Uterine Fibroids and Their Association with Acute and Chronic Venous Thromboembolic Disease—An Expert Review of the Literature
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Review of Observational Data, Including Case Series and Case Reports
2.1. Material and Methods
2.2. Patient Demographics
2.3. Clinical Presentation
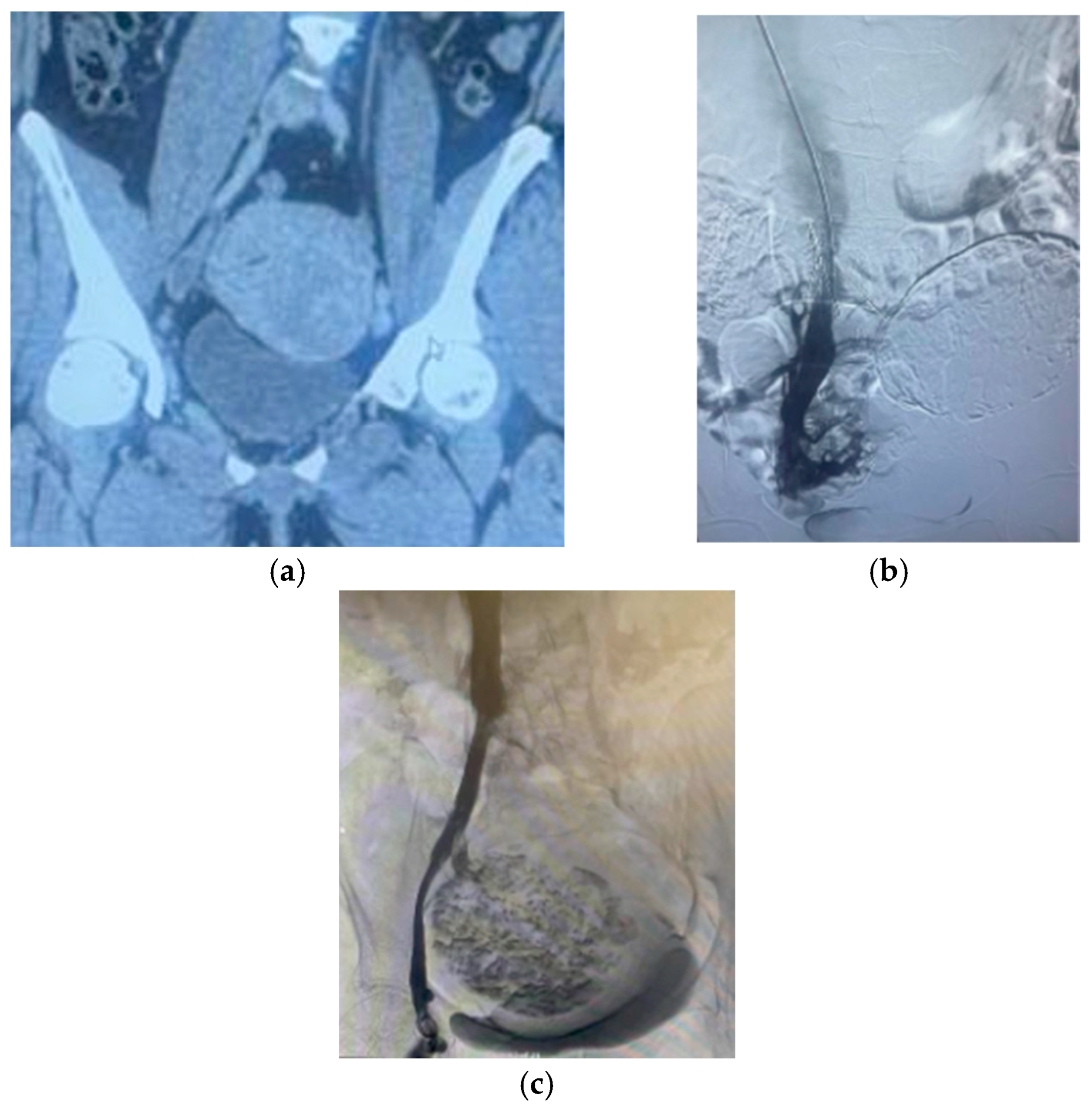
2.4. Characteristics of Fibroids
2.5. VTE Risk Factors
2.6. Management Strategies
3. Discussion
4. Future Direction
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stewart, E.A.; Cookson, C.L.; Gandolfo, R.A.; Schulze-Rath, R. Epidemiology of uterine fibroids: A systematic review. BJOG Int. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2017, 124, 1501–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Hendy, A.; Myers, E.R.; Stewart, E. Uterine Fibroids: Burden and Unmet Medical Need. Semin. Reprod. Med. 2017, 35, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mettler, L.; Schollmeyer, T.; Tinelli, A.; Malvasi, A.; Alkatout, I. Complications of Uterine Fibroids and Their Management, Surgical Management of Fibroids, Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy versus Hysterectomy, Haemorrhage, Adhesions, and Complications. Obstet. Gynecol. Int. 2012, 2012, 791248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Manyonda, I.T. Acute complications of fibroids. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2009, 23, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacharite-Roberge, A.; Raza, F.; Bashir, R.; Dass, C.A.; Moser, G.W.; Auger, W.R.; Toyoda, Y.; Forfia, P.R.; Vaidya, A. Case series of seven women with uterine fibroids associated with venous thromboembolism and chronic thromboembolic disease. Pulm. Circ. 2019, 9, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moores, L.; Bilello, K.L.; Murin, S. Sex and gender issues and venous thromboembolism. Clin. Chest. Med. 2004, 25, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speed, V.; Roberts, L.N.; Patel, J.P.; Arya, R. Venous thromboembolism and women’s health. Br. J. Haematol. 2018, 183, 346–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serena, T.; Bailey, W.; Bendix, S. Endovascular management of extensive iliocaval thrombosis secondary to synchronous uterine myoma compression and May-Thurner syndrome. J. Vasc. Surg. Cases Innov. Tech. 2022, 8, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekel, A.; Rabinerson, D.; Dicker, D.; Ben-Rafael, Z. Thrombosis of the pelvic veins associated with a large myomatous uterus. Obstet. Gynecol. 1998, 92, 646–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khademvatani, K.; Rezaei, Y.; Kerachian, A.; Seyyed-Mohammadzad, M.H.; Eskandari, R.; Rostamzadeh, A. Acute Pulmonary Embolism Caused by Enlarged Uterine Leiomyoma: A Rare Presentation. Am. J. Case Rep. 2014, 15, 300–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwano, T.; Miura Sichiro Nishikawa, H.; Shirai, K.; Saku, K. Venous Thrombosis Associated with a Large Uterine Myoma. Intern. Med. 2008, 47, 809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Kim, C.; Kim, S.; Lee, S. Deep Venous Thrombosis Caused by a Huge Uterine Myoma. Hong Kong J. Emerg. Med. 2012, 19, 361–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales Vidal, S.; Verma, G.; Goldschmidt, C.; Biller, J. Stroke due to Paradoxical Embolization Related to Fibroid Uterus Enlargement Compressing the Right Common Iliac Vein. Case Rep. Neurol. 2018, 10, 328–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, H.; Ideishi, M.; Nishimura, T.; Kawamura, A.; Kamochi, H.; Tahara, H.; Tsuchiya, Y.; Shirai, K.; Okabe, M.; Arakawa, K. Deep venous thrombosis and pulmonary thromboembolism associated with a huge uterine myoma—A case report. Angiology 2000, 51, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogden, L. Deep vein thrombosis secondary to compression by uterine leiomyoma. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 1998, 18, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podduturi, V.; Armstrong-Briley, D.R.; Guileyardo, J.M. Sudden Death by Pulmonary Thromboembolism due to a Large Uterine Leiomyoma with a Parasitic Vein to the Mesentery. Case Rep. Obstet. Gynecol. 2014, 2014, e181265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srettabunjong, S. Systemic Thromboembolism After Deep Vein Thrombosis Caused by Uterine Myomas. Am. J. Forensic Med. Pathol. 2013, 34, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, F.A.; Sousa, D. Leiomyoma as a cause of thrombotic events in different vascular territories. BMJ Case Rep. 2022, 15, e252906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Koo, J.; Lee, K. Simultaneously Occurring Ischemic Stroke, Leg Artery Occlusion, and Pulmonary Embolism Induced by a Uterine Myoma. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2022, 31, 106328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurakazu, M.; Ueda, T.; Matsuo, K.; Ishikura, H.; Kumagai, N.; Yoshizato, T.; Miyamoto, S. Percutaneous cardiopulmonary support for pulmonary thromboembolism caused by large uterine leiomyomata. Taiwan J. Obs. Gynecol. 2012, 51, 639–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norman, N.C.; Klein, P.A.; Choi, N.J.; Smith, D.G.; Klein, J.A. Pulmonary Embolism after Liposuction Totally by Tumescent Local Anesthesia in a Patient with Large Uterine Fibroids. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2023, 11, e4876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivatsa, A.; Burdett, J.; Gill, D. A 35-year-old woman with uterine fibroids and multiple embolic strokes. Neurology 2005, 64, 1479–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caparelli, M.L.; Perlman, S.; Lalezari, S. Unusual Causes of Venous Thrombosis: Bladder Distension and Uterine Mass. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2018, 46, 370.e9–370.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangeethaa, M.; Abeysekara, A. Management of a case of large uterine leiomyoma with deep vein thrombosis. Sri Lanka J. Obs. Gynaecol. 2023, 45, 27–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asciutto, G.; Mumme, A.; Marpe, B.; Hummel, T.; Asciutto, K.C.; Geier, B. Deep venous thrombosis in a patient with large uterine myomata. Case report. Minerva Ginecol. 2008, 60, 451–453. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bonito, M.; Gulemì, L.; Basili, R.; Brunetti, G.; Roselli, D. Thrombosis associated with a large uterine myoma: Case report. Clin. Exp. Obs. Gynecol. 2007, 34, 188–189. [Google Scholar]
- Ippolito, E.; Buora, A.; Belcaro, G.; Alari, G.; Arpaia, G.; Ciammaichella, G. Deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism in a patient affected by uterine fibroids: Clinical case. Panminerva Med. 2012, 54, 97–99. [Google Scholar]
- Khilanani, R.; Dandolu, V. Extensive iliac vein thrombosis as a rare complication of a uterine leiomyoma: A case report. J. Reprod. Med. 2007, 52, 537–538. [Google Scholar]
- Greene, J.F.; DeRoche, M.E.; Ingardia, C.; Curry, S.L. Large myomatous uterus resulting in complete obstruction of the inferior vena cava during pregnancy. BJOG Int. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2002, 109, 1189–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toru, S.; Murata, T.; Ohara, M.; Ishiguro, T.; Kobayashi, T. Paradoxical cerebral embolism with patent foramen ovale and deep venous thrombosis caused by a massive myoma uteri. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2013, 115, 760–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brucka, A.; Szyłło, K.; Stefańczyk, L.; Dobrowolski, Z. Deep venous thrombosis due to massive compression by uterine myoma. Menopause Rev. 2010, 9, 340–343. [Google Scholar]
- Anuradha, T.; Suchi, G.; Vasundhara, K. Large Uterine Fibromyoma: Association with DVT of Pelvic veins and Pulmonary Thromboembolism. A Series of Four Such Rare Cases. J. Obs. Gynecol. India. 2014, 64, 70–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satti, M.A.; Paredes Saenz, C.; Raju, R.; Cuthpert, S.; Kanzy, A.; Abhari, S.; Iii, J.H.; Rocha, F.G. Should Prophylactic Anticoagulation Be Considered with Large Uterine Leiomyoma? A Case Series and Literature Review. Case Rep. Obstet. Gynecol. 2016, 2016, e9803250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, Y.S.; Fong, Y.F.; Ng, S.C. Deep vein thrombosis in patients with large uterine myomata. Obstet. Gynecol. 1998, 92, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, I.; Ishtiaq, S. Uterine Myoma—A Rare Cause of Iliac Vein Thrombosis. Isra Med. J. 2016, 8, 263. [Google Scholar]
- Bekhit, M.T.; Hassanaien, M.; Thomas, E.; Cockburn, J. A large fibroid uterus presenting with bilateral DVT, treated with IVC filter and hysterectomy, a case report. Eur. J. Obs. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2007, 134, 135–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cărbunaru, A.; Herlea, V.; Ionescu, M.; Dumitraşcu, T. Extensive Left Iliac Veins and Inferior Vena Cava Thrombosis Revealing a Giant Uterine Myoma. Rom. J. Intern. Med. 2016, 54, 70–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabasa-Gorgas, L.; Benito-Vielba, M.; Ortega-Marcilla, S.; Tiempo-Marques MPdel Yagüe-Moreno, H.; Bolea-Tobajas, R. Pulmonary thromboembolism secondary to enormous uterine fibroid: Medical-surgical management. A case report. Ginecol. Obs. Mex. 2019, 87, 489–495. [Google Scholar]
- Huffman-Dracht, H.B.; Coates, W.C. Uterine Leiomyomata-Related Thromboembolic—Disease: A Case Report. J. Emerg. Med. 2010, 39, e101–e104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latif, H.; Baez Sosa, V.; Farid, S.; Fernandez, S.; Hazen, N.; Morozov, V.; Fitzpatrick, K.W. Venous Thromboembolism in Women with Uterine Fibroids. Blood 2020, 136, 28–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.-K.; Kor, C.-T.; Chen, C.-P.; Chen, H.-T.; Yang, P.-T.; Tsail, C.-D.; Huang, C.-H. Increased Risk of Venous Thromboembolism in Women with Uterine Leiomyoma: A Nationwide, Population-Based Case-Control Study. Acta Cardiol. Sin. 2018, 34, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiota, M.; Kotani, Y.; Umemoto, M.; Tobiume, T.; Tsuritani, M.; Shimaoka, M.; Hoshiai, H. Deep-Vein Thrombosis Is Associated with Large Uterine Fibroids. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2011, 224, 87–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fletcher, H.; Wharfe, G.; Williams, N.P.; Gordon-Strachan, G.; Pedican, M.; Brooks, A. Venous thromboembolism as a complication of uterine fibroids: A retrospective descriptive study. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2009, 29, 732–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finianos, E.S.; Yacoub, S.F.; Chammas, M.F. Ovarian Vein Thrombosis Complicated by Pulmonary Embolism after Cesarean Delivery in the Presence of a Large Fibroid: Case Report and Literature Review of Contributing Factors. Case Rep. Obstet. Gynecol. 2021, 2021, 6389713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, S.; Tokunaga, T.; Yamaguchi, A.; Kono, T.; Kasano, K.; Yoshiwara, H.; Hattori, E.; Niwa, A.; Hirao, K. Paradoxical embolism caused by ovarian vein thrombosis extending to inferior vena cava in a female with uterine myoma. J. Cardiol. Cases 2018, 18, 207–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.J.; Huang, K.H.; Liu, J. Ovarian vein thrombosis associated with compression by a uterine myoma. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2011, 159, 485–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, M.C.; Lu, B.Y.; Winkel, A.F. Ovarian Vein Thrombophlebitis Related to Large Uterine Myoma. Obstet. Gynecol. 2014, 123, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekkel, E.; Chandran, T.; Trpkovski, M.; Hans, S. Management of phlegmasia cerulea dolens caused by a giant leiomyoma. J. Vasc. Surg. Cases Innov. Tech. 2022, 8, 240–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutsukata, N.; Mashiko, K.; Matsumoto, H.; Hara, Y.; Sakamoto, Y.; Yokota, H. A Case of Successful Treatment of Acute Iliofemoral Venous Thrombosis Caused by Giant Myoma Through Combination of Simultaneous Hysterectomy and Thrombectomy. Ann. Vasc. Dis. 2009, 2, 114–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewer, M.B.; Woo, K.; Weaver, F.A. Venous thromboembolism secondary to uterine fibroids: A case of phlegmasia cerulea dolens and review of the literature. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2015, 29, 364.e5–364.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinawi, M. Massive Uterine Fibroid Resulting in Extensive Deep Venous Thrombosis, Compartment Syndrome and Rhabdomyolysis. Arch. Intern. Med. Res. 2020, 3, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnaby, J.; Martynov, A.; Shah, S.; Ramanathan, A. Giant subserosal myoma causing deep venous thrombosis in a patient with pre-existing May-Thurner syndrome. Radiol. Case Rep. 2020, 15, 644–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, S.C.; Tsai, M.J.; Hsu, C.F. May–Thurner syndrome caused by a huge uterine myoma. Tzu-Chi Med. J. 2017, 29, 235–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, A.F.; Antunes, J.D. May-Thurner Syndrome Variant—Compression of the Iliac Vein Caused by Uterine Myoma. Clin. Image Case Rep. J. 2022, 4, 283. [Google Scholar]
- Speranza, G.; Hager, E. Venous thromboembolism in a patient with an uncommon etiology of May-Thurner syndrome. J. Vasc. Surg. Cases Innov. Tech. 2021, 7, 549–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, R.; Takahashi, H.; Hori, Y.; Fukushima, K. May-Thurner Syndrome with Calcified Uterine Leiomyoma. Intern. Med. 2021, 60, 2343–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fletcher, H.M.; Wharfe, G. Intestinal obstruction and thromboembolism in a postmenopausal woman with large calcified fibroids. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2008, 28, 754–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, H.H. Uterine leiomyoma as a rare cause of acute abdomen and intestinal gangrene. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1998, 179, 830–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graff-Radford, J.; Jones, D.T.; Pruthi, R.K.; Flemming, K.D. A Neurological Complication of a Uterine Fibroid. Neurocrit. Care 2013, 18, 93–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unosawa, S.; Hata, M.; Sezai, A.; Niino, T.; Yoshitake, I.; Minami, K. Pulmonary Embolism with Myomatous Erythrocytosis Syndrome and Extreme Obesity. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2009, 57, 313–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Peker, D.; Greer, H.O.; Conner, M.G.; Novak, L. Extramedullary Hematopoiesis in Uterine Leiomyoma Associated with Numerous Intravascular Thrombi. Case Rep. Pathol. 2014, 2014, 957395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawes, J.; Lohr, J.; Blum, B.; Bhati, A.; Bhaskaran, J.; Engel, A. Large Uterine Fibroids Causing Mechanical Obstruction of the Inferior Vena Cava and Subsequent Thrombosis: A Case Report. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2006, 40, 425–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riat, R.; Chowdary, P.; Mavrides, E.; Magos, A.; Gatt, A. Is there an Association between Thrombosis and Fibroids? A single centre experience and literature review. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2013, 35, e13–e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsam, S.; Bagot, C.N.; Patel, R.K.; Sidhu, P.S.; Davies, A.; Arya, R. Extrinsic Venous Compression May Not Be a Sufficient Explanation for Venous Thromboembolism Due to Massive Fibroids. Blood 2006, 108, 4100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boos, C.J.; Calver, A.L.; Moors, A.; Dawkins, K.D.; Hacking, C.N. Uterine artery embolisation for massive uterine fibroids in the presence of submassive pulmonary emboli. BJOG Int. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2005, 112, 1440–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakiz, M.; But, I. Management of acute deep vein thrombosis due to enlarged symptomatic uterine fibroids. Int. J. Gynecol. Obstet. 2009, 105, 177–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casey, C.; Buckley, C.M.; Kearney, P.M.; Ali, F.; Ni Bhuachalla, C.; Roberts, G.; Perry, I.J.; Bradley, C.P. Proceedings of the RAMI Intern Section Meeting, 18th January 2014. Ir. J. Med. Sci 1971 2014, 183, 119–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nartey, Y.A.; Botchway, E.T.; Lovi, J. Case report: A challenging case of bilateral pulmonary embolism, deep venous thrombosis and bleeding uterine fibroids in a resource poor setting in Ghana. PAMJ Clin. Med. 2020, 2, 55. [Google Scholar]
- Nawaz, R.; Haque, S.; Shaha, K. Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism in a Woman with Uterine Myoma. Bangladesh J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2008, 23, 78–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanan, S.; Chapman-Wardy, J.; Watson, R. Bleeding versus Clotting: A Complex Case of a Large Fibroid Uterus Causing Menorrhagia and a DVT. Case Rep. Obstet. Gynecol. 2016, 2016, e4169565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, H.; Umekawa, T.; Kikukawa, T.; Nakamura, M.; Toyoda, N. Venous thromboembolic diseases associated with uterine myomas diagnosed before hysterectomy: A report of two cases. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 2002, 28, 300–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devabhaktuni, P.; Gupta, P.C.; Bhupatiraju, S.; Puranam, B.; Abdul, S.M. Uterine Fibromyoma and Intravascular Thrombosis—Eight Cases. Open J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2014, 04, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baird, D.D.; Dunson, D.B.; Hill, M.C.; Cousins, D.; Schectman, J.M. High cumulative incidence of uterine leiomyoma in black and white women: Ultrasound evidence. Am. J. Obs. Gynecol. 2003, 188, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, A.B.; Miller, C.H.; Hooper, W.C.; Lally, C.; Austin, H.D. High factor VIII, von Willebrand factor, and fibrinogen levels and risk of venous thromboembolism in blacks and whites. Ethn. Dis. 2014, 24, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zakai, N.A.; McClure, L.A.; Judd, S.E.; Safford, M.M.; Folsom, A.R.; Lutsey, P.L.; Cushman, M. Racial and regional differences in venous thromboembolism in the United States in 3 cohorts. Circulation 2014, 129, 1502–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Paul, E.N.; Grey, J.A.; Carpenter, T.J.; Madaj, Z.B.; Lau, K.H.; Givan, S.A.; Burns, G.W.; Chandler, R.L.; Wegienka, G.R.; Shen, H.; et al. Transcriptome and DNA methylome analyses reveal underlying mechanisms for the racial disparity in uterine fibroids. JCI Insight 2022, 7, e160274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Michels, A.; Lillicrap, D.; Yacob, M. Role of von Willebrand factor in venous thromboembolic disease. JVS Vasc Sci. 2021, 3, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Carnethon, M.R.; Pu, J.; Howard, G.; Albert, M.A.; Anderson, C.A.M.; Bertoni, A.G.; Mujahid, M.S.; Palaniappan, L.; Herman, A.T., Jr.; Willis, M.; et al. Cardiovascular Health in African Americans: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2017, 136, e393–e423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayan, A.; Eng, J.; Carmi, L.; McGrane, S.; Ahmed, M.; Sharrett, A.R.; Streiff, M.; Coresh, J.; Powe, N.; Hong, K. Iliac vein compression as risk factor for left- versus right-sided deep venous thrombosis: Case-control study. Radiology 2012, 265, 949–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Crowther, M.A.; Warkentin, T.E. Bleeding risk and the management of bleeding complications in patients undergoing anticoagulant therapy: Focus on new anticoagulant agents. Blood 2008, 111, 4871–4879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulder, J.K.; Siedhoff, M.T.; Till, S.R.; Moll, S. Management considerations for patients with uterine fibroids and concurrent venous thromboembolism. Curr. Opin. Obstet. Gynecol. 2016, 28, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Li, H.; Chan, Y.; Cui, D.; Cheng, S. Multidisciplinary staged management of iliofemoral venous thrombosis caused by huge uterine fibroid: A case report. Hong Kong Med. J. 2021, 27, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotsis, T.; Christoforou, P.; Chatziioannou, A.; Memos, N.; Theodoraki, K.; Konstadoulakis, M. Vena cava balloon occlusion for pulmonary embolism prevention during resection of giant uterus fibroids. J. Surg. Case Rep. 2022, 2022, rjac234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Wunster, S.; D’Oria, P.; Colonna, L.; Patelli, G. Ulipristal Acetate Efficacy in a Patient with Symptomatic Fibroid and Concomitant Pulmonary Embolism. Case Rep. Med. 2020, 2020, 3249268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.H.; McNally, R.; Kim, J.J.; Wei, J.J. Racial disparity in uterine leiomyoma: New insights of genetic and environmental burden in myometrial cells. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2024, 30, gaae004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Author | Country | Patient Population | Sample Size | Time Period | Prevalence | Incidence | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Latif et al., 2020 [40] | United States | Patients diagnosed with fibroids | 6095 | 2015–2019 | 2.2% a | n/a | |
| Huang et al., 2018 [41] | Taiwan | Female patients (>18y) with VTE | 2282 | 2000–2013 | n/a | n/a | Risk of VTE in fibroids: OR = 1.547 (95% CI: 1.27–1.88), p < 0.0001 |
| Shiota et al., 2011 [42] | Japan | Patients diagnosed with fibroids undergoing hysterectomy | 361 | 2003–2009 | n/a | n/a | DVT rate for uterine weight <1000 g = 3% DVT rate for uterine weight > = 1000 g = 11.5% |
| Fletcher et al., 2009 [43] | Kingston, Jamaica | Adult women diagnosed with VTE | 438 | 1999–2004 | n/a | n/a | Risk of VTE in fibroids: OR = 3.75 (95% CI: 2.92–4.78), p = 0.0001 |
| Characteristics | Findings | |
|---|---|---|
| Mean age (n = 93) | 43.6 ± 7.8 years | |
| Mean BMI (body mass index (n = 14) | 26.7 ± 6.5 kg/m2 | |
| Mean hemoglobin (n = 42) | 8.8 ± 3.6 g/dL | |
| Race (n = 35) | Caucasian | 7 (20%) |
| African American/African/Afro-Caribbean/Caribbean | 22 (62.9%) | |
| Asian | 6 (17.1%) | |
| Location of VTE (n = 97) | Proximal DVT (popliteal, femoral, iliac veins, IVC) | 37 (38%) |
| Distal DVT (peroneal, tibial, and muscular veins) with/without proximal DVT | 6 (6.1%) | |
| DVT and PE | 27 (27.6%) | |
| Acute PE only | 6 (6.1%) | |
| CTED/CTEPH | 7 (7.1%) | |
| Paradoxical embolus (PFO) | 9 (9.2%) | |
| Others | 5 (5.1%) | |
| Side of DVT (n = 80) | Left | 50 (63%) |
| Right | 19 (23.5%) | |
| Bilateral | 11 (13.6%) | |
| Symptoms on presentation ✝ (n = 99) | Lower extremity symptoms (swelling, pain) | 47 (47.5%) |
| Chest symptoms (pain, dyspnea), dizziness, syncope | 21 (21.2%) | |
| Lower extremity and chest symptoms | 11 (11.1%) | |
| Abdominal symptoms (pain, swelling) | 9 (9.1%) | |
| Neurological symptoms | 7 (7.1%) | |
| Others (headache, upper extremity symptoms, arterial thrombosis) | 4 (4%) | |
| Thrombophilia workup (n = 59) | Positive | 5 (8.5%) |
| Known risk factors of VTE (n = 100) | Medications, immobilization, health conditions, addictions | 38 (38%) |
| Signs of compression (n = 72) | Imaging/operative finding | 57 (79.2%) |
| Management of VTE ‡ (n = 83) | IVC a filter/balloon occlusion | 29 (35%) |
| Anticoagulation | 61 (73.5%) | |
| Thrombolysis | 15 (18%) | |
| Thrombectomy/thromboembolectomy | 15 (18%) | |
| Pulmonary thromboendarterectomy | 7 (8.4%) | |
| Management of fibroids (n = 83) | TAH b | 31 (37%) |
| TAH b and BSO c/BS d/oophorectomy | 21 (25%) | |
| Myomectomy | 11 (13%) | |
| Uterine artery embolization | 4 (5%) | |
| Drugs | 5 (6%) | |
| Surgery planned/refused treatment/lost to follow-up | 11 (13%) | |
| Prior diagnosis of fibroid (n = 48) | 32 (66.6%) | |
| Mean gestational age of uterus (n = 18) | 21.6 ± 4.5 weeks | |
| Mean weight of uterus as operative finding (n = 16) | 2231.9 ± 1343.7 g | |
| Mean largest diameter of fibroid (n = 26) | 13.5 ± 6.0 cm | |
| Median volume of fibroid (n = 23) | 2050.15 mL (75.5–26,250) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Afaq, M.; Zlotshewer, B.A.; Oliveros, E.; Bauman, S.G.; Vaidya, A.; Lakhter, V.; Forfia, P.; Sadek, A.S.; Hernandez, E.; Bashir, R. Uterine Fibroids and Their Association with Acute and Chronic Venous Thromboembolic Disease—An Expert Review of the Literature. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 4065. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124065
Afaq M, Zlotshewer BA, Oliveros E, Bauman SG, Vaidya A, Lakhter V, Forfia P, Sadek AS, Hernandez E, Bashir R. Uterine Fibroids and Their Association with Acute and Chronic Venous Thromboembolic Disease—An Expert Review of the Literature. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(12):4065. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124065
Chicago/Turabian StyleAfaq, Munaza, Brooke Alexa Zlotshewer, Estefania Oliveros, Sarah Gabrielle Bauman, Anjali Vaidya, Vladimir Lakhter, Paul Forfia, Ahmed S. Sadek, Enrique Hernandez, and Riyaz Bashir. 2025. "Uterine Fibroids and Their Association with Acute and Chronic Venous Thromboembolic Disease—An Expert Review of the Literature" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 12: 4065. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124065
APA StyleAfaq, M., Zlotshewer, B. A., Oliveros, E., Bauman, S. G., Vaidya, A., Lakhter, V., Forfia, P., Sadek, A. S., Hernandez, E., & Bashir, R. (2025). Uterine Fibroids and Their Association with Acute and Chronic Venous Thromboembolic Disease—An Expert Review of the Literature. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(12), 4065. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124065








