Safety, Cognitive, and Behavioral Outcomes in Patients with Dementia with Lewy Bodies Treated with Nilotinib
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Standard Protocol Approvals and Registrations
2.2. Randomization and Blinding
2.3. Participants
2.4. Study Design and Objectives
2.5. Sex as a Biological Variable
2.6. Data Analysis
2.7. Plasma and CSF Collection
2.8. Total Alpha-Synuclein ELISA
2.9. Aβ40, Aβ42, Total Tau, and p-Tau 181 ELISA
2.10. Quantification of Dopamine Metabolite HVA
2.11. Clinical Assessments
2.12. Positron Emission Tomography
3. Results
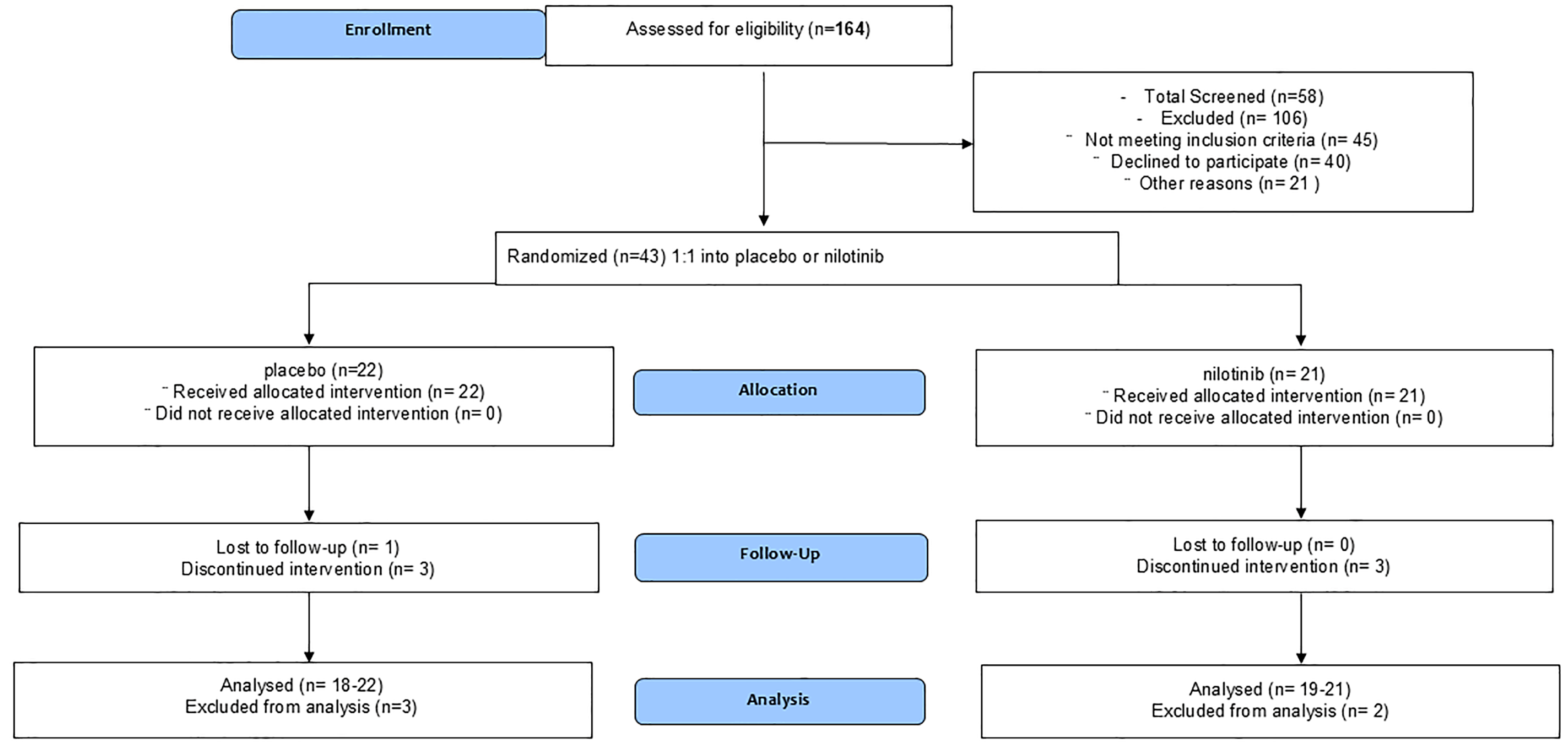
3.1. Enrollment and Demographics
3.2. Adverse Events
3.3. Biomarkers
3.4. Clinical Outcomes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DLB | Dementia with Lewy bodies |
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease |
| LP | Lumbar puncture |
| PD | Parkinson’s disease |
| Aβ | Amyloid-beta |
| LEDD | Levodopa equivalent daily dose |
| EOT | End of treatment |
| MCI | Mild cognitive impairment |
| MoCA | Montreal cognitive assessment |
| CAF | Clinicians assessment of fluctuation |
| ADAS-Cog | Alzheimer’s disease assessment scale—cognition |
| ADCS-ADL | Alzheimer’s disease co-operative study: activities of daily living |
| MDS-UPDRS | Movement disorders society-unified Parkinson’s disease rating scale |
| PBAs | Problem behaviors assessment-short |
| DDR1 | Discoidin domain receptor-1 |
| p-tau | Hyper-phosphorylated tau |
| IL | Interleukins |
| MMP | Matrix metalloproteases |
| DA | Dopamine |
| HVA | Homovanillic acid |
| AEs | Adverse Events |
References
- Savica, R.; Boeve, B.F.; Logroscino, G. Epidemiology of alpha-synucleinopathies: From Parkinson disease to dementia with Lewy bodies. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2016, 138, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kane, J.P.M.; Surendranathan, A.; Bentley, A.; Barker, S.A.H.; Taylor, J.P.; Thomas, A.J.; Allan, L.M.; McNally, R.J.; James, P.W.; McKeith, I.G.; et al. Clinical prevalence of Lewy body dementia. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2018, 10, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisberg, E.; Manley, P.W.; Breitenstein, W.; Bruggen, J.; Cowan-Jacob, S.W.; Ray, A.; Huntly, B.; Fabbro, D.; Fendrich, G.; Hall-Meyers, E.; et al. Characterization of AMN107, a selective inhibitor of native and mutant Bcr-Abl. Cancer Cell 2005, 7, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, R.S.; Hebron, M.L.; Lawler, A.; Mundel, E.E.; Yusuf, N.; Starr, J.N.; Anjum, M.; Pagan, F.; Torres-Yaghi, Y.; Shi, W.; et al. Nilotinib Effects on Safety, Tolerability, and Biomarkers in Alzheimer’s Disease. Ann. Neurol. 2020, 88, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagan, F.L.; Hebron, M.L.; Wilmarth, B.; Torres-Yaghi, Y.; Lawler, A.; Mundel, E.E.; Yusuf, N.; Starr, N.J.; Anjum, M.; Arellano, J.; et al. Nilotinib Effects on Safety, Tolerability, and Potential Biomarkers in Parkinson Disease: A Phase 2 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Neurol. 2020, 77, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, M.; Varghese, R.; Hebron, M.L.; Liu, X.; Ratliff, N.; Smith, A.; Turner, R.S.; Moussa, C. Inhibition of discoidin domain receptor (DDR)-1 with nilotinib alters CSF miRNAs and is associated with reduced inflammation and vascular fibrosis in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neuroinflamm. 2023, 20, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagan, F.; Hebron, M.; Valadez, E.H.; Torres-Yaghi, Y.; Huang, X.; Mills, R.R.; Wilmarth, B.M.; Howard, H.; Dunn, C.; Carlson, A.; et al. Nilotinib Effects in Parkinson’s disease and Dementia with Lewy bodies. J. Parkinsons Dis. 2016, 6, 503–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simuni, T.; Fiske, B.; Merchant, K.; Coffey, C.S.; Klingner, E.; Caspell-Garcia, C.; Lafontant, D.E.; Matthews, H.; Wyse, R.K.; Brundin, P.; et al. Efficacy of Nilotinib in Patients With Moderately Advanced Parkinson Disease: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Neurol. 2021, 78, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagan, F.L.; Wilmarth, B.; Torres-Yaghi, Y.; Hebron, M.L.; Mulki, S.; Ferrante, D.; Matar, S.; Ahn, J.; Moussa, C. Long-Term Safety and Clinical Effects of Nilotinib in Parkinson’s Disease. Mov. Disord. 2021, 36, 740–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKeith, I.G.; Boeve, B.F.; Dickson, D.W.; Halliday, G.; Taylor, J.P.; Weintraub, D.; Aarsland, D.; Galvin, J.; Attems, J.; Ballard, C.G.; et al. Diagnosis and management of dementia with Lewy bodies: Fourth consensus report of the DLB Consortium. Neurology 2017, 89, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarakad, A. Clinical Rating Scales and Quantitative Assessments of Movement Disorders. Neurol. Clin. 2020, 38, 231–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goetz, C.G.; Tilley, B.C.; Shaftman, S.R.; Stebbins, G.T.; Fahn, S.; Martinez-Martin, P.; Poewe, W.; Sampaio, C.; Stern, M.B.; Dodel, R.; et al. Movement Disorder Society-sponsored revision of the Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale (MDS-UPDRS): Scale presentation and clinimetric testing results. Mov. Disord. 2008, 23, 2129–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosen, W.G.; Mohs, R.C.; Davis, K.L. A new rating scale for Alzheimer’s disease. Am. J. Psychiatry 1984, 141, 1356–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, R.C.; Lopez, O.; Armstrong, M.J.; Getchius, T.S.D.; Ganguli, M.; Gloss, D.; Gronseth, G.S.; Marson, D.; Pringsheim, T.; Day, G.S.; et al. Practice guideline update summary: Mild cognitive impairment: Report of the Guideline Development, Dissemination, and Implementation Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology 2018, 90, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dyk, K.; Towns, S.; Tatarina, O.; Yeung, P.; Dorrejo, J.; Zahodne, L.B.; Stern, Y. Assessing Fluctuating Cognition in Dementia Diagnosis: Interrater Reliability of the Clinician Assessment of Fluctuation. Am. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. Other Demen 2016, 31, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, K.J.; Hietanen, H.; Markova, I.S.; Berrios, G.E. The Irritability Questionnaire: A new scale for the measurement of irritability. Psychiatry Res. 2008, 159, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNally, G.; Rickards, H.; Horton, M.; Craufurd, D. Exploring the Validity of the Short Version of the Problem Behaviours Assessment (PBA-s) for Huntington’s disease: A Rasch Analysis. J. Huntingt. Dis. 2015, 4, 347–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, J.L. The Neuropsychiatric Inventory: Assessing psychopathology in dementia patients. Neurology 1997, 48, S10–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allali, G.; Launay, C.P.; Blumen, H.M.; Callisaya, M.L.; De Cock, A.M.; Kressig, R.W.; Srikanth, V.; Steinmetz, J.P.; Verghese, J.; Beauchet, O.; et al. Falls, Cognitive Impairment, and Gait Performance: Results From the GOOD Initiative. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2017, 18, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amelio, M.; Serra, L.; Bozzali, M. Ventral Tegmental Area in Prodromal Alzheimer’s Disease: Bridging the Gap between Mice and Humans. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2018, 63, 181–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobili, A.; Latagliata, E.C.; Viscomi, M.T.; Cavallucci, V.; Cutuli, D.; Giacovazzo, G.; Krashia, P.; Rizzo, F.R.; Marino, R.; Federici, M.; et al. Dopamine neuronal loss contributes to memory and reward dysfunction in a model of Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Barbera, L.; Vedele, F.; Nobili, A.; Krashia, P.; Spoleti, E.; Latagliata, E.C.; Cutuli, D.; Cauzzi, E.; Marino, R.; Viscomi, M.T.; et al. Nilotinib restores memory function by preventing dopaminergic neuron degeneration in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Prog. Neurobiol. 2021, 202, 102031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousiges, O.; Bombois, S.; Schraen, S.; Wallon, D.; Quillard, M.M.; Gabelle, A.; Lehmann, S.; Paquet, C.; Amar-Bouaziz, E.; Magnin, E.; et al. Cerebrospinal fluid Alzheimer biomarkers can be useful for discriminating dementia with Lewy bodies from Alzheimer’s disease at the prodromal stage. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2018, 89, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, R.A.; Cairns, N.J.; Lantos, P.L. The spatial patterns of Lewy bodies, senile plaques, and neurofibrillary tangles in dementia with Lewy bodies. Exp. Neurol. 1998, 150, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, H.; Morikawa, Y.; Higuchi, M.; Matsui, T.; Clark, C.M.; Miura, M.; Machida, N.; Lee, V.M.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Sasaki, H. Cerebrospinal fluid tau levels in neurodegenerative diseases with distinct tau-related pathology. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1997, 236, 262–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aerts, M.B.; Esselink, R.A.; Claassen, J.A.; Abdo, W.F.; Bloem, B.R.; Verbeek, M.M. CSF tau, Abeta42, and MHPG differentiate dementia with Lewy bodies from Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2011, 27, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebron, M.; Peyton, M.; Liu, X.; Gao, X.; Wang, R.; Lonskaya, I.; Moussa, C.E. Discoidin domain receptor inhibition reduces neuropathology and attenuates inflammation in neurodegeneration models. J. Neuroimmunol. 2017, 311, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dyck, C.H.; Swanson, C.J.; Aisen, P.; Bateman, R.J.; Chen, C.; Gee, M.; Kanekiyo, M.; Li, D.; Reyderman, L.; Cohen, S.; et al. Lecanemab in Early Alzheimer’s Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, J.R.; Zimmer, J.A.; Evans, C.D.; Lu, M.; Ardayfio, P.; Sparks, J.; Wessels, A.M.; Shcherbinin, S.; Wang, H.; Monkul Nery, E.S.; et al. Donanemab in Early Symptomatic Alzheimer Disease: The TRAILBLAZER-ALZ 2 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2023, 330, 512–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, A.J.; Ahn, J.; Hebron, M.; Chiu, T.; Ayoub, R.; Mulki, S.; Ressom, H.; Torres-Yaghi, Y.; Wilmarth, B.; Pagan, F.L.; et al. CSF MicroRNAs Reveal Impairment of Angiogenesis and Autophagy in Parkinson Disease. Neurol. Genet. 2021, 7, e633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tie, Y.; Tang, F.; Peng, D.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, H. TGF-beta signal transduction: Biology, function and therapy for diseases. Mol. Biomed. 2022, 3, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bode, W.; Fernandez-Catalan, C.; Grams, F.; Gomis-Ruth, F.X.; Nagase, H.; Tschesche, H.; Maskos, K. Insights into MMP-TIMP interactions. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1999, 878, 73–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, M.; Xing, D.; Lu, Z.; Fan, Y.; Hou, W.; Dong, H.; Xiong, L.; Dong, H. DDR1 may play a key role in destruction of the blood-brain barrier after cerebral ischemia-reperfusion. Neurosci. Res. 2015, 96, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiusa, M.; Hu, W.; Liao, H.J.; Su, Y.; Borza, C.M.; de Caestecker, M.P.; Skrypnyk, N.I.; Fogo, A.B.; Pedchenko, V.; Li, X.; et al. The Extracellular Matrix Receptor Discoidin Domain Receptor 1 Regulates Collagen Transcription by Translocating to the Nucleus. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2019, 30, 1605–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flamant, M.; Placier, S.; Rodenas, A.; Curat, C.A.; Vogel, W.F.; Chatziantoniou, C.; Dussaule, J.C. Discoidin domain receptor 1 null mice are protected against hypertension-induced renal disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006, 17, 3374–3381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avivi-Green, C.; Singal, M.; Vogel, W.F. Discoidin domain receptor 1-deficient mice are resistant to bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 174, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Demographics | Placebo | Nilotinib (200 mg) |
|---|---|---|
| Total enrolled | n = 22 | n = 21 |
| Total finished end of Treatment | 18 (81%) | 18 (86%) |
| Total dropped out | 4 (18%) | 3 (14%) |
| Average age (years) ± SD | 73 ± 7 | 73 ± 10 |
| Weight (kg) ± SD | 74 ± 15 | 74 ± 15 |
| Height (cm) ± SD | 172 ± 9 | 172 ± 9 |
| Body Mass Index (BMI) ± SD | 25 ± 3 | 25 ± 3 |
| Male | 15 (68%) | 14 (66.6%) |
| Female | 7 (32%) | 7 (33.3%) |
| Race | 18 whites (81.8%) non-Hispanic | 16 whites (76.2%) non-Hispanic |
| 1 Black (4.5%) | 0 (0%) | |
| 1 Asian (4.5%) | 1 Asian (4.8%) | |
| 2 whites (9.2%) not reported | 4 whites (19%) not reported | |
| Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) at screening Mean ± SD | 19 ± 5.2 | 19 ± 3.3 |
| Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale (UPDRS)-Part 3 | 19 ± 9.19 | 19 ± 7.30 |
| Levodopa Equivalent Daily Dose (LEDD) at baseline | 126 mg ± 200 | 164 mg ± 227 (37%) |
| Levodopa Equivalent Daily Dose (LEDD) at 26 weeks (% increase) | 151 mg ± 254 | 160 mg ± 258.5 (5.5%) |
| Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors at baseline | 11.7 mg ± 4.75 | 11.7 mg ± 4.75 (0%) |
| Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors at 26 weeks (% increase) | 10.6 mg ± 3.4 | 10.6 mg ± 3.4 (0%) |
| Antidepressants and Anxiolytics | No change | No change |
| Antipsychotics | No change | No change |
| Serious Adverse Events (SAEs) | ||
| Event | Number of events (%) | Number of events (%) |
| Atrial fibrillation | 1 (4.5%) | 0 (0%) |
| Appendectomy | 1 (4.5%) | 0 (0%) |
| Dyskinesia | 0 (0%) | 1 (4.76%) (baseline) |
| Fall | 0 (0%) | 1 (4.76%) (baseline) |
| Total SAEs | 2 | 2 |
| Adverse Events (AEs) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| System Organ Class | Placebo (n = 22) | Nilotinib (n = 21) | |
| Preferred Term | Number of events (%) | Number of events (%) | |
| Cardiovascular Disorders | Atrial fibrillation (NOSD) | 1 (4.5%) | |
| Ecchymosis | 2 (9%) | ||
| Gastrointestinal Disorders | Diarrhea | 1 (4.5%) | |
| Nausea | 1 (4.76%) | ||
| Constipation | 1 (4.76%) | ||
| Stomach bug | 1 (4.76%) | ||
| General Disorders | Falls | 21 (95.5%) | 6 (28.6%) |
| Shingles | 1 (4.5%) | 1 (4.76%) | |
| COVID-19 | 18 (81%) | 3 (14.3%) | |
| Heavy chest | 1 (4.5%) | ||
| Ear infection | 1 (4.5%) | ||
| Sore throat | 1 (4.76%) | ||
| Low serum phosphorous (NOSD) | 1 (4.76%) | ||
| Joint and Muscle pain | 7 (31.8%) | 4 (19%) | |
| Rotator Cuff Tear | 1 (4.76%) | ||
| Eye Disorders | Cataract | 1 (4.5%) | |
| Nervous System Disorders | Post-Lumbar Puncture Headache | 1 (4.76%) | |
| Wandering at night | 1 (4.5%) | ||
| Agitation | 1 (4.5%) | ||
| Hallucinations | 3 (13.6%) | ||
| Delirium (COVID) | 1 (4.76%) | ||
| Tremor/akinesia | 1 (4.76%) | ||
| Blood patch | 1 (4.76%) | ||
| Renal and Urinary Disorders | Kidney stone | 1 (4.5%) | 1 (4.76%) |
| Urinary Tract Infection | 3 (4.5%) | 1 (4.76%) | |
| Hematuria | 1 (4.76%) | ||
| Cystoscopy | 1 (4.5%) | ||
| Prostate (PSA elevation) | 1 (4.5%) | ||
| Respiratory, Thoracic, and Mediastinal Disorders | Upper Respiratory infection | 2 (9%) | 1 (4.76%) |
| Skin and Subcutaneous Disorder | Abscess | 1 (4.5%) | |
| Gout | 1 (4.5%) | ||
| Lesions | 1 (4.5%) | 4 (19%) | |
| Tissue mass | 2 (9%) | ||
| Rash | 2 (9%) | 4 (19%) | |
| Mohs Procedure | 1 (4.76%) | ||
| Total AEs | 74 | 37 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pagan, F.; Torres-Yaghi, Y.; Hebron, M.; Wilmarth, B.; Turner, R.S.; Matar, S.; Liu, X.; Ferrante, D.; Esposito, G.; Ahn, J.; et al. Safety, Cognitive, and Behavioral Outcomes in Patients with Dementia with Lewy Bodies Treated with Nilotinib. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 4245. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124245
Pagan F, Torres-Yaghi Y, Hebron M, Wilmarth B, Turner RS, Matar S, Liu X, Ferrante D, Esposito G, Ahn J, et al. Safety, Cognitive, and Behavioral Outcomes in Patients with Dementia with Lewy Bodies Treated with Nilotinib. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(12):4245. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124245
Chicago/Turabian StylePagan, Fernando, Yasar Torres-Yaghi, Michaeline Hebron, Barbara Wilmarth, R. Scott Turner, Sara Matar, Xiaoguang Liu, Dalila Ferrante, Giuseppe Esposito, Jaeil Ahn, and et al. 2025. "Safety, Cognitive, and Behavioral Outcomes in Patients with Dementia with Lewy Bodies Treated with Nilotinib" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 12: 4245. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124245
APA StylePagan, F., Torres-Yaghi, Y., Hebron, M., Wilmarth, B., Turner, R. S., Matar, S., Liu, X., Ferrante, D., Esposito, G., Ahn, J., & Moussa, C. (2025). Safety, Cognitive, and Behavioral Outcomes in Patients with Dementia with Lewy Bodies Treated with Nilotinib. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(12), 4245. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124245





