Blood Type as a Potential Predictor of Hemorrhagic Risk in Patients Undergoing Partial Hepatectomy for Colorectal Liver Metastasis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
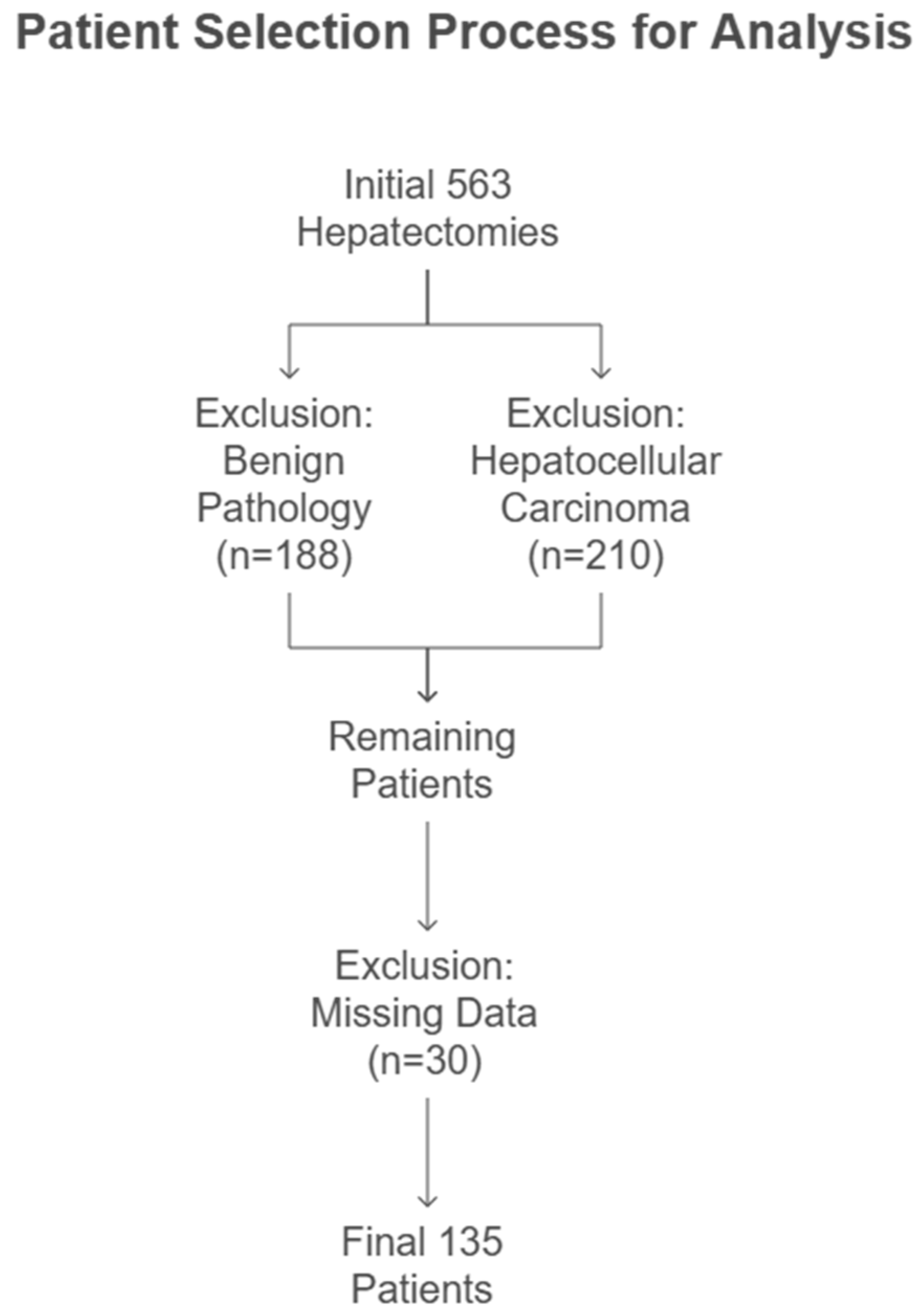
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Variables
2.3. Group Distribution
2.4. Sample Size Calculation and Power Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Strengths and Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| vWF | von Willebrand factor |
| CRLM | colorectal liver metastases |
| FLR | future liver remnant |
| IRB | institutional review board |
| INR | international normalized ratio |
| CA 19-9 | cancer antigen 19-9 |
| CEA | carcinoembryonic antigen |
| TLV | total liver volume |
| NCCN | National Comprehensive Cancer Network |
| CT | computed tomography |
| Hb | hemoglobin |
| POD-1 | postoperative day 1 |
| EBL | estimated blood loss |
References
- Farges, O.; Goutte, N.; Bendersky, N.; Falissard, B. ACHBT-French Hepatectomy Study Group Incidence and risks of liver resection: An all-inclusive French nationwide study. Ann. Surg. 2012, 256, 697–704; discussion 704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fong, Y.; Gonen, M.; Rubin, D.; Radzyner, M.; Brennan, M.F. Long-term survival is superior after resection for cancer in high-volume centers. Ann. Surg. 2005, 242, 540–544; discussion 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nathan, H.; Cameron, J.L.; Choti, M.A.; Schulick, R.D.; Pawlik, T.M. The volume-outcomes effect in hepato-pancreato-biliary surgery: Hospital versus surgeon contributions and specificity of the relationship. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2009, 208, 528–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheele, J.; Stang, R.; Altendorf-Hofmann, A.; Paul, M. Resection of colorectal liver metastases. World J. Surg. 1995, 19, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, K.; Kokudo, N.; Imamura, H.; Matsuyama, Y.; Aoki, T.; Minagawa, M.; Sano, K.; Sugawara, Y.; Takayama, T.; Makuuchi, M. Prognostic impact of anatomic resection for hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann. Surg. 2005, 242, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colli, J.L.; Colli, A. International comparisons of prostate cancer mortality rates with dietary practices and sunlight levels. Urol. Oncol. 2006, 24, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, M.; Ikeda, K.; Hosaka, T.; Sezaki, H.; Someya, T.; Akuta, N.; Suzuki, F.; Suzuki, Y.; Saitoh, S.; Arase, Y.; et al. Dysplastic nodules frequently develop into hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with chronic viral hepatitis and cirrhosis. Cancer 2006, 106, 636–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, M.; Matsumata, T.; Akazawa, K.; Kamakura, T.; Itasaka, H.; Sugimachi, K.; Nose, Y. Estimation of risk of major complications after hepatic resection. Am. J. Surg. 1994, 167, 399–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijer, C.; Wiezer, M.J.; Hack, C.E.; Boelens, P.G.; Wedel, N.I.; Meijer, S.; Nijveldt, R.J.; Statius Muller, M.G.; Wiggers, T.; Zoetmulder, F.A.; et al. Coagulopathy following major liver resection: The effect of rBPI21 and the role of decreased synthesis of regulating proteins by the liver. Shock 2001, 15, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanabe, G.; Sakamoto, M.; Akazawa, K.; Kurita, K.; Hamanoue, M.; Ueno, S.; Kobayashi, Y.; Mitue, S.; Ogura, Y.; Yoshidome, N. Intraoperative risk factors associated with hepatic resection. Br. J. Surg. 1995, 82, 1262–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franchini, M.; Rossi, C.; Mengoli, C.; Meschieri, M.; Frattini, F.; Crestani, S.; Giacomini, I.; Luppi, M.; Bonfanti, C. O blood group is a risk factor for severe mucosal hemorrhage in orally anticoagulated patients. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2013, 36, 358–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franchini, M.; Capra, F.; Targher, G.; Montagnana, M.; Lippi, G. Relationship between ABO blood group and von Willebrand factor levels: From biology to clinical implications. Thromb. J. 2007, 5, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assaf, W.; Wattad, A.; Ali-Saleh, M.; Shalabna, E.; Lavie, O.; Abramov, Y. Evaluation of blood type as a potential risk factor for hemorrhage during vaginal hysterectomy. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2024, 293, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonard, D.S.; Fenton, J.E.; Hone, S. ABO blood type as a risk factor for secondary post-tonsillectomy haemorrhage. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2010, 74, 729–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, G.A.; Moore, M.J.; El-Nakeep, S. Physiology, von willebrand factor. In StatPearls; Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Dentali, F.; Sironi, A.P.; Ageno, W.; Bonfanti, C.; Crestani, S.; Frattini, F.; Steidl, L.; Franchini, M. Relationship between ABO blood group and hemorrhage: A systematic literature review and meta-analysis. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2013, 39, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horwich, L.; Evans, D.A.; McConnell, R.B.; Donohoe, W.T. ABO blood groups in gastric bleeding. Gut 1966, 7, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Evans, D.A.; Horwich, L.; McConnell, R.B.; Bullen, M.F. Influence of the ABO blood groups and secretor status on bleeding and on perforation of duodenal ulcer. Gut 1968, 9, 319–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ionescu, D.A.; Marcu, I.; Bicescu, E. Cerebral thrombosis, cerebral haemorrhage, and ABO blood-groups. Lancet 1976, 1, 278–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeBot, M.; Eitel, A.P.; Moore, E.E.; Sauaia, A.; Lutz, P.; Schaid, T.R.; Hadley, J.B.; Kissau, D.J.; Cohen, M.J.; Kelher, M.R.; et al. Blood type o is a risk factor for hyperfibrinolysis and massive transfusion after severe injury. Shock 2022, 58, 492–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, S.E.; O’Sullivan, J.M.; O’Donnell, J.S. The relationship between ABO blood group, von Willebrand factor, and primary hemostasis. Blood 2020, 136, 2864–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maezawa, K.; Nozawa, M.; Gomi, M.; Sugimoto, M.; Maruyama, Y. Association of ABO blood group with postoperative total bleeding volume in patients undergoing total hip arthroplasty. Vox Sang. 2021, 116, 841–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archer, N.M.; Forbes, P.W.; Dargie, J.; Manganella, J.; Licameli, G.R.; Kenna, M.A.; Brugnara, C. Association of blood type with postsurgical mucosal bleeding in pediatric patients undergoing tonsillectomy with or without adenoidectomy. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e201804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welsby, I.J.; Jones, R.; Pylman, J.; Mark, J.B.; Brudney, C.S.; Phillips-Bute, B.; Mathew, J.P.; Campbell, M.L.; Stafford-Smith, M. Cardiothoracic Anesthesiology Research Endeavours (C.A.R.E.), Department of Anesthesiology, Duke University Medical Center ABO blood group and bleeding after coronary artery bypass graft surgery. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 2007, 18, 781–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Entezari, P.; Toskich, B.B.; Kim, E.; Padia, S.; Christopher, D.; Sher, A.; Thornburg, B.; Hohlastos, E.S.; Salem, R.; Collins, J.D.; et al. Promoting Surgical Resection through Future Liver Remnant Hypertrophy. Radiographics 2022, 42, 2166–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, R.B.; Aloia, T.A.; Loyer, E.; Pawlik, T.M.; Taouli, B.; Vauthey, J.-N.; Americas Hepato-Pancreato-Biliary Association; Society of Surgical Oncology; Society for Surgery of the Alimentary Tract. Selection for hepatic resection of colorectal liver metastases: Expert consensus statement. HPB 2013, 15, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shindoh, J.; Tzeng, C.-W.D.; Aloia, T.A.; Curley, S.A.; Zimmitti, G.; Wei, S.H.; Huang, S.Y.; Mahvash, A.; Gupta, S.; Wallace, M.J.; et al. Optimal future liver remnant in patients treated with extensive preoperative chemotherapy for colorectal liver metastases. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 20, 2493–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dindo, D.; Demartines, N.; Clavien, P.-A. Classification of surgical complications: A new proposal with evaluation in a cohort of 6336 patients and results of a survey. Ann. Surg. 2004, 240, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bird, G.W.; Wingham, J.; Watkins, W.M.; Greenwell, P.; Cameron, A.H. Inherited “mosaicism” within the ABO blood group system. J. Immunogenet. 1978, 5, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magen David Adom in Israel. Blood Type Distribution in Israel. 2022. Available online: https://www.mdais.org (accessed on 21 April 2025).
- Sun, W.; Wen, C.-P.; Lin, J.; Wen, C.; Pu, X.; Huang, M.; Tsai, M.K.; Tsao, C.K.; Wu, X.; Chow, W.-H. ABO blood types and cancer risk--a cohort study of 339,432 subjects in Taiwan. Cancer Epidemiol. 2015, 39, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Qu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Yan, P.; Yang, C.; Zhang, M.; Bai, Y.; Tang, M.; Wang, Y.; et al. Epidemiological and genetic evidence for the relationship between ABO blood group and human cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2023, 153, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeller, A.; Weippert-Kretschmer, M.; Prinz, H.; Kretschmer, V. Influence of ABO blood groups on primary hemostasis. Transfusion 2001, 41, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, J.C.; Endres-Brooks, J.; Bauer, P.J.; Marks, W.J.; Montgomery, R.R. The effect of ABO blood group on the diagnosis of von Willebrand disease. Blood 1987, 69, 1691–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadler, J.E.; Mannucci, P.M.; Berntorp, E.; Bochkov, N.; Boulyjenkov, V.; Ginsburg, D.; Meyer, D.; Peake, I.; Rodeghiero, F.; Srivastava, A. Impact, diagnosis and treatment of von Willebrand disease. Thromb. Haemost. 2000, 84, 160–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, J.D.; Herzog, T.J.; Tsui, J.; Ananth, C.V.; Lewin, S.N.; Lu, Y.-S.; Neugut, A.I.; Hershman, D.L. Nationwide trends in the performance of inpatient hysterectomy in the United States. Obstet. Gynecol. 2013, 122, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, C.H.; Haff, E.; Platt, S.J.; Rawlins, P.; Drews, C.D.; Dilley, A.B.; Evatt, B. Measurement of von Willebrand factor activity: Relative effects of ABO blood type and race. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2003, 1, 2191–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blustin, J.M.; McBane, R.D.; Mazur, M.; Ammash, N.; Sochor, O.; Grill, D.E.; Wysokinski, W.E. The association between thromboembolic complications and blood group in patients with atrial fibrillation. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2015, 90, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orstavik, K.H.; Magnus, P.; Reisner, H.; Berg, K.; Graham, J.B.; Nance, W. Factor VIII and factor IX in a twin population. Evidence for a major effect of ABO locus on factor VIII level. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1985, 37, 89–101. [Google Scholar]
- Larsen, T.B.; Johnsen, S.P.; Gislum, M.; Møller, C.A.I.; Larsen, H.; Sørensen, H.T. ABO blood groups and risk of venous thromboembolism during pregnancy and the puerperium. A population-based, nested case-control study. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2005, 3, 300–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jick, H.; Slone, D.; Westerholm, B.; Inman, W.H.; Vessey, M.P.; Shapiro, S.; Lewis, G.P.; Worcester, J. Venous thromboembolic disease and ABO blood type. A cooperative study. Lancet 1969, 1, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talbot, S.; Wakley, E.J.; Ryrie, D.; Langman, M.J. ABO blood-groups and venous thromboembolic disease. Lancet 1970, 1, 1257–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, V.M.; Daniel, M.; Bright, E.; Broad, S.R.; Moir, A.A. Is there an association between blood group O and epistaxis? J. Laryngol. Otol. 2008, 122, 366–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drukker, L.; Srebnik, N.; Elstein, D.; Levitt, L.; Samueloff, A.; Farkash, R.; Grisaru-Granovsky, S.; Sela, H.Y. The association between ABO blood group and obstetric hemorrhage. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2016, 42, 340–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahr, M.K.; Franke, D.; Brun, R.; Wisser, J.; Zimmermann, R.; Haslinger, C. Blood group O: A novel risk factor for increased postpartum blood loss? Haemophilia 2018, 24, e207–e212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatar Aksoy, H.; Eras, Z.; Canpolat, F.E.; Dilmen, U. The association between neonatal ABO blood group and intraventricular hemorrhage in extremely low birth weight infants. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2013, 11, 2074–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halonen, P.; Linko, K.; Wirtavuori, K.; Hästbacka, J.; Ikkala, E. Evaluation of risk factors in intraoperative bleeding tendency. Ann. Chir. Gynaecol. 1987, 76, 298–302. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ali-Saleh, M.; Lavie, O.; Abramov, Y. Evaluation of blood type as a potential risk factor for early postpartum hemorrhage. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0214840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirabe, K.; Kajiyama, K.; Harimoto, N.; Tsujita, E.; Wakiyama, S.; Maehara, Y. Risk factors for massive bleeding during major hepatectomy. World J. Surg. 2010, 34, 1555–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helling, T.S.; Blondeau, B.; Wittek, B.J. Perioperative factors and outcome associated with massive blood loss during major liver resections. HPB 2004, 6, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNally, S.J.; Revie, E.J.; Massie, L.J.; McKeown, D.W.; Parks, R.W.; Garden, O.J.; Wigmore, S.J. Factors in perioperative care that determine blood loss in liver surgery. HPB 2012, 14, 236–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Hilal, M.; Underwood, T.; Taylor, M.G.; Hamdan, K.; Elberm, H.; Pearce, N.W. Bleeding and hemostasis in laparoscopic liver surgery. Surg. Endosc. 2010, 24, 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Blood Type O n = 61 | Blood Type A, B, AB n = 74 | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 64.61 ± 9.86 | 62.46 ± 11.8 | 0.251 |
| Gender (male) | 31 (50.8%) | 45 (60.8%) | 0.175 |
| Operating Room Time (min) | 197.7 ± 74 | 200 ± 74 | 0.82 |
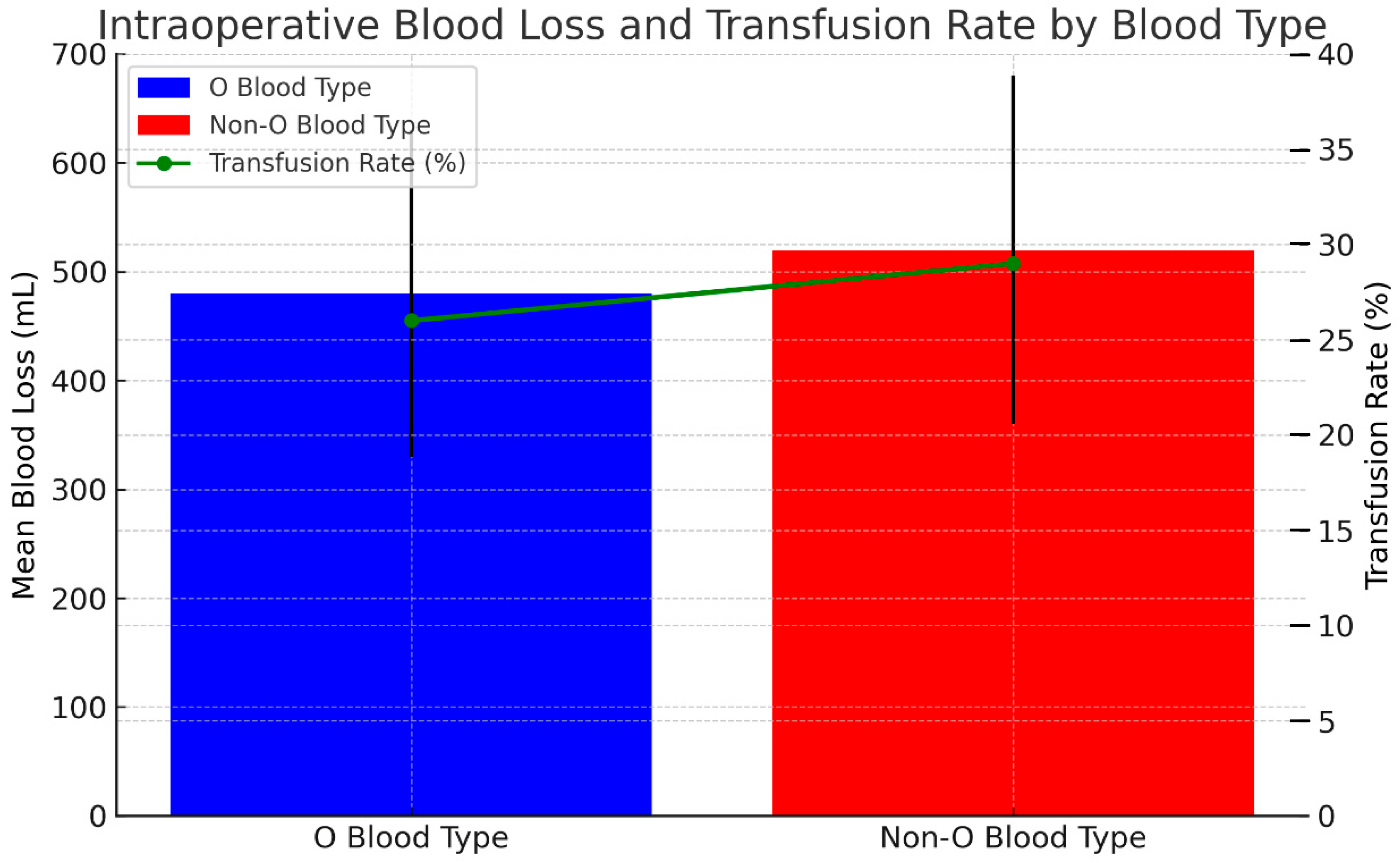
| Estimated Blood Loss (mL) | 474.3 ± 696 | 527.8 ± 599 | 0.295 |
| Intraoperative Blood Transfusion ∞ | 15 (24.59%) | 21 (28.37%) | 0.698 |
| Postoperative Blood Transfusion ∞ | 9 (14.8%) | 11 (14.9) | 0.906 |
| Size of Largest Lesion (mm) | 30.4 ± 24.0 | 25.3 ± 15.4 | 0.286 |
| Major Liver Resection β | 17 (22.9%) | 24 (32.4%) | 0.566 |
| Overall Complications | 18 (29.5%) | 32 (43.2%) | 0.088 |
| Grade of Complication µ 0–2 3 >4 | 56 (91.8%) 1 (1.6%) 4 (6.6%) | 66 (89.1%) 2 (2.7%) 6 (8.2%) | 0.899 |
| 30 Days Readmission | 12 (19.7%) | 16 (21.6%) | 0.807 |
| Recurrence of Colorectal Cancer | 30 (49.1%) | 37 (50%) | 0.685 |
| Blood Type O n = 61 | Blood Type A, B, AB n = 74 | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rh Positive | 58 (95.1%) | 65 (87.8%) | 0.141 |
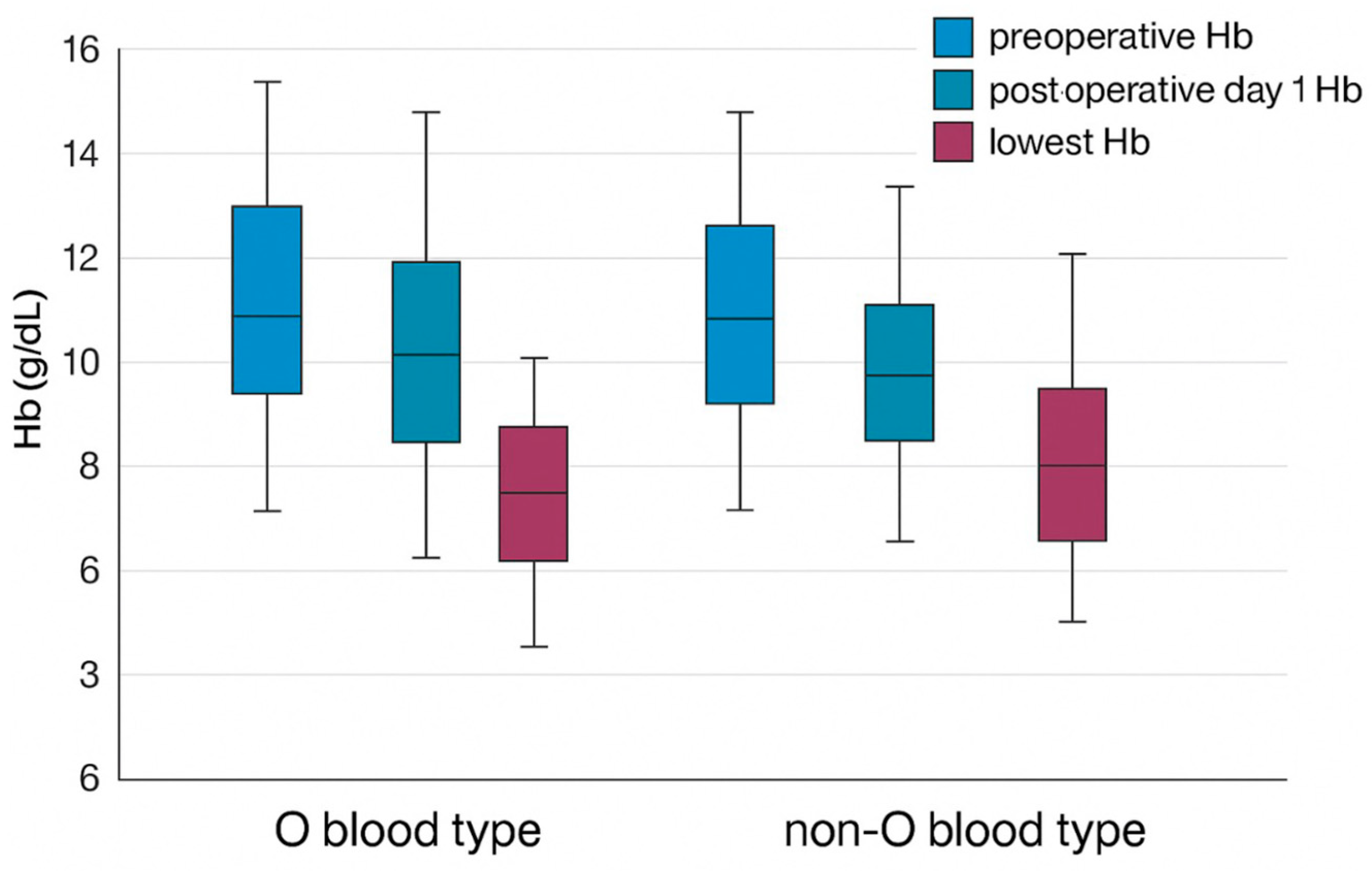
| Mean Preoperative Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 12.7 ± 1.5 | 12.0 ± 1.4 | 0.538 |
| Mean Postoperative Day 1 Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 11.1 ± 1.4 | 11.2 ± 1.6 | 0.517 |
| Mean Lowest Postoperative Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 9.5 ± 1.5 | 9.9 ± 1.4 | 0.128 |
| Mean Preoperative Platelet (g/uL) | 222.5 ± 59.6 | 211.9 ± 75.1 | 0.193 |
| Mean Preoperative Operative INR | 1.08 ± 0.41 | 1.06 ± 0.17 | 0.406 |
| Platelet—Matched to Lowest Hemoglobin (k/uL) | 179.9 ± 80.5 | 171.6 ± 74.7 | 0.404 |
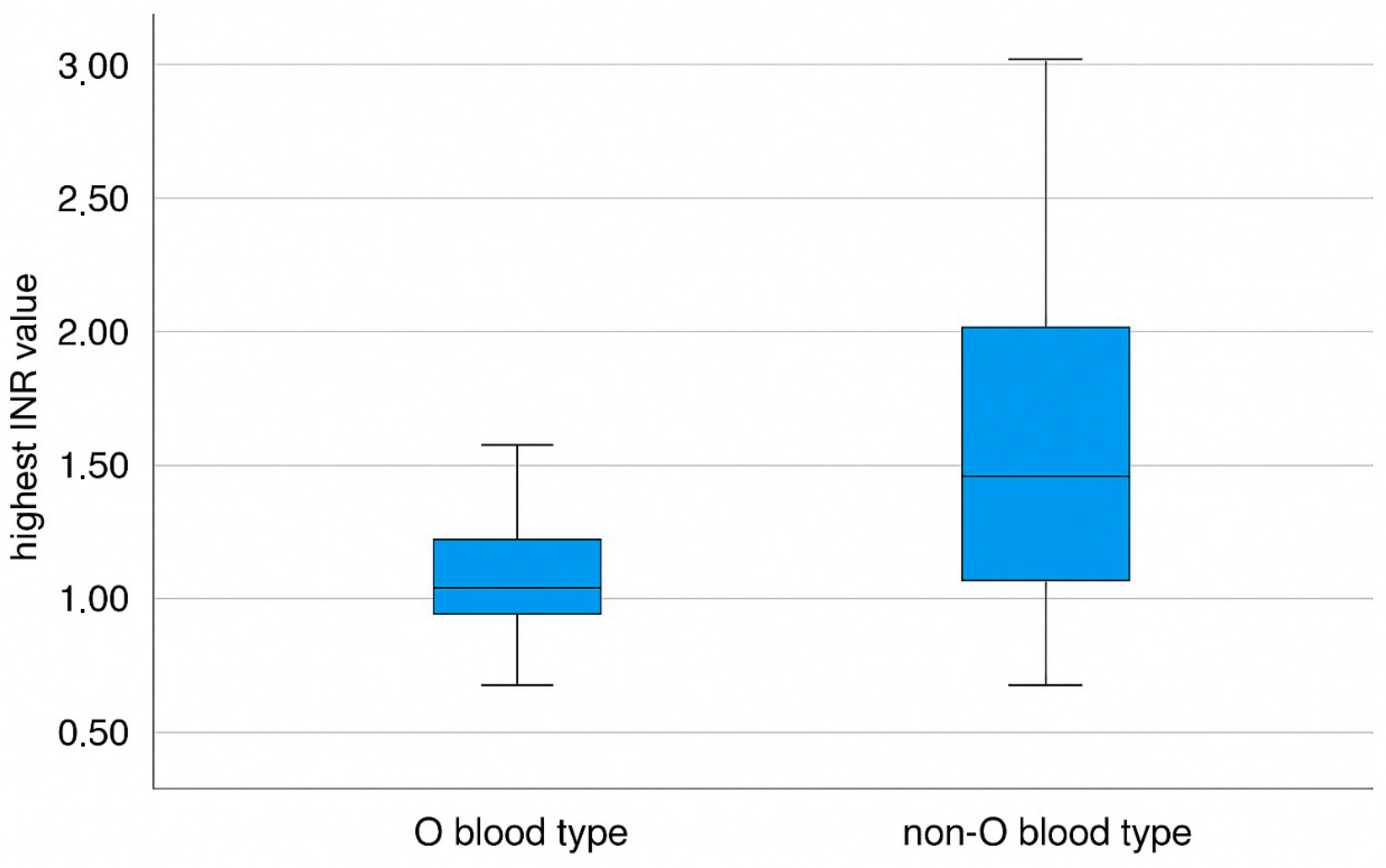
| Highest Postoperative INR | 1.41 ± 0.44 | 1.66 ± 0.68 | 0.035 |
| Preoperative White Blood Cells (k/dL) | 7.3 ± 2.6 | 6.7 ± 1.8 | 0.258 |
| Preoperative CEA (ng/mL) | 21.4 ± 34.8 | 40.9 ± 109.4 | 0.743 |
| Preoperative CA 19-9 (U/mL) | 46.8 ± 79.8 | 67.0 ± 169.5 | 0.409 |
| Preoperative Vitamin D (nmol/L) | 42.7 ± 26.8 | 37.4 ± 33.7 | 0.316 |
| Preoperative Albumin (g/dL) | 4.1 ± 0.43 | 4.1 ± 0.40 | 0.960 |
| Blood Type O n = 61 | Blood Type A, B, AB n = 74 | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| All Study Population | |||
| ∆Hemoglobin (g/dL) Preoperative and Postoperative Day 1 | 1.67 ± 1.46 | 1.74 ± 1.47 | 0.613 |
| ∆Hemoglobin (g/dL) Postoperative Day 1 and Lowest | 1.56 ± 0.97 | 1.30 ± 1.2 | 0.209 |
| ∆Hemoglobin Preoperative and Lowest | 3.2 ± 1.7 | 3.0 ± 1.4 | 0.582 |
| Patients without Intraoperative Blood Transfusion | |||
| ∆Hemoglobin (g/dL) Preoperative and Postoperative Day 1 | 1.60 ± 1.39 | 1.68 ± 1.26 | 0.522 |
| ∆Hemoglobin (g/dL) Postoperative Day 1 and Lowest | 1.43 ± 0.91 | 1.28 ± 1.1 | 0.354 |
| ∆Hemoglobin (g/dL) Preoperative and Lowest | 3.0 ± 1.7 | 3.0 ± 1.3 | 0.853 |
| Patients without Postoperative Blood Transfusion | |||
| ∆Hemoglobin (g/dL) Preoperative and Postoperative Day 1 | 1.53 ± 1.41 | 1.64 ± 1.21 | 0.459 |
| ∆Hemoglobin (g/dL) Postoperative Day 1 and Lowest | 1.51 ± 0.96 | 1.28 ± 1.2 | 0.163 |
| ∆Hemoglobin (g/dL) Preoperative Operative and Lowest | 3.1 ± 1.75 | 2.9 ± 1.3 | 0.793 |
| Patients without Intraoperative and Postoperative Blood Transfusion | |||
| ∆Hemoglobin (g/dL) Preoperative Operative and Postoperative Day 1 | 1.48 ± 1.37 | 1.72 ± 1.23 | 0.275 |
| ∆Hemoglobin (g/dL) Postoperative Day-1 and Lowest | 1.46 ± 0.96 | 1.16 ± 1.02 | 0.113 |
| ∆Hemoglobin (g/dL) Preoperative and Lowest | 2.93 ± 1.71 | 2.9 ± 1.3 | 0.963 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Assaf, W.; Kazlow, E.; Rowe, M.; Gawi, R.; Abu Shtaya, A.; Barsha, H.; Segev, Y.; Haddad, R.; Mahamid, A. Blood Type as a Potential Predictor of Hemorrhagic Risk in Patients Undergoing Partial Hepatectomy for Colorectal Liver Metastasis. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3905. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113905
Assaf W, Kazlow E, Rowe M, Gawi R, Abu Shtaya A, Barsha H, Segev Y, Haddad R, Mahamid A. Blood Type as a Potential Predictor of Hemorrhagic Risk in Patients Undergoing Partial Hepatectomy for Colorectal Liver Metastasis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(11):3905. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113905
Chicago/Turabian StyleAssaf, Wisam, Esther Kazlow, Max Rowe, Reem Gawi, Aasem Abu Shtaya, Hanin Barsha, Yakir Segev, Riad Haddad, and Ahmad Mahamid. 2025. "Blood Type as a Potential Predictor of Hemorrhagic Risk in Patients Undergoing Partial Hepatectomy for Colorectal Liver Metastasis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 11: 3905. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113905
APA StyleAssaf, W., Kazlow, E., Rowe, M., Gawi, R., Abu Shtaya, A., Barsha, H., Segev, Y., Haddad, R., & Mahamid, A. (2025). Blood Type as a Potential Predictor of Hemorrhagic Risk in Patients Undergoing Partial Hepatectomy for Colorectal Liver Metastasis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(11), 3905. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113905








