A Novel Approach to the Study of Pathophysiology in Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea Using the Iowa Oral Performance Instrument (IOPI)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
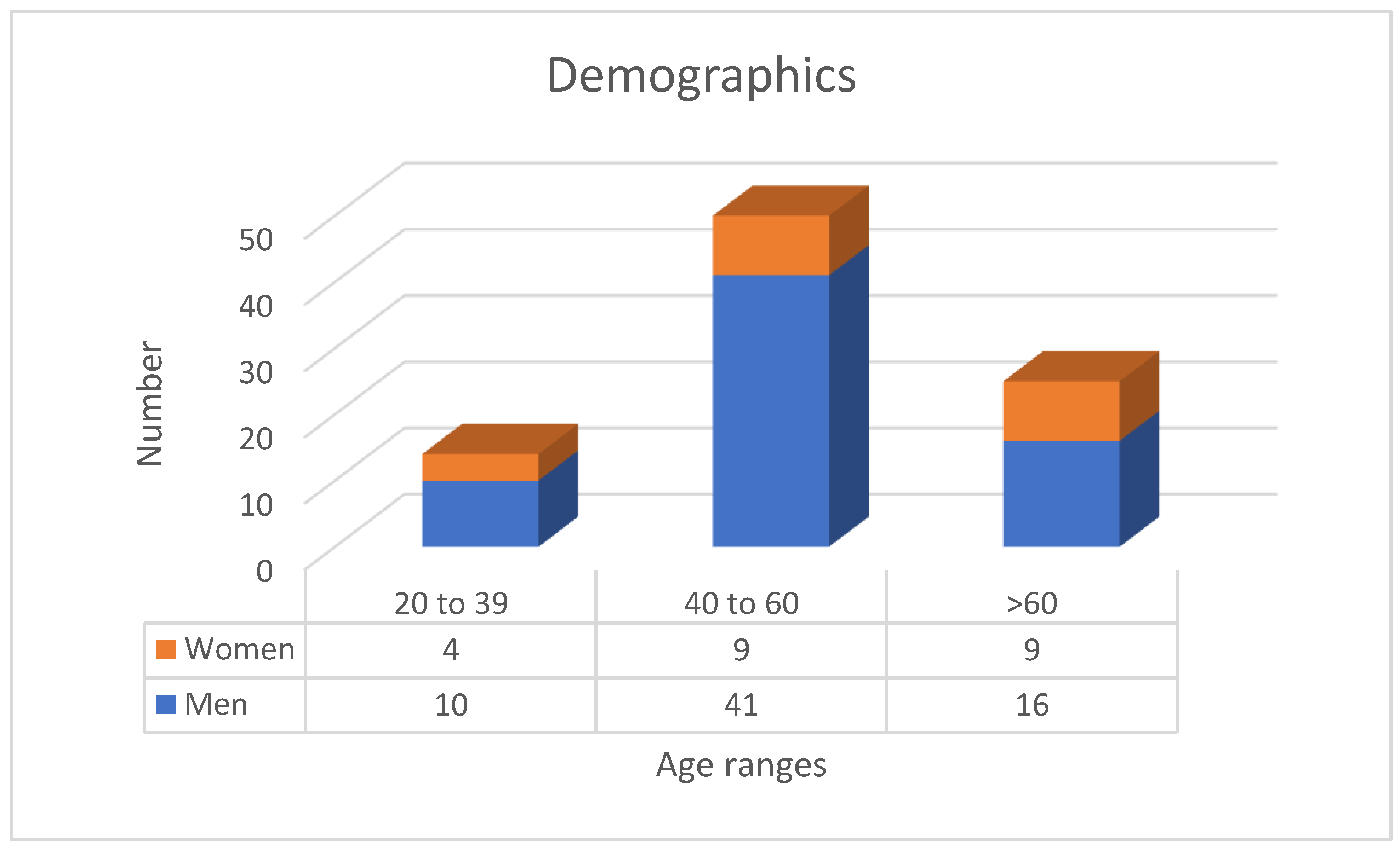
3.1. Population Description
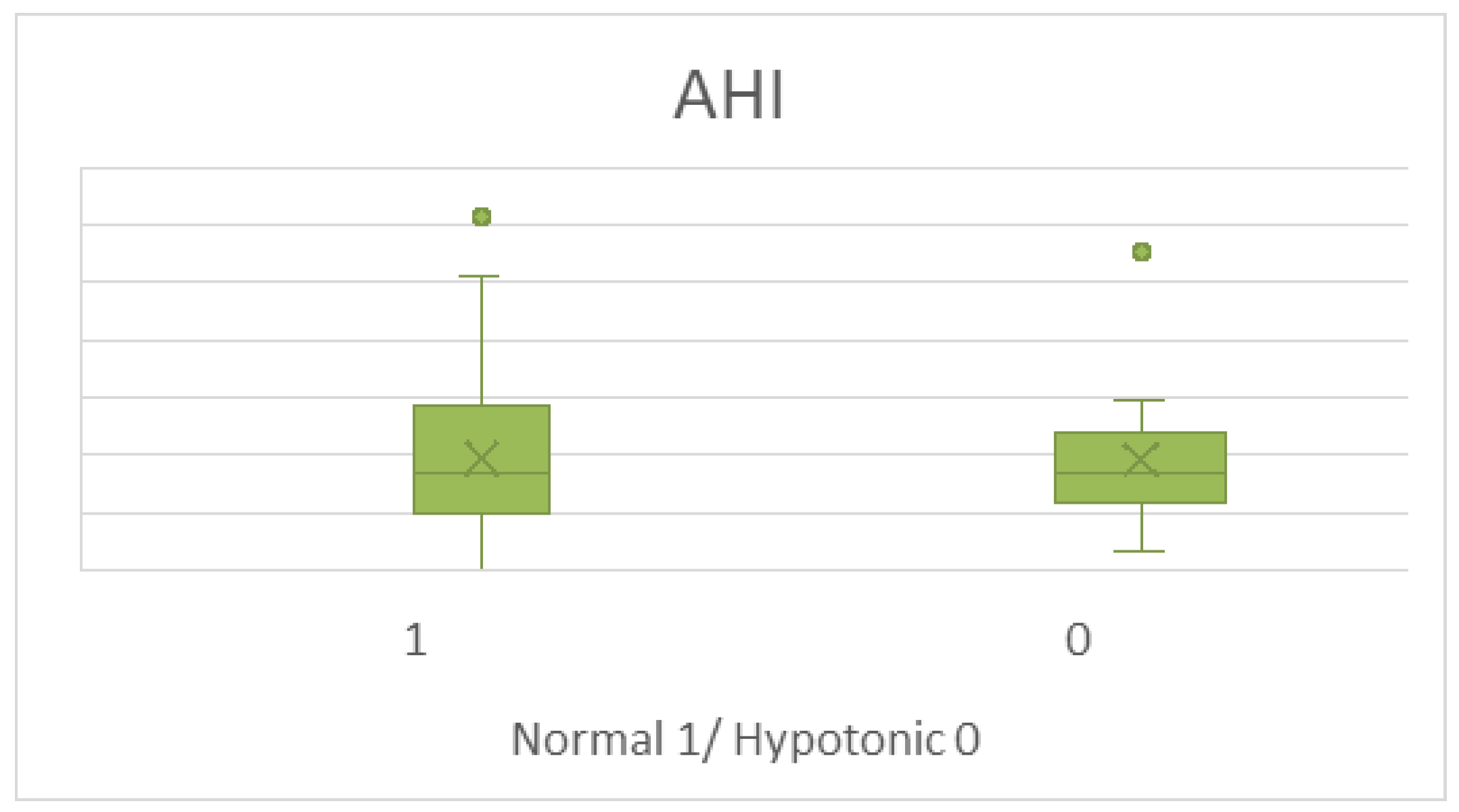
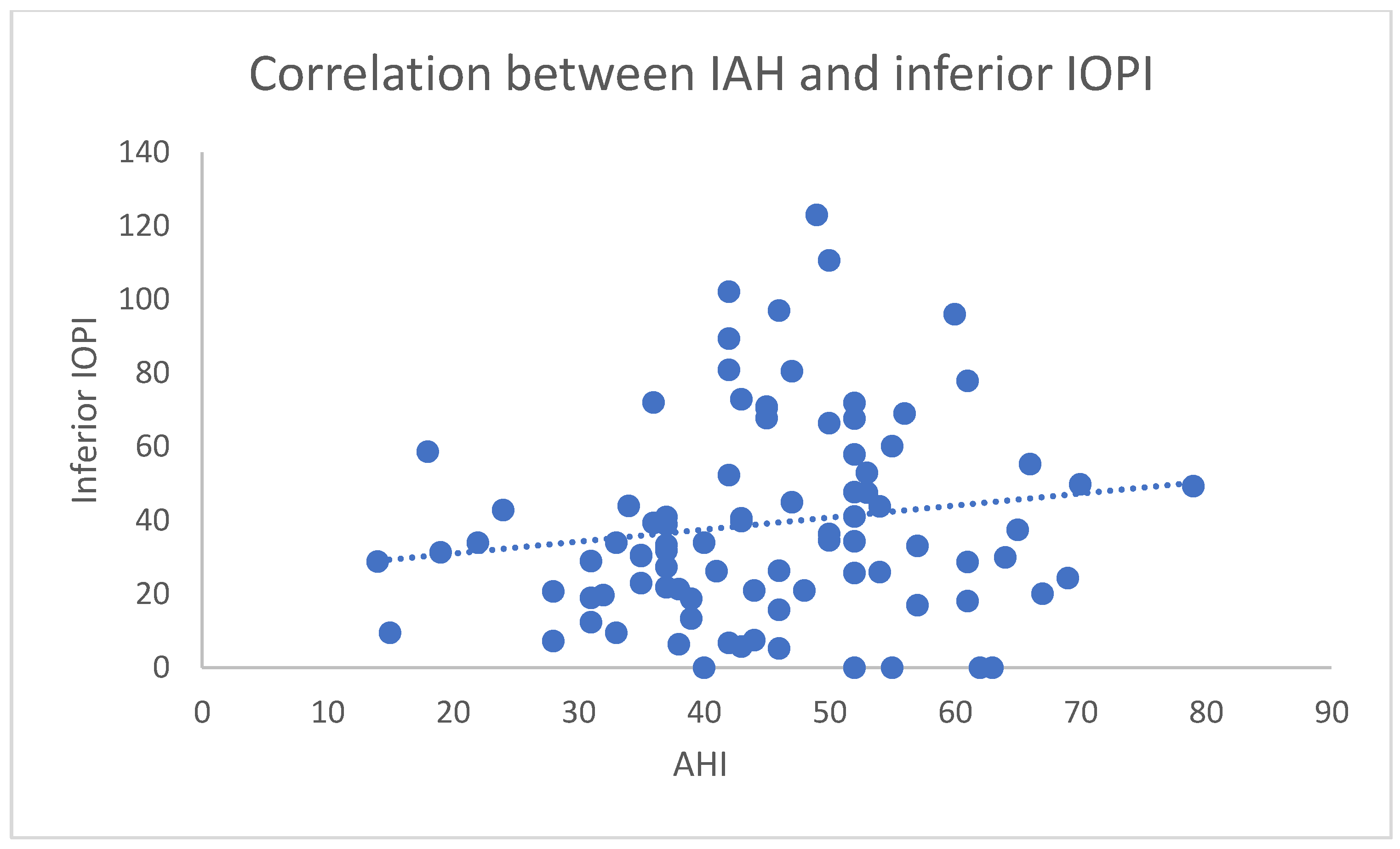
3.2. IOPI Results Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ENT | Ear, nose, and throat |
| AHI | Apnea–hypopnea index |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| CT90 | Cumulative time below 90% saturation |
| CPAP | Continuous positive airway pressure |
| IOPI | Iowa Oral Performance Instrument |
| ODI | Oxygen desaturation index |
| OSA | Obstructive sleep apnea |
References
- Suri, T.M.; Ghosh, T.; Mittal, S.; Hadda, V.; Madan, K.; Mohan, A. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the prevalence of obstructive sleep apnea in Indian adults. Sleep Med. Rev. 2023, 71, 101829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jennum, P.; Ibsen, R.; Ibsen, M.; Andersen, S.; Kjellberg, J. Long-term welfare consequences of sleep apnea in 20-64-year-olds—Influence of gender: A nationwide cohort study. Sleep 2025, zsaf057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Farsi, H.Y.; Al-Fahdi, E.Y.; Al-Balushi, M.A.; Al-Jahwari, A.N.; Al-Maskari, A.M.; Das, S. Sleep Disturbances Associated with Different Systems of the Body: Underlying Mechanisms Involved and Consequences. Curr. Med. Chem. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alakörkkö, I.; Törmälehto, S.; Leppänen, T.; McNicholas, W.T.; Arnardottir, E.S.; Sund, R. The economic cost of obstructive sleep apnea: A systematic review. Sleep Med. Rev. 2023, 72, 101854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raphelson, J.R.; Fuentes, A.L.; Holloway, B.; Malhotra, A. Obstructive Sleep Apnea Endophenotypes. Sleep Sci. 2024, 18, e109–e113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckert, D.J.; White, D.P.; Jordan, A.S.; Malhotra, A.; Wellman, A. Defining phenotypic causes of obstructive sleep apnea. Identification of novel therapeutic targets. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 188, 996–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, D.P. Pathogenesis of obstructive and central sleep apnea. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 172, 1363–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor-Reina, C.; Plaza, G.; Garcia-Iriarte, M.T.; Ignacio-Garcia, J.M.; Baptista, P.; Casado-Morente, J.C.; De Vicente, E. Tongue peak pressure: A tool to aid in the identification of obstruction sites in patients with obstructive sleep apnea/hypopnea syndrome. Sleep Breath. 2020, 24, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attali, V.; Weber, M.; Rivals, I.; Similowski, T.; Arnulf, I.; Gatignol, P. Moderate-to-severe obstructive sleep apnea syndrome is associated with altered tongue motion during wakefulness. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2023, 280, 2551–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cori, J.M.; O’Donoghue, F.J.; Jordan, A.S. Sleeping tongue: Current perspectives of genioglossus control in healthy individuals and patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Nat. Sci. Sleep 2018, 10, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliven, R.; Cohen, G.; Somri, M.; Schwartz, A.R.; Oliven, A. Relationship between the activity of the genioglossus, other peri-pharyngeal muscles and flow mechanics during wakefulness and sleep in patients with OSA and healthy subjects. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2020, 274, 103362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor-Reina, C.; Ignacio Garcia, J.M.; Rodriguez Ruiz, E.; Morillo Dominguez, M.D.C.; Ignacio Barrios, V.; Baptista Jardin, P.; Casado Morente, J.C.; Garcia Iriarte, M.T.; Plaza, G. Myofunctional Therapy App for Severe Apnea-Hypopnea Sleep Obstructive Syndrome: Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial. JMIR mHealth uHealth 2020, 8, e23123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poncin, W.; Correvon, N.; Tam, J.; Borel, J.C.; Berger, M.; Liistro, G.; Mwenge, B.; Heinzer, R.; Contal, O. The effect of tongue elevation muscle training in patients with obstructive sleep apnea: A randomised controlled trial. J. Oral. Rehabil. 2022, 49, 1049–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, M.P.; Evangelisti, M.; Martella, S.; Barreto, M.; Del Pozzo, M. Can myofunctional therapy increase tongue tone and reduce symptoms in children with sleep-disordered breathing? Sleep Breath. 2017, 21, 1025–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saba, E.S.; Kim, H.; Huynh, P.; Jiang, N. Orofacial Myofunctional Therapy for Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Laryngoscope 2024, 134, 480–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco-Llatas, M.; O’Connor-Reina, C.; Calvo-Henríquez, C. The Role of Myofunctional Therapy in Treating Sleep-Disordered Breathing: A State-of-the-Art Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 7291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, V.; Mathisen, B.; Baines, S.; Lazarus, C.; Callister, R. A systematic review and meta-analysis of measurements of tongue and hand strength and endurance using the Iowa Oral Performance Instrument (IOPI). Dysphagia 2013, 28, 350–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IOPI Medical LLC. Iowa Oral Performance Instrument: Users Manual. 2008. Available online: http://www.iopimedical.com (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- Clark, H.M.; O’Brien, K.; Calleja, A.; Corrie, S.N. Effects of directional exercise on lingual strength. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2009, 52, 1034–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, H.M.; Solomon, N.P. Age and sex differences in orofacial strength. Dysphagia 2012, 27, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarus, C.; Logemann, J.A.; Huang, C.F.; Rademaker, A.W. Effects of two types of tongue strengthening exercises in young normals. Folia Phoniatr. Logop. 2003, 55, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarus, C.L.; Logemann, J.A.; Pauloski, B.R.; Rademaker, A.W.; Larson, C.R.; Mittal, B.B.; Pierce, M. Swallowing and tongue function following treatment for oral and oropharyngeal cancer. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2000, 43, 1011–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robbins, J.; Levine, R.; Wood, J.; Roecker, E.B.; Luschei, E. Age effects on lingual pressure generation as a risk factor for dysphagia. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 1995, 50, M257–M262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, N.P.; Munson, B. The effect of jaw position on measures of tongue strength and endurance. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2004, 47, 584–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stierwalt, J.A.; Youmans, S.R. Tongue measures in individuals with normal and impaired swallowing. Am. J. Speech Lang. Pathol. 2007, 16, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youmans, S.R.; Youmans, G.L.; Stierwalt, J.A. Differences in tongue strength across age and gender: Is there a diminished strength reserve? Dysphagia 2009, 24, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youmans, S.R.; Stierwalt, J.A. Measures of tongue function related to normal swallowing. Dysphagia 2006, 21, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, N.L.; Nievergelt, Y.; Shriberg, L.D. Motor and speech disorders in classic galactosemia. JIMD Rep. 2013, 11, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neel, A.T.; Palmer, P.M. Is tongue strength an important influence on rate of articulation in diadochokinetic and reading tasks? J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2012, 55, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Alcalá, L.; Ignacio-García, J.M.; Serrano Angulo, M.S.; Casado Morente, J.C.; Benjumea Flores, F.; O’Connor-Reina, C. Tongue+ protocol for the diagnosis of obstructive sleep apnoea in Quirónsalud Marbella hospital. F1000Research 2022, 11, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Alcalá, L.; Martín-Lagos Martínez, J.; O’Connor-Reina, C.; Plaza, G. Assessment of muscular tone of the tongue using a digital measure spoon in a healthy population: A pilot study. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0245901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, M.; Yoshida, M.; Tsuga, K.; Akagawa, Y.; Groher, M.E. Comparison of three types of tongue pressure measurement devices. Dysphagia 2011, 26, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, M.; Fukuoka, T.; Mori, T.; Hiraoka, A.; Higa, C.; Kuroki, A.; Takeda, C.; Maruyama, M.; Yoshida, M.; Tsuga, K. Comparison of the Iowa Oral Performance Instrument and JMS tongue pressure measurement device. J. Dent. Sci. 2021, 16, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, J.A.; Mocchetti, V.; Rameau, A. Concurrent Validity of the IOPI and Tongueometer Orofacial Strength Measurement Devices. Laryngoscope 2023, 133, 3123–3131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curtis, J.A.; Diaz, C.; Lee, T.; Rameau, A. Validation of a Low-Cost Manometer to Assess of Tongue, Lip, Cheek, and Respiratory Strength: A Laboratory-Based Study. Laryngoscope 2025, 135, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrmann, P.F.; O’Connor-Reina, C.; Ignacio, J.M.; Rodriguez Ruiz, E.; Rodriguez Alcala, L.; Dzembrovsky, F.; Baptista, P.; Garcia Iriarte, M.T.; Casado Alba, C.; Plaza, G. Muscular Assessment in Patients with Severe Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome: Protocol for a Case-Control Study. JMIR Res. Protoc. 2021, 10, e30500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor-Reina, C.; Rodriguez-Alcala, L.; Ignacio, J.M.; Baptista, P.; Garcia-Iriarte, M.T.; Plaza, G. Assessment of Muscular Weakness in Severe Sleep Apnea Patients: A Prospective Study. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2023, 169, 725–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, K.P.; Kishore, S.; Kit, J.C.; Pang, E.B.; Chan, Y.H.; Keat, S.J.; Rotenberg, B. Pang-Rotenberg sign--snoring surgery prognosticator: A prospective clinical trial of 153 patients. Laryngoscope 2016, 126, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchesan, I.Q. Lingual frenulum protocol. Int. J. Orofac. Myol. Myofunct. Ther. 2012, 38, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchesan, I.Q. Lingual frenulum: Proposal of quantitative evaluation. Int. J. Orofac. Miol. 2005, 31, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arakawa, I.; Igarashi, K.; Imamura, Y.; Müller, F.; Abou-Ayash, S.; Schimmel, M. Variability in tongue pressure among elderly and young healthy cohorts: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Oral. Rehabil. 2021, 48, 430–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marín-Bernard, E.; Ruiz-López, M.D.; Gómez-Pozo, B.; Artacho, R. Maximum Anterior Tongue Strength and Maximum Lip Strength in Healthy Spanish Adults: A Proposal of Reference Values. Dysphagia 2024, 39, 881–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paris-Alemany, A.; Proy-Acosta, A.; Adraos-Juárez, D.; Suso-Martí, L.; La Touche, R.; Chamorro-Sánchez, J. Influence of the Craniocervical Posture on Tongue Strength and Endurance. Dysphagia 2021, 36, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VanRavenhorst-Bell, H.A.; Coufal, K.L.; Patterson, J.A.; Mefferd, A.S. A comparative study: Tongue muscle performance in weightlifters and runners. Physiol. Rep. 2018, 6, e13923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewald, D. Rethinking the muscles of obstructive sleep apnea. Cranio 2022, 40, 389–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliven, A.; Tov, N.; Geitini, L.; Steinfeld, U.; Oliven, R.; Schwartz, A.R.; Odeh, M. Effect of genioglossus contraction on pharyngeal lumen and airflow in sleep apnoea patients. Eur. Respir. J. 2007, 30, 748–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubin, L.; Davies, R. Mechanisms of upper airway hypotonia. In Sleep Apnea: Pathogenesis, Diagnosis and Treatment, 2nd ed.; Pack, A.I., Ed.; Informa Healthcare: London, UK, 2012; pp. 155–178. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Di, C.; Mona, S.; Wang, L.; Hans, M. Tongue Function: An Underrecognized Component in the Treatment of Obstructive Sleep Apnea with Mandibular Repositioning Appliance. Can. Respir. J. 2018, 2018, 2157974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanezaki, M.; Ogawa, T.; Izumi, T. Tongue Protrusion Strength in Arousal State Is Predictive of the Airway Patency in Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2015, 236, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortimore, I.L.; Bennett, S.P.; Douglas, N.J. Tongue protrusion strength and fatiguability: Relationship to apnoea/hypopnoea index and age. J. Sleep Res. 2000, 9, 389–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirth, M.; Unterhuber, D.; von Meyer, F.; Hofauer, B.; Ott, A.; Edenharter, G.; Eckert, D.J.; Heiser, C. Hypoglossal nerve stimulation therapy does not alter tongue protrusion strength and fatigability in obstructive sleep apnea. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2020, 16, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiegand, D.A.; Latz, B.; Zwillich, C.W.; Wiegand, L. Upper airway resistance and geniohyoid muscle activity in normal men during wakefulness and sleep. J. Appl. Physiol. 1990, 69, 1252–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marghalani, T.Y.; Salamah, R.M.; Alangari, H.M. A Novel Design of an Oral Appliance for Monitoring Electromyograms of the Genioglossus Muscle in Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome. Life 2024, 14, 952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jugé, L.; Burke, P.G.R.; Yeung, J.; Knapman, F.; Brown, E.C.; Chiang, A.; Eckert, D.J.; Butler, J.E.; Bilston, L.E. Compartmental inspiratory genioglossus electromyographic activity in supine, awake individuals with and without obstructive sleep apnoea. J. Physiol. 2025, 603, 2877–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Franciotti, R.; Di Maria, E.; D’Attilio, M.; Aprile, G.; Cosentino, F.G.; Perrotti, V. Quantitative Measurement of Swallowing Performance Using Iowa Oral Performance Instrument: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, A.; Hao, G.; Chou, S.Y.; Chen, S.C.; Chang, Y.J. Age-Related Changes in Tongue Strength and Endurance in Individuals with Obstructive Sleep Apnea. J. Oral. Rehabil. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliven, R.; Cohen, G.; Dotan, Y.; Somri, M.; Schwartz, A.R.; Oliven, A. Alteration in upper airway dilator muscle coactivation during sleep: Comparison of patients with obstructive sleep apnea and healthy subjects. J. Appl. Physiol. 2018, 124, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dotan, Y.; Pillar, G.; Schwartz, A.R.; Oliven, A. Asynchrony of lingual muscle recruitment during sleep in obstructive sleep apnea. J. Appl. Physiol. 2015, 118, 1516–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ji, C.; Sun, W.; Xiong, H.; Li, Z.; Huang, X.; Fan, T.; Xian, J.; Huang, Y. Characteristics and Mechanism of Upper Airway Collapse Revealed by Dynamic MRI During Natural Sleep in Patients with Severe Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Nat. Sci. Sleep 2023, 15, 885–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutzner, E.A.; Miot, C.; Liu, Y.; Renk, E.; Park, J.S.; Inman, J.C. Effect of genioglossus, geniohyoid, and digastric advancement on tongue base and hyoid position. Laryngoscope 2017, 127, 1938–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
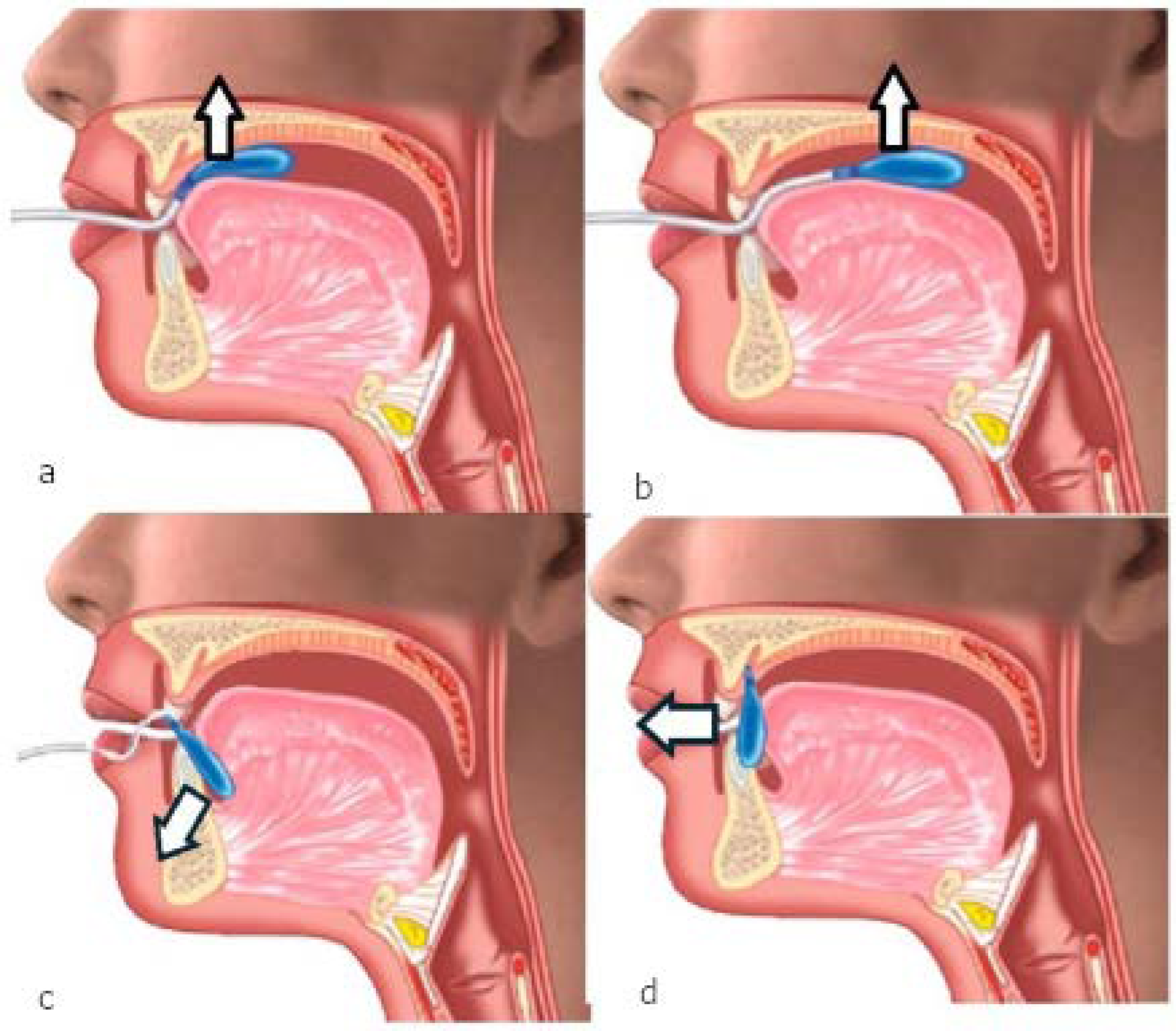
| Parameter | Mean | SD | Min | Max | P25 | Median (P50) | P75 | Units |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ODI | 37.98 | 27.29 | 1.6 | 124 | 20.0 | 31.25 | 46.1 | events/hour |
| Minimum SpO2 | 78.54 | 8.53 | 51.0 | 92 | 74.0 | 80.0 | 83.5 | % |
| CT90 | 15.6 | 20.51 | 0.0 | 81 | 1.5 | 5.5 | 20.9 | % time < 90% |
| Exercise | First Trial (kPa) | Second Trial (kPa) | Third Trial (kPa) | Mean (kPa) | Max (kPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anterior Tongue | 46.42 (12.98) | 49.80 (12.54) | 49.88 (13.02) | 48.70 (11.79) | 53.55 (12.87) |
| Posterior Tongue | 42.15 (14.41) | 44.87 (13.06) | 47.67 (14.24) | 44.9 (12.7) | 50.42 (14,24) |
| Tongue Propulsion | 56.36 (14.04) | 56.97 (13.05) | 55.87 (14.28) | 56.40 (12.81) | 60.53 (13.81) |
| Inferior Tongue | 37.08 (12.52) | 40.01 (12.21) | 40.63 (12.48) | 39.24 (11) | 45.00 (12.7) |
| Buccinator Right | 26.26 (9.18) | 28.55 (8.84) | 27.85 (8.68) | 27.55 (8.16) | 30.97 (9.44) |
| Buccinator Left | 26.52 (8.66) | 26.54 (8.41) | 27.28 (8.89) | 26.78 (8.28) | 29.22 (8.79) |
| Exercise | First vs. Mean | First vs. Max | Mean vs. Max |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anterior | 0.8779 | 0.7642 | 0.9416 |
| Posterior | 0.9017 | 0.7578 | 0.9449 |
| Inferior | 0.8489 | 0.7716 | 0.9501 |
| Propulsion | 0.9198 | 0.8619 | 0.9670 |
| Right Buccinator | 0.9145 | 0.8302 | 0.9565 |
| Left Buccinator | 0.9222 | 0.8768 | 0.9615 |
| Anterior 1 | Anterior 2 | Anterior 3 | Mean | Max | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anterior 1 | 1.0 | 0.7243 | 0.6659 | 0.8779 | 0.7642 |
| Anterior 2 | 0.7243 | 1.0 | 0.8007 | 0.9196 | 0.9073 |
| Anterior 3 | 0.6659 | 0.8007 | 1.0 | 0.9026 | 0.8723 |
| Mean | 0.8779 | 0.9196 | 0.9026 | 1.0 | 0.9416 |
| Max | 0.7642 | 0.9073 | 0.8723 | 0.9416 | 1.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Navarro, A.; Bosco, G.; Serrano, B.; Baptista, P.; O’Connor-Reina, C.; Plaza, G. A Novel Approach to the Study of Pathophysiology in Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea Using the Iowa Oral Performance Instrument (IOPI). J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 4781. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134781
Navarro A, Bosco G, Serrano B, Baptista P, O’Connor-Reina C, Plaza G. A Novel Approach to the Study of Pathophysiology in Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea Using the Iowa Oral Performance Instrument (IOPI). Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(13):4781. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134781
Chicago/Turabian StyleNavarro, Andrés, Gabriela Bosco, Bárbara Serrano, Peter Baptista, Carlos O’Connor-Reina, and Guillermo Plaza. 2025. "A Novel Approach to the Study of Pathophysiology in Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea Using the Iowa Oral Performance Instrument (IOPI)" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 13: 4781. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134781
APA StyleNavarro, A., Bosco, G., Serrano, B., Baptista, P., O’Connor-Reina, C., & Plaza, G. (2025). A Novel Approach to the Study of Pathophysiology in Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea Using the Iowa Oral Performance Instrument (IOPI). Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(13), 4781. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134781







