Rethinking Otorhinolaryngologic Care Pathways in Children with Down Syndrome: A Multidisciplinary Framework for Early Diagnosis and Management
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. ENT Manifestations
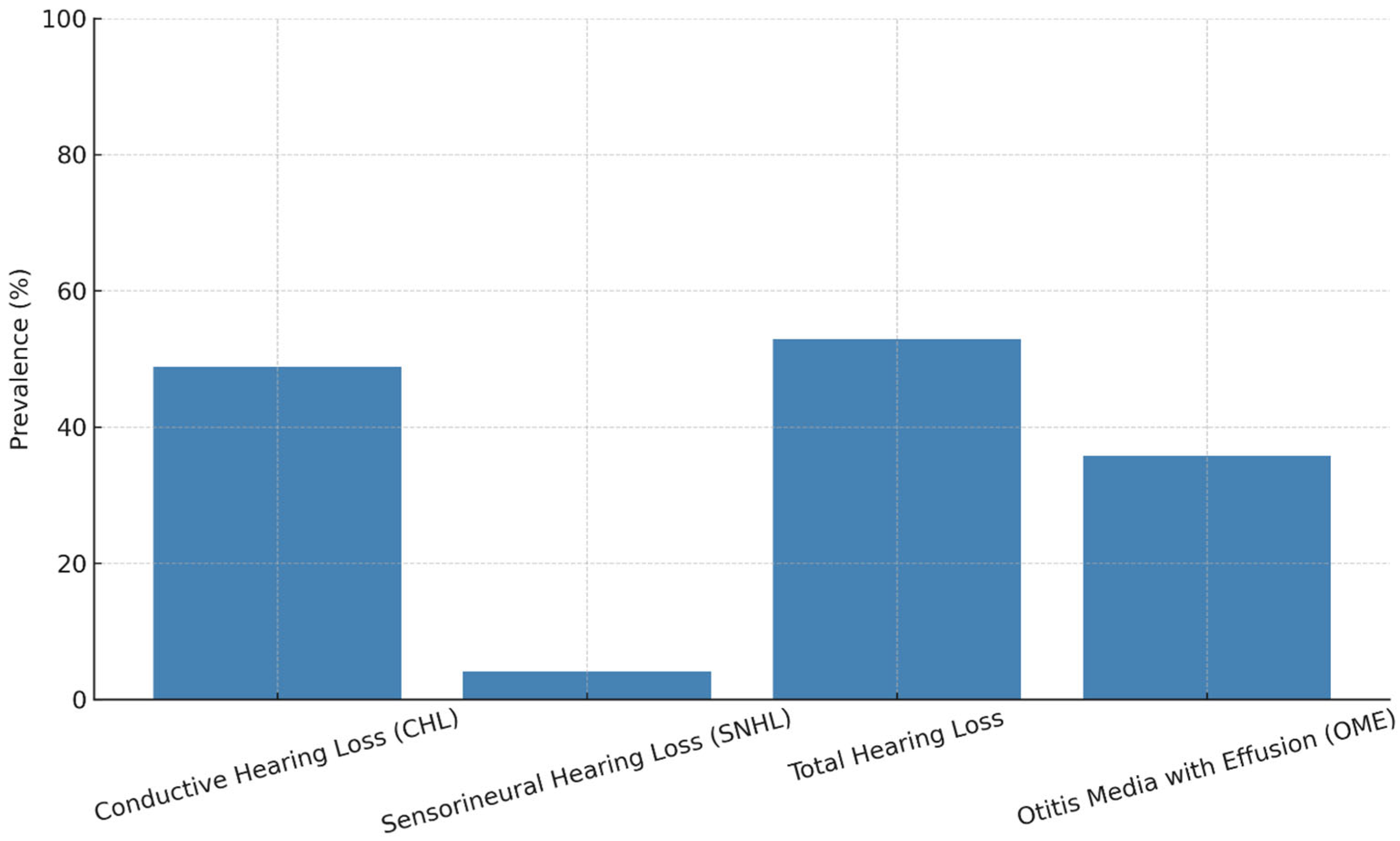
3.1. Hearing Impairment
3.2. Upper Respiratory Tract Infections
3.3. Obstructive Sleep Apnea
3.4. Dysphagia
4. Diagnosing and Monitoring
4.1. Hearing Impairment
4.2. Upper Respiratory Tract Infections
4.3. Obstructive Sleep Apnea
4.4. Dysphagia
5. Management
5.1. Management of Hearing Loss
5.2. Management of Upper Respiratory Tract Infections
5.3. Management of OSAS
5.4. Management of Dysphagia
6. Conclusions
7. Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Papavassiliou, P.; Charalsawadi, C.; Rafferty, K.; Jackson-Cook, C. Mosaicism for trisomy 21: A review. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2015, 167, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bull, M.J.; Committee on Genetics. Health supervision for children with Down syndrome. Pediatrics 2011, 128, 393–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weijerman, M.E.; de Winter, J.P. Clinical practice. The care of children with Down syndrome. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2010, 169, 1445–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shott, S.R. Down syndrome: Common otolaryngologic manifestations. Am. J. Med. Genet. C Semin. Med. Genet. 2006, 142, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali Khan, I. Role of Adenotonsillectomy and Tonsillectomy in Children with Down Syndrome Who Develop Obstructive Sleep Apnea by Obesity as a Risk Factor. Int. J. Pediatr. 2022, 2022, 8074094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Balkany, T.J.; Mischke, R.E.; Downs, M.P.; Jafek, B.W. Ossicular abnormalities in Down’s syndrome. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1979, 87, 372–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Lausnay, M.; Verhulst, S.; Boel, L.; Wojciechowski, M.; Boudewyns, A.; Van Hoorenbeeck, K. The prevalence of lower airway anomalies in children with Down syndrome compared to controls. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2020, 55, 1259–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Silva, H.; Shah, N.; Mathura, N.; Smith, C. Respiratory health outcomes of children with Down Syndrome following dysphagia management: A service evaluation. BMJ Paediatr. Open 2024, 8, e002982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starbuck, J.M.; Cole, T.M., 3rd; Reeves, R.H.; Richtsmeier, J.T. Trisomy 21 and facial developmental instability. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. 2013, 151, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Takahashi, H.; Honjo, I.; Fujita, A.; Kurata, K. Effects of adenoidectomy on sinusitis. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Belg. 1997, 51, 85–87. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Takizawa, H.; Takahashi, M.; Yoshida, H.; Yamaguchi, T.; Maki, K. Three-dimensional assessment of the nasopharyngeal airway in Down syndrome during the mixed dentition period: A case-control study. Angle Orthod. 2025, 95, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Laws, G.; Hall, A. Early hearing loss and language abilities in children with Down syndrome. Int. J. Lang. Commun. Disord. 2014, 49, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, R.S.; Hesketh, L.J. Language, cognition, and short-term memory in individuals with Down syndrome. Downs Syndr. Res. Pract. 2001, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruggeri, P.; Manti, S.; Li Pomi, A.; Lo Bello, F.; Morana, G.; Profazio, C.; Bushra, M.; Esquinas, A. Respiratory support in patients with Down syndrome: A systematic review. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2025, 34, 240070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Anil, M.A.; Shabnam, S.; Narayanan, S. Feeding and swallowing difficulties in children with Down syndrome. J. Intellect. Disabil. Res. 2019, 63, 992–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yahia, S.; Metawea, M.; Megahed, A.; ELshawaf, W.; Wahba, Y.; Mahmoud, R. The prevalence of hearing impairment in infants and children with down syndrome a cross sectional study in a Tertiary Care Center. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 7570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tedeschi, A.S.; Roizen, N.J.; Taylor, H.G.; Murray, G.; Curtis, C.A.; Parikh, A.S. The prevalence of congenital hearing loss in neonates with Down syndrome. J. Pediatr. 2015, 166, 168–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laws, G.; Bishop, D.V. A comparison of language abilities in adolescents with Down syndrome and children with specific language impairment. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2003, 46, 1324–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, A.G. Language deficit and hearing loss in Down’s syndrome. Child Care Health Dev. 1987, 13, 137–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basonbul, R.A.; Ronner, E.A.; Rong, A.; Rong, G.; Cohen, M.S. Audiologic testing in children with Down Syndrome: Are current guidelines optimal? Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2020, 134, 110017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, R.; Gallagher, D.; Leyden, P. Diagnosis and management of conductive hearing loss in children with trisomy 21. J. Paediatr. Child Health 2018, 54, 1242–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, A.; Pryce, H.; Bruce, I.A.; Callery, P.; Lakhanpaul, M.; Schilder, A.G.M. A mixed-methods study of the management of hearing loss associated with otitis media with effusion in children with Down syndrome. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2019, 44, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shott, S.R.; Joseph, A.; Heithaus, D. Hearing loss in children with Down syndrome. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2001, 61, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.F.; Lee, C.H.; Hsueh, W.Y.; Lin, M.T.; Kang, K.T. Prevalence of Obstructive Sleep Apnea in Children With Down Syndrome: A Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2018, 14, 867–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- de Miguel-Díez, J.; Villa-Asensi, J.R.; Alvarez-Sala, J.L. Prevalence of sleep-disordered breathing in children with Down syndrome: Polygraphic findings in 108 children. Sleep 2003, 26, 1006–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bower, C.M.; Gungor, A. Pediatric obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Otolaryngol. Clin. N. Am. 2000, 33, 49–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, A.; Maybee, J.; Moran, M.K.; Wolter-Warmerdam, K.; Hickey, F. Clinical Characteristics of Dysphagia in Children with Down Syndrome. Dysphagia 2016, 31, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, Y.; Kwon, Y.; DelRosso, L.; Sobremonte-King, M. Dysphagia severity is associated with worse sleep-disordered breathing in infants with Down syndrome. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2023, 19, 883–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Dorfman, L.; Jahagirdar, V.; Kaul, S.; El-Chammas, K.; Kaul, A. Comprehensive Manometric Evaluation of Dysphagia in Patients with Down Syndrome. Dysphagia 2023, 38, 1589–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordstrøm, M.; Retterstøl, K.; Hope, S.; Kolset, S.O. Nutritional challenges in children and adolescents with Down syndrome. Lancet Child Adolesc. Health 2020, 4, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phelan, E.; Pal, R.; Henderson, L.; Green, K.M.; Bruce, I.A. The management of children with Down syndrome and profound hearing loss. Cochlear Implants Int. 2016, 17, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cottrell, J.; Zahr, S.K.; Propst, E.J.; Narang, I.; Amin, R.; Chiang, J.; Al-Saleh, S.; Wolter, N.E. Morbidity and mortality from adenotonsillectomy in children with trisomy 21. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2020, 138, 110377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagan, N.C.; Mc Grane, F.; Huggard, D.; Sharkey, J.; Purcell, C.; Balfe, J.; Molloy, E. Implementation of a health surveillance clinic for children with Down syndrome. Arch. Dis. Child Educ. Pract. Ed. 2021, 106, 60–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulson, L.M.; Weaver, T.S.; Macarthur, C.J. Outcomes of tympanostomy tube placement in children with Down syndrome--a retrospective review. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2014, 78, 223–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nightengale, E.; Yoon, P.; Wolter-Warmerdam, K.; Daniels, D.; Hickey, F. Understanding Hearing and Hearing Loss in Children With Down Syndrome. Am. J. Audiol. 2017, 26, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roizen, N.J.; Wolters, C.; Nicol, T.; Blondis, T.A. Hearing loss in children with Down syndrome. J. Pediatr. 1993, 123, S9–S12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evenhuis, H.M.; van Zanten, G.A.; Brocaar, M.P.; Roerdinkholder, W.H. Hearing loss in middle-age persons with Down syndrome. Am. J. Ment. Retard. 1992, 97, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Boato, E.; Melo, G.; Filho, M.; Moresi, E.; Lourenço, C.; Tristão, R. The Use of Virtual and Computational Technologies in the Psychomotor and Cognitive Development of Children with Down Syndrome: A Systematic Literature Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 2955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shott, S.R.; Amin, R.; Chini, B.; Heubi, C.; Hotze, S.; Akers, R. Obstructive sleep apnea: Should all children with Down syndrome be tested? Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2006, 132, 432–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyken, M.E.; Lin-Dyken, D.C.; Poulton, S.; Zimmerman, M.B.; Sedars, E. Prospective polysomnographic analysis of obstructive sleep apnea in down syndrome. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 2003, 157, 655–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishman, S.L.; Maturo, S.; Schwartz, S.; McKenna, M.; Baldassari, C.M.; Bergeron, M.; Chernobilsky, B.; Ehsan, Z.; Gagnon, L.; Liu, Y.C.; et al. Expert Consensus Statement: Management of Pediatric Persistent Obstructive Sleep Apnea After Adenotonsillectomy. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2023, 168, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liu, P.; Kong, W.; Fang, C.; Zhu, K.; Dai, X.; Meng, X. Hypoglossal nerve stimulation in adolescents with down syndrome and obstructive sleep apnea: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 1037926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Caloway, C.L.; Diercks, G.R.; Keamy, D.; de Guzman, V.; Soose, R.; Raol, N.; Shott, S.R.; Ishman, S.L.; Hartnick, C.J. Update on hypoglossal nerve stimulation in children with down syndrome and obstructive sleep apnea. Laryngoscope 2020, 130, E263–E267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, D.K.; Hui, H.N.; Chan, C.H.; Kwok, K.L.; Chow, P.Y.; Cheung, J.M.; Leung, S.Y. Obstructive sleep apnoea in children with Down syndrome. Singap. Med. J. 2006, 47, 774–779. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Porter, H.L.; Grantham, D.W.; Ashmead, D.H.; Tharpe, A.M. Binaural masking release in children with Down syndrome. Ear Hear. 2014, 35, e134–e142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Aspect | Hearing Aids | Grommets (Timpanostomy Tubes) |
|---|---|---|
| Efficacy | Comparable efficacy to grommets for mild-to-moderate CHL | Effective for recurrent OME and AOM, especially with effusion |
| Invasiveness | Non-invasive | Invasive, require general anaesthesia |
| Risks | Minimal, skin irritation or device intolerance | Risks include otorrhea, tympanic membrane perforation, anaesthesia complications |
| Parental Perception | Preferred by many parents due to reduced emotional stress | Often associated with increased parental anxiety |
| Maintenance | Require regular monitoring and fitting | May require reinsertion or replacement; risk of extrusion |
| Indications | Persistent CHL without infection; non-surgical candidates | Recurrent AOM, OME > 3 months, failed conservative therapy |
| Contraindications | Significant hyperactivity, sensory intolerance | Craniofacial abnormalities or anaesthesia risks |
| ENT Condition | Estimated Prevalence | Key Causes | Clinical Consequences | Management | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conductive Hearing Loss | 48.8% | OME, eustachian tube dysfunction, craniofacial anomalies | Language delay, articulation disorders | Hearing aids, monitoring | [16] |
| Sensorineural Hearing Loss | 4.1% | Inner ear malformations, cochlear nerve dysfunction | Permanent hearing loss, speech impairment | Early diagnosis, cochlear implant (selected cases) | [16] |
| Otitis Media with Effusion | 35.8% | URTI, adenoid hypertrophy, Immune deficiency | Fluctuating hearing, CHL | Tympanometry, PETs, medical therapy | [16] |
| Obstructive Sleep Apnea | 45–76% | Macroglossia, midfacial hypoplasia, hypotonia, obesity | Cognitive decline, pulmonary hypertension | Polysomnography, adenotonsillectomy, CPAP | [5] |
| Dysphagia | >50% | Oromotor hypotonia, macroglossia, coordination issues | Aspiration risk, malnutrition | Feeding therapy, nutritional support | [15] |
| Language and Speech Delay | Nearly universal | Hearing loss, hypotonia, articulatory difficulty | Communication impairment, learning delay | Speech-language therapy, augmentative and alternative communication | [12] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Comisi, F.F.; Esposito, E.; Savasta, S. Rethinking Otorhinolaryngologic Care Pathways in Children with Down Syndrome: A Multidisciplinary Framework for Early Diagnosis and Management. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3889. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113889
Comisi FF, Esposito E, Savasta S. Rethinking Otorhinolaryngologic Care Pathways in Children with Down Syndrome: A Multidisciplinary Framework for Early Diagnosis and Management. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(11):3889. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113889
Chicago/Turabian StyleComisi, Francesco Fabrizio, Elena Esposito, and Salvatore Savasta. 2025. "Rethinking Otorhinolaryngologic Care Pathways in Children with Down Syndrome: A Multidisciplinary Framework for Early Diagnosis and Management" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 11: 3889. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113889
APA StyleComisi, F. F., Esposito, E., & Savasta, S. (2025). Rethinking Otorhinolaryngologic Care Pathways in Children with Down Syndrome: A Multidisciplinary Framework for Early Diagnosis and Management. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(11), 3889. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113889







