Soluble Urokinase Plasminogen Activator Receptor (suPAR) as a Biomarker of Erectile Dysfunction in Diabetic Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Setting
2.2. Erectile Function Assessment
2.3. Blood Sampling and Biochemical Analysis
2.4. Serum suPAR Measurement
2.5. Outcomes
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ED | Erectile dysfunction |
| DM | Diabetes mellitus |
| suPAR | Soluble urokinase plasminogen activator receptor |
| uPAR | Urokinase plasminogen activator receptor |
| NO | Nitric oxide |
| PDE5 | Phosphodiesterase type 5 |
| IIEF-5 | International Index of Erectile Function-5 |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| HbA1c | Glycated hemoglobin |
| PSA | Prostate-specific antigen |
| LH | Luteinizing hormone |
| FSH | Follicle-stimulating hormone |
| TSH | Thyroid-stimulating hormone |
| ROC | Receiver operating characteristic |
| IQR | Interquartile range |
| DM-NoED | Diabetic patients without erectile dysfunction |
| DMED | Diabetic patients with erectile dysfunction |
| ESR | Erythrocyte sedimentation rate |
| AUC | Area under the curve |
References
- Nutalapati, S.; Ghagane, S.C.; Nerli, R.B.; Jali, M.V.; Dixit, N.S. Association of erectile dysfunction and type II diabetes mellitus at a tertiary care centre of South India. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2020, 14, 649–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NIH Consensus Conference. Impotence. NIH Consensus Development Panel on Impotence. JAMA 1993, 270, 83–90. [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald, S.M.; Burnett, A.L. Physiology of Erection and Pathophysiology of Erectile Dysfunction. Urol. Clin. North. Am. 2021, 48, 513–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, C.; Konstantinidis, C. Neurogenic Erectile Dysfunction. Where Do We Stand? Medicines 2021, 8, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangiorgi, G.; Cereda, A.; Benedetto, D.; Bonanni, M.; Chiricolo, G.; Cota, L.; Martuscelli, E.; Greco, F. Anatomy, Pathophysiology, Molecular Mechanisms and Clinical Management of Erectile Dysfunction in Patients Affected by Coronary Artery Disease: A Review. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roychoudhury, S.; Chakraborty, S.; Choudhury, A.P.; Das, A.; Jha, N.K.; Slama, P.; Nath, M.; Massanyi, P.; Ruokolainen, J.; Kesari, K.K. Environmental Factors-Induced Oxidative Stress: Hormonal and Molecular Pathway Disruptions in Hypogonadism and Erectile Dysfunction. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, S.; Ma, S.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Z.; Yan, P. Causal relationship between worry, tension, insomnia, sensitivity to environmental stress and adversity and erectile dysfunction: A study using Mendelian randomization. Andrology 2024, 12, 1272–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Li, D.; Liu, L.; Xiang, Y.; Tang, Y. Comparison of characteristics between Chinese diabetes mellitus-induced erectile dysfunction populations and non-diabetes mellitus-induced erectile dysfunction populations: A cross-sectional study. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1096045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Jiang, H.; Liu, J.; Li, H. Non-Coding RNAs: New Dawn for Diabetes Mellitus Induced Erectile Dysfunction. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 888624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castela, Â.; Costa, C. Molecular mechanisms associated with diabetic endothelial-erectile dysfunction. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2016, 13, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Chen, Y.; Yuan, H.; Wang, T.; Feng, J.; Li, M.; Liu, J. NOX1/4 Inhibitor GKT-137831 Improves Erectile Function in Diabetic Rats by ROS Reduction and Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase Reconstitution. J. Sex. Med. 2021, 18, 1970–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musicki, B.; Hannan, J.L.; Lagoda, G.; Bivalacqua, T.J.; Burnett, A.L. Mechanistic link between erectile dysfunction and systemic endothelial dysfunction in type 2 diabetic rats. Andrology 2016, 4, 977–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neves, D. Advanced glycation end-products: A common pathway in diabetes and age-related erectile dysfunction. Free Radic. Res. 2013, 47 (Suppl. S1), 49–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seftel, A.D.; Vaziri, N.D.; Ni, Z.; Razmjouei, K.; Fogarty, J.; Hampel, N.; Polak, J.; Wang, R.-Z.; Ferguson, K.; Block, C.; et al. Advanced glycation end products in human penis: Elevation in diabetic tissue, site of deposition and possible effect through iNOS or eNOS. Urology 1997, 50, 1016–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldney, J.; Sargeant, J.A.; Davies, M.J. Incretins and microvascular complications of diabetes: Neuropathy, nephropathy, retinopathy and microangiopathy. Diabetologia 2023, 66, 1832–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pop-Busui, R.; Hotaling, J.; Braffett, B.H.; Cleary, P.A.; Dunn, R.L.; Martin, C.L.; Jacobson, A.M.; Wessells, H.; Sarma, A.V.; DCCT/EDIC Research Group. Cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy, erectile dysfunction and lower urinary tract symptoms in men with type 1 diabetes: Findings from the DCCT/EDIC. J. Urol. 2015, 193, 2045–2051, Erratum in: J. Urol. 2015, 194, 855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghuraman, R.; Bhuyan, A.K.; Baro, A.; Saikia, U.K. Male Sexual Dysfunction and Hypogonadism in Young Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Cross Sectional Study. J. Hum. Reprod. Sci. 2024, 17, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swiecicka, A. The efficacy of PDE5 inhibitors in diabetic patients. Andrology 2023, 11, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmusssen, L.J.H.; Petersen, J.E.V.; Eugen-Olsen, J. Soluble Urokinase Plasminogen Activator Receptor (suPAR) as a Biomarker of Systemic Chronic Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 780641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raggam, R.B.; Wagner, J.; Prüller, F.; Grisold, A.; Leitner, E.; Zollner-Schwetz, I.; Valentin, T.; Krause, R.; Hoenigl, M. Soluble urokinase plasminogen activator receptor predicts mortality in patients with systemic inflammatory response syndrome. J. Intern. Med. 2014, 276, 651–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padelli, M.; Gueye, P.; Guilloux, D.; Banydeen, R.; Campana, V.; Cabie, A.; Neviere, R. Soluble urokinase plasminogen activator receptor levels are predictive of COVID-19 severity in Afro-Caribbean patients. Biomark. Med. 2022, 16, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherif, E.M.; El Maksood, A.A.A.; Youssef, O.I.; Salah El-Din, N.Y.; Khater, O.K.M. Soluble urokinase plasminogen activator receptor in type 1 diabetic children, relation to vascular complications. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2019, 33, 628–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.-Z.; Chang, L.-C.; Lin, Y.-F.; Hung, Y.-J.; Pei, D.; Chu, N.-F.; Chen, J.-S. Urokinase plasminogen activator receptor and its soluble form in common biopsy-proven kidney diseases and in staging of diabetic nephropathy. Clin. Biochem. 2015, 48, 1324–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodchild, T.T.; Li, Z.; Lefer, D.J. Soluble urokinase plasminogen activator receptor: From biomarker to active participant in atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132, e165868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, A.; Hayek, S.S. Role of Soluble Urokinase-Type Plasminogen Activator Receptor in Cardiovascular Disease. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2023, 25, 1797–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.R.; Wang, M.Y.; Zhang, C.L.; Wang, Y. Endothelial dysfunction in vascular complications of diabetes: A comprehensive review of mechanisms and implications. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1359255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostopoulou, E.; Kalavrizioti, D.; Davoulou, P.; Sinopidis, X.; Papachristou, E.; Goumenos, D.S.; Dimitriou, G.; Spiliotis, B.E.; Papasotiriou, M. Soluble urokinase plasminogen activator receptor (suPAR) in children with obesity or type 1 diabetes as a marker of endothelial dysfunction: A cross-sectional study. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2024, 183, 2383–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, N.C.; Raffield, L.M.; Moxley, A.H.; Miller-Fleming, T.W.; Auer, P.L.; Franceschini, N.; Ngo, D.; Thornton, T.A.; Lange, E.M.; Li, Y.; et al. Soluble Urokinase Plasminogen Activator Receptor: Genetic Variation and Cardiovascular Disease Risk in Black Adults. Circ. Genom. Precis. Med. 2021, 14, e003421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corban, M.T.; Prasad, A.; Nesbitt, L.; Loeffler, D.; Herrmann, J.; Lerman, L.O.; Lerman, A. Local Production of Soluble Urokinase Plasminogen Activator Receptor and Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1 in the Coronary Circulation Is Associated with Coronary Endothelial Dysfunction in Humans. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2018, 7, e009881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iversen, E.; Kallemose, T.; Hornum, M.; Bengaard, A.K.; Nehlin, J.O.; Rasmussen, L.J.H.; Sandholdt, H.; Tavenier, J.; Feldt-Rasmussen, B.; Andersen, O.; et al. Soluble urokinase plasminogen activator receptor and decline in kidney function among patients without kidney disease. Clin. Kidney J. 2022, 15, 1534–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, R.C.; Riley, A.; Wagner, G.; Osterloh, I.H.; Kirkpatrick, J.; Mishra, A. The International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF): A multidimensional scale for assessment of erectile dysfunction. Urology 1997, 49, 822–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thunø, M.; Macho, B.; Eugen-Olsen, J. suPAR: The molecular crystal ball. Dis. Markers 2009, 27, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eugen-Olsen, J.; Andersen, O.; Linneberg, A.; Ladelund, S.; Hansen, T.W.; Langkilde, A.; Petersen, J.; Pielak, T.; Møller, L.N.; Jeppesen, J.; et al. Circulating soluble urokinase plasminogen activator receptor predicts cancer, cardiovascular disease, diabetes and mortality in the general population. J. Intern. Med. 2010, 268, 296–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hindy, G.; Tyrrell, D.J.; Vasbinder, A.; Wei, C.; Presswalla, F.; Wang, H.; Blakely, P.; Ozel, A.B.; Graham, S.; Holton, G.H.; et al. Increased soluble urokinase plasminogen activator levels modulate monocyte function to promote atherosclerosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132, e158788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wlazeł, R.N.; Szadkowska, I.; Bartnicki, P.; Rośniak-Bąk, K.; Rysz, J. Clinical and prognostic usefulness of soluble urokinase plasminogen activator receptor in hemodialysis patients. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2018, 50, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velissaris, D.; Zareifopoulos, N.; Koniari, I.; Karamouzos, V.; Bousis, D.; Gerakaris, A.; Platanaki, C.; Kounis, N. Soluble Urokinase Plasminogen Activator Receptor as a Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker in Cardiac Disease. J. Clin. Med. Res. 2021, 13, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curovic, V.R.; Theilade, S.; Winther, S.A.; Tofte, N.; Eugen-Olsen, J.; Persson, F.; Hansen, T.W.; Jeppesen, J.; Rossing, P. Soluble Urokinase Plasminogen Activator Receptor Predicts Cardiovascular Events, Kidney Function Decline and Mortality in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, 1112–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mörtberg, J.; Salzinger, B.; Lundwall, K.; Edfors, R.; Jacobson, S.H.; Wallén, H.N.; Jernberg, T.; Baron, T.; Erlinge, D.; Andell, P.; et al. Prognostic importance of biomarkers associated with haemostatic, vascular and endothelial disturbances in acute coronary syndrome patients in relation to kidney function. Int. J. Cardiol. 2023, 373, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
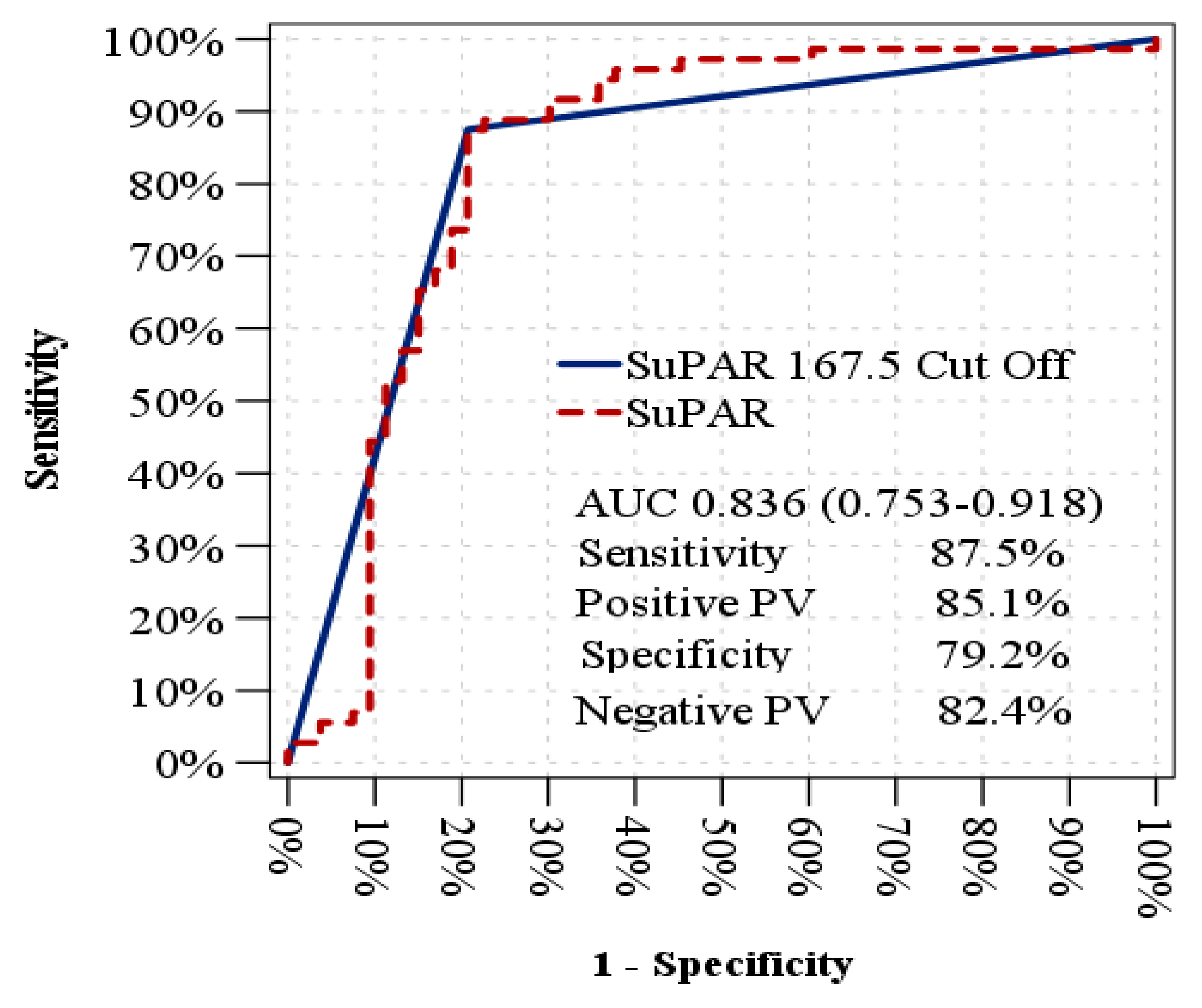

|
Healthy Control Group 1 (n = 46) |
DM-NoED Group 2 (n = 54) |
DMED Group 3 (n = 73) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 55 (51–61) | 57 (49–64) | 60 (51–64) | 0.055 |
| Smoking status, n (%) | ||||
| - Never | 29 (63) | 38 (70) | 45 (63) | 0.583 |
| - Ex-smoker | 5 (11) | 4 (8) | 6 (8) | |
| - Current smoker | 12 (25) | 12 (22) | 22 (30) | |
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | 23 (21.7–23.9) | 27.7 (25–30.5) | 28 (25.8–31) | <0.001 * |
| Systolic BP, mmHg Diastolic BP, mmHg | 120 (118–130) | 124 (119–130) | 130 (120–130) | 0.221 |
| 78 (70–85) | 80 (72–85) | 80 (70–90) | 0.151 | |
| Diabetes duration, years | - | 7 (3–14) | 14 (6–19.5) | <0.001 |
| ED duration, years | - | - | 4.1 | |
| IIEF-5 score | 23 (22–24) | 24 (23–25) | 11 (6–15) | <0.001 ** |
| ED severity, n (%) | ||||
| - Mild ED - Mild to moderate ED - Moderate ED - Severe ED | - | - | 15 (20.5) | |
| - | - | 19 (26) | ||
| - | - | 16 (22) | ||
| - | - | 23 (31.5) | ||
| Comorbid diseases, n (%) - Ischemic heart disease - Hypertension - Hyperlipidemia | ||||
| - | 12 (22.6) | 18 (24.6) | 0.782 | |
| - | 23 (43) | 40 (54.7) | 0.394 | |
| - | 19 (35.8) | 33 (45.2) | 0.674 | |
| Medication, n (%) | ||||
| - Metformin | - | 43 (79.6) | 57 (78) | 0.959 |
| - DPP4 inhibitors | - | 27 (50) | 39 (53) | 0.695 |
| - SGLT2 inhibitors | - | 24 (44) | 39 (53) | 0.300 |
| - Sulfonylureas | - | 11 (20) | 13 (17) | 0.681 |
| - Pioglitazone | - | 5 (9.2) | 12 (16.4) | 0.180 |
| - Insulin | - | 12 (22) | 26 (35.6) | 0.072 |
| - ACEI or ARB | - | 12 (22.2) | 25 (34) | 0.103 |
| - Statin and/or fibrate | - | 14 (25.9) | 30 (41) | 0.053 |
|
Healthy Control Group 1 (n = 46) |
DM-NoED Group 2 (n = 54) |
DMED Group 3 (n = 73) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| suPAR, pg/mL | 107.9 (102–116) | 130.3 (112–165) | 218 (192–249) | <0.001 * |
| FBG, mg/dL | 92 (84–96) | 148 (104–245) | 175 (130–221) | <0.001 ** |
| HbA1c, % | 5.7 (5.4–5.9) | 7.8 (6.8–9.6) | 8 (7.2–9.3) | <0.001 ** |
| HOMA-IR | 2.2 (1.5–3) | 4 (2.2–10.3) | 4.9 (1.7–8.7) | <0.001 ** |
| LDLc, mg/dL | 113 (91–137) | 98 (80–133) | 109 (80–133) | 0.368 |
| HDLc, mg/dL | 40 (36–45) | 39 (33–43) | 41 (34–48) | 0.204 |
| TG, mg/dL | 150 (107–200) | 145 (98–212) | 152 (104–234) | 0.582 |
| T.testosterone, ng/mL | 4.5 (2.9–5.5) | 3.4 (2.5–5) | 3.8 (2.8–5) | 0.131 |
| Total PSA, µg/L | 1.2 (0.8–2.7) | 1.3 (0.6–2.7) | 1.4 (0.5–2.5) | 0.413 |
| Prolactin, µg/mL | 11 (7.3–14.7) | 8.1 (6.8–12) | 9.9 (7.2–13.6) | 0.187 |
| FSH, IU/L | 8.8 (6.7–11.7) | 7.7 (5.7–9.4) | 8.1 (7–11.4) | 0.390 |
| LH, IU/L | 6.1 (5–7.9) | 6.2 (5.3–7.9) | 5.8 (4.7–7.1) | 0.508 |
| TSH, mIU/L | 1.5 (1–2.9) | 1.4 (1.1–2.5) | 2.1 (1.4–2.8) | 0.106 |
| Leukocytes, 103/uL | 7.8 (6.7–8.8) | 7.9 (6.4–9.8) | 8.3 (6.6–10) | 0.330 |
| Hemoglobin, g/dL | 14.9 (14.3–15.8) | 14.7 (13.6–15.7) | 14.8 (14–15.5) | 0.085 |
| Platelets, 103/uL | 242 (220–264) | 257 (212–293) | 249 (208–308) | 0.881 |
| Creatinine, mg/dL | 0.9 (0.8–1) | 0.9 (0.8–1) | 0.9 (0.6–1.1) | 0.664 |
| eGFR, mL/min/1.73 m2 | 93 (84–101) | 92 (80–104) | 91 (75–100) | 0.091 |
| ALT, U/L | 20 (14–28) | 16 (12–27) | 18 (15–23) | 0.316 |
| Total protein, g/L | 7.5 (7.3–7.7) | 7.2 (7.1–7.5) | 7.3 (7.2–7.5) | 0.490 |
| Albumin, g/L | 4.4 (4.2–4.7) | 4.5 (4.3–4.7) | 4.2 (4–4.7) | 0.056 |
| CRP, mg/L | 2.1 (1.3–3.4) | 2.3 (1.1–4.4) | 1.8 (0.9–4.1) | 0.623 |
| ESR, mm/h | 8 (6–12) | 11 (6–17) | 9 (6–14) | 0.232 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Erinc, O.; Yilmaz, O.; Kaya, T.Y.; Algemi, M.; Akarsu, M. Soluble Urokinase Plasminogen Activator Receptor (suPAR) as a Biomarker of Erectile Dysfunction in Diabetic Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 4029. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124029
Erinc O, Yilmaz O, Kaya TY, Algemi M, Akarsu M. Soluble Urokinase Plasminogen Activator Receptor (suPAR) as a Biomarker of Erectile Dysfunction in Diabetic Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(12):4029. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124029
Chicago/Turabian StyleErinc, Osman, Ozgur Yilmaz, Tacettin Yekta Kaya, Murvet Algemi, and Murat Akarsu. 2025. "Soluble Urokinase Plasminogen Activator Receptor (suPAR) as a Biomarker of Erectile Dysfunction in Diabetic Patients" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 12: 4029. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124029
APA StyleErinc, O., Yilmaz, O., Kaya, T. Y., Algemi, M., & Akarsu, M. (2025). Soluble Urokinase Plasminogen Activator Receptor (suPAR) as a Biomarker of Erectile Dysfunction in Diabetic Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(12), 4029. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14124029






