Clinical Features of Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm-Related Pancreatic Carcinomas in Long-Term Surveillance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Population and Surveillance of IPMNs
2.2. Evaluation of the Morphological Features of IPMNs in the Prediagnostic Stage of Pancreatic Carcinoma
2.3. Definition of Serious Medical Event and Active Medical Intervention
2.4. Statistical Analyses
2.5. Ethical Issues
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Characteristics of the Entire Study Population at the Initial Diagnosis of IPMN
3.2. Clinical Characteristics of the Populations with IPMN-DC, c-PDAC, and Routine Follow-Up at the Initial Diagnosis of IPMN
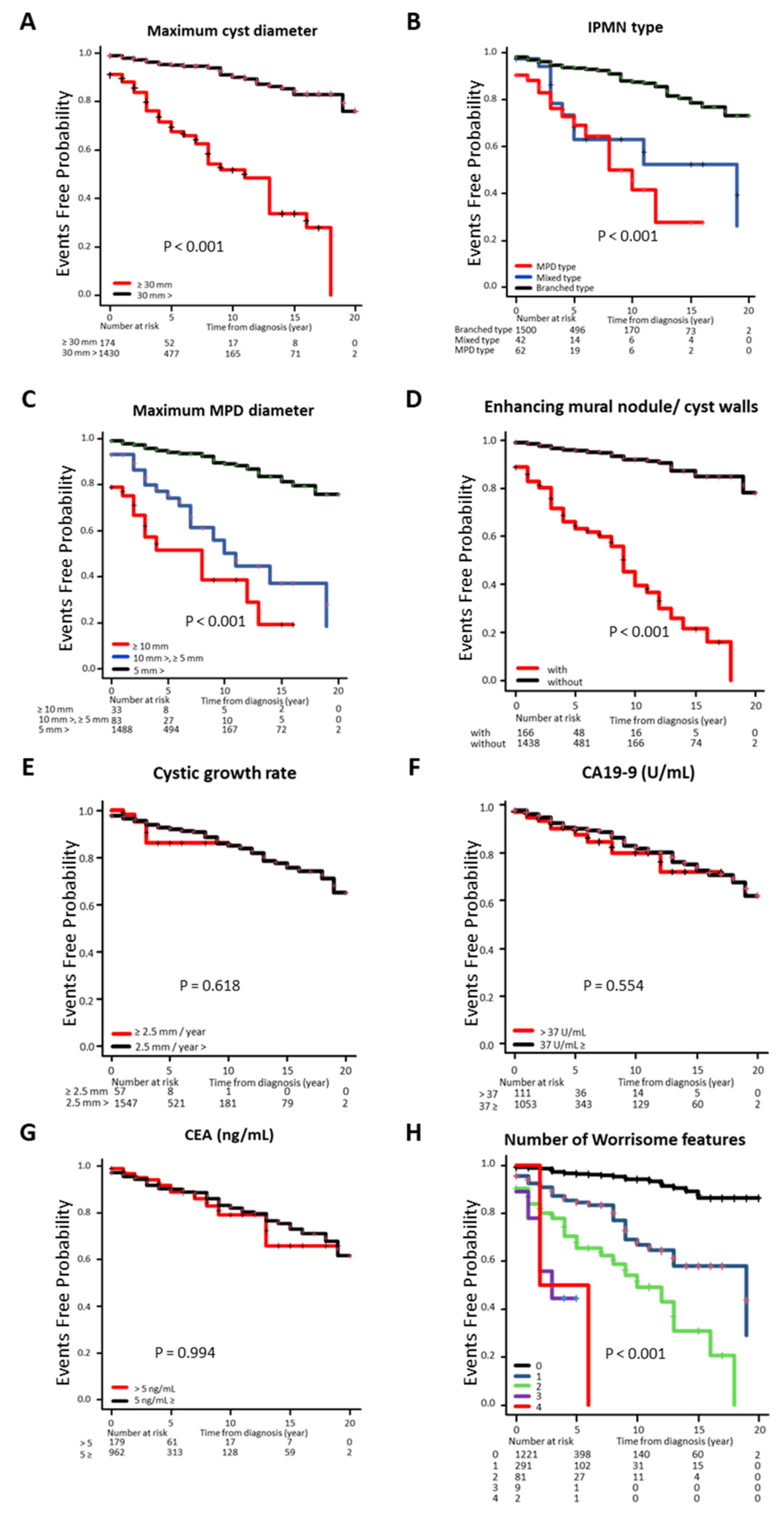
3.3. Cumulative Incidence Rate of IPMN-DC Classified by Clinical Factors
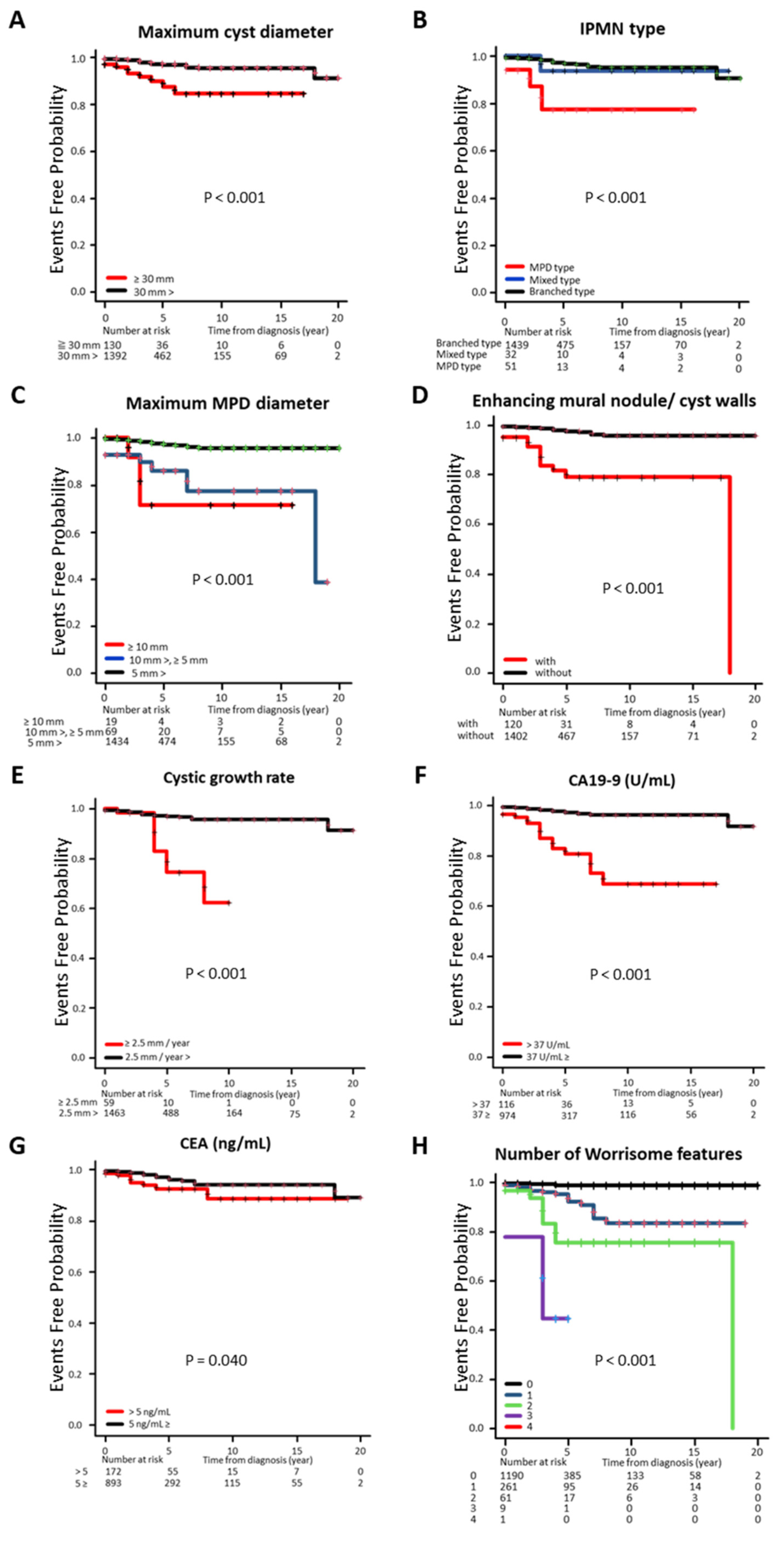
3.4. Cumulative Incidence Rate of c-PDAC Classified by Clinical Factors
3.5. Differences in the Timing of Diagnosis and Clinical Staging of Pancreatic Neoplasms Associated with IPMN
3.6. Risk Factor Analysis for the Development of IPMN-DC and c-PDAC
3.7. Frequency of Pancreatic Malignant Neoplasms by Each WF at the Initial Diagnosis of IPMN
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AMI | Active medical intervention |
| CT | Computed tomography |
| HRS | High-risk stigmata |
| IPMN | Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm |
| MPD | Main pancreatic duct |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| SNS | Septal nodal structure |
| WF | Worrisome feature |
References
- Brandi, N.; Renzulli, M. Toward a simplified and cost-effective diagnostic algorithm for the surveillance of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (IPMNs): Can we save contrast for later? Cancers 2024, 16, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizuno, S.; Isayama, H.; Nakai, Y.; Yoshikawa, T.; Ishigaki, K.; Matsubara, S.; Yamamoto, N.; Ijichi, H.; Tateishi, K.; Tada, M.; et al. Prevalence of pancreatic cystic lesions is associated with diabetes mellitus and obesity: An analysis of 5296 individuals who underwent a preventive medical examination. Pancreas 2017, 46, 801–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.R.; Park, J.K.; Jang, J.Y.; Kwon, W.; Yoon, J.H.; Kim, S.W. Incidental pancreatic cystic neoplasms in an asymptomatic healthy population of 21,745 individuals: A large-scale, single-center cohort study. Medicine 2016, 95, e5535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Fuente, J.; Chatterjee, A.; Lui, J.; Nehra, A.K.; Bell, M.G.; Lennon, R.J.; Kassmeyer, B.A.; Graham, R.P.; Nagayama, H.; Schulte, P.J.; et al. Long-term outcomes and risk of pancreatic cancer in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms. JAMA Net. Open 2023, 6, e2337799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kromrey, M.L.; Bülow, R.; Hübner, J.; Paperlein, C.; Lerch, M.M.; Ittermann, T.; Völzke, H.; Mayerle, J.; Kühn, J.P. Prospective study on the incidence, prevalence, and 5year pancreatic-related mortality of pancreatic cysts in a population-based study. Gut 2018, 67, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, S.; Tsujimae, M.; Masuda, A.; Inoue, J.; Inomata, N.; Uemura, H.; Kohashi, S.; Nagao, K.; Masuda, S.; Abe, S.; et al. Metabolic syndrome accelerates the age-related increase of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas. Pancreas 2024, 53, e9–e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moris, D.; Liapis, I.; Gupta, P.; Ziogas, I.A.; Karachaliou, G.S.; Dimitrokallis, N.; Nguyen, B.; Radkani, P. An overview for clinicians on intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (IPMNs) of the pancreas. Cancers 2024, 16, 3825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meziani, J.; Sprij, M.L.; Fuhler, G.M.; Bruno, M.J.; Marchegiani, G.; Cahen, D.L. Small cyst size and lack of growth as negative predictors of malignant transformation in low-risk intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas: A systematic review and meta-analysis. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2024, 13, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberg, D.S.; Gatsonis, C.; Zeh, H.J.; Carlos, R.C.; O’Dwyer, P.J.; EA2185 Team. Comparing the clinical impact of pancreatic cyst surveillance programs: A trial of the ECOG-ACRIN cancer research group (EA2185). Contemp. Clin. Trials. 2020, 97, 106144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyama, H.; Tada, M.; Takagi, K.; Tateishi, K.; Hamada, T.; Nakai, Y.; Hakuta, R.; Ijichi, H.; Ishigaki, K.; Kanai, S.; et al. Long-term risk of malignancy in branch-duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 226–237.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtsuka, T.; Maguchi, H.; Tokunaga, S.; Hijioka, S.; Takayama, Y.; Koshita, S.; Hanada, K.; Sudo, K.; Uehara, H.; Tanno, S.; et al. Prospective multicenter surveillance study of branch-duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas; risk of dual carcinogenesis. Pancreatology 2024, 24, 1141–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohtsuka, T.; Fernandez-del Castillo, C.; Furukawa, T.; Hijioka, S.; Jang, J.Y.; Lennon, A.M.; Miyasaka, Y.; Ohno, E.; Salvia, R.; Wolfgang, C.L.; et al. International evidence-based Kyoto guidelines for the management of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas. Pancreatology 2024, 24, 255–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, M.; Fernández-del Castillo, C.; Kamisawa, T.; Jang, J.Y.; Levy, P.; Ohtsuka, T.; Salvia, R.; Shimizu, Y.; Tada, M.; Wolfgang, C.L. Revisions of the international consensus Fukuoka guidelines for the management of IPMN of the pancreas. Pancreatology 2017, 17, 738–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, M.; Fernández-del Castillo, C.; Adsay, V.; Chari, S.; Falconi, M.; Jang, J.Y.; Kimura, W.; Levy, P.; Pitman, M.B.; Schmidt, C.M.; et al. International consensus guidelines 2012 for the management of IPMN and MCN of the pancreas. Pancreatology 2012, 12, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Chari, S.; Adsay, V.; Fernandez-del Castillo, C.; Falconi, M.; Shimizu, M.; Yamaguchi, K.; Yamao, K.; Matsuno, S. International consensus guidelines for management of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms and mucinous cystic neoplasms of the pancreas. Pancreatology 2006, 6, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamata, K.; Kitano, M. Endoscopic diagnosis of cystic lesions of the pancreas. Dig. Endosc. 2019, 31, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, Y. Investigation of the freely available easy-to-use software ‘EZR’ for medical statistics. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2013, 48, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyama, H.; Hamada, T.; Nakai, Y.; Tanaka, M.; Endo, G.; Hakuta, R.; Ishida, K.; Ishigaki, K.; Kanai, S.; Kurihara, K.; et al. Clinical trajectory of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms progressing to pancreatic carcinomas during long-term surveillance: A prospective series of 100 carcinoma cases. J. Gastroenterol. 2023, 58, 106880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pergolini, I.; Sahora, K.; Ferrone, C.R.; Morales-Oyarvide, V.; Wolpin, B.M.; Mucci, L.A.; Brugge, W.R.; Mino-Kenudson, M.; Patino, M.; Sahani, D.V. Long-term risk of pancreatic malignancy in patients with branch duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm in a referral center. Gastroenterology 2017, 153, 1284–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Oyarvide, V.; Mino-Kenudson, M.; Ferrone, C.R.; Sahani, D.V.; Pergolini, I.; Negreros-Osuna, A.A.; Warshaw, A.L.; Lillemoe, K.D.; Fernández-del Castillo, C. Diabetes mellitus in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas is associated with high-grade dysplasia and invasive carcinoma. Pancreatology 2017, 17, 920–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiesenauer, C.A.; Schmidt, C.M.; Cummings, O.W.; Yiannoutsos, C.T.; Howard, T.J.; Wiebke, E.A.; Goulet, R.J.; McHenry, L.; Sherman, S.; Lehman, G.A.; et al. Preoperative predictors of malignancy in pancreatic intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms. Arch. Surg. 2003, 138, 610–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales-Oyarvide, V.; Mino-Kenudson, M.; Ferrone, C.R.; Gonzalez-Gonzalez, L.A.; Warshaw, A.L.; Lillemoe, K.D.; Fernández-del Castillo, C. Acute pancreatitis in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms: A common predictor of malignant intestinal subtype. Surgery 2015, 158, 1219–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsutsumi, K.; Ohtsuka, T.; Oda, Y.; Sadakari, Y.; Mori, Y.; Aishima, S.; Takahata, S.; Nakamura, M.; Mizumoto, K.; Tanaka, M. A history of acute pancreatitis in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas is a potential predictive factor for the malignant papillary subtype. Pancreatology 2010, 10, 707–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, L.D.; Adsay, N.V.; Basturk, O.; Brosens, L.A.; Fukushima, N.; Hong, S.M.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, J.W.; Luchini, C.; Noë, M.; et al. Systematic review of challenging issues in pathology of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms. Pancreatology 2003, 23, 878–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kin, T.; Shimizu, Y.; Hijioka, S.; Hara, K.; Katanuma, A.; Nakamura, M.; Yamada, R.; Itoi, T.; Ueki, T.; Masamune, A.; et al. A comparative study between computed tomography and endoscopic ultrasound in the detection of a mural nodule in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm—Multicenter observational study in Japan. Pancreatology 2023, 23, 550–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, Y.; Ueda, K.; Itonaga, M.; Yoshida, T.; Maeda, H.; Maekita, T.; Iguchi, M.; Tamai, H.; Ichinose, M.; Kato, J. Tumor vessel depiction with contrast-enhanced endoscopic ultrasonography predicts the efficacy of chemotherapy in pancreatic cancer. Pancreas 2013, 42, 990–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
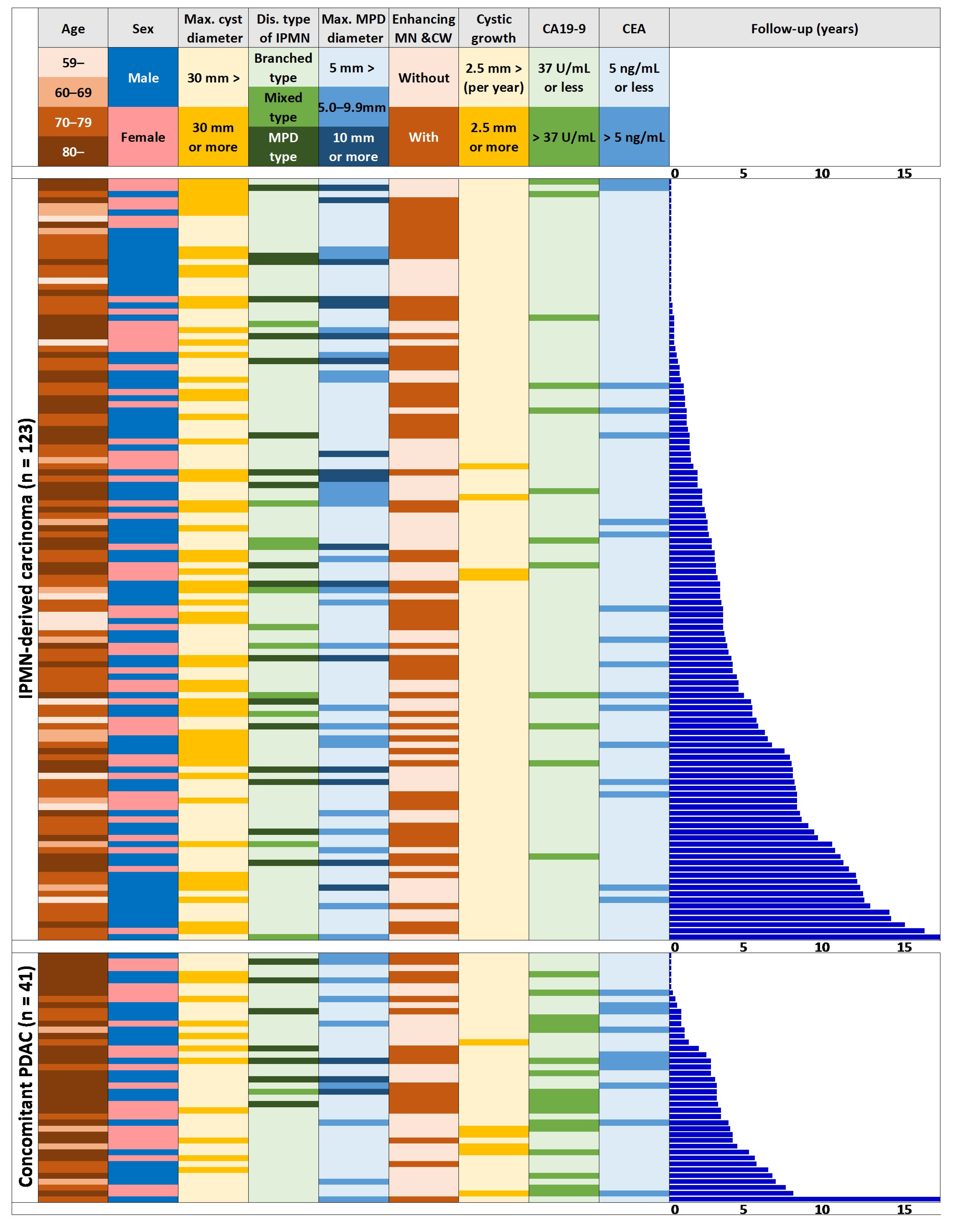
| Age (Years Old) | 79.0 [71.0–85.0] |
|---|---|
| Sex | |
| Male | 776 (47.2%) |
| Female | 869 (52.8%) |
| Follow-up periods (year) | 3.0 [0.0–6.0] |
| Disease location | |
| Uncus | 132 (8.1%) |
| Head | 595 (36.1%) |
| Body | 602 (36.6%) |
| Tail | 316 (19.2%) |
| Maximum cyst diameter (mm) | 13.0 [7.0–20.0] |
| Disease type of IPMN | |
| MPD type | 69 (4.2%) |
| Branched type | 1533 (93.2%) |
| Mixed type | 43 (2.6%) |
| Maximum MPD diameter (mm) | 2.0 [1.6–3.0] |
| Enhancing mural nodule/cyst walls | |
| With | 183 (11.1%) |
| Without | 1462 (88.9%) |
| Cystic growth rate (mm/year) | |
| ≥2.5 | 63 (3.8%) |
| 2.5> | 1582 (96.2%) |
| CA19-9 (U/mL) | 10.9 [6.5–20.2] |
| CEA (ng/mL) | 2.5 [1.6–4.0] |
| Routine Follow-Up (n = 1481) | IPMN-DC (n = 123) | Concomitant PDAC (n = 41) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Factors | (Percent, Cases) | (Percent, Cases) | p | (Percent, Cases) | p |
| Age | |||||
| –59 | 9.1% (135/1481) | 9.8% (12/123) | <0.001 | 0.0% (0/41) | 0.081 |
| 60–69 | 13.4% (199/1481) | 9.8% (12/123) | 9.8% (4/41) | ||
| 70–79 | 28.6% (424/1481) | 47.2% (58/123) | 24.4% (10/41) | ||
| 80– | 48.8% (723/1481) | 33.3% (41/123) | 65.9% (27/41) | ||
| Sex | |||||
| Male | 46.0% (682/1481) | 59.3% (73/123) | <0.01 | 51.2% (21/41) | 0.51 |
| Female | 54.0% (799/1481) | 40.7% (50/123) | 48.8% (20/41) | ||
| Maximum cyst diameter | |||||
| ≥30 mm | 8.0% (119/1481) | 44.7% (55/123) | <0.0001 | 26.8% (11/41) | <0.01 |
| 30 mm> | 92.0% (1362/1481) | 55.3% (68/123) | 73.2% (30/41) | ||
| Disease type of IPMN | |||||
| MPD type | 3.0% (44/1481) | 14.6% (18/123) | <0.0001 | 17.1% (7/41) | <0.0001 |
| Mixed type | 2.1% (31/1481) | 8.9% (11/123) | 2.4% (1/41) | ||
| Branched type | 94.9% (1406/1481) | 76.4% (94/123) | 80.5% (33/41) | ||
| Maximum MPD diameter | |||||
| ≥10 mm | 1.1% (16/1481) | 13.8% (17/123) | <0.0001 | 7.3% (3/41) | <0.0001 |
| 10 mm>, ≥5 mm | 4.1% (60/1481) | 18.7% (23/123) | 22.0% (9/41) | ||
| 5 mm> | 94.9% (1405/1481) | 67.5% (83/123) | 70.7% (29/41) | ||
| Enhancing MN/cyst walls | |||||
| With | 7.0% (103/1481) | 51.2% (63/123) | <0.0001 | 41.5% (17/41) | <0.0001 |
| Without | 93.0% (1378/1481) | 48.8% (60/123) | 58.5% (24/41) | ||
| Cystic growth rate | |||||
| ≥2.5 mm/year | 3.6% (53/1481) | 3.3% (4/123) | 1.00 | 14.6% (6/41) | <0.001 |
| 2.5 mm/year> | 96.4% (1428/1481) | 96.7% (119/123) | 85.4% (35/41) | ||
| CA19-9 | |||||
| >37 U/mL | 9.4% (99/1053) | 10.8% (12/111) | 0.63 | 45.9% (17/37) | <0.0001 |
| 37 U/mL≥ | 90.6% (954/1053) | 89.2% (99/111) | 54.1% (20/37) | ||
| CEA | |||||
| >5 ng/mL | 15.7% (162/1030) | 15.3% (17/111) | 0.91 | 28.6% (10/35) | <0.05 |
| 5 ng/mL≥ | 84.3% (868/1030) | 84.7% (94/111) | 71.4% (25/35) | ||
| IPMN-DC | Hazard Ratio [95% CI] | p |
|---|---|---|
| Enhancing mural nodule/cyst walls (with) | 5.18 [3.47–7.74] | <0.0001 |
| Maximum cyst diameter (≥30 mm) | 3.33 [2.25–4.92] | <0.0001 |
| Maximum MPD diameter (≥5 mm) | 2.61 [1.62–4.25] | <0.0001 |
| Sex (male) | 1.14 [0.78–1.65] | 0.38 |
| Disease type of IPMN (nonbranched type) | 1.17 [0.69–1.97] | 0.52 |
| Concomitant PDAC | Hazard Ratio [95% CI] | p |
| CA19-9 (>37 U/mL) | 5.02 [2.51–10.0] | <0.0001 |
| Enhancing mural nodule/cyst walls (with) | 4.76 [2.25–10.0] | <0.0001 |
| Maximum MPD diameter (≥5 mm) | 2.23 [0.90–5.54] | 0.08 |
| Maximum cyst diameter (≥30 mm) | 1.94 [0.90–4.17] | 0.09 |
| Age (years old) | 1.02 [0.98–1.06] | 0.40 |
| Disease type of IPMN (nonbranched type) | 1.25 [0.45–3.43] | 0.67 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Matsuura, K.; Nagamatsu, S.; Kikukawa, S.; Nishio, Y.; Komeda, Y.; Matsuo, Y.; Ohta, K.; Yamamoto, C.; Sueki, A.; Moriya, K. Clinical Features of Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm-Related Pancreatic Carcinomas in Long-Term Surveillance. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 4585. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134585
Matsuura K, Nagamatsu S, Kikukawa S, Nishio Y, Komeda Y, Matsuo Y, Ohta K, Yamamoto C, Sueki A, Moriya K. Clinical Features of Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm-Related Pancreatic Carcinomas in Long-Term Surveillance. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(13):4585. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134585
Chicago/Turabian StyleMatsuura, Kyohei, Shinsaku Nagamatsu, Shoma Kikukawa, Yuya Nishio, Yusuke Komeda, Yuya Matsuo, Kohei Ohta, Chisa Yamamoto, Ayana Sueki, and Kei Moriya. 2025. "Clinical Features of Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm-Related Pancreatic Carcinomas in Long-Term Surveillance" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 13: 4585. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134585
APA StyleMatsuura, K., Nagamatsu, S., Kikukawa, S., Nishio, Y., Komeda, Y., Matsuo, Y., Ohta, K., Yamamoto, C., Sueki, A., & Moriya, K. (2025). Clinical Features of Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm-Related Pancreatic Carcinomas in Long-Term Surveillance. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(13), 4585. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134585







