Diastolic Blood Pressure Abnormalities and Their Relationship with Glycemic Control in Pediatric Type 1 Diabetes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Group
2.2. Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring
2.3. Metabolic Control and T1D Duration
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring Results
3.3. Associations Between BP Disturbance, Glycemic Control, and T1D Duration
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Šuláková, T.; Strnadel, J.; Pavlíček, J.; Poláková, R.; Seeman, T.; Feber, J. Early Vascular Aging in Children with Type 1 Diabetes and Ambulatory Normotension. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 764004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drożdż, D.; Drożdż, M.; Wójcik, M. Endothelial dysfunction as a factor leading to arterial hypertension. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2022, 38, 2973–2985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjornstad, P.; Dart, A.; Donaghue, K.C.; Dost, A.; Feldman, E.L.; Tan, G.S.; Wadwa, R.P.; Zabeen, B.; Marcovecchio, M.L. ISPAD Clinical Practice Consensus Guidelines 2022: Microvascular and macrovascular complications in children and adolescents with diabetes. Pediatr. Diabetes 2022, 23, 1432–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margeirsdottir, H.D.; Larsen, J.R.; Brunborg, C.; Øverby, N.C.; Dahl-Jørgensen, K. High prevalence of cardiovascular risk factors in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes: A population-based study. Diabetologia 2008, 51, 554–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, B.L.; Dabelea, D.; Liese, A.D.; Fujimoto, W.; Waitzfelder, B.; Liu, L.; Bell, R.; Talton, J.; Snively, B.M.; Kershnar, A.; et al. Prevalence and correlates of elevated blood pressure in youth with diabetes mellitus: The SEARCH for diabetes in youth study. J. Pediatr. 2010, 157, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazeou, A.; Tittel, S.R.; Birkebaek, N.H.; Kordonouri, O.; Iotova, V.; Piccini, B.; Saboo, B.; Lyckå, A.P.; Seget, S.; Maahs, D.M.; et al. The Importance of Office Blood Pressure Measurement Frequency and Methodology in Evaluating the Prevalence of Hypertension in Children and Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes: The SWEET International Database. Diabetes Care 2022, 45, 1462–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suláková, T.; Janda, J.; Cerná, J.; Janstová, V.; Suláková, A.; Slaný, J.; Feber, J. Arterial HTN in children with T1DM—Frequent and not easy to diagnose. Pediatr. Diabetes 2009, 10, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dost, A.; Bechtold, S.; Fink, K.; Bonfig, W.; Wiemann, D.; Kapellen, T.M.; Witsch, M.; Schwab, K.O.; Holl, R.W. 2017 American Academy of Pediatrics Clinical Practice Guideline: Impact on Prevalence of Arterial Hypertension in Children and Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, 1311–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellizzari, M.; Speiser, P.W.; Carey, D.E.; Fort, P.; Kreitzer, P.M.; Frank, G.R. Twenty-four hour ambulatory blood pressure monitoring in adolescents with type 1 diabetes: Getting started. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2008, 2, 1087–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homhuan, W.; Poomthavorn, P.; Paksi, W.; Khlairit, P.; Nongnuch, A.; Pirojsakul, K. Masked hypertension and its associations with glycemic variability metrics in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2021, 36, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saygili, S.; Canpolat, N.; Cakir, A.; Konukoglu, D.; Turan, H.; Caliskan, S.; Ercan, O.; Evliyaoglu, O.; Sever, L. Factors influencing blood pressure and microalbuminuria in children with type 1 diabetes mellitus: Salt or sugar? Pediatr. Nephrol. 2020, 35, 1267–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lurbe, E.; Redon, J.; Kesania, A.; Pascual, J.M.; Tacons, J.; Alvarez, V.; Batlle, D. Increase in nocturnal blood pressure and progression to microalbuminuria in Type 1 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 347, 797–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torun, B.; Georg, A.; Ulla, B. Nondipping and Its Relation to Glomerulopathy and Hyperfiltration in Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2004, 27, 510–516. [Google Scholar]
- Sherwood, A.; Steffen, P.R.; Blumenthal, J.A.; Kuhn, C.; Hinderliter, A.L. Nighttime blood pressure dipping: The role of the sympathetic nervous system. Am. J. Hypertens. 2002, 15 Pt 1, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boggia, J.; Li, Y.; Thijs, L.; Hansen, T.W.; Kikuya, M.; Björklund-Bodegård, K.; Richart, T.; Ohkubo, T.; Kuznetsova, T.; Torp-Pedersen, C.; et al. Prognostic accuracy of day versus night ambulatory blood pressure: A cohort study. Lancet 2007, 370, 1219–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerståhl, M.; Hedvall Kallerman, P.; Hagman, E.; Ek, A.E.; Rössner, S.M.; Marcus, C. Nocturnal blood pressure non-dipping is prevalent in severely obese, prepubertal and early pubertal children. Acta Paediatr. 2014, 103, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouhanick, B.; Bongard, V.; Amar, J.; Bousquel, S.; Chamontin, B. Prognostic value of nocturnal blood pressure and reverse-dipping status on the occurrence of cardiovascular events in hypertensive diabetic patients. Diabetes Metab. 2008, 34, 560–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuspidi, C.; Vaccarella, A.; Leonetti, G.; Sala, C. Ambulatory blood pressure and diabetes: Targeting nondipping. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2010, 6, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basiratnia, M.; Abadi, S.F.; Amirhakimi, G.H.; Karamizadeh, Z.; Karamifar, H. Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring in children and adolescents with type-1 diabetes mellitus and its relation to diabetic control and microalbuminuria. Saudi J. Kidney Dis. Transpl. 2012, 23, 311–315. [Google Scholar]
- Rohani, F.; Hooman, N.; Moradi, S.; Mobarra, M.; Najafizadeh, M.; Tatarpoor, P. The Prevalence of Pre-hypertension in Children with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2014, 5 (Suppl. S1), S44–S49. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.H.; Kim, J.H.; Kang, M.J.; Lee, Y.A.; Won Yang, S.; Shin, C.H. Implications of nocturnal hypertension in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, 2180–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seeman, T.; Palyzová, D.; Dusek, J.; Janda, J. Reduced nocturnal blood pressure dip and sustained nighttime hypertension are specific markers of secondary hypertension. J. Pediatr. 2005, 147, 366–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flynn, J.T.; Kaelber, D.C.; Baker-Smith, C.M.; Blowey, D.; Carroll, A.E.; Daniels, S.R.; de Ferranti, S.D.; Dionne, J.M.; Falkner, B.; Flinn, S.K.; et al. Clinical Practice Guideline for Screening and Management of High Blood Pressure in Children and Adolescents. Pediatrics 2017, 140, e20171904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araszkiewicz, A.; Bandurska-Stankiewicz, E.; Borys, S.; Budzyński, A.; Cyganek, K.; Cypryk, K.; Czech, A.; Czupryniak, L.; Drzewoski, J.; Dzida, G.; et al. 2023 Guidelines on the management of patients with diabetes—A position of Diabetes Poland. Curr. Top. Diabetes 2023, 3, 1–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcovecchio, M.L.; Dalton, R.N.; Schwarze, C.P.; Prevost, A.T.; Neil, H.A.; Acerini, C.L.; Barrett, T.; Cooper, J.D.; Edge, J.; Shield, J.; et al. Ambulatory blood pressure measurements are related to albumin excretion and are predictive for risk of microalbuminuria in young people with type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia 2009, 52, 1173–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dost, A.; Klinkert, C.; Kapellen, T.; Lemmer, A.; Naeke, A.; Grabert, M.; Kreuder, J.; Holl, R.W. Arterial hypertension determined by ambulatory blood pressure profiles: Contribution to microalbuminuria risk in a multicenter invetigation in 2105 children and adolescents with diabetes mellitus type 1. Diabetes Care 2008, 31, 720–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameter | All Patients N = 357 Mean ± SD/n (%) | Abnormal Nocturnal Dipping of <10% N = 148 (41%) Mean ± SD/n (%) | Normal Nocturnal Dipping of ≥10% N = 209 (59%) Mean ± SD/n (%) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Girls | 172 (49%) | 75 (50.7%) | 97 (46.4%) | 0.4 |
| Age [years] | 16.1 ± 5.7 | 16.2 ± 2 | 16.2 ± 7.1 | 0.9 |
| Weight [kg] | 65.5 ± 15.3 | 65.8 ± 14.9 | 65.3 ± 15.7 | 0.7 |
| Height [cm] | 168.5 ± 12.1 | 168.9 ± 11.1 | 168.3 ± 12.7 | 0.6 |
| BMI [kg/m2] | 22.7 ± 3.8 | 22.9 ± 3.6 | 22.6 ± 4.0 | 0.5 |
| HbA1c [%] | 7.6 ± 1.5 | 7.6 ± 1.6 | 7.6 ± 1.5 | 0.9 |
| HbA1c > 6.5% | 276 (77%) | 114 (77%) | 162 (71%) | 0.9 |
| T1D duration [years] | 6.9 ± 3.5 | 7.1 ± 3.6 | 6.9 ± 3.5 | 0.7 |
| T1D > 5 years | 245 (69%) | 103 (70%) | 142 (70%) | 0.7 |
| Parameter | Value Mean ± SD/n (%) |
|---|---|
| Mean day SBP [mmHg] | 120.5 ± 12.5 |
| Mean day DBP [mmHg] | 70.9 ± 5.8 |
| Mean night SBP [mmHg] | 107.5 ± 13.5 |
| Mean night DBP [mmHg] | 58.8 ± 6.9 |
| Mean 24 h SBP load [%] | 16.7 ± 18.1 |
| Mean 24 h DBP load [%] | 15.2 ± 13.3 |
| Nocturnal dipping [%] | 10.7 ± 5.6 |
| Nocturnal dipping < 10% | 148 (41%) |
| AH | 36 (10%) |
| Parameter | HbA1c Mean ± SD/n (%) | p-Value | T1D Duration Mean ± SD/n (%) | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≤6.5% N = 81 (23%) | >6.5% N = 276 (77%) | ≤5 Years N = 112 (31%) | >5 Years N = 245 (69%) | |||
| Mean day SBP [mmHg] | 118.5 ± 14.1 | 121 ± 12 | 0.1 | 119.4 ± 13.4 | 120.9 ± 12.1 | 0.3 |
| Mean day DBP [mmHg] | 69.6 ± 6.1 | 71.4 ± 5.7 | 0.01 | 70.5 ± 6.2 | 71.2 ± 5.6 | 0.3 |
| Mean night SBP [mmHg] | 105.1 ± 14.8 | 108.1 ± 13.7 | 0.08 | 105.8 ± 16.5 | 108.1 ± 11.9 | 0.1 |
| Mean night DBP [mmHg] | 57.1 ± 8.7 | 59.3 ± 6.4 | 0.01 | 57.8 ± 8.2 | 59.3 ± 6.3 | 0.06 |
| Mean 24 h SBP [mmHg] | 117.1 ± 8.2 | 122.5 ± 60.7 | 0.4 | 126.7 ± 94.6 | 118.8 ± 9.6 | 0.2 |
| Mean 24 h DBP [mmHg] | 66.4 ± 8.7 | 69 ± 5.3 | 0.0009 | 67.4 ± 8.1 | 68.9 ± 5.2 | 0.04 |
| Mean 24 h arterial pressure [mmHg] | 84.3 ± 5.2 | 86.1 ± 5.7 | 0.01 | 85.2 ± 5.6 | 86 ± 5.7 | 0.2 |
| Mean SBP load [%] | 12.1 ± 14 | 18 ± 18.9 | 0.01 | 14.9 ± 18.5 | 17.5 ± 17.8 | 0.2 |
| Mean DBP load [%] | 12.5 ± 12.4 | 16 ± 13.4 | 0.03 | 14.1 ± 13.9 | 15.8 ± 13 | 0.2 |
| Nocturnal dipping [%] | 11.4 ± 5.6 | 10.6 ± 5.7 | 0.2 | 10.8 ± 5.8 | 10.8 ± 5.6 | 0.9 |
| Nocturnal dipping < 10% | 34 (42%) | 114 (41%) | 0.9 | 45 (40.2%) | 103 (42%) | 0.7 |
| Arterial hypertension | 2 (2.5%) | 34 (12.4%) | 0.009 | 12 (10.7%) | 24 (9.8%) | 0.8 |
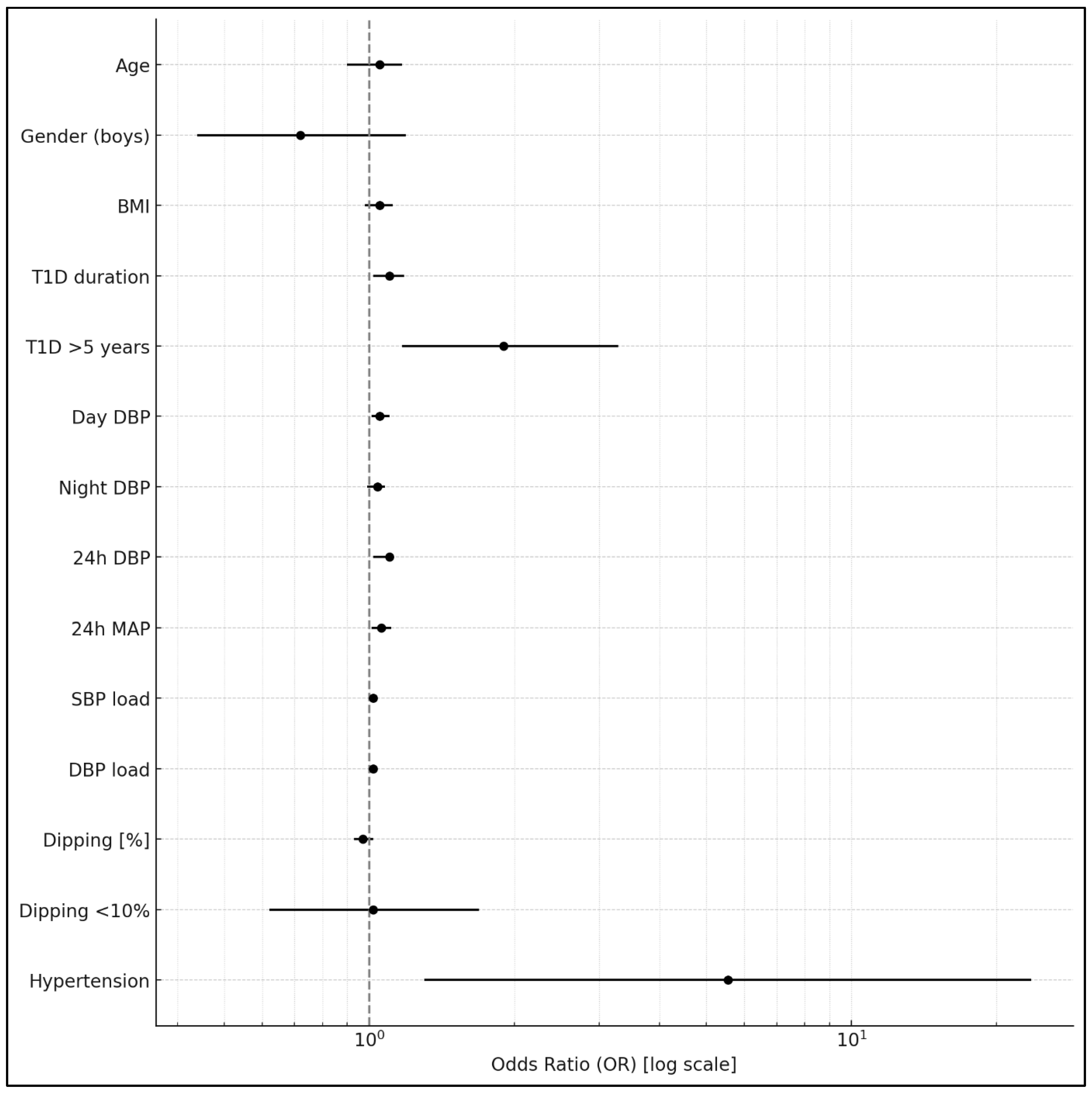
| Variable | Univariate Logistic Regression | Multivariate Logistic Regression (R2 = 0.06) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | p-Value | OR (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| Age [years] | 1.05 (0.9–1.17) | 0.3 | ||
| Gender [0—girls; 1—boys] | 0.72 (0.44–1.19) | 0.2 | ||
| BMI [kg/m2] | 1.05 (0.98–1.12) | 0.13 | ||
| T1D duration [years] | 1.1 (1.02–1.18) | 0.01 | 1.09 (1.01–1.17) | 0.03 |
| T1D [0–≤5 years 1–>5 years] | 1.9 (1.17–3.28) | 0.01 | ||
| Mean day DBP [mmHg] | 1.05 (1.01–1.1) | 0.01 | ||
| Mean night DBP [mmHg] | 1.04 (0.99–1.08) | 0.06 | ||
| Mean 24 h DBP [mmHg] | 1.1 (1.02–1.12) | 0.003 | 1.07 (1.02–1.12) | 0.007 |
| Mean 24 h arterial pressure [mmHg] | 1.06 (1.01–1.11) | 0.01 | ||
| Mean SBP load [%] | 1.02 (1.0–1.04) | 0.01 | ||
| Mean DBP load [%] | 1.02 (1.0–1.04) | 0.04 | ||
| Nocturnal dipping [%] | 0.97 (0.93–1.02) | 0.3 | ||
| Nocturnal dipping [0–<10%; 1–≥10%] | 1.02 (0.62–1.69) | 0.9 | ||
| Arterial hypertension [0—absent; 1—present] | 5.55 (1.3–23.6) | 0.02 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stępniewska, A.; Szczudlik, E.; Drożdż, D.; Nazim, J.; Starzyk, J.; Januś, D.; Wójcik, M. Diastolic Blood Pressure Abnormalities and Their Relationship with Glycemic Control in Pediatric Type 1 Diabetes. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 4704. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134704
Stępniewska A, Szczudlik E, Drożdż D, Nazim J, Starzyk J, Januś D, Wójcik M. Diastolic Blood Pressure Abnormalities and Their Relationship with Glycemic Control in Pediatric Type 1 Diabetes. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(13):4704. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134704
Chicago/Turabian StyleStępniewska, Anna, Ewa Szczudlik, Dorota Drożdż, Joanna Nazim, Jerzy Starzyk, Dominika Januś, and Małgorzata Wójcik. 2025. "Diastolic Blood Pressure Abnormalities and Their Relationship with Glycemic Control in Pediatric Type 1 Diabetes" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 13: 4704. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134704
APA StyleStępniewska, A., Szczudlik, E., Drożdż, D., Nazim, J., Starzyk, J., Januś, D., & Wójcik, M. (2025). Diastolic Blood Pressure Abnormalities and Their Relationship with Glycemic Control in Pediatric Type 1 Diabetes. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(13), 4704. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134704