Comparison of Validity and Reliability of Manual Consensus Grading vs. Automated AI Grading for Diabetic Retinopathy Screening in Oslo, Norway: A Cross-Sectional Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
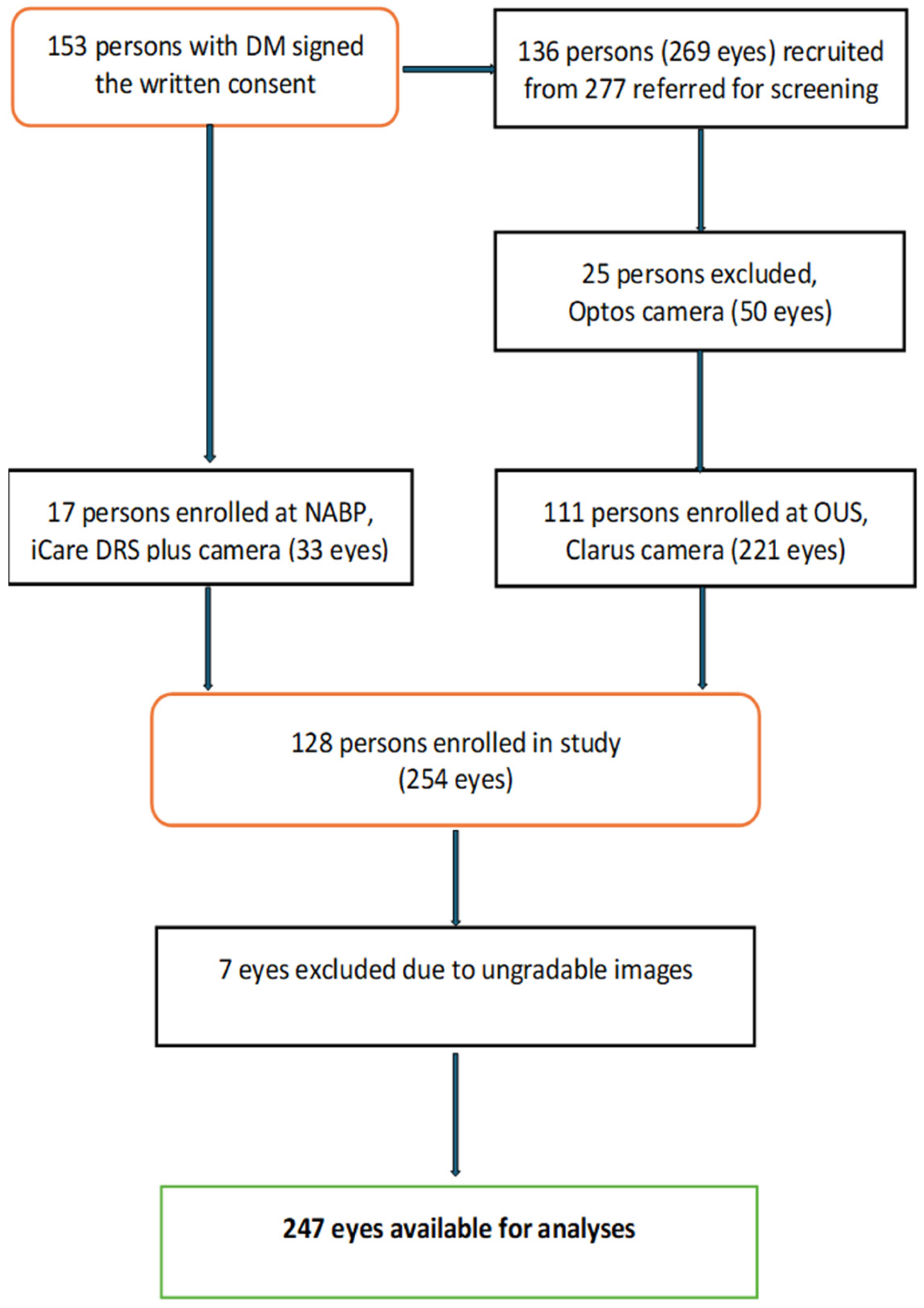
2.1. Study Design, Population, and Fundus Imaging
2.2. Grading of DR and Diabetic Macular Edema
2.3. Autonomous AI Diagnostic System/Automated DR Grading Software
2.4. Statistical Analysis
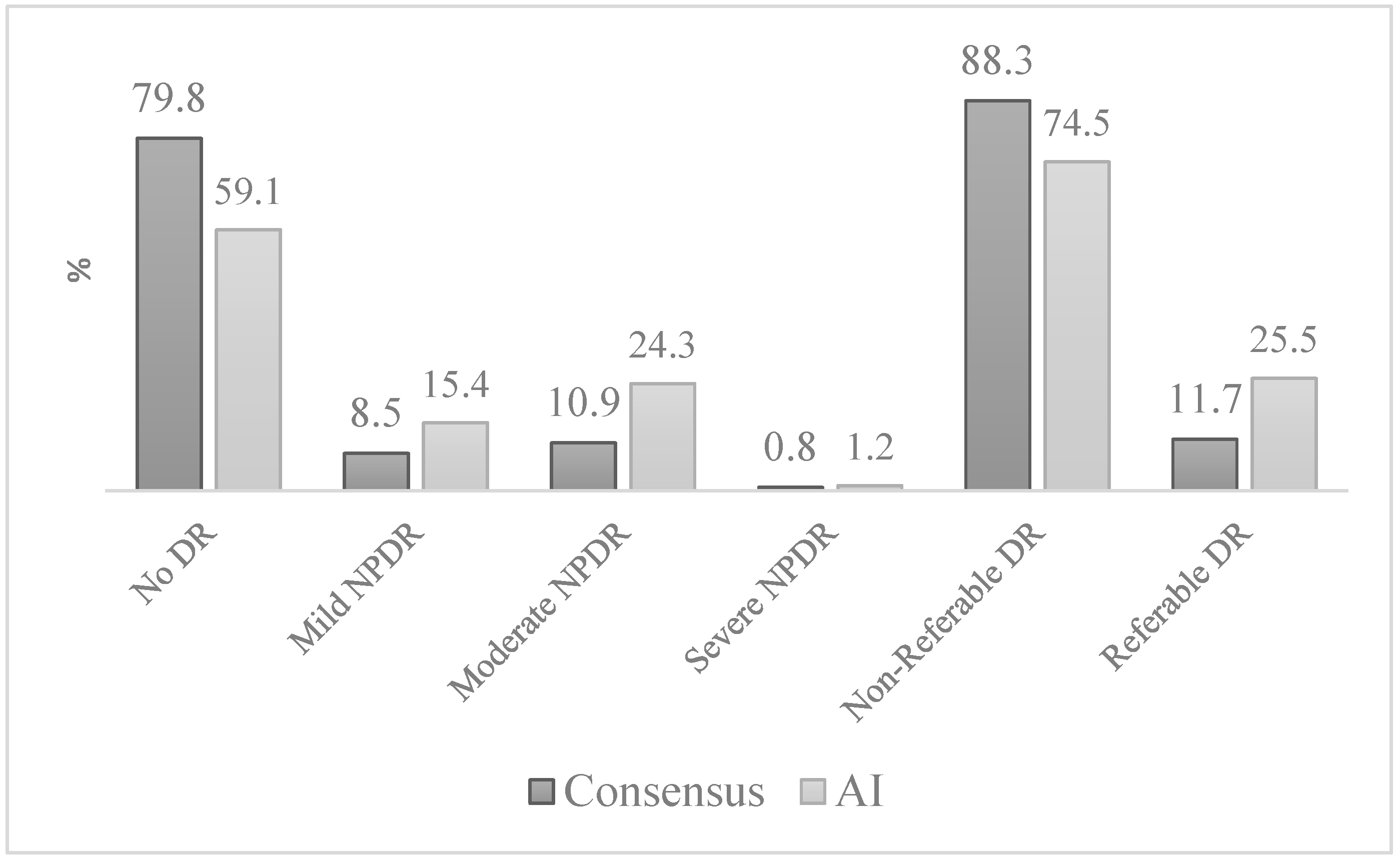
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Avogaro, A.; Fadini, G.P. Microvascular complications in diabetes: A growing concern for cardiologists. Int. J. Cardiol. 2019, 291, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, N.M.D.; Mitchell, P.P.; Wong, T.Y.P. Diabetic retinopathy. Lancet 2010, 376, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobrin Klein, B.E. Overview of Epidemiologic Studies of Diabetic Retinopathy. Ophthalmic Epidemiol 2007, 14, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leasher, J.L.; Bourne, R.R.A.; Flaxman, S.R.; Jonas, J.B.; Keeffe, J.; Naidoo, K.; Pesudovs, K.; Price, H.; White, R.A.; Wong, T.Y.; et al. Global estimates on the number of people blind or visually impaired by diabetic retinopathy: A meta-analysis from 1990 to 2010. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 1643–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinmetz, J.D.; Bourne, R.R.A.; Briant, P.S.; Flaxman, S.R.; Taylor, H.R.B.; Jonas, J.B.; Abdoli, A.A.; Abrha, W.A.; Abualhasan, A.; Abu-Gharbieh, E.G.; et al. Causes of blindness and vision impairment in 2020 and trends over 30 years, and prevalence of avoidable blindness in relation to VISION 2020: The Right to Sight: An analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet Glob. Health 2021, 9, e144–e160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Bourne, R.R.; Jonas, J.B.; Bron, A.M.; Cicinelli, M.V.; Das, A.; Flaxman, S.R.; Friedman, D.S.; E Keeffe, J.; Kempen, J.H.; Leasher, J.; et al. Prevalence and causes of vision loss in high-income countries and in Eastern and Central Europe in 2015: Magnitude, temporal trends and projections. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2018, 102, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauesund, E.S.; Jørstad, Ø.K.; Brunborg, C.; Moe, M.C.; Erke, M.G.; Fosmark, D.S.; Petrovski, G. A Pilot Study of Implementing Diabetic Retinopathy Screening in the Oslo Region, Norway: Baseline Results. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilstad, H.N.; Sjølie, A.K.; Gøransson, L.; Hapnes, R.; Henschien, H.J.; Alsbirk, K.E.; Fossen, K.; Bertelsen, G.; Holstad, G.; Bergrem, H. Prevalence of diabetic retinopathy in Norway: Report from a screening study. Acta Ophthalmol. 2012, 90, 609–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanlon, P.H.; Malhotra, R.; Thomas, G.; Foy, C.; Kirkpatrick, J.N.; Lewis-Barned, N.; Harney, B.; Aldington, S.J. The effectiveness of screening for diabetic retinopathy by digital imaging photography and technician ophthalmoscopy. Diabet. Med. 2003, 20, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vujosevic, S.; Aldington, S.J.; Silva, P.; Hernández, C.; Scanlon, P.; Peto, T.; Simó, R. Screening for diabetic retinopathy: New perspectives and challenges. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020, 8, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauesund, E.S.; Hertzberg, S.N.W.; Jørstad, Ø.K.; Moe, M.C.; Erke, M.G.; Fosmark, D.S.; Petrovski, G. A health economic pilot study comparing two diabetic retinopathy screening strategies. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 15618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohan, T.E.; Frost, C.D.; Wald, N.J. Prevention of blindness by screening for diabetic retinopathy: A quantitative assessment. BMJ 1989, 299, 1198–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diabetisk Retinopati-Screening Oslo University hospital Web Page. Available online: https://www.oslo-universitetssykehus.no/behandlinger/diabetisk-retinopati-screening/ (accessed on 22 February 2025).
- Hristova, E.; Koseva, D.; Zlatarova, Z.; Dokova, K. Diabetic retinopathy screening and registration in europe—Narrative review. Healthcare 2021, 9, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grauslund, J.; Andersen, N.; Andresen, J.; Flesner, P.; Haamann, P.; Heegaard, S.; Larsen, M.; Laugesen, C.S.; Schielke, K.; Skov, J.; et al. Evidence-based Danish guidelines for screening of diabetic retinopathy. Acta Ophthalmol. 2018, 96, 763–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Løvaas, K.F.; Madsen, T.V.; Cooper, J.G.; Sandberg, S.; Ernes, T.; Ueland, G.Å.; Norwegian Diabetes Registry for Adults. Data from Diabetes Clinics Diabetes Type 1 & Type 2 Annual Report for 2023; The Norwegian Organization for Quality Improvement of Laboratory Examinations: Bergen, Norway, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- The Saint Vincent Declaration. Acta Ophthalmol. Scand. 1997, 75, 63. [CrossRef]
- The Liverpool Declaration on Screening for Diabetic Retinopathy in Europe. In Proceedings of the Screening for Diabetic Retinopathy in Europe—5 Years after St. Vincent, Liverpool, UK, 17–18 November 2005; Available online: https://www.drscreening2005.org.uk/declaration_2005.html# (accessed on 22 February 2025).
- Hanberger, L.; Birkebaek, N.; Bjarnason, R.; Drivvoll, A.K.; Johansen, A.; Skrivarhaug, T.; Thorsson, A.V.; Samuelsson, U. Childhood Diabetes in the Nordic Countries: A Comparison of Quality Registries. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2014, 8, 738–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Health TNDo (Ed.) Retinopathy and Regular Retinal Examination in Diabetes; Norwegian Directorate of Health: Oslo, Norway, 2019; Available online: https://www.helsedirektoratet.no/retningslinjer/diabetes/retinopati-og-regelmessig-netthinneundersokelse-ved-diabetes (accessed on 22 February 2025).
- Diabetisk retinopati—Retningslinjer for screening. Norwegian Ophthalmological Society. 11.10.2022. Available online: https://www.legeforeningen.no/contentassets/c7fccca0ee554d7d80fd8c4818cdd739/godkjente-retningslinjer-for-screening-for-diabetisk-retinopati-05.11.2022.pdf (accessed on 22 February 2025).
- Ipp, E.; Liljenquist, D.; Bode, B.; Shah, V.N.; Silverstein, S.; Regillo, C.D.; Lim, J.I.; Sadda, S.; Domalpally, A.; Gray, G.; et al. Pivotal Evaluation of an Artificial Intelligence System for Autonomous Detection of Referrable and Vision-Threatening Diabetic Retinopathy. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2134254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramoff, M.D.; Lavin, P.T.; Birch, M.; Shah, N.; Folk, J.C. Pivotal trial of an autonomous AI-based diagnostic system for detection of diabetic retinopathy in primary care offices. NPJ Digit. Med. 2018, 1, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tufail, A.; Rudisill, C.; Egan, C.; Kapetanakis, V.V.; Salas-Vega, S.; Owen, C.G.; Lee, A.; Louw, V.; Anderson, J.; Liew, G.; et al. Automated Diabetic Retinopathy Image Assessment Software: Diagnostic Accuracy and Cost-Effectiveness Compared with Human Graders. Ophthalmology 2017, 124, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, S.; Rajan, R.P.; Sundar, B.; Venkatachalam, S.; Kempen, J.H.; Kim, R. Validation of diagnostic accuracy of retinal image grading by trained non-ophthalmologist grader for detecting diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular edema. Eye 2023, 37, 1577–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tufail, A.; Kapetanakis, V.V.; Salas-Vega, S.; Egan, C.; Rudisill, C.; Owen, C.G.; Lee, A.; Louw, V.; Anderson, J.; Liew, G.; et al. An observational study to assess if automated diabetic retinopathy image assessment software can replace one or more steps of manual imaging grading and to determine their cost-effectiveness. Health Technol. Assess. 2016, 20, 1–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uy, H.; Fielding, C.; Hohlfeld, A.; Ochodo, E.; Opare, A.; Mukonda, E.; Minnies, D.; Engel, M.E.; Fatumo, S. Diagnostic test accuracy of artificial intelligence in screening for referable diabetic retinopathy in real-world settings: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS Glob. Public Health 2023, 3, e0002160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhaskaranand, M.; Ramachandra, C.; Bhat, S.; Cuadros, J.; Nittala, M.G.; Sadda, S.R.; Solanki, K. The Value of Automated Diabetic Retinopathy Screening with the EyeArt System: A Study of More Than 100,000 Consecutive Encounters from People with Diabetes. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2019, 21, 635–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ting, D.S.W.; Cheung, C.Y.-L.; Lim, G.; Tan, G.S.W.; Quang, N.D.; Gan, A.; Hamzah, H.; Garcia-Franco, R.; Yeo, I.Y.S.; Lee, S.Y.; et al. Development and Validation of a Deep Learning System for Diabetic Retinopathy and Related Eye Diseases Using Retinal Images From Multiethnic Populations With Diabetes. JAMA 2017, 318, 2211–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Millana, A.; Saez-Saez, A.; Tornero-Costa, R.; Azzopardi-Muscat, N.; Traver, V.; Novillo-Ortiz, D. Artificial intelligence and its impact on the domains of universal health coverage, health emergencies and health promotion: An overview of systematic reviews. Int. J. Med Informatics 2022, 166, 104855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhelev, Z.; Peters, J.; Rogers, M.; Allen, M.; Kijauskaite, G.; Seedat, F.; Wilkinson, E.; Hyde, C. Test accuracy of artificial intelligence-based grading of fundus images in diabetic retinopathy screening: A systematic review. J. Med Screen. 2023, 30, 97–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.Y.; Lee, C.S.; Hunt, M.S.; Yanagihara, R.T.; Blazes, M.; Boyko, E.J. Multicenter, Head-to-Head, Real-World Validation Study of Seven Automated Artificial Intelligence Diabetic Retinopathy Screening Systems. Diabetes Care 2021, 44, e108–e109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellemo, V.; Lim, G.; Rim, T.H.; Tan, G.S.W.; Cheung, C.Y.; Sadda, S.; He, M.-G.; Tufail, A.; Lee, M.L.; Hsu, W.; et al. Artificial Intelligence Screening for Diabetic Retinopathy: The Real-World Emerging Application. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2019, 19, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meredith, S.; van Grinsven, M.; Engelberts, J.; Clarke, D.; Prior, V.; Vodrey, J.; Hammond, A.; Muhammed, R.; Kirby, P. Performance of an artificial intelligence automated system for diabetic eye screening in a large English population. Diabet. Med. 2023, 40, e15055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Council of Ophthalmology (ICO). Updated 2017 ICO Guidelines for Diabetic Eye Care; International Council of Ophthalmology (ICO): San Francisco, CA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Cleland, C. Comparing the International Clinical Diabetic Retinopathy (ICDR) severity scale. Community Eye Health 2023, 36, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson, C.; Ferris, F.L.; E Klein, R.; Lee, P.P.; Agardh, C.D.; Davis, M.; Dills, D.; Kampik, A.; Pararajasegaram, R.; Verdaguer, J.T. Proposed international clinical diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular edema disease severity scales. Ophthalmology 2003, 110, 1677–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grzybowski, A.; Brona, P. Approval and Certification of Ophthalmic AI Devices in the European Union. Ophthalmol. Ther. 2023, 12, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Autonomous AI Detection of Diabetic Retinopathy, Age-Related Macular Degeneration, and Glaucoma [Press Release]. 2023. Available online: https://www.globenewswire.com (accessed on 27 June 2024).
- Akoglu, H. User’s guide to correlation coefficients. Turk. J. Emerg. Med. 2018, 18, 91–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landis, J.R.; Koch, G.G. A One-Way Components of Variance Model for Categorical Data. Biometrics 1977, 33, 671–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viera, A.J.; Garrett, J.M. Understanding interobserver agreement: The kappa statistic. Fam. Med. 2005, 37, 360–363. [Google Scholar]
- Mead, A.; Burnett, S.; Davey, C. Diabetic retinal screening in the UK. J. R. Soc. Med. 2001, 94, 127–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, A.; McIntosh, A.; Peters, J.; O’Keeffe, C.; Khunti, K.; Baker, R.; Booth, A. Effectiveness of screening and monitoring tests for diabetic retinopathy—A systematic review. Diabet. Med. 2000, 17, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- British Diabetic Association. Retinal Photography Screening for Diabetic Eye Disease; British Dental Association: London, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, J.I.; Regillo, C.D.; Sadda, S.R.; Ipp, E.; Bhaskaranand, M.; Ramachandra, C.; Solanki, K. Artificial Intelligence Detection of Diabetic Retinopathy. Ophthalmol. Sci. 2023, 3, 100228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabeg, M.; Petrovski, G.; Hertzberg, S.N.; Erke, M.G.; Fosmark, D.S.; Russell, G.; Moe, M.C.; Volke, V.; Raudonis, V.; Verkauskiene, R.; et al. A pilot cost-analysis study comparing AI-based EyeArt® and ophthalmologist assessment of diabetic retinopathy in minority women in Oslo, Norway. Int. J. Retin. Vitr. 2024, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaskaranand, M.; Ramachandra, C.; Bhat, S.; Cuadros, J.; Nittala, M.G.; Sadda, S.; Solanki, K. Automated Diabetic Retinopathy Screening and Monitoring Using Retinal Fundus Image Analysis. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2016, 10, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vought, R.; Vought, V.; Shah, M.; Szirth, B.; Bhagat, N. EyeArt artificial intelligence analysis of diabetic retinopathy in retinal screening events. Int. Ophthalmol. 2023, 43, 4851–4859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heydon, P.; Egan, C.; Bolter, L.; Chambers, R.; Anderson, J.; Aldington, S.; Stratton, I.M.; Scanlon, P.H.; Webster, L.; Mann, S.; et al. Prospective evaluation of an artificial intelligence-enabled algorithm for automated diabetic retinopathy screening of 30 000 patients. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 105, 723–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokhashi, N.; Grachevskaya, J.; Cheng, L.; Yu, D.; Lu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Henderer, J.D. A Comparison of Artificial Intelligence and Human Diabetic Retinal Image Interpretation in an Urban Health System. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2021, 16, 1003–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olvera-Barrios, A.; Heeren, T.F.; Balaskas, K.; Chambers, R.; Bolter, L.; Egan, C.; Tufail, A.; Anderson, J. Diagnostic accuracy of diabetic retinopathy grading by an artificial intelligence-enabled algorithm compared with a human standard for wide-field true-colour confocal scanning and standard digital retinal images. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 105, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van, T.N.; Thi, H.L.V. Effectiveness of artificial intelligence for diabetic retinopathy screening in community in Binh Dinh Province, Vietnam. Taiwan J. Ophthalmol. 2024, 14, 394–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oke, J.L.; Stratton, I.M.; Aldington, S.J.; Stevens, R.J.; Scanlon, P.H. The use of statistical methodology to determine the accuracy of grading within a diabetic retinopathy screening programme. Diabet. Med. 2016, 33, 896–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, R.M.; Liu, T.A.; Thomas, C.; Prichett, L.; Zimmer-Galler, I.; Smith, K.; Abramoff, M.D.; Channa, R. The SEE Study: Safety, Efficacy, and Equity of Implementing Autonomous Artificial Intelligence for Diagnosing Diabetic Retinopathy in Youth. Diabetes Care 2021, 44, 781–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajalakshmi, R.; Subashini, R.; Anjana, R.M.; Mohan, V. Automated diabetic retinopathy detection in smartphone-based fundus photography using artificial intelligence. Eye 2018, 32, 1138–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertelsen, G.; Peto, T.; Lindekleiv, H.; Schirmer, H.; Solbu, M.D.; Toft, I.; Sjølie, A.K.; Njølstad, I. Tromsø eye study: Prevalence and risk factors of diabetic retinopathy. Acta Ophthalmol. 2013, 91, 716–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsbirk, K.E.; Seland, J.H.; Assmus, J. Diabetic retinopathy and visual impairment in a Norwegian diabetic coast population with a high dietary intake of fish oils. An observational study. Acta Ophthalmol. 2022, 100, E532–E538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, A.E.; Davidson, O.Q.; Lee, C.S.; Lee, A.Y. Artificial Intelligence and Diabetic Retinopathy: AI Framework, Prospective Studies, Head-to-head Validation, and Cost-effectiveness. Diabetes Care 2023, 46, 1728–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| n = 128 (%) | |
|---|---|
| Gender (women/men) | 51/77 (39.8/60.1) |
| Age (years) Median (IQR) range | 52.5 (44.5–64.5) 18–89 |
| Type of DM (T1D/T2D) | 31/97 (24.2/75.8) |
| Duration of DM (years) Median (IQR) range | 4.5 (1.0–8.0) 0.1–42.3 |
| HbA1c (mmol/mol) Median (IQR) range | 55.5 (48.0–60.0) 31.0–125.0 |
| Systolic BP (mmHg) Median (IQR) range | 130 (122.0–140) 90.0–164.0 |
| Diastolic BP (mmHg) Median (IQR) range | 79.8 (79.4–80.0) 60.0–100.0 |
| MC | AI | ||||
| n = 247 Eyes (%) | No DR n (%) | Mild DR n (%) | Moderate DR n (%) | Severe DR n (%) | |
| No DR | 143 (72.6) | 22 (11.2) | 32 (16.2) | − | |
| Mild DR | 3 (14.3) | 13 (61.9) | 5 (23.8) | − | |
| Moderate DR | − | 3 (11.1) | 22 (81.5) | 2 (7.4) | |
| Severe DR | − | − | 1 (50.0) | 1 (50.0) | |
| AI vs. MC | Any Type of DR n = 247 | RDR n = 247 |
|---|---|---|
| QWK (95% CI) Spearman’s r | 0.52 (0.50–0.58) 0.56 | 0.48 (0.35–0–61) 0.54 |
| Sensitivity (%, 95% CI) | 94.0 (91.0–96.9) | 89.7 (85.9–93.4) |
| Specificity (%, 95% CI) | 72.6 (67.0–78.1) | 83.0 (78.5–87.7) |
| AUC (%, 95% CI) | 83.5 (78.3–88.7) | 86.3 (79.3–93.4) |
| Prevalence (%, 95% CI) | 20.2 (15.2–25.2) | 11.7 (7.7–15.8) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Karabeg, M.; Petrovski, G.; Holen, K.; Steffenssen Sauesund, E.; Fosmark, D.S.; Russell, G.; Erke, M.G.; Volke, V.; Raudonis, V.; Verkauskiene, R.; et al. Comparison of Validity and Reliability of Manual Consensus Grading vs. Automated AI Grading for Diabetic Retinopathy Screening in Oslo, Norway: A Cross-Sectional Pilot Study. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 4810. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134810
Karabeg M, Petrovski G, Holen K, Steffenssen Sauesund E, Fosmark DS, Russell G, Erke MG, Volke V, Raudonis V, Verkauskiene R, et al. Comparison of Validity and Reliability of Manual Consensus Grading vs. Automated AI Grading for Diabetic Retinopathy Screening in Oslo, Norway: A Cross-Sectional Pilot Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(13):4810. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134810
Chicago/Turabian StyleKarabeg, Mia, Goran Petrovski, Katrine Holen, Ellen Steffenssen Sauesund, Dag Sigurd Fosmark, Greg Russell, Maja Gran Erke, Vallo Volke, Vidas Raudonis, Rasa Verkauskiene, and et al. 2025. "Comparison of Validity and Reliability of Manual Consensus Grading vs. Automated AI Grading for Diabetic Retinopathy Screening in Oslo, Norway: A Cross-Sectional Pilot Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 13: 4810. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134810
APA StyleKarabeg, M., Petrovski, G., Holen, K., Steffenssen Sauesund, E., Fosmark, D. S., Russell, G., Erke, M. G., Volke, V., Raudonis, V., Verkauskiene, R., Sokolovska, J., Moe, M. C., Kjellevold Haugen, I.-B., & Petrovski, B. E. (2025). Comparison of Validity and Reliability of Manual Consensus Grading vs. Automated AI Grading for Diabetic Retinopathy Screening in Oslo, Norway: A Cross-Sectional Pilot Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(13), 4810. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134810





