The Usefulness of 2-[18F]FDG PET or PET/CT in Extranodal Natural Killer/T-Cell Lymphoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Protocol
2.2. Search Strategy
2.3. Study Selection
2.4. Data Extraction and Collection
2.5. Quality Assessment (Risk of Bias Assessment)
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Literature Search
3.2. Studies and Patients Data
3.3. Risk of Bias and Applicability
3.4. Staging
3.5. Bone Marrow Evaluation
3.6. Prognosis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ENKTCL | Extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma |
| PET/CT | Positron emission tomography/computed tomography |
| 18F-FDG | Fluorine-18-fluorodeoxyglucose |
| EBV | Epstein-Barr virus |
| PPV | positive predictive value |
| NPV | negative predictive value |
| LR | likelihood ratios |
| DOR | diagnostic odds ratio |
| SROC | summary receiver operating characteristic |
| I2 | inconsistency index |
| SUV | standardized uptake value |
| MTV | metabolic tumor volume |
| TLG | total lesion glycolysis |
| BM | bone marrow |
| PFS | Progression-free survival |
| OS | overall survival |
| HL | Hodgkin lymphoma |
| NHL | non-Hodgkin lymphoma |
| DLBCL | diffuse large B-cell lymphoma |
| FL | follicular lymphoma |
| LD | Linear dichroism |
References
- Wang, H.; Fu, B.B.; Gale, R.P.; Liang, Y. NK-/T-cell lymphomas. Leukemia 2021, 35, 2460–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Gao, Y.; Li, Z.; Huang, H. Review on natural killer/T-cell lymphoma. Hematol. Oncol. 2023, 41, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, M.; Oguchi, M.; Suzuki, R. Extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma: Updates in biology and management strategies. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Haematol. 2018, 31, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Z.; Yao, S.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, W.; Yao, Z.; Liu, Y. Treatment of extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma: From past to future. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1088685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, R.O.; Pereira, J.; Lage, L.A.P.C.; Baiocchi, O.C.G. Extranodal NK-/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type: What advances have been made in the last decade? Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1175545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamsser, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.; Brenan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiting, P.F.; Rutjes, A.W.; Westwood, M.E.; Mallett, S.; Deeks, J.J.; Reitsma, J.B.; Leeflang, M.M.G.; Sterne, J.A.S.; Bossuyt, P.M.M. QUADAS-2 Group. QUADAS-2: A revised tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. Ann. Intern. Med. 2011, 155, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, R.; Treglia, G. Systematic reviews and meta-analyses of diagnostic studies: A practical guideline. Clin. Transl. Imaging 2017, 5, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kako, S.; Izutsu, K.; Ota, Y.; Minatani, Y.; Sugaya, M.; Momose, T.; Ohtamo, K.; Kanda, Y.; Chiba, S.; Motokura, T.; et al. FDG-PET in T-cell and NK-cell neoplasms. Ann. Oncol. 2007, 18, 1685–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukamoto, N.; Kojima, M.; Hasegawa, M.; Oriuchi, N.; Matsushima, T.; Yokohama, A.; Saitoh, T.; Handa, H.; Endo, K.; Murakami, H. The usefulness of (18)F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography ((18)F-FDG-PET) and a comparison of (18)F-FDG-pet with (67)gallium scintigraphy in the evaluation of lymphoma: Relation to histologic subtypes based on the World Health Organization classification. Cancer 2007, 110, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karantanis, D.; Subramaniam, R.M.; Peller, P.J.; Lowe, V.J.; Durski, J.M.; Collins, D.A.; Georgiou, E.; Ansell, S.M.; Wiseman, G.A. The value of [(18)F]fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography in extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma 2008, 8, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suh, C.; Kang, Y.K.; Roh, J.L.; Kim, M.R.; Kim, J.S.; Huh, J.; Lee, J.H.; Jang, Y.J.; Lee, B.J. Prognostic value of tumor 18F-FDG uptake in patients with untreated extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphomas of the head and neck. J. Nucl. Med. 2008, 49, 1783–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khong, P.L.; Pang, C.B.; Liang, R.; Kwong, Y.L.; Au, W.Y. Fluorine-18 fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography in mature T-cell and natural killer cell malignancies. Ann. Hematol. 2008, 87, 613–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feeney, J.; Horwitz, S.; Gönen, M.; Schöder, H. Characterization of T-cell lymphomas by FDG PET/CT. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2010, 195, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.B.; Wang, Q.S.; Wang, M.F.; Li, H.S.; Zhou, W.L.; Ye, X.H.; Wang, Q.Y. Utility of 18F-FDG PET/CT for staging NK/T-cell lymphomas. Nucl. Med. Commun. 2010, 31, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, H.; Maeda, Y.; Nawa, Y.; Yamakura, M.; Ennishi, D.; Miyazaki, Y.; Shinagawa, K.; Hara, M.; Matsue, K.; Tanimoto, M. The utility of positron emission tomography/computed tomography in the staging of extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma. Eur. J. Haematol. 2011, 87, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.H.; Cho, S.K.; Kim, W.S.; Kim, S.J.; Chan Ahn, Y.; Choe, Y.S.; Lee, K.H.; Kim, B.T.; Choi, J.Y. The role of 18F-FDG PET/CT for initial staging of nasal type natural killer/T-cell lymphoma: A comparison with conventional staging methods. J. Nucl. Med. 2013, 54, 1039–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Chen, C.; Li, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Chang, Y.; Lu, L.; Cui, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, M. Evaluation of bone marrow involvement in extranodal NK/T cell lymphoma by FDG-PET/CT. Ann. Hematol. 2015, 94, 963–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, Y.; Lee, J.M.; Woo, G.U.; Paeng, J.C.; Youk, J.; Yoon, S.S.; Kim, I.; Kang, K.W. FDG PET for Evaluation of Bone Marrow Status in T-Cell Lymphoma. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2019, 44, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; Yan, M.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, D.; Zhang, Y.; Huo, L.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, S. Prognostic value of interim 18F-FDG PET/CT in T-cell lymphomas. Leuk Lymphoma 2020, 61, 927–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaram, S.; Jizzini, M.; Lamonica, D.; Attwood, K.; Gravina, M.; Hernandez-Ilizaliturri, F.; Torka, P. Utility of bone marrow aspirate and biopsy in staging of patients with T-cell lymphoma in the PET-Era—Tissue remains the issue. Leuk Lymphoma 2020, 61, 3226–3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, J.J.; Zhao, R.Z.; Huang, C.; Shi, G.Q.; Zheng, H.; Tang, T.L.; Liao, S.Q.; Chen, J.H.; Shen, J.Z.; et al. The value of routine bone marrow examination in patients with extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma staged with PET/CT. Cancer 2022, 128, 3943–3950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Wu, W.; Zhou, H.; Zhao, S.; Tian, R.; Xiang, M.; Zou, L. 18F-FDG PET/CT Plays a Limited Role in Replacing Bone Marrow Biopsy for Newly Diagnosed Advanced-Stage Patients With Extranodal Natural Killer/T-Cell Lymphoma. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 894804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Huang, Z.; Gao, Z.; Wang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Bai, Y.; Wu, Q.; Wang, M. Prognostic Value of 18F-FDG PET/CT Radiomics in Extranodal Nasal-Type NK/T Cell Lymphoma. Korean J. Radiol. 2024, 25, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.M.; Peng, P.; Liu, X.; Qi, S.N.; Wang, S.L.; Fang, H.; Song, Y.W.; Liu, Y.P.; Jin, J.; Li, N.; et al. Optimizing the prognostic capacity of baseline 18F-FDG PET/CT metabolic parameters in extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma by using relative and absolute thresholds. Heliyon 2024, 10, e25184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Q.; Cui, Y.; Wang, Z.; Fang, X.; Chen, M.; Chen, Z.; Lin, T.; Jiang, Y.; Huang, H. Risk stratification based on changes in the standard maximal uptake value on PET/CT and the plasma Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) DNA status after two cycles of chemotherapy for extranodal NK-/T-cell lymphoma. Ann. Hematol. 2025, 104, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Qu, L.; Fu, K.; Teng, Y.; Lai, R.; Guo, R.; Ding, C.; Li, K.; et al. Robust and interpretable deep learning system for prognostic stratification of extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2025, 52, 1739–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Hao, S.; Chen, W.; Jing, M.; Li, S.; Zhang, W.; Liang, L.; Fan, W.; Zhang, Y. Prognostic value of interim [18F]FDG PET/CT after immunotherapy-based combinations in extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type. Eur. Radiol. 2025, 35, 4213–4222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zeng, L.J.; Wang, S.; Wei, L.Q.; Yang, J.; Li, M.; Wang, L. Evaluating early response assessment in extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma by analyzing ΔSUVlbm between baseline and interim 18F-FDG PET/CT scans. Leuk Lymphoma 2025, 66, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertagna, F.; Giubbini, R.; Albano, D. Chapter 9. Evidence-Based Positron Emission Tomography. Summary of Recent Meta-Analyses on PET. In Evidence-Based PET for Haematological Tumours; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Cheson, B.D.; Fisher, R.I.; Barrington, S.F.; Cavalli, F.; Schwartz, L.H.; Zucca, E.; Lister, T.A. Recommendations for initial evaluation, staging, and response assessment of Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphoma: The Lugano classification. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 3059–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juneja, S.K.; Wolf, M.M.; Cooper, I.A. Value of bilateral bone marrow biopsy specimens in non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. J. Clin. Pathol. 1990, 43, 630–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Suh, C.; Huh, J.; Jun, H.J.; Kim, K.; Jung, C.; Park, K.; Park, Y.H.; Ko, Y.H.; Kim, W.S. Effect of positive bone marrow EBV in situ hybridization in staging and survival of localized extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma, nasal-type. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 3250–3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Wang, R.; Hou, N.; Kuang, A.; Shen, G. FDG PET/CT may replace bone marrow biopsy for the evaluation of bone marrow involvement in selected mature T- and natural killer-cell lymphomas: A meta-analysis. Eur. J. Radiol. 2024, 172, 111353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrington, S.F.; Kluge, R. FDG PET for therapy monitoring in Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphomas. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2017, 44 (Suppl. S1), 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albano, D.; Pasinetti, N.; Dondi, F.; Giubbini, R.; Tucci, A.; Bertagna, F. Prognostic Role of Pre-Treatment Metabolic Parameters and Sarcopenia Derived by 2-[18F]-FDG PET/CT in Elderly Mantle Cell Lymphoma. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albano, D.; Bosio, G.; Re, A.; Pagani, C.; Giubbini, R.; Bertagna, F. Metabolic behavior and prognostic value of early and end of treatment 18F-FDG PET/CT in adult Burkitt′s lymphoma: The role of Deauville and IHP criteria. Leuk Lymphoma 2019, 60, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albano, D.; Ravanelli, M.; Durmo, R.; Versari, A.; Filice, A.; Rizzo, A.; Racca, M.; Pizzuto, D.A.; Bretagna, F.; Annunziata, S. Semiquantitative 2-[18F]FDG PET/CT-based parameters role in lymphoma. Front. Med. 2024, 11, 1515040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
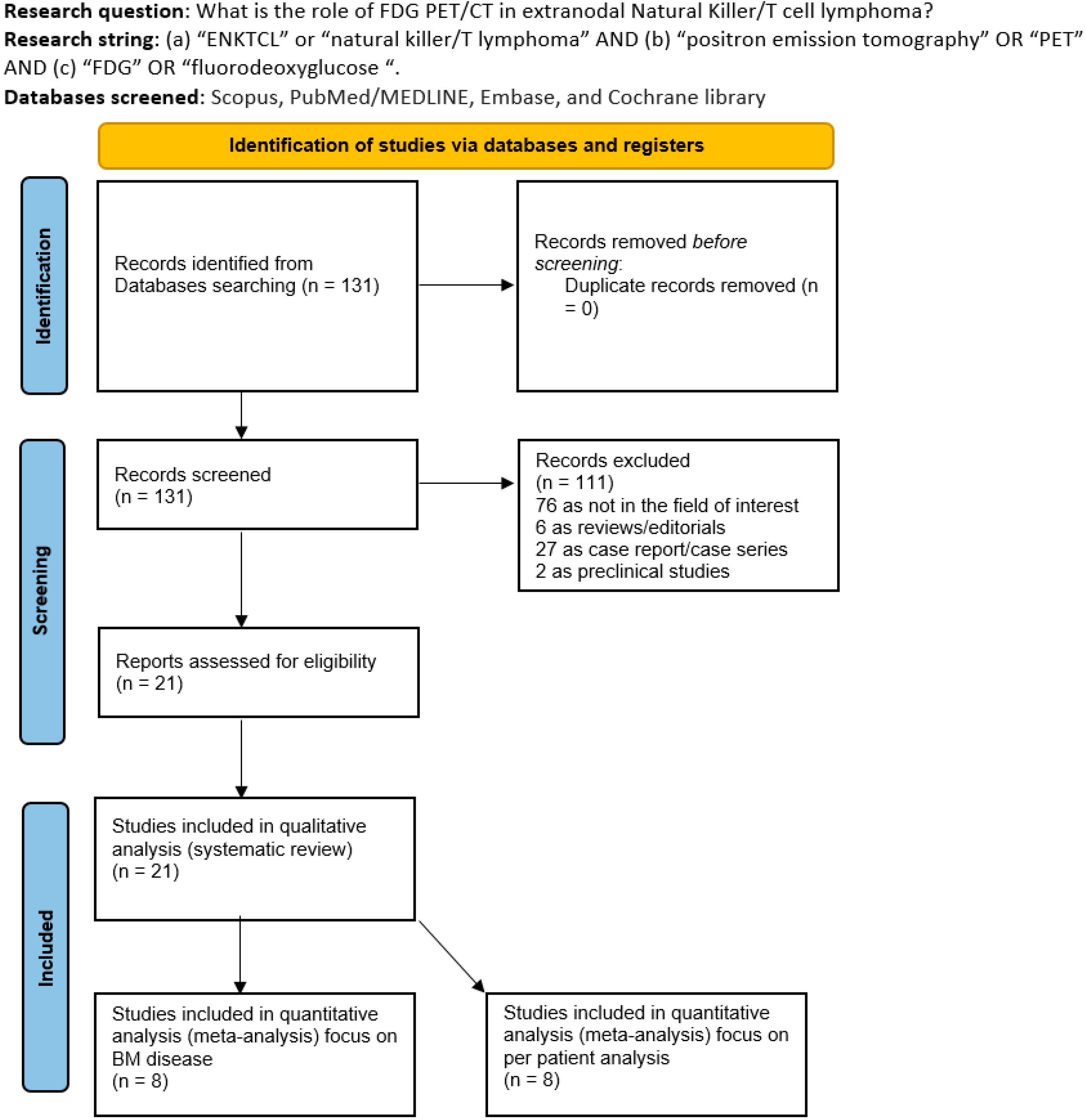
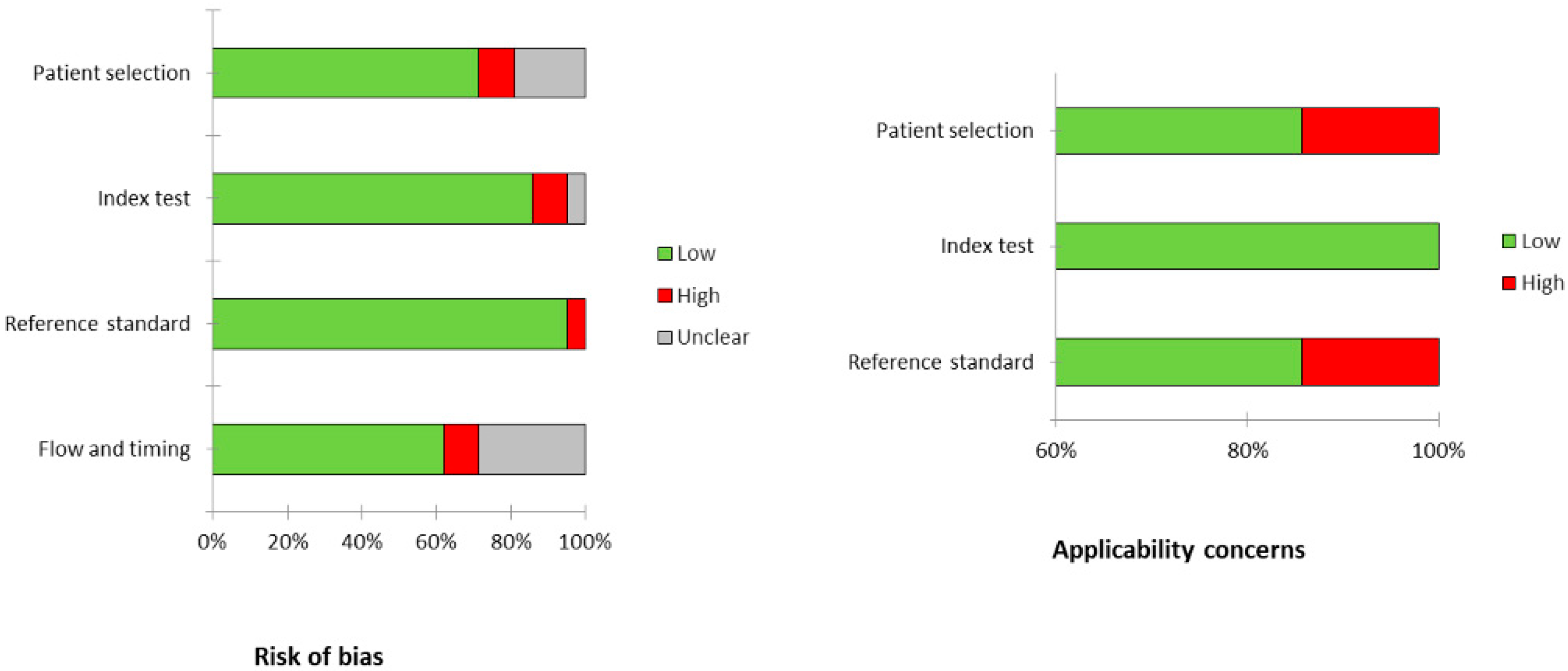
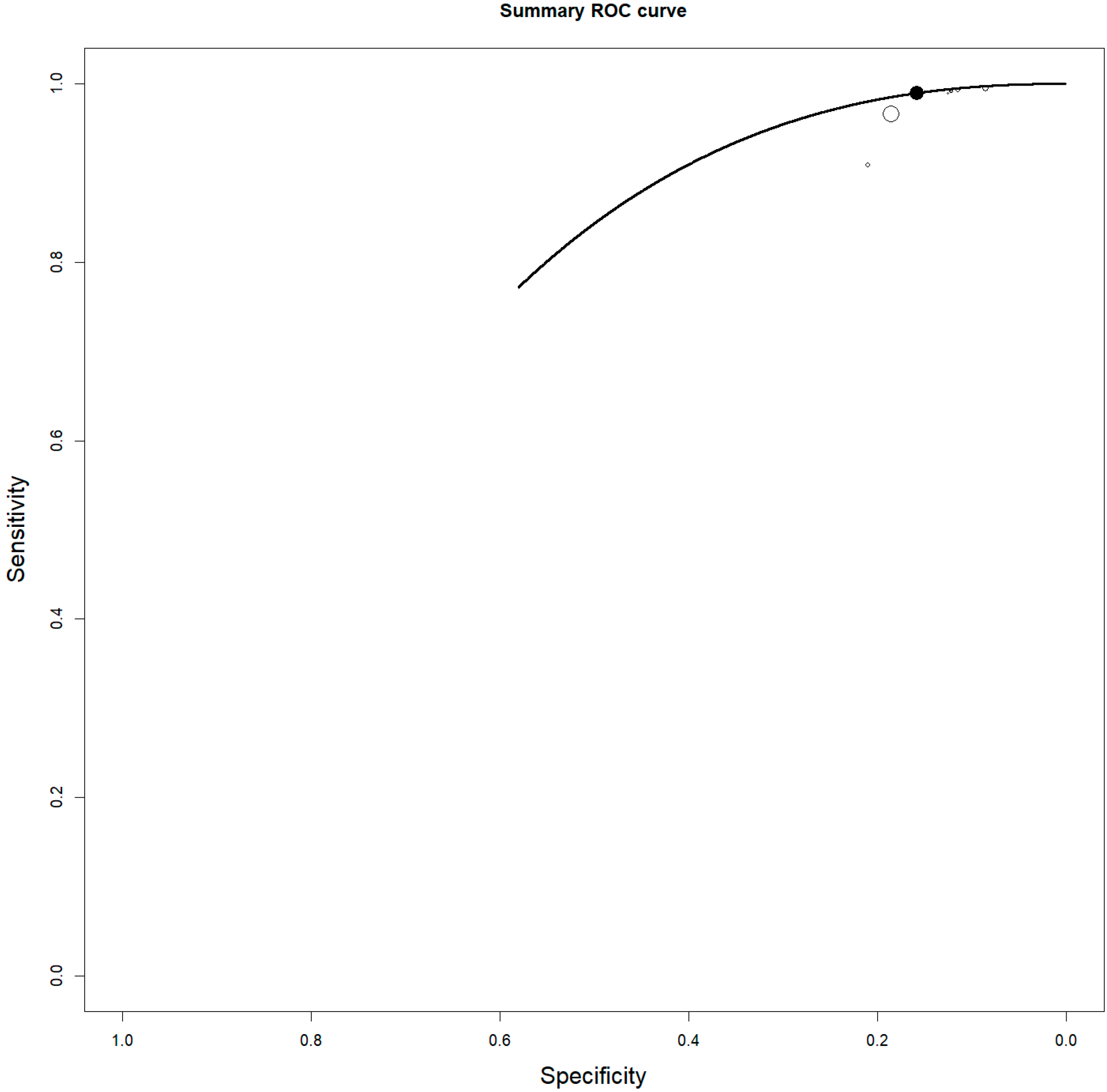
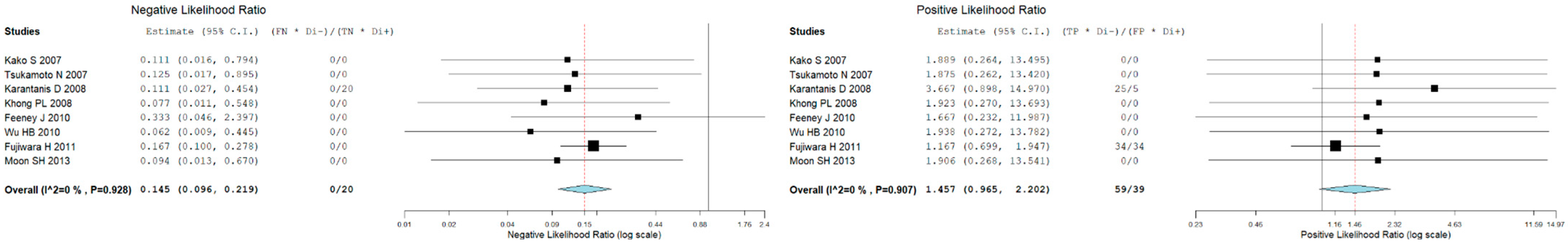
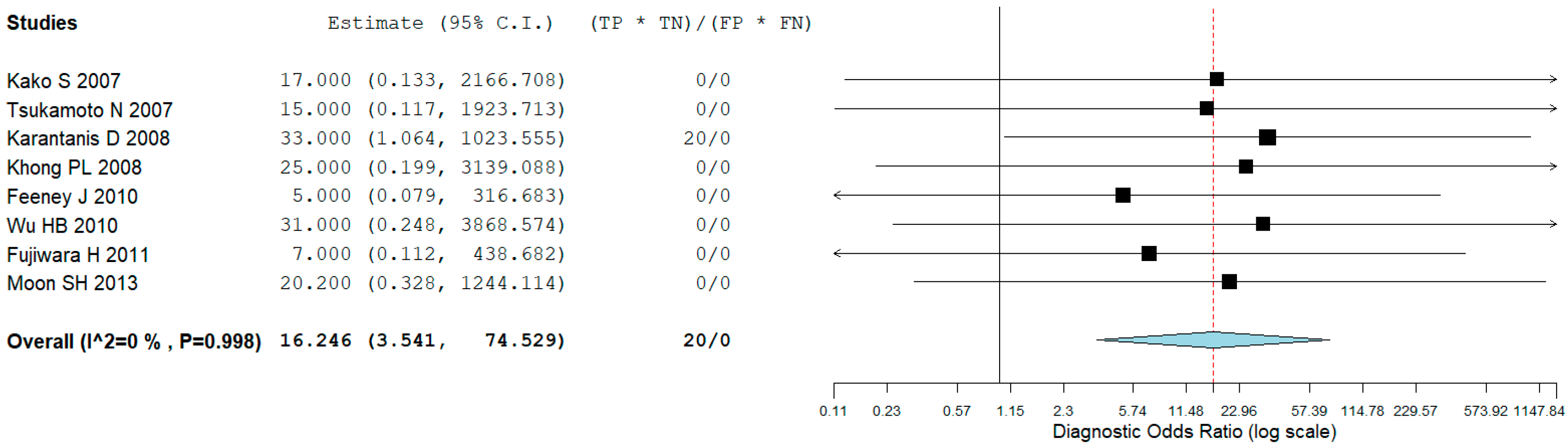
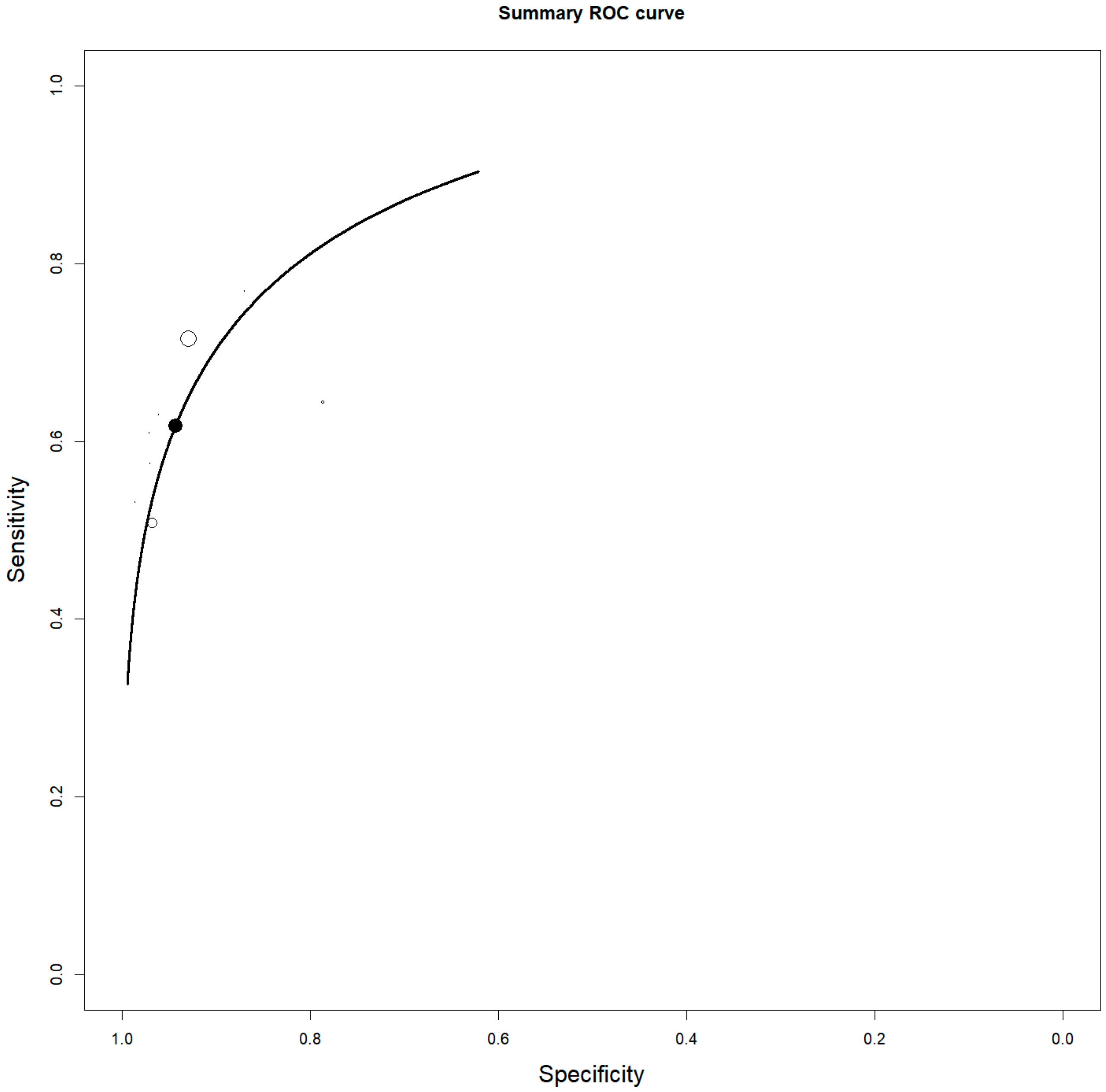
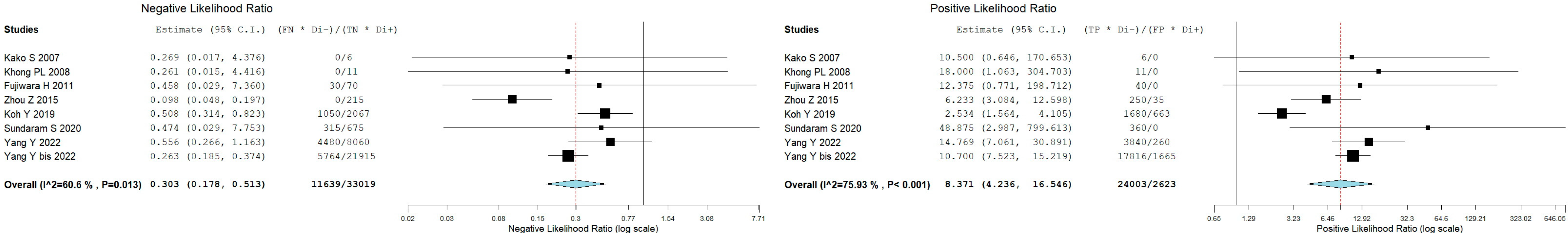
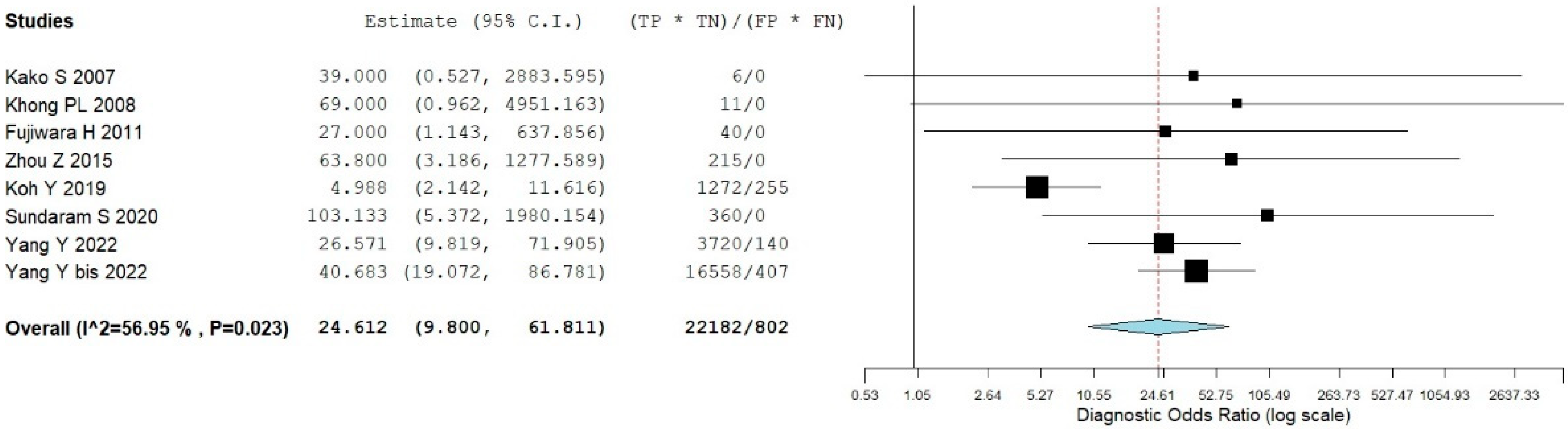
| First Author | Year | Country | Funding Source | Study Design | No. of ENKTCL Patients | M:F | Average Age (Range) | Purpose/s |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kako S [9] | 2007 | Japan | No | R | 8 | 5:03 | 54 (43–73) | Staging, BM evaluation |
| Tsukamoto N [10] | 2007 | Japan | No | R | 7 | na | na | Staging |
| Karantanis D [11] | 2008 | USA | No | R | 10 | 5:05 | 44.2 (27–60) | Staging |
| Suh C [12] | 2008 | Korea | No | R | 21 | 14:07 | 46 (17–78) | Prognosis |
| Khong PL [13] | 2008 | China | No | R | 12 * | 8:04 | 50.6 (17–79) | Staging, BM evaluation |
| Feeney J [14] | 2010 | USA | No | R | 12/122 | 11:01 | na | Staging |
| Wu HB [15] | 2010 | China | No | R | 15 | 11:04 | 42 (23–79) | Staging |
| Fujiwara H [16] | 2011 | Japan | No | R | 19 | 11:08 | 61 (13–90) | Staging, BM evaluation |
| Moon SH [17] | 2013 | Korea | No | R | 52 | 34:18:00 | 49.4 (24–74) | Staging |
| Zhou Z [18] | 2015 | China | No | R | 55 | 37:18:00 | 44 (18–72) | BM evaluation |
| Koh Y [19] | 2019 | Korea | National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant for the Global Core Research Center (No. 2011–0030001) and NRF grant for Research Center for Cellular Heterogeneity and Adaptation (No. NRF-2016R1A5A1011974) funded by the Korean government (Ministry of Science, ICT, and Future Planning). | R | 46/109 | 67:42:00 | 55.2 (15–89) | BM evaluation |
| Qian L [20] | 2020 | China | No | R | 15/51 | 27:24:00 | 35.2 (17–72) | Prognosis |
| Sundaram S [21] | 2020 | USA | No | R | Jul-60 | 34:26:00 | 58 ** (21–82) | BM evaluation |
| Yang Y [22] | 2022 | China | No | R | 356 | 1.78:1 | 45 ** (13–77) | BM evaluation |
| Yang Y bis [23] | 2022 | China | No | R | 742 | 531:211 | na | Staging, BM evaluation |
| Luo Y [24] | 2024 | China | Medical Science and Technology Research Project of Henan Province (SBGJ202101002) | R | 252 | 158:94 | na | Prognosis |
| Zhu YM [25] | 2024 | China | National Key Research and Development of China (2020AAA0109504), National Natural Science Foundation of China (81970185), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (3332022028). | R | 133 | 99:34:00 | 44 ** | Prognosis |
| Ren Q [26] | 2025 | China | Youth Program, Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province, People’s Republic of China (grant number 2022CFB713) | R | 119 | 79:40:00 | 44 ** (18–77) | Prognosis |
| Jiang C [27] | 2025 | China | National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant 81971653), the 1·3·5 project for disciplines of excellence, West China Hospital, Sichuan University (grant ZYAI24014), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (grant 2024M762244), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant 82171975). | R | 562 | 376:186 | 45 (35–55) | Prognosis |
| Liu L [28] | 2025 | China | No | R | 133 | 82:51:00 | 46 ** (15–82) | Prognosis |
| Yang L [29] | 2025 | China | No | R | 20 | 13:07 | 45 ** (30–71) | Prognosis |
| First Author | Device | Mean 2-[18F]FDG Injected Dose, MBq | Mean Uptake Time (min) | Image Analysis | Semiquantitative Variables |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kako S [9] | PET | 296 | 60 | Visual and semiquantitative analysis | SUVmax |
| Tsukamoto N [10] | PET | 275–370 | 40–60 | Visual and semiquantitative analysis | SUVmax |
| Karantanis D [11] | PET/CT | 550–740 | 60–90 | Visual and semiquantitative analysis | SUVmax |
| Suh C [12] | PET | 555 | 60 | Visual and semiquantitative analysis | SUVmax |
| Khong PL [13] | PET/CT | 222–370 | 60 | Visual and semiquantitative analysis | SUVmax |
| Feeney J [14] | PET/CT | 555 | 60–90 | Visual and semiquantitative analysis | SUVmax |
| Wu HB [15] | PET/CT | 277–511 | 60 | Visual and semiquantitative analysis | SUVmax |
| Fujiwara H [16] | PET/CT | 3–4.3/kg | 60–90 | Visual and semiquantitative analysis | SUVmax |
| Moon SH [17] | PET/CT | 5.5/kg | 60 | Visual and semiquantitative analysis | SUVmax |
| Zhou Z [18] | PET/CT | 4.4/kg | 60 | Visual and semiquantitative analysis | SUVmax |
| Koh Y [19] | PET/CT | 5.18/kg | 60 | Visual and semiquantitative analysis | SUVmax; MLR |
| Qian L [20] | PET/CT | na | na | Visual and semiquantitative analysis | SUVmax, DSUVmax |
| Sundaram S [21] | PET/CT | na | na | Visual analysis | |
| Yang Y [22] | PET/CT | 5.18/kg | 60 | Visual analysis | |
| Yang Y bis [23] | PET/CT | na | na | Visual analysis | |
| Luo Y [24] | PET/CT | 5.5/kg | 60 | Visual and semiquantitative analysis | SUVmax, MTV, TLG, texture analysis features |
| Zhu YM [25] | PET/CT | 4–5/kg | 60–70 | Visual and semiquantitative analysis | SUVmax, SUVmean, MTV, and TLG |
| Ren Q [26] | PET/CT | 5.55/kg | 45–60 | Visual and semiquantitative analysis | SUVmax |
| Jiang C [27] | PET/CT | 185–370 | 60 | Visual and semiquantitative analysis | SUVmax, MTV, TLG, texture analysis features |
| Liu L [28] | PET/CT | 3.7/kg | 60 | Visual and semiquantitative analysis | SUVmax |
| Yang L [29] | PET/CT | 3.7–5.55/kg | 60 | Visual and semiquantitative analysis | SUVlbm |
| First Author | TP | FP | FN | TN | Median SUVmax |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kako S [9] | 8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5.2 (2.1–13) |
| Tsukamoto N [10] | 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7.5 (4–14.5) |
| Karantanis D [11] | 5 | 1 | 0 | 4 | 16 (5–25) |
| Khong PL [13] | 12 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 8 (6.9–10) |
| Feeney J [14] | 12 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 10.8 (4.9–23.3) |
| Wu HB [15] | 15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10.01 |
| Fujiwara H [16] | 17 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 11.67 (3.73–41) |
| Moon SH [17] | 50 | 0 | 2 | 0 | na |
| Global | 126 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| First Author | TP | FP | FN | TN | Criteria for Positive PET | Standard Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kako S [9] | 1 | 0 | 0 | 6 | focal uptake | BMB |
| Khong PL [13] | 1 | 0 | 0 | 11 | focal or diffuse uptake higher than liver/spleen | BMB |
| Fujiwara H [16] | 4 | 0 | 3 | 10 | focal uptake | BMB |
| Zhou Z [18] | 5 | 7 | 0 | 43 | focal or diffuse uptake higher than liver | BMB |
| Koh Y [19] | 24 | 17 | 15 | 53 | focal or diffuse uptake higher than liver | BMB |
| Sundaram S [21] | 8 | 0 | 7 | 45 | focal uptake higher than liver | BMB |
| Yang Y [22] | 12 | 10 | 14 | 310 | focal or diffuse uptake higher than liver | BMB |
| Yang Y bis [23] | 34 | 37 | 11 | 487 | focal uptake higher than liver | BMB |
| Global | 89 | 71 | 50 | 965 |
| First Author | N° Patients | Parameters Considered | Endpoints | Main Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Suh C [12] | 21 | SUVmax | DSS | SUVmax > 5.5 was significantly associated with worse prognosis |
| Qian L [20] | 51 | DS at interim and ΔSUVmax | PFS and OS | DS significantly predict PFS and OS, ΔSUVmax significantly predict PFS |
| Luo Y [24] | 126 | texture analysis features | PFS and OS | deep learning model including PET features may help to stratify prognosis |
| Zhu YM [25] | 133 | SUVmax, SUVmean, MTV, and TLG with different thresholds | PFS and OS | all PET parameters were significantly associated with prognosis |
| Ren Q [26] | 119 | ΔSUVmax | treatment response after 2 cycles of chemotherapy, PFS, and OS | DSSTL ≥ 50% is associated with better prognosis |
| Jiang C [27] | 562 | texture analysis features | PFS and OS | deep learning model including PET features may help to stratify prognosis |
| Liu L [28] | 133 | DS, SUVmax, metabolic response on interim PET | PFS and OS | SUVmax (>9.2), DS 5, or with stable disease or relapsed/progressive disease associated with worse PFS and OS |
| Yang L [29] | 20 | ΔSUVmax baseline-interim PET | Treatment response at end of treatment | ΔSUVmax 66.75% may predict treatment response |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Albano, D.; Rodella, C.; Tucci, A.; Treglia, G.; Bertagna, F.; Chiti, A.; Fallanca, F. The Usefulness of 2-[18F]FDG PET or PET/CT in Extranodal Natural Killer/T-Cell Lymphoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 4582. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134582
Albano D, Rodella C, Tucci A, Treglia G, Bertagna F, Chiti A, Fallanca F. The Usefulness of 2-[18F]FDG PET or PET/CT in Extranodal Natural Killer/T-Cell Lymphoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(13):4582. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134582
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlbano, Domenico, Carlo Rodella, Alessandra Tucci, Giorgio Treglia, Francesco Bertagna, Arturo Chiti, and Federico Fallanca. 2025. "The Usefulness of 2-[18F]FDG PET or PET/CT in Extranodal Natural Killer/T-Cell Lymphoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 13: 4582. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134582
APA StyleAlbano, D., Rodella, C., Tucci, A., Treglia, G., Bertagna, F., Chiti, A., & Fallanca, F. (2025). The Usefulness of 2-[18F]FDG PET or PET/CT in Extranodal Natural Killer/T-Cell Lymphoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(13), 4582. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134582








