Characterizing Spinal Decompression for Foot Drop Caused by Lumbar Degenerative Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Cohorts
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Search Strategy and Resources
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Outcomes
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
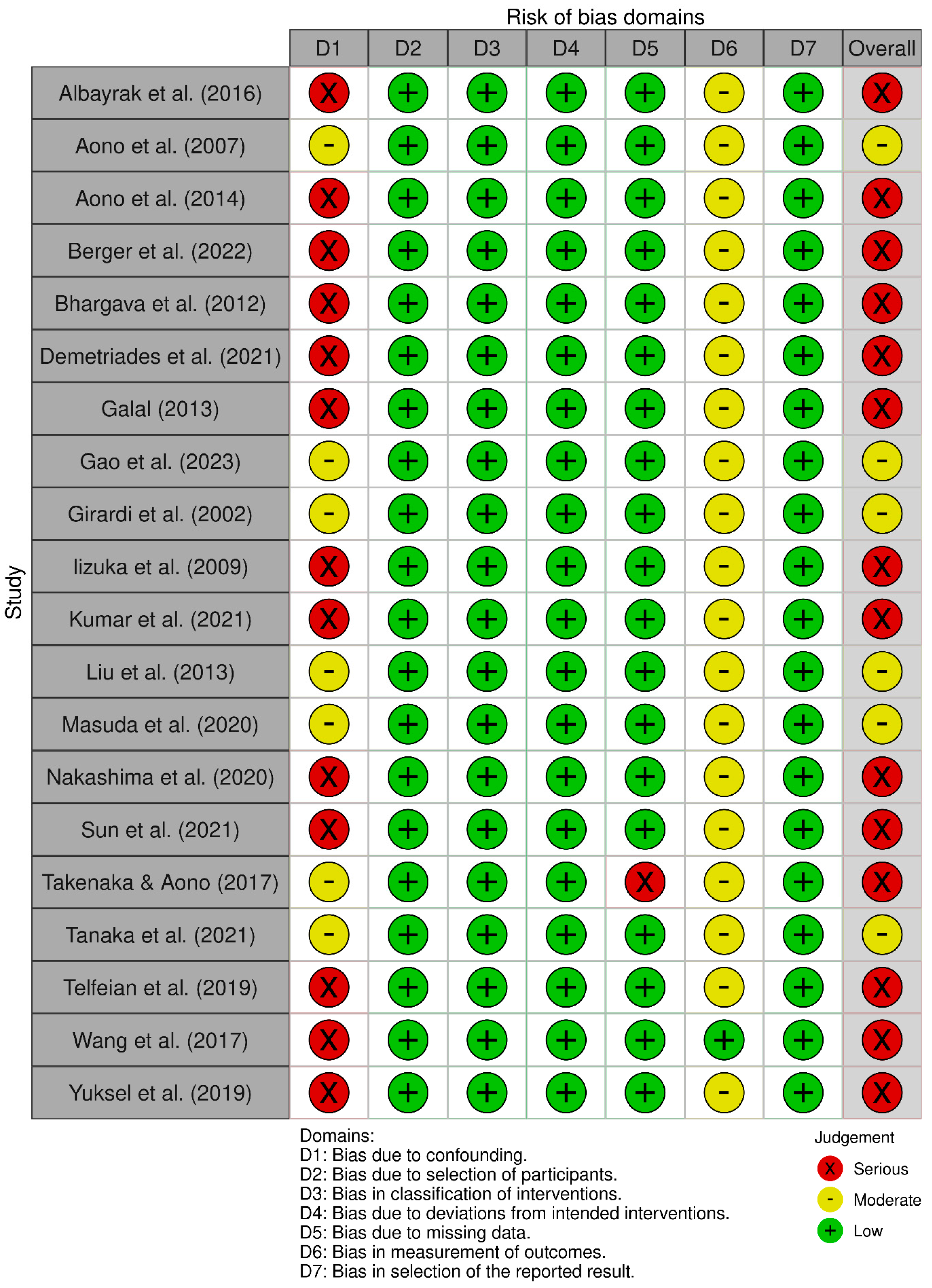
3.1. Risk of Bias
3.2. Preoperative Characteristics
3.3. Postoperative Outcomes
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CI | Confidence Interval |
| CT | Computed Tomography |
| LDD | Lumbar Degenerative Diseases |
| LDH | Lumbar Disc Herniation |
| LSS | Lumbar Spinal Stenosis |
| MRC | Medical Research Council |
| MMT | Manual Muscle Test |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| PRISMA | Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses |
| RCT | Randomized Controlled Trials |
| ROBINS-I | Risk Of Bias In Non-randomized Studies-of Interventions |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| VAS | Visual Analogue Scale |
References
- Song, S.Y.; Nam, D.C.; Moon, D.K.; Lee, D.Y.; Lee, E.C.; Kim, D.H. Surgical decompression timing for patients with foot drop from lumbar degenerative diseases: A meta-analysis. Eur. Spine J. 2022, 31, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girardi, F.P.; Cammisa, F.P., Jr.; Huang, R.C.; Parvataneni, H.K.; Tsairis, P. Improvement of preoperative foot drop after lumbar surgery. J. Spinal Disord. Tech. 2002, 15, 490–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, J.; Takamori, Y.; Shiokawa, T.; Shibata, R.; Nobutou, S.; Shirachi, H.; Yamamoto, T. Drop foot due to lumbar degenerative disease: Painless drop foot is difficult to recover. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2021, 206, 106696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakashima, H.; Ishikawa, Y.; Kanemura, T.; Kato, F.; Satake, K.; Ito, K.; Ito, K.; Ando, K.; Kobayashi, K.; Ishiguro, N.; et al. Neurological function following early versus delayed decompression surgery for drop foot caused by lumbar degenerative diseases. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2020, 72, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassel El-Osta, R.W. Concepts in Foot Drop Management- Review of the Current Literature. Acta Sci. Orthop. 2019, 2, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghahreman, A.; Ferch, R.D.; Rao, P.; Chandran, N.; Shadbolt, B. Recovery of ankle dorsiflexion weakness following lumbar decompressive surgery. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2009, 16, 1024–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Nataraj, A. Foot drop resulting from degenerative lumbar spinal diseases: Clinical characteristics and prognosis. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2014, 117, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhargava, D.; Sinha, P.; Odak, S.; Tyagi, A.; Towns, G.; Pal, D. Surgical outcome for foot drop in lumbar degenerative disease. Glob. Spine J. 2012, 2, 125–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.P.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, J.; Sun, Y.P.; An, J.L.; Ding, W.Y. Analysis of the clinical effects of transforaminal endoscopic discectomy on lumbar disk herniation combined with common peroneal nerve paralysis: A 2-year follow-up retrospective study on 32 patients. J. Pain. Res. 2017, 10, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Aono, H.; Nagamoto, Y.; Tobimatsu, H.; Takenaka, S.; Iwasaki, M. Surgical outcomes for painless drop foot due to degenerative lumbar disorders. J. Spinal Disord. Tech. 2014, 27, E258–E261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, F.; Mukherjee, S.; Chaudhuri, K.; Kerry, J.; Ahuja, S.; Pal, D. Prognostic indicators of surgical outcome in painful foot drop: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Spine J. 2021, 30, 3278–3288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baig Mirza, A.; Khizar Khoja, A.; Naidu, V.; Ullah, S.; Plume, J.; Iyer, P.S.; Baig, A.; Rashed, S.; Fayez, F.; Sharma, C.; et al. Prognostic factors and surgical outcomes of foot drop secondary to lumbar degenerative disease: A systematic review and Individual patient data meta-analysis. Eur. Spine J. 2025, 34, 1386–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, S.S.; Barak, G.; Truong, G.; Parker, M.W. Hierarchy of Evidence Within the Medical Literature. Hosp. Pediatr. 2022, 12, 745–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA Statement. Open Med. 2009, 3, e123–e130. [Google Scholar]
- Takenaka, S.; Aono, H. Prediction of Postoperative Clinical Recovery of Drop Foot Attributable to Lumbar Degenerative Diseases, via a Bayesian Network. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2017, 475, 872–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Li, Z.; Li, X.; Rudd, S.; Wang, H.; Gao, Z.; Ding, W.; Yang, S. The treatment effect of posterior lumbar fusion surgery on patients suffering from lumbar disc herniation concurrent with peroneal nerve paralysis. Front. Surg. 2022, 9, 1063528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Zhu, W.; Shi, J.; Jia, L.; Shi, G.; Wang, Y.; Liu, N. Foot drop caused by lumbar degenerative disease: Clinical features, prognostic factors of surgical outcome and clinical stage. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Lin, F.; Jiang, J.; Sun, J.; Shi, J. A Novel Capsule Lumbar Interbody Fusion (CLIF) in Treating Foot Drop due to Lumbar Degenerative Diseases: A Prospective, Observational Study. Pain Res. Manag. 2021, 2021, 6880956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telfeian, A.E.; Oyelese, A.; Fridley, J.; Doberstein, C.; Gokaslan, Z.L. Prognosis for Recovery of Foot Drop after Transforaminal Endoscopic Decompression of Far Lateral Lumbar 5-Sacral 1 Herniated Disc: Case Series. Pain Physician 2019, 22, E97–E103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, S.; Kanba, Y.; Kawai, J.; Ikeda, N. Prognostic Factors for Drop Foot Due to Lumbar Degenerative Diseases: The Impact of Surgical Timing on Postoperative Recovery. Clin. Spine Surg. 2020, 33, 160–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demetriades, A.K.; Mancuso-Marcello, M.; Baig Mirza, A.; Frantzias, J.; Bell, D.A.; Selway, R.; Gullan, R. Acute bilateral foot drop with or without cauda equina syndrome-a case series. Acta Neurochir. 2021, 163, 1191–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.; Jain, N.; Adsul, N.; Acharya, S.; Chahal, R.S.; Kalra, K.L. A Case Series of Acute Painless Bilateral Foot Drop Without Cauda Equina Syndrome. J. Orthop. Case Rep. 2021, 11, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DerSimonian, R.; Laird, N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin. Trials 1986, 7, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.; Thompson, S.G.; Deeks, J.J.; Altman, D.G. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 2003, 327, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cumpston, M.; Li, T.; Page, M.J.; Chandler, J.; Welch, V.A.; Higgins, J.P.; Thomas, J. Updated guidance for trusted systematic reviews: A new edition of the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 10, Ed000142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterne, J.A.; Egger, M. Funnel plots for detecting bias in meta-analysis: Guidelines on choice of axis. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2001, 54, 1046–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aono, H.; Iwasaki, M.; Ohwada, T.; Okuda, S.; Hosono, N.; Fuji, T.; Yoshikawa, H. Surgical outcome of drop foot caused by degenerative lumbar diseases. Spine 2007, 32, E262–E266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, A.; Mangel, L.; Basal, S.; Lidar, Z.; Regev, G.J.; Khashan, M.; Ofir, D.; Salame, K. Predictors of functional recovery following surgery for foot drop due to degenerative lumbar disease. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2022, 36, 408–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galal, A. Determinants of Recovery of Pre-operative Acute and Chronic Foot Drop after Microdiscectomy for Lumbar Disc Herniation. Egypt. J. Neurol. Psychiatry Neurosurg. 2013, 50, 257–264. [Google Scholar]
- Iizuka, Y.; Iizuka, H.; Tsutsumi, S.; Nakagawa, Y.; Nakajima, T.; Sorimachi, Y.; Ara, T.; Nishinome, M.; Seki, T.; Shida, K.; et al. Foot drop due to lumbar degenerative conditions: Mechanism and prognostic factors in herniated nucleus pulposus and lumbar spinal stenosis. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2009, 10, 260–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yüksel, M.O.; Çevik, S. The Effect of Time Elapsed from the Onset of Symptoms to Surgery on Prognosis in Patients with Foot Drop due to Lumbar Disc Hernia. Duzce Med. J. 2019, 21, 177–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albayrak, S.; Ucler, N.; Ayden, O.; Yucetas, C. Prognoses of 42 patients with foot drop caused by lumbar intervertebral disc pathologies. J. Spine Neurosurg. 2016, 5, 4689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Than, C.A.; Valiotis, A.K.; Prottoy, A.R.; Alexander, K.G.; Alogakos, M.; Adra, M.; Smayra, K.; Curtis, T.J.; Kim, G.E.; Nakanishi, H.; et al. Discectomy for Lumbar Disc Herniation in Pediatric and Adolescent Populations: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cureus 2024, 16, e63880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Y.; Liang, L.; Zhao, T.; Shi, H.; Shi, H.; Shi, J.; Shi, G. A meta-analysis of prognostic factors in surgical treatment of foot drop due to lumbar degenerative diseases. World Neurosurg. X 2023, 19, 100214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oosterbos, C.; Rummens, S.; Bogaerts, K.; Hoornaert, S.; Weyns, F.; Dubuisson, A.; Lemmens, R.; Theys, T. Conservative versus surgical treatment of foot drop in peroneal nerve entrapment: Rationale and design of a prospective, multi-centre, randomized parallel-group controlled trial. Trials 2022, 23, 1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carolus, A.E.; Becker, M.; Cuny, J.; Smektala, R.; Schmieder, K.; Brenke, C. The Interdisciplinary Management of Foot Drop. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2019, 116, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.L.; Zhao, X.W.; Ma, J.X.; Li, F.; Wang, Y.; Lu, B. Effectiveness of surgery versus conservative treatment for lumbar spinal stenosis: A system review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Int. J. Surg. 2017, 44, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, J.N.; Zimmerman, Z.E.; Mass, H.; Makhni, M.C. Diagnosis and Management of Lumbar Spinal Stenosis: A Review. JAMA 2022, 327, 1688–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nygaard, O.P.; Kloster, R.; Mellgren, S.I. Recovery of sensory nerve fibres after surgical decompression in lumbar radiculopathy: Use of quantitative sensory testing in the exploration of different populations of nerve fibres. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1998, 64, 120–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Sengupta, D.K. How fast pain, numbness, and paresthesia resolves after lumbar nerve root decompression: A retrospective study of patient’s self-reported computerized pain drawing. Spine 2014, 39, E529–E536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchesini, N.; Ricci, U.M.; Soda, C.; Teli, M. Acute bilateral foot drop due to lumbar disc herniation treated by bilateral interlaminar approach: Case report and literature review. Br. J. Neurosurg. 2023, 37, 899–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, L.; Jiang, X.; Zhao, S.; Guo, W.; You, D. A Comparison of Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques and Standard Open Discectomy for Lumbar Disc Herniation: A Network Meta-analysis. Pain. Physician 2024, 27, E305–E316. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Issack, P.S.; Cunningham, M.E.; Pumberger, M.; Hughes, A.P.; Cammisa, F.P., Jr. Degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis: Evaluation and management. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2012, 20, 527–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vande Kerckhove, M.; d’Astorg, H.; Ramos-Pascual, S.; Saffarini, M.; Fiere, V.; Szadkowski, M. SPINE: High heterogeneity and no significant differences in clinical outcomes of endoscopic foraminotomy vs fusion for lumbar foraminal stenosis: A meta-analysis. EFORT Open Rev. 2023, 8, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issa, T.Z.; Lambrechts, M.J.; Canseco, J.A.; Hilibrand, A.S.; Kepler, C.K.; Vaccaro, A.R.; Schroeder, G.D. Reporting demographics in randomized control trials in spine surgery—We must do better. Spine J. 2023, 23, 642–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Study | Country | Study Design | Patient (n) | M:F | Mean Age (Years) ± SD | Mean Follow-Up (Months) ± SD | Pain Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Albayrak et al. (2016) [32] | Turkey | Retrospective | 42 | 30:2 | 46.70 ± 9.93 | 17.80 ± 14.55 | NR |
| Aono et al. (2014) [10] | Japan | Retrospective | 20 | 12:8 | 52.00 ± 14.25 | 46.80 ± 21.00 | Painless |
| Aono et al. (2007) [27] | Japan | Retrospective | 46 | 27:19 | 56.60 ± 15.75 | 44.43 ± 21.02 | Both |
| Berger et al. (2022) [28] | Israel | Retrospective | 40 | 24:16 | 58.90 ± 17.90 | 62.40 ± 27.60 | Pain |
| Bhargava et al. (2012) [8] | UK | Retrospective | 26 | 15:11 | 48.00 ± 13.50 | NR | Pain |
| Demetriades et al. (2021) [21] | UK | Case series | 7 | 6:1 | 52.10 ± 6.25 | 20.86 ± 27.75 | Pain |
| Galal (2013) [29] | Egypt | Retrospective | 31 | 14:17 | NR | 9.80 ± NR | Both |
| Gao et al. (2023) [16] | China | Retrospective | 87 | 52:35 | 54.00 ± 11.00 | 81.00 ± 24.00 | Pain |
| Girardi et al. (2002) [2] | USA | Retrospective | 55 | 40:15 | 46.80 ± 13.00 | 36.00 ± 31.00 | Pain |
| Iizuka et al. (2009) [30] | Japan | Retrospective | 28 | 16:12 | 55.00 ± 12.75 | 19.80 ± 13.50 | NR |
| Kumar et al. (2021) [22] | India | Case series | 3 | 3:0 | 62.00 ± 7.75 | 1.33 ± 0.25 | Painless |
| Liu et al. (2013) [17] | China | Retrospective | 135 | 62:73 | 55.00 ± 5.25 | 27.60 ± 3.00 | Pain |
| Masuda et al. (2020) [20] | Japan | Retrospective | 87 | 52:35 | 66. 90 ± 14.75 | 20.30 ± 16.50 | Both |
| Nakashima et al. (2020) [4] | Japan | Retrospective | 60 | 38:22 | 54.60 ± 14.25 | 43.20 ± 10.20 | NR |
| Sun et al. (2021) [18] | China | Prospective | 27 | 21:6 | 46.00 ± 10.75 | 19.00 ± 3.75 | Pain |
| Takenaka & Aono (2017) [15] | Japan | Retrospective | 102 | 58:44 | 59.00 ± 17.03 | 30.00 ± 13.33 | Both |
| Tanaka et al. (2021) [3] | Japan | Retrospective | 55 | 37:18 | 61.80 ± 16.25 | 20.30 ± 11.25 | Both |
| Telfeian et al. (2019) [19] | USA | Case series | 5 | 1:4 | 65.60 ± 8.25 | 12.00 ± 0.00 | Pain |
| Wang et al. (2017) [9] | China | Retrospective | 32 | 18:14 | 48.70 ± 8.60 | 24.00 ± 0.00 | Pain |
| Yüksel et al. (2019) [31] | Turkey | Retrospective | 30 | 12:18 | 46.50 ± 13.50 | 0.03 ± 0.00 | NR |
| Proportion | 95% CI | I2 | Included Study Groups (n) | Sample Size (n) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Operative level | |||||
| L1/L2 | <0.01 | <0.01–0.01 | 0% | 17 | 749 |
| L2/L3 | 0.02 | <0.01–0.02 | 16% | 17 | 749 |
| L3/L4 | 0.20 | 0.12–0.60 | 89% | 17 | 749 |
| L4/L5 | 0.79 | 0.72–0.86 | 87% | 17 | 749 |
| L5/S1 | 0.25 | 0.16–0.33 | 90% | 17 | 749 |
| Involved Levels | |||||
| Single-level | 0.73 | 0.63–0.83 | 96% | 20 | 918 |
| Multi-level | 0.27 | 0.17–0.37 | 96% | 20 | |
| Aetiology | |||||
| Disc herniation | 0.79 | 0.72–0.85 | 96% | 19 | 891 |
| Spinal stenosis | 0.22 | 0.15–0.30 | 96% | 19 | 891 |
| Spondylolisthesis | 0.02 | 0.01–0.03 | 31% | 19 | 891 |
| Spondylolysis | 0.01 | <0.01–0.01 | 0% | 19 | 891 |
| Spondylitis | 0.01 | <0.01–0.01 | 0% | 19 | 891 |
| Herniation Grading | |||||
| Bulging | 0.02 | <0.01–0.05 | 0% | 7 | 157 |
| Protrusion/prolapse | 0.47 | 0.04–0.89 | 100% | 7 | 157 |
| Extrusion | 0.19 | 0.06–0.32 | 91% | 7 | 157 |
| Sequestration | 0.24 | 0.09–0.39 | 94% | 7 | 157 |
| Foot Drop Laterality | |||||
| Unilateral | 0.87 | 0.83–0.94 | 92% | 15 | 706 |
| Bilateral | 0.11 | 0.06–0.17 | 92% | 15 | 706 |
| Preoperative Imaging | |||||
| Radiography | 0.26 | −0.05–0.57 | 100% | 9 | 227 |
| CT | 0.16 | −0.09–0.40 | 100% | 9 | 227 |
| MRI | 0.99 | 0.97–1.00 | 0% | 10 | 269 |
| Proportion | 95% CI | I2 | Included Study Groups (n) | Sample Size (n) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Surgical Modality | |||||
| Fenestration | 0.04 | 0.02–0.05 | 82% | 20 | 918 |
| Laminectomy/Laminotomy | 0.06 | 0.03–0.08 | 92% | 20 | 918 |
| Microdiscectomy | 0.20 | 0.10–0.30 | 100% | 20 | 918 |
| Open Discectomy | 0.19 | 0.20–0.24 | 96% | 20 | 918 |
| Spondylolysis Repair | 0.01 | <0.01–0.01 | 0 | 20 | 918 |
| Transforaminal Endoscopic Discectomy | 0.10 | 0.04–0.16 | 99% | 20 | 918 |
| Tubular Discectomy | 0.01 | <0.01–0.03 | 66% | 20 | 918 |
| Unspecified Decompression | 0.14 | −0.08–0.36 | 100% | 20 | 918 |
| Fusion | 0.24 | 0.01–0.46 | 100% | 20 | 918 |
| Proportion | 95% CI | I2 | Included Study Groups (n) | Sample Size (n) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Comorbidities | |||||
| Cauda Equina | 0.04 | 0.01–0.06 | 75% | 16 | 637 |
| Diabetes | 0.04 | 0.02–0.06 | 64% | 16 | 637 |
| Dyslipidaemia | 0.01 | <0.01–0.02 | 0% | 16 | 637 |
| Hypertension | 0.02 | 0.01–0.04 | 47% | 16 | 637 |
| Ischemic Heart Disease | 0.01 | <0.01–0.02 | 0% | 16 | 637 |
| Osteoporosis | 0.01 | <0.01–0.02 | 0% | 16 | 637 |
| Spinal Trauma | 0.01 | <0.01–0.02 | 0% | 16 | 637 |
| Other * | 0.03 | 0.01–0.04 | 65% | 16 | 637 |
| Impairments | |||||
| Gluteus Medius Paralysis | 0.15 | −0.06–0.37 | 100% | 16 | 637 |
| Radiculopathy | 0.48 | 0.24–0.72 | 100% | 16 | 637 |
| Proportion | 95% CI | I2 | Included Study Groups (n) | Sample Size (n) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Preoperative MMT | |||||
| 0–1 | 0.47 | 0.24–0.70 | 99% | 16 | 764 |
| 2–3 | 0.51 | 0.34–0.68 | 97% | 16 | 764 |
| 4 | 0.01 | <0.01–0.02 | 44% | 16 | 764 |
| Postoperative MMT | |||||
| 0–1 | 0.13 | 0.08–0.18 | 88% | 15 | 650 |
| 2–3 | 0.24 | 0.13–0.36 | 95% | 15 | 650 |
| 4–5 (recovery) | 0.60 | 0.44–0.75 | 97% | 20 | 918 |
| Increase of MMT ≥ 1 | 0.82 | 0.76–0.88 | 89% | 18 | 784 |
| No improvement * | 0.18 | 0.12–0.24 | 89% | 17 | 724 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Than, C.A.; Hajeir, M.Y.; Al Darwashi, L.M.; Silnes, K.; Haroon, A.M.; Valiotis, A.K.; Shibib, D.; Khair, Y.J.; Milchem, H.; Iancu, P.; et al. Characterizing Spinal Decompression for Foot Drop Caused by Lumbar Degenerative Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Cohorts. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 4470. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134470
Than CA, Hajeir MY, Al Darwashi LM, Silnes K, Haroon AM, Valiotis AK, Shibib D, Khair YJ, Milchem H, Iancu P, et al. Characterizing Spinal Decompression for Foot Drop Caused by Lumbar Degenerative Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Cohorts. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(13):4470. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134470
Chicago/Turabian StyleThan, Christian A., May Y. Hajeir, Lamees M. Al Darwashi, Kelly Silnes, Aslam Mohamed Haroon, Angelique K. Valiotis, Diana Shibib, Yasmine J. Khair, Hugh Milchem, Persidiu Iancu, and et al. 2025. "Characterizing Spinal Decompression for Foot Drop Caused by Lumbar Degenerative Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Cohorts" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 13: 4470. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134470
APA StyleThan, C. A., Hajeir, M. Y., Al Darwashi, L. M., Silnes, K., Haroon, A. M., Valiotis, A. K., Shibib, D., Khair, Y. J., Milchem, H., Iancu, P., & Dannawi, Z. (2025). Characterizing Spinal Decompression for Foot Drop Caused by Lumbar Degenerative Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Cohorts. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(13), 4470. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14134470





