The Presence of Emphysema in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Lung Cancer: Impact on Tumor Features, Acute Exacerbation, and Survival
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Definitions of CPFE, IPF, and COPD with Emphysema
2.3. Diagnosis of Lung Cancer
2.4. Definition of AE
2.5. Data Collection
3. Statistical Analysis
4. Results
4.1. Clinical Characteristics in Patients with Lung Cancer
4.2. Comparison Between CPFE and Isolated IPF in LC Patients
4.3. Comparison of EGFR Mutations Among Different Groups
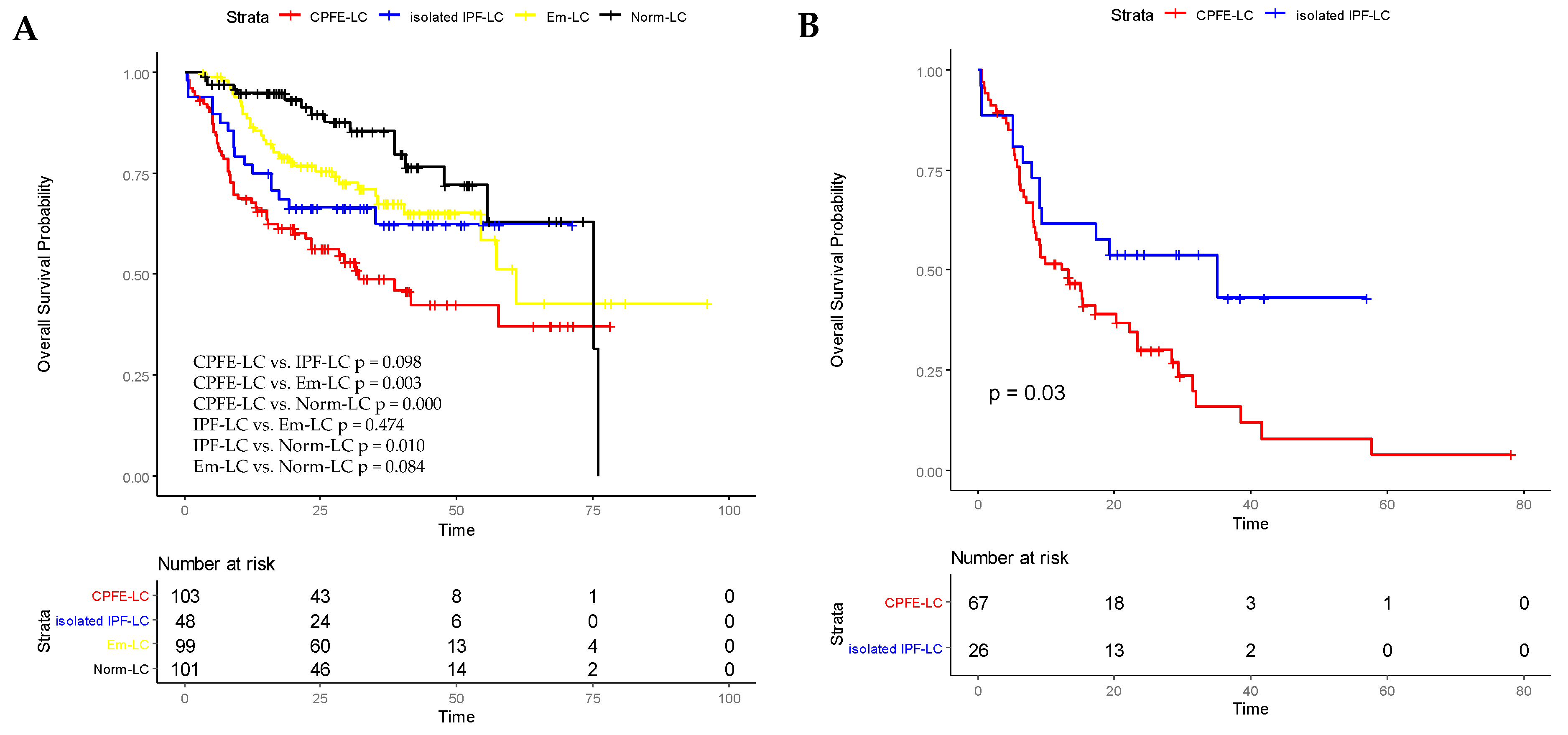
4.4. Overall Survival Analysis in All Patients and in IPF-LC Patients with AE
4.5. Prognostic Variables for Overall Survival in Patients with Lung Cancer
4.6. CPFE as a Predictor Associated with AE-Related Mortality in Patients with IPF and LC
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thai, A.A.; Solomon, B.J.; Sequist, L.V.; Gainor, J.F.; Heist, R.S. Lung Cancer. Lancet 2021, 398, 535–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christenson, S.A.; Smith, B.M.; Bafadhel, M.; Putcha, N. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Lancet 2022, 399, 2227–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghu, G.; Collard, H.R.; Egan, J.J.; Martinez, F.J.; Behr, J.; Brown, K.K.; Colby, T.V.; Cordier, J.-F.; Flaherty, K.R.; Lasky, J.A.; et al. An Official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Statement: Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Evidence-Based Guidelines for Diagnosis and Management. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 183, 788–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (an Update) and Progressive Pulmonary Fibrosis in Adults an Official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Clinical Practice Guideline-Web of Science Core Collection. Available online: https://webofscience.clarivate.cn/wos/woscc/full-record/WOS:000790561700001 (accessed on 4 February 2025).
- Cottin, V.; Nunes, H.; Brillet, P.-Y.; Delaval, P.; Devouassoux, G.; Tillie-Leblond, I.; Israel-Biet, D.; Court-Fortune, I.; Valeyre, D.; Cordier, J.-F.; et al. Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema: A Distinct Underrecognised Entity. Eur. Respir. J. 2005, 26, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottin, V.; Selman, M.; Inoue, Y.; Wong, A.W.; Corte, T.J.; Flaherty, K.R.; Han, M.K.; Jacob, J.; Johannson, K.A.; Kitaichi, M.; et al. Syndrome of Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema: An Official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Research Statement. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 206, e7–e41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottin, V. The Impact of Emphysema in Pulmonary Fibrosis. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2013, 22, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Liu, P.; Zhou, H.; Kong, H.; Xie, W. An Increased Risk of Lung Cancer in Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema Patients with Usual Interstitial Pneumonia Compared with Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Alone: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Ther. Adv. Respir. Dis. 2021, 15, 17534666211017050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biciusca, V.; Rosu, A.; Stan, S.I.; Cioboata, R.; Biciusca, T.; Balteanu, M.A.; Florescu, C.; Camen, G.C.; Cimpeanu, O.; Bumbea, A.M.; et al. A Practical Multidisciplinary Approach to Identifying Interstitial Lung Disease in Systemic Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases: A Clinician’s Narrative Review. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biciuşcă, V.; Popescu, I.A.S.; Traşcă, D.M.; Olteanu, M.; Stan, I.S.; Durand, P.; Camen, G.C.; Bălteanu, M.A.; Cazacu, I.M.; Demetrian, A.D.; et al. Diagnosis of Lung Cancer by Flexible Fiberoptic Bronchoscopy: A Descriptive Study. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2022, 63, 369–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usui, K.; Tanai, C.; Tanaka, Y.; Noda, H.; Ishihara, T. The Prevalence of Pulmonary Fibrosis Combined with Emphysema in Patients with Lung Cancer: Fibrosis and Emphysema in Lung Cancer. Respirology 2011, 16, 326–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumagai, S.; Marumo, S.; Yamanashi, K.; Tokuno, J.; Ueda, Y.; Shoji, T.; Nishimura, T.; Huang, C.-L.; Fukui, M. Prognostic Significance of Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema in Patients with Resected Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2014, 46, e113–e119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minegishi, Y.; Kokuho, N.; Miura, Y.; Matsumoto, M.; Miyanaga, A.; Noro, R.; Saito, Y.; Seike, M.; Kubota, K.; Azuma, A.; et al. Clinical Features, Anti-Cancer Treatments and Outcomes of Lung Cancer Patients with Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema. Lung Cancer 2014, 85, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, S.W.; Park, M.S.; Kim, Y.S.; Jang, J.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, C.-T.; Chung, J.-H.; Shim, H.S.; Lee, K.W.; Kim, S.-S.; et al. Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema and Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Impact on Survival and Acute Exacerbation. BMC Pulm. Med. 2019, 19, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuka, H.; Sugino, K.; Hata, Y.; Makino, T.; Koezuka, S.; Isobe, K.; Tochigi, N.; Shibuya, K.; Homma, S.; Iyoda, A. Clinical Features and Outcomes of Patients with Lung Cancer as Well as Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 5, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurashima, K.; Takayanagi, N.; Tsuchiya, N.; Kanauchi, T.; Ueda, M.; Hoshi, T.; Miyahara, Y.; Sugita, Y. The Effect of Emphysema on Lung Function and Survival in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema. Respirology 2010, 15, 843–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collard, H.R.; Ryerson, C.J.; Corte, T.J.; Jenkins, G.; Kondoh, Y.; Lederer, D.J.; Lee, J.S.; Maher, T.M.; Wells, A.U.; Antoniou, K.M.; et al. Acute Exacerbation of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. An International Working Group Report. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 194, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, M.; Chen, Y.; Ye, Q. Risk Factors for Acute Exacerbation of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Respir. J. 2018, 12, 1084–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, S.; Koike, T.; Hashimoto, T.; Ishikawa, H.; Okada, A.; Watanabe, T.; Tsuchida, M. Surgical Outcomes of Lung Cancer Patients with Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema and Those with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis without Emphysema. Ann. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2016, 22, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.Y.; Lee, Y.S.; Min, K.H.; Hur, G.Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Kang, K.H.; Shim, J.J. Impact and Prognosis of Lung Cancer in Patients with Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffus. Lung Dis. 2020, 37, e2020020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikuyama, Y.; Ushiki, A.; Kosaka, M.; Akahane, J.; Mukai, Y.; Araki, T.; Kitaguchi, Y.; Tateishi, K.; Urushihata, K.; Yasuo, M.; et al. Prognosis of Patients with Acute Exacerbation of Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema: A Retrospective Single-Centre Study. BMC Pulm. Med. 2020, 20, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghu, G.; Remy-Jardin, M.; Myers, J.L.; Richeldi, L.; Ryerson, C.J.; Lederer, D.J.; Behr, J.; Cottin, V.; Danoff, S.K.; Morell, F.; et al. Diagnosis of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. An Official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Clinical Practice Guideline. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 198, e44–e68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halpin, D.M.G.; Criner, G.J.; Papi, A.; Singh, D.; Anzueto, A.; Martinez, F.J.; Agusti, A.A.; Vogelmeier, C.F. Global Initiative for the Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention of Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease. The 2020 GOLD Science Committee Report on COVID-19 and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 203, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girard, N.; Marchand-Adam, S.; Naccache, J.-M.; Borie, R.; Urban, T.; Jouneau, S.; Marchand, E.; Ravel, A.-C.; Kiakouama, L.; Etienne-Mastroianni, B.; et al. Lung Cancer in Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema: A Series of 47 Western Patients. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2014, 9, 1162–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koo, H.J.; Do, K.-H.; Lee, J.B.; Alblushi, S.; Lee, S.M. Lung Cancer in Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.L.; Sima, C.S.; Chaft, J.; Paik, P.K.; Pao, W.; Kris, M.G.; Ladanyi, M.; Riely, G.J. Association of KRAS and EGFR Mutations with Survival in Patients with Advanced Lung Adenocarcinomas: Prognostic Value of KRAS in NSCLC. Cancer 2013, 119, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, P.; Zhang, C.; Ma, Z. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR): A Rising Star in the Era of Precision Medicine of Lung Cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 50209–50220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäki-Nevala, S.; Rönty, M.; Morel, M.; Gomez, M.; Dawson, Z.; Sarhadi, V.K.; Telaranta-Keerie, A.; Knuuttila, A.; Knuutila, S. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Mutations in 510 Finnish Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2014, 9, 886–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, G.; Thuler, L.C.S.; Ferreira, C.G. Epidemiological Changes in the Histological Subtypes of 35,018 Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Cases in Brazil. Lung Cancer 2016, 97, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanderLaan, P.A.; Rangachari, D.; Mockus, S.M.; Spotlow, V.; Reddi, H.V.; Malcolm, J.; Huberman, M.S.; Joseph, L.J.; Kobayashi, S.S.; Costa, D.B. Mutations in TP53, PIK3CA, PTEN and Other Genes in EGFR Mutated Lung Cancers: Correlation with Clinical Outcomes. Lung Cancer 2017, 106, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, G.; Tan, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Duan, Q.; Sun, T.; et al. Molecular and Clinicopathological Characteristics of Lung Cancer Concomitant Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2022, 17, 1601–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujimoto, D.; Tomii, K.; Otoshi, T.; Kawamura, T.; Tamai, K.; Takeshita, J.; Tanaka, K.; Matsumoto, T.; Monden, K.; Nagata, K.; et al. Preexisting Interstitial Lung Disease Is Inversely Correlated to Tumor Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Mutation in Patients with Lung Adenocarcinoma. Lung Cancer 2013, 80, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Xie, S.; Liu, H.; Liu, P.; Xiong, Y.; Da, J.; Que, C.; Dai, H.; Wang, C. Lung Cancer in Patients with Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema Revisited with the 2015 World Health Organization Classification of Lung Tumors. Clin. Respir. J. 2018, 12, 652–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, J.A.; Kim, D.; Chun, S.-M.; Bae, S.; Song, J.S.; Kim, M.Y.; Koo, H.J.; Song, J.W.; Kim, W.S.; Lee, J.C.; et al. Genomic Profiles of Lung Cancer Associated with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Genomic Profiles of IPF-LC. J. Pathol. 2018, 244, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballester, B.; Milara, J.; Cortijo, J. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Lung Cancer: Mechanisms and Molecular Targets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugino, K.; Ishida, F.; Kikuchi, N.; Hirota, N.; Sano, G.; Sato, K.; Isobe, K.; Sakamoto, S.; Takai, Y.; Homma, S. Comparison of Clinical Characteristics and Prognostic Factors of Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema versus Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Alone: Clinical Characteristics of CPFE. Respirology 2014, 19, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuya, K.; Sakamoto, S.; Shimizu, H.; Sekiya, M.; Kinoshita, A.; Isshiki, T.; Sugino, K.; Matsumoto, K.; Homma, S. Pirfenidone for Acute Exacerbation of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Retrospective Study. Respir. Med. 2017, 126, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottin, V.; Azuma, A.; Raghu, G.; Stansen, W.; Stowasser, S.; Schlenker-Herceg, R.; Kolb, M. Therapeutic Effects of Nintedanib Are Not Influenced by Emphysema in the INPULSIS Trials. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 53, 1801655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azuma, A.; Taniguchi, H.; Inoue, Y.; Kondoh, Y.; Ogura, T.; Homma, S.; Fujimoto, T.; Sakamoto, W.; Sugiyama, Y.; Nukiwa, T. Nintedanib in Japanese Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Subgroup Analysis of the INPULSIS® Randomized Trials: The INPULSIS® Trials: Japanese Patients. Respirology 2017, 22, 750–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kai, Y.; Matsuda, M.; Suzuki, K.; Kasamatsu, T.; Kajita, A.; Uno, K.; Muro, S. Tocilizumab and Baricitinib for Recovery From Acute Exacerbation of Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema Secondary to COVID-19 Infection: A Case Report. Cureus 2022, 14, e23411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, A.U.; Desai, S.R.; Rubens, M.B.; Goh, N.S.L.; Cramer, D.; Nicholson, A.G.; Colby, T.V.; du Bois, R.M.; Hansell, D.M. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Composite Physiologic Index Derived from Disease Extent Observed by Computed Tomography. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2003, 167, 962–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çiftci, F.; Gülpınar, B.; Atasoy, Ç.; Kayacan, O.; Saryal, S. Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema: How Does Cohabitation Affect Respiratory Functions? Adv. Med. Sci. 2019, 64, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, H.; Xu, F.; Gao, Z.; Wang, X.; Tao, G.; Chen, Y.; Rong, W.; et al. Clinical, Radiologic, and Physiologic Features of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF) with and without Emphysema. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2022, 16, 813–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, F.; Kitaguchi, Y.; Shiina, T.; Asaka, S.; Miura, K.; Yasuo, M.; Wada, Y.; Yoshizawa, A.; Hanaoka, M. The Preoperative Composite Physiologic Index May Predict Mortality in Lung Cancer Patients with Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema. Respiration 2017, 94, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| IPF-LC Group n = 151 | Em-LC Group n = 99 | Norm-LC Group n = 101 | IPF-LC vs. Em-LC p Value | IPF-LC vs. Norm-LC p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patient characteristics, number (%), or median (Q1–Q3) | |||||
| Age, years | 68 (64–73) | 66 (58–73) | 60 (53–67) | 0.167 | 0.000 |
| Sex (men) | 145/151 (96.0%) | 92/99 (92.9%) | 75/101 (74.3%) | 0.582 | 0.000 |
| Ex- or current smokers | 128/151 (84.8%) | 89/99 (89.9%) | 59/101 (58.4%) | 0.861 | 0.000 |
| Pack-years | 37.5 (19.5–50.0) | 40.0 (20.0–50.0) | 10.3 (5.0–30.0) | 0.742 | 0.000 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 22.9 (20.6–24.9) | 22.3 (20.4–24.2) | 22.2 (20.4–24.1) | 0.563 | 0.219 |
| Dust exposure | 4/151 (2.6%) | 1/99 (1.0%) | 0/101 (0.0%) | 0.427 | 0.233 |
| Previous pulmonary tuberculosis | 12/151 (7.9%) | 2/99 (2.0%) | 3/101 (3.0%) | 0.096 | 0.175 |
| Laboratory examinations and pulmonary function parameters, median (Q1–Q3) | |||||
| WBC, ×109/L | 7.99 (6.42–10.38) | 7.15 (5.49–9.51) | 6.71 (5.84–8.89) | 0.098 | 0.000 |
| ANC, ×109/L | 5.63 (4.12–8.14) | 4.93 (3.34–6.98) | 4.67 (3.74–6.68) | 0.284 | 0.100 |
| ALC, ×109/L | 1.44 (1.08–1.90) | 1.27 (0.96–1.97) | 1.39 (1.04–1.79) | 0.472 | 0.641 |
| NLR | 3.74 (2.49–6.47) | 3.31 (2.12–5.57) | 3.66 (2.46–5.14) | 0.157 | 0.540 |
| PLR | 133.2 (92.6–200.7) | 137.0 (83.3–213.7) | 139.8 (94.7–177.4) | 0.732 | 0.986 |
| CRP, mg/L | 52.7 (8.6–102.7) | 9.37 (3.95–37.40) | 18.9 (8.05–66.85) | 0.012 | 0.024 |
| IL-6, μg/L | 32.82 (11.2–97.55) | 10.72 (5.65–35.15) | 13.69 (5.27–29.8) | 0.020 | 0.039 |
| Fibrinogen, g/L | 4.94 (3.66–5.67) | 4.56 (3.15–5.18) | 4.13 (3.01–5.07) | 0.134 | 0.019 |
| C3, g/L | 0.97 (0.85–1.09) | 0.90 (0.80–0.98) | 1.07 (0.94–1.21) | 0.561 | 0.243 |
| CPI | 44.94 (30.88–46.97) | 15.57 (10.52–19.13) | 10.56 (7.38–15.61) | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| FVC, %pred | 83.4 (67.5–97.7) | 101.6 (80.1–120.9) | 97.5 (89.4–104.2) | 0.045 | 0.065 |
| FEV1, %pred | 90.5 (79.1–102.1) | 68.6 (43.9–86.4) | 99.5 (86.1–109.3) | 0.000 | 0.490 |
| FEV1/FVC, % | 76.9 (71.4–82.6) | 60.1 (48.3–68.4) | 83.4 (75.6–87.7) | 0.041 | 0.238 |
| DLCO, %pred | 56.8 (44.1–67.3) | 77.5 (58.4–89.6) | 102.0 (84.6–116.4) | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| Tumor characteristics, number (%) | |||||
| Localization | 0.001 | 0.126 | |||
| Upper lobe | 22/50 (44.0%) | 72/108 (66.6%) | 53/102 (52.0%) | ||
| Lower lobe | 28/50 (56.0%) | 36/108 (33.3%) | 49/102 (48.0%) | ||
| Pathological type | 0.504 | 0.063 | |||
| Adenocarcinoma | 63/151 (41.7%) | 40/99 (40.4%) | 59/101 (58.4%) | 0.041 | |
| Squamous carcinoma | 56/151 (37.1%) | 39/99 (39.4%) | 23/101 (22.8%) | 0.079 | |
| Others | 32/151 (21.2%) | 20/99 (20.2%) | 19/101 (18.8%) | 0.586 | |
| Staging | 0.139 | 0.049 | |||
| I–II | 27/151 (17.9%) | 25/99 (25.3%) | 38/101 (37.6%) | ||
| III–IV | 124/151 (82.1%) | 74/99 (74.7%) | 63/101 (62.4%) | ||
| CPFE-LC Group N = 103 | Isolated IPF-LC Group N = 48 | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient characteristics, number (%), or median (Q1–Q3) | |||
| Age, years | 68 (63–73) | 69 (64–74) | 0.261 |
| Sex (men) | 103/103 (100.0%) | 42/48 (87.5%) | 0.001 |
| Ex- or current smokers | 93/103 (90.3%) | 37/48 (77.1%) | 0.043 |
| Pack-years | 40 (21.25–50) | 27.5 (4.2–50) | 0.026 |
| Laboratory examinations and pulmonary function parameters, median (Q1–Q3) | |||
| WBC, ×109/L | 7.77 (6.43–10.28) | 8.85 (6.41–10.85) | 0.391 |
| ANC, ×109/L | 5.49 (4.08–7.67) | 6.23 (4.28–8.32) | 0.230 |
| ALC, ×109/L | 1.45 (1.05–1.91) | 1.42 (1.08–1.90) | 0.691 |
| NLR | 3.62 (2.41–6.37) | 3.99 (2.51–7.03) | 0.358 |
| PLR | 129.6 (89.5–206.9) | 151.6 (96.6–192.3) | 0.324 |
| CRP, mg/L | 30.2 (9.36–103.50) | 12.9 (5.31–78.3) | 0.031 |
| IL-6, μg/L | 24.95 (10.71–91.25) | 32.13 (9.88–59.77) | 0.104 |
| Fibrinogen, g/L | 5.08 (4.02–5.83) | 4.38 (3.53–5.17) | 0.009 |
| C3, g/L | 1.02 (0.85–1.10) | 0.93 (0.86–1.08) | 0.847 |
| CPI | 46.68 (26.88–56.64) | 45.24 (21.35–56.67) | 0.112 |
| VC, %pred | 90.0 (79.2–97.7) | 85.2 (67.9–102.3) | 0.201 |
| FVC, %pred | 83.4 (71.5–100.6) | 92.6 (60.7–95.6) | 0.943 |
| FEV1, %pred | 89.5 (78.6–103.4) | 92.6 (80.2–100.5) | 0.716 |
| FEV1/FVC, % | 76.3 (68.8–80.7) | 80.7 (76.6–85.43) | 0.004 |
| DLCO, %pred | 57.4 (47.1–68.4) | 50.6 (39.9–63.6) | 0.085 |
| Tumor characteristics, number (%) | |||
| localization | 0.315 | ||
| Upper lobe | 42/103 (40.8%) | 22/48 (45.8%) | |
| Lower lobe | 61/103 (59.2%) | 26/48 (54.2%) | |
| Cancer in fibrosis areas | 59/103 (57.3%) | 33/48 (68.8%) | 0.214 |
| Pathological type | 0.451 | ||
| Adenocarcinoma | 43/103 (41.7%) | 20/48 (41.7%) | |
| Squamous carcinoma | 37/103 (35.9%) | 19/48 (39.6%) | |
| Others | 23/103 (22.4) | 9/48 (18.8%) | |
| Staging | 0.170 | ||
| I–II | 15/103 (14.6%) | 12/48 (25.0%) | |
| III–IV | 88/103 (85.4%) | 36/48 (75.0%) | |
| CPFE-LC Group N = 103 | Isolated IPF-LC Group N = 48 | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| AE | 67/103 (65.0%) | 26/48 (54.2%) | 0.136 |
| Treatment-induced AE | 51/103 (49.5%) | 14/48 (29.2%) | 0.038 |
| Natural course associated AE | 16/103 (15.5%) | 12/48 (25.0%) | 0.589 |
| Mortality | 50/103 (48.5%) | 17/48 (35.4%) | 0.095 |
| Main cause of death | |||
| Lung cancer progression | 24/50 (48.0%) | 10/17 (58.8%) | 0.736 |
| Acute exacerbation | 14/50 (28.0%) | 2/17 (11.8%) | 0.045 |
| Severe pneumonia | 10/50 (20.0%) | 4/17 (23.5%) | 0.684 |
| Asphyxia | 1/50 (2.0%) | 0/17 (0.0%) | 0.848 |
| Acute pulmonary embolism | 0/50 (0.0%) | 1/17 (5.9%) | 0.073 |
| Acute myocardial infarction | 1/50 (2.0%) | 0/17 (0.0%) | 0.848 |
| IPF-LC Group | Em-LC Group | Norm-LC Group | IPF-LC vs. Em-LC p Value | IPF-LC vs. Norm-LC p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| In adenocarcinoma patients | 8/49 (16.3%) | 5/30 (16.7%) | 27/53 (50.9%) | 0.899 | 0.000 |
| In ex- or current smokers | 3/34 (8.8%) | 3/27 (11.1%) | 11/27 (40.7%) | 0.316 | 0.003 |
| In never smokers | 5/15 (33.3%) | 2/3 (66.7%) | 16/26 (61.5%) | 0.079 | 0.092 |
| Variable | Univariate Analyses | Multivariate Analyses | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | p Value | HR (95% CI) | p Value | |
| Sex: women | Re | |||
| men | 2.747 (1.276–5.915) | 0.010 | ||
| Age <65 years | Re | |||
| ≥65 years | 1.023 (1.002–1.044) | 0.030 | ||
| Smoking history: Never | Re | |||
| Ex- or current smokers | 2.481 (1.416–4.347) | 0.002 | ||
| Pack-years < 20 | Re | |||
| ≥20 | 2.416 (1.191–4.903) | 0.015 | ||
| WBC, ×109/L | 0.992 (0.987–1.007) | 0.181 | ||
| CRP, mg/L | 1.004 (0.999–1.009) | 0.057 | ||
| Fibrinogen, g/L | 1.187 (1.047–1.345) | 0.025 | ||
| CPI < 40 | Re | |||
| CPI ≥ 40 | 1.978 (1.049–6.718) | 0.034 | 2.087 (1.715–6.089) | 0.012 |
| Staging I–II | Re | |||
| III–IV | 3.121 (1.704–5.715) | 0.039 | ||
| EGFR mutation | Re | |||
| EGFR wild-type | 2.247 (1.175–4.297) | 0.014 | ||
| Normal Lung | Re | |||
| COPD | 2.196 (1.120–4.304) | 0.038 | 2.281 (1.139–4.569) | 0.040 |
| Isolated IPF | 4.270 (2.455–7.426) | 0.022 | 5.703 (2.516–12.925) | 0.000 |
| CPFE | 4.320 (2.007–9.299) | 0.000 | 6.275 (3.379–11.652) | 0.000 |
| Variable | Univariate Analyses | Multivariate Analyses | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | p Value | OR (95% CI) | p Value | |
| Sex: women | Re | |||
| men | 1.888 (0.182–2.164) | 0.151 | ||
| Smoking history: never | Re | |||
| Ex- or current smokers | 1.164 (0.991–1.827) | 0.854 | ||
| Pack-years < 20 | Re | |||
| Pack-years ≥ 20 | 2.906 (1.562–5.406) | 0.573 | ||
| Fibrinogen, g/L | 2.481 (1.416–3.347) | 0.044 | ||
| CRP, mg/L | 1.004 (0.999–1.009) | 0.102 | ||
| Non-CPFE | Re | |||
| CPFE | 2.996 (1.120–4.304) | 0.030 | 3.494 (2.014–6.063) | 0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, X.; Zeng, W.; Lv, X.; Liang, B.; Ou, X. The Presence of Emphysema in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Lung Cancer: Impact on Tumor Features, Acute Exacerbation, and Survival. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3862. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113862
Feng X, Zeng W, Lv X, Liang B, Ou X. The Presence of Emphysema in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Lung Cancer: Impact on Tumor Features, Acute Exacerbation, and Survival. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(11):3862. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113862
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Xiaoyi, Wenjing Zeng, Xiafei Lv, Binmiao Liang, and Xuemei Ou. 2025. "The Presence of Emphysema in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Lung Cancer: Impact on Tumor Features, Acute Exacerbation, and Survival" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 11: 3862. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113862
APA StyleFeng, X., Zeng, W., Lv, X., Liang, B., & Ou, X. (2025). The Presence of Emphysema in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Lung Cancer: Impact on Tumor Features, Acute Exacerbation, and Survival. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(11), 3862. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113862






