Comparison of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Scales for Assessment of Interval Changes of Arthropathy in Boys with Severe Hemophilia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Data
2.2. Patient Joint Examinations
2.3. Physical Examination
2.4. Radiographic (Plain X-Ray) Scoring System
2.5. MRI Scoring Systems
- 10-point Denver progressive scale [Supplementary Table S3] [12].
- 10-point Compatible IPSG MRI progressive scale (MRI-P) [Supplementary Table S4] [13].
- 20-point Compatible IPSG MRI additive scale (MRI-A) [Supplementary Table S4] [13].
- 17-point IPSG MRI additive scale [Supplementary Table S5] [14].
2.6. X-Ray Imaging Acquisition
2.7. MR Imaging Acquisition
2.8. MR Image Interpretation
2.9. Statistical Methods
3. Results
3.1. Imaging Studies at Study Entry
3.2. Changes in Joint Scores over the Study Period
3.3. Tailored Prophylaxis Group [Nine Boys (54 Index Joints) Who Completed MRI Evaluations Were Available at Study Entry and Exit]
3.4. Standard Prophylaxis Group [Eight Boys Who Completed MRI Evaluations Were Available at Study Entry (48 Index Joints) and Exit (47 Index Joints)]
3.5. Correlations Among Scores of the Four MRI Scales and Between Scores of These Scales and Physical Examination and X-Ray Scales
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nilsson, I.M.; Berntorp, E.; Löfqvist, T.; Pettersson, H. Twenty-five years’ experience of prophylactic treatment in severe haemophilia A and B. J. Intern. Med. 1992, 232, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, K.; Ljung, R. Primary prophylaxis in haemophilia care: Guideline update 2016. Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 2017, 67, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oldenburg, J.; Mahlangu, J.N.; Kim, B.; Schmitt, C.; Callaghan, M.U.; Young, G.; Santagostino, E.; Kruse-Jarres, R.; Negrier, C.; Kessler, C.; et al. Emicizumab Prophylaxis in Hemophilia A with Inhibitors. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 809–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahlangu, J.; Oldenburg, J.; Paz-Priel, I.; Negrier, C.; Niggli, M.; Mancuso, M.E.; Schmitt, C.; Jiménez-Yuste, V.; Kempton, C.; Dhalluin, C.; et al. Emicizumab Prophylaxis in Patients who have Hemophilia A without Inhibitors. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 811–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, K.; Poonnoose, P.; Dunn, A.L.; Babyn, P.; Manco-Johnson, M.J.; David, J.A.; van der Net, J.; Feldman, B.; Berger, K.; Carcao, M.; et al. Choosing outcome assessment tools in haemophilia care and research: A multidisciplinary perspective. Haemophilia 2017, 23, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manco-Johnson, M.J.; Pettersson, H.; Petrini, P.; Babyn, P.S.; Bergstrom, B.; Bradley, C.; Doria, A.S.; Feldman, B.M.; Funk, S.; Hilliard, P.; et al. Physical therapy and imaging outcome measures in a haemophilia population treated with factor prophylaxis: Current status and future directions. Haemophilia 2004, 10 (Suppl. S4), 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holden, R.B. Face validity. In The Corsini Encyclopedia of Psychology; Weiner, I.B., Craighead, W.E., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 637–638. [Google Scholar]
- Gravetter, F.J.; Forzano, A.B. Research Methods for the Behavioral Sciences; Cengage Learning: Wadsworth, OH, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Manco-Johnson, M.J.; Nuss, R.; Funk, S.; Murphy, J. Joint evaluation instruments for children and adults with haemophilia. Haemophilia 2000, 6, 649–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manco-Johnson, M.J.; Nuss, R.; Lear, J.; Wiedel, J.; Geraghty, S.J.; Hacker, M.R.; Funk, S.; Kilcoyne, R.F.; Murphy, J. 32P Radiosynoviorthesis in children with hemophilia. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2002, 24, 534–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersson, H.; Ahlberg, A.; Nilsson, I.M. A radiologic classification of hemophilic arthropathy. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1980, 149, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuss, R. MRI findings in haemophilic joints treated with radiosynoviorthesis with development of an MRI scale of joint damage. Haemophilia 2000, 6, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundin, B.; Babyn, P.; Doria, A.S.; Kilcoyne, R.; Ljung, R.; Miller, S.; Nuss, R.; Rivard, G.E.; Pettersson, H.; International Prophylaxis Study Group. Compatible scales for progressive and additive MRI assessments of haemophilic arthropathy. Haemophilia 2005, 11, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundin, B.; Manco-Johnson, M.L.; Ignas, D.M.; Moineddin, R.; Blanchette, V.S.; Dunn, A.L.; Gibikote, S.V.; Keshava, S.N.; Ljung, R.; Manco-Johnson, M.J.; et al. An MRI scale for assessment of haemophilic arthropathy from the International Prophylaxis Study Group. Haemophilia 2012, 6, 962–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carcao, M.; Selvaratnam, V.; Blatny, J. How much prophylaxis is enough in haemophilia? Haemophilia 2024, 30 (Suppl. S3), 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ljung, R.; Fischer, K.; Carcao, M.; Santagostino, E.; Manco-Johnson, M.J.; Mathew, P.; INPH group. Practical considerations in choosing a factor VIII prophylaxis regimen: Role of clinical phenotype and trough levels. Thromb. Haemost. 2016, 115, 913–920. [Google Scholar]
- Carcao, M.D.; Aledort, L. Prophylactic factor replacement in hemophilia. Blood Rev. 2004, 18, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altman, D.G. Practical Statistics for Medical Research; Chapman and Hall: London, UK, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Betz, F.; Horthorn, T.; Westfall, P. Multiple Comparisons Using R; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Farcomeni, A. A review of modern multiple hypothesis testing, with particular attention to the false discovery proportion. Stat. Methods Med. Res. 2008, 17, 347–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.; Brewer, A.K.; Mauser-Bunschoten, E.P.; Key, N.S.; Kitchen, S.; Llinas, A.; Ludlam, C.A.; Mahlangu, J.N.; Mulder, K.; Poon, M.C.; et al. Guidelines for the management of hemophilia. Haemophilia 2013, 19, 1–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ljung, R.; Andersson, N.G. The current status of prophylactic replacement therapy in children and adults with haemophilia. Br. J. Haematol. 2015, 169, 777–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraft, J.; Blanchette, V.; Babyn, P.; Feldman, B.; Cloutier, S.; Israels, S.; Pai, M.; Rivard, G.; Gomer, S.; McLIMONT, M.; et al. Magnetic resonance imaging and joint outcomes in boys with severe hemophilia A treated with tailored primary prophylaxis in Canada. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2012, 10, 2494–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Genderen, F.R.; Fischer, K.; Heijnen, L.; de Kleijn, P.; van den Berg, H.M.; Helders, P.J.; van Meeteren, N.L. Pain and functional limitations in patients with severe haemophilia. Haemophilia 2006, 12, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doria, A.S.; Keshava, S.N.; Mohanta, A.; Jarrin, J.; Blanchette, V.; Srivastava, A.; Moineddin, R.; Kavitha, M.L.; Hilliard, P.; Poonnoose, P.; et al. Diagnostic accuracy of ultrasound for assessment of hemophilic arthropathy: MRI correlation. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2015, 204, W336–W347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunel, T.; Lobet, S.; Deschamps, K.; Hermans, C.; Peerlinck, K.; Vandesande, J.; Pialat, J.B. Reliability and clinical features associated with the IPSG MRI tibiotalar and subtalar joint scores in children, adolescents and young adults with haemophilia. Haemophilia 2018, 24, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plut, D.; Kotnik, B.F.; Zupan, I.P.; Kljucevsek, D.; Vidmar, G.; Snoj, Z.; Martinoli, C.; Salapura, V. Diagnostic accuracy of haemophilia early arthropathy detection with ultrasound (HEAD-US): A comparative magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) study. Radiol. Oncol. 2019, 53, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Drygalski, A.; Barnes, R.F.W.; Jang, H.; Ma, Y.; Wong, J.H.; Berman, Z.; Du, J.; Chang, E.Y. Advanced magnetic resonance imaging of cartilage components in haemophilic joints reveals that cartilage hemosiderin correlates with joint deterioration. Haemophilia 2019, 25, 851–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Leeuwen, F.H.; van Bergen, E.D.; Timmer, M.A.; van Vulpen, L.F.; Schutgens, R.E.; de Jong, P.A.; Fischer, K.; Foppen, W. Magnetic resonance imaging evidence for subclinical joint bleeding in a Dutch population of people with severe hemophilia on prophylaxis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2023, 21, 1156–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stimec, J.; Dover, S.; Pullenayegum, E.; Blanchette, V.S.; Doria, A.S.; Feldman, B.M.; Carcao, M.; Rivard, G.E.; Israels, S.J.; Chan, A.K.; et al. Magnetic resonance imaging in boys with severe hemophilia A: Serial and end-of-study findings from the Canadian Hemophilia Primary Prophylaxis Study. Res. Pr. Thromb. Haemost. 2021, 5, e12565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foppen, W.; van der Schaaf, I.C.; Beek, F.J.A.; Mali, W.P.T.M.; Fischer, K. MRI predicts 5-year joint bleeding and development of arthropathy on radiographs in hemophilia. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouw, S.C.; Timmer, M.A.; Srivastava, A.; de Kleijn, P.; Hilliard, P.; Peters, M.; Blanchette, V.; Fischer, K. Measurement of joint health in persons with haemophilia: A systematic review of the measurement properties of haemophilia-specific instruments. Haemophilia 2018, 25, e1–e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manco-Johnson, M.J.; Abshire, T.C.; Shapiro, A.D.; Riske, B.; Hacker, M.R.; Kilcoyne, R.; Ingram, J.D.; Manco-Johnson, M.L.; Funk, S.; Jacobson, L.; et al. Prophylaxis versus episodic treatment to prevent joint disease in boys with severe hemophilia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, M.; Daruge, P.; Dertkigil, S.S.J.; De Avila Fernandes, E.; Negrao, J.R.; de Aguiar Vilela Mitraud, S.; Sakuma, E.T.I.; Fernandes, A.R.C.; Zhang, N.; Huo, A.; et al. Imaging of haemophilic arthropathy in growing joints: Pitfalls in ultrasound and MRI. Haemophilia 2017, 23, 660–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutten, C.; Soliman, M.; Panwar, J.; Mohanta, A.; Zhou, A.; Hilliard, P.; Rayner, T.; Weiss, R.; Man, C.; Moineddin, R.; et al. Evaluation of Point-of-Care Ultrasound in Paediatric Haemophilic Arthropathy: A Prospective Comparative Study With Comprehensive Ultrasound and MRI. Heamophilia 2025, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundin, B.; Bakeer, N.; Dunn, A.L.; Gibikote, S.; Keshava, S.N.; Ljung, R.C.R.; Papakonstantinou, O.; Pergantou, H.; Strike, K.; von Drygalski, A.; et al. International Prophylaxis Study Group (IPSG) haemophilia joint MRI scale version 2.0. Haemophilia 2024, 30, 862–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
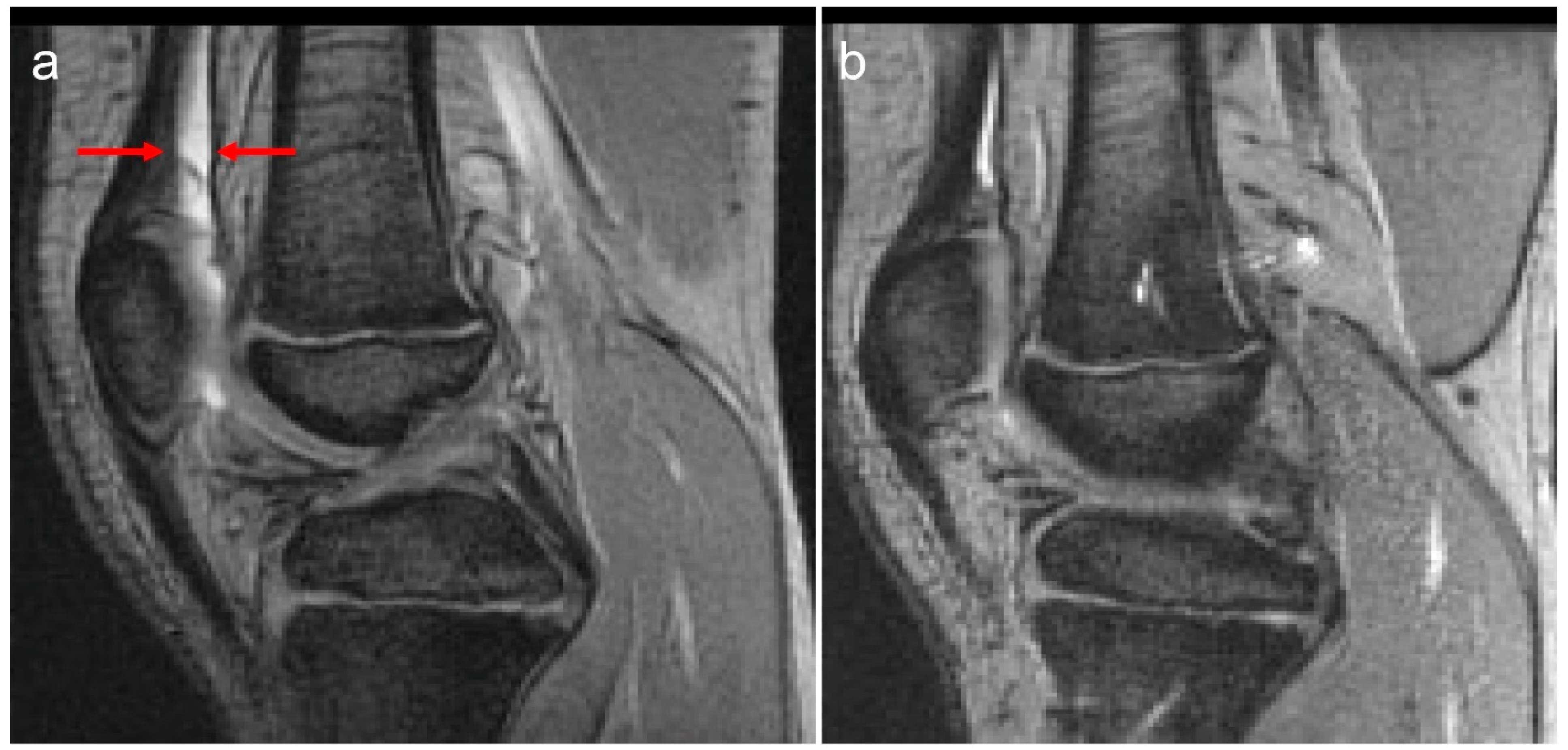
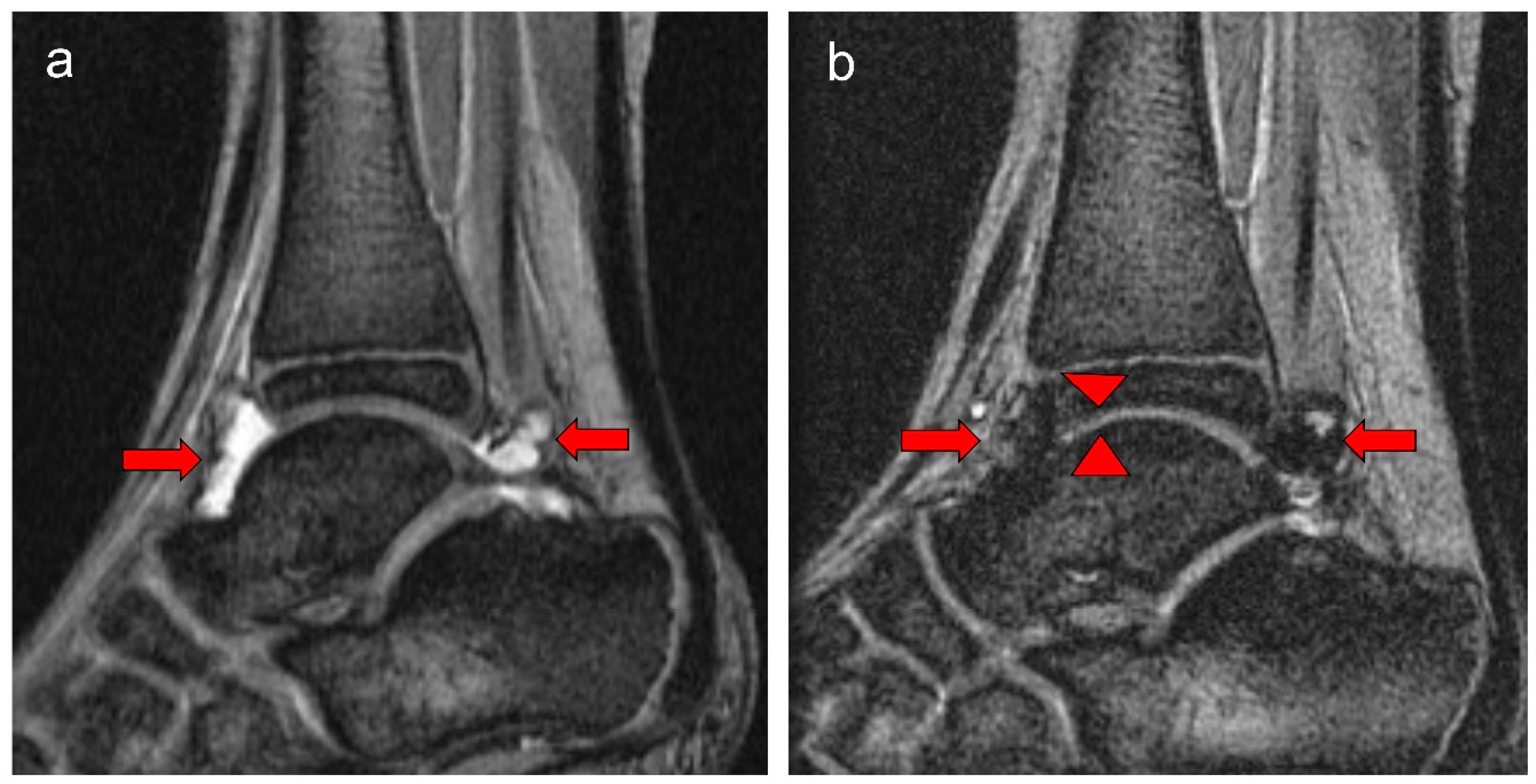

| Standard Prophylaxis (SP) Study Arm Entry | Tailored Prophylaxis (TP) Study Arm Entry | p Value | Standard Prophylaxis (SP) Study Arm Exit | Tailored Prophylaxis (TP) Study Arm Exit | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of participants | 8 | 9 | 8 | 9 | ||
| Age (years) | 10 (7–16) * | 12 (8–15) | 0.8290 | – | – | |
| Child PE score | 6 (2–15) | 8 (3–16) | 0.8943 | 6.5 (6–14) | 13 (4–17) | 0.6812 |
| Pettersson X-ray score | 0 (0–4) | 2 (0–13) | 0.5882 | 0 (0–4) | 2 (0–14) | 0.6985 |
| MRI (17-point IPSG scale) scores for 6 index joints: | ||||||
| Soft tissue total score | 2.5 (0–11) | 6 (0–15) | 0.8137 | 3 (0–7) ** | 7 (1–14) | 0.5798 |
| Effusion/hemarthrosis | 0 (0–3) | 2 (0–4) | 0.1669 | 0.5 (0–2) | 1 (0–3) | 0.2519 |
| Synovial hypertrophy | 1 (0–3) | 2 (0–6) | 0.3973 | 1 (0–2) | 2 (0–6) | 0.2558 |
| Hemosiderin | 1 (0–5) | 3 (0–6) | 0.5579 | 1 (0–4) | 3 (0–6) | 0.4020 |
| Osteochondral total score | 0 (0–4) | 5 (0–10) | 0.3240 | 0.5 (0–4) | 6 (0–11) | 0.3460 |
| Surface erosions | 0 (0–1) | 2 (0–3) | 0.0005 | 0 (0–1) | 2 (0–3) | 0.0005 |
| Subchondral cysts | 0 (0–2) | 1 (0–4) | 0.1474 | 0 (0–2) | 2 (0–4) | 0.0429 |
| Cartilage degradation | 0 (0–2) | 2 (0–4) | 0.0429 | 0.5 (0–2) | 2 (0–6) | 0.1978 |
| Total score | 5.5 (0–12) | 11 (0–20) | 0.7939 | 6 (0–8) | 11 (1–22) | 0.7046 |
| Standard Prophylaxis (SP) Study Arm Entry | Tailored Prophylaxis (TP) Study Arm Entry | p-Value | Standard Prophylaxis (SP) Study Arm Exit | Tailored Prophylaxis (TP) Study Arm Exit | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | |||
| Soft tissue items | 12/48 (25.0) | 19/54 (35.2) | 0.2887 | 11/47 (23.4) * | 20/54 (37.0) | 0.2751 |
| Effusion/hemarthrosis | 6/12 | 12/19 | 0.7098 | 6/11 | 11/20 | 0.7116 |
| Synovial hypertrophy | 6/12 | 9/19 | 1.0 | 6/11 | 9/20 | 1.0 |
| Hemosiderin | 9/12 | 13/19 | 1.0 | 9/11 | 14/20 | 0.6722 |
| Osteochondral items | 3/48 (6.3) | 11/54 (20.4) | 0.0466 | 4/47 (8.5) * | 13/54 (24.1) | 0.1593 |
| Surface erosions | 2/3 | 10/11 | 0.3956 | 2/4 | 10/13 | 0.1538 |
| Subchondral cysts | 2/3 | 7/11 | 1.0 | 2/4 | 8/13 | 1.0 |
| Cartilage degradation | 3/3 | 11/11 | 1.0 | 4/4 | 13/13 | 1.0 |
| Total items | 12/48 (25.0) | 23/54 (42.6) | 0.0940 | 11/47 (23.4) * | 23/54 (42.6) | 0.0574 |
| Arm | Participant | Index Joint | Joint Entry Score | Joint Exit Score | IPSG 17-Point Item Element that Changed | Item Entry Score | Item Exit Score | Total Change by Item |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tailored Prophylaxis | 1 | RE | 9 | 12 | surface erosions | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| subchondral cysts | 0 | 2 | 2 | |||||
| LA | 1 | 0 | effusion/hemarthrosis | 1 | 0 | −1 | ||
| 2 | LA | 4 | 8 | effusion/hemarthrosis | 2 | 1 | −1 | |
| synovial hypertrophy | 1 | 3 | 2 | |||||
| hemosiderin | 1 | 3 | 2 | |||||
| cartilage degradation | 0 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| 3 | LA | 5 | 6 | hemosiderin | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| 4 | LA | 4 | 5 | cartilage degradation | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| RA | 7 | 6 | effusion/hemarthrosis | 2 | 0 | −2 | ||
| cartilage degradation | 1 | 2 | 1 | |||||
| 5 | LA | 0 | 1 | effusion/hemarthrosis | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| 6 | RA | 9 | 10 | hemosiderin | 1 | 2 | 1 | |
| 9 | LE | 3 | 4 | cartilage degradation | 1 | 2 | 1 | |
| LA | 3 | 4 | cartilage degradation | 1 | 2 | 1 | ||
| Standard Prophylaxis | 16 | LK | 1 | 0 | effusion/hemarthrosis | 1 | 0 | −1 |
| LA | 1 | 0 | effusion/hemarthrosis | 1 | 0 | −1 | ||
| RA | 8 | 6 | synovial hypertrophy | 3 | 2 | −1 | ||
| hemosiderin | 3 | 2 | −1 | |||||
| 17 | LA | 4 | 5 | cartilage degradation | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| 18 | RA | 6 | 7 | effusion/hemarthrosis | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| 20 | LA | 0 | 2 | effusion/hemarthrosis | 0 | 2 | 2 |
| Values | MRI Scales | 17-Point IPSG Scale | MRI A-Scale | MRI P-Scale | Denver Scale | Child PE Scale | Pettersson |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r-value | 17-point IPSG scale | 1.00 | * 0.59 | 0.61 | 0.61 | 0.02 | 0.53 |
| p-value | <0.0001 | 0.009 | 0.007 | 0.007 | 0.93 | 0.02 | |
| r-value | MRI A-scale | * 0.59 | 1.00 | 0.67 | 0.67 | 0.51 | 0.78 |
| p-value | 0.009 | <0.0001 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.03 | 0.0002 | |
| r-value | MRI P-scale | 0.61 | 0.67 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.37 | 0.57 |
| p-value | 0.007 | 0.002 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.13 | 0.01 | |
| r-value | Denver scale | 0.61 | 0.67 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.37 | 0.57 |
| p-value | 0.007 | 0.002 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.13 | 0.01 | |
| r-value | Child PE scale | 0.02 | 0.51 | 0.37 | 0.37 | 1.00 | 0.28 |
| p-value | 0.93 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | <0.0001 | 0.25 | |
| r-value | Pettersson | 0.53 | 0.78 | 0.57 | 0.57 | 0.28 | 1.00 |
| p-value | 0.02 | 0.0002 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.25 | <0.0001 |
| Values | MRI Scales | 17-Point IPSG Scale | MRI A-Scale | MRI P-Scale | Denver Scale | Child PE Scale | Pettersson |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r-value | 17-point IPSG scale | 1.00 | 0.65 | 0.95 | 0.95 | −0.16 | 0.45 |
| p-value | <0.0001 | 0.006 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.55 | 0.07 | |
| r-value | MRI A-scale | 0.65 | 1.00 | * 0.64 | * 0.64 | 0.016 | −0.22 |
| p-value | 0.006 | <0.0001 | 0.008 | 0.008 | 0.95 | 0.41 | |
| r-value | MRI P-scale | 0.95 | * 0.64 | 1.00 | 1.00 | −0.18 | 0.48 |
| p-value | <0.0001 | 0.008 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.50 | 0.06 | |
| r-value | Denver scale | 0.95 | * 0.64 | 1.00 | 1.00 | −0.18 | 0.48 |
| p-value | <0.0001 | 0.008 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.50 | 0.06 | |
| r-value | Child PE scale | −0.16 | 0.02 | −0.18 | −0.18 | 1.00 | −0.21 |
| p-value | 0.55 | 0.9 | 0.50 | 0.50 | <0.0001 | 0.44 | |
| r-value | Pettersson | 0.46 | −0.22 | 0.48 | 0.48 | −0.21 | 1.00 |
| p-value | 0.07 | 0.41 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.44 | <0.0001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, N.; Carcao, M.; Ignas, D.M.; Feldman, B.M.; Hilliard, P.; Moineddin, R.; Stain, A.M.; Babyn, P.; Blanchette, V.S.; Doria, A.S. Comparison of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Scales for Assessment of Interval Changes of Arthropathy in Boys with Severe Hemophilia. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 4792. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134792
Zhang N, Carcao M, Ignas DM, Feldman BM, Hilliard P, Moineddin R, Stain AM, Babyn P, Blanchette VS, Doria AS. Comparison of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Scales for Assessment of Interval Changes of Arthropathy in Boys with Severe Hemophilia. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(13):4792. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134792
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Ningning, Manuel Carcao, Danial M. Ignas, Brian M. Feldman, Pamela Hilliard, Rahim Moineddin, Ann Marie Stain, Paul Babyn, Victor S. Blanchette, and Andrea S. Doria. 2025. "Comparison of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Scales for Assessment of Interval Changes of Arthropathy in Boys with Severe Hemophilia" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 13: 4792. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134792
APA StyleZhang, N., Carcao, M., Ignas, D. M., Feldman, B. M., Hilliard, P., Moineddin, R., Stain, A. M., Babyn, P., Blanchette, V. S., & Doria, A. S. (2025). Comparison of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Scales for Assessment of Interval Changes of Arthropathy in Boys with Severe Hemophilia. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(13), 4792. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134792







