Indeterminate Biliary Strictures: A Retrospective Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Statistical Analysis
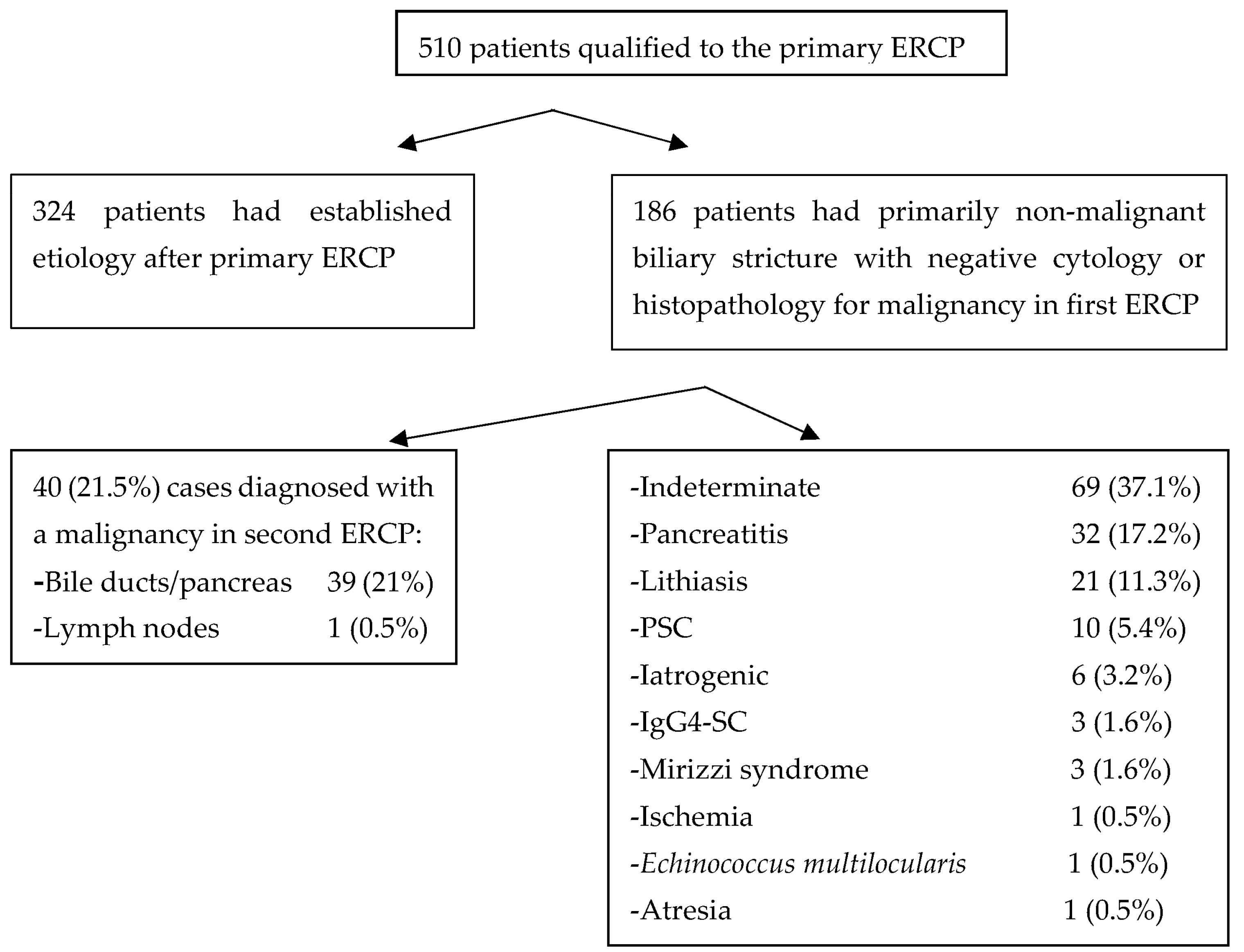
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kapoor, B.S.; Mauri, G.; Lorenz, J.M. Management of Biliary Strictures: State-of-the-Art Review. Radiology 2018, 289, 590–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, M.X.; Jayasekeran, V.; Chong, A.K. Benign biliary strictures: Prevalence, impact, and management strategies. Clin. Exp. Gastroenterol. 2019, 12, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumonceau, J.M.; Delhaye, M.; Charette, N.; Farina, A. Challenging biliary strictures: Pathophysiological features, differential diagnosis, diagnostic algorithms, and new clinically relevant biomarkers—Part 1. Therap. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2020, 13, 1756284820927292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handy, B. The Clinical Utility of Tumor Markers. Lab. Med. 2009, 40, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.S.; Huang, J.X.; Yu, H. Elevated serum level of carbohydrate antigen 19-9 in benign biliary stricture diseases can reduce its value as a tumor marker. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2014, 7, 744–750. [Google Scholar]
- Navaneethan, U.; Njei, B.; Lourdusamy, V.; Konjeti, R.; Vargo, J.J.; Parsi, M.A. Comparative effectiveness of biliary brush cytology and intraductal biopsy for detection of malignant biliary strictures: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2015, 81, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draganov, P.V.; Chauhan, S.; Wagh, M.S.; Gupte, A.R.; Lin, T.; Hou, W.; Forsmark, C.E. Diagnostic accuracy of conventional and cholangioscopy-guided sampling of indeterminate biliary lesions at the time of ERCP: A prospective, long-term follow-up study. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2012, 75, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weilert, F.; Bhat, Y.M.; Binmoeller, K.F.; Kane, S.; Jaffee, I.M.; Shaw, R.E.; Cameron, R.; Hashimoto, Y.; Shah, J.N. EUS-FNA is superior to ERCP-based tissue sampling in suspected malignant biliary obstruction: Results of a prospective, single-blind, comparative study. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2014, 80, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimbach, J.K.; Sanchez, W.; Rosen, C.B.; Gores, G.J. Trans-peritoneal fine needle aspiration biopsy of hilar cholangiocarcinoma is associated with disease dissemination. HPB 2011, 13, 356–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nur, A.M.; Salim, M.; Boerner, S.; Li, S.; Law, C.C.Y.; Edwards, L.; Ryan, K.; James, P.D. High Diagnostic Yield of Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography Brush Cytology for Indeterminate Strictures. J. Can. Assoc. Gastroenterol. 2022, 5, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alali, A.; Moris, M.; Martel, M.; Streutker, C.; Cirocco, M.; Mosko, J.; Kortan, P.; Barkun, A.; May, G.R. Predictors of Malignancy in Patients With Indeterminate Biliary Strictures and Atypical Biliary Cytology: Results From Retrospective Cohort Study. J. Can. Assoc. Gastroenterol. 2021, 4, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadlapati, S.; Mulki, R.; Sanchez-Luna, S.A.; Ahmed, A.M.; Kyanam Kabir Baig, K.R.; Peter, S. Clinical approach to indeterminate biliary strictures: Clinical presentation, diagnosis, and workup. World J. Gastroenterol. 2023, 29, 5198–5210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitman, M.B.; Centeno, B.A.; Ali, S.Z.; Genevay, M.; Stelow, E.; Mino-Kenudson, M.; Fernandez-del Castillo, C.; Max Schmidt, C.; Brugge, W.; Layfield, L.; et al. Standardized terminology and nomenclature for pancreatobiliary cytology: The Papanicolaou Society of Cytopathology guidelines. Diagn. Cytopathol. 2014, 42, 338–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumonceau, J.M.; Tringali, A.; Papanikolaou, I.S.; Blero, D.; Mangiavillano, B.; Schmidt, A.; Vanbiervliet, G.; Costamagna, G.; Deviere, J.; Garcia-Cano, J.; et al. Endoscopic biliary stenting: Indications, choice of stents, and results: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Clinical Guideline—Updated October 2017. Endoscopy 2018, 50, 910–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varadarajulu, S.; Bang, J.Y.; Hasan, M.K.; Navaneethan, U.; Hawes, R.; Hebert-Magee, S. Improving the diagnostic yield of single-operator cholangioscopy-guided biopsy of indeterminate biliary strictures: ROSE to the rescue? (with video). Gastrointest. Endosc. 2016, 84, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethi, R.; Singh, K.; Warner, B.; Mahadeva, U.; Wilkinson, M. The impact of brush cytology from endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) on patient management at a UK teaching hospital. Frontline Gastroenterol. 2016, 7, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ince, A.T.; Yildiz, K.; Baysal, B.; Danalioglu, A.; Kocaman, O.; Tozlu, M.; Gangarapu, V.; Sarbay Kemik, A.; Uysal, O.; Senturk, H. Roles of serum and biliary CEA, CA19-9, VEGFR3, and TAC in differentiating between malignant and benign biliary obstructions. Turk. J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 25, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lankisch, T.O.; Metzger, J.; Negm, A.A.; Vosskuhl, K.; Schiffer, E.; Siwy, J.; Weismuller, T.J.; Schneider, A.S.; Thedieck, K.; Baumeister, R.; et al. Bile proteomic profiles differentiate cholangiocarcinoma from primary sclerosing cholangitis and choledocholithiasis. Hepatology 2011, 53, 875–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farid, S.G.; Craven, R.A.; Peng, J.; Bonney, G.K.; Perkins, D.N.; Selby, P.J.; Rajendra Prasad, K.; Banks, R.E. Shotgun proteomics of human bile in hilar cholangiocarcinoma. Proteomics 2011, 11, 2134–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navaneethan, U.; Parsi, M.A.; Gutierrez, N.G.; Bhatt, A.; Venkatesh, P.G.; Lourdusamy, D.; Grove, D.; Hammel, J.P.; Jang, S.; Sanaka, M.R.; et al. Volatile organic compounds in bile can diagnose malignant biliary strictures in the setting of pancreatic cancer: A preliminary observation. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2014, 80, 1038–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navaneethan, U.; Parsi, M.A.; Lourdusamy, V.; Bhatt, A.; Gutierrez, N.G.; Grove, D.; Sanaka, M.R.; Hammel, J.P.; Stevens, T.; Vargo, J.J.; et al. Volatile organic compounds in bile for early diagnosis of cholangiocarcinoma in patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis: A pilot study. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2015, 81, 943–949.e941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourdusamy, V.; Tharian, B.; Navaneethan, U. Biomarkers in bile-complementing advanced endoscopic imaging in the diagnosis of indeterminate biliary strictures. World J. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2015, 7, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Feature | Result |
|---|---|
| Age, y, mean ± SD | 65.1 ± 14.8 |
| Sex n (%): | |
- Males | 106 (57) |
- Females | 80 (43) |
| Height, cm, mean ± SD | 169.8 ± 10.1 |
| Weight, kg, mean ± SD | 70.7 ± 13.7 |
| Stricture’s localization, n (%): | |
- liver hilum | 55 (29.6) |
- common bile duct | 22 (11.8) |
- intrapancreatic | 108 (58.1) |
| Cytology/histopathology, n (%): | |
- Fibrosis | 47 (22.7) |
- Atypia | 40 (19) |
- Dysplasia | 25 (12) |
- Metaplasia | 6 (3) |
- Inflammation: | 86 (41.5) |
○ Neutrocytes | 28 (13.5) |
○ Plasmocytes | 9 (4.3) |
○ Lymphocytes | 9 (4.3) |
○ Eosinophils | 1 (0.5) |
- Malignancy (in subsequent ERCP) | 37 (18) |
| Important clinical data and ERCP findings, n (%): | |
- Concomitant cholelithiasis | 130 (63) |
- Concomitant cholangitis | 95 (46) |
- Cholecystectomy | 65 (31) |
| Diagnosed biliary stricture etiology, n (%): | |
- Indeterminate | 69 (37.1) |
- Bile ducts/pancreatic malignancy * | 39 (21) |
- Pancreatitis (chronic, or complications of acute) | 32 (17.2) |
- Lithiasis | 21 (11.3) |
- PSC | 10 (5.4) |
- Iatrogenic | 6 (3.2) |
- IgG4-SC | 3 (1.5) |
- Mirizzi syndrome | 3 (1.5) |
- Lymph node mass effect | 1 (0.5) |
- Ischemia | 1 (0.5) |
- Echinococcus multilocularis | 1 (0.5) |
- Atresia | 1 (0.5) |
| Liver Hilum N = 55 | CBD N = 22 | Intrapancreatic N = 108 | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, y, mean ± SD | 61 ± 17 | 64.8 ± 15.8 | 67 ± 13 | <0.17 |
| Sex: Males/Females | 32/23 | 14/8 | 59/49 | <0.72 |
| Height, cm, mean ± SD | 171 ± 10 | 169 ± 11 | 169 ± 14 | <0.43 |
| Weight, kg, mean ± SD | 73 ± 13 | 69.2 ± 12.5 | 69.5 ± 10 | <0.45 |
| Cytology/histopathology: | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | |
- Fibrosis | 17 (30) | 4 (18) | 25 (23) | <0.49 |
- Atypia | 23 (40) | 2 (9) | 15 (14) | <0.0001 |
- Dysplasia | 9 (16) | 2 (9) | 14 (13) | <0.72 |
- Metaplasia | 2 (3.5) | 3 (13) | 3 (2.8) | <0.90 |
- Inflammation: | 24 (42) | 5 (23) | 55 (51) | <0.05 |
○ Neutrocytes | 12 (21) | 3 (13) | 13 (12) | <0.30 |
○ Plasmocytes | 4 (7) | 0 | 3 (2.8) | <0.29 |
○ Lymphocytes | 4 (7) | 0 | 5 (4.6) | <0.42 |
○ Eosinophils | 1 (1.8) | 0 | 0 | <0.32 |
| Malignancy (diagnosed in second ERCP) | 19 (33) | 3 (13) | 15 (14) | <0.01 |
| Important clinical data and ERCP findings: | ||||
- Concomitant cholelithiasis | 37 (66) | 8 (36) | 69 (64) | <0.02 |
- Concomitant cholangitis | 40 (70) | 10 (45.5) | 37 (34.5) | <0.001 |
- Cholecystectomy | 19 (33) | 8 (36) | 35 (32) | <0.94 |
| Diagnosed biliary stricture etiology: | ||||
- Indeterminate | 17 (30) | 9 (41) | 43 (40) | <0.41 |
- Lithiasis | 0 | 1 (4.5) | 20 (12) | <0.001 |
- Bile ducts/pancreatic malignancy * | 17 (30) | 5 (23) | 17 (16) | <0.10 |
- Pancreatitis (chronic or complications of acute) | 4 (7) | 4 (18) | 23 (21) | <0.06 |
- PSC | 8 (14) | 1 (4.5) | 1 (1) | <0.002 |
- IgG4-SC | 2 (4) | 1 (4.5) | 0 | <0.12 |
- Lymph node mass effect * | 1 (2) | 0 | 0 | <0.32 |
- Ischemia | 1 (2) | 0 | 0 | <0.32 |
- Mirizzi syndrome | 2 (4) | 0 | 1 | <0.37 |
- Echinococcus multilocularis | 1 (2) | 0 | 0 | <0.32 |
- Iatrogenic | 3 (6) | 1 (4.5) | 2 (2) | <0.70 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nehring, P.; Ciszewska, M.; Przybyłkowski, A. Indeterminate Biliary Strictures: A Retrospective Study. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3797. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113797
Nehring P, Ciszewska M, Przybyłkowski A. Indeterminate Biliary Strictures: A Retrospective Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(11):3797. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113797
Chicago/Turabian StyleNehring, Piotr, Magdalena Ciszewska, and Adam Przybyłkowski. 2025. "Indeterminate Biliary Strictures: A Retrospective Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 11: 3797. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113797
APA StyleNehring, P., Ciszewska, M., & Przybyłkowski, A. (2025). Indeterminate Biliary Strictures: A Retrospective Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(11), 3797. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113797





