Clinical Characteristics of Patients with Intra-Abdominal Infection Caused by Stenotrophomonas maltophilia
Abstract
1. Introduction
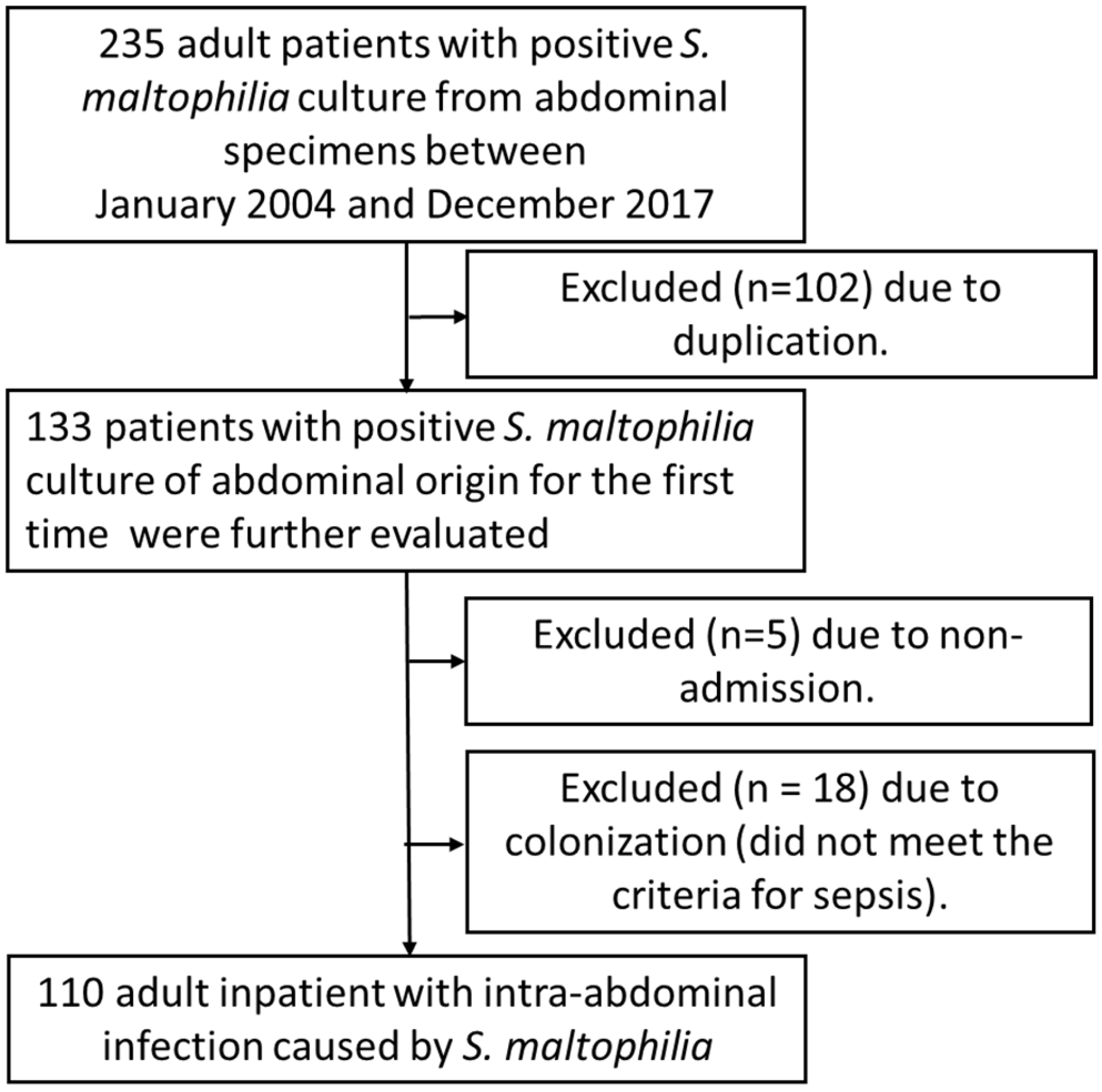
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Data Collection
2.2. Microbiology Examination
2.3. Statistical Analyses
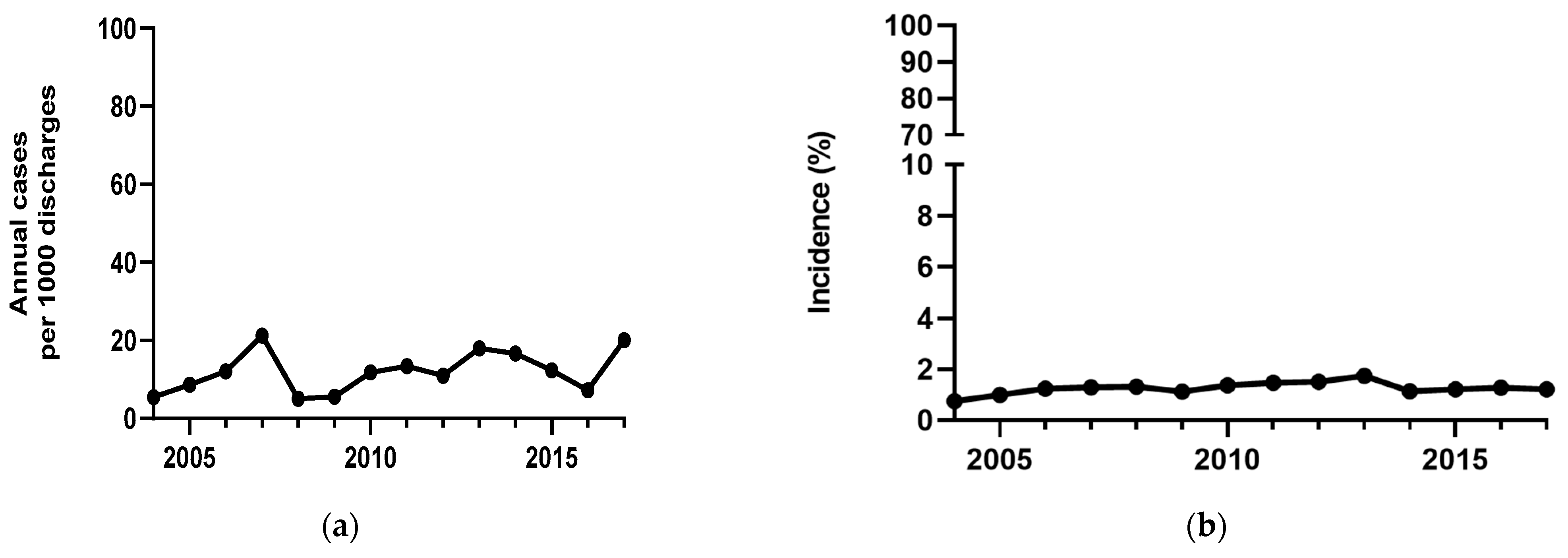
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IAI | Intra-abdominal infection |
| SOFA | Sequential Organ Failure Assessment |
| IQR | Interquartile range |
| OR | Odds ratio |
| CI | Confidence interval |
References
- Looney, W.J.; Narita, M.; Muhlemann, K. Stenotrophomonas maltophilia: An emerging opportunist human pathogen. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2009, 9, 312–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denton, M.; Kerr, K.G. Microbiological and clinical aspects of infection associated with Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1998, 11, 57–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senol, E. Stenotrophomonas maltophilia: The significance and role as a nosocomial pathogen. J. Hosp. Infect. 2004, 57, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooke, J.S. New strategies against Stenotrophomonas maltophilia: A serious worldwide intrinsically drug-resistant opportunistic pathogen. Expert. Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2014, 12, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooke, J.S. Advances in the Microbiology of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2021, 34, e0003019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kullar, R.; Wenzler, E.; Alexander, J.; Goldstein, E.J.C. Overcoming Stenotrophomonas maltophilia Resistance for a More Rational Therapeutic Approach. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2022, 9, ofac095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.T.; Lin, C.Y.; Chen, Y.H.; Hsueh, P.R. Update on infections caused by Stenotrophomonas maltophilia with particular attention to resistance mechanisms and therapeutic options. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.L.; Chen, H.F.; Chang, C.Y.; Lee, T.M.; Wu, W.J. Contribution of integrons, and SmeABC and SmeDEF efflux pumps to multidrug resistance in clinical isolates of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2004, 53, 518–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falagas, M.E.; Kastoris, A.C.; Vouloumanou, E.K.; Rafailidis, P.I.; Kapaskelis, A.M.; Dimopoulos, G. Attributable mortality of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia infections: A systematic review of the literature. Future Microbiol. 2009, 4, 1103–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paez, J.I.; Costa, S.F. Risk factors associated with mortality of infections caused by Stenotrophomonas maltophilia: A systematic review. J. Hosp. Infect. 2008, 70, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Wang, H.; Chen, M.; Ni, Y.; Yu, Y.; Hu, B.; Sun, Z.; Huang, W.; Hu, Y.; Ye, H.; et al. Surveillance of antimicrobial susceptibility of aerobic and facultative Gram-negative bacilli isolated from patients with intra-abdominal infections in China: The 2002–2009 Study for Monitoring Antimicrobial Resistance Trends (SMART). Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2010, 36, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apisarnthanarak, A.; Fraser, V.J.; Dunne, W.M.; Little, J.R.; Hoppe-Bauer, J.; Mayfield, J.L.; Polish, L.B. Stenotrophomonas maltophilia intestinal colonization in hospitalized oncology patients with diarrhea. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2003, 37, 1131–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirai, J.; Mori, N.; Sakanashi, D.; Shibata, Y.; Asai, N.; Hagihara, M.; Mikamo, H. Intra-Abdominal Abscess and Bacteremia Due to Stenotrophomonas maltophilia After Total Gastrectomy: A Case Report and Literature Review. Infect. Drug Resist. 2023, 16, 7197–7204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzanetou, K.; Triantaphillis, G.; Tsoutsos, D.; Petropoulou, D.; Ganteris, G.; Malamou-Lada, E.; Ziroyiannis, P. Stenotrophomonas maltophilia peritonitis in CAPD patients: Susceptibility to antibiotics and treatment outcome: A report of five cases. Perit. Dial. Int. 2004, 24, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, M.M.; Fink, M.P.; Marshall, J.C.; Abraham, E.; Angus, D.; Cook, D.; Cohen, J.; Opal, S.M.; Vincent, J.L.; Ramsay, G.; et al. 2001 SCCM/ESICM/ACCP/ATS/SIS International Sepsis Definitions Conference. Intensive Care Med. 2003, 29, 530–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, N.D.; Kaye, K.S.; Stout, J.E.; McGarry, S.A.; Trivette, S.L.; Briggs, J.P.; Lamm, W.; Clark, C.; MacFarquhar, J.; Walton, A.L.; et al. Health care–associated bloodstream infections in adults: A reason to change the accepted definition of community-acquired infections. Ann. Intern. Med. 2002, 137, 791–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlson, M.; Szatrowski, T.P.; Peterson, J.; Gold, J. Validation of a combined comorbidity index. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1994, 47, 1245–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, M.; Deutschman, C.S.; Seymour, C.W.; Shankar-Hari, M.; Annane, D.; Bauer, M.; Bellomo, R.; Bernard, G.R.; Chiche, J.D.; Coopersmith, C.M.; et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA 2016, 315, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooke, J.S. Stenotrophomonas maltophilia: An emerging global opportunistic pathogen. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 25, 2–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Lin, Q.; Li, J.; Feng, X.; Zhen, S.; Mi, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, F.; Xiao, Z.; Jiang, E.; et al. Stenotrophomonas maltophilia bacteremia in adult patients with hematological diseases: Clinical characteristics and risk factors for 28-day mortality. Microbiol. Spectr. 2025, 13, e01011-24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, E.L.; Gill, C.M.; McEvoy, C. Validation of a Stenotrophomonas maltophilia bloodstream infection prediction score in the hematologic malignancy population. Ann. Hematol. 2024, 103, 1745–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boktour, M.; Hanna, H.; Ansari, S.; Bahna, B.; Hachem, R.; Tarrand, J.; Rolston, K.; Safdar, A.; Raad, I. Central venous catheter and Stenotrophomonas maltophilia bacteremia in cancer patients. Cancer 2006, 106, 1967–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Lin, L.; Kuo, S. Risk factors for mortality in Stenotrophomonas maltophilia bacteremia—A meta-analysis. Infect. Dis. 2024, 56, 335–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, C.R. Stenotrophomonas maltophilia: To be or not to be a cystic fibrosis pathogen. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2012, 18, 628–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Tang, C.; Wang, L. Risk Factors for Acquired Stenotrophomonas maltophilia Pneumonia in Intensive Care Unit: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 808391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.L.; Chang, P.H.; Liu, Y.W.; Lai, W.H.; Chen, Y.J.; Chen, I.L.; Li, W.F.; Wang, C.C.; Lee, I.K. Gram-negative bacterial infections in surgical intensive care unit patients following abdominal surgery: High mortality associated with Stenotrophomonas maltophilia infection. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2024, 13, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Chen, Q.; Huang, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Wang, X.; Xia, L.; Hu, L. The Prognosis of Patients Tested Positive for Stenotrophomonas maltophilia from Different Sources. Infect. Drug Resist. 2023, 16, 4779–4787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husain, U.; Gupta, V. Liver abscess caused by multidrug-resistant pathogen Stenotrophomonas maltophilia: A rare case report. J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care 2023, 12, 174–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, S.; Merza, N.; Haider, M.; Zafar, Y.; Din, N.; Ligresti, R.; Sebti, R. Necrotizing Pancreatitis Infected with Stenotrophomonas maltophilia: An Emerging Rare Multidrug-Resistant Organism. Case Rep. Gastrointest. Med. 2023, 2023, 8071158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azak, A.; Kocak, G.; Huddam, B.; Iscan, G.; Duranay, M. An unusual cause of continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis-associated outpatient peritonitis: Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. Am. J. Infect. Control 2011, 39, 618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaito, S.; Sekiya, N.; Najima, Y.; Sano, N.; Horiguchi, S.; Kakihana, K.; Hishima, T.; Ohashi, K. Fatal Neutropenic Enterocolitis Caused by Stenotrophomonas maltophilia: A Rare and Underrecognized Entity. Intern. Med. 2018, 57, 3667–3671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerr, K.G.; Corps, C.M.; Hawkey, P.M. Infections due to Xanthomonas maltophilia in patients with hematologic malignancy. Rev. Infect. Dis. 1991, 13, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatsuta, K.; Taki, Y.; Nakatani, E.; Higashizono, K.; Nagai, E.; Nishida, M.; Sato, S.; Ohata, K.; Watanabe, M.; Kanemoto, H.; et al. Risk Factors for Candidiasis as an Intra-Abdominal Infection after Gastrectomy in Patients with Gastric Cancer. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 75, 461–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variables | Total (n = 110) | Survivors (n = 65) | Non-Survivors (n = 45) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years a | 60 (49–69) | 58 (48.5–68.5) | 61 (51.5–71.0) | 0.275 |
| Male, n (%) | 76 (69.1) | 45 (69.2) | 31 (68.9) | 0.970 |
| Community-acquired, n (%) | 3 (2.7) | 2 (3.1) | 1 (2.2) | 1.000 |
| Hospital stay before isolation a | 16 (4–32.25) | 13 (3.5–24) | 26 (8–43) | 0.005 |
| Underlying disease, n (%) | ||||
| Cerebrovascular accident | 15 (13.6) | 9 (13.8) | 6 (13.3) | 0.939 |
| Heart failure | 8 (7.3) | 3 (4.6) | 5 (11.1) | 0.179 |
| Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | 4 (3.6) | 4 (6.2) | 0 (0) | 0.117 |
| Diabetes Mellitus | 30 (27.2) | 15 (23.1) | 15 (33.3) | 0.166 |
| Chronic kidney disease b | 27 (24.5) | 16 (24.6) | 11 (24.4) | 0.584 |
| Peptic ulcer disease | 38 (34.5) | 19 (29.2) | 19 (42.2) | 0.114 |
| Malignancy | 62 (56.3) | 30 (46.2) | 32 (71.1) | 0.008 |
| Liver cirrhosis | 39 (35.5) | 20 (30.8) | 19 (42.2) | 0.151 |
| Charlson comorbidity index a | 6.5 (4–8) | 5 (3–8) | 7 (6–8.5) | 0.012 |
| Causes of intra-abdominal infection, n (%) | ||||
| Biliary tract infection | 47 (42.7) | 30 (46.2) | 17 (37.8) | 0.383 |
| Abdominal surgery-related | 39 (35.4) | 26 (40.0) | 13 (28.9) | 0.231 |
| Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis | 22 (20.0) | 8 (12.3) | 14 (31.1) | 0.015 |
| Others c | 2 (1.8) | 1 (1.5) | 1 (2.2) | 1.000 |
| Previous antibiotic use before IAI onset, n (%) | 104 (94.5) | 62 (95.4) | 42 (93.3) | 0.687 |
| Polymicrobial infection, n (%) | 84 (76.4) | 47 (72.3) | 37 (82.2) | 0.165 |
| Disease severity, n (%) | ||||
| SOFA score a | 4 (2–8) | 3 (1–5) | 7 (4–9.5) | <0.001 |
| Neutropenia, n (%) | 1 (0.9) | 0 (0) | 1 (2.2) | 0.409 |
| Septic shock, n (%) | 23 (20.9) | 5 (7.7) | 18 (40.0) | <0.01 |
| Appropriate antibiotic targeting for S. maltophilia within 48 h, n (%) | 15 (13.6) | 12 (18.5) | 3 (6.7) | 0.065 |
| Infection control measures, n (%) | 82 (74.5) | 49 (75.4) | 33 (73.3) | 0.808 |
| Pathogen | Total (n = 140) |
|---|---|
| Gram-positive aerobic bacteria | |
| Enterococcus spp. | 25 |
| Lactobacillus spp. | 1 |
| Leuconostoc spp. | 1 |
| Coagulase-negative staphylococci | 7 |
| Staphylococcus saprophyticus | 2 |
| Staphylococcus aureus | 5 |
| Viridans streptococci | 2 |
| Subtotal | 43 |
| Gram-positive anaerobic bacteria | |
| Clostridium sporogenes | 1 |
| Peptostreptococcus magnus | 1 |
| Subtotal | 2 |
| Gram-negative aerobic bacteria | |
| Achromobacter xylosoxidans | 2 |
| Acinetobacter spp. | 10 |
| Aeromonas hydrophila | 2 |
| Burkholderia cepacia | 1 |
| Burkholderia multivorans | 1 |
| Chryseobacterium indologenes | 8 |
| Chryseobacterium meningosepticus | 1 |
| Citrobacter freundii | 1 |
| Delftia acidovorans | 1 |
| Enterobacter cloacae | 5 |
| Escherichia coli | 12 |
| Klebsiella pneumoniae | 5 |
| Pseudomonas spp. | 15 |
| Rhizobium radiobacter | 1 |
| Serratia marcescens | 4 |
| Sphingomonas paucimobilis | 1 |
| Subtotal | 70 |
| Gram-negative anaerobic bacteria | |
| Bacteroides spp. | 10 |
| Fusobacterium nucleatum | 1 |
| Subtotal | 11 |
| Fungi | |
| Candida spp. | 14 |
| Subtotal | 14 |
| Variable | Unadjusted OR (95% CI) | p-Value | Adjusted OR (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 1.013 (0.989–1.038) | 0.299 | ||
| Sex | 0.984 (0.433–2.239) | 0.970 | ||
| Underlying disease | ||||
| Cerebrovascular accident | 0.957 (0.315–2.907) | 0.939 | ||
| Heart failure | 2.583 (0.585–11.411) | 0.210 | ||
| Diabetes Mellitus | 1.667 (0.715–3.887) | 0.237 | ||
| Chronic kidney disease | 0.991 (0.410–2.397) | 0.984 | ||
| Peptic ulcer disease | 1.769 (0.797–3.927) | 0.161 | ||
| Malignancy | 2.872 (1.280–6.445) | 0.011 | 4.433 (1.585–12.394) | 0.005 |
| Liver cirrhosis | 1.644 (0.745–3.630) | 0.219 | ||
| Causes of intra-abdominal Infection | ||||
| Biliary tract infection | 0.708 (0.326–1.538) | 0.383 | ||
| Abdominal surgery-related | 0.609 (0.270–1.375) | 0.233 | ||
| Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis | 3.218 (1.217–8.510) | 0.019 | 2.144 (0.666–6.897) | 0.201 |
| Disease severity | ||||
| SOFA score | 1.298 (1.150–1.466) | <0.01 | 1.312 (1.109–1.552) | 0.002 |
| Shock | 8.000 (2.690–23.793) | <0.01 | 2.302 (0.538–9.859) | 0.261 |
| Appropriate antibiotic targeting for S. maltophilia within 48 h | 0.315 (0.084–1.191) | 0.089 | 0.168 (0.034–0.837) | 0.029 |
| Infection control measures | 0.608 (0.256–1.443) | 0.259 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, C.-L.; Tsai, C.-C.; Chen, W.-P.; Chang, F.-Y.; Yu, C.-M.; Shang, H.-S.; Siu, L.-K.; Yang, Y.-S.; Lin, J.-C.; Wang, C.-H. Clinical Characteristics of Patients with Intra-Abdominal Infection Caused by Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3974. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113974
Chen C-L, Tsai C-C, Chen W-P, Chang F-Y, Yu C-M, Shang H-S, Siu L-K, Yang Y-S, Lin J-C, Wang C-H. Clinical Characteristics of Patients with Intra-Abdominal Infection Caused by Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(11):3974. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113974
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Chien-Liang, Chun-Chou Tsai, Wei-Ping Chen, Feng-Yee Chang, Ching-Mei Yu, Hung-Sheng Shang, Leung-Kei Siu, Ya-Sung Yang, Jung-Chung Lin, and Ching-Hsun Wang. 2025. "Clinical Characteristics of Patients with Intra-Abdominal Infection Caused by Stenotrophomonas maltophilia" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 11: 3974. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113974
APA StyleChen, C.-L., Tsai, C.-C., Chen, W.-P., Chang, F.-Y., Yu, C.-M., Shang, H.-S., Siu, L.-K., Yang, Y.-S., Lin, J.-C., & Wang, C.-H. (2025). Clinical Characteristics of Patients with Intra-Abdominal Infection Caused by Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(11), 3974. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113974







