The Pharmacokinetics of Saliva and Plasma N-Oxides Following a Single Administration of a Plant-Based Bioequivalent Inorganic Nitrate Oral Supplement in an Open-Label, Phase 1, Single-Arm Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
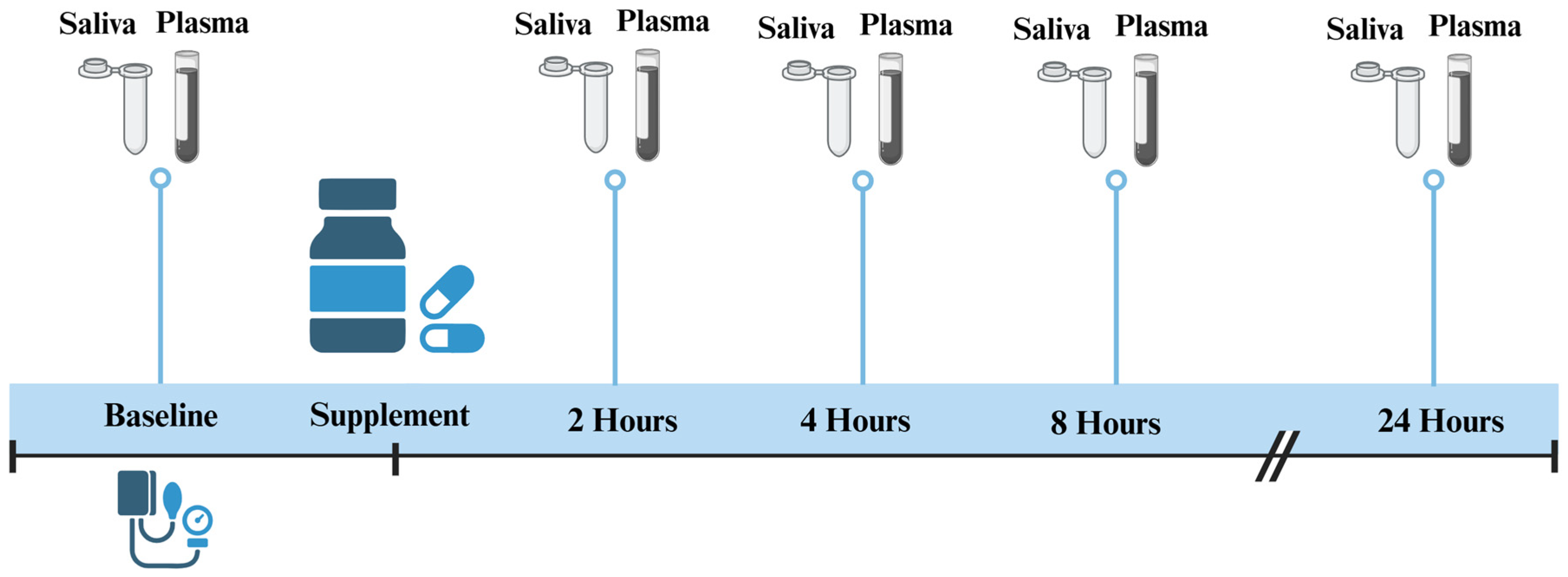
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Preparation and Content of Capsules
2.3. Participants
2.4. Saliva and Plasma Sample Collection
2.5. NO3− and NO2− Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participant Characteristics
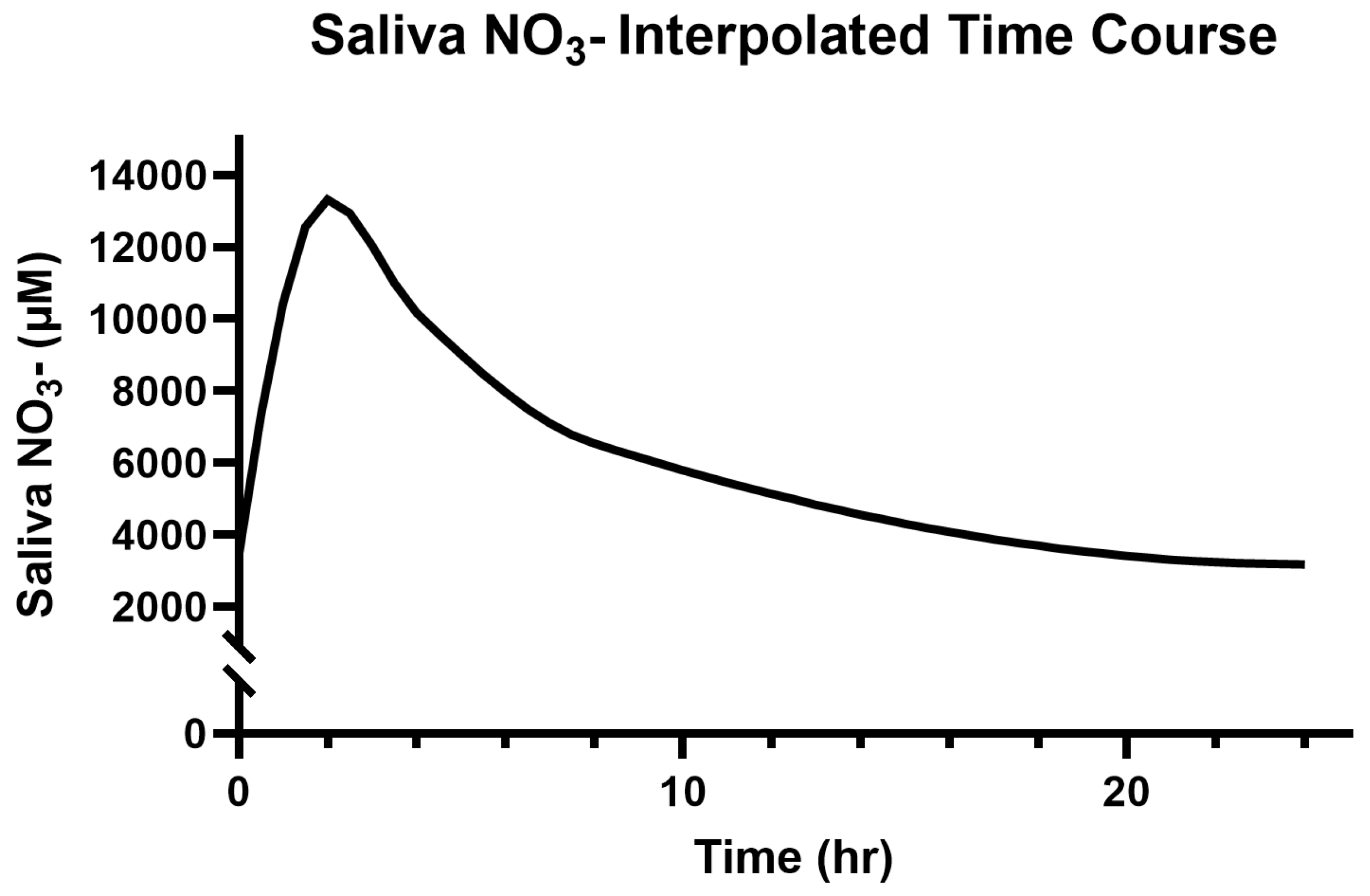
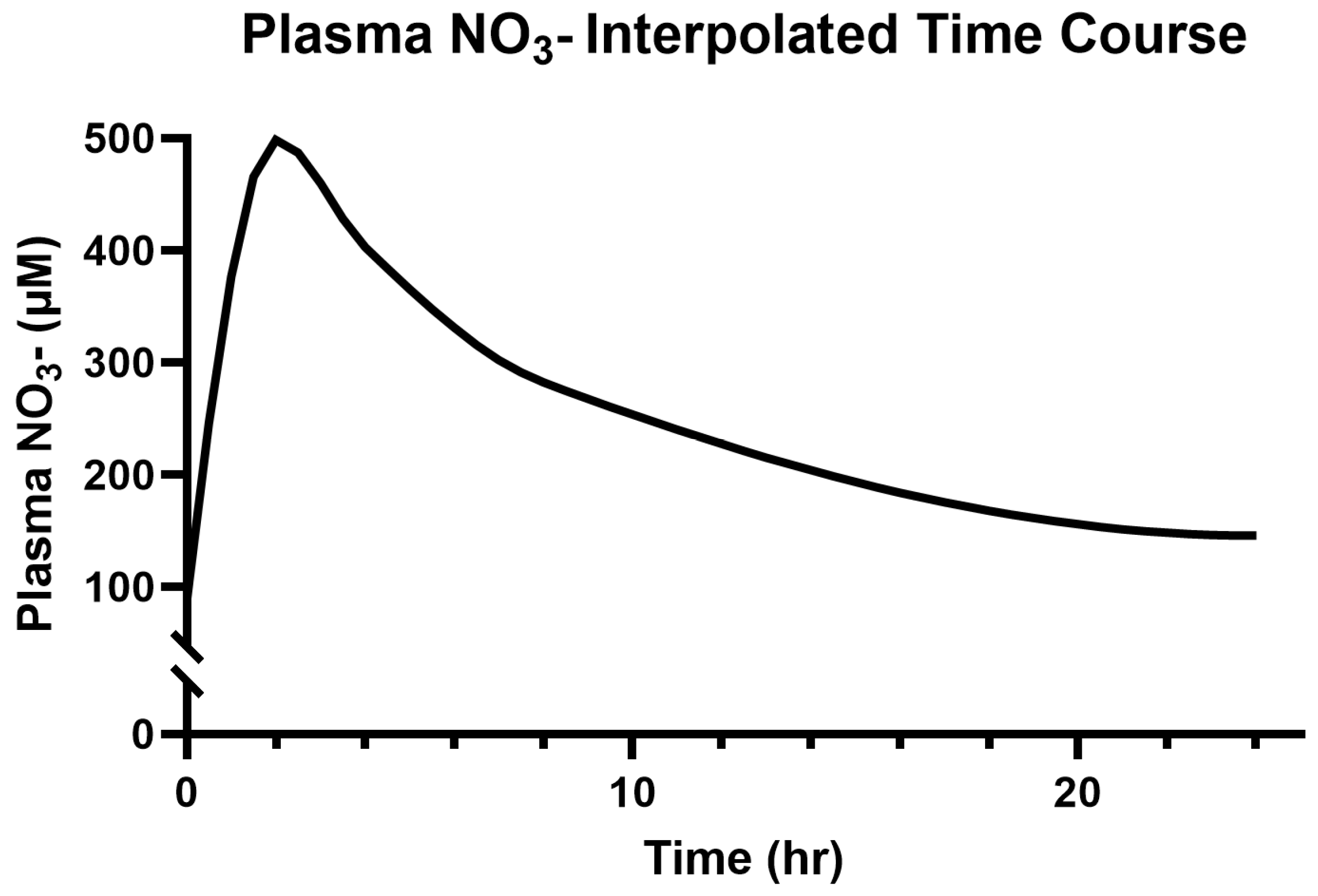
3.2. Saliva and Plasma NO3−
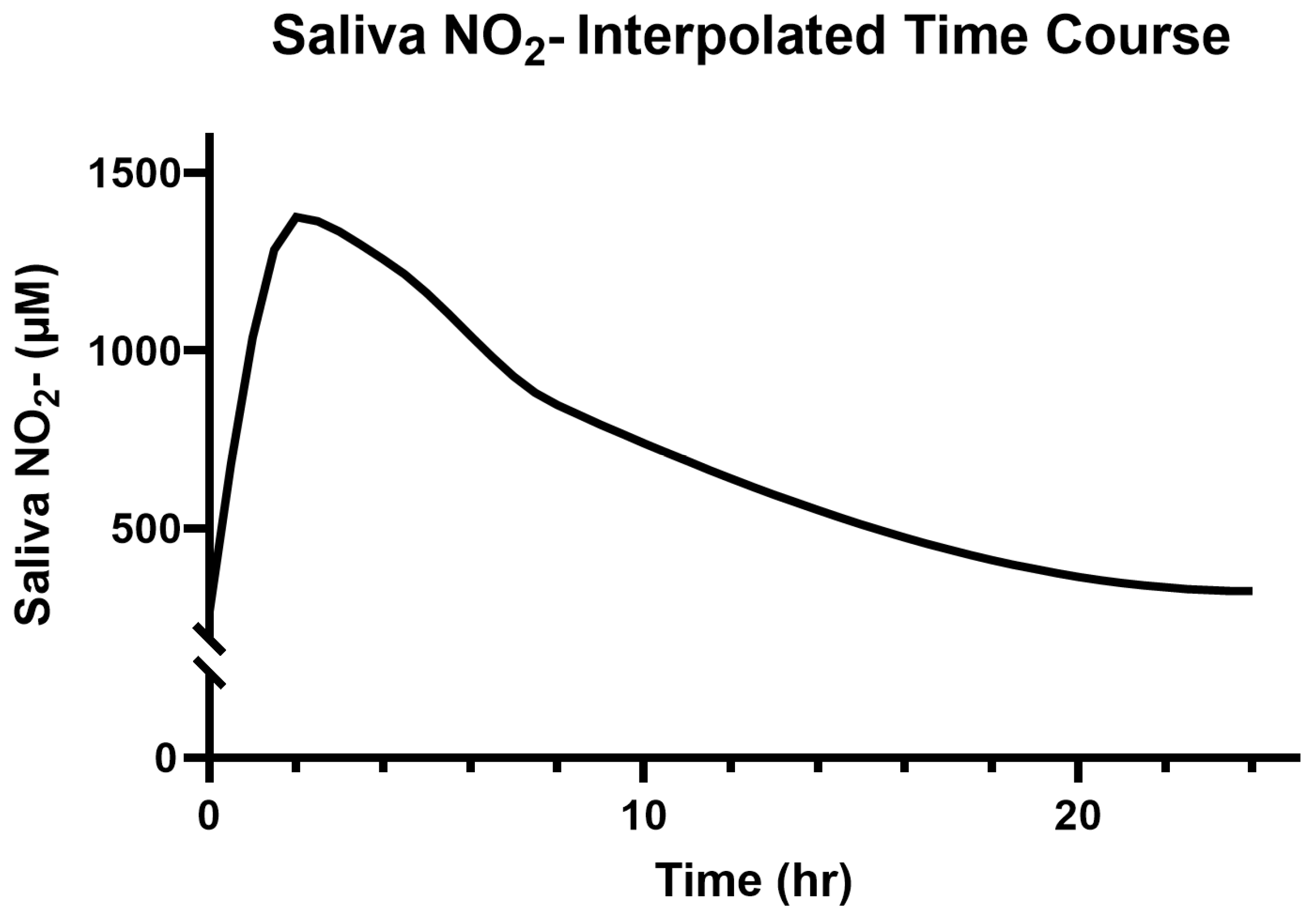
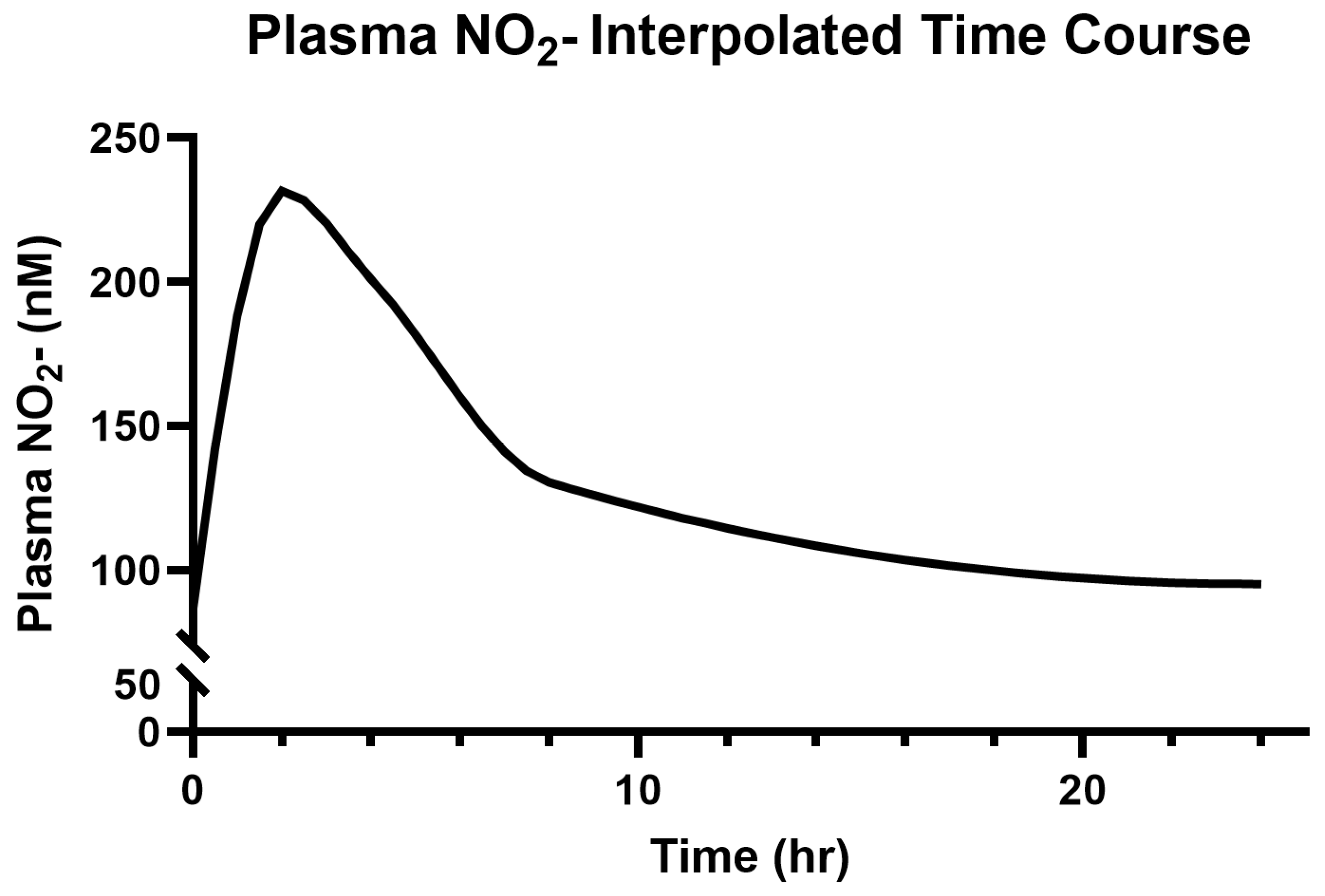
3.3. Saliva and Plasma NO2−
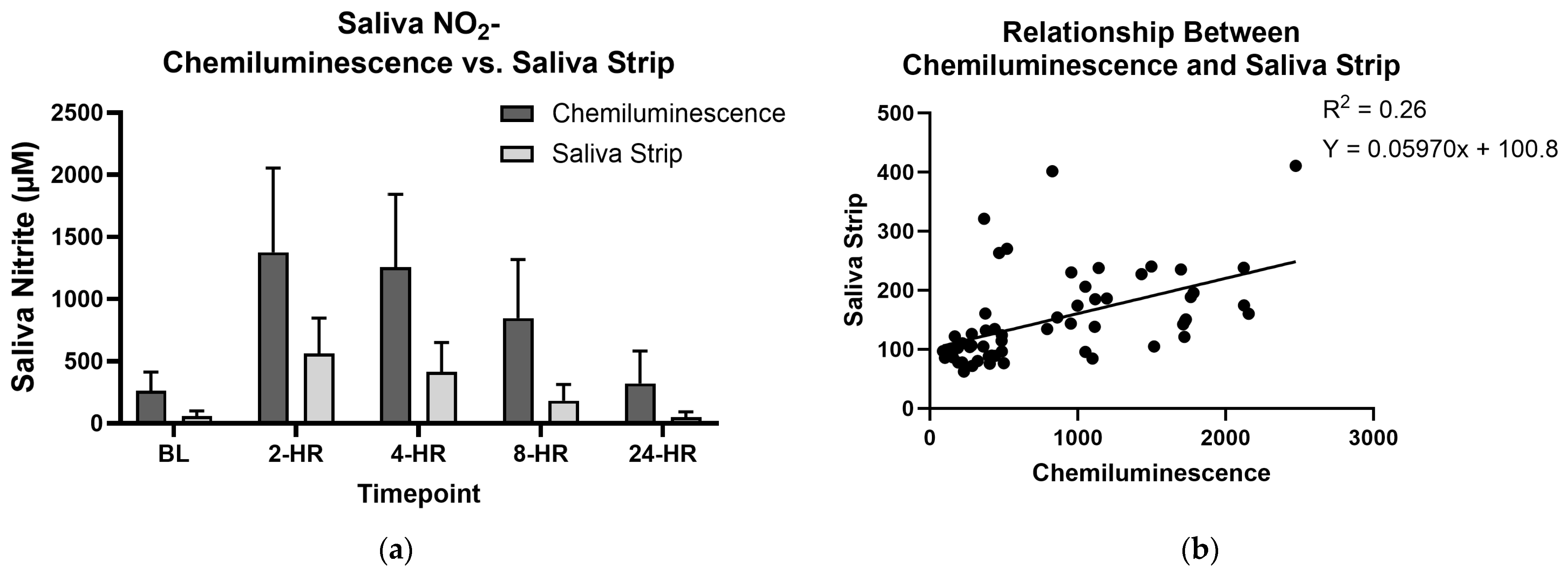
3.4. Saliva Test Strips and Chemiluminescence
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NO | Nitric Oxide |
| NO3− | Nitrate |
| NO2− | Nitrite |
| BP | Blood Pressure |
| SBP | Systolic Blood Pressure |
| DBP | Diastolic Blood Pressure |
| CVD | Cardiovascular Disease |
References
- Unger, T.; Borghi, C.; Charchar, F.; Khan, N.A.; Poulter, N.R.; Prabhakaran, D.; Ramirez, A.; Schlaich, M.; Stergiou, G.S.; Tomaszewski, M.; et al. 2020 International Society of Hypertension Global Hypertension Practice Guidelines. Hypertension 2020, 75, 1334–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayden, M.R. Peripheral Artery Disease: Atherosclerosis, Decreased Nitric Oxide, and Vascular Arterial Stiffening. J. Vasc. Dis. 2025, 4, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahadoran, Z.; Mirmiran, P.; Kashfi, K.; Ghasemi, A. Vascular nitric oxide resistance in type 2 diabetes. Cell Death Dis. 2023, 14, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivy, J.L. Inorganic Nitrate Supplementation for Cardiovascular Health. Methodist. DeBakey Cardiovasc. J. 2019, 15, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapil, V.; Khambata, R.S.; Robertson, A.; Caulfield, M.J.; Ahluwalia, A. Dietary nitrate provides sustained blood pressure lowering in hypertensive patients: A randomized, phase 2, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Hypertension 2015, 65, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Nishi, S.K.; Jovanovski, E.; Zurbau, A.; Komishon, A.; Mejia, S.B.; Khan, T.A.; Sievenpiper, J.L.; Milicic, D.; Jenkins, A.; et al. Repeated administration of inorganic nitrate on blood pressure and arterial stiffness: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Hypertens. 2020, 38, 2122–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamim, C.J.R.; Porto, A.A.; Valenti, V.E.; Sobrinho, A.; Garner, D.M.; Gualano, B.; Bueno Júnior, C.R. Nitrate Derived From Beetroot Juice Lowers Blood Pressure in Patients With Arterial Hypertension: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 823039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.M.; Wu, Z.F.; Pang, B.X.; Jin, L.Y.; Qin, L.Z.; Wang, S.L. From Nitrate to Nitric Oxide: The Role of Salivary Glands and Oral Bacteria. J. Dent. Res. 2016, 95, 1452–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapil, V.; Weitzberg, E.; Lundberg, J.O.; Ahluwalia, A. Clinical evidence demonstrating the utility of inorganic nitrate in cardiovascular health. Nitric Oxide 2014, 38, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryan, N.S.; Burleigh, M.C.; Easton, C. The oral microbiome, nitric oxide and exercise performance. Nitric Oxide 2022, 125–126, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woessner, M.; Smoliga, J.M.; Tarzia, B.; Stabler, T.; Van Bruggen, M.; Allen, J.D. A stepwise reduction in plasma and salivary nitrite with increasing strengths of mouthwash following a dietary nitrate load. Nitric Oxide 2016, 54, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondonno, C.P.; Liu, A.H.; Croft, K.D.; Considine, M.J.; Puddey, I.B.; Woodman, R.J.; Hodgson, J.M. Antibacterial Mouthwash Blunts Oral Nitrate Reduction and Increases Blood Pressure in Treated Hypertensive Men and Women. Am. J. Hypertens. 2015, 28, 572–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonagh, S.T.; Wylie, L.J.; Winyard, P.G.; Vanhatalo, A.; Jones, A.M. The Effects of Chronic Nitrate Supplementation and the Use of Strong and Weak Antibacterial Agents on Plasma Nitrite Concentration and Exercise Blood Pressure. Int. J. Sports Med. 2015, 36, 1177–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherukuri, L.; Birudaraju, D.; Kinninger, A.; Chaganti, B.T.; Shekar, C.; Hamal, S.; Shaikh, K.; Flores, F.; Roy, S.K.; Sotka, W.; et al. Effect of a plant-based bioequivalent inorganic nitrate (NO(3)(-)) complex with vitamins, antioxidants and phytophenol rich food extracts in hypertensive individuals—A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2020, 40, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taddei, S.; Virdis, A.; Mattei, P.; Ghiadoni, L.; Gennari, A.; Fasolo, C.B.; Sudano, I.; Salvetti, A. Aging and Endothelial Function in Normotensive Subjects and Patients With Essential Hypertension. Circulation 1995, 91, 1981–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Infante, T.; Costa, D.; Napoli, C. Novel Insights Regarding Nitric Oxide and Cardiovascular Diseases. Angiology 2021, 72, 411–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assmann, T.S.; Brondani, L.A.; Bouças, A.P.; Rheinheimer, J.; de Souza, B.M.; Canani, L.H.; Bauer, A.C.; Crispim, D. Nitric oxide levels in patients with diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nitric Oxide 2016, 61, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, R.; Wilcox, J.; Webb, A.J.; O’Gallagher, K. Dysfunctional and Dysregulated Nitric Oxide Synthases in Cardiovascular Disease: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobbs, D.A.; Kaffa, N.; George, T.W.; Methven, L.; Lovegrove, J.A. Blood pressure-lowering effects of beetroot juice and novel beetroot-enriched bread products in normotensive male subjects. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 108, 2066–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, F.J.; Ekblom, B.; Sahlin, K.; Lundberg, J.O.; Weitzberg, E. Effects of dietary nitrate on blood pressure in healthy volunteers. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 2792–2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, J.D.; Cobb, F.R.; Gow, A.J. Regional and whole-body markers of nitric oxide production following hyperemic stimuli. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2005, 38, 1164–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rassaf, T.; Heiss, C.; Hendgen-Cotta, U.; Balzer, J.; Matern, S.; Kleinbongard, P.; Lee, A.; Lauer, T.; Kelm, M. Plasma nitrite reserve and endothelial function in the human forearm circulation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2006, 41, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Hu, L.; Feng, X.; Wang, S. Nitrate and Nitrite in Health and Disease. Aging Dis. 2017, 9, 938–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosier, B.T.; Buetas, E.; Moya-Gonzalvez, E.M.; Artacho, A.; Mira, A. Nitrate as a potential prebiotic for the oral microbiome. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siervo, M.; Lara, J.; Ogbonmwan, I.; Mathers, J.C. Inorganic nitrate and beetroot juice supplementation reduces blood pressure in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Nutr. 2013, 143, 818–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani, H.; De Joode, M.E.J.R.; Hossein, I.J.; Henckens, N.F.T.; Guggeis, M.A.; Berends, J.E.; De Kok, T.M.C.M.; Van Breda, S.G.J. The benefits and risks of beetroot juice consumption: A systematic review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 788–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakubcik, E.M.; Rutherfurd-Markwick, K.; Chabert, M.; Wong, M.; Ali, A. Pharmacokinetics of Nitrate and Nitrite Following Beetroot Juice Drink Consumption. Nutrients 2021, 13, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wylie, L.J.; Kelly, J.; Bailey, S.J.; Blackwell, J.R.; Skiba, P.F.; Winyard, P.G.; Jeukendrup, A.E.; Vanhatalo, A.; Jones, A.M. Beetroot juice and exercise: Pharmacodynamic and dose-response relationships. J. Appl. Physiol. 2013, 115, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ormesher, L.; Myers, J.E.; Chmiel, C.; Wareing, M.; Greenwood, S.L.; Tropea, T.; Lundberg, J.O.; Weitzberg, E.; Nihlen, C.; Sibley, C.P.; et al. Effects of dietary nitrate supplementation, from beetroot juice, on blood pressure in hypertensive pregnant women: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled feasibility trial. Nitric Oxide 2018, 80, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, A.; Alhulaefi, S.; Hayes, E.J.; Matu, J.; Brandt, K.; Watson, A.; Siervo, M.; Shannon, O.M. Exploring the Advantages and Disadvantages of a Whole Foods Approach for Elevating Dietary Nitrate Intake: Have Researchers Concentrated Too Much on Beetroot Juice? Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 7319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, S.J.; Winyard, P.; Vanhatalo, A.; Blackwell, J.R.; DiMenna, F.J.; Wilkerson, D.P.; Tarr, J.; Benjamin, N.; Jones, A.M. Dietary nitrate supplementation reduces the O2 cost of low-intensity exercise and enhances tolerance to high-intensity exercise in humans. J. Appl. Physiol. 2009, 107, 1144–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watts, A.R.; Lennard, M.S.; Mason, S.L.; Tucker, G.T.; Woods, H.F. Beeturia and the biological fate of beetroot pigments. Pharmacogenetics 1993, 3, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, A.J.; Patel, N.; Loukogeorgakis, S.; Okorie, M.; Aboud, Z.; Misra, S.; Rashid, R.; Miall, P.; Deanfield, J.; Benjamin, N.; et al. Acute blood pressure lowering, vasoprotective, and antiplatelet properties of dietary nitrate via bioconversion to nitrite. Hypertension 2008, 51, 784–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norouzzadeh, M.; Hasan Rashedi, M.; Payandeh, N.; Mirdar Harijani, A.; Shahinfar, H. The effects of dietary nitrate on blood pressure and vascular Health: An umbrella review and updated Meta-Analysis and meta-regression. J. Funct. Foods 2024, 114, 106082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, A.J.; Bulpitt, C.J.; Fletcher, A.E.; Beevers, D.G.; Coles, E.C.; Ledingham, J.G.; O’Riordan, P.W.; Petrie, J.C.; Rajagopalan, B.E.; Webster, J.; et al. Relation between blood pressure and stroke mortality. Hypertension 1992, 20, 601–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Webb, A.J.S.; Werring, D.J. New Insights Into Cerebrovascular Pathophysiology and Hypertension. Stroke 2022, 53, 1054–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taddei, S.; Virdis, A.; Ghiadoni, L.; Mattei, P.; Sudano, I.; Bernini, G.; Pinto, S.; Salvetti, A. Menopause is associated with endothelial dysfunction in women. Hypertension 1996, 28, 576–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogwood, A.C.; Ortiz de Zevallos, J.; Weeldreyer, N.; Clark, J.R.; Mazzella, V.; Cain, L.; Myaing, D.; Love, K.M.; Weltman, A.; Allen, J.D. The acute effects of exercise intensity and inorganic nitrate supplementation on vascular health in females after menopause. J. Appl. Physiol. 2023, 135, 1070–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, K.; Singh, S.; Parasuraman, S.K.; Rudd, A.; Shepstone, L.; Feelisch, M.; Minnion, M.; Ahmad, S.; Madhani, M.; Horowitz, J.; et al. Inorganic Nitrate in Angina Study: A Randomized Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Trial. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2017, 6, e006478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bock, J.M.; Treichler, D.P.; Norton, S.L.; Ueda, K.; Hughes, W.E.; Casey, D.P. Inorganic nitrate supplementation enhances functional capacity and lower-limb microvascular reactivity in patients with peripheral artery disease. Nitric Oxide 2018, 80, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proctor, D.N.; Neely, K.A.; Mookerjee, S.; Tucker, J.; Somani, Y.B.; Flanagan, M.; Kim-Shapiro, D.B.; Basu, S.; Muller, M.D.; Jin-Kwang Kim, D. Inorganic nitrate supplementation and blood flow restricted exercise tolerance in post-menopausal women. Nitric Oxide 2022, 122–123, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinheiro, V.d.S.; Proctor, D.N.; Nogueira Soares, R.; Alvares, T.S. Effect of 12-wk dietary nitrate supplementation on carotid arterial stiffness in postmenopausal females. Am. J. Physiol.-Heart Circ. Physiol. 2025, 328, H937–H944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woessner, M.N.; McIlvenna, L.C.; Ortiz de Zevallos, J.; Neil, C.J.; Allen, J.D. Dietary nitrate supplementation in cardiovascular health: An ergogenic aid or exercise therapeutic? Am. J. Physiol.-Heart Circ. Physiol. 2018, 314, H195–H212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stahl, M.E.; Grammer, E.E.; Allen, J.D.; Weltman, A. The Pharmacokinetics of Saliva and Plasma N-Oxides Following a Single Administration of a Plant-Based Bioequivalent Inorganic Nitrate Oral Supplement in an Open-Label, Phase 1, Single-Arm Study. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 4581. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134581
Stahl ME, Grammer EE, Allen JD, Weltman A. The Pharmacokinetics of Saliva and Plasma N-Oxides Following a Single Administration of a Plant-Based Bioequivalent Inorganic Nitrate Oral Supplement in an Open-Label, Phase 1, Single-Arm Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(13):4581. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134581
Chicago/Turabian StyleStahl, Macy E., Emily E. Grammer, Jason D. Allen, and Arthur Weltman. 2025. "The Pharmacokinetics of Saliva and Plasma N-Oxides Following a Single Administration of a Plant-Based Bioequivalent Inorganic Nitrate Oral Supplement in an Open-Label, Phase 1, Single-Arm Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 13: 4581. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134581
APA StyleStahl, M. E., Grammer, E. E., Allen, J. D., & Weltman, A. (2025). The Pharmacokinetics of Saliva and Plasma N-Oxides Following a Single Administration of a Plant-Based Bioequivalent Inorganic Nitrate Oral Supplement in an Open-Label, Phase 1, Single-Arm Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(13), 4581. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134581





