Screening for Systemic Light-Chain Amyloidosis in Patients Over 60 with λ Monoclonal Gammopathies
Abstract
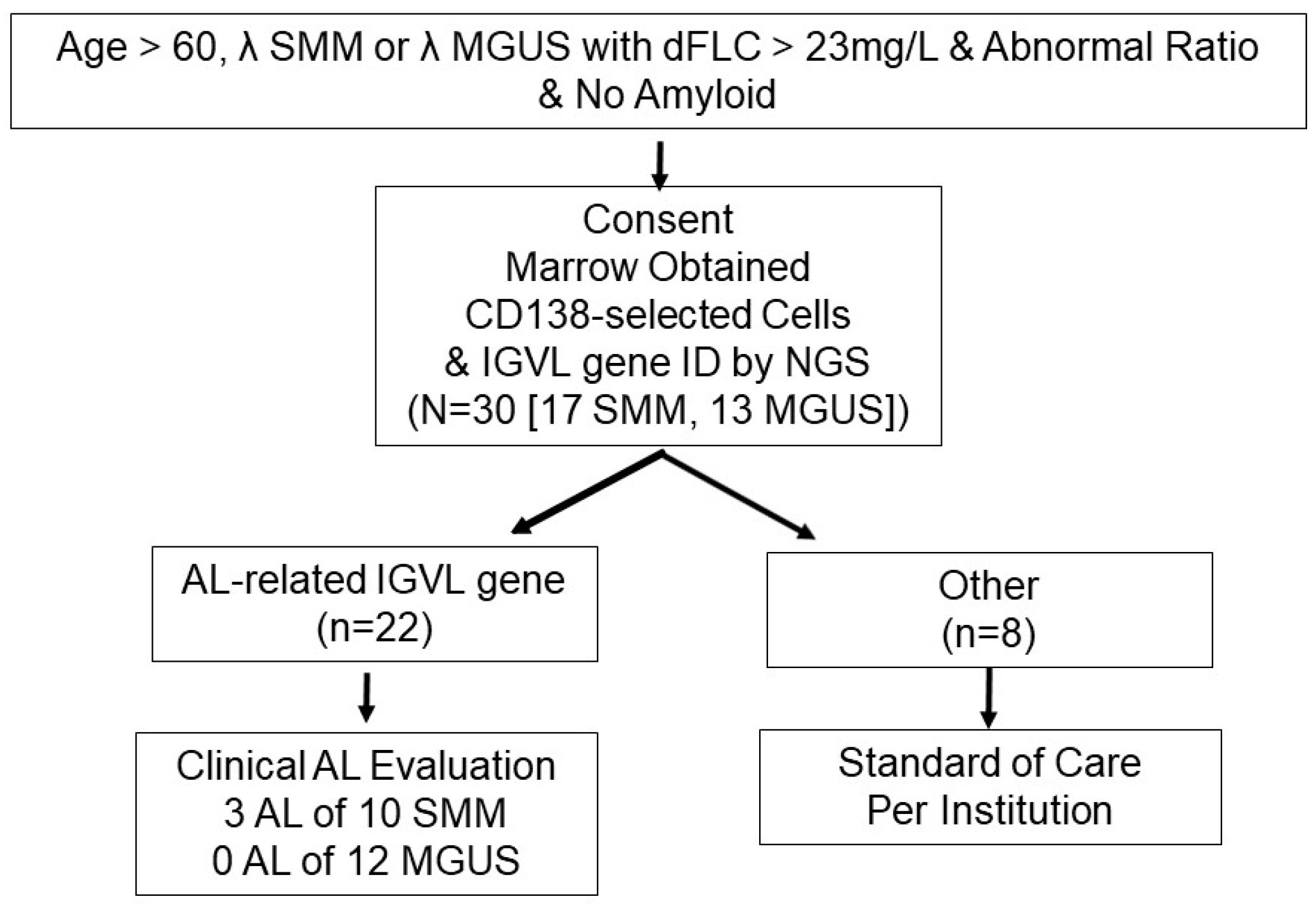
1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. IGVL Gene Identification
2.3. Biostatistics
3. Results
3.1. Patients
3.2. Marrow Findings
3.3. Subjects Found to Have AL
3.4. Marrow Mononuclear Cells (MNC)
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kastritis, E.; Palladini, G.; Minnema, M.C.; Wechalekar, A.D.; Jaccard, A.; Lee, H.C.; Sanchorawala, V.; Gibbs, S.; Mollee, P.; Venner, C.P.; et al. Daratumumab-Based Treatment for Immunoglobulin Light-Chain Amyloidosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varga, C.; Comenzo, R.L. High-dose melphalan and stem cell transplantation in systemic AL amyloidosis in the era of novel anti-plasma cell therapy: A comprehensive review. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2019, 54, 508–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianchi, G.; Zhang, Y.; Comenzo, R.L. AL Amyloidosis: Current Chemotherapy and Immune Therapy Treatment Strategies: JACC: CardioOncology State-of-the-Art Review. JACC CardioOncol. 2021, 3, 467–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyle, R.A.; Remstein, E.D.; Therneau, T.M.; Dispenzieri, A.; Kurtin, P.J.; Hodnefield, J.M.; Larson, D.R.; Plevak, M.F.; Jelinek, D.F.; Fonseca, R.; et al. Clinical course and prognosis of smoldering (asymptomatic) multiple myeloma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 356, 2582–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lousada, I.; Comenzo, R.L.; Landau, H.; Guthrie, S.; Merlini, G. Light Chain Amyloidosis: Patient Experience Survey from the Amyloidosis Research Consortium. Adv. Ther. 2015, 32, 920–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neben, K.; Jauch, A.; Hielscher, T.; Hillengass, J.; Lehners, N.; Seckinger, A.; Granzow, M.; Raab, M.S.; Ho, A.D.; Goldschmidt, H.; et al. Progression in smoldering myeloma is independently determined by the chromosomal abnormalities del(17p), t(4;14), gain 1q, hyperdiploidy, and tumor load. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 4325–4332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer, M.S.; Elliott, P.; Comenzo, R.; Semigran, M.; Rapezzi, C. Addressing Common Questions Encountered in the Diagnosis and Management of Cardiac Amyloidosis. Circulation 2017, 135, 1357–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCausland, K.L.; White, M.K.; Guthrie, S.D.; Quock, T.; Finkel, M.; Lousada, I.; Bayliss, M.S. Light Chain (AL) Amyloidosis: The Journey to Diagnosis. Patient 2018, 11, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gertz, M.A. Immunoglobulin light chain amyloidosis: 2018 Update on diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment. Am. J. Hematol. 2018, 93, 1169–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, B.M.; Hebreo, J.; Cordaro, D.V.; Roschewski, M.J.; Baker, T.P.; Abbott, K.C.; Olson, S.W. Increased serum free light chains precede the presentation of immunoglobulin light chain amyloidosis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 2699–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comenzo, R.L. Plasma cell neoplasms, their precursor States, and their prediction of organ damage. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 2679–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, P.; Mansukhani, M.M.; Yeh, R.; Lu, J.; Xia, H.; Koganti, L.; Pang, J.; Toskic, D.; Scalia, S.; Ma, X.; et al. Seeking Amyloidosis Very Early: Free light Chain Difffferentials and IGLV Gene Use as Screening Variables for Light-chain Amyloidosis in λ Monoclonal Gammopathies. Br. J. Cancer 2024, 7, 681–686. [Google Scholar]
- Muchtar, E.; Gertz, M.A.; Kyle, R.A.; Lacy, M.Q.; Dingli, D.; Leung, N.; Buadi, F.K.; Hayman, S.R.; Kapoor, P.; Hwa, Y.L.; et al. A Modern Primer on Light Chain Amyloidosis in 592 Patients with Mass Spectrometry-Verified Typing. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2019, 94, 472–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahir, U.A.; Doros, G.; Kim, J.S.; Connors, L.H.; Seldin, D.C.; Sam, F. Predictors of Mortality in Light Chain Cardiac Amyloidosis with Heart Failure. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palladini, G.; Dispenzieri, A.; Gertz, M.A.; Kumar, S.; Wechalekar, A.; Hawkins, P.N.; Schonland, S.; Hegenbart, U.; Comenzo, R.; Kastritis, E.; et al. New criteria for response to treatment in immunoglobulin light chain amyloidosis based on free light chain measurement and cardiac biomarkers: Impact on survival outcomes. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 4541–4549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchison, C.A.; Basnayake, K.; Cockwell, P. Serum free light chain assessment in monoclonal gammopathy and kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2009, 5, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Ma, X.; Iyer, L.; Chaulagain, C.; Comenzo, R.L. One siRNA pool targeting the lambda constant region stops lambda light-chain production and causes terminal endoplasmic reticulum stress. Blood 2014, 123, 3440–3451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodi, K.; Prokaeva, T.; Spencer, B.; Eberhard, M.; Connors, L.H.; Seldin, D.C. AL-Base: A visual platform analysis tool for the study of amyloidogenic immunoglobulin light chain sequences. Amyloid 2009, 16, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, D.; van der Burg, M.; Garcia-Sanz, R.; Fenton, J.A.; Langerak, A.W.; Gonzalez, M.; van Dongen, J.J.; San Miguel, J.F.; Morgan, G.J. Immunoglobulin gene rearrangements and the pathogenesis of multiple myeloma. Blood 2007, 110, 3112–3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, V.; Moshier, E.; Leng, S.; Barlogie, B.; Cho, H.J.; Jagannath, S.; Madduri, D.; Mazumdar, M.; Parekh, S.; Chari, A. Risk stratification of smoldering multiple myeloma: Predictive value of free light chains and group-based trajectory modeling. Blood Adv. 2018, 2, 1470–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, T.M.; Fonseca, R.; Usmani, S.Z. Chromosome 1q21 abnormalities in multiple myeloma. Blood Cancer J. 2021, 11, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochtler, T.; Hegenbart, U.; Kunz, C.; Benner, A.; Kimmich, C.; Seckinger, A.; Hose, D.; Goldschmidt, H.; Granzow, M.; Dreger, P.; et al. Prognostic impact of cytogenetic aberrations in AL amyloidosis patients after high-dose melphalan: A long-term follow-up study. Blood 2016, 128, 594–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, P.; Hoffman, J.; Landau, H.; Hassoun, H.; Iyer, L.; Comenzo, R.L. Clonal plasma cell pathophysiology and clinical features of disease are linked to clonal plasma cell expression of cyclin D1 in systemic light-chain amyloidosis. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2012, 12, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kourelis, T.V.; Dasari, S.; Theis, J.D.; Ramirez-Alvarado, M.; Kurtin, P.J.; Gertz, M.A.; Zeldenrust, S.R.; Zenka, R.M.; Dogan, A.; Dispenzieri, A. Clarifying immunoglobulin gene usage in systemic and localized immunoglobulin light-chain amyloidosis by mass spectrometry. Blood 2017, 129, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, G.J.; Nau, A.N.; Wong, S.; Spencer, B.H.; Shen, Y.; Hua, A.; Bullard, M.J.; Sanchorawala, V.; Prokaeva, T. An updated AL-base reveals ranked enrichment of immunoglobulin light chain variable genes in AL amyloidosis. Amyloid 2024, 32, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlini, G.; Lousada, I.; Ando, Y.; Dispenzieri, A.; Gertz, M.A.; Grogan, M.; Maurer, M.S.; Sanchorawala, V.; Wechalekar, A.; Palladini, G.; et al. Rationale, application and clinical qualification for NT-proBNP as a surrogate end point in pivotal clinical trials in patients with AL amyloidosis. Leukemia 2016, 30, 1979–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schanz, M.; Liechti, T.; Zagordi, O.; Miho, E.; Reddy, S.T.; Gunthard, H.F.; Trkola, A.; Huber, M. High-throughput sequencing of human immunoglobulin variable regions with subtype identification. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyle, R.A.; Larson, D.R.; Therneau, T.M.; Dispenzieri, A.; Melton, L.J., 3rd; Benson, J.T.; Kumar, S.; Rajkumar, S.V. Clinical course of light-chain smouldering multiple myeloma (idiopathic Bence Jones proteinuria): A retrospective cohort study. Lancet Haematol. 2014, 1, e28–e36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, A.; Bazou, D.; O’Gorman, P. Smoldering multiple myeloma: Prevalence and current evidence guiding treatment decisions. Blood Lymphat. Cancer 2018, 8, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comenzo, R.L.; Zhang, Y.; Martinez, C.; Osman, K.; Herrera, G.A. The tropism of organ involvement in primary systemic amyloidosis: Contributions of Ig V(L) germ line gene use and clonal plasma cell burden. Blood 2001, 98, 714–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Gregorio, C.; Trimarchi, G.; Faro, D.C.; De Gaetano, F.; Campisi, M.; Losi, V.; Zito, C.; Tamburino, C.; Di Bella, G.; Monte, I.P. Myocardial Work Appraisal in Transthyretin Cardiac Amyloidosis and Nonobstructive Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Am. J. Cardiol. 2023, 208, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Gregorio, C.; Trimarchi, G.; Faro, D.C.; Poleggi, C.; Teresi, L.; De Gaetano, F.; Zito, C.; Lofrumento, F.; Koniari, I.; Licordari, R.; et al. Systemic Vascular Resistance and Myocardial Work Analysis in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy and Transthyretin Cardiac Amyloidosis with Preserved Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Licordari, R.; Trimarchi, G.; Teresi, L.; Restelli, D.; Lofrumento, F.; Perna, A.; Campisi, M.; de Gregorio, C.; Grimaldi, P.; Calabro, D.; et al. Cardiac Magnetic Resonance in HCM Phenocopies: From Diagnosis to Risk Stratification and Therapeutic Management. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorbala, S.; Ando, Y.; Bokhari, S.; Dispenzieri, A.; Falk, R.H.; Ferrari, V.A.; Fontana, M.; Gheysens, O.; Gillmore, J.D.; Glaudemans, A.; et al. ASNC/AHA/ASE/EANM/HFSA/ISA/SCMR/SNMMI expert consensus recommendations for multimodality imaging in cardiac amyloidosis: Part 2 of 2-Diagnostic criteria and appropriate utilization. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 2019, 14, e000029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, C.; Dorbala, S.; Lousada, I.; Polydefkis, M.J.; Wechalekar, A.; Maurer, M.S.; Comenzo, R.L. The diagnostic challenges of cardiac amyloidosis: A practical approach to the two main types. Blood Rev. 2021, 45, 100720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillmore, J.D.; Maurer, M.S.; Falk, R.H.; Merlini, G.; Damy, T.; Dispenzieri, A.; Wechalekar, A.D.; Berk, J.L.; Quarta, C.C.; Grogan, M.; et al. Nonbiopsy Diagnosis of Cardiac Transthyretin Amyloidosis. Circulation 2016, 133, 2404–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirmess, K.M.; Meyer, M.R.; Holubasch, M.S.; Knapik, S.S.; Hu, Y.; Jackson, E.N.; Harpstrite, S.E.; Verghese, P.B.; West, T.; Fogelman, I.; et al. The PrecivityAD test: Accurate and reliable LC-MS/MS assays for quantifying plasma amyloid beta 40 and 42 and apolipoprotein E proteotype for the assessment of brain amyloidosis. Clin. Chim. Acta 2021, 519, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Age | Characteristic |
|---|---|
| Median (range) years | 69 (58–92) |
| Distribution—no. (%) | |
| <65 y | 7 (23) |
| ≥65 y | 23 (77) |
| Sex, no. (%) | |
| Male | 19 (63) |
| Female | 11 (37) |
| Median months from SMM diagnosis to enrollment | 13 (1–132) |
| Median serum creatinine (normal 0.55–1.3 mg/dL) | 1.0 (0.60–3.08) |
| Median alkaline phosphatase (normal 30–130 U/L) | 81 (37–180) |
| MGUS/SMM (n) | 13/17 |
| MGUS | |
| Median iFLC (mg/L) | 326 (42–1328) |
| Median FLC ratio | 0.11 (0.02–0.30) |
| t(11;14) (number) | 1 |
| gain 1q21 (number) | 3 |
| SMM | |
| Median iFLC (mg/L) | 201 (83–1040) |
| Median FLC ratio | 0.06 (0.01–0.26) |
| t(11;14) (number) | 6 |
| gain 1q21 (number) | 6 * |
| SMM IGVL | NCT04615572 (n = 17 SMM) | GenBank # |
|---|---|---|
| LV1-44 | 2 | OQ912884 OQ912876 |
| LV1-47 | 2 | OQ884472 OR506910 |
| LV2-8 | 3 | OQ912883 OQ912886 OQ912887 |
| LV2-11 | 1 | OQ912882 |
| LV2-14 | 1 | OQ912877 |
| LV2-23 | 2 (1 AL) | OR506909 OQ912881 |
| LV3-1 | 3 (2 AL) | OQ819165 OQ912879 OQ912885 |
| LV3-12 | 1 | OQ912875 |
| LV3-21 | 2 | OQ912880 OQ912878 |
| Age/Sex | SMM | dFLC>23mg/L | AL-Related Gene | t(11;14) or Gain 1q | AL | AL Cardiac * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 70M | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 60M | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |
| 71F | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 73M | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||
| 67M | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||
| 65M | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||
| 92M | √ | √ | ||||
| 66M | √ | √ | ||||
| 67M | √ | √ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, P.; Mansukhani, M.M.; Yeh, R.; Lu, J.; Xia, H.; Koganti, L.; Pang, J.; Toskic, D.; Scalia, S.; Ma, X.; et al. Screening for Systemic Light-Chain Amyloidosis in Patients Over 60 with λ Monoclonal Gammopathies. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 4146. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124146
Zhou P, Mansukhani MM, Yeh R, Lu J, Xia H, Koganti L, Pang J, Toskic D, Scalia S, Ma X, et al. Screening for Systemic Light-Chain Amyloidosis in Patients Over 60 with λ Monoclonal Gammopathies. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(12):4146. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124146
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Ping, Mahesh M. Mansukhani, Raymond Yeh, Jiesheng Lu, Hongai Xia, Lahari Koganti, Jiuhong Pang, Denis Toskic, Stephanie Scalia, Xun Ma, and et al. 2025. "Screening for Systemic Light-Chain Amyloidosis in Patients Over 60 with λ Monoclonal Gammopathies" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 12: 4146. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124146
APA StyleZhou, P., Mansukhani, M. M., Yeh, R., Lu, J., Xia, H., Koganti, L., Pang, J., Toskic, D., Scalia, S., Ma, X., Lee, L. X., Wong, S. W., Chung, A., Tuchman, S. A., Fogaren, T., Coady Lyons, N., Varga, C., Lentzsch, S., & Comenzo, R. L. (2025). Screening for Systemic Light-Chain Amyloidosis in Patients Over 60 with λ Monoclonal Gammopathies. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(12), 4146. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124146






