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2005, 80, 607–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altman, E.; Rutsky, O.; Shturman, A.; Yampolsky, Y.; Atar, S. Anterior parasternal approach for creation of a pericardial window. Ann. R. Coll. Surg. Engl. 2015, 97, 375–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, J.E.; Ryan, M.B.; Blumenstock, D.A. Eleven years’ experience with pericardial-peritoneal window in the management of malignant and benign pericardial effusions. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 1995, 2, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salim, E.F.; Rezk, M.E. Thoracoscopic versus subxiphoid pericardial window in patients with end-stage renal disease. J. Egypt. Soc. Cardio-Thorac. Surg. 2018, 26, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piehler, J.M.; Pluth, J.R.; Schaff, H.V.; Danielson, G.K.; Orszulak, T.A.; Puga, F.J. Surgical management of effusive pericardial disease. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 1985, 90, 506–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.S.; Rentschler, R.; Wilbur, D. Surgical management of pericardial effusion in patients with malignancies. Comparison of subxiphoid window versus pericardiectomy. Cancer 1991, 67, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkes, J.D.; Fidias, P.; Vaickus, L.; Perez, R.P. Malignancy-related pericardial effusion. 127 cases from the roswell park cancer institute. Cancer 1995, 76, 1377–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, K.B.; Faber, L.P.; Warren, W.H.; Shaar, C.J. Pericardial effusion: Subxiphoid pericardiostomy versus percutaneous catheter drainage. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 1999, 67, 437–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, P.K.H.; Kucharczuk, J.C.; Marshall, M.B.; Friedberg, J.S.; Chen, Z.; Kaiser, L.R.; Shrager, J.B. Comparative Study of Subxiphoid Versus Video-Thoracoscopic Pericardial “Window”. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2005, 80, 2013–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balla, S.; Zea-Vera, R.; Kaplan, R.A.; Rosengart, T.K.; Wall, M.J.; Ghanta, R.K. Mid-Term Efficacy of Subxiphoid Versus Transpleural Pericardial Window for Pericardial Effusion. J. Surg. Res. 2020, 252, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, J.M.; Meyers, B.F.; Guthrie, T.J.; Battafarano, R.J.; Cooper, J.D.; Patterson, G.A. Comparison of open subxiphoid pericardial drainage with percutaneous catheter drainage for symptomatic pericardial effusion. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2003, 76, 811–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horr, S.E.; Mentias, A.; Houghtaling, P.L.; Toth, A.J.; Blackstone, E.H.; Johnston, D.R.; Klein, A.L. Comparison of Outcomes of Pericardiocentesis Versus Surgical Pericardial Window in Patients Requiring Drainage of Pericardial Effusions. Am. J. Cardiol. 2017, 120, 883–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, M.I. The pericardial window: Is a video-assisted thoracoscopy approach better than a surgical approach? Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2011, 12, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagristà-Sauleda, J. Diagnosis and management of pericardial effusion. World J. Cardiol. 2011, 3, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Liu, J.; Zeng, Y.; Chen, S.; Zheng, Y.; Ye, S.; Lan, L.; Liu, Q.; Weig, H.-J. Causes of moderate to large pericardial effusion requiring pericardiocentesis in 140 Han Chinese patients. Herz 2012, 37, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Haddad, D.; Iliescu, C.; Yusuf, S.W.; William, W.N.; Khair, T.H.; Song, J.; Mouhayar, E.N. Outcomes of Cancer Patients Undergoing Percutaneous Pericardiocentesis for Pericardial Effusion. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2015, 66, 1119–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myers, F.; Aggarwal, V.; Bass, J.L.; Berry, J.M.; Knutson, S.; Narasimhan, S.; Steinberger, J.; Ambrose, M.; Shah, K.M.; Hiremath, G. Anatomic Approach and Outcomes in Children Undergoing Percutaneous Pericardiocentesis. Pediatr. Cardiol. 2021, 42, 918–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigusch, H.H.; Geisler, W.; Surber, R.; Schönweiß, M.; Gerth, J. Percutaneous balloon pericardiotomy: Efficacy in a series of malignant and nonmalignant cases. Scand. Cardiovasc. J. 2022, 56, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, T.S.M.; Enriquez-Sarano, M.; Freeman, W.K.; Barnes, M.E.; Sinak, L.J.; Gersh, B.J.; Bailey, K.R.; Seward, J.B. Consecutive 1127 Therapeutic Echocardiographically Guided Pericardiocenteses: Clinical Profile, Practice Patterns, and Outcomes Spanning 21 Years. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2002, 77, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Permanyer-Miralda, G.; Sagristá-Sauleda, J.; Soler-Soler, J. Primary acute pericardial disease: A prospective series of 231 consecutive patients. Am. J. Cardiol. 1985, 56, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercé, J.; Sagristà-Sauleda, J.; Permanyer-Miralda, G.; Soler-Soler, J. Should pericardial drainage be performed routinely in patients who have a large pericardial effusion without tamponade? Am. J. Med. 1998, 105, 106–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaitkus, P.T. Treatment of Malignant Pericardial Effusion. JAMA J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1994, 272, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulle, M.V.; Bansal, M.; Asaf, B.B.; Puri, H.V.; Bishnoi, S.; Kumar, A. Safety and feasibility of thoracoscopic pericardial window in recurrent pericardial effusion—A single-centre experience. J. Minimal Access Surg. 2024, 20, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girardi, L.N.; Ginsberg, R.J.; Burt, M.E. Pericardiocentesis and Intrapericardial Sclerosis: Effective Therapy for Malignant Pericardial Effusions. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 1997, 64, 1422–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsang, T.S.M.; El-Najdawi, E.K.; Seward, J.B.; Hagler, D.J.; Freeman, W.K.; O’Leary, P.W. Percutaneous Echocardiographically Guided Pericardiocentesis in Pediatric Patients: Evaluation of Safety and Efficacy. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 1998, 11, 1072–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maher, E.A.; Shepherd, F.A.; Todd, T.J.R. Pericardial sclerosis as the primary management of malignant pericardial effusion and cardiac tamponade. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 1996, 112, 637–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafique, A.M.; Patel, N.; Biner, S.; Eshaghian, S.; Mendoza, F.; Cercek, B.; Siegel, R.J. Frequency of Recurrence of Pericardial Tamponade in Patients with Extended Versus Nonextended Pericardial Catheter Drainage. Am. J. Cardiol. 2011, 108, 1820–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naunheim, K.; Kesler, K.; Fiore, A.; Turrentine, M.; Hammell, L.; Brown, J.; Mohammed, Y.; Pennington, D. Pericardial drainage: Subxiphoid vs. transthoracic approach. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 1991, 5, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langdon, S.E.; Seery, K.; Kulik, A. Contemporary outcomes after pericardial window surgery: Impact of operative technique. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2016, 11, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Portillo-Navarrete, J.H.; Pizano, A.; Benavides, J.; Palacio, A.M.; Moreno-Medina, K.; Cabrales, J.; Echeverri, D. Unveiling the causes of pericardial effusion in a contemporary case series of pericardiocentesis in Latin America. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 16010, Erratum in Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 19517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Luis, S.A.; Kane, G.C.; Luis, C.R.; Oh, J.K.; Sinak, L.J. Overview of Optimal Techniques for Pericardiocentesis in Contemporary Practice. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2020, 22, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, L.H. THE ELECTROCARDIOGRAM AS A SAFEGUARD IN PERICARDIOCENTESIS. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1956, 162, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotoi, S.; Moldovan, D.; Caraşcă, E.; Incze, A.; Herszenyi, L.; Podoleanu, D. Sinus node dysfunction occurring immediately after pericardiocentesis. Physiol. Bucar. 1987, 24, 63–68. [Google Scholar]
- Hsia, H.H.; Kander, N.H.; Shea, M.J. Persistent ST-segment elevation following pericardiocentesis: Caution with thrombolytic therapy. Intensive Care Med. 1988, 14, 77–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazaros, G.; Imazio, M.; Tsioufis, P.; Lazarou, E.; Vlachopoulos, C.; Tsioufis, C. Chronic pericardial effusion: Causes and management. Can. J. Cardiol. 2023, 39, 1121–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mudra, S.E.; Rayes, D.; Kumar, A.K.; Li, J.Z.; Njus, M.; McGowan, K.; Charalampous, C.; Kalam, K.A.; Syed, A.; Majid, M.; et al. Malignant Pericardial Effusion: A Systematic Review. CJC Open 2024, 6, 967–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]



| Etiology of Pericardial Effusion | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study | Technique | Total Procedures (N) | Uremia (N) | Trauma (N) | Malignancy (N) | Collagen Vascular Disease (N) | Tuberculosis (N) |
| Studies Investigating Individual Pericardial Effusion Management Techniques | |||||||
| Palatianos, 1989 [7] | Subxiphoid Pericardial window | 41 | 9 | 0 | 14 | 0 | 2 |
| Trigt, 1993 [8] | Subxiphoid Pericardial window | 57 | 7 | 0 | 13 | 7 | 0 |
| Moores, 1995 [9] | Subxiphoid Pericardial window | 155 | 0 | 0 | 82 | 10 | 3 |
| Sarigül, 1999 [10] | Subxiphoid Pericardial window | 305 | 93 | 0 | 41 | 0 | 21 |
| Becit, 2003 [11] | Subxiphoid Pericardial window | 240 | 101 | 9 | 34 | 0 | 25 |
| Daugirdas, 1986 [12] | Subxiphoid Pericardial window | 16 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Dosios, 2003 [13] | Subxiphoid Pericardial window | 104 | 0 | 0 | 46 | 3 | 3 |
| Porte, 1999 [14] | Subxiphoid Pericardial window | 114 | 0 | 0 | 43 | 0 | 0 |
| Wall, 1992 [15] | Subxiphoid Pericardial window | 57 | 7 | 0 | 13 | 7 | 3 |
| Olsen, 1991 [16] | Left anterior thoracotomy | 60 | 4 | 1 | 28 | 0 | 1 |
| Celik, 2012 [17] | Left anterior thoracotomy | 48 | 0 | 0 | 26 | 0 | 2 |
| Çardak, 2023 [18] | VATS | 20 | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR |
| Georghiou, 2005 [19] | VATS | 18 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| Altman, 2015 [20] | Anterior parasternal approach | 30 | 0 | 0 | 9 | 0 | 0 |
| Olson, 1995 [21] | Pericardial-peritoneal window through a subxiphoid approach | 33 | 3 | 0 | 18 | 3 | 0 |
| Salim, 2018 [22] | Total | 30 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Subxiphoid Pericardial window | 15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| VATS | 15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Piehler, 1985 [23] | Total | 145 | 2 | 1 | 72 | 9 | 0 |
| Subxiphoid Pericardial window | 13 | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | |
| Left anterior thoracotomy | 118 | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | |
| Median sternotomy | 7 | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | |
| Right thoracotomy | 7 | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | |
| Park, 1991 [24] | Total | 28 | 0 | 0 | 19 | 0 | 0 |
| Subxiphoid Pericardial window | 10 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 | |
| Left anterior thoracotomy | 6 | 0 | 0 | 14 | 0 | 0 | |
| Median sternotomy | 12 | ||||||
| Wilkes,1995 [25] | Total | 127 | 1 | 0 | 70 | 0 | 0 |
| Subxiphoid Pericardial window | 85 | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | |
| Thoracotomy with pleuro-pericardial window | 7 | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | |
| Anterior thoracotomy with pericardiotomy | 6 | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | |
| Laparotomy with pericardiotomy | 2 | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | |
| Naunheim, 1991 [4] | Total | 131 | 24 | 7 | 38 | 8 | 0 |
| Subxiphoid Pericardial window | 53 | 4 | NR | 16 | 4 | 0 | |
| Transthoracic | 78 | 20 | NR | 22 | 4 | 0 | |
| Allen, 1999 [26] | Total | 117 | 9 | NR | 75 | 4 | 0 |
| Subxiphoid Pericardial window | 94 | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | |
| O’Brien, 2005 [27] | Total | 71 | 0 | 0 | 50 | 3 | 0 |
| Subxiphoid Pericardial window | 56 | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | |
| VATS | 15 | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | |
| Langdon, 2016 [4] | Total | 179 | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR |
| Subxiphoid Pericardial window | 127 | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | |
| Left anterior thoracotomy | 52 | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | |
| Balla, 2020 [28] | Total | 46 | 8 | 0 | 22 | 4 | 0 |
| Subxiphoid Pericardial window | 31 | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | |
| Trans pleural | 15 | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | |
| McDonald, 2003 [29] | Total | 246 | 0 | 11 | 79 | 0 | 0 |
| Subxiphoid Pericardial window | 150 | 0 | 8 | 52 | 0 | 0 | |
| Horr, 2017 [30] | Total | 1281 | 0 | 0 | 215 | 0 | 0 |
| Subxiphoid Pericardial window | 521 | 0 | 0 | 75 | 0 | 0 | |
| Muhammad, 2011 [31] | Total | 30 | 6 | 0 | 17 | 0 | 0 |
| Subxiphoid | 15 | 4 | 0 | 7 | 0 | 0 | |
| VATS | 15 | 2 | 0 | 10 | 0 | 0 | |
| Etiology of Pericardial Effusion | |||||||
| Study | Post Cardiotomy/Cardiac Catheterization (N) | Idiopathic (N) | Infection (N) | Autoimmune Disease (N) | Radiation/Irradiation (N) | Other (N) | |
| Studies Investigating Individual Pericardial Effusion Management Techniques | |||||||
| Palatianos, 1989 [7] | 0 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7 | |
| Trigt, 1993 [8] | 0 | 4 | 15 | 0 | 8 | 5 | |
| Moores, 1995 [9] | 17 | 14 | 17 | 0 | 0 | 12 | |
| Sarigül, 1999 [10] | 0 | 29 | 54 | 0 | 0 | 67 | |
| Becit, 2003 [11] | 0 | 52 | 12 | 0 | 0 | 7 | |
| Daugirdas, 1986 [12] | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 16 | |
| Dosios, 2003 [13] | 2 | 27 | 9 | 0 | 1 | 13 | |
| Porte, 1999 [14] | 0 | 33 | 10 | 0 | 20 | 8 | |
| Wall, 1992 [15] | 0 | 4 | 8 | 0 | 8 | 8 | |
| Olsen, 1991 [16] | 0 | 13 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 8 | |
| Celik, 2012 [17] | 0 | 15 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 1 | |
| Çardak, 2023 [18] | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | |
| Georghiou, 2005 [19] | 0 | 11 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | |
| Altman, 2015 [20] | 0 | 17 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | |
| Olson,1995 [21] | 0 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Studies investigating multiple pericardial effusion management techniques | |||||||
| Salim, 2018 [22] | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 30 | |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 15 | ||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 15 | ||
| Piehler, 1985 [23] | 0 | 42 | 4 | 0 | 15 | 0 | |
| NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | ||
| NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | ||
| NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | ||
| NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | ||
| Park, 1991 [24] | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 0 | |
| 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | ||
| 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | ||
| Wilkes, 1995 [25] | 0 | 42 | 6 | 0 | 4 | 4 | |
| NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | ||
| NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | ||
| NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | ||
| NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | ||
| Naunheim, 1991 [4] | 0 | 15 | 27 | 0 | 9 | 3 | |
| 0 | NR | 16 | 0 | 3 | 15 | ||
| 0 | NR | 22 | 0 | 6 | 10 | ||
| Allen, 1999 [26] | 4 | 19 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 3 | |
| NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | ||
| O’Brien, 2005 [27] | 2 | 12 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | |
| NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | ||
| NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | ||
| Langdon, 2016 [4] | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | |
| NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | ||
| NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | ||
| Balla, 2020 [28] | 0 | 12 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | ||
| NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | ||
| McDonald, 2003 [29] | 43 | 0 | 27 | 31 | 0 | 55 | |
| 27 | 0 | 19 | 14 | 0 | 30 | ||
| Horr, 2017 [30] | 656 | 190 | 70 | 265 | 0 | 187 | |
| 336 | 50 | 20 | 100 | 0 | 17 | ||
| Muhammad, 2011 [31] | 0 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 0 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Intraoperative Details | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study | Technique | Operative Pericardial Effusion Drainage (mL) | Post Operative Pericardial Effusion Drainage. (mL) | Operative Time (min) | Chest Tube Drainage (Day) | Intraoperative Complications | ||||||
| Studies Investigating Individual Pericardial Effusion Management Techniques. | ||||||||||||
| Palatianos, 1989 [7] | Subxiphoid pericardial window | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | ||||||
| Trigt, 1993 [8] | Subxiphoid pericardial window | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | ||||||
| Moores, 1995 [9] | Subxiphoid pericardial window | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | ||||||
| Sarigül, 1999 [10] | Subxiphoid pericardial window | Benign effusion {975.3 ± 48.5}, Malignant effusion {1131.3 ± 97.5} | NR | NR | NR | NR | ||||||
| Becit, 2003 [11] | Subxiphoid pericardial window | 696.0 ± 32.0 | NR | NR | NR | NR | ||||||
| Daugirdas, 1986 [12] | Subxiphoid pericardial window | Median 600 (300–1500) | NR | NR | (2.0–4.0) | NR | ||||||
| Dosios, 2003 [13] | Subxiphoid pericardial window | NR | NR | (35.0–50.0) | NR | NR | ||||||
| Porte, 1999 [14] | Subxiphoid pericardial window | 750 mL (range 50 mL in a patient with previous transcutaneous drainage, to 1600 mL). | NR | 36 min (range: 21 ± 74) | 5 days (range 4 ± 6 | PCS was complete in 112 of the 114 patients (98%). The two incomplete explorations were due to a cardiac arrest during the induction of anesthesia in one case, and the presence of neoplastic tissue hindering introduction of the pericardioscope in the other. | ||||||
| Wall, 1992 [15] | Subxiphoid pericardial window | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | ||||||
| Olsen, 1991 [16] | Left anterior thoracotomy | 800.0 {250.0–2100.0} | NR | NR | NR | NR | ||||||
| Celik, 2012 [17] | Left anterior thoracotomy | 862.50 ± 390.37 | NR | 28.3 ± 3.8 | 6.0 ± 1.5 | NR | ||||||
| Çardak, 2023 [18] | VATS | 700.0 ± 307.0 | NR | 44.0 ± 13.0 | 1.0 {1.0–1.0} | NR | ||||||
| Georghiou, 2005 [19] | VATS | NR | NR | Mean 46 (30–160) | Mean 2.3 (1.0–5.0) | 0.0 | ||||||
| Altman, 2015 [20] | Anterior parasternal approach | 700.0 ± 139.0 | NR | 73.0 ± 21.0 | NR | NR | ||||||
| Olson, 1995 [21] | Pericardial–peritoneal window through a subxiphoid approach | 500.0 {50.0–1600.0} | NR | 78.0 {25.0–143.0} | NR | (1 hypotension without sequela) (3—chest tubes for later pleurodesis coexisting malignant pleural effusions) intraoperative entry into left pleural space (n = 1) | ||||||
| Studies investigating multiple pericardial effusion management techniques. | ||||||||||||
| Salim, 2018 [22] | Subxiphoid pericardial window | 591.8 ± 154.4 | NR | 34.5 ± 2.7 | 3.34 d- + 0.5 | NR | ||||||
| VATS | 532.1 ± 106.9 | NR | 58.9 ± 4.6 | 2.4 ± 0.5 | NR | |||||||
| Piehler, 1985 [23] | Total | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | ||||||
| Subxiphoid pericardial window | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | |||||||
| Left anterior thoracotomy | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | |||||||
| Median sternotomy | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | |||||||
| Right thoracotomy | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | |||||||
| Park, 1991 [24] | Subxiphoid pericardial window | NR | NR | NR | 3.2 (1.0–5.0) | NR | ||||||
| Transthoracic (left anterior thoracotomy median sternotomy) | NR | NR | NR | 7.3 (3.0–16.0) | NR | |||||||
| Wilkes, 1995 [25] | Total | 509.0 (5.0–2300.0) | NR | NR | NR | NR | ||||||
| Subxiphoid pericardial window | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | |||||||
| Thoracotomy with pleuro-pericardial window | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | |||||||
| Anterior thoracotomy with pericardiotomy | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | |||||||
| Laparotomy with pericardiotomy | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | |||||||
| Naunheim, 1991 [4] | Subxiphoid pericardial window | 455.0 ± 388.0 | NR | NR | 5.4 ± 6.3 | NR | ||||||
| Transthoracic (sternotomy and anterior thoracotomy) | 487.0 ± 359.0 | NR | NR | 4.0 ± 2.5 | NR | |||||||
| Allen, 1999 [26] | Subxiphoid pericardial window | NR | NR | NR | 5.0 | NR | ||||||
| O’Brien, 2005 [27] | Subxiphoid pericardial window | 433.0 ± 417.0 | NR | 81.1 ± 25.5 | 4.0 ± 1.6 | The pleural chest tube was placed intraoperatively for a clinical tension pneumothorax after pericardial drainage | ||||||
| VATS | 735.0 ± 742.0 | NR | 117.1 ± 32.4 | 3.3 ± 1.4 | Two required additional chest tubes for pneumothorax after chest tube removal, 1 was discharged home with a Heimlich valve for ongoing air leak from injury to a trapped lung, and 1 was readmitted for drainage from a chest tube site that was self-limited | |||||||
| Langdon, 2016 [4] | Subxiphoid pericardial window | 512.0 ± 303.0 | NR | NR | NR | NR | ||||||
| Left anterior thoracotomy | 452.0 ± 267.0 | NR | NR | NR | NR | |||||||
| Balla, 2020 [28] | Total | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | ||||||
| Subxiphoid pericardial window | 500.0 {413.0–600.0} | NR | 165.0 {96.0–218.0} | 7.0 {6.0–9.0} | NR | |||||||
| Trans pleural | 450.0 {400.0–575.0} | NR | 96.0 {95.0–208.0} | 4.0 {4.0–6.0} | NR | |||||||
| McDonald, 2003 [29] | Subxiphoid pericardial window | 317.0 ± 132.0 | NR | NR | 4.5 ± 2.7 | Single episode of ventricular fibrillation requiring defibrillation | ||||||
| Horr, 2017 [30] | Surgical pericardial window | NR | NR | NR | 2.9 ± 2.2 | NR | ||||||
| Muhammad, 2011 [31] | Subxiphoid pericardial window | NR | NR | 75.2 ± 25.4 | 4.1 ± 1.4 | NR | ||||||
| VATS | NR | NR | 111.3 ± 30.7 | 3.4 ± 1.5 | NR | |||||||
| Postoperative Outcomes | ||||||||||||
| Study | Technique | Length of Hospital Stay (Day) | 30-Day Early Mortality (N) | 30 Days < Late Mortality (N) | Pericardial Effusion Recurrence (N) | Pneumonia (N) | Cardiac Arrhythmia (N) | Renal Failure (N) | Wound Infection (N) | Bleeding (N) | Stroke (N) | Other (N) |
| Studies Investigating Individual Pericardial Effusion Management Techniques | ||||||||||||
| Palatianos, 1989 [7] | Subxiphoid pericardial window | NR | 8.0 | 7.0 | 1.0 | NR | 2.0 | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR |
| Trigt, 1993 [8] | Subxiphoid pericardial window | NR | 7.0 | 21.0 | 9.0 | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | 2.0 |
| Moores, 1995 [9] | Subxiphoid pericardial window | NR | 31.0 | NR | 4.0 | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR |
| Sarigül, 1999 [10] | Subxiphoid pericardial window | NR | 50.0 | NR | 31.0 | 11.0 | NR | 13.0 | 3.0 | NR | NR | 34.0 |
| Becit, 2003 [11] | Subxiphoid pericardial window | 6.3 | 3.0 | 14.0 | 24.0 | NR | NR | NR | 12.0 | NR | NR | NR |
| Daugirdas, 1986 [12] | Subxiphoid pericardial window | NR | NR | 12.0 | 1.0 | NR | NR | NR | 3.0 | NR | NR | 5.0 |
| Dosios, 2003 [13] | Subxiphoid pericardial window | NR | 17.0 | NR | 2.0 | NR | 9.0 | NR | NR | NR | NR | 5.0 |
| Porte, 1999 [14] | Subxiphoid pericardial window | 5 days (range: 4 ± 9) | 4.0 | 81.0 | 5.0 | 2.0 | 36.0 | NR | 5.0 | NR | NR | NR |
| Wall, 1992 [15] | Subxiphoid pericardial window | NR | 7.0 | 16.0 | 7.0 | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | 2.0 |
| Olsen, 1991 [16] | Left anterior thoracotomy | NR | 10.0 | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR |
| Celik, 2012 [17] | Left anterior thoracotomy | 9.5 ± 7.2 | 4.0 | NR | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | NR | 2.0 | NR | NR | 3.0 |
| Çardak, 2023 [18] | VATS | 1.0 {1.0–2.0} | 2.0 | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR |
| Georghiou, 2005 [19] | VATS | Mean 6.4 (3–16) | 1.0 | NR | NR | NR | 1.0 | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR |
| Altman, 2015 [20] | Anterior parasternal approach | 10.0 ± 6.8 | 8.0 | NR | 4.0 | 3.0 | 6.0 | NR | NR | NR | 21.0 | |
| Olson,1995 [21] | Pericardial–peritoneal window through a subxiphoid approach | 9.0 {3.0–47.0} | 3.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | NR | NR | NR | NR | 3.0 |
| Studies investigating multiple pericardial effusion management techniques. | ||||||||||||
| Salim, 2018 [22] | Subxiphoid pericardial window | 13.3 ± 1.1 | NR | NR | 5.0 | 1.0 | 4.0 | NR | 2.0 | NR | NR | NR |
| VATS | 8.7 ± 0.5 | NR | NR | 1.0 | 1.0 | 3.0 | NR | 1.0 | NR | NR | 1.0 | |
| Piehler, 1985 [23] | Total | NR | 18.0 | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR |
| Subxiphoid pericardial window | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | |
| Left anterior thoracotomy | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | |
| Median sternotomy | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | |
| Right thoracotomy | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | |
| Park, 1991 [24] | Subxiphoid pericardial window | 10.3 (4.0–29.0) | NR | 10.0 | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR |
| Transthoracic (left anterior thoracotomy, median sternotomy) | 14.9 (6.0–32.0) | NR | 16 | NR | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | NR | NR | NR | 15.0 | |
| Wilkes,1995 [25] | Total | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR |
| Subxiphoid pericardial window | NR | 1% | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | 5% overall | |
| Thoracotomy with pleuro-pericardial window | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | |
| Anterior thoracotomy with pericardiotomy | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | |
| Laparotomy with pericardiotomy | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | |
| Naunheim, 1991 [4] | Subxiphoid pericardial window | 11.5 ± 11.2 | 8.0 | NR | 3.0 | 3.0 | NR | 3.0 | 2.0 | NR | NR | 42.0 |
| Transthoracic (sternotomy and anterior thoracotomy) | 14.4 ± 12.7 | 10.0 | NR | 3.0 | 7.0 | NR | 4.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 78.0 | |
| Allen, 1999 [26] | Subxiphoid pericardial window | NR | 0.0 | NR | 1.0 | NR | NR | NR | NR | 1.0 | NR | NR |
| O’Brien, 2005 [27] | Subxiphoid pericardial window | 10.4 ± 12.2 | 7.0 | 43.0 | 5.0 | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | 29.0 |
| VATS | 12.4 ± 22.8 | 0.0 | 9.0 | 1.0 | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | 7.0 | |
| Langdon, 2016 [4] | Subxiphoid pericardial window | 11.0 ± 7.5 | 9.0 | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR |
| Left anterior thoracotomy | 11.1 ± 9.5 | 4.0 | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | |
| Balla, 2020 [28] | Total | NR | 9.0 | NR | 8.0 | NR | 3.0 | NR | NR | NR | NR | 7.0 |
| Subxiphoid pericardial window | 9.0 {7.0–11.0} | 5.0 | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | |
| Trans pleural | 7.0 {6.0–12.0} | 3.0 | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | |
| McDonald, 2003 [29] | Subxiphoid pericardial window | NR | 16.0 | NR | 7.0 | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR |
| Horr, 2017 [30] | Surgical pericardial window | NR | 23.0 | NR | 52.0 | NR | NR | NR | NR | 5.0 | 5.0 | 28.0 |
| Muhammad, 2011 [31] | Subxiphoid pericardial window | 12.3 ± 22.6 | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | 1.0 |
| VATS | 10.2 ± 12.1 | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qasba, R.K.; Cangut, B.; Alhazmi, A.; Naseer, J.; Mubasher, A.; Talapaneni, S.; Fatima, M.; Nasir, A.; Shafqat, S.; Avilala, S.; et al. Surgical Management Strategies for Pericardial Effusion—A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 4985. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14144985
Qasba RK, Cangut B, Alhazmi A, Naseer J, Mubasher A, Talapaneni S, Fatima M, Nasir A, Shafqat S, Avilala S, et al. Surgical Management Strategies for Pericardial Effusion—A Systematic Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(14):4985. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14144985
Chicago/Turabian StyleQasba, Ruman K., Busra Cangut, Amnah Alhazmi, Javeria Naseer, Ayesha Mubasher, Sriharsha Talapaneni, Maurish Fatima, Afsheen Nasir, Shanzil Shafqat, Shreya Avilala, and et al. 2025. "Surgical Management Strategies for Pericardial Effusion—A Systematic Review" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 14: 4985. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14144985
APA StyleQasba, R. K., Cangut, B., Alhazmi, A., Naseer, J., Mubasher, A., Talapaneni, S., Fatima, M., Nasir, A., Shafqat, S., Avilala, S., & Hameed, I. (2025). Surgical Management Strategies for Pericardial Effusion—A Systematic Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(14), 4985. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14144985






