Clinical Insights and Therapeutic Strategies for the Treatment of Interstitial Lung Disease in Patients with Anti-Neutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-Associated Vasculitis: Current Trends and Future Directions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Epidemiology
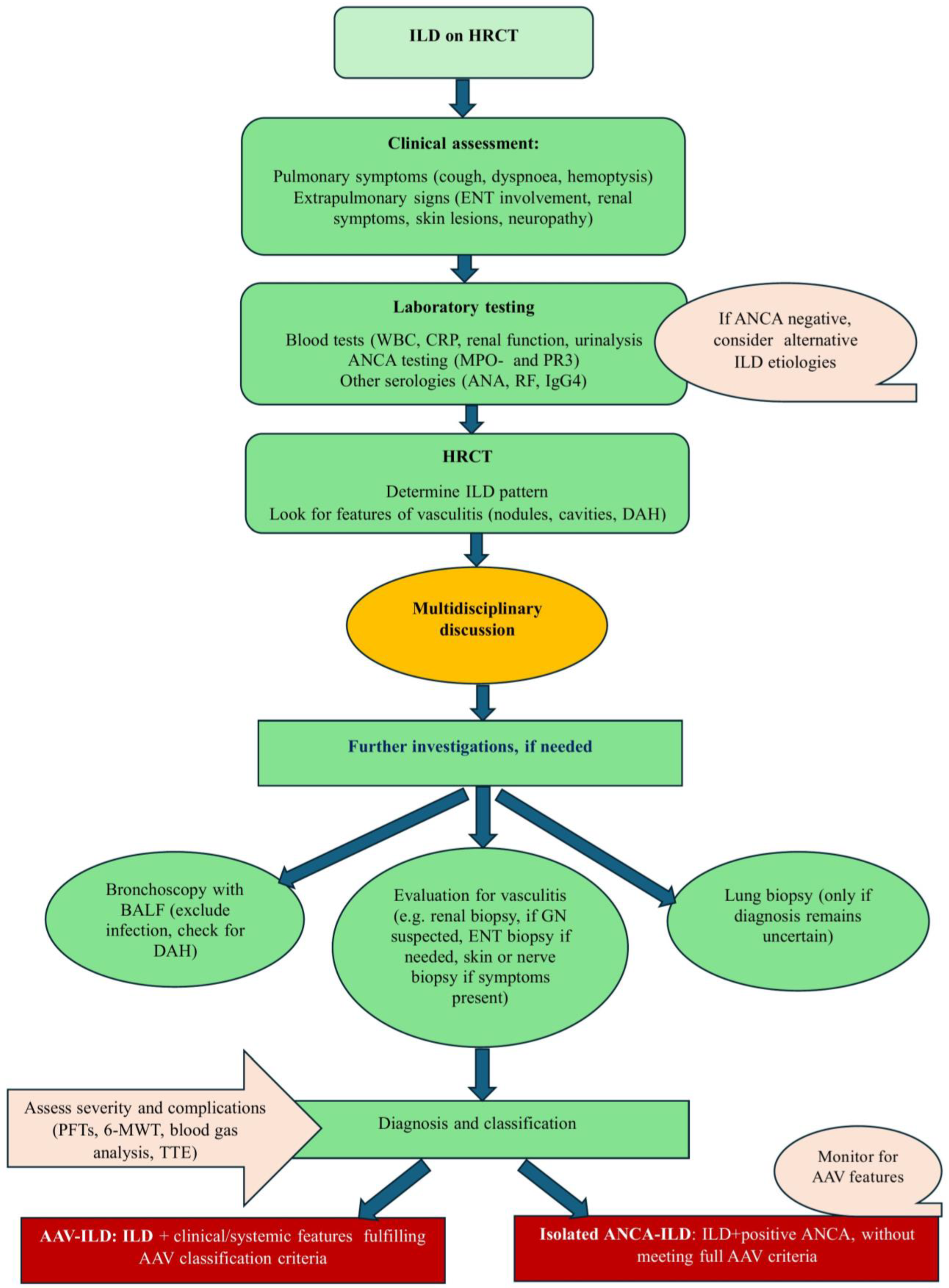
3. Pathogenesis
4. Diagnosis
4.1. Clinical Features
4.2. Serology and Laboratory Studies
4.3. Pulmonary Function Tests
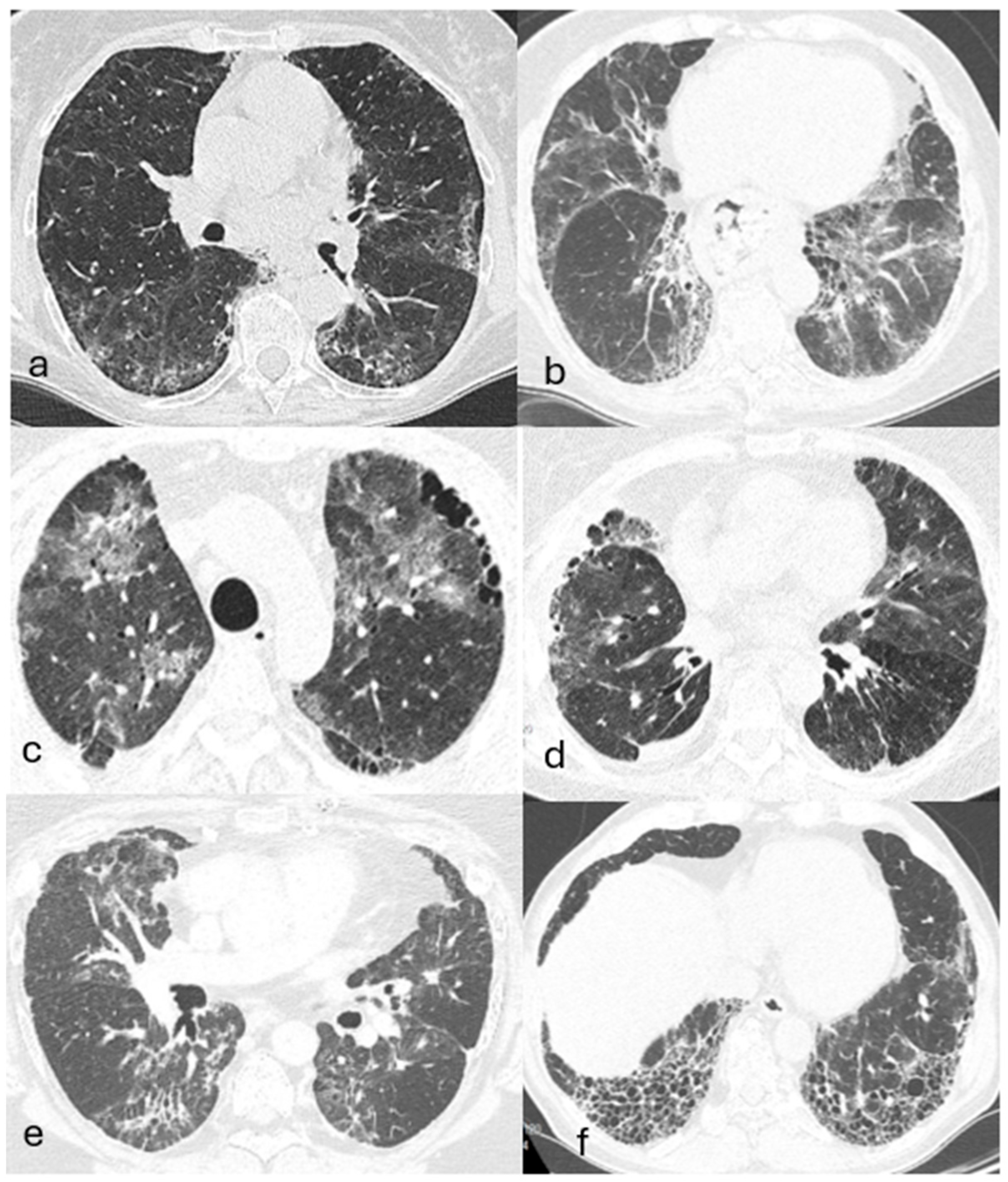
4.4. Imaging
4.5. Bronchoscopy
4.6. Biopsy and Histopathology
4.7. Disease Burden and Complications
5. Phenotypes
6. Outcomes and Prognostic Factors
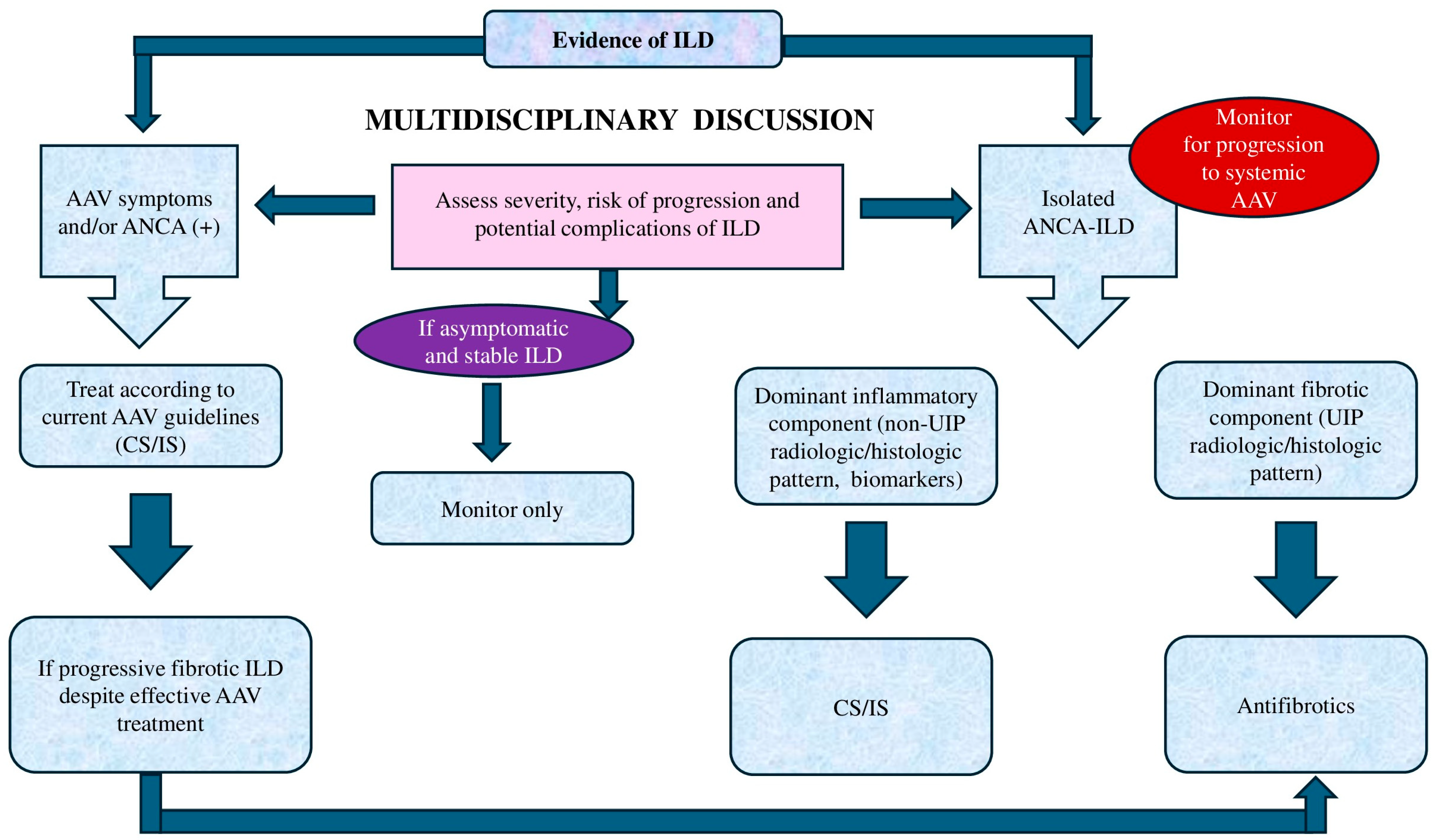
7. Isolated ANCA-Positive ILD: A Distinct AAV Phenotype or a Separate Entity? Clinical Significance of ANCA in ILD and the Risk of Developing AAV
8. Treatment Considerations
8.1. Choosing the Optimal Treatment Strategy
8.2. When to Initiate Treatment
8.3. Current Treatment Approaches
8.3.1. Standard Treatment
8.3.2. Antifibrotic Therapy
8.4. Emerging Therapies and Future Directions
Precision Medicine
8.5. Supportive Care
8.6. Lung Transplantation
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Jennette, J.C.; Falk, R.J.; Bacon, P.A.; Basu, N.; Cid, M.C.; Ferrario, F.; Flores-Suarez, L.F.; Gross, W.L.; Guillevin, L.; Hagen, E.C.; et al. 2012 Revised International Chapel Hill Consensus Conference Nomenclature of Vasculitides. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 65, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kronbichler, A.; Bajema, I.M.; Bruchfeld, A.; Kirsztajn, G.M.; Stone, J.H. Diagnosis and management of ANCA-associated vasculitis. Lancet 2024, 403, 683–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinico, R.A.; Di Toma, L.; Maggiore, U.; Bottero, P.; Radice, A.; Tosoni, C.; Grasselli, C.; Pavone, L.; Gregorini, G.; Monti, S.; et al. Prevalence and clinical significance of antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies in Churg-Strauss syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 2005, 52, 2926–2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sable-Fourtassou, R.; Cohen, P.; Mahr, A.; Pagnoux, C.; Mouthon, L.; Jayne, D.; Blockmans, D.; Cordier, J.F.; Delaval, P.; Puechal, X.; et al. Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies and the Churg-Strauss syndrome. Ann. Intern. Med. 2005, 143, 632–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fijolek, J.; Wiatr, E.; Bujnowski, P.; Piotrowska-Kownacka, D.; Roszkowski-Sliz, K. Evaluation of prognostic factors for patients with eosinophilic granulomatosis and polyangiitis recruited at the pneumonological centre and mainly ANCA negativity: A retrospective analysis of a single cohort in Poland. Modern Rheumatol. 2023, 34, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, P.A.; Rayner, T.F.; Trivedi, S.; Holle, J.U.; Watts, R.A.; Jayne, D.R.W.; Baslund, B.; Brenchley, P.; Bruchfeld, A.; Chaudhry, A.N.; et al. Genetically distinct subsets within ANCA-associated vasculitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, P.A.; Peters, J.E.; Alberici, F.; Liley, J.; Coulson, R.M.R.; Astle, W.; Baldini, C.; Bonatti, F.; Cid, M.C.; Elding, H.; et al. Genome-wide association study of eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis reveals genomic loci stratified by ANCA status. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fijolek, J.; Radzikowska, E. Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis—Advances in pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1145257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potentas-Policewicz, M.; Fijolek, J. Granulomatosis with polyangiitis: Clinical characteristics and updates in diagnosis. Front. Med. 2024, 11, 1369233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, T.M. Interstitial lung disease. JAMA 2024, 331, 1655–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijsenbeek, M.; Suzuki, A.; Maher, T.M. Interstitial lung diseases. Lancet 2022, 400, 769–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nada, A.K.; Torres, V.E.; Ryu, J.H.; Holley, K.E. Pulmonary fibrosis as an unusual clinical manifestation of a pulmonary-renal vasculitis in elderly patients. Mayo Clin. Proc. 1990, 65, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foulon, G.; Delaval, P.; Valeyre, D.; Wallaert, B.; Debray, M.P.; Brauner, M.; Nicaise, P.; Cadranel, J.; Cottin, V.; Tazi, A.; et al. ANCA-associated lung fibrosis: Analysis of 17 patients. Respir. Med. 2008, 102, 1392–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozu, T.; Kondo, M.; Suzuki, K.; Tamaoki, J.; Nagai, A. A comparison of the clinical features of ANCA-positive and ANCA-negative idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis patients. Respiration 2009, 77, 401–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadura, S.; Raghu, G. Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated interstitial lung disease: A review. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2021, 30, 210123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvati, L.; Palterer, B.; Lazzeri, E.; Vivarelli, E.; Amendola, M.; Allinovi, M.; Caroti, L.; Mazzoni, A.; Lasagni, L.; Emmi, G.; et al. Presentation and progression of MPO-ANCA interstitial lung disease. J. Transl. Autoimmun. 2024, 8, 100235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WGET Research Group. Design of the Wegener’s Granulomatosis Etanercept Trial (WGET). Control. Clin. Trials 2002, 23, 450–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Ma, J.; Wang, G. Impact of interstitial lung disease on mortality in ANCA-associated vasculitis: A systematic literature review and meta-analysis. Chronic Respir. Dis. 2021, 18, 1479973121994562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, A.J.; Jacobsson, L.T.H.; Mahr, A.D.; Sturfelt, G.; Segelmark, M. Prevalence of Wegener’s granulomatosis, microscopic polyangiitis, polyarteritis nodosa and Churg-Strauss syndrome within a defined population in southern Sweden. Rheumatology 2007, 46, 1329–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berti, A.; Cornec, D.; Crowson, C.S.; Specks, U.; Matteson, E.L. Epidemiology of antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody-associated vasculitis in Olmsted County, Minnesota. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017, 69, 2338–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, A.; Sakamoto, S.; Kurosaki, A.; Kurihara, Y.; Satoh, K.; Usui, Y.; Nanki, T.; Arimura, Y.; Makino, H.; Okada, Y.; et al. Chest High-Resolution CT findings of microscopic polyangiitis: A Japanese first nationwide prospective cohort study. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2019, 213, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastiani, M.; Manfredi, A.; Vacchi, C.; Gassone, G.; Faverio, P.; Cavazza, A.; Sverzellati, N.; Salvarani, C.; Luppi, F. Epidemiology and management of interstitial lung disease in ANCA-associated vasculitis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2020, 38, S221–S231. [Google Scholar]
- Doliner, B.; Rodriguez, K.; Montesi, S.B.; Fu, X.; Sharma, A.; Wallace, Z.S. Interstitial lung disease in ANCA-associated vasculitis: Associated factors, radiographic features and mortality. Rheumatology 2023, 62, 716–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzelepis, G.E.; Kokosi, M.; Tzioufas, A.; Toya, S.P.; Boki, K.A.; Zormpala, A.; Moutsopoulos, H.M. Prevalence and outcome of pulmonary fibrosis in microscopic polyangiitis. Eur. Respir. J. 2010, 36, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arulkumaran, N.; Periselneris, N.; Gaskin, G.; Strickland, N.; Ind, P.W.; Pusey, C.D.; Salama, A.D. Interstitial lung disease and ANCA-associated vasculitis: A retrospective observational cohort study. Rheumatology 2011, 50, 2035–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.K.; Hwang, J.W.; Lee, J.; Jeon, C.H.; Cha, H.S.; Koh, E.M. Clinical features and outcome of microscopic polyangiitis under a new consensus algorithm of ANCA-associated vasculitides in Korea. Rheumatol. Int. 2012, 32, 2979–2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Wang, Y.X.; Jiang, C.G.; Liu, J.; Xu, K.; Xu, Z.J. A retrospective study of microscopic polyangiitis patients presenting with pulmonary fibrosis in China. BMC Pulm. Med. 2014, 14, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casarez, M.F.; Gonzales, A.; Fielli, M.; Caputo, F.; Bottinelli, Y.; Zamboni, M. Microscopic polyangiitis associated with pulmonary fibrosis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2015, 34, 1273–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, N.; Niiro, H.; Ueda, A.; Sawabe, T.; Nishizaka, H.; Furugo, I.; Yoshizawa, S.; Yoshizawa, S.; Tsukamoto, H.; Kiyohara, C.; et al. Characteristics of MPO-ANCA-positive granulomatosis with polyangiitis: A retrospective multi-center study in Japan. Rheumatol. Int. 2015, 35, 555–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhzoum, J.P.; Grayson, P.C.; Ponte, C.; Robson, J.; Suppiah, R.; Watts, R.A.; Luqmani, R.; Merkel, P.A.; Pagnoux, C.; for the DCVAS Collaborators. Pulmonary involvement in primary systemic vasculitides. Rheumatology 2022, 61, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potentas-Policewicz, M.; Gawryluk, D.; Wiatr, E.; Fijolek, J. Age-related variations in the clinical presentation and treatment outcomes of new-onset GPA: A longitudinal study. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, K.; Fisher, J.H.; Pagnoux, C. Interstitial lung disease in ANCA-associated vasculitis: Pathogenic considerations and impact for patients’ outcomes. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2022, 24, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hozumi, H.; Enomoto, N.; Oyama, Y.; Kono, M.; Fujisawa, T.; Inui, N.; Nakamura, Y.; Suda, T. Clinical implication of proteinase-3—Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody in patients with idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. Lung 2016, 194, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ando, M.; Miyazaki, E.; Ishii, T.; Mukai, Y.; Yamasue, M.; Fujisaki, H.; Ito, T.; Nureki, S.I.; Kumamoto, T. Incidence of myeloperoxidase anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody positivity and microscopic polyangiitis in the course of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respir. Med. 2013, 107, 608–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kagiyama, N.; Takayanagi, N.; Kanauchi, T.; Ishiguro, T.; Yanagisawa, T.; Sugita, Y. Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-positive conversion and microscopic polyangiitis development in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. BMJ Open Resp. Res. 2015, 2, e000058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.J.; Ventura, I.B.; Achtar-Zadeh, N.; Elicker, B.M.; Jones, K.D.; Wolters, P.J.; Collard, H.R.; Adegunsoye, A.; Strek, M.E.; Ley, B. Prevalence and clinical significance of antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies in North American patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Chest 2019, 156, 715–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirayama, K.; Kobayashi, M.; Usui, J.; Arimura, J.; Sugiyama, H.; Nitta, K.; Muso, E.; Wada, T.; Matsuo, S.; Yamagata, K.; et al. Pulmonary involvements of anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody-associated renal vasculitis in Japan. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2015, 30, i83–i93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Yu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, M.H. Antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody-associated vasculitis in older patients. Medicine 2008, 87, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Suarez, L.F.; Ruiz, N.; Rivera, L.M.S.; Pensado, L. Reduced survival in microscopic polyangiitis patients with pulmonary fibrosis in a respiratory referral centre. Clin. Rheumatol. 2015, 34, 1653–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kono, M.; Nakamura, Y.; Enomoto, N.; Hashimoto, D.; Fujisawa, T.; Inui, N.; Maekawa, M.; Suda, T.; Colby, T.V.; Chida, K. Usual interstitial pneumonia preceding collagen vascular disease: A retrospective case control study of patients initially diagnosed with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudin, P.B.; Askin, F.B.; Falk, R.J.; Jennette, J.C. The pathologic spectrum of pulmonary lesions in patients with anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibodies specific for anti-proteinase 3 and anti-myeloperoxidase. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1995, 104, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comarmond, C.; Crestani, B.; Tazi, A.; Hervier, B.; Adam-Marchand, S.; Nunes, H.; Cohen-Aubart, F.; Wislez, M.; Cadranel, J.; Housset, B.; et al. Pulmonary fibrosis in antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCA)-associated vasculitis. A series of 49 patients and review of the literature. Medicine 2014, 93, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alba, M.A.; Flores-Suarez, L.F.; Henderson, A.G.; Xiao, H.; Hu, P.; Nachman, P.H.; Falk, R.J.; Jennette, J.C. Interstitial lung disease in ANCA vasculitis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2017, 16, 722–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valero-Martinez, C.; Valenzuela, C.; Acha, J.P.B.; Martinez-Besteiro, E.; Quiroga-Colina, P.; Alfranca, A.; Vicente-Rabaneda, E.F.; Muniz, S.H.; Castaneda, S.; Garcia-Vicuna, R. Clinical profiles, survival, and lung function outcomes in ANCA-associated interstitial lung disease: An observational study. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngyuen, Y.; Pagnoux, C.; Karras, A.; Quemeneur, T.; Maurier, F.; Hamidou, M.; Le Quellec, A.; Chiche, N.J.; Cohen, P.; Regent, A.; et al. Microscopic polyangiitis: Clinical characteristics and long-term outcomes of 378 patients from the French Vasculitis Study Group Registry. J. Autoimmun. 2020, 112, 102467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujimoto, S.; Watts, R.A.; Kobayashi, S.; Suzuki, K.; Jayne, D.R.W.; Scott, D.G.I.; Hashimoto, H.; Nunoi, H. Comparison of the epidemiology of anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis between Japan and the UK. Rheumatology 2011, 50, 1916–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuta, S.; Chaudhry, A.N.; Arimura, Y.; Dobashi, H.; Fujimoto, S.; Homma, S.; Rasmussen, N.; Jayne, D.R. Comparison of the phenotype and outcome of granulomatosis with polyangiitis between UK and Japanese cohort. J. Rheumatol. 2017, 44, 2016–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilpain, P.; Chereau, C.; Goulvestre, C.; Servettaz, A.; Montani, D.; Tamas, N.; Pagnoux, C.; Hachulla, E.; Weill, B.; Guillevin, L.; et al. The oxidation induced by antimyeloperoxidase antibodies triggers fibrosis in microscopic polyangiitis. Eur. Respir. J. 2011, 37, 1503–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrysanthopoulou, A.; Mitroulis, I.; Apostolidou, E.; Arelaki, S.; Mikroulis, D.; Konstantinidis, T.; Sivridis, E.; Koffa, M.; Giatromanolaki, A.; Boumpas, D.; et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps promote differentiation and function of fibroblasts. J. Pathol. 2014, 233, 294–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, S.; Kitching, A.R.; Witko-Sarsat, V.; Wiech, T.; Specks, U.; Klapa, S.; Comdühr, S.; Stähle, A.; Müller, A.; Lamprecht, P. Myeloperoxidase-specific antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis. Lancet 2024, 6, e300–e313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travis, W.D.; Hoffman, G.S.; Leavitt, R.Y.; Pass, H.I.; Fauci, A.S. Surgical pathology of the lung in Wegener’s granulomatosis. Review of 87 open lung biopsies from 67 patients. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 1991, 15, 315–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namba, N.; Kawasaki, A.; Sada, K.E.; Firano, F.; Kobayashi, S.; Yamada, H.; Furukawa, H.; Shimada, K.; Hashimoto, A.; Matsui, T.; et al. Association of MUC5B promoter polymorphism with interstitial lung disease in myeloperoxidase-antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 1144–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawasaki, A.; Namba, N.; Sada, K.E.; Hirano, F.; Kobayashi, S.; Nagasaka, K.; Sugihara, T.; Ono, N.; Fujimoto, T.; Kusaoi, M.; et al. Association of TERT and DSP variants with microscopic polyangiitis and myeloperoxidase-ANCA positive vasculitis in a Japanese population: A genetic association study. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2020, 22, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maillet, T.; Goletto, T.; Beltramo, G.; Dupuy, H.; Jouneau, S.; Borie, R.; Crestani, B.; Cottin, V.; Blockmans, D.; Lazaro, E.; et al. Usual interstitial pneumonia in ANCA-associated vasculitis: A poor prognostic factor. J. Autoimmun. 2020, 106, 102338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borie, R.; Crestani, B. Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated lung fibrosis. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 39, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellmich, B.; Sanchez-Alamo, B.; Schirmer, J.H.; Berti, A.; Blockmans, D.; Cid, M.C.; Holle, J.U.; Hollinger, N.; Karadag, O.; Kronbichler, A.; et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of ANCA-associated vasculitis: 2022 update. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2024, 83, 30–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossuyt, X.; Cohen Tervaert, J.W.; Arimura, Y.; Blockmans, D.; Flores-Suarez, L.F.; Guillevin, L.; Hellmich, B.; Jayne, D.; Jennette, J.C.; Kallenberg, C.G.M.; et al. Position paper: Revised 2017 international consensus on testing of ANCAs in granulomatosis with polyangiitis and microscopic polyangiitis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2017, 13, 683–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moiseev, S.; Cohen Tervaert, J.W.; Arimura, Y.; Bogdanos, D.P.; Csernok, E.; Damoiseaux, J.; Ferrante, M.; Flores-Suarez, L.F.; Fritzler, M.J.; Invernizzi, P.; et al. 2020 international consensus on ANCA testing beyond systemic vasculitis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2020, 19, 102618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lionaki, S.; Blyth, E.; Hogan, S.L.; Hu, Y.; Senior, B.A.; Jennette, C.E.; Nachman, P.H.; Jennette, J.C.; Falk, R.J. Classification of antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody vasculitides: The role of antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody specificity for myeloperoxidase or proteinase 3 in disease recognition and prognosis. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 3452–3462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unizony, S.; Villarreal, M.; Miloslavsky, E.M.; Lu, N.; Merkel, P.A.; Spiera, R.; Seo, P.; Langford, C.A.; Hoffman, G.S.; Kallenberg, C.G.M.; et al. Clinical outcomes of treatment of anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)-associated vasculitis based on ANCA type. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 1166–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houben, E.; Bax, W.A.; van Dam, B.; Slieker, W.A.T.; Verhave, G.; Frerichs, F.C.P.; van Eijk, I.C.; Boersma, W.G.; de Kuyper, G.T.M.; Penne, E.L. Diagnosing ANCA-associated vasculitis in ANCA positive patients: A retrospective analysis on the role of clinical symptoms and the ANCA titre. Medicine 2016, 95, e5096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.-Y.; Qiu, X.-Y.; Li, Y.-N.; Zhang, H.-M.; Chen, H.-S.; Gu, Q.; Yan, T.-K.; Jia, J.-Y.; Xu, P.-C. Serum ferritin is a superior biomarker for evaluating disease activity and kidney injury compared with C-reactive protein in anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2025, 44, 2009–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conticini, E.; d’Alessandro, M.; Bergantini, L.; Castillo, D.; Cameli, P.; Frediani, B.; Cantarini, L.; Bargagli, E. KL-6 in ANCA-associated vasculitis patients with and without ILD: A machine learning approach. Biology 2022, 11, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonasdottir, A.D.; Antovic, A.; Qureshi, A.R.; Nordin, A.; Malström, V.; Gunnarsson, I.; Bruchfeld, A. Pentraxin-3—A potential biomarker in ANCA-associated vasculitis. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2023, 52, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juto, A.; Martin, M.; Björk, A.; Padyukov, L.; Grönwall, C.; Antovic, A.; Bruchfeld, A.; Gunnarsson, I.; Blom, A.M. Association of C4d with disease activity in anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis: Evidence for classical/lectin complement pathway activation. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2025, 27, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieterich, J.; Hellmich, B.; Mahrhold, J.; Feng, Y.; Rai, A.E.; Nessyt, F.; Specks, U.; Hetzel, J.; Löffler, C. Pulmonary function in patients with ANCA-associated vasculitis. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffuse Lung Dis. 2024, 41, e2024025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fussner, L.A.; Flores-Suárez, L.F.; Cartin-Ceba, R.; Specks, U.; Cox, P.G.; Jayne, D.R.W.; Merkel, P.A.; Walsh, M. and PEXIVAS Investigators. Alveolar hemorrhage in antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis: Results of an international randomized controlled trial (PEXIVAS). Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2024, 209, 1141–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, M.; Lee, A.S.; Mira-Avendano, I.; Rojas, C.A.; Grage, R.; Abril, A. Interstitial lung disease in antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis patients: Comparison with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2021, 27, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juman, S.; Haque, S.; Chaudhuri, N. Interstitial lung disease associated with ANCA positivity: A retrospective analysis. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 54, PA1362. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammad, A.J.; Mortensen, K.H.; Babar, J.; Smith, R.; Jones, R.B.; Nakagomi, D.; Sivasothy, P.; Jayne, D.R.W. Pulmonary involvement in antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCA)—Associated vasculitis: The influence of ANCA subtype. J. Rheumatol. 2017, 44, 1458–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baqir, M.; Yi, E.E.; Colby, T.V.; Cox, C.W.; Ryu, J.H.; Specks, U. Radiologic and pathologic characteristics of myeloperoxidase-antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated interstitial lung disease: A retrospective analysis. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffuse Lung Dis. 2019, 36, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casal Moura, M.; Tandon, Y.K.; Hartman, T.E.; Ryu, J.H.; Baqir, M. Interstitial lung disease in patients with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis: Chest CT patterns and correlation with survival. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2025, 73, 152726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, P.; Li, Z.; Gao, L.; Zhao, B.; Que, C.; Li, H.; Ma, J.; Wang, G. Patterns of interstitial lung disease and prognosis in antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis. Respiration 2023, 102, 257–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Novoa-Laurentiev, J.; Cook, C.; Srivatsan, S.; Hua, Y.; Miloslavsky, E.; Choi, H.K.; Zhou, L.; Wallace, Z.S. Identification of an ANCA-associated vasculitis cohort using deep learning and electronic health records. Int. J. Med. Inf. 2025, 196, 105797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermejo-Peláez, D.; Ash, S.Y.; Washko, G.R.; San José Estépar, R.; Ledesma-Carbayo, M.J. Classification of interstitial lung abnormality patterns with an ensemble of deep convolutional neural networks. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lami, K.; Ozasa, M.; Che, X.; Uegami, W.; Kato, Y.; Zaizen, Y.; Tsuyama, N.; Mori, I.; Ichihara, S.; Yoon, H.; et al. Enhancing interstitial lung disease diagnoses through multimodal AI integration of histopathological and CT image data. Respirology 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosoda, C.; Baba, T.; Hagiwara, E.; Ito, H.; Matsuo, N.; Kitamura, H.; Iwasawa, T.; Okudela, K.; Takemura, T.; Ogura, T. Clinical features of usual interstitial pneumonia with anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody in comparison with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respirology 2016, 21, 920–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores-Suarez, L.F.; Sacoto, G. Interstitial lung disease and ANCA-associated vasculitis. Curr. Treat. Options Rheum. 2019, 5, 213–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durheim, M.T.; Kim, S.; Gulack, B.C.; Burfeind, W.R.; Gaissert, H.A.; Kosinski, A.S.; Hartwig, M.G. Mortality and respiratory failure after thoracoscopic lung biopsy for interstitial lung disease. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2017, 104, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troy, L.K.; Grainge, C.; Corte, T.J.; Williamson, J.P.; Vallely, M.P.; Cooper, W.A.; Mahar, A.; Myers, J.L.; Lai, S.; Mulyadi, E.; et al. Diagnostic accuracy of transbronchial lung cryobiopsy for interstitial lung disease diagnosis (COLDICE): A prospective, comparative study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homma, S.; Matsushita, H.; Nakata, K. Pulmonary fibrosis in myeloperoxidase antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitides. Respirology 2004, 9, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, T.; Otani, K.; Egashira, R.; Kashima, Y.; Taniguchi, H.; Kondoh, Y.; Kataoka, K.; Shiraki, A.; Kitasato, Y.; Leslie, K.O.; et al. Interstitial pneumonia associated with MPO-ANCA: Clinicopathological features of nine patients. Respir. Med. 2012, 106, 1765–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfredi, A.; Cassone, G.; Izzo, R.; Dallagiacoma, G.; Felicetti, M.; Cariddi, A.; Berti, A.; Giollo, A.; Nannini, C.; Bettiol, S.; et al. Interstitial lung disease in microscopic polyangiitis and granulomatosis with polyangiitis: Demographic, clinical, serological and radiological features of an Italian cohort from the Italian Society for Rheumatology. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2023, 41, 821–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Chai, D.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhan, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Ye, Q. Patterns of lung diseases predict survival in patients with MPO-ANCA-associated vasculitis: A single-center retrospective study. Clin. Rheumatol. 2022, 41, 783–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, S.; Kotani, T.; Suzuka, T.; Kiboshi, T.; Fukui, K.; Wakama, M.; Ishida, T.; Fujiki, Y.; Shiba, H.; Nagai, K.; et al. Evaluation of poor prognostic factors of respiratory related death in microscopic polyangiitis complicated by interstitial lung disease. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Li, Z.; Gao, L.; Que, C.; Li, H.; Ma, J.; Wang, G.; Chen, M. Pulmonary involvement of ANCA-associated vasculitis in adult Chinese patients. BMC Pulm. Med. 2022, 22, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Yuan, W.; Yang, Y.; Ji, J.; Chen, X. Risk factors for poor prognosis in ANCA-associated vasculitis with interstitial lung disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2025, 44, 1675–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellino, J.; Orentas, M.; Moran, J.; Fair, J.; Zhang, Y.; Bukiej, A. Interstitial lung disease in ANCA-associated vasculitis: A retrospective study of clinical characteristics, radiographic features, and outcomes [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024, 76 (Suppl. 9). Available online: https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/interstitial-lung-disease-in-anca-associated-vasculitis-a-retrospective-study-of-clinical-characteristics-radiographic-features-and-outcomes/ (accessed on 15 May 2025).
- Libra, A.; Muscato, G.; Ielo, G.; Spicuzza, L.; Palmucci, S.; Fagone, E.; Fruciano, M.; Gili, E.; Sambataro, G.; Vancheri, C. Clinical and prognostic significance of p-ANCA positivity in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A retrospective observational study. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolotin, D.; O’Brien, C.; Ranganath, V.K.; Kermani, T.A. ANCA-associated vasculitis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A single-center cohort study. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2025, 71, 152648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Cao, C.; Cen, Z.; Zhou, H.; Lv, D.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, Q. Prevalence and clinical significance of anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies in interstitial lung disease: A retrospective cohort study. Rheumatology 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimamura, T.; Furusawa, H.; Ejima, M.; Ozawa, A.; Adachi, T.; Tateishi, U.; Miyazaki, Y. Clinical characteristics and prognostic factors for MPO-ANCA positive interstitial lung disease: A comparative study of ANCA associated vasculitis (AA)—ILD and pulmonary limited vasculitis. Respir. Investig. 2025, 63, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, H.C.; Bui, K.A.; Richard, R.; Toban, N.; Levesque, M.; Meunier, R.S.; Ross, C.; Makhzoum, J.P. Comparison of interstitial lung disease between antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies positive and negative patients: A retrospective cohort study. ACR Open Rheumatol. 2024, 6, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, S.; Suzuki, A.; Homma, S.; Usui, Y.; Shimizu, H.; Sekiya, M.; Miyoshi, S.; Nakamura, Y.; Urabe, N.; Isshiki, T.; et al. Outcomes and prognosis of progressive pulmonary fibrosis in patients with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-positive interstitial lung disease. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 17616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, A.; Antoniou, K.M.; Brown, K.K.; Cadranel, J.; Corte, T.J.; du Bois, R.M.; Lee, J.S.; Leslie, K.O.; Lynch, D.A.; Matteson, E.L.; et al. On behalf of the ERS/ATS Task Force on Undifferentiated Forms of CTD-ILD. An official European Respiratory Society/American Thoracic Society research statement: Interstitial pneumonia with autoimmune features. Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 46, 976–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Zhou, C.; Sun, X.; Xue, P.; Li, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, T.; Peng, M.; Shi, J.; et al. Interstitial lung diseases associated with ANCA positivity: A different disease spectrum from interstitial pneumonia with autoimmune features. Respir. Med. Res. 2024, 86, 101111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suppiah, R.; Robson, J.C.; Grayson, P.C.; Ponte, C.; Craven, A.; Khalid, S.; Judge, A.; Hutchings, A.; Merkel, P.A.; Luqmani, R.A.; et al. 2022 American College of Rheumatology/European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology classification criteria for microscopic polyangiitis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2022, 81, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fidler, L.M.; Kandel, S.; Fisher, J.H.; Mittoo, S.; Shapera, S. Utility of anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody screening in idiopathic interstitial lung disease. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffuse Lung Dis. 2021, 38, e2021015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghu, G.; Remy-Jardin, M.; Richeldi, L.; Thomson, C.C.; Inoue, Y.; Johkoh, T.; Kreuter, M.; Lynch, D.A.; Maher, T.M.; Martinez, F.J.; et al. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (an update) and progressive pulmonary fibrosis in adults: An official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT clinical practice guideline. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 205, e18–e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, G.E.; Specks, U. Update on the management of respiratory manifestations of the antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies-associated vasculitides. Clin. Chest Med. 2019, 40, 573–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Clinical Research Network; Raghu, G.; Anstrom, K.J.; King, T.E., Jr.; Lasky, J.A.; Martinez, F.J. Prednisone, azathioprine, and N-acetylcysteine for pulmonary fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 1968–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behr, J.; Salisbury, M.L.; Walsh, S.L.F.; Podolanczuk, A.J.; Hariri, L.P.; Hunninghake, G.M.; Kolb, M.; Ryerson, C.J.; Cottin, V.; Beasley, M.B.; et al. The role of inflammation and fibrosis in interstitial lung disease treatment decisions. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2024, 210, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamakawa, H.; Toyoda, Y.; Baba, T.; Kishaba, T.; Fukuda, T.; Takemura, T.; Kuwano, K. Anti-inflammatory and/or anti-fibrotic treatment of MPO-ANCA-positive interstitial lung disease: A short review. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhan, X.; Wang, J.; Fan, Y.; Ma, R.; Ye, Q. Serum oncomarkers in patients with MPO-ANCA-positive vasculitis: Diagnostic and prognostic predictive values for interstitial lung disease. Lung 2022, 200, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flaherty, K.R.; Wells, A.U.; Cottin, V.; Devaraj, A.; Walsh, S.L.F.; Inoue, Y.; Richeldi, L.; Kolb, M.; Tetzlaff, K.; Stowasser, S.; et al. Nintedanib in progressive fibrosing interstitial lung diseases. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1718–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luppi, F.; Sebastiani, M.; Salvarani, C.; Bendstrup, E.; Manfredi, A. Acute exacerbation of interstitial lung disease associated with rheumatic disease. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2022, 18, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, J.H.; Johannson, K.A.; Assayag, D.; Morisset, J.; de Boer, K.; Manganas, H.; Shapera, S.; Fell, C.D.; Ryerson, C.J.; Kolb, M. Long-term monitoring of patients with fibrotic interstitial lung disease: A Canadian Thoracic Society position statement. Can. J. Respir. Crit. Care Sleep Med. 2020, 4, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, J.L.; Maher, T.M.; Quint, J.K.; Adamson, A.; Wu, Z.; Smith, D.J.F.; Rawal, B.; Nair, A.; Walsh, S.L.F.; Desai, S.R.; et al. Combination of BAL and computed tomography differentiates progressive and non-progressive fibrotic lung diseases. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2023, 208, 975–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, G.; Thould, H.; Wells, M.; Tsaneva-Atanasova, K.; Scotton, C.J.; Gibbons, M.A.; Barratt, S.L.; Rodrigues, J.C.L. A systematic review of the role of quantitative CT in the prognostication and disease monitoring of interstitial lung disease. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2025, 34, 240194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, J.H.; Merkel, P.A.; Spiera, R.; Seo, P.; Langford, C.A.; Hoffman, G.S.; Kallenberg, C.G.M.; St Clair, E.W.; Turkiewicz, A.; Tchao, N.K.; et al. Rituximab versus cyclophosphamide for ANCA-associated vasculitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillevin, L.; Pagnoux, C.; Karras, A.; Khouatra, C.; Aumaitr, O.; Cohen, P.; Maurier, F.; Decaux, O.; Ninet, J.; Gobert, P.; et al. Rituximab versus azathioprine for maintenance in ANCA-associated vasculitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 1771–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.B.; Hiemstra, T.F.; Ballarin, J.; Blockmans, D.E.; Brogan, P.; Bruchfeld, A.; Cid, M.M.; Dahlsveen, K.; de Zoysa, J.; Espigol-Frigole, G.; et al. Mycophenolate mofetil versus cyclophosphamide for remission induction in ANCA-associated vasculitis: A randomised, non-inferiority trial. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berti, A.; Alsawas, M.; Jawaid, T.; Prokop, L.J.; Lee, J.M.; Jeong, G.H.; Quintana, L.F.; Moiseev, S.; Vaglio, A.; Tesar, V.; et al. Induction and maintenance of remission with mycophenolate mofetil in ANCA-associated vasculitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2022, 37, 2190–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayne, D.R.W.; Merkel, P.A.; Schall, T.J.; Bekker, P.; Advocate Study Group. Avacopan for the Treatment of ANCA-Associated Vasculitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 384, 599–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ding, Q.; Lv, C.; Ying, Y.; Cen, Z.; Zhou, H.; Wu, T. Clinical significance of microscopic polyangiitis with interstitial lung disease and bronchiectasis: Probability of preexisting comorbidities. Ann. Med. 2023, 55, 2204449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajan, S.K.; Cottin, V.; Dhar, R.; Danoff, S.; Flaherty, K.R.; Brown, K.K.; Mohan, A.; Renzoni, E.; Mohan, M.; Udwadia, Z.; et al. Progressive pulmonary fibrosis: An expert group consensus statement. Eur. Respir. J. 2023, 61, 2103187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashkin, D.P.; Elashoff, R.; Clements, P.J.; Goldin, J.; Roth, M.D.; Furst, D.E.; Arriola, E.; Silver, R.; Strange, C.; Bolster, M.; et al. Cyclophosphamide versus placebo in scleroderma lung disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 2655–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashkin, D.P.; Roth, M.D.; Clements, P.J.; Furst, D.E.; Khanna, D.; Kleerup, E.C.; Goldin, J.; Arriola, E.; Volkmann, E.R.; Kafaja, S.; et al. Mycophenolate mofetil versus oral cyclophosphamide in scleroderma-related interstitial lung disease (SLS II): A randomised controlled, double-blind, parallel group trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2016, 4, 708–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liossis, S.N.C.; Bounia1, C.A. Treating autoimmune-related interstitial lung disease with B cell depletion. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 937561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouros, D.; Wells, A.U.; Nicholson, A.G.; Colby, T.V.; Polychronopoluos, V.; Pantelidis, P.; Haslam, P.L.; Vassilakis, D.A.; Black, C.M.; du Bois, R.M. Histopathologic subsets of fibrosing alveolitis in patients with systemic sclerosis and their relationship to outcome. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 165, 1581–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Gao, Y.; Petnak, T.; Cheungpasitporn, W.; Thongprayoon, C.; Zhang, X.; Moua, T. Effect size of rituximab on pulmonary function in the treatment of connective-tissue disease-related interstitial lung disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Respir. Res. 2022, 23, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maher, T.M.; Tudor, V.A.; Saunders, P.; Gibbons, M.A.; Fletcher, S.V.; Denton, C.P.; Hoyles, R.K.; Parfrey, H.; Renzoni, E.A.; Kokosi, M.; et al. Rituximab versus intravenous cyclophosphamide in patients with connective tissue disease-associated interstitial lung disease in the UK (RECITAL): A double-blind, double-dummy, randomised, controlled, phase 2b trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2023, 11, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mankikian, J.; Caille, A.; Reynaud-Gaubert, M.; Agier, M.S.; Bermudez, J.; Bonniaud, P.; Borie, R.; Brillet, P.Y.; Cadranel, J.; Court-Fortune, I.; et al. Rituximab and mycophenolate mofetil combination in patients with interstitial lung disease (EVER-ILD): A double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Eur. Respir. J. 2023, 61, 2202071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, M.; Bejan-Angoulvant, T.; Marchand-Adam, S.; Mousset, E.; Mureau, E.; Jouneau, S.; Nunes, H.; Montani, D.; Chenivesse, C.; Cadranel, J.; et al. Evaluation of efficacy and safety of rituximab in patients with progressive interstitial lung disease (ILD) with inflammatory component (EvER-ILD2): A multicentre double-blind placebo-controlled randomized trial. Respir. Med. Res. 2024, 87, 101144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, S.R.; Bernstein, E.J.; Bolster, M.B.; Chung, J.H.; Danoff, S.K.; George, M.D.; Khanna, D.; Guyatt, G.; Mirza, R.D.; Aggarwal, R.; et al. 2023 American College of Rheumatology (ACR)/American College of Chest Physicians (CHEST) Guideline for the Treatment of Interstitial Lung Disease in People with Systemic Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases. Arthritis Care Res. 2024, 76, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noble, P.W.; Albera, C.; Bradford, W.Z.; Costabel, U.; Glassberg, M.K.; Kardatzke, D.; King, T.E., Jr.; Lancaster, L.; Sahn, S.A.; Szwarcberg, J.; et al. Pirfenidone in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (CAPACITY): Two randomised trials. Lancet 2011, 377, 1760–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richeldi, L.; Cottin, V.; du Bois, R.M.; Selman, M.; Kimura, T.; Bailes, Z.; Schlenker-Herceg, R.; Stowasser, S.; Brown, K.K. Nintedanib in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Combined evidence from the TOMORROW and INPULSIS® trials. Respir. Med. 2016, 113, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petnak, T.; Lertjitbanjong, P.; Thongprayoon, C.; Moua, T. Impact of antifibrotic therapy on mortality and acute exacerbation in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Chest 2021, 160, 1751–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan, S.D.; Albera, C.; Bradford, W.Z.; Costabel, U.; Glaspole, I.; Glassberg, M.K.; Kardatzke, D.R.; Daigl, M.; Kirchgaessler, K.U.; Lancaster, L.H.; et al. Effect of pirfenidone on mortality: Pooled analyses and meta-analyses of clinical trials in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Lancet Respir. Med. 2017, 5, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Distler, O.; Highland, K.B.; Gahlemann, M.; Azuma, A.; Fischer, A.; Mayes, M.D.; Raghu, G.; Sauter, W.; Girard, M.; Alves, M.; et al. Nintedanib for Systemic Sclerosis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 2518–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behr, J.; Prasse, A.; Kreuter, M.; Johow, K.; Rabe, K.F.; Bonella, F.; Bonnet, R.; Grohe, C.; Held, M.; Wilkens, H.; et al. Pirfenidone in patients with progressive fibrotic interstitial lung diseases other than idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (RELIEF): A double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 2b trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, 476–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, J.J.; Danoff, S.K.; Woodhead, F.A.; Hurwitz, S.; Maurer, R.; Glaspole, I.; Dellaripa, P.F.; Gooptu, B.; Vassallo, R.; Cox, P.G.; et al. Safety, tolerability, and efficacy of pirfenidone in patients with rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2 study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2023, 11, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández Pérez, E.R.; Crooks, J.L.; Lynch, D.A.; Humphries, S.M.; Koelsch, T.L.; Swigris, J.J.; Solomon, J.J.; Mohning, M.P.; Groshong, S.D.; Fier, K. Pirfenidone in fibrotic hypersensitivity pneumonitis: A double-blind, randomised clinical trial of efficacy and safety. Thorax 2023, 78, 1097–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ushio, Y.; Wakiya, R.; Kameda, T.; Nakashima, S.; Shimada, H.; Miyagi, T.; Sugihara, K.; Mino, R.; Mizusaki, M.; Chujo, K.; et al. Nintedanib combined with immunosuppressive agents improves forced vital capacity in connective tissue disease-associated PF-ILD: A single-center study. BMC Rheumatol. 2024, 8, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottin, V.; Koschel, D.; Günther, A.; Albera, C.; Azuma, A.; Sköld, C.M.; Tomassetti, S.; Hormel, P.; Stauffer, J.L.; Strombom, I.; et al. Long-term safety of pirfenidone: Results of the prospective, observational PASSPORT study. ERJ Open Res. 2018, 4, 00084–02018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, T.; Shah, A.; Saluja, P.; Kocurek, E. Combination therapy with pirfenidone and nintedanib in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Chest 2023, 164, A3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkmann, E.R.; Denton, C.P.; Kolb, M.; Wjisenbeek-Lourens, M.S.; Emson, C.; Hudson, K.; Amatucci, A.J.; Distler, O.; Allanore, Y.; Khanna, D. Lysophosphatidic acid receptor 1 inhibition: A potential treatment target for pulmonary fibrosis. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2024, 33, 240015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corte, T.J.; Behr, J.; Cottin, V.; Glassberg, M.K.; Kreuter, M.; Martinez, F.J.; Ogura, T.; Suda, T.; Wijsenbeek, M.; Berkowitz, E.; et al. Efficacy and safety of Admilparant, an LPA1 antagonist, in pulmonary fibrosis: A phase 2 randomized clinical trial. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2025, 211, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reininger, D.; Fundel-Clemens, K.; Mayr, C.H.; Wollin, L.; Laemmle, B.; Quast, K.; Nickolaus, P.; Herrmann, F.E. PDE4B inhibition by nerandomilast: Effects on lung fibrosis and transcriptome in fibrotic rats and on biomarkers in human lung epithelial cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2024, 181, 4766–4781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richeldi, L.; Azuma, A.; Cottin, V.; Hesslinger, C.; Stowasser, S.; Valenzuela, C.; Wijsenbeek, M.S.; Zoz, D.F.; Voss, F.; Maher, T.M. and 1305-0013 Trial Investigators. Trial of a preferential Phosphodiesterase 4B inhibitor for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 2178–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richeldi, L.; Azuma, A.; Cottin, V.; Kreuter, M.; Maher, T.M.; Martinez, F.J.; Oldham, J.M.; Valenzuela, C.; Gordat, M.; Liu, Y.; et al. Design of a phase III, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled trial of BI 1015550 in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (FIBRONEER-IPF). BMJ Open Respir. Res. 2023, 10, e001563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maher, T.M.; Assassi, S.; Azuma, A.; Cottin, V.; Hoffman-Vold, A.M.; Kreuter, M.; Oldham, J.M.; Richeldi, L.; Valenzuela, C.; Wijsenbeek, M.S.; et al. Design of a phase III, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled trial of BI 1015550 in patients with progressive pulmonary fibrosis (FIBRONEER-ILD). BMJ Open Respir. Res. 2023, 10, e001580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richeldi, L.; Azuma, A.; Cottin, V.; Kreuter, M.; Maher, T.M.; Martinez, F.J.; Oldham, J.N.; Valenzuela, C.; Clerisme-Beaty, E.; Gordat, M.; et al. Nerandomilast in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2025, 392, 2193–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, A.; Chaudhuri, N.; Barczyk, A.; Wilsher, M.L.; Hopkins, P.; Glaspole, I.; Corte, T.J.; Šterclová, M.; Veale, A.; Jassem, E.; et al. Inhaled pirfenidone solution (AP01) for IPF: A randomised, open-label, dose-response trial. Thorax 2023, 78, 882–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, M.; Reisner, C.; Nair, D.; Woodhead, F.; Lazarus, H.; Conoscenti, C. Inhalation innovation: Phase IIb study design of inhaled pirfenidone in the treatment of progressive pulmonary fibrosis. EMJ Respir. 2024, 12, 84–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein-Shochet, G.; Pham, S.; Beck, S.; Naiel, S.; Mekhael, O.; Revill, S.; Hayat, A.; Vierhout, M.; Bardestein-Wald, B.; Shitrit, D.; et al. Inhalation: A means to explore and optimize nintedanib’s pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic relationship. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 63, 101933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surber, M.W.; Beck, S.; Pham, S.; Marsden, A.T.; Gandi, S.K.; Baily, J.; McElroy, M.C. Inhaled nintedanib is well-tolerated and delivers key pharmacokinetic parameters required to treat bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 63, 101938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Goyal, M.; Gadhave, D.; Gupta, V. Inhaled nintedanib nanoparticles for enhanced efficacy in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) treatment—Evidence in disease-relevant in-vitro models. J. Drug Delivery Sci. Technol. 2024, 95, 105615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waxman, A.; Restrepo-Jaramillo, R.; Thenappan, T.; Ravichandran, A.; Engel, P.; Bajwa, A.; Allen, R.; Feldman, J.; Argula, R.; Smith, P.; et al. Inhaled Treprostinil in pulmonary hypertension due to interstitial lung disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan, S.D.; Behr, J.; Cottin, V.; Lancaster, L.; Smith, P.; Deng, C.Q.; Pearce, N.; Bell, H.; Peterson, L.; Flaherty, K.R.; et al. Study design and rationale for the TETON phase 3, randomised, controlled clinical trials of inhaled treprostinil in the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. BMJ Open Respir. Res. 2022, 9, e001310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan, S.D.; Behr, J.; Cottin, V.; Lancaster, L.; Smith, P.; Deng, C.Q.; Breytenbach, N.; Bell, H.; Peterson, L.; Flaherty, K.R. Study design and rationale for the TETON-PPF Phase 3, randomized, controlled clinical trial of inhaled Treprostinil in the treatment of progressive pulmonary fibrosis. Chest Pulm. 2025, 3, 100124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Agnano, V.; Perrotta, F.; Fomez, R.; Carrozzo, V.M.; Schiatarella, A.; Zamparelli, S.S.; Pagliaro, R.; Bianco, A.; Mariniello, D.F. Pharmacological treatment of interstitial lung diseases: A novel landscape for inhaled agents. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, R.; Guo, Q.; Hu, J.; Li, N.; Gao, R.; Mi, L.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, H.; Guo, Z.; Zhao, H.; et al. Therapeutic potential of Janus kinase inhibitors for the management of interstitial lung disease. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2022, 16, 991–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milara, J.; Hernandez, G.; Ballester, B.; Morell, A.; Roger, I.; Montero, P.; Escriva, J.; Lloris, J.M.; Molina-Molina, M.; Morcillo, E.; et al. The JAK2 pathway is activated in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respir. Res. 2018, 19, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venerito, V.; Manfredi, A.; Carletto, A.; Gentileschi, S.; Atzeni, F.; Guiducci, S.; Lavista, M.; La Corte, L.; Pedrollo, E.; Scardapane, A.; et al. Evolution of rheumatoid-arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease in patients treated with JAK inhibitors: A retrospective exploratory study. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyoncu, U.; Bilgin, E.; Erden, A.; Satış, H.; Tufan, A.; Tekgöz, E.; Ateş, A.; Coşkun, B.N.; Yağız, B.; Küçükşahin, O.; et al. Effectiveness and safety of tofacitinib in rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease: TReasure real-life data. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2022, 40, 2071–2077. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Narváez, J.; Aguilar-Coll, M.; Roig-Kim, M.; Maymō-Paituvi, P.; Palacios-Olid, J.; Nolla, J.M.; LLop, D. Janus kinase inhibitors in rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2024, 23, 103636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Ji, Z.; Yu, W.; Wu, S.; Chen, H.; Ma, L.; Ding, Z.; Jiang, L. Tofacitinib for the treatment of antineutrophil cytoplasm antibody-associated vasculitis: A pilot study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, 1631–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linde, L.; Faurschou, M.; Krintel, S.B.; Baslund, B. Response to treatment with Tofacitinib in 11 patients with refractory granulomatosis with polyangiitis. J. Rheumatol. 2023, 50, 1088–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrotta, F.; Zamparelli, S.S.; D’Agnano, V.; Montella, A.; Fomez, R.; Pagliaro, R.; Schiatarella, A.; Cazzola, M.; Bianxco, A.; Marinello, D.F. Genomic Profiling for Predictive Treatment Strategies in Fibrotic Interstitial Lung Disease. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuart, B.D.; Lee, J.S.; Kozlitina, J.; Noth, I.; Devine, M.S.; Glazer, C.S.; Torres, F.; Kaza, V.; Girod, C.E.; Jones, K.; et al. Effect of telomere length on survival in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: An observational cohort study with independent validation. Lancet Respir. Med. 2014, 2, 557–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ley, B.; Newton, C.A.; Arnould, I.; Elicker, B.M.; Henry, T.S.; Vittinghoff, E.; Golden, J.; Jones, K.D.; Batra, K.; Torrealba, J.; et al. The MUC5B promoter polymorphism and telomere length in patients with chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis: An observational cohort-control study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2017, 5, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moura, M.C.; Deng, Z.; Brooks, S.R.; Tew, W.; Fervenza, F.C.; Kallenberg, C.M.; Langford, C.A.; Merkel, P.A.; Monach, P.A.; Seo, P.; et al. Risk of relapse of ANCA-associated vasculitis among patients homozygous for the proteinase 3 gene Val119Ile polymorphism. RMD Open 2023, 9, e002935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, A.; Sada, K.E.; Kusumawati, P.A.; Hirano, F.; Kobayashi, S.; Nagasaka, K.; Sugihara, T.; Ono, N.; Fujimoto, T.; Kusaoi, M.; et al. Association of HLA-class II alleles with risk of relapse in myeloperoxidase-antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody positive vasculitis in the Japanese population. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1119064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Steffens, A.; Olson, A.L.; Anderson, A.; Basra, G.; Veeranki, P.; de Andrade, J.A. Supplemental oxygen therapy use among patients with fibrosing interstitial lung disease in the United States. Respir. Res. 2025, 26, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, R.K.; Humphreys, C.; Morisset, J.; Holland, A.E.; Johannson, K.A. Oxygen in patients with fibrotic interstitial lung disease: An international Delphi survey. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 54, 1900421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visca, D.; Mori, L.; Tsipouri, V.; Fleming, S.; Firouzi, A.; Bonini, M.; Pavitt, M.J.; Alfieri, V.; Canu, S.; Bonifazi, M.; et al. Effect of ambulatory oxygen on quality of life for patients with fibrotic lung disease (AmbOx): A prospective, open-label, mixed-method, crossover randomised controlled trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2018, 6, 759–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.E.; Kim, T.H.; Jang, J.H.; Jang, H.J.; Yi, J.; Jung, S.Y.; Kim, D.W.; Lee, J.H. The Efficacy of pulmonary rehabilitation in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Life 2023, 13, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunetti, G.; Malovini, A.; Maniscalco, M.; Balestrino, A.; Carone, M.; Visca, D.; Capelli, A.; Vitacca, M.; Bellazzi, R.; Piaggi, G.; et al. Pulmonary rehabilitation in patients with interstitial lung diseases: Correlates of success. Respir. Med. 2021, 185, 106473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrier, B.; Richert, L.; Pugnet, G.; Aumaitre, O.; Moranne, O.; Diot, E.; Karras, A.; Bonnet, F.; De Moreuil, C.; Hachulla, E.; et al. Innovative anti-pneumococcal vaccine strategies versus standard vaccination regimen in patients with ANCA-associated vasculitides receiving rituximab therapy: A multicenter randomized controlled trial (PNEUMOVAS) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022, 74 (Suppl. 9). Available online: https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/innovative-anti-pneumococcal-vaccine-strategies-versus-standard-vaccination-regimen-in-patients-with-anca-associated-vasculitides-receiving-rituximab-therapy-a-multicenter-randomized-controlled-trial/ (accessed on 16 May 2025).
- Lim, C.Y.; Khan, S.W.; Alsibai, T.; Sathiyamoorthy, G. Examining cough’s role and relief strategies in interstitial lung disease. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raman, L.; Stewart, I.; Barratt, S.L.; Chua, F.; Chaudhuri, N.; Crawshaw, A.; Gibbons, M.; Hogben, C.; Hoyles, R.; Kouranos, V.; et al. Nintedanib for non-IPF progressive pulmonary fibrosis: 12-month outcome data from a real-world multicentre observational study. ERJ Open Res. 2023, 9, 00423–02022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijsenbeek, M.; Swigris, J.J.; Inoue, Y.; Kreuter, M.; Maher, T.M.; Suda, T.; Baldwin, M.; Mueller, H.; Rohr, K.B.; Flaherty, K.R. and INBUILD Trial Investigators. Effects of nintedanib on symptoms in patients with progressive pulmonary fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2024, 63, 2300752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turgeon, D.; Balter, M.S.; Pagnoux, C. Interstitial lung disease in patients with anti-neutrophil cytoplasm antibody-associated vasculitis: An update on pathogenesis and treatment. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2023, 29, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leard, L.E.; Holm, A.M.; Valapour, M.; Glanville, A.R.; Attawar, S.; Aversa, M.; Campos, S.V.; Christon, L.M.; Cypel, M.; Dellgren, G.; et al. Consensus document for the selection of lung transplant candidates: An update from the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2021, 40, 1349–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameter | Fibrotic-Predominant Disease | Inflammatory-Predominant Disease | Clinical Priority/Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| FVC decline | High | Moderate | Main functional parameter used in most studies |
| TL,co decline | High | Moderate | Sensitive to gas exchange impairment |
| HRCT progression | High | High | Useful in both phenotypes; qualitative and quantitative assessment |
| 6-MWT | Moderate | Moderate | Reflects functional status, influenced by comorbidities |
| CRP/ESR | Low | High | Useful markers of systemic inflammation |
| ANCA titers | Low to moderate | High | Dynamic changes may have clinical relevance, though not fully validated |
| Renal function/ urinalysis | High | High | Critical for detecting systemic involvement (e.g., glomerulonephritis) |
| Study Name (ClinicalTrials.gov ID) | Studied Drug | Estimated Enrolment | Primary Outcome | Phase | Status | Estimated Completion Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ENDURRANCE-1 (NCT03942887) | Combination of RTX and CYC vs RTX monotherapy | GPA MPA (N = 100) | Number of RTX-tailored infusions | 3 | Active, recruiting | April, 2025 |
| HAVEN (NCT04316494) | Hydroxychloroquine added to background treatment | GPA MPA EGPA (N = 76) | Patients (%) with either: uncontrolled AAV (BVAS > 3), or controlled AAV (BVAS ≤ 3) but requiring > 7.5 mg/day of prednisolone (any reason) at week 12 | 4 | Active, not recruiting | May, 2025 |
| SATELITE (NCT04871191) | RTX + DMARD vs RTX + tocilizumab vs RTX + abatacept in induction of remission | GPA (N = 42) | Patients (%) with response or remission at week 12 | 3 | Not yet recruiting | January, 2029 |
| NCT05376319 | Obinutuzumab (anti-CD20) | PR3-AAV (N = 6) | Patients achieving CR and ANCA seronegativity at 6 months | 2 | Early terminated (due to sponsor funding withdrawal) | |
| AVACOSTAR (NCT05897684) | Avacopan vs. CYC- or RTX-based induction regimens for severe AAV | AAV (N = 500) | The incidence of MESIs in patients commencing Avacopan | Observational | Recruiting | December, 2030 |
| NCT05197842 | BDB-001 (anti-C5RA1 monoclonal antibody activating the toll-like receptor) | AAV (N = 100) | Proportion of patients achieving CR or PR at 12 weeks | 1/2 | Recruiting | March, 2025 |
| IDEAL (NCT06590545) | anti-CD19 CAR-T cell antibodies | AAV refractory, with ANCA-IgG-positivity (N = 8) | Number of subjects experiencing CRS up to 4 weeks ANCA seroconversion rate at 24 weeks AEs and SAEs up to 52 weeks | 1/2 | Not yet recruiting | July, 2027 |
| NCT06462144 | IMPT-514 (anti-CD19/CD20 CAR-T cell antibodies) | AAV SLE IIM (N = 36) | Incidence of DLTs, SAEs, and TEAEs up to 28 days post-infusion | 1 | Recruiting | October, 2026 |
| Ntrust-2 (NCT06733935) | NKX019 (allogeneic CAR-NK cell targeting CD19) | Immune-mediated diseases including AAV (N = 72) | Incidence of DLTs and TEAEs | 1 | Recruiting | October, 2028 |
| TTCAAVREM (NCT05962840) | Telitacicept (targeting Blys and APRIL) + RTX in induction vs Telitacicept alone in maintenance | AAV (N = 40) | Time to first relapse during 24-month follow-up in two groups | 4 | Recruiting | December, 2026 |
| NCT06277427 | PRG-1801 (CAR-T cell targeting B-cell maturation antigen) | AAV (N = 24) | AEs incidence at 24 months after infusion Types and incidence of DLTs at 28 days and 3 months after infusion | Not applicable | Recruiting | January, 2027 |
| NCT06388941 | Iptacopan (factor B inhibitor) added to standard of care therapy | GPA (N = 78) | Sustained remission through week 48 (CR at week 24 without major relapse) | 2 | Recruiting | October, 2027 |
| NCT06226662 | NM8074 (antibody inhibiting Bb component of complement) added to standard of care therapy | GPA MPA RLV (N = 12) | Proportion of subjects with disease response at day 85 | 2 | Recruiting | September, 2027 |
| NCT06196905 | MT-2990 (monoclonal antibody targeting IL-33) | GPA MPA EGPA (N = 10) | No primary endpoint; exploratory analyses: change in BVAS/VDI and FVC up to 24 weeks | 1 | Recruiting | February, 2026 |
| Study Name (ClinicalTrials.gov ID) | Studied Molecule (Mechanism) | Estimated Enrolment | Primary Outcome | Phase | Status | Estimated Completion Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REVERT-IPF (NCT05671835) | TTI-101 (STAT3 inhibitor) | N = 75 | Participants with AEs at 16 weeks | 2 | Recruiting | July, 2025 |
| NCT05483907 | BBT-877 (selective autotaxin inhibitor) | N = 129 | FVC change from baseline at 24 weeks | 2 | Active, not recruiting | February, 2025 |
| NCT05571059 | Ifetroban (selective thromboxane antagonist) | N = 128 | FVC change from baseline at 12 months | 2 | Recruiting | January, 2026 |
| MAXPIRe (NCT06132256) | Axatilimab (CSF-1R targeting antibody) | N = 135 | Annualized FVC decline (morning pre-dose) at 26 weeks | 2 | Recruiting | June, 2025 |
| BEACON-IPF (NCT06097260) | Bexotegrast PLN-74809 (αVβ1 and αVβ6 integrin inhibitor) | N = 360 | Change from baseline in absolute FVC at week 52 | 2 | Active, not recruiting | September, 2025 |
| ALOFT-IPF (NCT06003426) | Admilparant BMS-986278 (LPA1 antagonist) | N = 1185 | Participants with SSEs and FVC change from baseline up to week 52 | 3 | Recruiting | October, 2026 |
| RIN-PF-301 (NCT04708782) | Inhaled treprostinil (prostacyclin analog) | N = 576 | Absolute FVC change from baseline to week 52 | 3 | Active, not yet recruiting | June, 2025 |
| RIN-PF-303 (NCT05255991) | Inhaled treprostinil (prostacyclin analog) | N = 597 | FVC change (absolute) from baseline to week 52 | 3 | Active, not yet recruiting | July, 2025 |
| NCT05785624 | Vixarelimab (IL-31 inhibitor) | IPF SSc-ILD N = 320 | FVC change (absolute) from baseline to week 52 | 2 | Recruiting | August, 2027 |
| NCT05389215 | DWN12088 (prolyl-tRNA synthetase inhibitor) | N = 102 | FVC decline rate at week 24 and incidence of AEs | 2 | Recruiting | December, 2025 |
| NCT05195918 | EGCG (green tea extract reducing mRNA levels and collagen I accumulation) | N = 50 | Participants with AEs up to 12 weeks | 1 | Recruiting | April, 2026 |
| PRECRSIONS (NCT04300920) | N-acetylocysteine (antioxidant) | IPF patients with TOLLIP rs3750920 TT genotype N = 202 | Time to composite endpoint: 10% FVC decline, respiratory hospitalization, lung transplant, or death (24 months) | 3 | Active, not recruiting | February, 2026 |
| TIPAL (NCT04965298) | Lansoprazole (proton pump inhibitor) | N = 298 | Absolute %pred FVC change at 12 months post-randomisation | 3 | Recruiting | February, 2025 |
| NCT03312400 | Danazol (androgen hormone) | Telomere related diseases, including IPF N = 40 | Telomere attrition reduction at 6 months and pulmonary function progression at 6 and 12 mths (secondary outcome) | 2 | Recruiting | October, 2027 |
| TELO-SCOPE (NCT04638517) | Danazol (androgen hormone) | IPF in children and adults N = 50 | Absolute telomere length change from baseline at 12 months and FVC and DLCO change at 6 and 12 months (secondary outcome) | 2 | Recruiting | June, 2025 |
| WHISTLE-PF (NCT06422884) | ENV-101 (Hedgehog inhibitor) | N = 200 | Rate of %ppFVC change vs. placebo at 24 weeks | 2 | Recruiting | June, 2026 |
| NCT05515627 | Atezolizumab (PD-L1 targeting antibody) | N = 24 | Incidence of treatment-emergent AEs over 24 weeks | 1 | Recruiting | April, 2026 |
| NCT06125327 | Sufenidone SC1011 (antifibrotic) | N = 210 | Annual FVC decline rate at 52 weeks | 2/3 | Recruiting | December, 2027 |
| TRANFORM (NCT06317285) | GSK3915393 (TG-2 inhibitor) | N = 150 | Absolute FVC change from baseline at week 26 | 2 | Recruiting | March, 2026 |
| ELEVATE (NCT05321420) | Duepirfenidone LYT-100 (antifibrotic—selective deuterated pirfenidone) | N = 240 | FVC decline rate at 26 weeks | 2 | Active, not recruiting | December, 2025 |
| NCT05537025 | Inhaled ARO-MMP7 (MMP7 expression reduction) | IPF and healthy volunteers N = 97 | Participants with treatment-emergent AEs over time | 1/2 | Recruiting | March, 2025 |
| Study Name (ClinicalTrials.gov ID) | Studied Molecule (Mechanism) | Patient Cohort Estimated Enrolment | Primary Outcome | Phase | Status | Estimated Completion Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EvER-ILD2 (NCT05596786) | RTX (anti-CD20 antibody) | PF-ILD with inflammatory component (N = 126) | FVC change at 6 months | 3 | Recruiting | July, 2026 |
| EvER-ILD3 (NCT06549231) | RTX combined with MMF (T/B cell proliferation inhibitor) vs MMF alone | SSc-ILD N = 102 | Change in ppFVC from baseline to week 24 | 3 | Not yet recruiting | November, 2028 |
| BEconneCTD-ILD (NCT06572384) | Belimumab (BLys inhibitor) | CTD-ILD N = 440 | Absolute change in FVC from baseline at week 52 | 3 | Recruiting | December, 2028 |
| RAILDTo (NCT05246293) | Tofacitinib (JAK1-3 kinase inhibitor) | RA-ILD N = 60 | Incidence and severity of AEs | 2 | Unknown | March, 2025 |
| FIBRONEER-ON (NCT06238622) | Nerandomilast BI-1015550 | PF-ILD/IPF N = 1700 | Occurrence of AEs up to 99 weeks and 3 days | 3 | Recruiting | May, 2027 |
| NCT06806592 | Nerandomilast BI-1015550 | RA-ILD N = 400 | Absolute change in QILD score (%) at week 26 | 3 | Not yet recruiting | March, 2027 |
| NCT06440746 | Olokizumab (anti-IL6 antibody) | PF-ILD N = 138 | FVC decline rate over 48 weeks | 2/3 | Recruiting | December, 2028 |
| NCT05828953 | Anlotinib (TK inhibitor) | PF-ILD IPF N = 30 | Absolute change in FVC at week 52 | 2/3 | Recruiting | July, 2025 |
| SOLIS (NCT06325696) | Hymecromone H01 (hyaluronan synthesis inhibitor) | ILD Lung fibrosis N = 37 | Serum HA levels over 72 weeks and change in clinical and functional measures (secondary outcome) | 2 | Recruiting | December, 2027 |
| NCT06329401 | Inhaled pirfenidone APO1 (antifibrotic) | PF-ILD N = 300 | Change in FVC from baseline at week 52 | 2 | Recruiting | April, 2026 |
| NCT06574581 | AD-MSC (adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stromal cells) | CTD-ILD N = 16 | Safety profile over 48 weeks | 1/2 | Recruiting | May, 2026 |
| NCT06825169 | NCR101 (human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived mesenchymal stromal cells | Variable ILDs including IPF, HP, CTD-ILD N = 30 | Incidence of AEs and SAEs | 1/2 | Not yet recruiting | September, 2028 |
| ALOFT-PPF (NCT06025578) | Admilparant BMS-986278 (LPA receptor antagonist) | PF-ILD N = 1092 | Number of participants with SSEs at 4 weeks and absolute change in FVC at week 52 | 3 | Recruiting | December, 2027 |
| TETON-PPF (NCT05943535) | Inhaled treprostnil (prostacyclin analog) | PF-ILD N = 698 | Change in absolute FVC from baseline to week 52 | 3 | Recruiting | November, 2027 |
| NCT05649722 | Treprostinil palmitil inhalation powder-TPIP (prostacyclin analog) | HP-ILD N = 31 | Number of participants with TEAEs up to 25 months | 2/3 | Active, not recruiting | March, 2026 |
| NCT05505409 | Pirfenidone (antifibrotic) | CTD-ILD N = 120 | Change in % FVC from 6 months to baseline | 4 | Recruiting | December, 2025 |
| NCT04928586 | Pirfenidon combined with IS | CTD-ILD N = 200 | Change in FVC and DLCO at 12 months | 4 | Active, nor recruiting | June, 2025 |
| FIBROPOC (NCT06714123) | Senicapoc (gardos channel blocker) | PF-ILD/IPF N = 140 | The rate of decline in ppFVC over 26 weeks | 2 | Not yet recruiting | December, 2028 |
| NCT05892614 | Efzofitimod (tRNA synthetase inhibitor) | SSc-ILD N = 25 | Absolute change in FVC at 24 weeks and change in HRCT fibrosis score | 2 | Recruiting | December, 2024 |
| INTENSE (NCT05503030) | Nintedanib (TK inhibitor) | CTD-ILD N = 87 | Change in dyspnea and cough at 24 months | Observational | Observational | December, 2026 |
| NINTOC-TU (NCT06297096) | Nintedanib and Tocilizumab (IL-6 targeting) vs conventional IS | SSc-ILD N = 86 | Decrease in FVC after 56 weeks | 3 | Not yet recruiting | March, 2028 |
| NCT06189495 | Genakumab GenSci 048 (BLys/APRIL dual antagonist) | RA-ILD SSc-ILD N = 30 | Change in FVC and DLCO up to 2 years | 2 | Recruiting | October, 2026 |
| ATHENA-SSc-ILD (NCT05270668) | Tulisokibart MK-7240/PRA023 (TNF-TL1A inhibitor) | SSc-ILD N = 152 | Number of participants experiencing AEs and change in FVC at week 50 | 2 | Recruiting | June, 2029 |
| NCT05139719 | Yfenidone (HEC585) (TGF-α and TGF-β inhibitor—Pirfenidone analog) | PF-ILD N = 110 | Change in FVC from baseline to week 24 | 2 | Recruiting | December, 2026 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fijolek, J.; Sniady, A. Clinical Insights and Therapeutic Strategies for the Treatment of Interstitial Lung Disease in Patients with Anti-Neutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-Associated Vasculitis: Current Trends and Future Directions. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 4631. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134631
Fijolek J, Sniady A. Clinical Insights and Therapeutic Strategies for the Treatment of Interstitial Lung Disease in Patients with Anti-Neutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-Associated Vasculitis: Current Trends and Future Directions. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(13):4631. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134631
Chicago/Turabian StyleFijolek, Justyna, and Anna Sniady. 2025. "Clinical Insights and Therapeutic Strategies for the Treatment of Interstitial Lung Disease in Patients with Anti-Neutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-Associated Vasculitis: Current Trends and Future Directions" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 13: 4631. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134631
APA StyleFijolek, J., & Sniady, A. (2025). Clinical Insights and Therapeutic Strategies for the Treatment of Interstitial Lung Disease in Patients with Anti-Neutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-Associated Vasculitis: Current Trends and Future Directions. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(13), 4631. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134631





