Level of Agreement of Intraocular Lens Power Measurements Between a Swept-Source OCT Biometer and a Partial Coherence Interferometer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Setting
2.2. Participants
2.3. Examination Technique—Data Collection
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACD | Anterior chamber depth |
| AL | Axial length |
| CI | Confidence Interval |
| D | Diopters |
| DDART | Democritus Digital Visual Acuity Reading Test |
| IOL | Intraocular lens |
| J0 | Jackson cross-cylinder power at axis 0° and 90° |
| J45 | Jackson cross-cylinder power at axis 45° and 135° |
| K1 | Flat keratometry value |
| K2 | Steep keratometry value |
| Km | Mean keratometry value |
| ME | Mean Error |
| PCI | Partial Coherence Interferometry |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| SE | Standard Error |
| SRK/T | Sanders-Retzlaff-Kraff/Theoretical |
| SS-OCT | Swept-Source Optical Coherence Tomography |
| WTW | White-to-white distance |
References
- Omoto, M.K.; Torii, H.; Masui, S.; Ayaki, M.; Tsubota, K.; Negishi, K. Ocular Biometry and Refractive Outcomes Using Two Swept-Source Optical Coherence Tomography-Based Biometers with Segmental or Equivalent Refractive Indices. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6557, Erratum in Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brick, D.C. Risk Management Lessons from a Review of 168 Cataract Surgery Claims. Surv. Ophthalmol. 1999, 43, 356–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Wang, G.Y.; Cheng, Y.H.; Pei, C. Comparison of IOLMaster 700 and IOLMaster 500 Biometers in Ocular Biological Parameters of Adolescents. Int. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 14, 1013–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reitblat, O.; Levy, A.; Kleinmann, G.; Assia, E.I. Accuracy of Intraocular Lens Power Calculation Using Three Optical Biometry Measurement Devices: The OA-2000, Lenstar-LS900 and IOLMaster-500. Eye 2018, 32, 1244–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.M.; Lim, D.H.; Kim, H.J.; Chung, T.Y. Comparison of Two Swept-Source Optical Coherence Tomography Biometers and a Partial Coherence Interferometer. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0223114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, K.; Gurnani, B.; Das, P. Insights into IOLMaster®: A Useful Tool for Cataract Surgeons. Kerala J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 32, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higashiyama, T.; Mori, H.; Nakajima, F.; Ohji, M. Comparison of a New Biometer Using Swept-Source Optical Coherence Tomography and a Conventional Biometer Using Partial Coherence Interferometry. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Románek, J.; Sluková, K. Comparison of Optical Biometers ARGOS and IOLMaster 700. Čes. Slov. Oftalmol. 2021, 77, 295–299. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Ye, Z.; Luo, Y.; Li, Z. Comparing the Accuracy of the New-Generation Intraocular Lens Power Calculation Formulae in Axial Myopic Eyes: A Meta-Analysis. Int. Ophthalmol. 2023, 43, 619–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savini, G.; Taroni, L.; Hoffer, K.J. Recent Developments in Intraocular Lens Power Calculation Methods—Update 2020. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thibos, L.N.; Horner, D. Power Vector Analysis of the Optical Outcome of Refractive Surgery. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 2001, 27, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thibos, L.N.; Wheeler, W.; Horner, D. Power Vectors: An Application of Fourier Analysis to the Description and Statistical Analysis of Refractive Error. Optom. Vis. Sci. 1997, 74, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labiris, G.; Panagiotopoulou, E.K.; Ntonti, P. Development and Validation of a Lighting Facility for the Objective Assessment of the Visual Performance of Presbyopic Patients in a Series of Activities of Daily Living. Cureus 2022, 14, e24548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drexler, W.; Findl, O.; Menapace, R.; Rainer, G.; Vass, C.; Hitzenberger, C.K.; Fercher, A.F. Partial Coherence Interferometry: A Novel Approach to Biometry in Cataract Surgery. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1998, 126, 524–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagiotopoulou, E.K.; Ntonti, P.; Gkika, M.; Konstantinidis, A.; Perente, I.; Dardabounis, D.; Ioannakis, K.; Labiris, G. Image-Guided Lens Extraction Surgery: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 12, 135–151. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Labiris, G.; Panagiotopoulou, E.K.; Ntonti, P.; Gkika, M.; Konstantinidis, A.; Perente, I.; Dardabounis, D.; Ioannakis, K. Level of Agreement of Intraocular Lens Power Measurements Between an Image-Guided System and Partial Coherence Interferometry. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 2020, 46, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Chen, H.; Li, Y.; Chen, Z.; Gao, R.; Yu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Lu, W.; McAlinden, C.; Wang, Q. Comprehensive Comparison of Axial Length Measurement with Three Swept-Source OCT-Based Biometers and Partial Coherence Interferometry. J. Refract. Surg. 2019, 35, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussaindeen, J.R.; Mariam, E.G.; Arunachalam, S.; Bhavatharini, R.; Gopalakrishnan, A.; Narayanan, A.; Agarkar, S.; Sivaraman, V. Comparison of Axial Length Using a New Swept-Source Optical Coherence Tomography-Based Biometer—ARGOS with Partial Coherence Interferometry-Based Biometer—IOLMaster among School Children. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0209356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whang, W.J.; Yoo, Y.S.; Kang, M.J.; Joo, C.K. Predictive Accuracy of Partial Coherence Interferometry and Swept-Source Optical Coherence Tomography for Intraocular Lens Power Calculation. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shammas, H.J.; Ortiz, S.; Shammas, M.C.; Kim, S.H.; Chong, C. Biometry Measurements Using a New Large-Coherence-Length Swept-Source Optical Coherence Tomographer. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 2016, 42, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gjerdrum, B.; Gundersen, K.G.; Nilsen, C.; Gundersen, M.; Jensen, P. Refractive Predictability and Biometry Agreement of a Combined Swept-Source Optical Coherence and Reflectometry Biometer Compared to an Optical Low Coherence Reflectometry Biometer and an SS-OCT Biometer. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2023, 17, 1439–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemeth, G.; Modis, L., Jr. Ocular Measurements of a Swept-Source Biometer: Repeatability Data and Comparison with an Optical Low-Coherence Interferometry Biometer. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 2019, 45, 789–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cummings, A.B.; Naughton, S.; Coen, A.M.; Brennan, E.; Kelly, G.E. Comparative Analysis of Swept-Source Optical Coherence Tomography and Partial Coherence Interferometry Biometers in the Prediction of Cataract Surgery Refractive Outcomes. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2020, 14, 4209–4220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooke, D.L.; Cooke, T.L. A Comparison of Two Methods to Calculate Axial Length. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 2019, 45, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montés-Micó, R. Evaluation of 6 Biometers Based on Different Optical Technologies. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 2022, 48, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, R.; Yu, J.; Savini, G.; Ye, J.; Ning, R.; Xiong, J.; Chen, S.; Huang, J. Agreement Between Two Optical Biometers Based on Large Coherence Length SS-OCT and Scheimpflug Imaging/Partial Coherence Interferometry. J. Refract. Surg. 2020, 36, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabatino, F.; Matarazzo, F.; Findl, O.; Maurino, V. Comparative Analysis of 2 Swept-Source Optical Coherence Tomography Biometers. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 2019, 45, 1124–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savini, G.; Hoffer, K.J.; Carballo, L.; Taroni, L.; Schiano-Lomoriello, D. Comparison of Different Methods to Calculate the Axial Length Measured by Optical Biometry. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 2022, 48, 685–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galzignato, A.; Lupardi, E.; Hoffer, K.J.; Barboni, P.; Schiano-Lomoriello, D.; Savini, G. Repeatability of a New Optical Biometer and Agreement with 2 Validated Optical Biometers, All Based on SS-OCT. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 2023, 49, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamaoki, A.; Kojima, T.; Hasegawa, A.; Yamamoto, M.; Kaga, T.; Tanaka, K.; Ichikawa, K. Clinical Evaluation of a New Swept-Source Optical Coherence Biometer That Uses Individual Refractive Indices to Measure Axial Length in Cataract Patients. Ophthalmic Res. 2019, 62, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameter | Mean ± SD | Difference | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IOLMaster | Argos | Mean ± SE | 95% CI | p Value | |
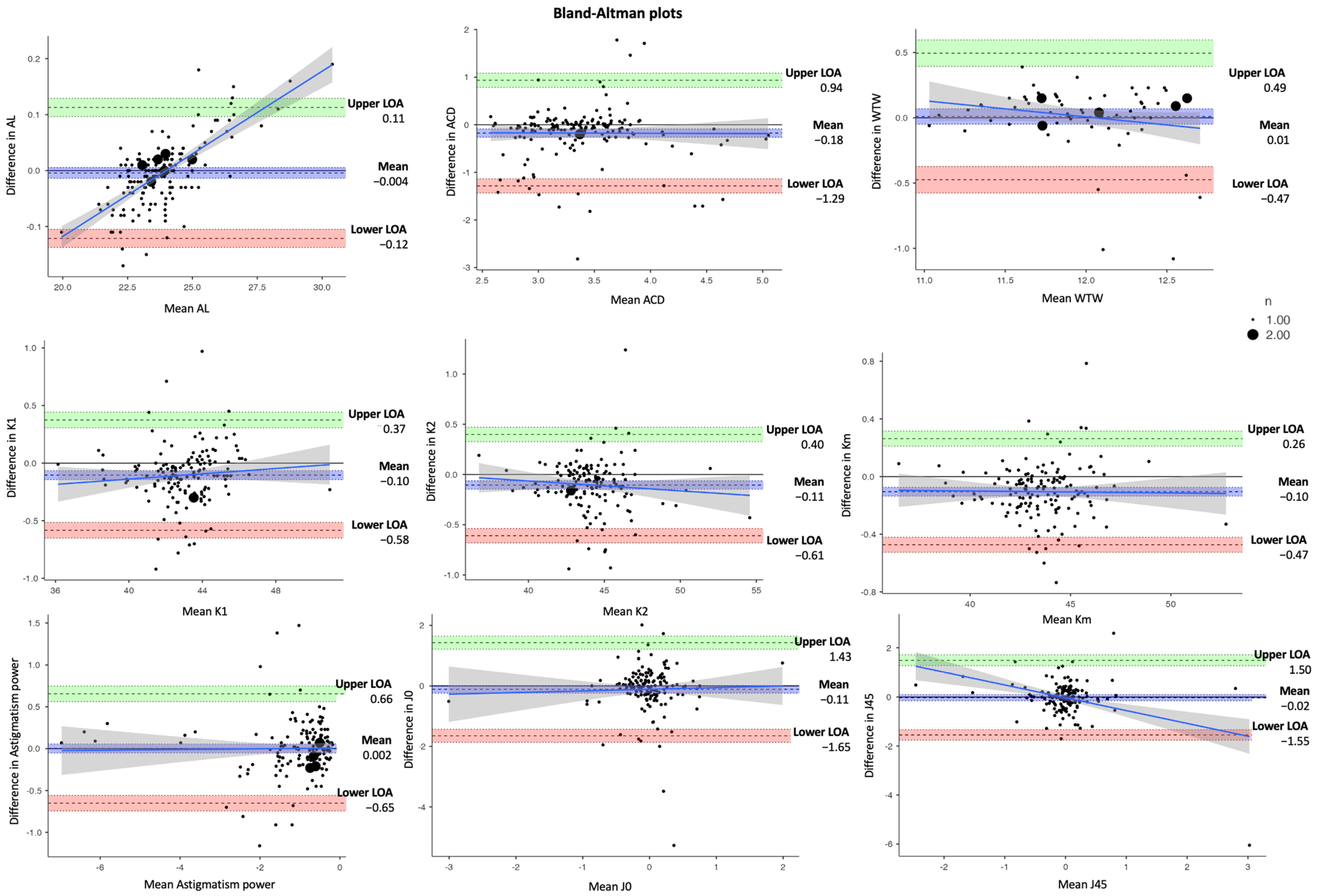
| AL (mm) | 23.84 ± 1.45 | 23.845 ± 1.40 | −0.004 ± 0.005 | −0.01, 0.005 | 0.385 |
| ACD (mm) | 3.30 ± 0.54 | 3.47 ± 0.54 | −0.18 ± 0.04 | −0.26, −0.09 | <0.001 * |
| K1 (D) | 42.97 ± 1.88 | 43.07 ± 1.86 | −0.10 ± 0.02 | −0.14, −0.06 | <0.001 * |
| K2 (D) | 44.08 ± 2.19 | 44.19 ± 2.21 | −0.11 ± 0.02 | −0.15, −0.06 | <0.001 * |
| Km (D) | 43.53 ± 1.96 | 43.63 ± 1.96 | −0.10 ± 0.02 | −0.14 ± 0.07 | <0.001 * |
| Astigmatism power (D) | −1.114 ± 1.12 | −1.116 ± 1.11 | 0.002 ± 0.03 | −0.05, 0.06 | 0.943 |
| J0 vector (D) | −0.08 ± 0.58 | 0.03 ± 0.56 | −0.11 ± 0.06 | −0.24, 0.01 | 0.068 |
| J45 vector (D) | −0.02± 0.53 | −0.04 ± 0.56 | −0.02 ± 0.05 | −0.08, 0.11 | 0.740 |
| WTW (mm) | 11.90 ± 0.39 | 11.95 ± 0.44 | 0.01 ± 0.03 | −0.05, 0.07 | 0.729 |
| Parameters | Pearson’s r | p Value |
|---|---|---|
| AL | 0.715 | <0.001 ** |
| ACD | 0.518 | <0.001 ** |
| WTW | 0.118 | 0.331 |
| K1 | 0.152 | 0.064 |
| K2 | −0.025 | 0.758 |
| Km | 0.034 | 0.681 |
| Astigmatism power | 0.162 | 0.048 * |
| J0 | 0.699 | <0.001 ** |
| J45 | 0.518 | <0.001 ** |
| IOL | Mean IOL Power ± SD (D) | Difference (IOLMaster–Argos) (D) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IOLMaster | Argos | Mean ± SE | 95% CI | p Value | |
| A. SRK/T | |||||
| SA60AT | 20.2 ± 3.31 | 20.4 ± 3.32 | −0.20 ± 0.03 | −0.26, −0.14 | <0.001 ** |
| SN60WF | 20.6 ± 3.10 | 20.4 ± 3.03 | 0.16 ± 0.03 | 0.10, 0.23 | <0.001 ** |
| Clareon (CNA0T0) | 20.5 ± 3.51 | 20.3 ± 3.46 | 0.16 ± 0.03 | 0.09, 0.22 | <0.001 ** |
| Tecnis ZCB00 | 20.3 ± 3.65 | 20.4 ± 3.63 | −0.08 ± 0.03 | −0.15, −0.02 | 0.015 * |
| Vivity (DFT015) | 20.8 ± 3.04 | 20.7 ± 3.05 | 0.14 ± 0.03 | 0.07, 0.20 | <0.001 ** |
| Panoptix (TFTN00) | 20.5 ± 3.36 | 20.4 ± 3.32 | 0.15 ± 0.03 | 0.09, 0.21 | <0.001 ** |
| SN6ATx | 20.8 ± 3.07 | 20.5 ± 3.06 | 0.27 ± 0.03 | 0.20, 0.33 | <0.001 ** |
| Vivity Toric (DFTx15) | 20.8 ± 3.04 | 20.7 ± 3.05 | 0.14 ± 0.03 | 0.07, 0.20 | <0.001 ** |
| Panoptix Toric (TFNTx) | 20.5 ± 3.36 | 20.4 ± 3.32 | 0.15 ± 0.03 | 0.09, 0.21 | <0.001 ** |
| B. Holladay 1 | |||||
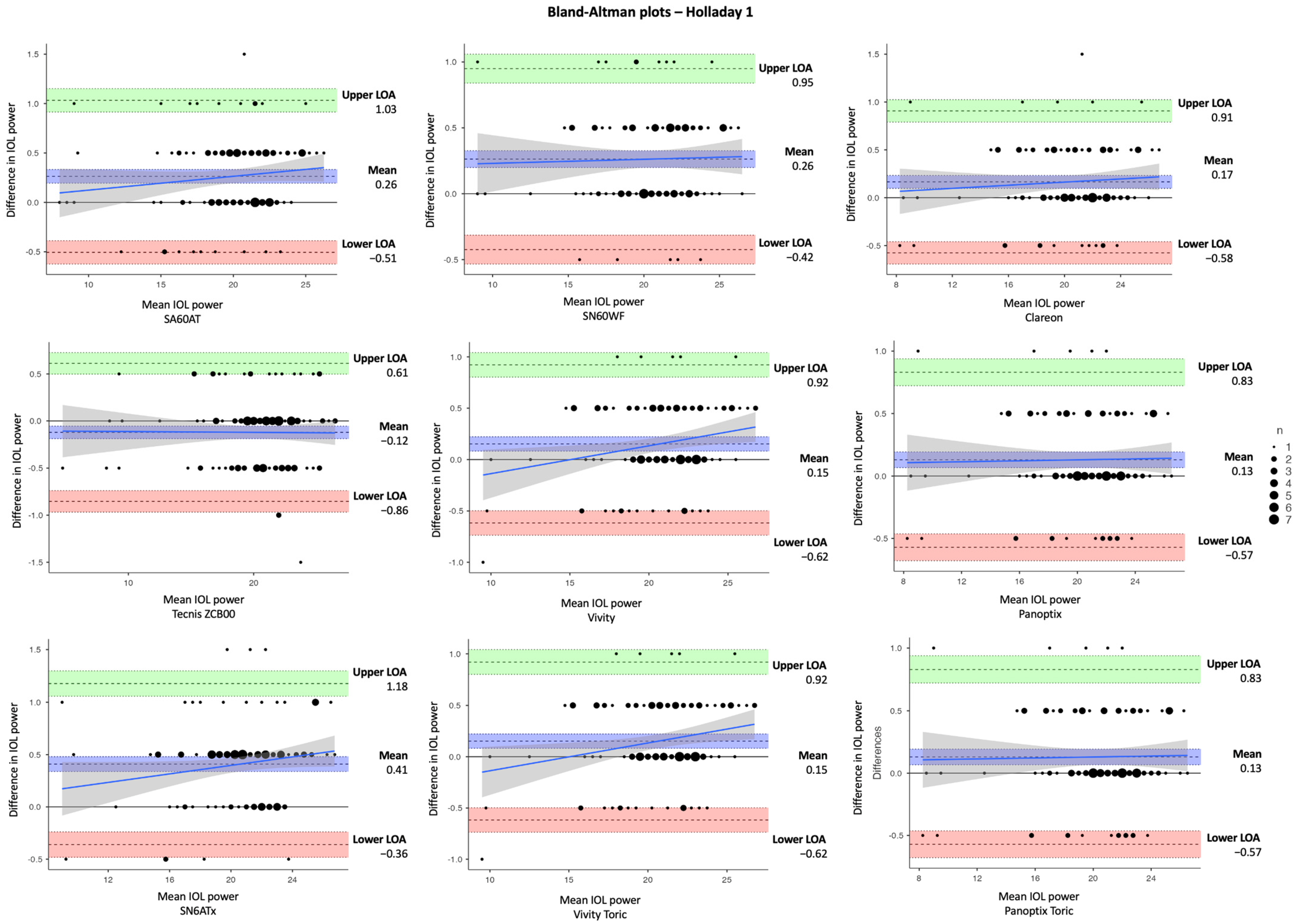
| SA60AT | 20.1 ± 3.49 | 19.8 ± 3.43 | 0.26 ± 0.05 | 0.12, 0.31 | <0.001 ** |
| SN60WF | 20.7 ± 3.35 | 20.2 ± 3.57 | 0.26 ± 0.05 | 0.13, 0.30 | <0.001 ** |
| Clareon (CNA0T0) | 20.4 ± 3.57 | 20.3 ± 3.57 | 0.17 ± 0.05 | 0.03, 0.22 | <0.001 ** |
| Tecnis ZCB00 | 20.2 ± 3.93 | 20.3 ± 3.90 | −0.12 ± 0.05 | −0.28, −0.08 | <0.001 ** |
| Vivity (DFT015) | 20.8 ± 3.28 | 20.6 ± 3.20 | 0.15 ± 0.05 | 0.08, 0.22 | <0.001 ** |
| Panoptix (TFTN00) | 20.4 ± 3.56 | 20.3 ± 3.55 | 0.13 ± 0.03 | 0.07, 0.19 | <0.001 ** |
| SN6ATx | 20.8 ± 3.35 | 20.4 ± 3.28 | 0.41 ± 0.04 | 0.34, 0.48 | < 0.001 ** |
| Vivity Toric (DFTx15) | 20.8 ± 3.28 | 20.6 ± 3.20 | 0.15 ± 0.05 | 0.08, 0.22 | < 0.001 ** |
| Panoptix Toric (TFNTx) | 20.4 ± 3.56 | 20.3 ± 3.55 | 0.13 ± 0.03 | 0.07, 0.19 | < 0.001 ** |
| C. Hoffer Q | |||||
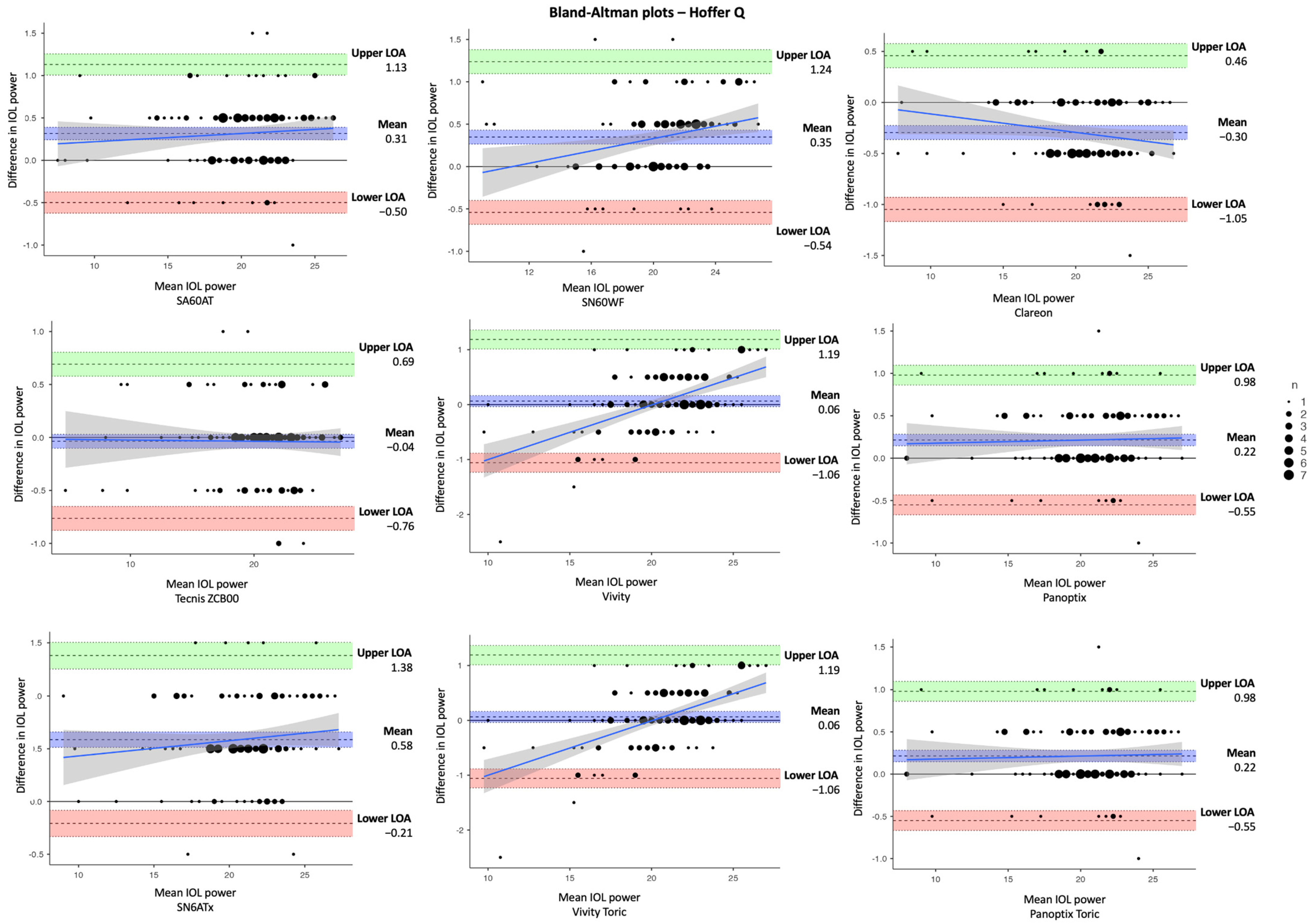
| SA60AT | 20.1 ±3.60 | 19.8 ±3.56 | 0.31 ± 0.04 | 0.24, 0.39 | < 0.001 ** |
| SN60WF | 20.7 ± 3.41 | 20.3 ± 3.29 | 0.35 ± 0.04 | 0.27, 0.44 | < 0.001 ** |
| Clareon (CNA0T0) | 20.5 ± 3.66 | 21.0 ± 3.72 | −0.30 ± 0.03 | −0.36, −0.23 | < 0.001 ** |
| Tecnis ZCB00 | 20.2 ± 3.96 | 20.3 ± 3.96 | −0.04 ± 0.04 | −0.10, 0.03 | 0.280 |
| Vivity (DFT015) | 20.8 ± 3.36 | 2075 ± 3.05 | 0.06 ± 0.05 | −0.04, 0.16 | 0.216 |
| Panoptix (TFTN00) | 20.5 ± 3.66 | 20.3 ± 3.65 | 0.22 ± 0.03 | 0.17, 0.28 | < 0.001 ** |
| SN6ATx | 21.0 ± 3.41 | 20.4 ± 3.36 | 0.58 ± 0.04 | 0.51, 0.66 | < 0.001 ** |
| Vivity Toric (DFTx15) | 20.8 ± 3.36 | 2075 ± 3.05 | 0.06 ± 0.05 | −0.04, 0.16 | 0.216 |
| Panoptix Toric (TFNTx) | 20.5 ± 3.66 | 20.3 ± 3.65 | 0.22 ± 0.03 | 0.17, 0.28 | < 0.001 ** |
| D. Haigis | |||||
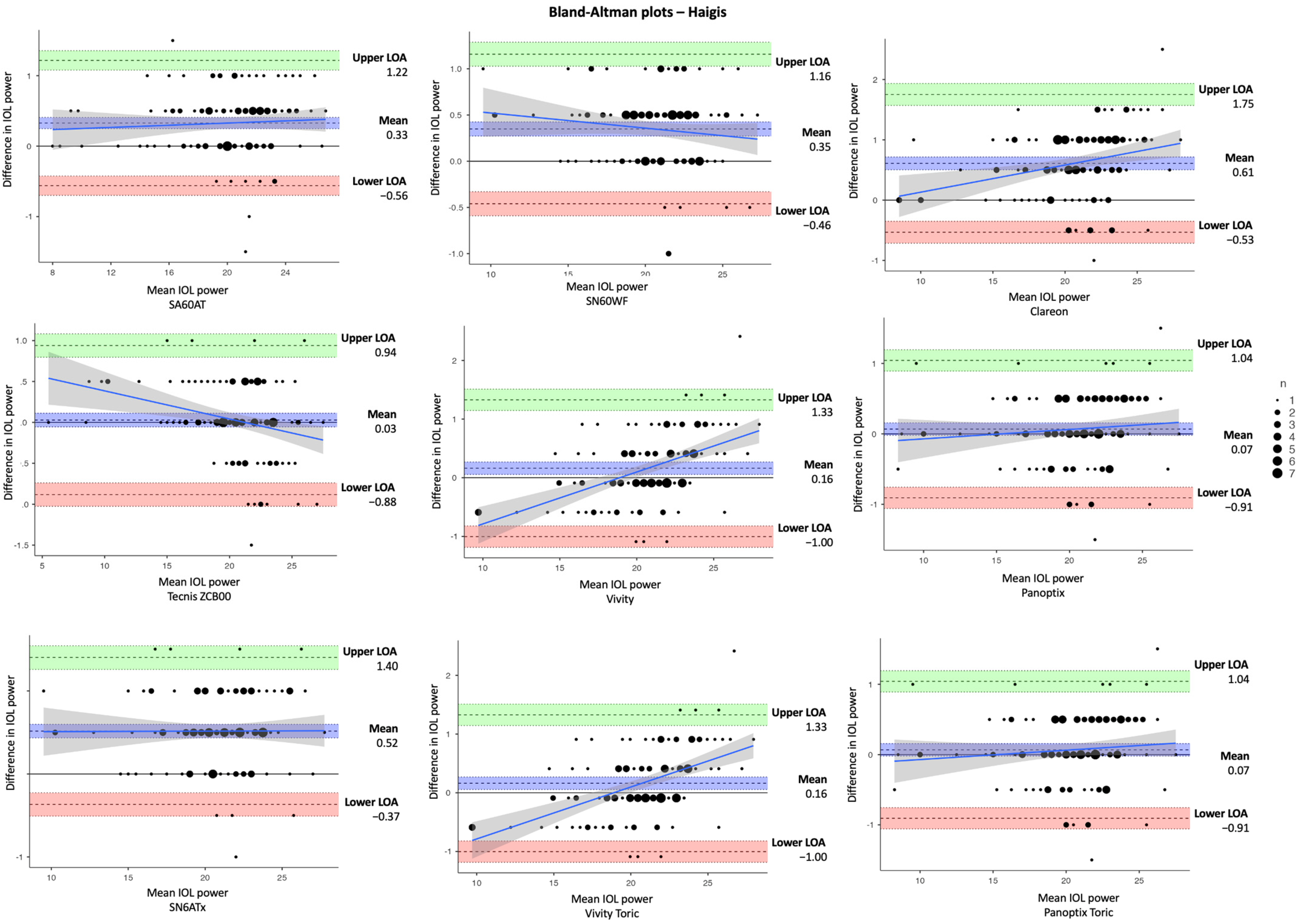
| SA60AT | 20.2 ± 3.54 | 19.9 ± 3.49 | 0.33 ± 0.04 | 0.25, 0.41 | < 0.001 ** |
| SN60WF | 20.7 ± 3.27 | 20.4 ± 3.632 | 0.35 ± 0.04 | 0.27, 0.43 | < 0.001 ** |
| Clareon (CNA0T0) | 20.9 ± 3.86 | 20.3 ± 3.69 | 0.61 ± 0.05 | 0.50, 0.72 | < 0.001 ** |
| Tecnis ZCB00 | 20.4 ± 3.77 | 20.4 ± 3.90 | 0.03 ± 0.04 | −0.05, 0.11 | 0.497 |
| Vivity (DFT015) | 20.8 ± 3.59 | 20.6 ± 3.28 | 0.16 ± 0.05 | 0.06, 0.27 | 0.003 * |
| Panoptix (TFTN00) | 20.4 ± 3.66 | 20.4 ± 3.61 | 0.07 ± 0.04 | −0.02, 0.16 | 0.129 |
| SN6ATx | 21.0 ± 3.34 | 20.5 ± 3.33 | 0.52 ± 0.04 | 0.44, 0.60 | < 0.001 ** |
| Vivity Toric (DFTx15) | 20.8 ± 3.59 | 20.6 ± 3.28 | 0.16 ± 0.05 | 0.06, 0.27 | 0.003 * |
| Panoptix Toric (TFNTx) | 20.4 ± 3.66 | 20.4 ± 3.61 | 0.07 ± 0.04 | −0.02, 0.16 | 0.129 |
| Mean Error ± SD (D) | Difference (IOLMaster–Argos) (D) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IOLMaster | Argos | Mean ± SE | 95% CI | p-Value | ||
| Panoptix | ||||||
| SRK/T | 0.095 ± 0.136 | −0.168 ± 0.173 | 0.263 ± 0.044 | 0.17, 0.36 | <0.001 ** | |
| Holladay 1 | 0.070 ± 0.164 | −0.194 ± 0.111 | 0.264 ± 0.044 | 0.17, 0.36 | <0.001 ** | |
| Hoffer Q | 0.050 ± 0.157 | −0.210 ± 0.118 | 0.260 ± 0.033 | 0.19, 0.33 | <0.001 ** | |
| Haigis | 0.330 ± 0.446 | −0.188 ± 0.137 | 0.518 ± 0.081 | 0.35, 0.69 | <0.001 ** | |
| SN60WF | ||||||
| SRK/T | 0.290 ± 0.299 | 0.172 ± 0.208 | 0.118 ± 0.058 | −0.01, 0.24 | 0.060 | |
| Holladay 1 | 0.366 ± 0.324 | 0.162 ± 0.223 | 0.204 ± 0.066 | 0.06, 0.35 | 0.008 * | |
| Hoffer Q | 0.440 ± 0.389 | 0.164 ± 0.272 | 0.276 ± 0.066 | 0.13, 0.41 | <0.001 ** | |
| Haigis | 0.796 ± 0.572 | 0.140 ± 0.222 | 0.656 ± 0.100 | 0.44, 0.87 | <0.001 ** | |
| IOL/Formula | ME: ±0.25 D (%) | ME: ±0.50 D (%) | ME: ±1.00 D (%) | ME: ±2.00 D (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IOLMaster | Argos | IOLMaster | Argos | IOLMaster | Argos | IOLMaster | Argos | |
| Panoptix | ||||||||
| SRK/T | 87.5 | 87.5 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Holladay 1 | 79.7 | 81.3 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Hoffer Q | 100 | 79.8 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Haigis | 59.4 | 62.5 | 67.2 | 98.4 | 81.3 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| SN60WF | ||||||||
| SRK/T | 66.7 | 47.8 | 86.9 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Holladay 1 | 46.4 | 40.6 | 81.2 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Hoffer Q | 27.5 | 33.3 | 79.7 | 100 | 81.2 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Haigis | 21.7 | 59.4 | 42.0 | 96.9 | 60.9 | 98.6 | 100 | 100 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Panagiotopoulou, E.-K.; Polychroniadis, T.; Bakirtzis, M.; Tsinopoulos, I.; Ziakas, N.; Labiris, G. Level of Agreement of Intraocular Lens Power Measurements Between a Swept-Source OCT Biometer and a Partial Coherence Interferometer. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3903. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113903
Panagiotopoulou E-K, Polychroniadis T, Bakirtzis M, Tsinopoulos I, Ziakas N, Labiris G. Level of Agreement of Intraocular Lens Power Measurements Between a Swept-Source OCT Biometer and a Partial Coherence Interferometer. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(11):3903. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113903
Chicago/Turabian StylePanagiotopoulou, Eirini-Kanella, Thomas Polychroniadis, Minas Bakirtzis, Ioannis Tsinopoulos, Nikolaos Ziakas, and Georgios Labiris. 2025. "Level of Agreement of Intraocular Lens Power Measurements Between a Swept-Source OCT Biometer and a Partial Coherence Interferometer" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 11: 3903. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113903
APA StylePanagiotopoulou, E.-K., Polychroniadis, T., Bakirtzis, M., Tsinopoulos, I., Ziakas, N., & Labiris, G. (2025). Level of Agreement of Intraocular Lens Power Measurements Between a Swept-Source OCT Biometer and a Partial Coherence Interferometer. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(11), 3903. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113903









