Abstract
Background: The management of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) has advanced significantly with the introduction of biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARDs). Despite these therapeutic strides, RA prognosis remains profoundly affected by comorbid conditions, particularly cardiovascular and metabolic complications, which increase both morbidity and mortality. The role of bDMARDs in modulating comorbidities remains underexplored, with limited evidence on their effects across various non-RA conditions, such as respiratory, diabetic, and hematologic disorders. This systematic review aimed to evaluate the impact of bDMARDs on the progression and outcomes of comorbidities in RA patients, providing insights to guide personalized treatment approaches. Methods: This systematic review was registered in PROSPERO (CRD42022345903) and followed the PRISMA guidelines. Original research articles from PubMed and Scopus, published up to 18 July 2024, were included. Studies assessing the impact of bDMARDs on comorbidities in RA patients met the eligibility criteria. Results: A total of thirteen studies met the inclusion criteria. They were published from inception until July 2024. The studied comorbidities included pulmonary conditions (asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and interstitial lung disease) (n = 2); diabetes (n = 3); anemia (n = 3); and malignancies (n = 3). The bDMARDs studied were tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFis) (n = 9); Rituximab (n = 5); Tocilizumab (n = 5); Abatacept (n = 5); and Anakinra (n = 2). The most reported effects of bDMARDs on comorbidities were the following: (i) an exacerbation of pulmonary comorbidities for Abatacept and TNFis; (ii) patients switched to or initiated on Abatacept as their first targeted disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (tDMARD) showed directionally lower rates and costs of T2DM-related complications compared with patients switching to or initiating other tDMARDs; (iii) there was no difference between Abatacept and TNFis or Rituximab/Tocilizumab regarding diabetes treatment switching or intensification; (iv) Anakinra significantly reduced the HbA1c%; (v) decreased serum hepcidin levels and improvement in anemia were observed in patients treated with TNFis or Tocilizumab; and (vi) no decrease in overall survival time or the significant incident malignancy rate was noted in RA patients. Conclusions: Overall, bDMARDs appear safe for use in RA patients with comorbidities and may even provide specific benefits for conditions such as anemia and diabetes. These findings suggest that clinicians could consider tailoring biologic therapy based on each patient’s comorbidity profile, potentially enhancing both RA management and comorbidity outcomes. For instance, selecting biologics such as Anakinra or Tocilizumab might be advantageous for RA patients with concurrent diabetes or anemia, given their observed metabolic and hematologic benefits. This personalized approach could improve the quality of life and reduce healthcare costs by addressing RA and associated comorbidities more effectively.
1. Introduction
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune condition characterized by chronic synovial inflammation and gradual joint destruction, which frequently causes disability and a lower quality of life [1,2]. Comorbidities in RA patients contribute to increased morbidity and mortality, leading to a reduced quality of life and a significant socioeconomic burden [3]. Biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic medicines (bDMARDs) have revolutionized RA treatment by targeting inflammatory cytokines including the following: (i) Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha (TNF-α) inhibitors (TNFis), such as Adalimumab, Etanercept, Infliximab, Golimumab, and Certolizumab, block TNF-α, a pro-inflammatory cytokine central to RA pathogenesis, thereby reducing joint inflammation and damage [3,4]; (ii) Tocilizumab (TCZ), an interleukin-6 receptor (IL-6R) inhibitor, blocks IL-6 signaling—a key pathway implicated in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis—thereby reducing systemic inflammation [3,4]; (iii) Abatacept (ABA), a selective T-cell costimulation modulator, inhibits T-cell activation by binding to CD80/CD86 on antigen-presenting cells, disrupting the CD28-CD80/86 interaction [5]; (iv) Rituximab (RTX), a monoclonal antibody targeting CD20 on B cells, depletes B cells, which play a role in autoantibody production and inflammation [6]; and (v) Anakinra (ANA), an IL-1 receptor antagonist, inhibits IL-1β, a cytokine involved in RA and metabolic dysregulation [7,8].
In RA patients, bDMARDs have demonstrated efficacy in reducing disease progression, decreasing structural joint deterioration, and improving physical function [9]. However, many RA patients have comorbidities such as cardiovascular disease, respiratory disorders (such as interstitial lung disease), diabetes, anemia, and cancer, all of which complicate RA care and worsen the prognosis [6].
These comorbidities, whether resulting from systemic inflammation or the adverse effects of treatments, can alter the response to bDMARDs and impact overall patient outcomes [10]. On the other hand, the effects of bDMARDs on these coexisting diseases remain unclear.
Despite the therapeutic benefits of biologic agents in the management of RA, there are still conflicting results regarding their effect on pre-existing comorbidities. Some studies suggest that specific biologics, such as TNF inhibitors, may worsen pulmonary diseases in high-risk patients, mainly those with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and interstitial lung disease (ILD) [11]. Additionally, concerns exist about an increased risk of malignancy, as persistent immunosuppression may elevate the risk of certain malignancies [12,13]. On the other hand, the benefits of IL-6 inhibitors appear to extend to improved control of glucose and HbA1c levels in RA patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) [14]. The disparities in the effects of various bDMARDs on RA-associated comorbidities highlight the complexity of managing RA in patients with coexisting conditions. These findings suggest that the choice of bDMARDs should be tailored according to the patient’s comorbidity profile to optimize therapeutic outcomes.
The existing corpus of research lacks high-quality trials that accurately investigate the effects of bDMARDs on specific comorbidities in patients with RA. Most studies focus on RA-related outcomes, while comorbidities are often treated as secondary endpoints rather than primary objectives. Furthermore, observational studies frequently report the results of large populations without stratifying patients by comorbidity type or severity, making it difficult to understand how specific bDMARDs affect these conditions [15]. Differences in the study design, outcome measures, and definitions of comorbidities across studies hinder data synthesis and limit the reliability of evidence regarding the safety and efficacy of bDMARDs in patients with complex comorbidity profiles [16].
Given the limited availability of high-quality evidence, the scarcity of comorbidity-focused studies, and the inconsistencies among the existing findings, this systematic review aimed to evaluate the impact of bDMARDs on the progression and outcomes of specific comorbidities in RA patients, including respiratory, metabolic, hematologic, and malignancy-related conditions.
2. Methods
2.1. Protocol and Eligibility Criteria
This systematic review adhered to the guidelines set by the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) [17]. The protocol was registered with the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO) under the reference number (CRD42022345903).
The criteria for inclusion were developed using the following PICO tool questions [18]: P (population) = individuals with rheumatoid arthritis and at least one comorbidity; I (intervention/exposure) = exposure to bDMARDs; C (comparison) = absence of bDMARDs or comparisons among bDMARD molecules; and O (outcome) = outcomes related to comorbidities.
There were no limitations concerning the study design, setting, country, or timeframe. Our research utilized two databases: PubMed and Scopus, searched from their inception until 18 December 2024. All studies included involved patients diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) who received bDMARD treatment and had at least one comorbidity. Only original articles in English were accepted. Publications that did not align with the objectives of this systematic review or did not constitute original research, such as reviews, editorials, qualitative studies, case reports, and letters to the editor, were excluded. Studies that focused on adverse events (e.g., infections and hypersensitivity reactions) as primary outcomes were also left out. In contrast, analyses concerning comorbidity-related outcomes, such as major adverse cardiovascular events (MACEs) in cardiovascular disease or glycemic control in diabetes, or other comorbidities (obesity, anemia, depression, osteoporosis, pulmonary conditions, or solid-organ cancers were applicable), were relevant, as these illustrate the progression of RA-related conditions rather than direct drug toxicity. Additionally, articles discussing the influence of bDMARDs on comorbidity risk factors and those focusing on infectious comorbidities were excluded.
2.2. Information Sources and Search
PubMed and Scopus were searched without any time constraints or filters. In PubMed, the search utilized keywords associated with “comorbidity” and “biologic drugs”. The keywords were selected based on the Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) terminology used in PubMed. The specific combination of Boolean operators and keywords can be found in Table 1. We compiled a list of comorbidities that are most often linked to RA, drawing on literature data [19,20]: diabetes (35.3%) [21], obesity (18 to 34%) [22], anemia (33 to 70%) [23], depression (17%) [24], cardiovascular disease (8.5%) [25], osteoporosis (6.3% to 36.3% for the hip) [26], pulmonary conditions (asthma (6.6%) and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (3.6%)) [27], ulcers (1.2%) [28], and solid-organ cancers (5%) [19].

Table 1.
Applied terms in the present systematic review.
For PubMed, the search encompassed the article titles for all terms and the abstracts for those related to “comorbidity”. In Scopus, the search included article titles for all terms and abstracts and keywords for terms associated with the concept of “comorbidity”. Only studies involving humans were considered. The reference lists of selected articles were also reviewed. The first two authors of this systematic review came to a consensus on the articles to be included in this paper. All aspects of the systematic review methods were defined before commencing the review.
2.3. Study Selection
The first two authors of this systematic review independently gathered the data. They utilized a pilot-tested extraction form and resolved any disagreements through a consensus-based approach. During the initial online literature search, article titles were evaluated separately, followed by the elimination of duplicate articles. The abstracts of the selected articles were reviewed to see if they met the inclusion criteria. Full-text versions of the qualifying articles were then read to assess eligibility and retention. The extracted data encompassed the main methodological attributes of the articles, including study data (publication year, country, study design, number and average age of participants, inclusion and exclusion criteria, and evaluation methods), primary outcomes, and results. Any disputes between authors about eligibility were settled by consensus.
2.4. Methodological Quality Assessment
The assessment of methodological quality was conducted using the Joanna Briggs Institute (JBI) Critical Appraisal Tool, specifically the Checklist for Cohort Studies [29] and the Checklist for Randomized Controlled Trials (RCTs) [30].
The Checklist for Cohort Studies comprises 11 items focusing on (1) recruitment, (2) exposure measurement, (3) reliability of exposure measurement, (4) identification of confounding factors, (5) strategies to manage confounding factors, (6) ensuring participants were outcome-free at the study’s start, (7) validity and reliability of outcome measurement, (8) reported follow-up timeframe, (9) completeness of follow-up and strategies for handling incomplete follow-up, and (10) appropriate statistical analysis.
The RCT checklist consists of 13 items covering (1) randomization for participant assignment to treatment groups, (2) treatment group allocation, (3) baseline similarity of treatment groups, (4) participants’ blindness to treatment assignment, (5) blinding of those administering treatment to assignment, (6) blinding of outcome assessors to treatment assignment, (7) treatment group similarity apart from the intervention of interest, (8) completeness of follow-up and strategies for addressing incomplete follow-up, (9) ensuring participants were analyzed in their randomized groups, (10) consistent measurement of outcomes across treatment groups, (11) reliability of outcome measurements, (12) appropriate statistical analysis, and (13) appropriate trial design, including any deviations from standard RCT design. Each item on both checklists is scored as ‘yes’, ‘no’, ‘unclear’, or ‘not applicable’.
The first two authors independently evaluated the retained studies, resolving any discrepancies through discussion and reaching consensus on any disagreements regarding scoring.
3. Results
The initial search resulted in 2044 papers. After removing duplicates, we screened 298 papers. During the title and abstract review, 1576 studies were excluded because they did not meet our objectives or were not published in English. From the remaining studies, 20 were removed for failing to meet the inclusion criteria. Additionally, 138 studies were excluded, including 12 systematic reviews, 13 case reports, 3 letters to the editor, and 110 studies unrelated to the topic and animals. Ultimately, 13 articles were retained [31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43]. Figure 1 presents the search results.
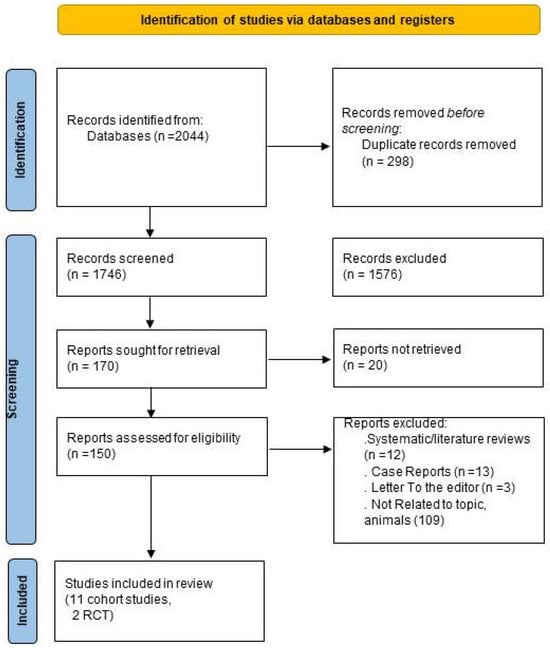
Figure 1.
Flowchart outlining the protocol adopted in this systematic review.
3.1. Methodological Quality Assessment Results
All thirteen studies [31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43] underwent evaluation for methodological quality. Regarding the cohort studies [31,32,33,34,35,37,38,40,41,42,43]: the number of items present in each study ranged from 7 [31,37,41,42] to 10 [32] out of a possible total of 11, with an average of 7.57. Each study included details on item 11. Only one study [42] addressed item 10, while the others lacked strategies for managing incomplete follow-up. All studies reported on items 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, and 11. Five studies did not meet the criteria for item 1 [31,37,41,42,43]. Regarding the two RCTs [36,39], all items were recorded, except for items 4 and 5 [36,39] and item 6 in one study [39]. A summary of the methodology quality assessment for the cohort studies is presented in Table 2.

Table 2.
Methodology quality evaluation of the cohort studies by the Joanna Briggs Institute Critical Appraisal Tool.
3.2. Study Selection and Characteristics
Nine studies compared groups of patients under bDMARDs [31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,43]. Four studies compared RA under bDMARDs and RA without bDMARDs [39,40,41,42]. Among the studies included in our systematic review, two enrolled healthy control groups [38,39]. The studies were published between 2016 [41] and 2024 [32,33]. They were conducted in the United States [31,32,33,37,40,42], Italy [36], Japan [38,43], Egypt [39], Germany [34], and the UK [41]. Eight studies utilized national registry data [31,32,33,34,35,37,40,41]. The study design was reported in all studies [31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43]. Three designs were employed: a prospective design with repeated measures (n = 4) [31,33,34,38], a retrospective descriptive design (n = 7) [32,35,37,40,41,42,43], and a randomized controlled trial (RCT) (n = 2) [36,39]. Eleven studies reported the follow-up duration [31,32,33,34,35,37,39,40,41,42,43], which ranged from 1 [31] to 11 [37] years. All the studies mentioned the number of enrolled patients (39 to 153,788) [36,40] and the number of patients in the subgroup [31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43]. Eleven studies reported the patient’s age, which ranged from 42.04 ± 6.7 [34] to 73.7 ± 5.9 [35]. Respiratory comorbidities were reported in two studies [31,32], cardiovascular risk factors in two other studies [33,34], type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) in three studies [35,36,37], anemia in three additional studies [37,38,39,40], and malignancy in three further studies [41,42,43]. The biologic drugs studied were TNFis [31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43], ABA [31,35,37,40,42,43], TCZ [32,33,35,37,38,40,42,43], ANA [35,36], and RTX [35,37,40,41,42]. In one study [42], bDMARDs other than TNFis were not specified. Table 3 exposes the main characteristics and methodological points of the retained studies.

Table 3.
The main characteristics and results of the selected studies aiming to evaluate the effects of biologic drugs on comorbidity outcomes in RA.
4. bDMARD Impact on Comorbidities
4.1. bDMARD Impact on Respiratory Comorbidities
There were two studies [31,32] identifying RA patients with pulmonary comorbidities: interstitial lung disease (ILD), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and asthma. Patients were initiated on ABA or a TNF inhibitor (Adalimumab (ADA), Etanercept (ETA), Certolizumab Pegol (CTZ), Golimumab (GLM), or Infliximab (IFX)) [31,32]. Exacerbations requiring inpatient or emergency department visits occurred frequently after ABA or TNFi initiation, with no significant difference in the risk of ILD, COPD, or asthma exacerbation between the two treatments. RA-ILD patients treated with ABA may face a higher risk of mortality and mechanical ventilation compared to those receiving TNFis, especially among specific subgroups such as younger patients, those with cardiovascular risk factors, and ACPA-positive individuals [32].
4.2. bDMARD Impact on Cardiovascular Comorbidities
Two cohort studies investigated the effect of bDMARDs on cardiovascular comorbidities [33,34]. One examined the impact of bDMARDs on lipid changes, specifically LDL-C levels [33], while the other focused on the incidence of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACEs) [34].
- -
- The first study concluded that TCZ increased LDL-C levels, and this increase was independent of clinical response. The Framingham score increased only with TCZ; however, risk scores remained stable across all biologics [33]. Moreover, despite the lipid increase associated with bDMARDs, there was no corresponding rise in cardiovascular risk, as indicated by the Reynolds Risk Score (RRS) [33]. The second study [29] found that JAK inhibitors (JAKis), bDMARDs, and conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (csDMARDs) did not increase the risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACEs) compared to TNFis [34].
4.3. bDMARD Impact on Diabetes
Three studies investigated the effect of bDMARDs on T2DM [35,36,37]: two cohort studies (n = 2) [35,37] and one RCT (n = 1) [36]. One study aimed to examine the impact of bDMARDs on T2DM-related consequences or complications [35]. Another study examined their effects on HbA1c%, and the remaining research examined their impact on treatment intensification [37]. The treatments assessed were TNFis (n = 3 studies) [35,36,37] and ANA (n = 2) [35,36]. RTX, TCZ, and ABA were investigated in two studies [35,37]. Sarilumab (a fully human anti-interleukin 6 (IL-6) receptor monoclonal IgG1 antibody) and Baricitinib (a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor) were examined in one study [35]. One study enrolled patients aged 65 years or older [35]. Patients switched to or initiating ABA as their first targeted disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (tDMARD) experienced directionally lower rates and costs of T2DM-related complications compared to patients switching to or initiating other tDMARDs [35]. ANA significantly reduced the HbA1c% level, while TNFi treatment did not [36]. There is no difference between ABA and TNFis, RTX, or TCZ regarding switching or the intensification of diabetes treatment [37].
4.4. bDMARD Impact on Anemia
Three studies dealt with anemia in RA patients [38,39,40]. Anemia was present at the index date in all patients in one study [39]. It was present in only 66% of patients in one study [38] and varied between 21 and 29% (according to the subgroups) in the remaining study [40]. Two studies examined the serum hepcidin-25 level and the hemoglobin (Hb) level after treatment with biologics [38,39], while one study considered only the Hb level [40]. Only one study specified that the authors investigated only anemia of chronic disease (ACD) [39]. The two other studies investigated anemia of different etiologies [38,40]. One study compared the impact of TCZ versus TNFi on anemia [38], another study compared the effect of ETN versus ADA [39], and the third study compared the effect of TCZ versus Tofacitinib or other bDMARDs [40]. Two studies enrolled a healthy control group [39]. All studies concluded that bDMARDs significantly increase Hb levels [38,39,40]. TNFis and TCZ improve anemia within 2 weeks [38]. The serum hepcidin level significantly decreases in patients treated with TNFis [5,6] and TCZ [38]. TCZ has shown the best results in improving anemia [38,40]. The decrease in serum hepcidin-25 levels in patients treated with TNFis was accompanied by a reduction in the serum IL-6 level [38].
A dramatic decrease in serum hepcidin-25 levels was observed after 4 months in patients treated with ETA or ADA, combined with methotrexate, and a significant improvement in anemia was noted (p < 0.05) [39].
4.5. bDMARD Impact on Solid Tumors
Three studies investigated the impact of bDMARDs on solid tumors [41,42,43]. They were cohort studies. One study examined the effect of bDMARDs on overall survival [42]. The two other studies examined the rate of incident malignancy (new primaries, local recurrences, and metastases) [41,43]. TNFis (without further specification) and RTX were investigated in two studies [41,42]. ETA, ADA, CTZ, GLM, ABA, and TCZ were studied in one study [42]. ABA was studied in one study [43]. Patients with RA and prior malignancy on TNFis or RTX did not have an increased risk of future incident malignancy [41]. ABA was as effective and safe in RA patients with and without a history of malignancy [43].
There was no significant difference in overall survival among RA patients treated with bDMARDs [42,43]. The use of TNFis was associated with improved survival, although the results were not statistically significant [42]. However, patients receiving non-TNFi agents had a 10% greater hazard compared with patients who did not receive any bDMARDs. The landmark analysis at 2—and 3-year time points after a cancer diagnosis shows numerically greater hazards in patients who received a bDMARD compared with patients who did not [42].
5. Discussion
This systematic review aimed to evaluate the effects of bDMARDs on specific comorbidities in patients with RA, including respiratory, metabolic, hematologic, and malignancy-related conditions. Our review indicated that bDMARDs were generally considered safe and effective for managing RA symptoms. Still, their impact on comorbidities required caution, as it varied based on the specific drug and the patient’s comorbidity profile.
We included 13 studies. According to the JBI critical appraisal tool, the methodological quality of the selected studies was considered “good,” with a mean score of 7.57 items. Although most studies have enrolled a large sample size of patients, the non-inclusion of a healthy control group in the majority of the studies [31,35,37,38,40,41,42,43] can be considered as a bias since the variations in the assessed parameters cannot be exclusively attributed to bDMARDs. In addition, due to the ‘real-life’ study design [31,35,37,38,40,41,42,43], the ongoing use of other medications, such as corticosteroids and methotrexate, could affect the outcome, as confounding factors were not exhaustively assessed (not all potential confounding factors were identified). Open design and unplanned interim analysis are more prone to bias than a double-blind controlled trial. Moreover, as most studies relied on diagnostic codes for patient assessment, there remains a potential risk of outcome misclassification. Another source of confusion is that treatments were prescribed based on clinical judgment in most cohort studies. Patients treated with one bDMARD were likely to differ from those treated with another bDMARD in multiple respects. As a result, comparisons between patients receiving different treatment regimens may be confounded by factors such as disease severity and baseline risk of the outcomes of interest. Unfortunately, meta-analyses were impossible due to the heterogeneous nature of the studies for each factor.
5.1. bDMARDs and Pulmonary Comorbidities
Regarding our review, only two studies assessed the impact of bDMARDs (TNFis and ABA) on pulmonary comorbidities [31,32]. The first one included RA patients with ILD, COPD, and asthma and found that pulmonary exacerbations were common among these patients, especially in the COPD group, regardless of the bDMARDs (ABA or TNFi) [31].
The other study focused on patients with RA-ILD and reported that ABA may be associated with a higher risk of mortality and mechanical ventilation compared to TNFis, particularly in specific subgroups such as younger patients, individuals with cardiovascular risk factors, and those who are ACPA-positive [32].
Biologic therapies in RA exhibit varying influences on pulmonary involvement, especially interstitial lung disease (ILD), a common and potentially serious extra-articular manifestation of the disease. TNFis have been associated with both new-onset and worsening ILD, although the evidence for a direct causal relationship remains inconclusive. In contrast, agents such as rituximab and ABA have shown a more favorable pulmonary safety profile, with reports indicating stabilization or even improvement in respiratory function. Tocilizumab presents mixed outcomes, with documented cases of both improvement and progression of ILD [44]. Some studies have reported increased mortality in patients with RA-ILD treated with TNF inhibitors (TNFis), raising concerns about the benefit–risk balance of this therapeutic class in such patients [45,46]. However, these studies have significant biases, warranting a reassessment of TNFi use in RA-ILD in light of ongoing scientific research.
Although less frequently reported than anti-TNF agents, Abatacept has been associated with both improvement and worsening of interstitial lung disease in patients with rheumatoid arthritis [47,48,49,50,51,52]. Case reports and small series suggest a relatively safer pulmonary profile, but exacerbations can still occur [53].
Rituximab has been the subject of encouraging therapeutic trials in interstitial lung diseases associated with other autoimmune conditions [54,55]. Additionally, four uncontrolled studies specifically involving RA-ILD patients (n = 133) demonstrated improvements in FVC and DLCO after the initiation of rituximab [56,57,58].
Some randomized controlled trials have been conducted to evaluate the efficacy of TNFis in treating COPD [59] or asthma [40], but most have not demonstrated any efficacy [59,60,61]. There may be confounding factors, particularly related to a history of smoking, the duration or severity of RA, and the severity of baseline lung conditions.
In clinical practice, the management of RA patients with pulmonary involvement requires an individualized approach to biologic therapy, guided by the nature and extent of interstitial lung disease, its progression, and associated comorbidities. Close collaboration between rheumatologists and pulmonologists plays a key role in developing effective treatment plans and reducing the risk of respiratory adverse effects. International societies such as the EULAR (European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology) and the ACR (American College of Rheumatology) have not yet issued specific recommendations regarding the management of rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease (RA-ILD). However, the French Society of Rheumatology (Société Française de Rhumatologie, SFR) has provided clear guidance on this matter: “When a targeted synthetic DMARD (tDMARD) is needed in a patient with RA-ILD, abatacept or rituximab should be preferred, due to their more favorable pulmonary safety profile” [62].
5.2. bDMARDs and Cardiovascular Comorbidities
The effective control of disease activity by bDMARDs suggests a potential role of these agents in reducing cardiovascular risk [63]. However, the impact of bDMARDs on cardiovascular manifestations remains a topic of increasing interest. Several studies suggest that anti-TNF therapy may affect cardiovascular outcomes in patients with autoimmune diseases [64]. A recent review highlighted the dual nature of these effects: while anti-TNF agents generally offer a protective effect against cardiovascular events in this population, their use, particularly at high doses, in patients with pre-existing heart failure or a history of myocardial infarction may be ineffective or potentially harmful [65].
Additionally, clinical trials testing Etanercept in heart failure patients, such as RENAISSANCE and RECOVER, were prematurely terminated due to the lack of favorable effects on events, with a trend towards a deleterious impact in RENAISSANCE [66].
In this review, among the two enrolled studies, one examined the impact of bDMARDs on lipid changes, specifically LDL-C levels [33], while the other focused on the incidence of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACEs) [34].
In the first study, Tocilizumab was associated with increased LDL-C levels, regardless of the clinical response. However, the increase in lipid levels related to bDMARD treatment was not found to be linked to an increased CVD risk by the RRS. The latter remained stable across biologics. In contrast, Framingham’s score increased only with Tocilizumab [19]. It is well recognized that increases in serum total cholesterol, HDL-C, LDL-C, and triglyceride levels accompany tocilizumab administration. This has led to the recommendation of monitoring its use, particularly in patients with dyslipidemia and high CV risk.
The second study evaluated four treatments: JAKis (baricitinib, filgotinib, tofacitinib, or upadacitinib), TNFis (adalimumab, certolizumab, etanercept, golimumab, or infliximab), other bDMARDs (abatacept, rituximab, sarilumab, or tocilizumab), and csDMARDs [34]. This study provided real-world evidence that the incidence of MACEs in patients with RA was similar across all groups [34]. However, adverse cardiovascular events were not stratified in the other bDMARD group. Thus, the impact of Tocilizumab was not evaluated separately.
In summary, while anti-TNF therapy has shown benefits in treating inflammatory diseases, its effects on cardiovascular health are complex and may vary depending on the patient’s underlying cardiovascular condition. Tocilizumab should be avoided in patients with a high CV risk.
5.3. bDMARDs and Diabetes
We included three studies evaluating the impact of bDMARDs on diabetes [35,36,37], all of which reported a beneficial effect.
Patients receiving biologic therapies (ABA, TNFi, RTX, TCZ) did not require modification or intensification of their antidiabetic treatment, which may suggest that these therapies do not adversely affect glycemic control [37]. On the contrary, bDMARDs such as Anakinra significantly reduced HbA1c levels [36]. ABA was associated with lower rates and costs of T2DM-related complications than other TDMARDs [35].
Biologic DMARDs have been reported to have beneficial effects on glucose metabolism, including reductions in glucose and insulin levels, as well as significant improvements in the HbA1c percentage [67]. Other authors have reported a beneficial effect of an IL-1 inhibitor (in RA patients with T2D) on the HbA1c rate, confirming that Anakinra could improve insulin secretion [68,69]. Furthermore, clinical studies have demonstrated that IL-1 inhibitors and TNF inhibitors improve glucose metabolism through their anti-inflammatory actions [68]. A recent hypothesis suggests that ABA treatment may directly influence glucose metabolism by increasing insulin sensitivity [67]. Indeed, RA patients treated with ABA, compared to those treated with TNFi, had a lower risk of incident diabetes mellitus [67]. Evidence suggests that inhibiting T cell costimulation reduces the effect of T cells in adipose tissues and improves regulatory T cell function, which is thought to improve insulin sensitivity [70]. Moreover, observational reports have shown improvements in HbA1c% in RA patients treated with TCZ [71,72], supporting the preclinical evidence of IL-6’s key role in inflammation and metabolism [73]. Thus, ANA and ABA should be preferred in RA patients with T2DM.
5.4. bDMARDs and Anemia
While both TNFis and TCZ were associated with decreased serum hepcidin-25 levels and a significant improvement in anemia, the effects were more pronounced with TCZ [39]. The decrease in serum hepcidin-25 levels in patients treated with TNFis is accompanied by a reduction in the serum IL-6 level [38]. These findings suggest that IL-6 suppression may contribute to the improvement in anemia.
The findings of this review align with those of Doyle et al. [73]. Indeed, the authors, through a pooled analysis of three large, multicenter, double-blind, randomized clinical trials, concluded that treatment with IFX plus MTX significantly improved hemoglobin levels among anemic RA patients compared to treatment with placebo plus MTX, regardless of disease activity improvement [74].
According to the studies, the prevalence of anemia in RA patients ranges from 30 to 70% [75,76]. CDA and iron deficiency anemia are considered the most common [77]. Treatments with anti-cytokine agents such as IFX, TCZ, and ANA have been shown to significantly decrease serum Hb levels in RA patients [78,79,80,81,82]. Indeed, TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1 are thought to contribute to RA-anemia development by modulating iron metabolism and suppressing bone marrow erythropoiesis [82,83,84], particularly by affecting the serum hepcidin level.
In a recent meta-analysis, the authors demonstrated that RA patients with anemia have higher serum hepcidin levels than those without anemia (SMD = 0.400, 95% CI = 0.080 to 0.720, p = 0.014) [85]. Indeed, hepcidin, a type II acute protein, is an inflammatory mediator produced in response to inflammatory cytokines such as interleukin-6 [86,87]. Its expression is regulated by inflammation, anemia, and hypoxia [88]. In addition to its inflammatory action, it modulates the iron-regulating hormone by binding to the ferroportin iron transporter and inducing its internalization and degradation [89,90].
In summary, TNFis and TCZ should be considered as therapeutic options for RA patients with anemia, with tocilizumab being the preferred agent due to its superior efficacy.
5.5. bDMARD and Solid Tumors
Although the efficacy of bDMARDs has been firmly established, concerns remain regarding their long-term safety, specifically the potential risk of malignancy [91]. Indeed, an increased risk of malignancies, particularly lymphoma, has been reported in some studies [91]. However, this increased risk may be attributable to the underlying chronic disease, the severity of the condition, and the use of concomitant medications.
The putative association between bDMARDs and malignancy is hard to establish given the complex role of cytokines, lymphocytes, and other elements of immune competence in cancer pathogenesis. For instance, TNF-α has both anti- and pro-cancer effects [92]. Similarly, IL-6 directly promotes cancer cell proliferation by activating signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3), which drives cell cycle progression [93].
In this review, all three included studies concluded that bDMARDs are safe [40,41,42]. Patients with RA and prior malignancy on TNFis, RTX, and ABA did not have an increased risk of future incident malignancy [40,42]. ABA was as effective and safe in RA patients with a history of malignancy as in those without [42].
Nevertheless, these results must be interpreted with caution. The median follow-up duration was 6.8 years [40]. Thus, the rate of IM could be increased with a longer follow-up duration. Furthermore, the small number of each type of IM does not allow for the analysis of specific cancer risks. Another limitation is that various potential confounding factors could be a source of bias: patients’ baseline characteristics, the disease activity (which may be responsible for an underlying inflammation, leading to malignant transformation), the primitive cancer type and extension, and factors associated with prior cancer that led to a decision not to start a biologic in certain patients [40].
Regarding ABA, an international, up to 10-year observational safety study assessed the incidence of malignancy in four real-world data sources: two bDMARD registries (the Anti-Rheumatic Therapy in Sweden register and the Rheumatoid Arthritis Observation of Biologic Therapy German registry), a disease registry (The National Databank for Rheumatic Diseases in the USA), and an administrative health claims database (the population-based British Columbia Canadian RA Cohort [94].
The authors demonstrated that ABA was not associated with a significantly increased overall cancer risk compared to cs/b/tsDMARDs, (breast cancer or lung cancer). However, the Swedish registry showed a significantly increased risk of lymphoma with ABA vs. b/tsDMARDs. Recently, the EULAR Task Force formulated five overarching principles and eight points to consider before the initiation of targeted therapies in patients with inflammatory arthritis and a history of cancer [95]. In patients with cancer in remission, targeted therapy should not be delayed. However, if the tumor is not in remission and the RA is active, a shared decision-making process is necessary between the patient, rheumatologist, and oncologist. The EULAR TASK Force recommended targeted therapy, depending on the clinical context. B-cell-depleting therapy may be preferred in patients with a history of lymphoma, while TNFis may be preferred in patients with a history of solid cancer. JAKis and ABA should only be considered in the absence of other therapeutic alternatives, due to the lack of data regarding their safety in patients with a history of malignancy.
5.6. bDMARD Impact on Osteoporosis and Depression
RA is often complicated by comorbidities such as osteoporosis and depression, which impair quality of life, complicate management, and worsen functional prognosis [96,97]. The direct impact of biologics on these comorbidities remains poorly documented. We conducted a targeted review based on the PICO criteria, which did not identify any articles that strictly met these criteria. However, several publications provide indirect, valuable evidence for understanding these comorbidities in RA.
- a.
- Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a frequent comorbidity in RA, driven by chronic systemic inflammation, reduced mobility, and long-term glucocorticoid use. In a systematic review and meta-analysis using Mendelian randomization, Ji et al. [96] investigated genetic determinants of bone mineral density and fracture risk. Although not RA-specific, this study highlights the multifactorial nature of osteoporosis, suggesting that therapeutic control of inflammation alone, such as with biologics, may not be sufficient to mitigate bone loss fully. These findings reinforce the importance of incorporating targeted osteoporosis prevention strategies into the overall care of RA patients.
- b.
- Depression
Biologic therapies, particularly TNFis, have been extensively studied for their impact on depression in patients with RA. Evidence suggests that TNFis may reduce the risk of depression by controlling inflammation, which is known to contribute to depressive symptoms in RA [97]. However, some reports indicate that the initiation or switching of biologic therapies can be associated with increased psychological distress and the use of antidepressants, reflecting a complex and variable effect on mental health [98]. Specifically, etanercept has been shown to have a more favorable profile regarding depression risk compared to infliximab [99]. Additionally, biologics improve quality of life and psychological well-being in RA patients [100]. Social support further enhances these outcomes, highlighting the importance of integrating psychosocial care into RA management [101]. Despite these findings, our PICO-based literature search found no studies directly addressing the impact of biologic therapies on osteoporosis and depression outcomes in RA, revealing a significant gap for future research.
5.7. Potential Role of Genetic and Ethnic Variability in Treatment Response and Safety Profile
The response to biologic therapies, such as TNF inhibitors, rituximab, and tocilizumab, varies significantly according to patients’ genetic backgrounds. Polymorphisms in Fc gamma receptors, notably FCGR3A F158V and FCGR2A R131H, influence treatment efficacy by modulating systemic inflammation, a key factor in reducing cardiovascular and metabolic risks [102,103]. Genotype-guided therapy holds promise for optimizing both articular and systemic outcomes. In parallel, epigenetic modifications contribute to the persistence of chronic inflammation by activating synovial fibroblasts and immune cells, thereby accelerating the progression of comorbidities. Biologic agents that target these pathways may indirectly help mitigate complications such as atherosclerosis and osteoporosis [104]. However, no single biomarker has yet proven reliable in predicting the therapeutic response to anti-TNF agents or their impact on associated comorbidities. This underscores the importance of multi-marker strategies for truly personalized treatment approaches [105]. Moreover, ethnicity-related genetic variations influence both the efficacy and safety of biologics. Specific allelic variants—more prevalent in Asian or Caucasian populations—can partly explain the interethnic differences in treatment response and adverse effects, including susceptibility to infections. Therefore, integrating genetic and ethnic factors into clinical decision-making is crucial for optimizing therapeutic outcomes and reducing risk [102,103].
Integrating genetic, epigenetic, and clinical data can enhance personalized medicine approaches, improving the control of both RA symptoms and associated comorbidities, thereby enhancing patient quality of life [106].
To the author’s knowledge, no previous systematic review has focused on the effect of bDMARDs on RA comorbidities. We demonstrated that bDMARDs may enable the therapeutic targeting of both disorders (RA and some comorbidities), and using a single agent may help manage both inflammatory and metabolic diseases. However, this result should be interpreted cautiously, given that only thirteen studies were included in this systematic review.
6. Limitations
This review has several limitations. We explicitly acknowledge a key limitation of our review: it was necessarily constrained by the current literature’s availability of evidence. While our selection of comorbidities was systematic and guided by EULAR recommendations and existing data, many other potential comorbidities were not evaluated due to a lack of available studies. This absence reflects a gap in the literature rather than a limitation of our search strategy. Moreover, most included studies were cohort studies, introducing potential selection bias in prescribing bDMARDs. In addition, there were considerable differences in sample sizes and the proportions of bDMARD users across studies; notably, three studies [34,36,38] had small sample sizes, which limited their ability to detect significant associations. Third, most studies compared biological drugs without a control group, which may have introduced bias in the findings. Additionally, this review only covered four types of comorbidities, as studies meeting our inclusion criteria were not available for other conditions. While these findings offer valuable insights, they should be confirmed by rigorous RCTs. However, such trials are challenging to conduct due to ethical and funding constraints and the need for extended follow-up periods.
7. Conclusions
Our systematic review highlights the complexities of managing rheumatoid arthritis in patients with multiple comorbidities, underscoring the importance of a personalized therapeutic approach tailored to individual needs. Identifying and consistently monitoring comorbidities before and during RA treatment is critical to improving patient outcomes. This study suggests that bDMARDs can be carefully chosen depending on individual comorbidities, potentially providing dual advantages in addressing both RA and related illnesses such as anemia and diabetes. Our findings support a tailored approach that takes into account both the inflammatory and metabolic elements of RA, as well as its comorbidities:
- ABA may stabilize or even improve lung function. It should not be systematically avoided in patients with interstitial lung disease associated with RA (ILD-RA). It remains a valid treatment option alongside TNF inhibitors, anti-CD20, and IL-6 inhibitors, depending on the patient’s clinical profile.
- ABA and, to a lesser extent, anakinra, may have beneficial effects on glucose metabolism and could help reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. However, these findings need further confirmation through large-scale controlled studies.
- Despite its impact on lipid profiles, TCZ has not been consistently associated with increased cardiovascular events. It may be considered in patients with high cardiovascular risk, provided close monitoring is implemented.
- TNFis and TCZ should be considered in patients with anemia, with TCZ being the preferred agent due to its superior efficacy.
- Targeted therapies should not be delayed in patients with cancer in remission. In active RA with ongoing malignancy, treatment should follow shared decision-making. In patients with a history of malignancy in remission, anti-CD20 is recommended for prior lymphoma and TNFis for solid tumors, while JAK inhibitors and abatacept should only be considered for cases lacking safer alternatives.
More rigorous RCTs are needed to address the existing gaps and enhance therapeutic decision-making. These studies should focus on comorbidity-related outcomes, employ standardized measures, and provide robust evidence to refine treatment guidelines, particularly for patients with complex comorbidity profiles. Additionally, further research is needed to better elucidate the effects of biologic therapies on a broader range of comorbidities.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.B. and H.S.; methodology, S.B., H.İ.C., I.D. and M.H.; investigation, M.A., K.Z., S.R. (Safa Rahmouni), I.G. and R.I.M.; software, M.H. and N.B.; visualization, R.D. and S.R. (Safa Rahmouni); writing—original draft preparation, S.B., R.D., S.R. (Safa Rahmouni), H.İ.C., M.H., M.A., K.Z., I.D., S.R. (Sonia Rekik), N.B., I.G., R.I.M. and H.S.; writing—review and editing; S.B., R.D., S.R. (Safa Rahmouni), H.İ.C., M.H., M.A., K.Z., I.D., S.R. (Sonia Rekik), N.B., I.G., R.I.M. and H.S.; supervision, H.İ.C. and I.D.; Funding acquisition, R.I.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The protocol was registered using the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO), with the corresponding reference number (CRD42022345903) on 11 July 2022.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were generated.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
List of Abbreviations
| ABA | Abatacept |
| ANA | Anakinra |
| ACR/EULAR | American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism |
| ADA | Adalimumab |
| bDMARDS | Biologic Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs |
| csDMARDs | Conventional Synthetic Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs |
| JAKi | Janus Kinase Inhibitor |
| CDA | Chronic Disease Anemia |
| COPD | Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease |
| ETA | Etanercept |
| GLM | Golimumab |
| Hb | Hemoglobin |
| IFX | Infliximab |
| ILD | Interstitial Lung Disease |
| IL6Ri | Interleukin 6 Receptor Inhibitor |
| JBI | Joanna Briggs Institute |
| MTX | Methotrexate |
| PICOS | Population, Intervention, Comparison, Outcomes, and Study Design |
| PRISMA | Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses |
| RA | Rheumatoid Arthritis |
| RCT | Randomized Controlled Trial |
| RTX | Rituximab |
| TCZ | Tocilizumab |
| tDMARDs | Targeted Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs |
| TNFi | Tumor Necrosis Factor Inhibitor |
| T2DM | Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus |
| UK | United Kingdom |
References
- Dhahri, R.; Mejri, I.; Ghram, A.; Dghaies, A.; Slouma, M.; Boussaid, S.; Metoui, L.; Gharsallah, I.; Ayed, K.; Moatemri, Z.; et al. Assessment Tools for Pulmonary Involvement in Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis: Is Diaphragmatic Ultrasonography Correlated to Spirometry? J. Multidiscip. Healthc. 2023, 16, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smolen, J.S.; Aletaha, D.; McInnes, I.B. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 2016, 388, 2023–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Vollenhoven, R.F. Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: State of the art 2009. Nature reviews. Rheumatology 2009, 5, 531–541. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Reino, J.J.; Rodríguez-Lozano, C.; Campos-Fernández, C.; Montoro, M.; Sanmartí, R.; Belmonte-Serrano, M.Á. Abatacept: Mechanism of action and concordance with the rheumatoid arthritis synovial profile. Reumatol. Clin. 2012, 8 (Suppl. S2), 3–7. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Bishri, J.; Attar, S.; Bassuni, N.; Al-Nofaiey, Y.; Qutbuddeen, H.; Al-Harthi, S.; Subahi, S. Comorbidity profile among patients with rheumatoid arthritis and the impact on prescriptions trend. Clin. Med. Insights Arthritis Musculoskelet. Disord. 2013, 6, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabay, C. Cytokine inhibitors in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2002, 2, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabay, C. IL-1 inhibitors: Novel agents in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2000, 9, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, J.R.; Singh, J.A. Use of biologics in rheumatoid arthritis: Current and emerging paradigms of care. Clin. Ther. 2011, 33, 679–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choy, E.H.; Panayi, G.S. Cytokine pathways and joint inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 907–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donath, M.Y. Targeting inflammation in the treatment of type 2 diabetes: Time to start. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2014, 13, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Olivo, M.A.; Tayar, J.H.; Martinez-Lopez, J.A.; Pollono, E.N.; Cueto, J.P.; Gonzales-Crespo, M.R.; Fulton, S.; Suarez-Almazor, M.E. Risk of malignancies in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with biologic therapy: A meta-analysis. JAMA 2012, 308, 898–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.A.; Cameron, C.; Noorbaloochi, S.; Cullis, T.; Tucker, M.; Christensen, R.; Ghogomu, E.T.; Coyle, D.; Clifford, T.; Tugwell, P.; et al. Risk of serious infection in biological treatment of patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 2015, 386, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klareskog, L.; van der Heijde, D.; de Jager, J.P.; Gough, A.; Kalden, J.; Malaise, M.; Martín Mola, E.; Pavelka, K.; Sany, J.; Settas, L.; et al. Therapeutic effect of the combination of etanercept and methotrexate compared with each treatment alone in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: Double-blind randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2004, 363, 675–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaujoux-Viala, C.; Smolen, J.S.; Landewé, R.; Dougados, M.; Kvien, T.K.; Mola, E.M.; Scholte-Voshaar, M.; van Riel, P.; Gossec, L. Current evidence for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: A systematic literature review informing the EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 69, 1004–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramiro, S.; Sepriano, A.; Chatzidionysiou, K.; Nam, J.L.; Smolen, J.S.; van der Heijde, D.; Dougados, M.; van Vollenhoven, R.; Bijlsma, J.W.; Burmester, G.R.; et al. Safety of synthetic and biological DMARDs: A systematic literature review informing the 2016 update of the EULAR recommendations for management of rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 1101–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraenkel, L.; Bathon, J.M.; England, B.R.; St Clair, E.W.; Arayssi, T.; Carandang, K.; Deane, K.D.; Genovese, M.; Huston, K.K.; Kerr, G.; et al. 2021 American College of Rheumatology Guideline for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Care Res. 2021, 73, 924–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 10, 89. [Google Scholar]
- Eriksen, M.B.; Frandsen, T.F. The impact of patient, intervention, comparison, outcome (PICO) as a search strategy tool on literature search quality: A systematic review. J. Med. Libr. Assoc. 2018, 106, 420–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, P.C.; Atzeni, F.; Balsa, A.; Gossec, L.; Müller-Ladner, U.; Pope, J. The key comorbidities in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A narrative review. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kłodziński, Ł.; Wisłowska, M. Comorbidities in rheumatic arthritis. Reumatologia 2018, 56, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, E.H.; Jin, Y.; Brill, G.; Lewey, J.; Patorno, E.; Desai, R.J.; Kim, S.C. Comparative cardiovascular risk of abatacept and tumor necrosis factor inhibitors in patients with rheumatoid arthritis with and without diabetes mellitus: A multidatabase cohort study. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2018, 7, e007393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, J.F.; England, B.R.; Mikuls, T.R.; Sayles, H.; Cannon, G.W.; Sauer, B.C.; George, M.D.; Caplan, L.; Michaud, K. Obesity, Weight Loss, and Progression of Disability in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Care Res. 2018, 70, 1740–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galushko, E.A. The clinical significance of hepcidin detection in the patients with anemia and rheumatoid arthritis. Klin. Med. 2014, 92, 21–27. [Google Scholar]
- Matcham, F.; Rayner, L.; Steer, S.; Hotopf, M. The prevalence of depression in rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Rheumatology 2013, 52, 2136–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappas, D.A.; Nyberg, F.; Kremer, J.M.; Lampl, K.; Reed, G.W.; Horne, L.; Ho, M.; Onofrei, A.; Malaviya, A.N.; Rillo, O.L.; et al. Prevalence of cardiovascular disease and major risk factors in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A multinational cross-sectional study. Clin. Rheumatol. 2018, 37, 2331–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.T.; Kwon, S.R.; Jung, J.Y.; Kim, H.A.; Kim, S.S.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, J.M.; Park, J.H.; Suh, C.H. Prevalence and Fracture Risk of Osteoporosis in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Multicenter Comparative Study of the FRAX and WHO Criteria. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dougados, M.; Soubrier, M.; Antunez, A.; Balint, P.; Balsa, A.; Buch, M.H.; Casado, G.; Detert, J.; El-Zorkany, B.; Emery, P.; et al. Prevalence of comorbidities in rheumatoid arthritis and evaluation of their monitoring: Results of an international, cross-sectional study (COMORA). Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 73, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steen, K.S.; Nurmohamed, M.T.; Visman, I.; Heijerman, M.; Boers, M.; Dijkmans, B.A.; Lems, W.F. Decreasing incidence of symptomatic gastrointestinal ulcers and ulcer complications in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2008, 67, 256–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Checklist for Cohort Studies, Critical Appraisal Tools. Available online: https://jbi.global/critical-appraisal-tools (accessed on 10 January 2025).
- Checklist for Randomized Controlled Studies, Critical Appraisal Tools. Available online: https://jbi.global/critical-appraisal-tools (accessed on 10 January 2025).
- Kang, E.H.; Jin, Y.; Desai, R.J.; Liu, J.; Sparks, J.A.; Kim, S.C. Risk of exacerbation of pulmonary comorbidities in patients with rheumatoid arthritis after initiation of abatacept versus TNF inhibitors: A cohort study. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2020, 50, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, P.C.; Lai, C.C.; Zou, Q.H.; Wang, S.I.; Huang, X.Y.; Wei, J.C. Abatacept versus tumor necrosis factor inhibitors on mortality and medical utilizations in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis associated interstitial lung disease: A large-scale real-world retrospective cohort study. Clin. Exp. Med. 2024, 24, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappas, D.A.; Reed, G.; Kane, K.; Curtis, R.J.; Charles-Schoeman, C.; Giles, J.T.; Kremer, M.J. Effect of biologic agents and inflammation on lipid levels and cardiovascular risk in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2024, 68, 152504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meissner, Y.; Schäfer, M.; Albrecht, K.; Kekow, J.; Zinke, S.; Tony, H.P.; Strangfeld, A. Risk of major adverse cardiovascular events in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with conventional synthetic, biologic and targeted synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: Observational data from the German RABBIT register. RMD Open 2023, 9, e003489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, V.; Pulungan, Z.; Shah, A.; Jones, B.; Petrilla, A.; Ferri, L.; Han, X.; Michaud, K. Diabetes-Related Complications and Costs in Medicare Beneficiaries with Comorbid Rheumatoid Arthritis and Diabetes Treated with Abatacept Versus Other Targeted DMARDs. Rheumatol. Ther. 2022, 9, 1091–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruscitti, P.; Masedu, F.; Alvaro, S.; Airò, P.; Battafarano, N.; Cantarini, L.; Cantatore, F.P.; Carlino, G.; D’ABrosca, V.; Frassi, M.; et al. Anti-interleukin-1 treatment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and type 2 diabetes (TRACK): A multicentre, open-label, randomised controlled trial. PLoS Med. 2019, 16, e1002901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.K.; Lee, H.; Jin, Y.; Liu, J.; Kim, S.C. Use of biologic or targeted-synthetic disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs and risk of diabetes treatment intensification in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and diabetes mellitus. Rheumatol. Adv. Pract. 2020, 4, rkaa027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.N.; Iwahashi, M.; Tomosugi, N.; Uno, K.; Yamana, J.; Yamana, S.; Isobe, T.; Ito, H.; Kawabata, H.; Yoshizaki, K. Comparative evaluation of the effects of treatment with tocilizumab and TNF-α inhibitors on serum hepcidin, anemia response and disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2013, 15, R141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Zaida, M.H.; El morsya, S.; Rageha, E.M.; Shahbab, A.; Gaberc, A.R. The effectiveness of etanercept and adalimumab on anemia of chronic disease and serum hepcidin in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, a comparative study. Egypt. Rheumatol. 2018, 40, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.K.; Montvida, O.; Best, J.H.; Gale, S.; Pethoe-Schramm, A.; Sarsour, K. Effectiveness of Biologic and Non-biologic Antirheumatic Drugs on Anaemia Markers in 153,788 Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: New Evidence from Real-World Data. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2018, 47, 478–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva-Fernández, L.; Lunt, M.; Kearsley-Fleet, L.; Watson, K.D.; Dixon, W.G.; Symmons, D.P.M.; Hyrich, K.L. The incidence of cancer in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and a prior malignancy who receive TNF inhibitors or rituximab: Results from the British Society for Rheumatology Biologics RegisterRheumatoid Arthritis. Rheumatology 2016, 55, 20332039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pundole, X.; Zamora, N.V.; Siddhanamatha, H.; Lin, H.; Tayar, J.; Leung, C.H.; Li, L.; Suarez-Almazo, M.E. Overall survival in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and solid malignancies receiving biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic therapy. Clin. Rheum. 2020, 39, 2943–2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunishita, Y.; Ichikawa, K.; Uzawa, Y.; Mitsuhashi, M.; Yoshioka, Y.; Okubo, T.; Nagaoka, S. Efficacy and safety of abatacept in patients with rheumatoid arthritis with previous malignancy. Ther. Adv. Musculoskelet. Dis. 2023, 15, 1759720X231186874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrington, R.; Harkins, P.; Conway, R. Targeted Therapy in Rheumatoid-Arthritis-Related Interstitial Lung Disease. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 6657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Álvarez, R.; Pérez-de-Lis, M.; Díaz-Lagares, C.; Pego-Reigosa, J.M.; Retamozo, S.; Bove, A.; Brito-Zeron, P.; Bosch, X.; Ramos-Casals, M. Interstitial lung disease induced or exacerbated by TNF-targeted therapies: Analysis of 122 cases. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 41, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mena-Vázquez, N.; Rojas-Giménez, M.; Romero-Barco, C.M.; Manrique-Arija, S.; Francisco, E.; Aguilar-Hurtado, M.C.; Añón-Oñate, I.; Pérez-Albaladejo, L.; Ortega-Castro, R.; Godoy-Navarrete, F.J.; et al. Predictors of progression and mortality in patients with prevalent rheumatoid arthritis and interstitial lung disease: A prospective cohort study. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Songcharoen, S.; Cleary, J.D.; Jenkins, J.; DeShazo, M. T. asahii pulmonary infection as a complication of TNF-inhibitor and steroids: Posaconazole pharmacotherapy and risk analysis. J. Miss. State Med. Assoc. 2011, 52, 339–343. [Google Scholar]
- Hewitt, R.; Farne, H.; Ritchie, A.; Luke, E.; Johnston, S.L.; Mallia, P. The role of viral infections in exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma. Ther. Adv. Respir. Dis. 2016, 10, 158–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curtis, J.R.; Yang, S.; Patkar, N.M.; Chen, L.; Singh, J.A.; Cannon, G.W.; Mikuls, T.R.; Delzell, E.; Saag, K.G.; Safford, M.M.; et al. Risk of hospitalized bacterial infections associated with biologic treatment among US veterans with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Care Res. 2014, 66, 990–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, H.; Xie, F.; Delzell, E.; Levitan, E.B.; Chen, L.; Lewis, J.D.; Saag, K.G.; Beukelman, T.; Winthrop, K.L.; Baddley, J.W.; et al. Comparative Risk of Hospitalized Infection Associated with Biologic Agents in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Enrolled in Medicare. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016, 68, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, H.; Xie, F.; Delzell, E.; Chen, L.; Levitan, E.B.; Lewis, J.D.; Saag, K.G.; Beukelman, T.; Winthrop, K.; Baddley, J.W.; et al. Risk of hospitalised infection in rheumatoid arthritis patients receiving biologics following a previous infection while on treatment with antiTNF therapy. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 1065–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinblatt, M.; Combe, B.; Covucci, A.; Aranda, R.; Becker, J.C.; Keystone, E. Safety of the selective costimulation modulator abatacept in rheumatoid arthritis patients receiving background biologic and nonbiologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: A oneyear randomized, placebo-controlled study. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2006, 54, 2807–2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Díaz, C.; Castañeda, S.; Melero-González, R.B.; Ortiz-Sanjuán, F.; Juan-Mas, A.; Carrasco-Cubero, C.; Casafont-Solé, I.; Olivé, A.; Rodríguez-Muguruza, S.; Almodóvar-González, R.; et al. Abatacept in interstitial lung disease associated with rheumatoid arthritis: National multicenter study of 263 patients. Rheumatology 2020, 59, 3906–3916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maher, T.M.; Tudor, V.A.; Saunders, P.; A Gibbons, M.; Fletcher, S.V.; Denton, C.P.; Hoyles, R.K.; Parfrey, H.; A Renzoni, E.; Kokosi, M.; et al. Rituximab versus intravenous cyclophosphamide in patients with connective tissue disease-associated interstitial lung disease in the UK (RECITAL): A double-blind, double-dummy, randomised, controlled, phase 2b trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2023, 11, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mankikian, J.; Caille, A.; Reynaud-Gaubert, M.; Agier, M.-S.; Bermudez, J.; Bonniaud, P.; Borie, R.; Brillet, P.-Y.; Cadranel, J.; Court-Fortune, I.; et al. Rituximab and mycophenolate mofetil combination in patients with interstitial lung disease (EVER-ILD): A double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Eur. Respir. J. 2023, 61, 2202071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Md Yusof, M.Y.; Kabia, A.; Darby, M.; Lettieri, G.; Beirne, P.; Vital, E.M.; Dass, S.; Emery, P. Effect of rituximab on the progression of rheumatoid arthritis-related interstitial lung disease: 10 years’ experience at a single centre. Rheumatology 2017, 56, 1348–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, B.; Cordeiro, A.; Paiva-Lopes, M.J. Rituximab revisited: Successful management of severe childhood atopic dermatitis. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2019, 29, 94–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narváez, J.; Robles-Pérez, A.; Molina-Molina, M.; Vicens-Zygmunt, V.; Luburich, P.; Yañez, M.A.; Alegre, J.J.; Nolla, J.M. Real-world clinical effectiveness of rituximab rescue therapy in patients with progressive rheumatoid arthritis-related interstitial lung disease. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2020, 50, 902–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matera, M.G.; Calzetta, L.; Cazzola, M. TNF-alpha inhibitors in asthma and COPD: We must not throw the baby out with the bath water. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 23, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, D.; Brightling, C. TNF-alpha antagonism in severe asthma? Recent. Pat. Inflamm. Allergy Drug Discov. 2010, 4, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parulekar, A.D.; Boomer, J.S.; Patterson, B.M.; Yin-Declue, H.; Deppong, C.M.; Wilson, B.S.; Jarjour, N.N.; Castro, M.; Green, J.M. A randomized controlled trial to evaluate inhibition of T-cell costimulation in allergen-induced airway inflammation. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 187, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fautrel, B.; Kedra, J.; Juge, P.-A.; Rempenault, C.; Drouet, J.; Avouac, J.; Baillet, A.; Brocq, O.; Alegria, G.C.; Constantin, A.; et al. Recommendations and metaanalyses 2024 update of the recommendations of the French Society of Rheumatology for the diagnosis and management of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Jt. Bone Spine 2024, 91, 105790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meissner, Y.; Zink, A.; Kekow, J.; Rockwitz, K.; Liebhaber, A.; Zinke, S.; Gerhold, K.; Richter, A.; Listing, J.; Strangfeld, A. Impact of disease activity and treatment of Comorbidities on the risk of myocardial infarction in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2016, 18, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padfield, G.J.; Din, J.N.; Koushiappi, E.; Mills, N.L.; Robinson, S.D.; Le May Cruden, N.; Lucking, A.J.; Chia, S.; A Harding, S.; E Newby, D. Cardiovascular effects of tumour necrosis factor α antagonism in patients with acute myocardial infarction: A first in human study. Heart 2013, 99, 1330–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.Y.; Huang, X.B.; Yang, G.M.; Zhao, S. TNF inhibitors associated with cardiovascular diseases and cardiometabolic risk factors: A Mendelian randomization study. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2023, 27, 8556–8578. [Google Scholar]
- Dufresne, L.; Dufresne, M. Les anti-TNF et le cardiologue. Cardiol. Pract. 2017, 15, 45–50. [Google Scholar]
- Desai, R.J.; Dejene, S.; Jin, Y.; Liu, J.; Kim, S.C. Comparative risk of diabetes mellitus in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with biological drugs or synthetic drugs to alter the disease: A cohort study. ACR Open Rheumatol. 2020, 2, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berchtold, L.A.; Prause, M.; Størling, J.; Mandrup-Poulsen, T. Cytokines and Pancreatic β-Cell Apoptosis. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2016, 75, 99–158. [Google Scholar]
- Ruscitti, P.; Cipriani, P.; Di Benedetto, P.; Liakouli, V.; Berardicurti, O.; Carubbi, F.; Ciccia, F.; Alvaro, S.; Triolo, G.; Giacomelli, R. Monocytes from patients with rheumatoid arthritis and type 2 diabetes mellitus display an increased production of interleukin (IL)-1beta via the nucleotide-binding domain and leucine-rich repeat containing family pyrin 3 (NLRP3)-inflammasome activation: A possible implication for therapeutic decision in these patients. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2015, 182, 35–44. [Google Scholar]
- Paquot, N.; Castillo, M.J.; Lefèbvre, P.J.; Scheen, A.J. No increased insulin sensitivity after a single intravenous administration of a recombinant human tumor necrosis factor receptor: Fc fusion protein in obese insulin-resistant patients. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2000, 85, 1316–1319. [Google Scholar]
- Ursini, F.; Russo, E.; Ruscitti, P.; Giacomelli, R.; De Sarro, G. The effect of non-TNF-targeted biologics and small molecules on insulin resistance in inflammatory arthritis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2018, 17, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristiansen, O.P.; Mandrup-Poulsen, T. Interleukin-6 and diabetes: The good, the bad, or the indifferent? Diabetes 2005, 54, S114–S124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, M.K.; Rahman, M.U.; Han, C.; Han, J.; Giles, J.; Bingham, C.O., III; Bathon, J. Treatment with infliximab plus methotrexate improves anemia in patients with rheumatoid arthritis independent of improvement in other clinical outcome measures-a pooled analysis from three large, multicenter, double-blind, randomized clinical trials. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 39, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, N.E. The anaemia of chronic disorders: A bag of unsolved questions. Scand. J. Haematol. 1983, 31, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeters, H.R.; Jongen-Lavrencic, M.; Raja, A.N.; Ramdin, H.S.; Vreugdenhil, G.; Breedveld, F.C.; Swaak, A.J. Course and characteristics of anaemia in patients with rheumatoid arthritis of recent onset. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1996, 55, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahle, M. Anemia in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Z. Rheumatol. 2012, 71, 864–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maini, R.; St Clair, E.W.; Breedveld, F.; Furst, D.; Kalden, J.; Weisman, M.; Smolen, J.; Emery, P.; Harriman, G.; Feldmann, M.; et al. For the ATTRACT Group: Infliximab (chimeric anti-tumour necrosis factor α monoclonal antibody) versus placebo in rheumatoid arthritis patients receiving concomitant methotrexate: A randomised phase III trial. Lancet 1999, 354, 1932–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinarello, C.A. The many worlds of reducing interleukin-1. Arthritis Rheum. 2005, 52, 1960–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimoto, N.; Hashimoto, J.; Miyasaka, N.; Yamamoto, K.; Kawai, S.; Takeuchi, T.; Murata, N.; van der Heijde, D.; Kishimoto, T. Study of active controlled monotherapy used for rheumatoid arthritis, an IL-6 inhibitor (SAMURAI): Evidence of clinical and radiographic benefit from an x ray reader-blinded randomised controlled trial of tocilizumab. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2007, 66, 1162–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smolen, J.S.; Beaulieu, A.; Rubbert-Roth, A.; Ramos-Remus, C.; Rovensky, J.; Alecock, E.; Woodworth, T.; Alten, R.; OPTION Investigators. Effect of interleukin-6 receptor inhibition with tocilizumab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (OPTION study): A double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomised trial. Lancet 2008, 371, 987–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voulgari, P.V.; Kolios, G.; Papadopoulos, G.K.; Katsaraki, A.; Seferiadis, K.; Drosos, A.A. Role of cytokines in the pathogenesis of anemia of chronic disease in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Immunol. 1999, 92, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Means, R.T., Jr.; Dessypris, E.N.; Krantz, S.B. Inhibition of human colony-forming-unit erythroid by tumor necrosis factor requires accessory cells. J. Clin. Investig. 1990, 86, 538–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masson, C. Rheumatoid anemia. Jt. Bone Spine 2011, 78, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xu, W.; Yang, H.; Shao, M.; Xu, S.; Deng, J.; Gao, X.; Liu, H.; Shuai, Z.; Xu, Z.; et al. Serum Levels of Hepcidin in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Its Correlation with Disease Activity and Anemia: A Meta-analysis. Immunol. Investig. 2021, 50, 243–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemeth, E.; Valore, E.V.; Territo, M.; Schiller, G.; Lichtenstein, A.; Ganz, T. Hepcidin, a putative mediator of anemia of inflammation, is a type II acute-phase protein. Blood 2003, 101, 2461–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, N.C. Anemia of inflammation: The cytokine-hepcidin link. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 113, 1251–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolas, G.; Chauvet, C.; Viatte, L.; Danan, J.L.; Bigard, X.; Devaux, I.; Beaumont, C.; Kahn, A.; Vaulont, S. The gene encoding the iron regulatory peptide hepcidin is regulated by anemia, hypoxia, and inflammation. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 110, 1037–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Domenico, I.; Ward, D.M.; Langelier, C.; Vaughn, M.B.; Nemeth, E.; Sundquist, W.I.; Ganz, T.; Musci, G.; Kaplan, J. The molecular mechanism of hepcidin-mediated ferroportin down-regulation. Mol. Biol. Cell 2007, 18, 2569–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geerts, I.; Vermeersch, P.; Joosten, E. Evaluation of the first commercial hepcidin ELISA for the differential diagnosis of anemia of chronic disease and iron deficiency anemia in hospitalized geriatric patients. ISRN Hematol. 2012, 2012, 567491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nemeth, E.; Tuttle, M.S.; Powelson, J.; Vaughn, M.B.; Donovan, A.; Ward, D.M.; Ganz, T.; Kaplan, J. Hepcidin regulates cellular iron efflux by binding to ferroportin and inducing its internalization. Science 2004, 306, 2090–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, B.; Basyal, B.; Sarao, M.S.; Nookala, V.; Thein, Y. Prevalence of Cancer in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Epidemiological Study Based on the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES). Cureus 2020, 12, e7870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balkwill, F. TNF-alpha in promotion and progression of cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2006, 25, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Tanaka, T.; Narazaki, M.; Kishimoto, T. Targeting Interleukin-6 Signaling in Clinic. Immunity 2019, 50, 1007–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simona, T.A.; Suissab, S.; Boersc, M.; Hochbergd, M.C.; Skovrona, M.L.; Asklinge, J.; Michaudf, K.; Strangfeldh, A.; Pedrog, S.; Frisell, T. Malignancy outcomes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with abatacept and other disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: Results from a 10-year international post-marketing study. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2024, 64, 152240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sebbag, E.; Lauper, K.; Molina-Collada, J.; Aletaha, D.; Askling, J.; Gente, K.; Bertheussen, H.; Bitoun, S.; Bolek, E.C.; Burmester, G.R.; et al. 2024 EULAR points to consider on the initiation of targeted therapies in patients with inflammatory arthritis and a history of cancer. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2025, 84, 388–397. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, W.; Pan, B.; Chen, X.; Lao, Z.; Yang, W.; Qian, Y. Mendelian randomization studies of risk and protective factors for osteoporosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Endocrinol. 2025, 15, 1486188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, A.; Dwibedi, N.; LeMasters, T.; Hornsby, J.A.; Wei, W.; Sambamoorthi, U. Tumor necrosis factor inhibitor therapy and the risk for depression among working-age adults with rheumatoid arthritis. Am. Health Drug Benefits 2019, 12, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eslami, A.; Allami, P.; KamaliZonouzi, S.; Ravanbakhsh, M.; Razi, S.; Yazdanpanah, N.; Rezaei, N. Prevalence of anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder during the COVID-19 lockdown in patients with rheumatoid arthritis or systemic lupus erythematosus: A systematic review. BMC Psychiatry 2025, 25, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Yan, W.; Su, R.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; Li, Z.; Qin, D.; Peng, J. Research progress on rheumatoid arthritis-associated depression. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2023, 16, 992223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizaj, D.; Kelmendi, A. Quality of life, depression, and psychological distress among patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with biologics. Cureus 2024, 16, e72384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coyle, N.; Kuit, S.; Dunne, S. Investigating the association between social support and quality of life in people with rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review of the literature. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2025, 28, e70234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.H.; Song, G.G. Association between the functional FCGR3A F158V and FCGR2A R131H polymorphisms and responsiveness to biologics in rheumatoid arthritis patients: A meta-analysis. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2023, 26, 1295–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sofi, R.F.; Bergmann, M.S.; Nielsen, C.H.; Andersen, V.; Skov, L.; Loft, N. The Association between Genetics and Response to Treatment with Biologics in Patients with Psoriasis, Psoriatic Arthritis, Rheumatoid Arthritis, and Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makkar, R.; Sehgal, A.; Singh, S.; Sharma, N.; Rawat, R.; Rashid, S.; Vargas-De-La-Cruz, C.; Yadav, S.; Bungau, S.G.; Behl, T. Current trends in epigenetic, cellular and molecular pathways in management of rheumatoid arthritis. Inflammopharmacology 2023, 31, 1577–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wientjes, M.H.M.; den Broeder, A.A.; Welsing, P.M.J.; Verhoef, L.M.; Bemt, B.J.F.v.D. Prediction of response to anti-TNF treatment using laboratory biomarkers in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review. RMD Open 2022, 8, e002570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakeel, L.; Shaukat, A.; Khaliq, N.; Kashif, A.M.; Mujeeb, A.M.; Adnan, Z.M.; Taj, J.M.; Akilimali, A. Rheumatoid arthritis: A comprehensive overview of genetic markers, emerging therapies, and personalized medicine. Ann. Med. Surg. 2025, 87, 696–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).