The Detection of Early Changes in Inflammatory Response After Pulmonary Vein Isolation in Patients with Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation Can Predict Late Atrial Fibrillation Recurrence
Abstract
1. Introduction
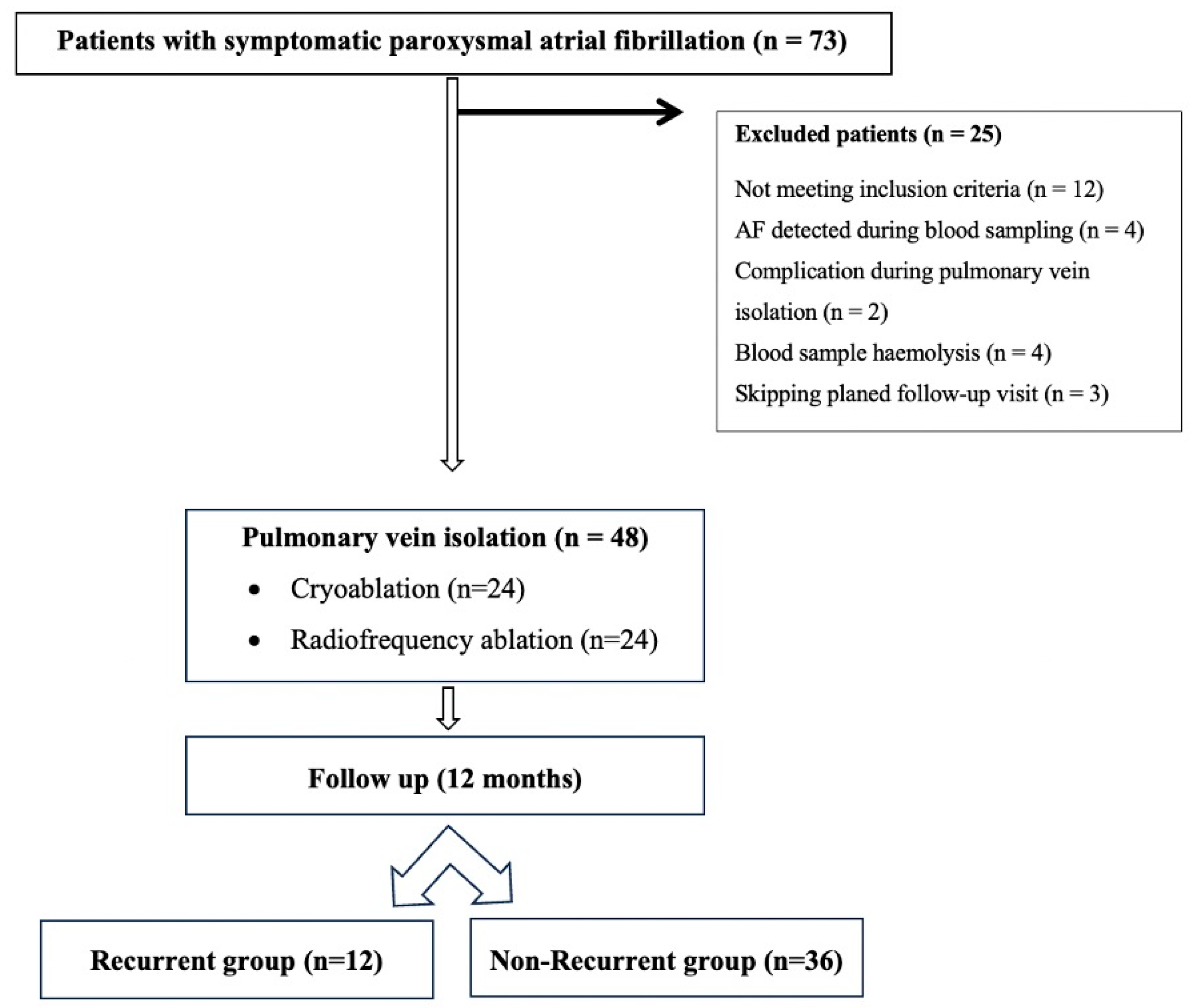
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Participants
2.2. Treatment Before Ablation
2.2.1. Blood Sampling
2.2.2. Biomarker Analysis
2.2.3. Routine Laboratory Tests
2.2.4. Echocardiographic Examination
2.3. Procedure Details
2.3.1. Radiofrequency Ablation
2.3.2. Cryoablation
2.4. Post-Procedure Management and Follow-Up
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic and Echocardiographic Characteristics
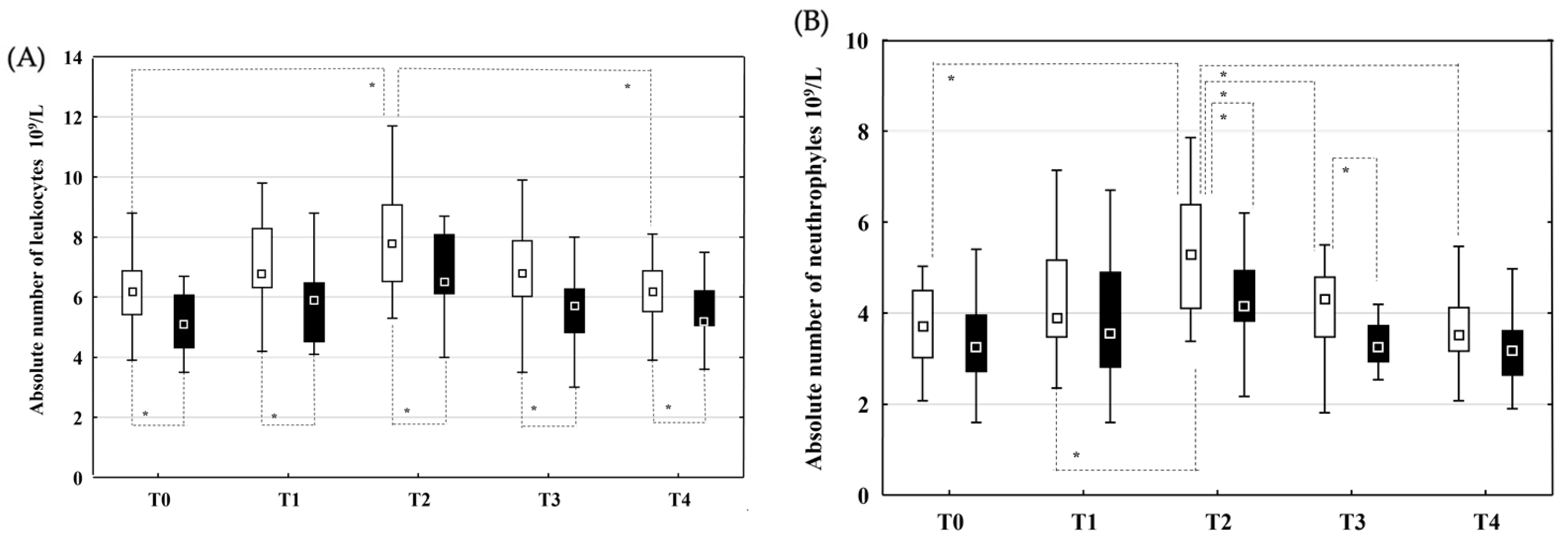
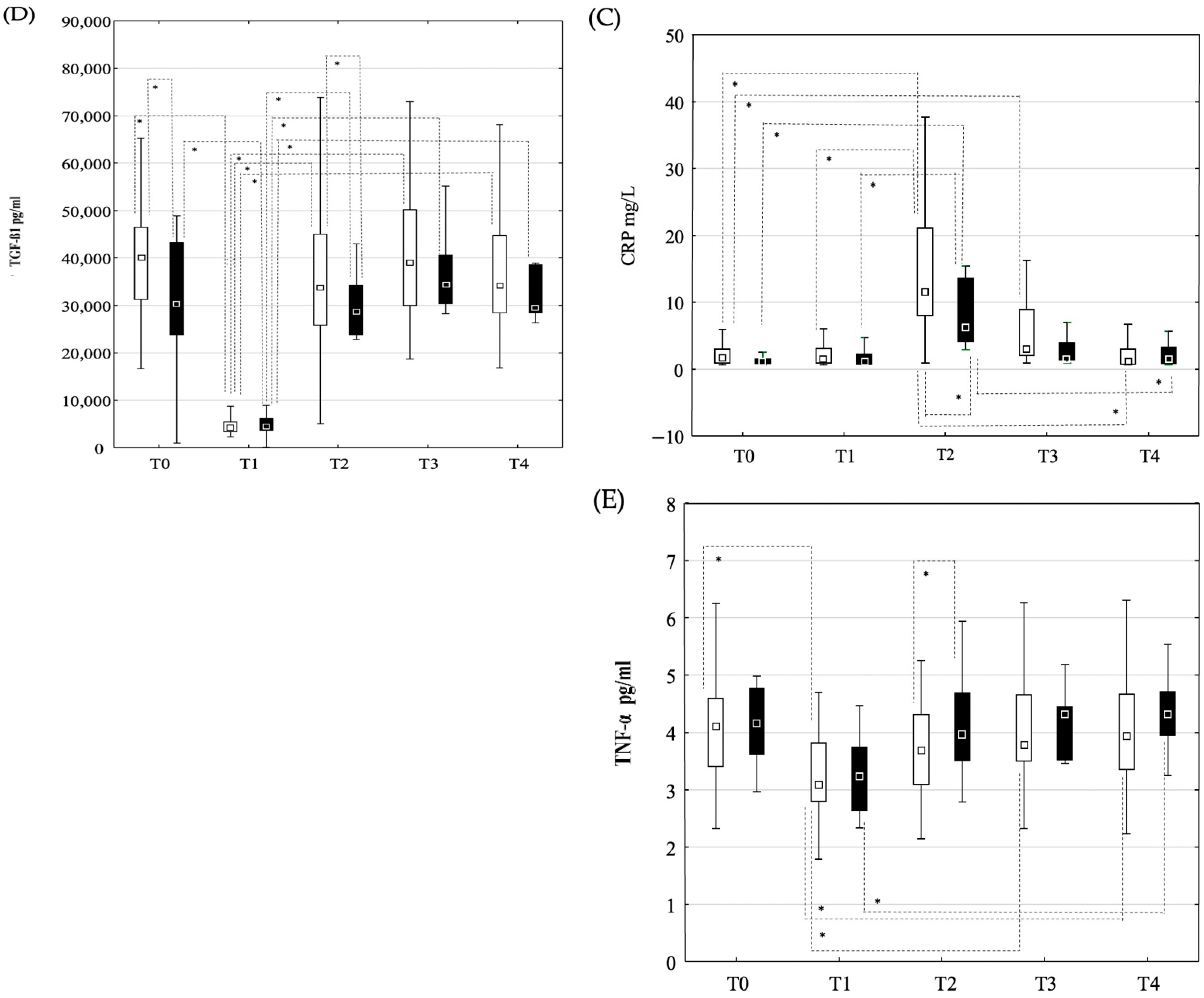
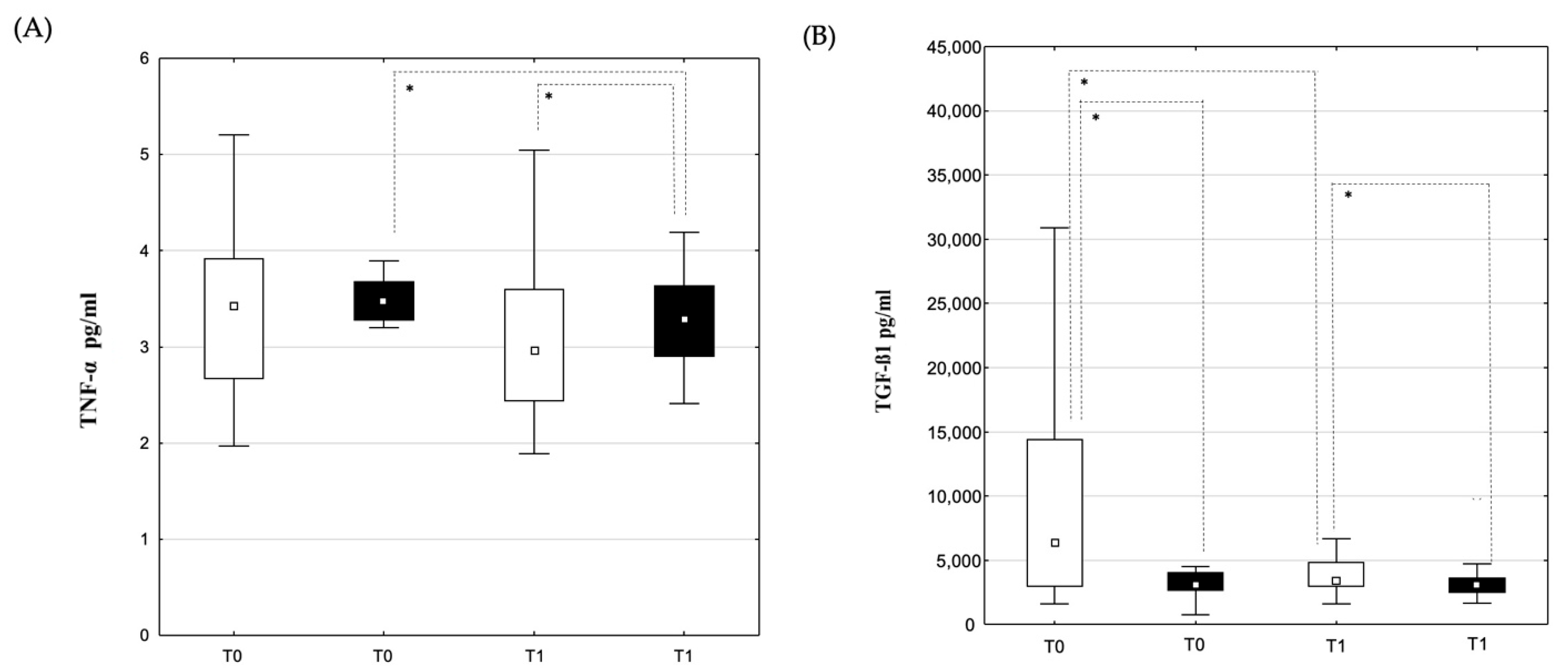
3.2. Changes in Laboratory Parameters and Cytokine Concentrations
3.2.1. Peripheral Blood Samples
3.2.2. Blood Samples from the Coronary Sinus
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rahman, F.; Kwan, G.F.; Benjamin, E.J. Global epidemiology of atrial fibrillation. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2014, 11, 639–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hindricks, G.; Potpara, T.; Dagres, N.; Arbelo, E.; Bax, J.J.; Blomström-Lundqvist, C.; Boriani, G.; Castella, M.; Dan, G.A.; Dilaveris, P.E.; et al. ESC Scientific Document Group. 2020 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS): The Task Force for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Developed with the special contribution of the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA) of the ESC. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 373–498. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Haïssaguerre, M.; Jaïs, P.; Shah, D.C.; Takahashi, A.; Hocini, M.; Quiniou, G.; Garrigue, S.; Le Mouroux, A.; Le Métayer, P.; Clémenty, J. Spontaneous initiation of atrial fibrillation by ectopic beats originating in the pulmonary veins. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 339, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.H.; Lu, Z.Y.; Xiang, Y.; Hou, J.W.; Wang, Q.; Lin, H.; Li, Y.G. Cryoablation vs. radiofrequency ablation for treatment of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Europace 2017, 19, 784–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boano, G.; Aneq, M.Å.; Spyrou, G.; Enocsson, H.; Charitakis, E.; Vánky, F. Biochemical response to cryothermal and radiofrequency exposure of the human myocardium at surgical ablation of atrial fibrillation: A randomized controlled trial. Transl. Med. Commun. 2020, 5, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghdiri, A. Inflammation and arrhythmogenesis: A narrative review of the complex relationship. Int. J. Arrhythm. 2024, 25, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordignon, S.; Barra, S.; Providencia, R.; de Asmundis, C.; Marijon, E.; Farkowski, M.M.; Anic, A.; Guerra, J.M.; Kosiuk, J.; Iliodromitis, K.T. The blanking period after atrial fibrillation ablation: An European Heart Rhythm Association survey on contemporary definition and management. Europace 2022, 24, 1684–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.G.; Boo, K.Y.; Choi, J.I.; Choi, Y.Y.; Choi, H.Y.; Roh, S.Y.; Shim, J.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, Y.H. Early Recurrence Is Reliable Predictor of Late Recurrence After Radiofrequency Catheter Ablation of Atrial Fibrillation. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2021, 7, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Chen, Y.C.; Chen, Y.J.; Chang, S.L.; Tai, C.T.; Wongcharoen, W.; Yeh, H.I.; Lin, C.I.; Chen, S.A. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha alters calcium handling and increases arrhythmogenesis of pulmonary vein cardiomyocytes. Life Sci. 2007, 80, 1806–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.; Revis, D.; Herrick, S.; Baillie, R.; Thorgeirson, S.; Ferguson, M.; Roberts, A. Role of elevated plasma transforming growth factor-beta1 levels in wound healing. Am. J. Pathol. 1999, 154, 1115–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carballo, D.; Noble, S.; Carballo, S.; Stirnemann, J.; Muller, H.; Burri, H.; Vuilleumier, N.; Talajic, M.; Tardif, J.C.; Keller, P.F.; et al. Biomarkers and arrhythmia recurrence following radiofrequency ablation of atrial fibrillation. J. Int. Med. Res. 2018, 46, 5183–5194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaroonpipatkul, S.; Trongtorsak, A.; Kewcharoen, J.; Thangjui, S.; Pokawattana, A.; Navaravong, L. High sensitivity C reactive protein levels and atrial fibrillation recurrence after catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Arrhythm. 2023, 39, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Bao, Y.; Lin, C.; Xie, Y.; Luo, Q.; Zhang, N.; Wu, L. Early recurrence after cryoballoon versus radiofrequency ablation for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: Mechanism and implication in long-term outcome. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2022, 22, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, B.; Liu, P.; Zhang, F.; Hui, J.; He, L. Predicting Values of Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (NLR), High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein (hs-CRP), and Left Atrial Diameter (LAD) in Patients with Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation Recurrence After Radiofrequency Ablation. Med. Sci. Monit. 2022, 28, e934569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letsas, K.P.; Weber, R.; Bürkle, G.; Mihas, C.C.; Minners, J.; Kalusche, D.; Arentz, T. Pre-ablative predictors of atrial fibrillation recurrence following pulmonary vein isolation: The potential role of inflammation. Europace 2009, 11, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Dai, L.; Song, Z.; Li, H.; Shu, M. Association between C-reactive protein and atrial fibrillation recurrence after catheter ablation: A meta-analysis. Clin. Cardiol. 2013, 36, 548–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richter, B.; Derntl, M.; Marx, M.; Lercher, P.; Gössinger, H.D. Therapy with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor blockers, and statins: No effect on ablation outcome after ablation of atrial fibrillation. Am. Heart J. 2007, 153, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, W.; Yin, Y.; Qin, M. Role of serum TGF-β1 level in atrial fibrosis and outcome after catheter ablation for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Medicine 2017, 96, e9210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, J.H.; Werner, J.H.; Plitt, G.D.; Noble, V.V.; Spring, J.T.; Stephens, B.A.; Siddique, A.; Merritt-Genore, H.L.; Moulton, M.J.; Agrawal, D.K. Immunopathogenesis and biomarkers of recurrent atrial fibrillation following ablation therapy in patients with preexisting atrial fibrillation. Expert Rev. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2019, 17, 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babapoor-Farrokhran, S.; Tarighati, R.R.; Gill, D.; Alzubi, J.; Mainigi, S.K. How transforming growth factor contributes to atrial fibrillation? Life Sci. 2021, 266, 118823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, Y.; Ng, C.Y.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, T.; Li, G. Association of Plasma Transforming Growth Factor-β1 Levels and the Risk of Atrial Fibrillation: A Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.H.; Hu, Y.F.; Chou, C.Y.; Lin, Y.J.; Chang, S.L.; Lo, L.W.; Tuan, T.C.; Li, C.H.; Chao, T.F.; Chung, F.P.; et al. Transforming growth factor-β1 level and outcome after catheter ablation for nonparoxysmal atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm. 2013, 10, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishima, H.; Mine, T.; Takahashi, S.; Ashida, K.; Ishihara, M.; Masuyama, T. The Impact of Transforming Growth Factor-β1 Level on Outcome After Catheter Ablation in Patients With Atrial Fibrillation. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2017, 28, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Xue, Y.M.; Zhan, X.Z.; Liao, H.T.; Guo, H.M.; Wu, S.L. Role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in the pathogenesis of atrial fibrillation. Chin. Med. J. 2011, 124, 1976–1982. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Taghji, P.; El Haddad, M.; Phlips, T.; Wolf, M.; Knecht, S.; Vandekerckhove, Y.; Tavernier, R.; Nakagawa, H.; Duytschaever, M. Evaluation of a Strategy Aiming to Enclose the Pulmonary Veins With Contiguous and Optimized Radiofrequency Lesions in Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation: A Pilot Study. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2018, 4, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsiachris, D.; Antoniou, C.K.; Doundoulakis, I.; Manolakou, P.; Sougiannis, D.; Kordalis, A.; Gatzoulis, K.A.; Chierchia, G.B.; de Asmundis, C.; Stefanadis, C.; et al. Best Practice Guide for Cryoballoon Ablation in Atrial Fibrillation: The Compilation Experience of More than 1000 Procedures. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2023, 10, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lip, G.Y.; Frison, L.; Halperin, J.L.; Lane, D.A. Identifying patients at high risk for stroke despite anticoagulation: A comparison of contemporary stroke risk stratification schemes in an anticoagulated atrial fibrillation cohort. Stroke 2010, 41, 2731–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, H.; Li, S.; Guo, X.; Jiang, C.; Zhou, L.; He, L.; Wang, W.; Li, S.; Tang, R.; Liu, N.; et al. Antiarrhythmic Drug Use in the Blanking Period After Re-Ablation and Recurrence in Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2025, 48, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottlieb, L.A.; Dekker, L.R.C.; Coronel, R. The Blinding Period Following Ablation Therapy for Atrial Fibrillation: Proarrhythmic and Antiarrhythmic Pathophysiological Mechanisms. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2021, 7, 416–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Lip, G.Y.; Apostolakis, S. Inflammatory Biomarkers and Atrial Fibrillation: Potential Role of Inflammatory Pathways in the Pathogenesis of Atrial Fibrillation-induced Thromboembolism. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2015, 13, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Li, G.; Li, L.; Korantzopoulos, P. Association between C-reactive protein and recurrence of atrial fibrillation after successful electrical cardioversion: A meta-analysis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2007, 49, 1642–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kallergis, E.M.; Manios, E.G.; Kanoupakis, E.M.; Mavrakis, H.E.; Kolyvaki, S.G.; Lyrarakis, G.M.; Chlouverakis, G.I.; Vardas, P.E. The role of the post-cardioversion time course of hs-CRP levels in clarifying the relationship between inflammation and persistence of atrial fibrillation. Heart 2008, 94, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Li, L.; Korantzopoulos, P.; Goudevenos, J.A.; Li, G. Meta-analysis of association between C-reactive protein and immediate success of electrical cardioversion in persistent atrial fibrillation. Am. J. Cardiol. 2008, 101, 1749–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurotobi, T.; Iwakura, K.; Inoue, K.; Kimura, R.; Okamura, A.; Koyama, Y.; Toyoshima, Y.; Ito, N.; Fujii, K. A pre-existent elevated C-reactive protein is associated with the recurrence of atrial tachyarrhythmias after catheter ablation in patients with atrial fibrillation. Europace 2010, 12, 1213–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lellouche, N.; Sacher, F.; Wright, M.; Nault, I.; Brottier, J.; Knecht, S.; Matsuo, S.; Lomas, O.; Hocini, M.; Haïssaguerre, M.; et al. Usefulness of C-reactive protein in predicting early and late recurrences after atrial fibrillation ablation. Europace 2009, 11, 662–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyama, T.; Sekiguchi, Y.; Tada, H.; Arimoto, T.; Yamasaki, H.; Kuroki, K.; Machino, T.; Tajiri, K.; Zhu, X.D.; Kanemoto, M.; et al. Comparison of characteristics and significance of immediate versus early versus no recurrence of atrial fibrillation after catheter ablation. Am. J. Cardiol. 2009, 103, 1249–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Fang, P.H.; Dibs, S.; Hou, Y.; Li, X.F.; Zhang, S. High-sensitivity C-reactive protein as a predictor of atrial fibrillation recurrence after primary circumferential pulmonary vein isolation. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2011, 34, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.; Wazni, O.M.; Marrouche, N.F.; Martin, D.O.; Kilicaslan, F.; Minor, S.; Schweikert, R.A.; Saliba, W.; Cummings, J.; Burkhardt, J.D.; et al. Pre-existent left atrial scarring in patients undergoing pulmonary vein antrum isolation: An independent predictor of procedural failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2005, 45, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, D.S.; Buggins, P.; Hughes, E.; Lip, G.Y. Relationship of interleukin-6 and C-reactive protein to the prothrombotic state in chronic atrial fibrillation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2004, 43, 2075–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijesurendra, R.S.; Casadei, B. Mechanisms of atrial fibrillation. Heart 2019, 105, 1860–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wick, G.; Grundtman, C.; Mayerl, C.; Wimpissinger, T.F.; Feichtinger, J.; Zelger, B.; Sgonc, R.; Wolfram, D. The immunology of fibrosis. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 31, 107–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Cao, H.; Su, L.; Ling, Z.; Liu, Z.; Lan, X.; Xu, Y.; Chen, W.; Yin, Y. NT-proBNP, but not ANP and C-reactive protein, is predictive of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation in patients undergoing pulmonary vein isolation. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. 2012, 33, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, T.C.; Anderson, M.E.; Moots, R.J. The many faces of interleukin-6: The role of IL-6 in inflammation, vasculopathy, and fibrosis in systemic sclerosis. Int. J. Rheumatol. 2011, 2011, 721608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.I.; Chung, A.C.; Zhou, L.; Huang, X.R.; Liu, F.; Fu, P.; Fan, J.M.; Szalai, A.J.; Lan, H.Y. C-reactive protein promotes acute renal inflammation and fibrosis in unilateral ureteral obstructive nephropathy in mice. Lab. Investig. 2011, 91, 837–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steele, H.; Cheng, J.; Willicut, A.; Dell, G.; Breckenridge, J.; Culberson, E.; Ghastine, A.; Tardif, V.; Herro, R. TNF superfamily control of tissue remodeling and fibrosis. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1219907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, C.; Boisson, C.; Haccoun, M.; Thomachot, L.; Mege, J.L. Patterns of cytokine evolution (tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-6) after septic shock, hemorrhagic shock, and severe trauma. Crit. Care Med. 1997, 25, 1813–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, L.; Joo, D.; Sun, S.C. NF-κB signaling in inflammation. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2017, 2, 17023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillesberg, F.S.; Pehrsson, M.; Bay-Jensen, A.C.; Frederiksen, P.; Karsdal, M.; Deleuran, B.W.; Kragstrup, T.W.; Kubo, S.; Tanaka, Y.; Mortensen, J.H. Regulation of fibronectin and collagens type I, III and VI by TNF-α, TGF-β, IL-13, and tofacitinib. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Ma, C.; Dong, J.; Liu, X.; Long, D.; Tian, Y.; Yu, R. The fibrosis and atrial fibrillation: Is the transforming growth factor-beta 1 a candidate etiology of atrial fibrillation. Med. Hypotheses 2008, 70, 317–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Li, M.; Ju, W.; Gu, L.; Zhang, F.; Chen, H.; Gu, K.; Yang, B.; Chen, M. Serum level of transforming growth factor beta 1 is associated with left atrial voltage in patients with chronic atrial fibrillation. Indian Pacing Electrophysiol. J. 2018, 18, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blakytny, R.; Erkell, L.J.; Brunner, G. Inactivation of active and latent transforming growth factor beta by free thiols: Potential redox regulation of biological action. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2006, 38, 1363–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Greef, Y.; Schwagten, B.; Chierchia, G.B.; de Asmundis, C.; Stockman, D.; Buysschaert, I. Diagnosis-to-ablation time as a predictor of success: Early choice for pulmonary vein isolation and long-term outcome in atrial fibrillation: Results from the Middelheim-PVI Registry. Europace 2018, 20, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Parameter | Non-Recurrence Group (n = 36) | Recurrence Group (n = 12) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (yr) | 59.9 (53.5–68) | 60 (58–66.5) | 0.971 |
| Gender (M/F) | 22/14 | 5/7 | 0.40 |
| Arterial hypertension | 23/13 | 7/5 | 0.73 |
| Diabetes mellitus type 2 | 2/34 | 2/10 | 0.22 |
| Hyperlipoproteinemia | 20/16 | 4/8 | 0.18 |
| AF duration (mth) | 40.5 (5–53.5) | 58 (14.5–96) | 0.05 |
| Ablation (cryoablation/RF ablation) | 19/17 | 5/7 | 0.504 |
| Antiarrhythmic therapy during blanking period | 23/13 | 8/4 | 0.86 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 27.8 (24.9–31.2) | 26.3 (24–30.13) | 0.127 |
| CHA2DS2VASc score | 2 (0–5) | 2 (0–4) | 0.27 |
| HAS BLED score | 1 (0–1) | 1 (0–2) | 0.80 |
| H2FpEFF score (%) | 66.4 (60.25–78.6) | 63.3 (52.35–78.7) | 0.45 |
| Parameter | Non-Recurrence Group (n = 36) | Recurrence Group (n = 12) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| LVEF (%) | 60 (56–62) | 58.5 (55.5–60) | 0.066 |
| LAD (mm) | 42 (38–44) | 39.5 (38–43.5) | 0.060 |
| LAVI (mL/m2) | 25 (21–33.5) | 30 (24–35) | 0.35 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lanca Bastiancic, A.; Grgic Romic, I.; Hrabric Vlah, S.; Sotošek, V.; Klasan, M.; Baumgartner, P.; Mavric, M.; Brusich, S. The Detection of Early Changes in Inflammatory Response After Pulmonary Vein Isolation in Patients with Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation Can Predict Late Atrial Fibrillation Recurrence. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3874. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113874
Lanca Bastiancic A, Grgic Romic I, Hrabric Vlah S, Sotošek V, Klasan M, Baumgartner P, Mavric M, Brusich S. The Detection of Early Changes in Inflammatory Response After Pulmonary Vein Isolation in Patients with Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation Can Predict Late Atrial Fibrillation Recurrence. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(11):3874. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113874
Chicago/Turabian StyleLanca Bastiancic, Ana, Ivana Grgic Romic, Snjezana Hrabric Vlah, Vlatka Sotošek, Marina Klasan, Petra Baumgartner, Mate Mavric, and Sandro Brusich. 2025. "The Detection of Early Changes in Inflammatory Response After Pulmonary Vein Isolation in Patients with Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation Can Predict Late Atrial Fibrillation Recurrence" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 11: 3874. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113874
APA StyleLanca Bastiancic, A., Grgic Romic, I., Hrabric Vlah, S., Sotošek, V., Klasan, M., Baumgartner, P., Mavric, M., & Brusich, S. (2025). The Detection of Early Changes in Inflammatory Response After Pulmonary Vein Isolation in Patients with Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation Can Predict Late Atrial Fibrillation Recurrence. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(11), 3874. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113874






