A Systematic Review of Heated Intrathoracic Chemotherapy for Thymic Epithelial Tumors and the First Case Report of a Robotic Approach: Could a Minimally Invasive Approach Offer a New Paradigm of Care?
Abstract
1. Introduction
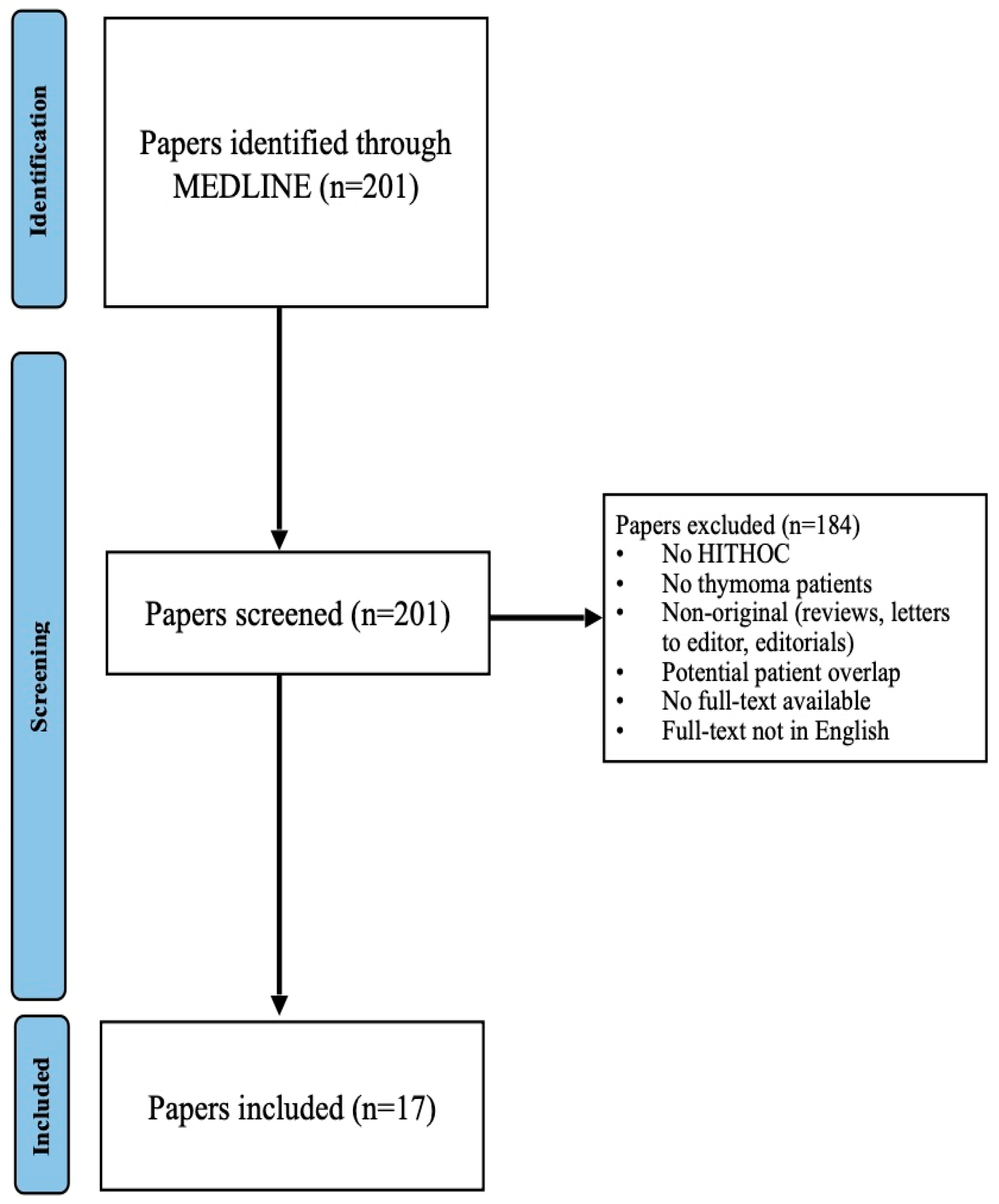
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Study Selection
2.3. Data Extraction
2.4. Risk of Bias Assessment
3. Results
3.1. HITHOC Protocols and Renoprotective Strategies
3.2. Adverse Events
3.3. Follow-Up Regimens
3.4. Clinical and Oncologic Outcomes
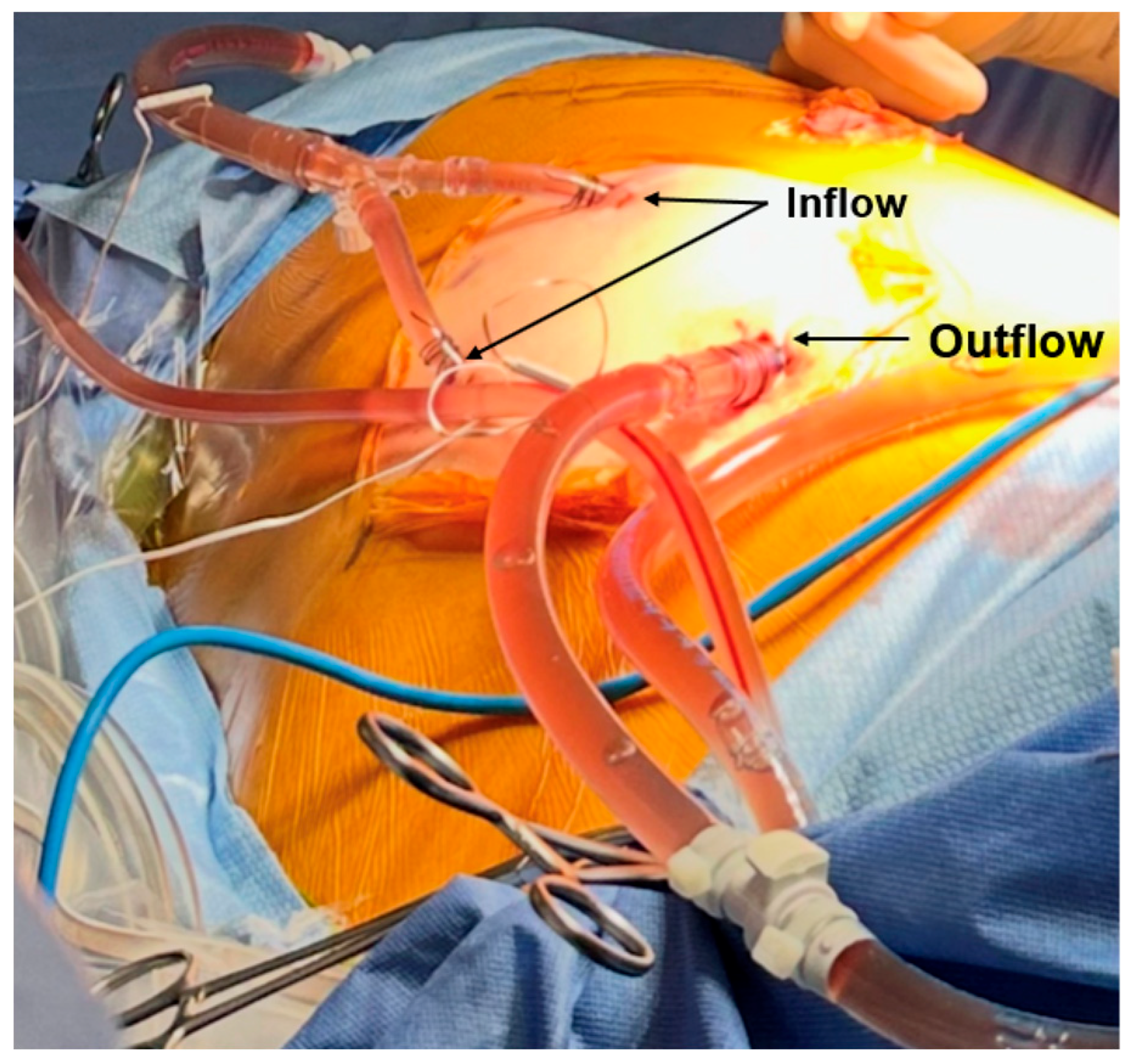
4. Discussion: Our Experience with Minimally Invasive Delivery of HITHOC
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HITHOC | Hyperthermic intrathoracic chemotherapy |
| HIPEC | Hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy |
| TPR | Thymoma with pleural recurrence |
| DNT | De novo thymoma with pleural dissemination |
References
- Tartarone, A.; Lerose, R.; Lettini, A.R.; Tartarone, M. Current Treatment Approaches for Thymic Epithelial Tumors. Life 2023, 13, 1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Girard, N.; Ruffini, E.; Marx, A.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Peters, S. ESMO Guidelines Committee. Thymic epithelial tumours: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26 (Suppl. 5), v40–v55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabezón-Gutiérrez, L.; Pacheco-Barcia, V.; Carrasco-Valero, F.; Palka-Kotlowska, M.; Custodio-Cabello, S.; Khosravi-Shahi, P. Update on thymic epithelial tumors: A narrative review. Mediastinum 2024, 8, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weissferdt, A. Common thymomas: Classification, histology, staging and prognosis. Diagn. Histopathol. 2023, 29, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, T.; Chen-Yoshikawa, T. Managing recurrent thymic epithelial tumors after resection: Outcomes and role of re-resection. Mediastinum 2024, 8, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aprile, V.; Bacchin, D.; Korasidis, S.; Nesti, A.; Marrama, E.; Ricciardi, R.; Petrini, I.; Ambrogi, M.C.; Paladini, P.; Lucchi, M. Surgical treatment of pleural recurrence of thymoma: Is hyperthermic intrathoracic chemotherapy worthwhile? Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2020, 30, 765–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnar, T.F.; Drozgyik, A. Narrative review of theoretical considerations regarding HITHOC between past and future. Ann. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyoda, A.; Yusa, T.; Hiroshima, K.; Fujisawa, T. Surgical resection combined with intrathoracic hyperthermic perfusion for thymic carcinoma with an intrathoracic disseminated lesion: A case report. Anticancer. Res. 1999, 19, 699–702. [Google Scholar]
- Ambrogi, M.C.; Korasidis, S.; Lucchi, M.; Fanucchi, O.; Giarratana, S.; Melfi, F.; Mussi, A. Pleural recurrence of thymoma: Surgical resection followed by hyperthermic intrathoracic perfusion chemotherapy. Eur. J. Cardio-Thorac. Surg. 2016, 49, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bree, E.; van Ruth, S.; Baas, P.; Rutgers, E.J.; van Zandwijk, N.; Witkamp, A.J.; Zoetmulder, F.A. Cytoreductive surgery and intraoperative hyperthermic intrathoracic chemotherapy in patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma or pleural metastases of thymoma. Chest 2002, 121, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappuy, B.; Drevet, G.; Clermidy, H.; Rosamel, P.; Duruisseaux, M.; Couraud, S.; Grima, R.; Soldea, V.; Chalabreysse, L.; Tronc, F.; et al. Subtotal Pleurectomy with Intrathoracic Chemo Hyperthermia (HITHOC) for IVa Thymomas: De Novo Versus Recurrent Pleural Disease. Cancers 2022, 14, 5035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolan, D.P.; Polhemus, E.; Lee, D.N.; Mazzola, E.; Jaklitsch, M.T.; Wee, J.O.; Bueno, R.; Swanson, S.; White, A. Hyperthermic intraoperative chemotherapy (HIOC) for Stage IVa thymic malignancy may improve 5-year disease-free survival. J. Surg. Oncol. 2023, 127, 734–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klotz, L.V.; Gruenewald, C.; Bulut, E.L.; Eichhorn, F.; Thomas, M.; Shah, R.; Kriegsmann, M.; Schmidt, W.; Kofler, O.; Winter, H.; et al. Cytoreductive Thoracic Surgery Combined with Hyperthermic Chemoperfusion for Pleural Malignancies: A Single-Center Experience. Respiration 2021, 100, 1165–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodama, K.; Higashiyama, M.; Okami, J.; Tokunaga, T.; Fujiwara, A.; Imamura, F.; Nakayama, T. Cytoreductive surgery and post-operative heated pleural chemotherapy for the management of pleural surface malignancy. Int. J. Hyperth. 2013, 29, 653–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, D.L.; Parks, C.S.; Ange, B.; Bonta, I.R.; Rich, P.T. Hyperthermic intrathoracic extracorporeal chemotherapy for secondary malignant pleural disease. J. Surg. Oncol. 2023, 128, 604–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monneuse, O.; Beaujard, A.C.; Guibert, B.; Gilly, F.N.; Mulsant, P.; Carry, P.Y.; Benoit, M.; Glehen, O. Long-term results of intrathoracic chemohyperthermia (ITCH) for the treatment of pleural malignancies. Br. J. Cancer 2003, 88, 1839–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, M.D.; Damodaran, D.; Rangole, A.; Shaikh, S.; Shah, K.; Bagwade, R.; Bhatt, A. Hyperthermic Intrathoracic Chemotherapy (HITHOC) for Pleural Malignancies-Experience from Indian Centers. Indian J. Surg. Oncol. 2019, 10 (Suppl. 1), 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refaely, Y.; Simansky, D.A.; Paley, M.; Gottfried, M.; Yellin, A. Resection and perfusion thermochemotherapy: A new approach for the treatment of thymic malignancies with pleural spread. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2001, 72, 366–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ried, M.; Hassan, M.; Passlick, B.; Schmid, S.; Markowiak, T.; Müller, K.; Huppertz, G.; Koller, M.; Winter, H.; Klotz, L.V.; et al. Surgical cytoreduction and hyperthermic intrathoracic chemotherapy for thymic tumours with pleural spread is effective on survival: Results from the multicentre German hyperthermic intrathoracic chemotherapy study. Interdiscip. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2023, 36, ivad032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yellin, A.; Simansky, D.A.; Ben-Avi, R.; Perelman, M.; Zeitlin, N.; Refaely, Y.; Ben-Nun, A. Resection and heated pleural chemoperfusion in patients with thymic epithelial malignant disease and pleural spread: A single-institution experience. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2013, 145, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Jing, Y.; Ma, S.; Li, F.; Zhang, Y.F. Cytoreductive surgery combined with hyperthermic intrapleural chemotherapy to treat thymoma or thymic carcinoma with pleural dissemination. OncoTargets Ther. 2013, 6, 517–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Pulle, M.V.; Asaf, B.B.; Puri, H.V.; Bishnoi, S. Is Hyperthermic Intrathoracic Chemotherapy (HITHOC) Safe and Efficacious in Masaoka-Koga Stage-IVA Thymoma? A Pilot Study. Indian J. Surg. Oncol. 2021, 12, 830–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markowiak, T.; Neu, R.; Ansari, M.K.A.; Großer, C.; Klinkhammer-Schalke, M.; Hofmann, H.S.; Ried, M. Surgical Cytoreduction and HITOC for Thymic Malignancies with Pleural Dissemination. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2021, 69, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maury, J.M.; Girard, N.; Tabutin, M.; Grima, R.; Chalabreysse, L.; Pavlakovic, I.; Sayag-Beaujard, A.; Leroux, C.; Souquet, P.J.; Glehen, O.; et al. Intra-Thoracic Chemo-Hyperthermia for pleural recurrence of thymoma. Lung Cancer 2017, 108, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yellin, A.; Simansky, D.A.; Paley, M.; Refaely, Y. Hyperthermic pleural perfusion with cisplatin: Early clinical experience. Cancer 2001, 92, 2197–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| First Author (Year Published) | Enrollment Period | County of Study | Sample Size | Sex (% Male) | Inclusion Criteria | Paraneoplastic Syndromes (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ambrogi et al. (2016) [9] | 2005–2012 | Italy | 13 | 7/13 (53.4%) | Patients with a history of TET s/p prior resection of primary tumor with pleural recurrence of TET who underwent surgical cytoreduction followed by HITHOC |
|
| Aprile et al. (2020) [6] | 2005–2017 | Italy | 27 | 9/27 (33.3%) | Patients with a history of TET s/p prior resection of primary tumor with pleural recurrence of TET who underwent surgical cytoreduction followed by HITHOC | MG: 23/27 (85.2%) |
| de Bree et al. (2022) [10] | 1998–2000 | The Netherlands | 3 | 0/3 (0%) | Patients with a history of TET s/p prior resection of primary tumor with pleural recurrence of TET who underwent surgical cytoreduction followed by HITHOC | MG: 1/3 (33.3%) |
| Chappuy et al. (2022) [11] | 1997–2021 | France | 40 | 15/40 (37.5%) | Patients with pleural involvement of TET (both de novo and pleural recurrence following primary resection) who underwent surgical cytoreduction followed by HITHOC | MG: 17/40 (42%) |
| Dolan et al. (2022) [12] | 1990–2020 | USA | 12 | 3/12 (25%) | Patients with pleural involvement of TET (both de novo and pleural recurrence following primary resection) who underwent surgical cytoreduction followed by HITHOC | - |
| Klotz et al. (2021) [13] | 2014–2018 | Germany | 12 | 63/76 * (82.9%) | Patients with TET with de novo pleural involvement who underwent surgical cytoreduction followed by HITHOC | - |
| Kodama et al. (2013) [14] | 1987–2010 | Japan | 12 | 7/12 (58.3%) | Patients with pleural involvement of TET (both de novo and pleural recurrence following primary resection) who underwent surgical cytoreduction followed by HITHOC | MG: 0/12 (0%) |
| Kumar et al. (2021) [22] | 2015–2018 | India | 6 | 5/6 (83.3%) | Patients with TET with de novo pleural involvement who underwent surgical cytoreduction followed by HITHOC | MG: 4/6 (66.7%) |
| Markowiak et al. (2021) [23] | 2008–2017 | Germany | 29 | 17/29 (58.6%) | Patients with pleural involvement of TET (both de novo and pleural recurrence following primary resection) who underwent surgical cytoreduction followed by HITHOC | - |
| Maury et al. (2017) [24] | 1997–2015 | France | 19 | 8/19 (42.1%) | Patients with a history of thymoma (thymic carcinoma excluded) s/p prior resection of primary tumor with pleural recurrence of thymoma who underwent surgical cytoreduction followed by HITHOC | MG: 9/19 (47.4%) |
| Miller et al. (2023) [15] | 2014–2021 | USA | 14 | 14/35 * (40%) | Patients with TET with de novo pleural involvement who underwent surgical cytoreduction followed by HITHOC. Additional inclusion criteria:
| - |
| Monneuse et al. (2003) [16] | 1990–2000 | France | 1 | 0/1 (0%) | Patients with TET with de novo pleural involvement who underwent surgical cytoreduction followed by HITHOC | - |
| Patel et al. (2018) [17] | 2011–2018 | India | 1 | 1/1 (100%) | Patients with TET with de novo pleural involvement who underwent surgical cytoreduction followed by HITHOC. Additional inclusion criteria:
| - |
| Refaely et al. (2011) [18] | 1995–2000 | Israel | 15 | 11/15 (73.3%) | Patients with pleural involvement of TET (both de novo and pleural recurrence following primary resection) who underwent surgical cytoreduction followed by HITHOC | MG: 5/15 (33.3%) |
| Ried et al. (2023) [19] | 2008–2019 | Germany | 58 | 36/58 (62.1%) | Patients with pleural involvement of TET (both de novo and pleural recurrence following primary resection) who underwent surgical cytoreduction followed by HITHOC | - |
| Yellin et al. (2013) [20] | 1995–2012 | Israel | 35 | 25/35 (71.4%) | Patients with pleural involvement of TET (both de novo and pleural recurrence following primary resection) who underwent surgical cytoreduction followed by HITHOC | MG: 15/35 (42.9%) |
| Yu et al. (2013) [21] | 2008–2012 | China | 4 | 1/4 (25%) | Patients with pleural involvement of TET (both de novo and pleural recurrence following primary resection) who underwent surgical cytoreduction followed by HITHOC | MG: 1/4 (25%) |
| Study | Additional Treatment Details | WHO Histologic Classification | Side of Metastasis | Masaoka–Koga Primary Tumor Stage † | Local Infiltration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ambrogi et al. (2016) [9] |
|
| - |
|
|
| Aprile et al. (2020) [6] | Adjuvant therapy after primary surgery:
|
| - |
|
|
| de Bree et al. (2022) [10] |
| - |
| - | - |
| Chappuy et al. (2022) [11] | - |
| - | - | - |
| Dolan et al. (2022) [12] | Neoadjuvant therapy:
|
| - | - | - |
| Klotz et al. (2021) [13] | - |
|
| - | - |
| Kodama et al. (2013) [14] | - | - | - | - | - |
| Kumar et al. (2021) [22] |
| - |
| - | - |
| Markowiak et al. (2021) [23] |
|
|
| - | - |
| Maury et al. (2017) [24] |
|
| - |
| - |
| Miller et al. (2023) [15] | - | - | - | - | - |
| Monneuse et al. (2003) [16] | No adjuvant radiotherapy | - | - | - | - |
| Patel et al. (2018) [17] | Adjuvant chemotherapy: 1/1 (100%) | - | - | - | - |
| Refaely et al. (2011) [18] |
|
|
| - | |
| Ried et al. (2023) [19] |
|
|
| - | - |
| Yellin et al. (2013) [20] |
|
|
| - | - |
| Yu et al. (2013) [21] |
| - |
| - | - |
| Study | Chemotherapeutic Agent(s) | Dose (mg/m2 Unless Otherwise Specified) | Duration (Minutes) | Perfusion Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ambrogi et al. (2016) [9] | Cisplatin in combination with Doxorubicin |
| 60 | - |
| Aprile et al. (2020) [6] | Cisplatin in combination with Epirubicin |
| 60 | - |
| de Bree et al. (2022) [10] | Cisplatin in combination with Doxorubicin |
| 90 | 1000 mL/min |
| Chappuy et al. (2022) [11] | Cisplatin in combination with Mitomycin |
| 90 | - |
| Dolan et al. (2022) [12] | Cisplatin alone | 175 | 60 1 | - |
| Klotz et al. (2021) [13] | Cisplatin alone | 200 mg/L | 60 | 1000 mL/min |
| Kodama et al. (2013) [14] | Cisplatin alone or Carboplatin alone |
| 60 | - |
| Kumar et al. (2021) [22] | Cisplatin alone | 130–150 | 60 | - |
| Markowiak et al. (2021) [23] | Cisplatin alone or Cisplatin in combination with Doxorubicin |
| 60 | 1500 mL/min |
| Maury et al. (2017) [24] | Mitomycin in combination with Cisplatin |
| 90 | 200 mL/min |
| Miller et al. (2023) [15] | Cisplatin alone | 225 | 60 | 1500–1700 mL/min |
| Monneuse et al. (2003) [16] | Mitomycin in combination with Cisplatin |
| 60 | - |
| Patel et al. (2018) [17] | Cisplatin alone or Cisplatin in combination with Adriamycin or Cisplatin in combination with Mitomycin C |
| 60–90 | - |
| Refaely et al. (2011) [18] | Cisplatin alone |
| 60 | 1000–2000 mL/min |
| Ried et al. (2023) [19] | Cisplatin alone or Cisplatin in combination with Doxorubicin |
| 60 | 1200 mL/min |
| Yellin et al. (2013) [20] | Cisplatin alone or Cisplatin in combination with Doxorubicin |
| 60 1 | 1000–2500 mL/min |
| Yu et al. (2013) [21] | Cisplatin alone | 100 | 120 | 1800–2300 mL/min |
| Study | Air Leak n/N (%) | Bleeding n/N (%) | Return to Operating Room n/N (%) | Pneumonia n/N (%) | Nephrotoxicity n/N (%) | Arrhythmia n/N (%) | Myasthenic Flare n/N (%) | Early Postoperative Mortality n/N (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ambrogi et al. (2016) [9] | 1/13 (7.7%) | 3/13 (23%) | 0/13 (0%) | 0/13 (0%) | 0/13 (0%) | 0/13 (0%) | 0/13 (0%) | 0/13 (0%) |
| Aprile et al. (2020) [6] | 3/27 (11%) | 7/27 (26%) | 0/27 (0%) | 0/27 (0%) | 0/27 (0%) | 0/27 (0%) | 0/27 (0%) | 0/27 (0%) |
| de Bree et al. (2022) [10] | 0/3 (0%) | 0/3 (0%) | 0/3 (0%) | 0/3 (0%) | 1/3 (33%) | 0/3 (0%) | 0/3 (0%) | 0/3 (0%) |
| Chappuy et al. (2022) [11] | 2/40 (5.0%) | 0/40 (0%) | 0/40 (0%) | 6/40 (15%) | 4/40 | 0/40 (0%) | 0/40 (0%) | 1/40 (2.5%) |
| Dolan et al. (2022) [12] | 7/12 (58%) | 4/12 (33%) | 3/12 (25%) | 0/12 (0%) | 1/12 (8.3%) | 3/12 (25%) | 0/12 (0%) | 0/12 (0%) |
| Klotz et al. (2021) [13] | - | - | - | - | 0/12 (0%) | - | - | 0/12 (0%) |
| Kodama et al. (2013) [14] | - | - | - | - | 0/12 (0%) | - | - | 0/12 (0%) |
| Kumar et al. (2021) [22] | 1/6 (17%) | 0/6 (0%) | 0/6 (0%) | 0/6 (0%) | 1/6 (17%) | 2/6 (33%) | 1/6 (17%) | 0/6 (0%) |
| Markowiak et al. (2021) [23] | 0/29 (0%) | 1/29 (3.5%) | 6/29 (21%) | 0/29 (0%) | 2/29 (6.9%) | 0/29 (0%) | 0/29 (0%) | 1/29 (3.5%) |
| Maury et al. (2017) [24] | 0/19 (0%) | 0/19 (0%) | 0/19 (0%) | 1/19 (5.3%) | 2/19 (11%) | 0/19 (0%) | 0/19 (0%) | 0/19 (0%) |
| Miller et al. (2023) [15] | - | - | - | - | 0/14 (0%) | - | - | 0/14 (0%) |
| Monneuse et al. (2003) [16] | 0/1 (0%) | 0/1 (0%) | 0/1 (0%) | 0/1 (0%) | 0/1 (0%) | 0/1 (0%) | 0/1 (0%) | 0/1 (0%) |
| Patel et al. (2018) [17] | 0/1 (0%) | 0/1 (0%) | 0/1 (0%) | 0/1 (0%) | 0/1 (0%) | 0/1 (0%) | 0/1 (0%) | 0/1 (0%) |
| Refaely et al. (2011) [18] | 1/15 (6.7%) | 1/15 (6.7%) | 1/15 (6.7%) | 0/15 (0%) | 0/15 (0%) | 0/15 (0%) | 1/15 (6.7%) | 0/15 (0%) |
| Ried et al. (2023) [19] | 3/58 (5.2%) | 2/58 (3.5%) | 8/58 (14%) | 8/58 (14%) | 4/58 (6.9%) | 2/58 (3.5%) | 0/58 (0%) | 1/58 (1.7%) |
| Yellin et al. (2013) [20] | 2/35 (5.7%) | 1/35 (1.9%) | 0/35 (0%) | 1/35 (2.9%) | 0/35 (0%) | 0/35 (0%) | 2/35 (5.7%) | 0/35 (0%) |
| Yu et al. (2013) [21] | 0/4 (0%) | 0/4 (0%) | 0/4 (0%) | 1/4 (25%) | 0/4 (0%) | 0/4 (0%) | 0/4 (0%) | 0/4 (0%) |
| All Studies | 20/263 (7.6%) | 19/263 (7.2%) | 18/263 (6.8%) | 17/263 (6.5%) | 11/301 (3.7%) | 7/263 (2.7%) | 4/263 (1.5%) | 3/301 (1.0%) |
| Study | Early/In-Hospital Outcomes | Long-Term Oncologic Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
| Ambrogi et al. (2016) [9] |
|
|
| Aprile et al. (2020) [6] |
|
|
| de Bree et al. (2022) [10] |
|
|
| Chappuy et al. (2022) [11] |
|
|
| Dolan et al. (2022) [12] |
|
|
| Klotz et al. (2021) [13] |
|
|
| Kodama et al. (2013) [14] | - |
|
| Kumar et al. (2021) [22] |
|
|
| Markowiak et al. (2021) [23] |
|
|
| Maury et al. (2017) [24] |
|
|
| Miller et al. (2023) [15] |
|
|
| Monneuse et al. (2003) [16] |
|
|
| Patel et al. (2018) [17] |
|
|
| Refaely et al. (2011) [18] |
|
|
| Ried et al. (2023) [19] |
|
|
| Yellin et al. (2013) [20] | - |
|
| Yu et al. (2013) [21] | - |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martins, R.S.; Christophel, E.; Poulikidis, K.; Razi, S.S.; Latif, M.J.; Luo, J.; Bhora, F.Y. A Systematic Review of Heated Intrathoracic Chemotherapy for Thymic Epithelial Tumors and the First Case Report of a Robotic Approach: Could a Minimally Invasive Approach Offer a New Paradigm of Care? J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 4094. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124094
Martins RS, Christophel E, Poulikidis K, Razi SS, Latif MJ, Luo J, Bhora FY. A Systematic Review of Heated Intrathoracic Chemotherapy for Thymic Epithelial Tumors and the First Case Report of a Robotic Approach: Could a Minimally Invasive Approach Offer a New Paradigm of Care? Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(12):4094. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124094
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartins, Russell Seth, Elizabeth Christophel, Kostantinos Poulikidis, Syed Shahzad Razi, M. Jawad Latif, Jeffrey Luo, and Faiz Y. Bhora. 2025. "A Systematic Review of Heated Intrathoracic Chemotherapy for Thymic Epithelial Tumors and the First Case Report of a Robotic Approach: Could a Minimally Invasive Approach Offer a New Paradigm of Care?" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 12: 4094. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124094
APA StyleMartins, R. S., Christophel, E., Poulikidis, K., Razi, S. S., Latif, M. J., Luo, J., & Bhora, F. Y. (2025). A Systematic Review of Heated Intrathoracic Chemotherapy for Thymic Epithelial Tumors and the First Case Report of a Robotic Approach: Could a Minimally Invasive Approach Offer a New Paradigm of Care? Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(12), 4094. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124094







