Clinical Application of Patient-Specific Bolus Based on Molding and Casting Method in Radiotherapy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Treatments
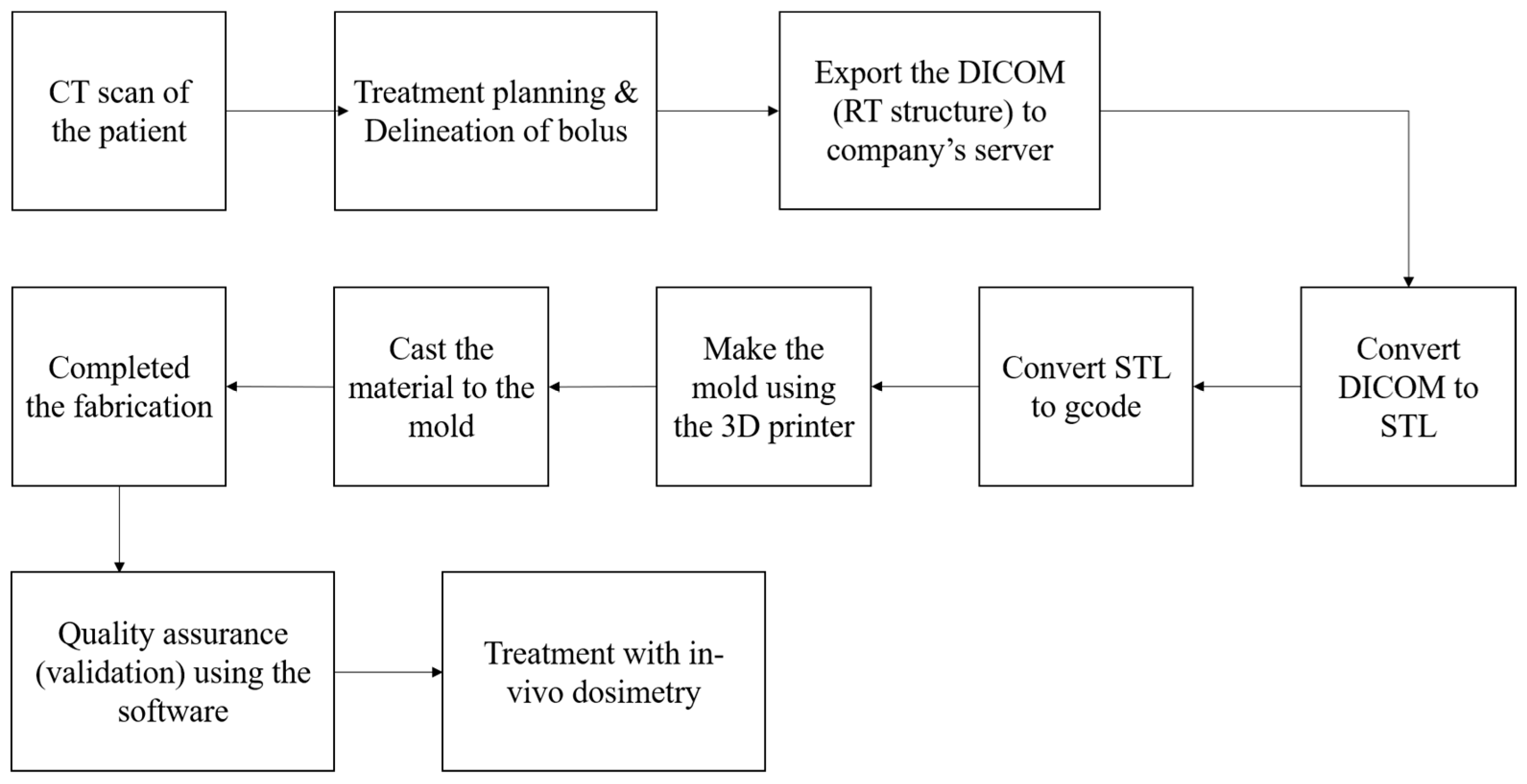
2.2. Clinical Workflow for the Fabrication of Patient-Specific Bolus
2.3. Physical & Biological Evaluation
2.4. Evaluation of Geometric Accuracy
2.5. Dosimetric Evaluation
3. Results
3.1. Physical & Biological Evaluation
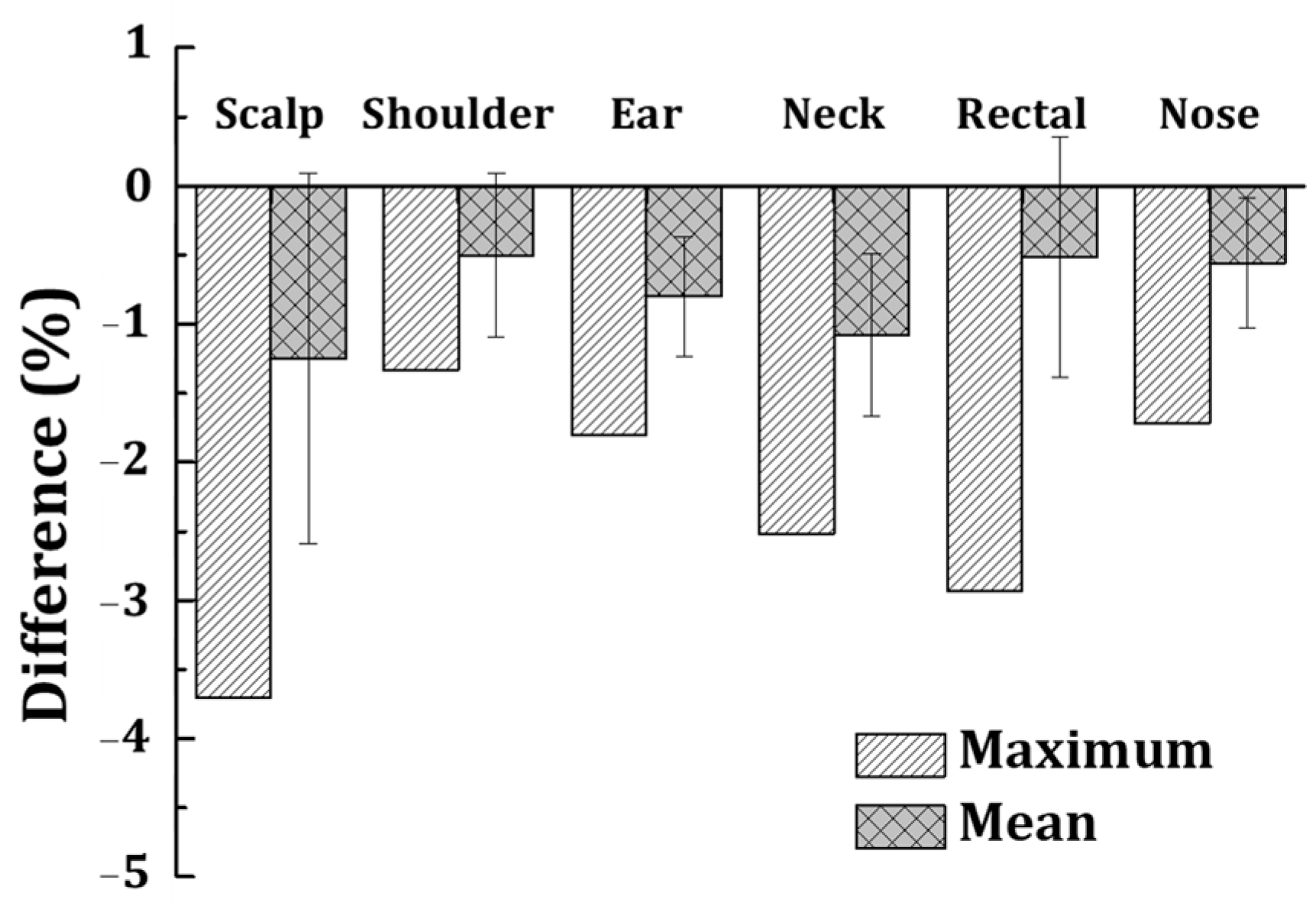
3.2. Evaluation of Geometric Accuracy
3.3. Dosimetric Evaluation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MV | megavoltage |
| M&C | mold and casting |
| IRB | Institutional Review Board |
| TPS | treatment planning system |
| ICP | iterative closest point |
References
- Abdel-Rahman, W.; Seuntjens, J.P.; Verhaegen, F.; Deblois, F.; Podgorsak, E.B. Validation of Monte Carlo calculated surface doses for megavoltage photon beams. Med. Phys. 2005, 32, 286–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biggs, P.; Russell, M. An investigation into the presence of secondary electrons in megavoltage photon beams (radiotherapy application). Phys. Med. Biol. 1983, 28, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kesen, N.; Koksal, C. Investigation of surface and buildup region doses for 6 MV high energy photon beams in the presence of a thermoplastic mask. Int. J. Radiat. Res. 2020, 18, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaanders, J.H.; Fleming, T.J.; Ang, K.K.; Maor, M.H.; Peters, L.J. Devices valuable in head and neck radiotherapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1992, 23, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geara, F.; Le Bourgeois, J.P.; Piedbois, P.; Pavlovitch, J.M.; Mazeron, J.J. Radiotherapy in the management of cutaneous epidemic Kaposi’s sarcoma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1991, 21, 1517–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyer, R.F.; McElroy, W.; O’Brien, J.; Chamberlain, C. A surface bolus material for high-energy photon and electron therapy. Radiology 1983, 146, 531–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endarko, E.; Aisyah, S.; Carina, C.C.C.; Nazara, T.; Sekartaji, G.; Nainggolan, A. Evaluation of dosimetric properties of handmade bolus for megavoltage electron and photon radiation therapy. J. Biomed. Phys. Eng. 2021, 11, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Tian, J.; Lei, P.; Meng, C.; Fu, J.; Cao, L.; Cheng, J.; Zhou, F.; Zhang, H.; Song, H. The impact of bolus on clinical outcomes for post-mastectomy breast cancer patients treated with IMRT: Data from China. Radiat. Oncol. 2024, 19, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gül, O.V. Investigation of Effect of Air Gap between Surface and Bolus on Dose Distribution for 6 MV Photon Beam. Celal Bayar Univ. J. Sci. 2023, 19, 389–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butson, M.J.; Cheung, T.; Yu, P.; Metcalfe, P. Effects on skin dose from unwanted air gaps under bolus in photon beam radiotherapy. Radiat. Meas. 2000, 32, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphries, S.M.; Boyd, K.; Cornish, P.; Newman, F.D. Comparison of Super Stuff and paraffin wax bolus in radiation therapy of irregular surfaces. Med. Dosim. 1996, 21, 155–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCallum, S.; Maresse, S.; Fearns, P. Evaluating 3D-printed bolus compared to conventional bolus types used in external beam radiation therapy. Curr. Med. Imaging Rev. 2021, 17, 820–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Lewin, W.; Cullen, A.; Thommen, D.; Hill, R. Evaluation of 3D-printed bolus for radiotherapy using megavoltage X-ray beams. Radiol. Phys. Technol. 2023, 16, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Merchan, J.; Español-Castro, C.; Martinez-Ovalle, S.; Vega-Carrillo, H. Bolus 3D printing for radiotherapy with conventional PLA, ABS and TPU filaments: Theoretical-experimental study. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2023, 199, 110908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Ahn, S.H.; Choi, S.H.; Ahn, W.S.; Jung, I.-H. Clinical application of a customized 3D-printed bolus in radiation therapy for distal extremities. Life 2023, 13, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyer, B.A.; Campos, D.D.; Hernandez, D.D.; Wright, C.L.; Perks, J.R.; Lucero, S.A.; Bewley, A.F.; Yamamoto, T.; Zhu, X.; Rao, S.S. Characterization and clinical validation of patient-specific three-dimensional printed tissue-equivalent bolus for radiotherapy of head and neck malignancies involving skin. Phys. Med. 2020, 77, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-W.; Shin, H.-J.; Kay, C.S.; Son, S.H. A customized bolus produced using a 3-dimensional printer for radiotherapy. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malone, C.; Gill, E.; Lott, T.; Rogerson, C.; Keogh, S.; Mousli, M.; Carroll, D.; Kelly, C.; Gaffney, J.; McClean, B. Evaluation of the quality of fit of flexible bolus material created using 3D printing technology. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2022, 23, e13490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amor-Coarasa, A.; Goddard, L.; DuPré, P.; Wake, N. 3D printing in nuclear medicine and radiation therapy. In 3D Printing for the Radiologist; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 143–156. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.M.; Son, J.; An, H.J.; Kim, J.H.; Wu, H.-G.; Kim, J.-I. Bio-compatible patient-specific elastic bolus for clinical implementation. Phys. Med. Biol. 2019, 64, 105006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miron, V.M.; Lämmermann, S.; Çakmak, U.; Major, Z. Material characterization of 3D-printed silicone elastomers. Procedia Struct. Integr. 2021, 34, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieva-Esteve, G.; Agulló, N.; Grande-Molina, M.; Adell, N.; Tarrado, X.; Calvo-Duarte, L.; Valls-Esteve, A.; Krauel, L.; Fenollosa-Artés, F.; Bartes, R.T. Developing tuneable viscoelastic silicone gel-based inks for precise 3D printing of clinical phantoms. Mater. Adv. 2024, 5, 3706–3720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Z.; Zhuang, Z.; Hu, L.; Sun, C.; Yu, Y.; Yang, W. Hardness and modulus programmable tuning for silicone 3D printing device and experiment. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2023, 29, 1536–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 10993-5; Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices—Part 5: Tests for In Vitro Cytotoxicity. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009.
- ISO 10993-12; Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices—Part 12: Sample Preparation and Reference Materials. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021.
- ISO 10993-10; Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices—Part 10: Tests for Skin Sensitization. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021.
- ISO 10993-23; Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices—Part 23: Tests for Irritation. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021.
- An, H.J.; Kim, M.S.; Kim, J.; Son, J.; Choi, C.H.; Park, J.M.; Kim, J.-I. Geometric evaluation of patient-specific 3D bolus from 3D printed mold and casting method for radiation therapy. Prog. Med. Phys. 2019, 30, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyas, V.; Palmer, L.; Mudge, R.; Jiang, R.; Fleck, A.; Schaly, B.; Osei, E.; Charland, P. On bolus for megavoltage photon and electron radiation therapy. Med. Dosim. 2013, 38, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuya, T.; Lee, Y.K.; Archibald-Heeren, B.R.; Byrne, M.; Bosco, B.; Phua, J.H.; Shimizu, H.; Hashimoto, S.; Tanaka, H.; Sahgal, A. Evaluation of multi-institutional end-to-end testing for post-operative spine stereotactic body radiation therapy. Phys. Imaging Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 16, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taneja, S.; Barbee, D.L.; Cohen, R.F.; Malin, M. Implementation of a Stereoscopic Camera System for Clinical Electron Simulation and Treatment Planning. Pract. Radiat. Oncol. 2024, 14, e291–e300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Patient | Treatment Site | Volume of PTV in TPS |
|---|---|---|
| Patient 1 | Scalp | 1076.2 cm3 |
| Patient 2 | Shoulder | 150.2 cm3 |
| Patient 3 | Ear | 36.0 cm3 |
| Patient 4 | Neck | 5.7 cm3 |
| Patient 5 | Rectal | 716.5 cm3 |
| Patient 6 | Nose | 93.8 cm3 |
| Property | Index |
|---|---|
| Viscosity (cps) | 14,000 ± 1000 |
| Shore Hardness | 36 Shore 00 |
| Tear strength (kN/m) | 7.5 + 2.0/−2.0 |
| Tensile strength (Mpa) | 2.1 + 1.0/−1.0 |
| Shrinkage (%) | ≤0.1 |
| Elongation (%) | 900~1000 |
| Density (g/cm) | 1.02 |
| CS 1 (mm) | CS 2 (mm) | CS 3 (mm) | CS 4 (mm) | CS 5 (mm) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max. | Ave. | Max. | Ave. | Max. | Ave. | Max. | Ave. | Max. | Ave. | |
| Patient 1 | 2.6 | 0.6 ± 1.6 | 2.1 | 0.8 ± 1.9 | 2.2 | 0.7 ± 1.8 | 2.4 | 0.8 ± 2.0 | 2.1 | 0.7 ± 1.7 |
| Patient 2 | 1.6 | 0.4 ± 1.0 | 2.2 | −0.4 ± 1.4 | 2.1 | 0.9 ± 1.4 | 1.9 | −0.4 ± 1.1 | 2.2 | −0.4 ± 1.3 |
| Patient 3 | 2.3 | 0.7 ± 1.5 | 2.1 | −0.6 ± 1.2 | 1.9 | −0.4 ± 1.3 | 2.4 | −0.7 ± 1.6 | 2.4 | −0.3 ± 1.5 |
| Patient 4 | 1.9 | 0.6 ± 1.3 | 2.2 | 0.7 ± 1.4 | 2.1 | −0.8 ± 1.3 | 2.2 | 0.9 ± 1.5 | 2.8 | 0.6 ± 1.9 |
| Patient 5 | 2.1 | 0.6 ± 1.6 | 2.3 | 0.8 ± 1.4 | 2.6 | 0.7 ± 1.9 | 1.9 | 0.9 ± 1.1 | 2.4 | 0.9 ± 1.6 |
| Patient 6 | 1.9 | 0.5 ± 0.6 | 1.6 | 0.3 ± 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.1 ± 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.1 ± 0.1 | 0.6 | 0.1 ± 0.3 |
| Volume | Surface | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Planned (cm3) | Fabricated (cm3) | %Diff. | Planned (cm2) | Fabricated (cm2) | %Diff. | |
| Patient 1 | 1044.6 | 1016.0 | 2.7 | 2788.1 | 2719.0 | 2.5 |
| Patient 2 | 148.7 | 144.3 | 3.0 | 377.6 | 367.1 | 2.8 |
| Patient 3 | 367.8 | 372.0 | 1.1 | 419.0 | 416.2 | 0.7 |
| Patient 4 | 27.3 | 27.8 | 1.8 | 135.2 | 132.1 | 2.3 |
| Patient 5 | 314.2 | 305.5 | 2.8 | 695.5 | 675.4 | 2.9 |
| Patient 6 | 32.2 | 31.9 | 0.9 | 153.2 | 149.8 | 2.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Son, J.; Kang, S.; Jin, J.; Park, H.; Lee, I.; Huh, Y.; Choi, C.H.; Kim, J.-i.; Wu, H.-G. Clinical Application of Patient-Specific Bolus Based on Molding and Casting Method in Radiotherapy. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3796. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113796
Son J, Kang S, Jin J, Park H, Lee I, Huh Y, Choi CH, Kim J-i, Wu H-G. Clinical Application of Patient-Specific Bolus Based on Molding and Casting Method in Radiotherapy. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(11):3796. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113796
Chicago/Turabian StyleSon, Jaeman, Seonghee Kang, Jegal Jin, Hyojun Park, Inbum Lee, Yoonsuk Huh, Chang Heon Choi, Jung-in Kim, and Hong-Gyun Wu. 2025. "Clinical Application of Patient-Specific Bolus Based on Molding and Casting Method in Radiotherapy" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 11: 3796. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113796
APA StyleSon, J., Kang, S., Jin, J., Park, H., Lee, I., Huh, Y., Choi, C. H., Kim, J.-i., & Wu, H.-G. (2025). Clinical Application of Patient-Specific Bolus Based on Molding and Casting Method in Radiotherapy. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(11), 3796. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113796





