Advancements and Challenges of Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Electroencephalography in Epilepsy Management
Abstract
1. Introduction
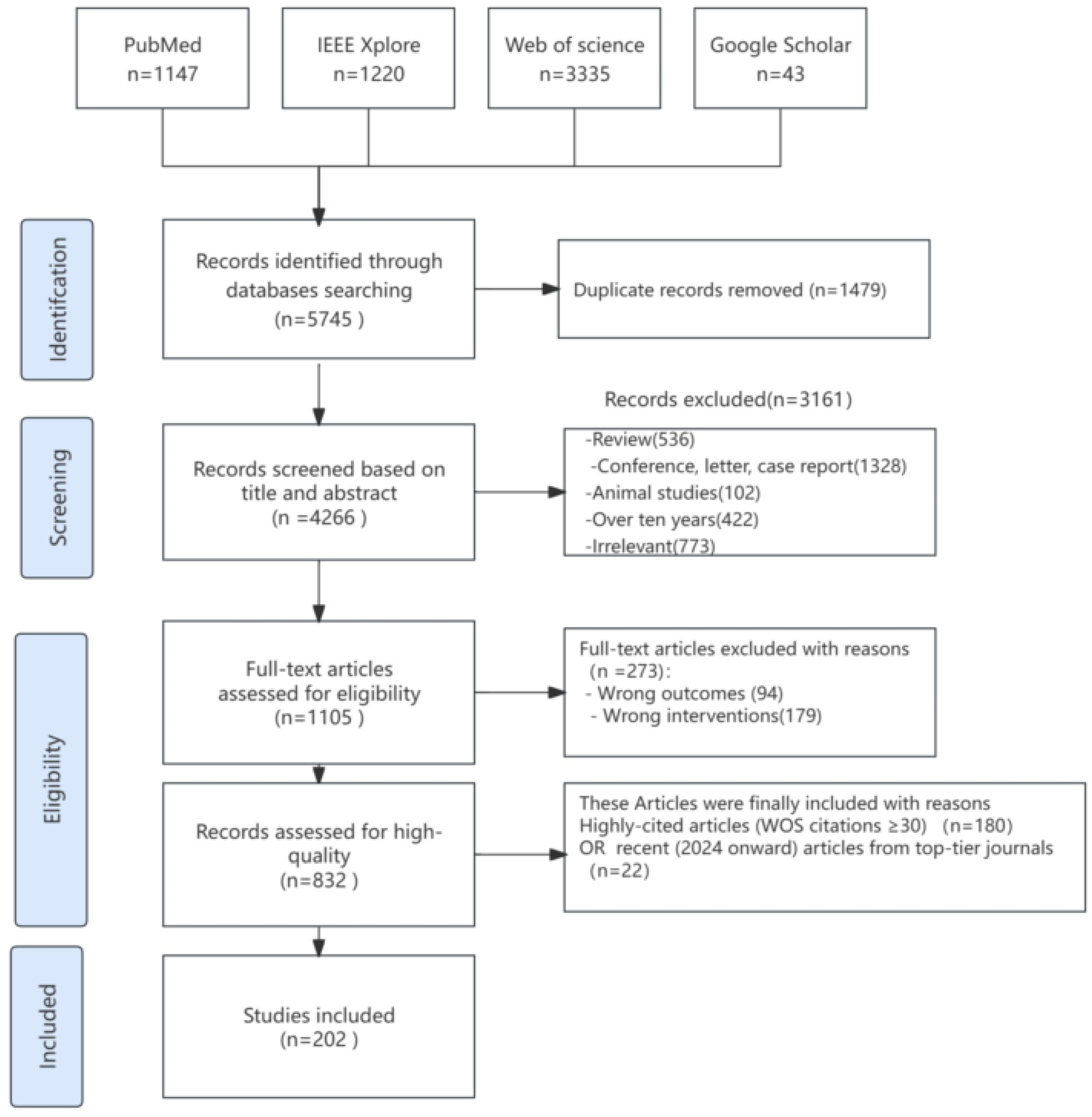
2. Methodology
2.1. Identifying the Research Question
- ① What types of AI models are utilized for EEG analysis in epilepsy?
- ② What are the roles of AI systems in epilepsy management?
- ③ What are the challenges in implementing AI for EEG-driven epilepsy care?
2.2. Search Strategy
2.3. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
- ① Study type: Randomized controlled trials, pilot studies, pre-post trials, quasi-experiments, cross-over trials, observational studies, qualitative studies, and mixed-method studies.
- ② Language: English or Chinese publications.
- ③ Participants: Patients diagnosed with epilepsy.
- ④ Intervention: AI models (e.g., machine learning, deep learning) applied to EEG data for seizure management like seizure detection, prediction.
- ⑤ Outcomes: performance metrics.
- ① Non-eligible publication types: reviews, conference papers, case reports, letters, and animal studies.
- ② Studies older than 10 years.
- ③ Irrelevant topics (e.g., non-AI/EEG applications, non-epilepsy research).
- ④ Full-text unavailable or insufficient methodological details.
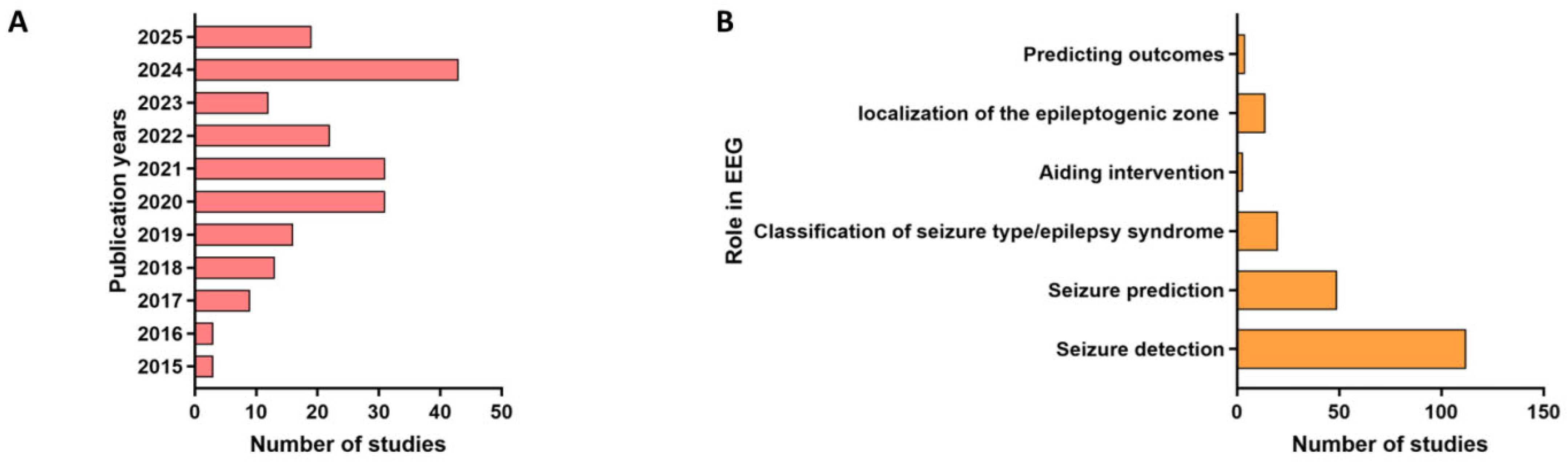
3. Characteristics of the Included Studies
3.1. What Is Artificial Intelligence and How Did It Work?
3.2. Seizure Prediction
3.3. Seizure Detection
3.4. Epileptic Syndrome Classification
3.5. Epilepsy Surgery Planning
3.6. Prognosis and Outcome Prediction
3.7. AI Aiding Closed-Loop Seizure Suppression
4. Challenges of EEG
4.1. Dataset Bias and Representativeness
4.2. External Validation Deficits and Real-World Generalizability: A Notable Issue Is the Variability in Gold Standards
4.3. Research Gap and Ethical Barriers
5. Future Research Directions
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kerr, W.T.; McFarlane, K.N. Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence Applications to Epilepsy: A Review for the Practicing Epileptologist. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2023, 23, 869–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beeraka, S.M.; Kumar, A.; Sameer, M.; Ghosh, S.; Gupta, B. Accuracy Enhancement of Epileptic Seizure Detection: A Deep Learning Approach with Hardware Realization of SIFT. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 2022, 41, 461–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miltiadous, A.; Tzimourta, K.D.; Giannakeas, N.; Tsipouras, M.G.; Glavas, E.; Kalafatakis, K.; Tzallas, A.T. Machine Learning Algorithms for Epilepsy Detection Based on Published EEG Databases: A Systematic Review. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 564–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangarajoo, R.G.; Reaz, M.B.I.; Srivastava, G.; Haque, F.; Ali, S.H.M.; Bakar, A.A.A.; Bhuiyan, M.A.S. Machine Learning-Based Epileptic Seizure Detection Methods Using Wavelet and EMD-Based Decomposition Techniques: A Review. Sensors 2021, 21, 8485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acharya, U.R.; Vinitha Sree, S.; Swapna, G.; Martis, R.J.; Suri, J.S. Automated EEG analysis of epilepsy: A review. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2013, 45, 147–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganaie, M.A.; Kumari, A.; Malik, A.K.; Tanveer, M. EEG signal classification using improved intuitionistic fuzzy twin support vector machines. Neural Comput. Appl. 2024, 36, 163–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Feng, Y.; Zheng, R.; Cui, X.; Zhao, W.; Jiang, T.; Gao, F. Two-Stream Attention 3-D Deep Network-Based Childhood Epilepsy Syndrome Classification. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 72, 2503412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahan, S.; Nowsheen, F.; Antik, M.M.; Rahman, M.S.; Kaiser, M.S.; Hosen, A.S.M.S.; Ra, I.-H. AI-Based Epileptic Seizure Detection and Prediction in Internet of Healthcare Things: A Systematic Review. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 30690–30725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, A.; Revell, A.; Davis, K.A. Artificial intelligence in epilepsy—applications and pathways to the clinic. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2024, 20, 319–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaji, S.S.; Parhi, K.K. Seizure Onset Zone Identification from iEEG: A Review. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 62535–62547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Que, Z.; Lin, C.J. One-Class SVM Probabilistic Outputs. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2024, 36, 6244–6256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adnan, N.; Umer, F. Understanding deep learning—Challenges and prospects. J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 2022, 72 (Suppl. S1), S59–S63. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y.; Ren, Y.; Wong, N.; Ngai, E.C.H. Hyperdimensional Computing with Multiscale Local Binary Patterns for Scalp EEG-Based Epileptic Seizure Detection. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 26046–26061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, W.; Acosta, S.; Kwan, P.; Worrell, G.; Mikati, M.A. Artificial Intelligence: Fundamentals and Breakthrough Applications in Epilepsy. Epilepsy Curr. 2024, 15357597241238526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winterhalder, M.; Maiwald, T.; Voss, H.; Aschenbrenner-Scheibe, R.; Schulze-Bonhage, A.; Timmer, J. Seizure prediction methods: Assessment and comparison of three methods by means of the seizure prediction characteristic. In Quantitative Neuroscience; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2004; pp. 103–116. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Huang, Q.; Chen, F. A review of epilepsy detection and prediction methods based on EEG signal processing and deep learning. Front. Neurosci. 2024, 18, 1468967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, S.M.; Khalid, S.; Akhtar, R.; Bortolotto, Z.; Bashir, Z.; Qiu, H. Using scalp EEG and intracranial EEG signals for predicting epileptic seizures: Review of available methodologies. Seizure 2019, 71, 258–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotman, J. Automatic recognition of epileptic seizures in the EEG. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1982, 54, 530–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zisheng, Z.; Parhi, K.K. Seizure prediction using polynomial SVM classification. In Proceedings of the Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Milan, Italy, 25–29 August 2015; Volume 2015, pp. 5748–5751. [Google Scholar]
- Bandarabadi, M.; Dourado, A.; Teixeira, C.A.; Netoff, T.I.; Parhi, K.K. Seizure prediction with bipolar spectral power features using Adaboost and SVM classifiers. In Proceedings of the Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Osaka, Japan, 3–7 July 2013; Volume 2013, pp. 6305–6308. [Google Scholar]
- Ramgopal, S.; Thome-Souza, S.; Jackson, M.; Kadish, N.E.; Sánchez Fernández, I.; Klehm, J.; Bosl, W.; Reinsberger, C.; Schachter, S.; Loddenkemper, T. Seizure detection, seizure prediction, and closed-loop warning systems in epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav. 2014, 37, 291–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinton, G.E.; Salakhutdinov, R.R. Reducing the dimensionality of data with neural networks. Science 2006, 313, 504–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yochum, M.; Kachenoura, A.; Aud’hui, M.; Kaminska, A.; Nabbout, R.; Wendling, F.; Kuchenbuch, M.; Benquet, P. Deep learning-based early detection of absence seizures in children. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2025, 100, 106845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.; Xu, L.; Zhang, J. A Compact Graph Convolutional Network with Adaptive Functional Connectivity for Seizure Prediction. In IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering: A Publication of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2024; Volume 32, pp. 3531–3542. [Google Scholar]
- Dissanayake, T.; Fernando, T.; Denman, S.; Sridharan, S.; Fookes, C. Deep Learning for Patient-Independent Epileptic Seizure Prediction Using Scalp EEG Signals. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 9377–9388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Liu, J.; Yang, R.; Wang, Y.; Wang, A.; Li, K.; Liu, W.; Yang, C. Exploring the Applicability of Transfer Learning and Feature Engineering in Epilepsy Prediction Using Hybrid Transformer Model. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. Publ. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2023, 31, 1321–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assali, I.; Ghazi Blaiech, A.; Ben Abdallah, A.; Ben Khalifa, K.; Carrère, M.; Hédi Bedoui, M. CNN-based classification of epileptic states for seizure prediction using combined temporal and spectral features. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2023, 82, 104519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugam, S.; Dharmar, S. A CNN-LSTM hybrid network for automatic seizure detection in EEG signals. Neural Comput. Appl. 2023, 35, 20605–20617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeilpour, A.; Tabarestani, S.S.; Niazi, A. Deep learning-based seizure prediction using EEG signals: A comparative analysis of classification methods on the CHB-MIT dataset. Eng. Rep. 2024, 6, e12918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Wang, F.; Min, T.; Zang, T.; Wang, Y. Prediction for High Risk Clinical Symptoms of Epilepsy Based on Deep Learning Algorithm. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 77596–77605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Truong, N.D.; Nikpour, A.; Zhou, L.; Kavehei, O. Epileptic Seizure Classification with Symmetric and Hybrid Bilinear Models. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2020, 24, 2844–2851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nafea, M.S.; Ismail, Z.H. Supervised Machine Learning and Deep Learning Techniques for Epileptic Seizure Recognition Using EEG Signals-A Systematic Literature Review. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffer, I.E.; Berkovic, S.; Capovilla, G.; Connolly, M.B.; French, J.; Guilhoto, L.; Hirsch, E.; Jain, S.; Mathern, G.W.; Moshé, S.L.; et al. ILAE classification of the epilepsies: Position paper of the ILAE Commission for Classification and Terminology. Epilepsia 2017, 58, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, L.; Jain, P.; Nayak, D. Role of Video-EEG in Children. Indian J. Pediatr. 2021, 88, 1007–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascino, G.D. Video-EEG monitoring in adults. Epilepsia 2002, 43 (Suppl. S3), 80–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, W.; Nurse, E.S.; Lambert, E.; Cook, M.J.; Kameneva, T. Classification of Epileptic and Psychogenic Non-Epileptic Seizures Using Electroencephalography and Electrocardiography. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. Publ. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2023, 31, 2831–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo Giudice, M.; Varone, G.; Ieracitano, C.; Mammone, N.; Tripodi, G.G.; Ferlazzo, E.; Gasparini, S.; Aguglia, U.; Morabito, F.C. Permutation Entropy-Based Interpretability of Convolutional Neural Network Models for Interictal EEG Discrimination of Subjects with Epileptic Seizures vs. Psychogenic Non-Epileptic Seizures. Entropy 2022, 24, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo Giudice, M.; Ferlazzo, E.; Mammone, N.; Gasparini, S.; Cianci, V.; Pascarella, A.; Mammì, A.; Mandic, D.; Morabito, F.C.; Aguglia, U. Convolutional Neural Network Classification of Rest EEG Signals among People with Epilepsy, Psychogenic Non Epileptic Seizures and Control Subjects. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 15733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinchliffe, C.; Yogarajah, M.; Tang, L.; Abasolo, D. Electroencephalogram Connectivity for the Diagnosis of Psychogenic Non-epileptic Seizures. In Proceedings of the 2022 44th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC), Glasgow, UK, 11–15 July 2022; pp. 301–304. [Google Scholar]
- Hinchliffe, C.; Yogarajah, M.; Elkommos, S.; Tang, H.; Abasolo, D. Entropy Measures of Electroencephalograms towards the Diagnosis of Psychogenic Non-Epileptic Seizures. Entropy 2022, 24, 1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varone, G.; Boulila, W.; Lo Giudice, M.; Benjdira, B.; Mammone, N.; Ieracitano, C.; Dashtipour, K.; Neri, S.; Gasparini, S.; Morabito, F.C.; et al. A Machine Learning Approach Involving Functional Connectivity Features to Classify Rest-EEG Psychogenic Non-Epileptic Seizures from Healthy Controls. Sensors 2021, 22, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Wang, W.F.; Patnaik, L.M.; Zhang, B.C.; Weng, S.J.; Xiao, S.X.; Wei, D.Z.; Zhou, H.F. Residual and bidirectional LSTM for epileptic seizure detection. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 2024, 18, 1415967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djemal, A.; Kallel, A.Y.; Ouni, C.; El Baccouch, R.; Bouchaala, D.; Kammoun Feki, F.; Charfi Triki, C.; Fakhfakh, A.; Kanoun, O. Fast processing and classification of epileptic seizures based on compressed EEG signals. Comput. Biol. Med. 2024, 184, 109346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinka, E.; Cock, H.; Hesdorffer, D.; Rossetti, A.O.; Scheffer, I.E.; Shinnar, S.; Shorvon, S.; Lowenstein, D.H. A definition and classification of status epilepticus—Report of the ILAE Task Force on Classification of Status Epilepticus. Epilepsia 2015, 56, 1515–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, C.; Schriger, D.; Weingrow, D. Rapid Electroencephalography and Artificial Intelligence in the Detection and Management of Nonconvulsive Seizures. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2024, 84, 422–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez Aldana, Y.; Marañón Reyes, E.J.; Macias, F.S.; Rodríguez, V.R.; Chacón, L.M.; Van Huffel, S.; Hunyadi, B. Nonconvulsive epileptic seizure monitoring with incremental learning. Comput. Biol. Med. 2019, 114, 103434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldana, Y.R.; Hunyadi, B.; Reyes, E.J.M.; Rodriguez, V.R.; Van Huffel, S. Nonconvulsive Epileptic Seizure Detection in Scalp EEG Using Multiway Data Analysis. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2019, 23, 660–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tveit, J.; Aurlien, H.; Plis, S.; Calhoun, V.D.; Tatum, W.O.; Schomer, D.L.; Arntsen, V.; Cox, F.; Fahoum, F.; Gallentine, W.B.; et al. Automated Interpretation of Clinical Electroencephalograms Using Artificial Intelligence. JAMA Neurol. 2023, 80, 805–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, N.; Gao, W.; Li, L.; Chen, J.; Liang, Z.; Yuan, G.; Sun, H.; Liu, Q.; Chen, J.; Jin, L.; et al. vEpiNet: A multimodal interictal epileptiform discharge detection method based on video and electroencephalogram data. Neural Netw. Off. J. Int. Neural Netw. Soc. 2024, 175, 106319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.; Liu, C.; Friedman, D. Artificial intelligence/machine learning for epilepsy and seizure diagnosis. Epilepsy Behav. 2024, 155, 109736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gleason, A.; Richter, F.; Beller, N.; Arivazhagan, N.; Feng, R.; Holmes, E.; Glicksberg, B.S.; Morton, S.U.; La Vega-Talbott, M.; Fields, M.; et al. Detection of neurologic changes in critically ill infants using deep learning on video data: A retrospective single center cohort study. eClinicalMedicine 2024, 78, 102919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.Y.; Larijani, H.; Gibson, R.M.; Liarokapis, D. Random Neural Network Based Epileptic Seizure Episode Detection Exploiting Electroencephalogram Signals. Sensors 2022, 22, 2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albarrak, A. Challenges and Prospects in Epilepsy Monitoring Units: A Comprehensive Review of Logistic Barriers. Cureus 2024, 16, e59559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katyayan, A.; Diaz-Medina, G. Epilepsy: Epileptic Syndromes and Treatment. Neurol. Clin. 2021, 39, 779–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Specchio, N.; Wirrell, E.C.; Scheffer, I.E.; Nabbout, R.; Riney, K.; Samia, P.; Guerreiro, M.; Gwer, S.; Zuberi, S.M.; Wilmshurst, J.M.; et al. International League Against Epilepsy classification and definition of epilepsy syndromes with onset in childhood: Position paper by the ILAE Task Force on Nosology and Definitions. Epilepsia 2022, 63, 1398–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirrell, E.C.; Grossardt, B.R.; Wong-Kisiel, L.C.; Nickels, K.C. Incidence and classification of new-onset epilepsy and epilepsy syndromes in children in Olmsted County, Minnesota from 1980 to 2004: A population-based study. Epilepsy Res. 2011, 95, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Cao, J.; Hu, D.; Wang, T.; Jiang, T.; Gao, F. Regional Scalp EEGs Analysis and Classification on Typical Childhood Epilepsy Syndromes. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Dev. Syst. 2023, 15, 662–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Hu, D.; Lin, P.; Cao, J.; Lai, X.; Wang, T.; Jiang, T.; Gao, F. Deep feature fusion based childhood epilepsy syndrome classification from electroencephalogram. Neural Netw. 2022, 150, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosl, W.J.; Loddenkemper, T.; Nelson, C.A. Nonlinear EEG biomarker profiles for autism and absence epilepsy. Neuropsychiatr. Electrophysiol. 2017, 3, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, P.; Gunnarsdottir, K.M.; Li, A.; Razskazovskiy, V.; Craley, J.; Chandler, A.; Wyeth, D.; Wyeth, E.; Zaghloul, K.A.; Inati, S.K.; et al. Diagnosing Epilepsy with Normal Interictal EEG Using Dynamic Network Models. Ann. Neurol. 2025, 97, 907–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porat Rein, A.; Kramer, U.; Mitelpunkt, A. Development of Ontology for Self-limited Epilepsy with Centrotemporal Spikes and Application of Data Mining Algorithms to Identify New Subtypes. Isr. Med. Assoc. J. 2019, 21, 503. [Google Scholar]
- Nabbout, R.; Kuchenbuch, M.; Tinuper, P.; Cross, J.H.; Wirrell, E. 3D figure of epilepsy syndromes. Epilepsia Open 2023, 8, 217–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, R.; Yao, R.; Jarrar, R.; Buchhalter, J.; Gonzalez, G. Text Classification towards Detecting Misdiagnosis of an Epilepsy Syndrome in a Pediatric Population. AMIA Annu. Symp. Proc. AMIA Symp. 2014, 2014, 1082–1087. [Google Scholar]
- Oğulata, S.N.; Sahin, C.; Erol, R. Neural network-based computer-aided diagnosis in classification of primary generalized epilepsy by EEG signals. J. Med. Syst. 2009, 33, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi-Pooya, A.A.; Brigo, F.; Lattanzi, S.; Blumcke, I. Adult epilepsy. Lancet 2023, 402, 412–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajmirriahi, M.; Rabbani, H. A Review of EEG-based Localization of Epileptic Seizure Foci: Common Points with Multimodal Fusion of Brain Data. J. Med. Signals Sens. 2024, 14, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, C.L.; Chou, C.C.; Chen, H.H.; Chen, Y.H.; Lin, C.F.; Chen, C.; Yu, H.Y.; Chen, Y.W.; Lee, C.C. Frame-based versus robot-assisted stereo-electro-encephalography for drug-resistant epilepsy. Acta Neurochir. 2024, 166, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmedt-Aristizabal, D.; Fookes, C.; Dionisio, S.; Nguyen, K.; Cunha, J.P.S.; Sridharan, S. Automated analysis of seizure semiology and brain electrical activity in presurgery evaluation of epilepsy: A focused survey. Epilepsia 2017, 58, 1817–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.M.; Arski, O.N.; Workewych, A.M.; Donner, E.; Ochi, A.; Otsubo, H.; Snead, O.C., 3rd; Ibrahim, G.M. Detection of high-frequency oscillations in electroencephalography: A scoping review and an adaptable open-source framework. Seizure 2021, 84, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.E.; Triebkorn, P.; Lemarechal, J.-D.; Jha, J.; Woodman, M.; Dollomaja, B.; Vattikonda, A.; Sip, V.; Hashemi, M.; Jirsa, V. Codes: Delineating epileptogenic networks using brain imaging data and personalized modelling in drug-resistant epilepsy. Zenodo 2023, 15, eabp8982. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y.; Sun, B.; Lu, R.; Zhang, C.; Wu, H. A method for detecting high-frequency oscillations using semi-supervised k-means and mean shift clustering. Neurocomputing 2019, 350, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto Ramos, A.; Krishnan, B.; Alexopoulos, A.V.; Bingaman, W.; Najm, I.; Bulacio, J.C.; Serletis, D. Epileptic network identification: Insights from dynamic mode decomposition of sEEG data. J. Neural Eng. 2024, 21, 046061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chybowski, B.; Klimes, P.; Cimbalnik, J.; Travnicek, V.; Nejedly, P.; Pail, M.; Peter-Derex, L.; Hall, J.; Dubeau, F.; Jurak, P.; et al. Timing matters for accurate identification of the epileptogenic zone. Clin. Neurophysiol. Off. J. Int. Fed. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2024, 161, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jrad, N.; Kachenoura, A.; Merlet, I.; Bartolomei, F.; Nica, A.; Biraben, A.; Wendling, F. Automatic Detection and Classification of High-Frequency Oscillations in Depth-EEG Signals. IEEE Trans. Bio-Med. Eng. 2017, 64, 2230–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, M.; Schindler, K.; Goodfellow, M.; Pollo, C.; Rummel, C.; Steimer, A. Evaluating resective surgery targets in epilepsy patients: A comparison of quantitative EEG methods. J. Neurosci. Methods 2018, 305, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimbalnik, J.; Klimes, P.; Sladky, V.; Nejedly, P.; Jurak, P.; Pail, M.; Roman, R.; Daniel, P.; Guragain, H.; Brinkmann, B.; et al. Multi-feature localization of epileptic foci from interictal, intracranial EEG. Clin. Neurophysiol. Off. J. Int. Fed. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2019, 130, 1945–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fürbass, F.; Koren, J.; Hartmann, M.; Brandmayr, G.; Hafner, S.; Baumgartner, C. Activation patterns of interictal epileptiform discharges in relation to sleep and seizures: An artificial intelligence driven data analysis. Clin. Neurophysiol. Off. J. Int. Fed. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2021, 132, 1584–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ntolkeras, G.; Makaram, N.; Bernabei, M.; De La Vega, A.C.; Bolton, J.; Madsen, J.R.; Stone, S.S.D.; Pearl, P.L.; Papadelis, C.; Grant, E.P.; et al. Interictal EEG source connectivity to localize the epileptogenic zone in patients with drug-resistant epilepsy: A machine learning approach. Epilepsia 2024, 65, 944–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chari, A.; Adler, S.; Wagstyl, K.; Seunarine, K.; Tahir, M.Z.; Moeller, F.; Thornton, R.; Boyd, S.; Das, K.; Cooray, G.; et al. Lesion detection in epilepsy surgery: Lessons from a prospective evaluation of a machine learning algorithm. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2024, 66, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Guo, K.; Lu, K.; Meng, K.; Lu, J.; Pang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Hu, Y.; Yu, R.; Zhang, R. Localizing the seizure onset zone and predicting the surgery outcomes in patients with drug-resistant epilepsy: A new approach based on the causal network. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2025, 258, 108483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millán, A.P.; van Straaten, E.C.W.; Stam, C.J.; Nissen, I.A.; Idema, S.; Mieghem, P.V.; Hillebrand, A. Individualized epidemic spreading models predict epilepsy surgery outcomes: A pseudo-prospective study. Netw. Neurosci. 2024, 8, 437–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varotto, G.; Susi, G.; Tassi, L.; Gozzo, F.; Franceschetti, S.; Panzica, F. Comparison of Resampling Techniques for Imbalanced Datasets in Machine Learning: Application to Epileptogenic Zone Localization From Interictal Intracranial EEG Recordings in Patients with Focal Epilepsy. Front. Neuroinf. 2021, 15, 715421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Si, W.; Yao, C.; Li, X.; Duan, C.; Heng, P.A. Automatic Localization of Seizure Onset Zone from High-Frequency SEEG Signals: A Preliminary Study. IEEE J. Transl. Eng. Health Med. 2021, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou Jaoude, M.; Jacobs, C.S.; Sarkis, R.A.; Jing, J.; Pellerin, K.R.; Cole, A.J.; Cash, S.S.; Westover, M.B.; Lam, A.D. Noninvasive Detection of Hippocampal Epileptiform Activity on Scalp Electroencephalogram. JAMA Neurol. 2022, 79, 614–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, M.H.; Usman, S.M.; Khalid, S.; Anwar, A.; Alroobaea, R.; Hussain, S.; Almotiri, J.; Ullah, S.S.; Yasin, A. Classification of EEG Signals for Prediction of Epileptic Seizures. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 7251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R. Localization of epileptic surgical area using automated hybrid approach based on higher-order statistics with sensitivity analysis and residual wavelet transform. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2023, 86, 105192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoganathan, K.; Malek, N.; Torzillo, E.; Paranathala, M.; Greene, J. Neurological update: Structural and functional imaging in epilepsy surgery. J. Neurol. 2023, 270, 2798–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas, A.; Scheid, B.H.; Pattnaik, A.R.; Gallagher, R.; Mojena, M.; Tranquille, A.; Prager, B.; Gleichgerrcht, E.; Gong, R.; Litt, B.; et al. iEEG-recon: A fast and scalable pipeline for accurate reconstruction of intracranial electrodes and implantable devices. Epilepsia 2024, 65, 817–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F. Epileptic Electrophysiological Brain Networks Modeling with Partially Observable Brain Regions; The Trustees of the Stevens Institute of Technology: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Goel, A.; Seri, S.; Agrawal, S.; Kumar, R.; Sudarsanam, A.; Carr, B.; Lawley, A.; Macpherson, L.; Oates, A.J.; Williams, H.; et al. The utility of Multicentre Epilepsy Lesion Detection (MELD) algorithm in identifying epileptic activity and predicting seizure freedom in MRI lesion-negative paediatric patients. Epilepsy Res. 2024, 206, 107429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbasi, B.; Goldenholz, D.M. Machine learning applications in epilepsy. Epilepsia 2019, 60, 2037–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheikh, S.; Jehi, L. Predictive models of epilepsy outcomes. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2024, 37, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilley, C.; Rozen-Zvi, M.; Harrington, J.; Goldschmidt, Y.; Clark, C.; Fritz, P.; Devinsky, O. Antiepileptic drug therapy and model predictions of treatment success. Epilepsy Curr. 2015, 15, 197. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.H.; Han, X.; Zhao, H.W.; Zhao, D.; Wang, N.; Zhao, T.; He, G.N.; Zhu, X.R.; Zhang, Y.; Han, J.Y.; et al. Personalized prediction model for seizure-free epilepsy with levetiracetam therapy: A retrospective data analysis using support vector machine. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2018, 84, 2615–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Cai, M.; Chen, Y.; Shen, C.; Shi, L.; Guo, Y. Prediction of antiepileptic drug treatment outcomes of patients with newly diagnosed epilepsy by machine learning. Epilepsy Behav. 2019, 96, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Han, X.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, N.; Zhao, P.; Li, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, T.; Chen, Y.; Ren, Z.; et al. EEG-Driven Prediction Model of Oxcarbazepine Treatment Outcomes in Patients with Newly-Diagnosed Focal Epilepsy. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 781937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Cao, G.; Guo, J.; Wei, P.; Feng, T.; Dai, Y.; Huang, J.; Kang, G.; Zhao, G. SEEG-Net: An explainable and deep learning-based cross-subject pathological activity detection method for drug-resistant epilepsy. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 148, 105703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Han, J.; Xue, T.; Lin, J.; Chen, S.; Zhu, C.; Lin, H.; Chen, X.; Lin, W.; Huang, H. Predicting cognitive impairment in outpatients with epilepsy using machine learning techniques. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 20002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miron, G.; Müller, P.M.; Holtkamp, M.; Meisel, C. Prediction of epilepsy surgery outcome using foramen ovale EEG—A machine learning approach. Epilepsy Res. 2023, 191, 107111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomlinson, S.B.; Porter, B.E.; Marsh, E.D. Interictal network synchrony and local heterogeneity predict epilepsy surgery outcome among pediatric patients. Epilepsia 2017, 58, 402–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Wang, Y.; Ji, T.; Jiang, Y.; Zhou, X.H. Brain functional connectivity-based prediction of vagus nerve stimulation efficacy in pediatric pharmacoresistant epilepsy. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2023, 29, 3259–3268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonoda, M.; Rothermel, R.; Carlson, A.; Jeong, J.W.; Lee, M.H.; Hayashi, T.; Luat, A.F.; Sood, S.; Asano, E. Naming-related spectral responses predict neuropsychological outcome after epilepsy surgery. Brain J. Neurol. 2022, 145, 517–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Xu, Y.; Chen, C.; Zhou, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, M.; Meng, L.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, W. Automatic and Quantitative Electroencephalographic Characterization of Drug-Resistant Epilepsy in Neonatal KCNQ2 Epileptic Encephalopathy. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2023, 31, 3004–3014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.C.; Chang, M.Y.; Chiu, Y.H.; Chiang, C.T.; Wu, R.C.; Yang, R.C.; Ouyang, C.S. Prediction of seizure recurrence using electroencephalogram analysis with multiscale deep neural networks before withdrawal of antiepileptic drugs. Pediatr. Neonatol. 2022, 63, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Altaf, M.A.B.; Yoo, J. Design and Implementation of an On-Chip Patient-Specific Closed-Loop Seizure Onset and Termination Detection System. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2016, 20, 996–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spahr, A.; Bernini, A.; Ducouret, P.; Baumgartner, C.; Koren, J.P.; Imbach, L.; Beniczky, S.; Larsen, S.A.; Rheims, S.; Fabricius, M.; et al. Deep learning-based detection of generalized convulsive seizures using a wrist-worn accelerometer. Epilepsia 2025. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva Lima, G.; Cota, V.R.; Bessa, W.M. Intelligent Control to Suppress Epileptic Seizures in the Amygdala: In Silico Investigation Using a Network of Izhikevich Neurons. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2025, 33, 868–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansilla, D.; Tveit, J.; Aurlien, H.; Avigdor, T.; Ros-Castello, V.; Ho, A.; Abdallah, C.; Gotman, J.; Beniczky, S.; Frauscher, B. Generalizability of electroencephalographic interpretation using artificial intelligence: An external validation study. Epilepsia 2024, 65, 3028–3037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tjepkema-Cloostermans, M.C.; Tannemaat, M.R.; Wieske, L.; van Rootselaar, A.F.; Stunnenberg, B.C.; Keijzer, H.M.; Koelman, J.; Tromp, S.C.; Dunca, I.; van der Star, B.J.; et al. Expert level of detection of interictal discharges with a deep neural network. Epilepsia 2025, 66, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdaltawab, A.; Chang, L.C.; Mansour, M.; Koubeissi, M. How accurate are machine learning models in predicting anti-seizure medication responses: A systematic review. Epilepsy Behav. 2025, 163, 110212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Zhou, W.; Cao, C.; Liu, G.; Liu, Z.; Shang, W. A Novel SE-TCN-BiGRU Hybrid Network for Automatic Seizure Detection. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 127328–127340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Japaridze, G.; Loeckx, D.; Buckinx, T.; Armand Larsen, S.; Proost, R.; Jansen, K.; MacMullin, P.; Paiva, N.; Kasradze, S.; Rotenberg, A.; et al. Automated detection of absence seizures using a wearable electroencephalographic device: A phase 3 validation study and feasibility of automated behavioral testing. Epilepsia 2023, 64 (Suppl. S4), S40–S46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quon, R.J.; Meisenhelter, S.; Camp, E.J.; Testorf, M.E.; Song, Y.; Song, Q.; Culler, G.W.; Moein, P.; Jobst, B.C. AiED: Artificial intelligence for the detection of intracranial interictal epileptiform discharges. Clin. Neurophysiol. Off. J. Int. Fed. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2022, 133, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, A.D.; Zepeda, R.; Cole, A.J.; Cash, S.S. Widespread changes in network activity allow non-invasive detection of mesial temporal lobe seizures. Brain J. Neurol. 2016, 139, 2679–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kural, M.A.; Jing, J.; Fürbass, F.; Perko, H.; Qerama, E.; Johnsen, B.; Fuchs, S.; Westover, M.B.; Beniczky, S. Accurate identification of EEG recordings with interictal epileptiform discharges using a hybrid approach: Artificial intelligence supervised by human experts. Epilepsia 2022, 63, 1064–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiezadeh, S.; Duma, G.M.; Mento, G.; Danieli, A.; Antoniazzi, L.; Cristaldi, F.D.P.; Bonanni, P.; Testolin, A. Methodological Issues in Evaluating Machine Learning Models for EEG Seizure Prediction: Good Cross-Validation Accuracy Does Not Guarantee Generalization to New Patients. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 4262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pothuganti, S. Review on over-fitting and under-fitting problems in Machine Learning and solutions. Int. J. Adv. Res. Electr. Electron. Instrum. Eng. 2018, 7, 3692–3695. [Google Scholar]
- Bejani, M.M.; Ghatee, M. A systematic review on overfitting control in shallow and deep neural networks. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2021, 54, 6391–6438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Gu, R.; Deng, G.; Lin, Y.; Gan, T.; Cui, F.; Liu, C.; Luo, Y.J. Psychological and Brain Responses to Artificial Intelligence’s Violation of Community Ethics. Cyberpsychol. Behav. Soc. Netw. 2024, 27, 562–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervantes, J.A.; López, S.; Rodríguez, L.F.; Cervantes, S.; Cervantes, F.; Ramos, F. Artificial Moral Agents: A Survey of the Current Status. Sci. Eng. Ethics 2020, 26, 501–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnefon, J.F.; Rahwan, I.; Shariff, A. The Moral Psychology of Artificial Intelligence. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2024, 75, 653–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.; Chen, L.; Hu, D.; Dong, F.; Jiang, T.; Gao, W.; Gao, F. Unsupervised Eye Blink Artifact Detection From EEG with Gaussian Mixture Model. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2021, 25, 2895–2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, F.; Leal, A.; Medeiros, J.; Pinto, M.F.; Dourado, A.; Duempelmann, M.; Teixeira, C. Automatic Electroencephalogram Artifact Removal Using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 149955–149970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soroush, M.Z.; Tahvilian, P.; Nasirpour, M.H.; Maghooli, K.; Sadeghniiat-Haghighi, K.; Harandi, S.V.; Abdollahi, Z.; Ghazizadeh, A.; Dabanloo, N.J. EEG artifact removal using sub-space decomposition, nonlinear dynamics, stationary wavelet transform and machine learning algorithms. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 910368. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Cao, J.; Hu, D.; Jiang, T.; Gao, F. Eye Blink Artifact Detection with Novel Optimized Multi-Dimensional Electroencephalogram Features. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2021, 29, 1494–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.; Ou, Z.; Zhou, D.; Wu, X. Advancements and Challenges of Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Electroencephalography in Epilepsy Management. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 4270. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124270
Chen Y, Ou Z, Zhou D, Wu X. Advancements and Challenges of Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Electroencephalography in Epilepsy Management. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(12):4270. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124270
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yujie, Zhujing Ou, Dong Zhou, and Xintong Wu. 2025. "Advancements and Challenges of Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Electroencephalography in Epilepsy Management" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 12: 4270. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124270
APA StyleChen, Y., Ou, Z., Zhou, D., & Wu, X. (2025). Advancements and Challenges of Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Electroencephalography in Epilepsy Management. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(12), 4270. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124270






