An Integrative Review of Potential Diagnostic Biomarkers for Complex Regional Pain Syndrome
Abstract
1. Introduction
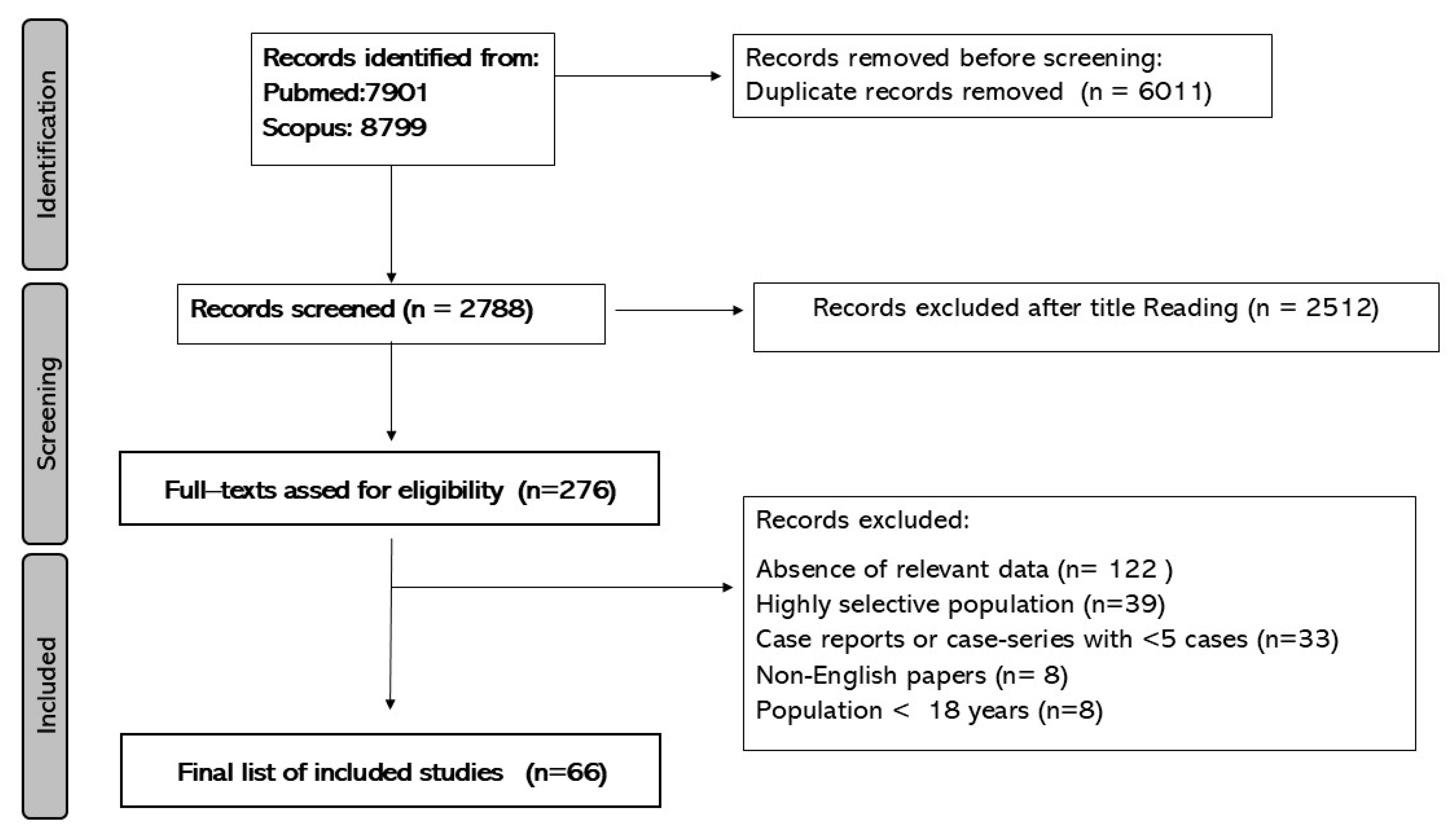
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Risk of Bias Assessment
2.2. Data Extraction and Synthesis
3. Results
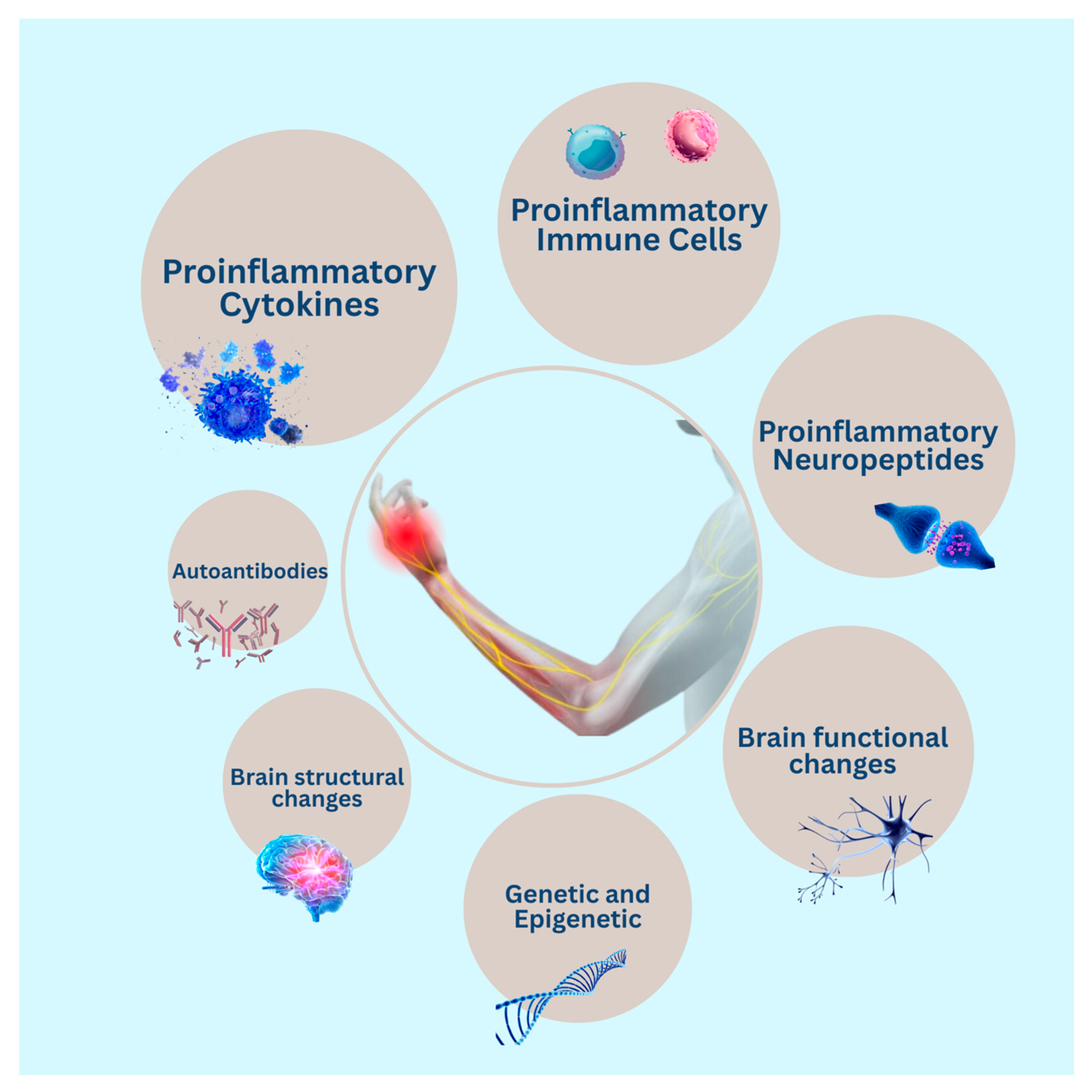
3.1. Immune System Cells
3.2. Autoantibodies
3.3. Cytokines
3.4. Other Immune-Related Proteins
3.5. Neuropeptides and Neurogenic Inflammation
3.6. Genetic and Epigenetics
3.7. Brain Structural and Functional Alterations
3.8. Other Biomarkers
3.9. Risk of Bias Assessment of the Studies
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van Velzen, G.A.J.; Perez, R.S.G.M.; Van Gestel, M.A.; Huygen, F.J.P.M.; Van Kleef, M.; Van Eijs, F.; Dahan, A.; Van Hilten, J.J.; Marinus, J. Health-Related Quality of Life in 975 Patients with Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Type 1. Pain 2014, 155, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Souza, R.S.; Klasova, J.; Saini, C.; Chang, A.; Music, S.; Shah, J.D.; Elmati, P.R.; Chitneni, A.; To, J.; Prokop, L.J.; et al. Global Burden of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome in At-Risk Populations: Estimates of Prevalence From 35 Countries Between 1993 and 2023. Anesth. Analg. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harden, R.N.; McCabe, C.S.; Goebel, A.; Massey, M.; Suvar, T.; Grieve, S.; Bruehl, S. Complex Regional Pain Syndrome: Practical Diagnostic and Treatment Guidelines, 5th Edition. Pain Med. 2022, 23, S1–S53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goebel, A.; Barker, C.; Birklein, F.; Brunner, F.; Casale, R.; Eccleston, C.; Eisenberg, E.; McCabe, C.S.; Moseley, G.L.; Perez, R.; et al. Standards for the Diagnosis and Management of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome: Results of a European Pain Federation Task Force. Eur. J. Pain 2019, 23, 641–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limerick, G.; Christo, D.K.; Tram, J.; Moheimani, R.; Manor, J.; Chakravarthy, K.; Karri, J.; Christo, P.J. Complex Regional Pain Syndrome: Evidence-Based Advances in Concepts and Treatments. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2023, 27, 269–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghaly, L.; Bargnes, V.; Rahman, S.; Tawfik, G.-A.; Bergese, S.; Caldwell, W. Interventional Treatment of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruehl, S. Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. BMJ 2015, 351, h2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangnus, T.J.P.; Bharwani, K.D.; Dirckx, M.; Huygen, F.J.P.M. From a Symptom-Based to a Mechanism-Based Pharmacotherapeutic Treatment in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. Drugs 2022, 82, 511–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Wen, B.; Xu, L.; Huang, Y. Identification of Potential Inflammation-Related Genes and Key Pathways Associated with Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Li, Z.-Y.; Yu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Ni, M.-H.; Xie, H.; Wang, W.; Huang, Y.-X.; Li, J.-L.; Cui, G.-B.; et al. Gray Matter Abnormalities in Patients with Complex Regional Pain Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Voxel-Based Morphometry Studies. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharwani, K.D.; Dirckx, M.; Stronks, D.L.; Dik, W.A.; Schreurs, M.W.J.; Huygen, F.J.P.M. Elevated Plasma Levels of sIL-2R in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome: A Pathogenic Role for T-Lymphocytes? Mediat. Inflamm. 2017, 2017, 2764261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parkitny, L.; McAuley, J.H.; Di Pietro, F.; Stanton, T.R.; O’Connell, N.E.; Marinus, J.; Van Hilten, J.J.; Moseley, G.L. Inflammation in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Neurology 2013, 80, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birklein, F.; Schmelz, M. Neuropeptides, Neurogenic Inflammation and Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS). Neurosci. Lett. 2008, 437, 199–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Well, G.; Shea, B.; O’Connell, D.; Peterson, J.; Welch, V.; Losos, M.; Tugwell, P. The NewcastleOttawa Scale (NOS) for Assessing the Quality of Nonrandomized Studies in Meta-Analysis. Available online: https://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp (accessed on 11 January 2024).
- Alexander, G.M.; Reichenberger, E.; Peterlin, B.L.; Perreault, M.J.; Grothusen, J.R.; Schwartzman, R.J. Plasma Amino Acids Changes in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. Pain Res. Treat. 2013, 2013, 742407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, G.M.; Perreault, M.J.; Reichenberger, E.R.; Schwartzman, R.J. Changes in Immune and Glial Markers in the CSF of Patients with Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. Brain. Behav. Immun. 2007, 21, 668–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, G.M.; van Rijn, M.A.; van Hilten, J.J.; Perreault, M.J.; Schwartzman, R.J. Changes in Cerebrospinal Fluid Levels of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines in CRPS. Pain 2005, 116, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azqueta-Gavaldon, M.; Youssef, A.M.; Storz, C.; Lemme, J.; Schulte-Göcking, H.; Becerra, L.; Azad, S.C.; Reiners, A.; Ertl-Wagner, B.; Borsook, D.; et al. Implications of the Putamen in Pain and Motor Deficits in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. Pain 2020, 161, 595–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baerlecken, N.T.; Gaulke, R.; Pursche, N.; Witte, T.; Karst, M.; Bernateck, M. Autoantibodies against P29ING4 Are Associated with Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. Immunol. Res. 2019, 67, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barad, M.J.; Ueno, T.; Younger, J.; Chatterjee, N.; Mackey, S. Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Is Associated with Structural Abnormalities in Pain-Related Regions of the Human Brain. J. Pain 2014, 15, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharwani, K.D.; Dirckx, M.; Stronks, D.L.; Dik, W.A.; Huygen, F.J.P.M.; Dozio, E. Serum Soluble Interleukin-2 Receptor Does Not Differentiate Complex Regional Pain Syndrome from Other Pain Conditions in a Tertiary Referral Setting. Mediat. Inflamm. 2020, 2020, 6259064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birklein, F.; Schmelz, M.; Schifter, S.; Weber, M. The Important Role of Neuropeptides in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. Neurology 2001, 57, 2179–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birklein, F.; Drummond, P.D.; Li, W.; Schlereth, T.; Albrecht, N.; Finch, P.M.; Dawson, L.F.; Clark, J.D.; Kingery, W.S. Activation of Cutaneous Immune Responses in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. J. Pain 2014, 15, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaes, F.; Schmitz, K.; Tschernatsch, M.; Kaps, M.; Krasenbrink, I.; Hempelmann, G.; Bräu, M.E. Autoimmune Etiology of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (M. Sudeck). Neurology 2004, 63, 1734–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, S.J.; Chinthagada, M.; Hoppenstehdt, D.; Kijowski, R.; Fareed, J. Role of Neuropeptides in Pathogenesis of Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy. Acta Orthop. Belg. 1998, 64, 448–451. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bruehl, S.; Gamazon, E.R.; Van De Ven, T.; Buchheit, T.; Walsh, C.G.; Mishra, P.; Ramanujan, K.; Shaw, A. DNA Methylation Profiles Are Associated with Complex Regional Pain Syndrome after Traumatic Injury. Pain 2019, 160, 2328–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delon-Martin, C.; Lefaucheur, J.-P.; Hodaj, E.; Sorel, M.; Dumolard, A.; Payen, J.-F.; Hodaj, H. Neural Correlates of Pain-Autonomic Coupling in Patients With Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Treated by Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation of the Motor Cortex. Neuromodul. J. Int. Neuromodul. Soc. 2024, 27, 188–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Pietro, F.; Lee, B.; Henderson, L.A. Altered Resting Activity Patterns and Connectivity in Individuals with Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2020, 41, 3781–3793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirckx, M.; Stronks, D.L.; van Bodegraven-Hof, E.a.M.; Wesseldijk, F.; Groeneweg, J.G.; Huygen, F.J.P.M. Inflammation in Cold Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2015, 59, 733–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirckx, M.; Schreurs, M.W.J.; de Mos, M.; Stronks, D.L.; Huygen, F.J.P.M. The Prevalence of Autoantibodies in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Type I. Mediators Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 718201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domin, M.; Strauss, S.; McAuley, J.H.; Lotze, M. Complex Regional Pain Syndrome: Thalamic GMV Atrophy and Associations of Lower GMV With Clinical and Sensorimotor Performance Data. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 722334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenberg, E.; Erlich, T.; Zinder, O.; Lichinsky, S.; Diamond, E.; Pud, D.; Davar, G. Plasma Endothelin-1 Levels in Patients with Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. Eur. J. Pain Lond. Engl. 2004, 8, 533–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geha, P.Y.; Baliki, M.N.; Harden, R.N.; Bauer, W.R.; Parrish, T.B.; Apkarian, A.V. The Brain in Chronic CRPS Pain: Abnormal Gray-White Matter Interactions in Emotional and Autonomic Regions. Neuron 2008, 60, 570–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartmannsberger, B.; Scriba, S.; Guidolin, C.; Becker, J.; Mehling, K.; Doppler, K.; Sommer, C.; Rittner, H.L. Transient Immune Activation without Loss of Intraepidermal Innervation and Associated Schwann Cells in Patients with Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. J. Neuroinflamm. 2024, 21, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heijmans-Antonissen, C.; Wesseldijk, F.; Munnikes, R.J.; Huygen, F.J.; van der Meijden, P.; Hop, W.C.J.; Hooijkaas, H.; Zijlstra, F.J. Multiplex Bead Array Assay for Detection of 25 Soluble Cytokines in Blister Fluid of Patients with Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Type 1. Mediators Inflamm. 2006, 2006, 28398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hok, P.; Strauss, S.; McAuley, J.; Domin, M.; Wang, A.P.; Rae, C.; Moseley, G.L.; Lotze, M. Functional Connectivity in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome: A Bicentric Study. NeuroImage 2024, 301, 120886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.; Suh, C.; Namgung, E.; Ha, E.; Lee, S.; Kim, R.Y.; Song, Y.; Oh, S.; Lyoo, I.K.; Jeong, H.; et al. Aberrant Resting-State Functional Connectivity in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome: A Network-Based Statistics Analysis. Exp. Neurobiol. 2023, 32, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotta, J.; Saari, J.; Koskinen, M.; Hlushchuk, Y.; Forss, N.; Hari, R. Abnormal Brain Responses to Action Observation in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. J. Pain 2017, 18, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotta, J.; Saari, J.; Harno, H.; Kalso, E.; Forss, N.; Hari, R. Somatotopic Disruption of the Functional Connectivity of the Primary Sensorimotor Cortex in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Type 1. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2023, 44, 6258–6274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huygen, F.J.P.M.; De Bruijn, A.G.J.; De Bruin, M.T.; Groeneweg, J.G.; Klein, J.; Zijlstra, F.J. Evidence for Local Inflammation in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Type 1. Mediat. Inflamm. 2002, 11, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huygen, F.J.P.M.; Ramdhani, N.; van Toorenenbergen, A.; Klein, J.; Zijlstra, F.J. Mast Cells Are Involved in Inflammatory Reactions during Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Type 1. Immunol. Lett. 2004, 91, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janicki, P.K.; Alexander, G.M.; Eckert, J.; Postula, M.; Schwartzman, R.J. Analysis of Common Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome: Genome Wide Association Study Approach and Pooled DNA Strategy. Pain Med. 2016, 17, 2344–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, E.-H.; Zhang, E.; Ko, Y.; Sim, W.S.; Moon, D.E.; Yoon, K.J.; Hong, J.H.; Lee, W.H. Genome-Wide Expression Profiling of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, Y.-H.; Kim, H.; Lee, D.; Lee, J.-Y.; Lee, W.J.; Moon, J.Y.; Kim, Y.C.; Choi, S.-H.; Kang, D.-H. Disruption of Homeostasis Based on the Right and Left Hemisphere in Patients with Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. Neuroimmunomodulation 2019, 26, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.-H.; Kim, H.; Jeon, S.Y.; Kwon, J.M.; Lee, D.; Choi, S.-H.; Kang, D.-H. Aberrant Interactions of Peripheral Measures and Neurometabolites with Lipids in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Using Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy: A Pilot Study. Mol. Pain 2018, 14, 1744806917751323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufmann, I.; Eisner, C.; Richter, P.; Huge, V.; Beyer, A.; Chouker, A.; Schelling, G.; Thiel, M. Lymphocyte Subsets and the Role of Th1/Th2 Balance in Stressed Chronic Pain Patients. Neuroimmunomodulation 2007, 14, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufmann, I.; Hauer, D.; Huge, V.; Vogeser, M.; Campolongo, P.; Chouker, A.; Thiel, M.; Schelling, G. Enhanced Anandamide Plasma Levels in Patients with Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Following Traumatic Injury: A Preliminary Report. Eur. Surg. Res. Eur. Chir. Forsch. Rech. Chir. Eur. 2009, 43, 325–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohler, M.; Strauss, S.; Horn, U.; Langner, I.; Usichenko, T.; Neumann, N.; Lotze, M. Differences in Neuronal Representation of Mental Rotation in Patients With Complex Regional Pain Syndrome and Healthy Controls. J. Pain 2019, 20, 898–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohr, D.; Singh, P.; Tschernatsch, M.; Kaps, M.; Pouokam, E.; Diener, M.; Kummer, W.; Birklein, F.; Vincent, A.; Goebel, A.; et al. Autoimmunity against the Β2 Adrenergic Receptor and Muscarinic-2 Receptor in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. Pain 2011, 152, 2690–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohr, D.; Tschernatsch, M.; Schmitz, K.; Singh, P.; Kaps, M.; Schäfer, K.-H.; Diener, M.; Mathies, J.; Matz, O.; Kummer, W.; et al. Autoantibodies in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Bind to a Differentiation-Dependent Neuronal Surface Autoantigen. Pain 2009, 143, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- König, S.; Steinebrey, N.; Herrnberger, M.; Escolano-Lozano, F.; Schlereth, T.; Rebhorn, C.; Birklein, F. Reduced Serum Protease Activity in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome: The Impact of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme and Carboxypeptidases. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 205, 114307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krämer, H.H.; Hofbauer, L.C.; Szalay, G.; Breimhorst, M.; Eberle, T.; Zieschang, K.; Rauner, M.; Schlereth, T.; Schreckenberger, M.; Birklein, F. Osteoprotegerin: A New Biomarker for Impaired Bone Metabolism in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome? Pain 2014, 155, 889–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.; Di Pietro, F.; Henderson, L.A.; Austin, P.J. Altered Basal Ganglia Infraslow Oscillation and Resting Functional Connectivity in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. J. Neurosci. Res. 2022, 100, 1487–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.-H.; Lee, K.-J.; Cho, K.I.K.; Noh, E.C.; Jang, J.H.; Kim, Y.C.; Kang, D.-H. Brain Alterations and Neurocognitive Dysfunction in Patients With Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. J. Pain 2015, 16, 580–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenz, M.; Höffken, O.; Stude, P.; Lissek, S.; Schwenkreis, P.; Reinersmann, A.; Frettlöh, J.; Richter, H.; Tegenthoff, M.; Maier, C. Bilateral Somatosensory Cortex Disinhibition in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Type I. Neurology 2011, 77, 1096–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munnikes, R.J.M.; Muis, C.; Boersma, M.; Heijmans-Antonissen, C.; Zijlstra, F.J.; Huygen, F.J.P.M. Intermediate Stage Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Type 1 Is Unrelated to Proinflammatory Cytokines. Mediators Inflamm. 2005, 2005, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlova, I.A.; Alexander, G.M.; Qureshi, R.A.; Sacan, A.; Graziano, A.; Barrett, J.E.; Schwartzman, R.J.; Ajit, S.K. MicroRNA Modulation in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. J. Transl. Med. 2011, 9, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkitny, L.; McAuley, J.H.; Herbert, R.D.; Di Pietro, F.; Cashin, A.G.; Ferraro, M.C.; Moseley, G.L. Post-Fracture Serum Cytokine Levels Are Not Associated with a Later Diagnosis of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome: A Case-Control Study Nested in a Prospective Cohort Study. BMC Neurol. 2022, 22, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pleger, B.; Draganski, B.; Schwenkreis, P.; Lenz, M.; Nicolas, V.; Maier, C.; Tegenthoff, M. Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Type I Affects Brain Structure in Prefrontal and Motor Cortex. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribbers, G.M.; Oosterhuis, W.P.; van Limbeek, J.; de Metz, M. Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy: Is the Immune System Involved? Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 1998, 79, 1549–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritz, B.W.; Alexander, G.M.; Nogusa, S.; Perreault, M.J.; Peterlin, B.L.; Grothusen, J.R.; Schwartzman, R.J. Elevated Blood Levels of Inflammatory Monocytes (CD14+ CD16+) in Patients with Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2011, 164, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, M.A.; Georgius, P.; Pires, A.S.; Heng, B.; Allwright, M.; Guennewig, B.; Santarelli, D.M.; Bailey, D.; Fiore, N.T.; Tan, V.X.; et al. Novel Immune Biomarkers in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. J. Neuroimmunol. 2020, 347, 577330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, M.A.; Fiore, N.T.; Van Vreden, C.; Bailey, D.; Santarelli, D.M.; McGuire, H.M.; Fazekas De St Groth, B.; Austin, P.J. Expansion and Activation of Distinct Central Memory T Lymphocyte Subsets in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. J. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 16, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schinkel, C.; Scherens, A.; Köller, M.; Roellecke, G.; Muhr, G.; Maier, C. Systemic Inflammatory Mediators in Post-Traumatic Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS I)—Longitudinal Investigations and Differences to Control Groups. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2009, 14, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schinkel, C.; Gaertner, A.; Zaspel, J.; Zedler, S.; Faist, E.; Schuermann, M. Inflammatory Mediators Are Altered in the Acute Phase of Posttraumatic Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. Clin. J. Pain 2006, 22, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaikh, S.S.; Goebel, A.; Lee, M.C.; Nahorski, M.S.; Shenker, N.; Pamela, Y.; Drissi, I.; Brown, C.; Ison, G.; Shaikh, M.F.; et al. Evidence of a Genetic Background Predisposing to Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Type 1. J. Med. Genet. 2024, 61, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiraishi, S.; Kobayashi, H.; Nihashi, T.; Kato, K.; Iwano, S.; Nishino, M.; Ishigaki, T.; Ikeda, M.; Kato, T.; Ito, K.; et al. Cerebral Glucose Metabolism Change in Patients with Complex Regional Pain Syndrome: A PET Study. Radiat. Med. 2006, 24, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokouhi, M.; Clarke, C.; Morley-Forster, P.; Moulin, D.E.; Davis, K.D.; St Lawrence, K. Structural and Functional Brain Changes at Early and Late Stages of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. J. Pain 2018, 19, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, E.C.T.H.; Oyen, W.J.G.; Goris, R.J.A. Leukocytes in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Type I. Inflammation 2005, 29, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turton, A.J.; McCabe, C.S.; Harris, N.; Filipovic, S.R. Sensorimotor Integration in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome: A Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Study. Pain 2007, 127, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walton, K.D.; Dubois, M.; Llinás, R.R. Abnormal Thalamocortical Activity in Patients with Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS) Type I. Pain 2010, 150, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Üçeyler, N.; Eberle, T.; Rolke, R.; Birklein, F.; Sommer, C. Differential Expression Patterns of Cytokines in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. Pain 2007, 132, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wesseldijk, F.; van Toorenenbergen, A.W.; van Wijk, R.G.; Huygen, F.J.; Zijlstra, F.J. IgE-Mediated Hypersensitivity: Patients with Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Type 1 (CRPS1) vs the Dutch Population. A Retrospective Study. Pain Med. 2009, 10, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wesseldijk, F.; Fekkes, D.; Huygen, F.J.; Bogaerts-Taal, E.; Zijlstra, F.J. Increased Plasma Serotonin in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Type 1. Anesth. Analg. 2008, 106, 1862–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wesseldijk, F.; Fekkes, D.; Huygen, F.J.P.M.; van de Heide-Mulder, M.; Zijlstra, F.J. Increased Plasma Glutamate, Glycine, and Arginine Levels in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Type 1. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2008, 52, 688–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesseldijk, F.; Huygen, F.J.P.M.; Heijmans-Antonissen, C.; Niehof, S.P.; Zijlstra, F.J. Six Years Follow-up of the Levels of TNF-Alpha and IL-6 in Patients with Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Type 1. Mediat. Inflamm. 2008, 2008, 469439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yetişgin, A.; Tutoğlu, A.; Cinakli, A.; Kul, M.; Boyaci, A. Platelet and Erythrocyte Indexes in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Type I. Arch. Rheumatol. 2016, 31, 359–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Hotta, J.; Lehtinen, M.K.; Forss, N.; Hari, R. Enlargement of Choroid Plexus in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruehl, S.; Harden, R.N.; Galer, B.S.; Saltz, S.; Backonja, M.; Stanton-Hicks, M. Complex Regional Pain Syndrome: Are There Distinct Subtypes and Sequential Stages of the Syndrome? Pain 2002, 95, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesage, S.; Goodnow, C.C. Organ-Specific Autoimmune Disease. J. Exp. Med. 2001, 194, F31–F36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangnus, T.J.P.; Bharwani, K.D.; Dik, W.A.; Baart, S.J.; Dirckx, M.; Huygen, F.J.P.M. Is There an Association between Serum Soluble Interleukin-2 Receptor Levels and Syndrome Severity in Persistent Complex Regional Pain Syndrome? Pain Med. 2023, 24, 1234–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalita, J.; Shukla, R.; Pandey, P.C. Effect of Prednisolone on Clinical and Cytokine mRNA Profiling in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. J. Mol. Neurosci. MN 2024, 74, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huygen, F.J.P.M.; Niehof, S.; Zijlstra, F.J.; van Hagen, P.M.; van Daele, P.L.A. Successful Treatment of CRPS 1 with Anti-TNF. J. Pain Symptom Manag. 2004, 27, 101–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dirckx, M.; Groeneweg, G.; Wesseldijk, F.; Stronks, D.L.; Huygen, F.J.P.M. Report of a Preliminary Discontinued Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial of the Anti-TNF-α Chimeric Monoclonal Antibody Infliximab in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. Pain Pract. Off. J. World Inst. Pain 2013, 13, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orstavik, K. Pathological C-Fibres in Patients with a Chronic Painful Condition. Brain 2003, 126, 567–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahmoush, A.J.; Schwartzman, R.J.; Hopp, J.L.; Grothusen, J.R. Quantitative Sensory Studies in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Type 1/RSD. Clin. J. Pain 2000, 16, 340–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Author, Year | n | Cytocines | Cells | Autoantibodies | Neuropeptides | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hartmannsberger et al., 2024 [34] | 25 | ↑Local mast cells and Langerhans cells (acute phase) ±Local mast cells and Langerhans cells (chronic phase) | ||||
| Parkitny et al., 2022 [58] | 69 | ±immediate post fracture levels of IL ** | ±immediate post fracture levels of T Cells | |||
| Bharwani et al., 2020 [21] | 23 | ↑ sIL-2R | ||||
| Russo et al., 2020 [62] | 44 | ↓ IL-37, ↓ GM-CSF | ||||
| Baerlecken et al., 2019 [19] | 36 | IgG to P29ING4 | ||||
| Russo et al., 2019 [63] | 14 | ↓ number of central memory CD8+, CD4+ T lymphocytes | ↑ p38 signaling in CD1+ mDCs (dendritic cell type activation?) | |||
| Bharwani et al., 2017 [11] | 80 | ↑ sIL-2R | ||||
| Yetişgin et al.,2016 [77] | 21 | ±blood cellular counts | ±: VS, CRP | |||
| Dirckx et al., 2015 [29] | 66 | ↑ IL-6, TNF-a | ||||
| Dirckx et al., 2015 [30] | 296 | Antineuronal IgG | ||||
| Antinuclear IgG | ||||||
| Birklein et al., 2014 [23] | 55 | ↑ local IL-6 | ↑ Local mast cells | ↑ local tryptase | ||
| ↑ local TNF-α | ||||||
| Ritz et al., 2011 [61] | 25 | ±proinflammatory cytokines (IL-6, IL-8, TNF-a) | ↑ CD14+ CD16+ monocytes | |||
| ±IL-10 | ±T helper cells (CD4+ CD8−), T cytotoxic cells (CD4− CD8+), NK cells (CD56+), B cells (CD19+), monocytes/macrophages (CD14+) | |||||
| Orlova et al., 2011 [57] | 41 | ↑ interleukin1 receptor antagonist | ||||
| ↑ monocyte chemotactic protein-1 | ||||||
| ±IL-6, TNFα | ||||||
| ±Interferon-gamma, IL-1β, IL-2, IL-4, IL-5, IL-7, IL-8, IL-10 | ||||||
| Kohr et al., 2011 [49] | 20 | IgG to b2 adrenergic and/or the muscarinic-2 receptors | ||||
| Kaufmann et al., 2009 [47] | 10 | ↑ anandamide | ||||
| Kohr et al., 2009 [50] | 30 | IgG to SH-SY5Y (inducible autonomic nervous system autoantigen) | ||||
| Schinkel et al., 2009 [64] | 25 | ± IL-4, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, IL-11, IL-12 | ±White Blood Cell Count | ↑ Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide | ↑ Soluble TNF Receptor I and II | |
| ± TNF, IL6 | ↑ Substance P | ±CRP | ||||
| Wesseldijk et al., 2009 [73] | 66 | ±IgE, tryptase | ||||
| Wesseldijk et al., 2008 [76] | 12 | ↑ local TNF-α | ||||
| ↑ local IL-6 | ||||||
| Chronic phase | ±IL6, TNF-α | |||||
| Kaufmann et al., 2007 [46] | 15 | ±Lymphocites | ||||
| ↓ cytotoxic CD8+ lymphocytes; IL-2-producing T cell | ||||||
| Uçeyler et al., 2007 [72] | 40 | ↓ IL-10, Transforming growth factor beta 1 | ±Whole blood counts | ±CPR | ||
| ↑IL-2 | ||||||
| ±TNF-α, IL-6 | ||||||
| ±IL-4 | ||||||
| Alexander et al., 2007 [16] | 22 | ↑ CSF IL-6 | ||||
| ↓ CSF IL-2, IL-10 | ||||||
| ↑ CSF Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 | ||||||
| Heijmans-Antonissen et al., 2006 [35] | 22 | ↑ local IL-6 | ||||
| ↑ local TNF-α | ||||||
| ±local IFNγ, IL-2, IL-2R, IL-4, IL-5, and IL-10 | ||||||
| ↓eotaxin | ||||||
| Schinkel et al., 2006 [65] | 25 | ↑ IL-8 | ±leukocytes | ↑ Substance P | ↓ soluble forms of selectins | |
| ±IL-6 | ±Neuropeptide Y | ±CRP | ||||
| ±CGRP | ↑ soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor I/II | |||||
| Tan et al., 2005 [69] | 6 | ↑ Local leukocytes | ||||
| Alexander et al., 2005 [17] | 24 | ↑ CSF IL-6/IL-1 | ||||
| ±CSF TNF-α | ||||||
| Munnikes et al., 2005 [56] | 25 | ↑ local IL-6 | ||||
| ↑ local TNF-α | ||||||
| Chronic phase | ±local IL-6 | |||||
| Chronic phase | ±local TNF-α | |||||
| Blaes et al., 2004 [24] | 12 | ↑ IgG Myenteric plexus | ||||
| Huygen et al., 2004 [41] | 20 | ↑ local IL-6 | ↑ tryptase | |||
| ↑ local TNF-α | ||||||
| Huygen et al., 2002 [40] | 9 | ↑ local IL-6 | ||||
| ↑ local TNF-α | ||||||
| ±local IL-1b, IL-1b | ||||||
| Birklein et al., 2001 [22] | 19 | ↑ Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide | ||||
| Ribbers et al., 1998 [60] | 13 | ±Cell distribution (B and T lymphocyte populations) | ||||
| Blair et al., 1998 [25] | 61 | ↑ Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide | ||||
| ±Neurokinin | ||||||
| ↑Bradykinin |
| Author, Year | n | Genetic and Epigenetics | Brain Imaging | Functional Neurophysiological | Other Biomarkers | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Structural | Metabolic | |||||
| Hok et al., 2024 [36] | 51 | ↓ antinociceptive modulation via the brainstem antinociceptive system | ||||
| Shaikh et al., 2024 [66] | Single-nucleotide polymorphism of genes ANO10, P2RX7, PRKAG1 and SLC12A9 | |||||
| Hotta et al., 2023 [39] | 17 | Sustained somatotopic alteration of the somatosensory cortex | ||||
| Delon-Martin et al., 2023 [27] | 11 | ↑ localized activation in the primary somatosensory cortex (transcranial magnetic stimulation) | ||||
| Zhu et al., 2023 [9] | 9 | Five top five hub genes: MMP9, PTGS2, CXCL8, OSM, TLN1 | ||||
| Hong et al., 2023 [37] | 21 | ↑ functional connectivity in the somatosensory (S1) subnetworks | ||||
| ↓functional connectivity in the prefronto-parieto-cingulo-thalamic subnetworks | ||||||
| Lee et al., 2022 [53] | 15 | ↑ Basal ganglia infra-slow oscillations | ||||
| ↑ Basal ganglia resting connectivity | ||||||
| Domin et al., 2021 [31] | 24 | ↓ insula and bilateral grey matter medial thalamus. | ||||
| König et al., 2021 [51] | 25 | ↓ activity of angiotensin-converting enzyme | ||||
| Azqueta-Gavaldon et al., 2020 [18] | 20 | ↓gray matter density in the putamen/functional connectivity increases amongst the putamen and pre-/postcentral gyri and cerebellum | ||||
| Russo et al., 2020 [62] | 44 | ↓ tryptophan | ||||
| Di Pietro et al., 2020 [28] | 15 | ↑ thalamo-S1 functional connectivity | ||||
| Bruehl et al., 2019 [26] | 9 | Altered methylation of specific genes (COL11A1 and HLA-DRB6) | ||||
| Jung et al., 2019 [44] | 12 | Disruption of interactions between specific central and metabolic metabolites * in the thalamus | ||||
| Kohle et al., 2019 [48] | 15 | ↓ activation of subthalamic nucleus, nucleus accumbens, and putamen | ||||
| Jung, et al., 2018 [45] | 12 | Anormal interactions of lipid13a and L f lipid 09 in the thalamus with peripheral tCr | ||||
| Hotta et al., 2017 [38] | 13 | Abnormal neural activity in sensorimotor and pain-related areas | ||||
| Shokouhi et al., 2017 [68] | 28 | ↓grey matter in somatosensory cortex, and limbic system | ↓ perfusion in somatosensory cortex, and limbic system (early phase) | |||
| ↑ perfusion in somatosensory cortex, and limbic system (late phase) | ||||||
| Janicki et al., 2016 [42] | 230 | ±Common Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms | ||||
| Zhou et al., 2015 [78] | 35 | ↑ volume of choroid plexus | ||||
| Lee et al., 2015 [54] | 25 | ↓ cortical thinning in the prefrontal cortex | ||||
| Pleger et al., 2014 [59] | 15 | ↑ in gray matter density in dorsomedial prefrontal | ||||
| ↑ in gray matter density located in the primary motor cortex (contralateral to the affected limb) | ||||||
| Krämer et al., 2014 [52] | 33 | ↑ Osteoprotegerin | ||||
| Barad et al., 2013 [20] | 15 | ↓ Grey matter volume in pain-related areas (dorsal insula, orbitofrontal cortex, cingulate cortex. | ||||
| Jin et al., 2013 [43] | 24 | Increased expression of MMP9 | ||||
| Alexander et al., 2013 [15] | 160 | ↑ AA: L-Aspartate, L-glutamate, L-ornithine | ||||
| ↓ L-tryptophan and L-arginine | ||||||
| Lenz et al., 2011 [55] | 21 | ↓ Somatosensory cortex inhibition | ||||
| Orlova et al., 2011 [57] | 41 | ↑ Specific microRNA: hsa-miR-532-3p | ↑ Vascular endothelial growth factor | |||
| Walton et al., 2010 [71] | 64 | Altered magneto-encephalographic imaging (thalamo-cortical Dysrhythmia) | ||||
| Wesseldijk et al., 2008 [75] | 64 | ↑ NMDA excitatory amino acids: glutamate, glutamine, glycine, taurine, and arginine | ||||
| Wesseldijk et al., 2008 [74] | 35 | ↑ serotonin | ||||
| Geha et al., 2008 [33] | 26 | ↓ insula, ventromedial prefrontal cortex, nucleus accumbens; fractional anisotropy in cingulum-callosal bundle | ||||
| Turton et al., 2007 [70] | 8 | ↓ motor response to TMS | ||||
| Alexander et al., 2007 [16] | 22 | ↑ CSF Calcium and glutamate | ||||
| ↑ CSF Glial fibrillary acidic protein | ||||||
| ↑ CSF Nitric oxide metabolites | ||||||
| Uçeyler et al., 2007 [72] | 40 | ↓ mRNA IL-4, IL-8, IL-10 | ||||
| ± transforming growth factor-b1mRNA | ||||||
| ↑ TNF and IL-2 mRNA level | ||||||
| Janicki et al., 2016 [42] | 230 | ±Common Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms | ||||
| Shiraishi et al., 2006 [67] | 18 | ↑ activity in somatosensory cortex | ||||
| ↓ contralateral activity in specific motor areas | ||||||
| Huygen et al., 2004 [41] | 20 | ±prostaglandin E2 | ||||
| Eisenberg et al., 2004 [32] | 38 | ±Endothelin-1 | ||||
| Newcastle–Ottawa Scale Items | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study | S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | C | O | Total |
| Hartmannsberger et al., 2024 [34] | * | - | * | ** | * | ** | 7 |
| Delon-Martin et al., 2024 [27] | * | - | * | ** | * | ** | 7 |
| Bharwani et al., 2020 [21] | * | - | * | ** | * | ** | 7 |
| Baerlecken et al., 2019 [19] | * | - | * | ** | * | *** | 9 |
| Dirckx et al., 2015 [30] | * | - | * | ** | * | ** | 7 |
| Kohr et al., 2011 [49] | * | - | * | ** | * | * | 6 |
| Alexander et al., 2007 [16] | * | - | * | ** | - | * | 5 |
| Heijmans-Antonissen et al., 2006 [35] | * | - | * | ** | * | * | 6 |
| Alexander et al., 2005 [17] | * | - | * | ** | * | ** | 7 |
| Blaes et al., 2004 [24] | * | - | * | * | * | * | 5 |
| Blair et al., 1998 [25] | * | - | * | * | * | * | 5 |
| Newcastle–Ottawa Scale Items | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study | S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | C | E | Total |
| Shaikh et al., 2024 [66] | * | * | * | * | ** | *** | 9 |
| Hok et al., 2024 [36] | * | * | - | * | ** | ** | 7 |
| Hotta et al., 2023 [39] | * | * | * | * | ** | ** | 8 |
| Hong et al., 2023 [37] | * | * | * | * | ** | ** | 8 |
| Zhu et al., 2023 [9] | * | * | * | * | ** | *** | 9 |
| Lee et al., 2022 [53] | * | * | * | * | ** | ** | 8 |
| Parkitny et al., 2022 [58] | * | * | - | * | ** | *** | 8 |
| Orlova et al., 2011 [57] | * | * | - | * | ** | ** | 7 |
| König et al., 2021 [51] | * | * | - | * | ** | ** | 7 |
| Domin et al., 2021 [31] | |||||||
| Azqueta-Gavaldon et al., 2020 [18] | * | * | - | * | ** | ** | 7 |
| Russo et al., 2020 [62] | * | * | - | * | ** | ** | 7 |
| Di Pietro et al., 2020 [28] | * | * | - | * | ** | ** | 7 |
| Russo et al., 2019 [63] | * | * | - | * | * | ** | 6 |
| Kohler et al., 2019 [48] | * | * | * | * | ** | ** | 8 |
| Jung et al., 2019 [44] | * | * | - | * | ** | ** | 7 |
| Jung et al., 2018 [45] | * | * | - | * | * | ** | 6 |
| Bruehl et al., 2019 [26] | * | * | - | * | ** | *** | 8 |
| Wesseldijk et al., 2009 [73] | * | * | * | * | ** | *** | 9 |
| Wesseldijk et al., 2008 [76] | * | * | - | * | ** | ** | 7 |
| Shokouhi et al., 2017 [68] | * | * | - | * | ** | ** | 7 |
| Bharwani et al., 2017 [11] | * | * | - | * | ** | ** | 7 |
| Hotta et al., 2017 [38] | * | * | - | * | ** | * | 6 |
| Yetişgin et al., 2016 [77] | * | * | - | * | ** | ** | 7 |
| Zhou et al., 2015 [78] | * | * | - | * | ** | ** | 7 |
| Lee et al., 2015 [54] | * | * | * | * | ** | ** | 8 |
| Dirckx et al., 2015 [29] | * | * | - | * | ** | ** | 7 |
| Barad et al., 2014 [20] | * | * | - | * | ** | ** | 7 |
| Krämer et al., 2014 [52] | * | * | - | * | ** | ** | 7 |
| Birklein et al., 2014 [23] | * | * | * | * | ** | ** | 8 |
| Pleger et al., 2014 [59] | * | * | * | * | ** | ** | 8 |
| Jin et al., 2013 [43] | * | * | * | * | ** | *** | 9 |
| Alexander et al., 2013 [15] | * | - | - | * | ** | ** | 6 |
| Lenz et al., 2011 [55] | * | * | * | * | ** | *** | 9 |
| Ritz et al., 2011 [61] | * | * | * | * | ** | ** | 8 |
| Walton et al., 2010 [71] | * | * | - | * | ** | ** | 7 |
| Kaufmann et al., 2009 [47] | * | - | - | * | * | ** | 5 |
| Kohr et al., 2009 [50] | * | * | * | * | ** | ** | 8 |
| Schinkel et al., 2009 [64] | * | * | * | * | ** | ** | 8 |
| Geha et al., 2008 [33] | * | * | - | * | ** | ** | 7 |
| Wesseldijk et al., 2008 [75] | * | * | - | * | ** | ** | 7 |
| Wesseldijk et al., 2008 b [74] | * | * | - | * | ** | ** | 7 |
| Kaufmann et al.,2007 [46] | * | - | - | * | * | *** | 6 |
| Uçeyler et al., 2007 [72] | * | * | - | * | ** | ** | 7 |
| Turton et al., 2007 [70] | * | * | - | * | ** | ** | 7 |
| Janicki et al., 2016 [42] | * | * | - | * | ** | ** | 7 |
| Schinkel et al., 2006 [65] | * | * | * | * | ** | *** | 9 |
| Shiraishi et al., 2006 [67] | * | * | - | * | ** | ** | 7 |
| Munnikes et al., 2005 [56] | * | - | - | * | ** | ** | 6 |
| Tan et al., 2005 [69] | * | * | - | * | ** | ** | 7 |
| Eisenberg et al., 2004 [32] | * | * | - | * | ** | *** | 8 |
| Huygen et al., 2004 [41] | * | * | - | * | ** | ** | 7 |
| Huygen et al., 2002 [40] | * | * | - | * | ** | ** | 7 |
| Birklein et al., 2001 [22] | * | * | - | * | ** | ** | 7 |
| Ribbers et al., 1998 [60] | * | * | * | * | ** | ** | 8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lopes, R.; Santos, A.; Gomes, T.; Ribeiro, J.; Rodrigues, I.; Paiva, B.; Nzwalo, I.; Catamo, D.; Baco, J.; Buque, H.; et al. An Integrative Review of Potential Diagnostic Biomarkers for Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3751. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113751
Lopes R, Santos A, Gomes T, Ribeiro J, Rodrigues I, Paiva B, Nzwalo I, Catamo D, Baco J, Buque H, et al. An Integrative Review of Potential Diagnostic Biomarkers for Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(11):3751. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113751
Chicago/Turabian StyleLopes, Revelino, André Santos, Teresa Gomes, Júlia Ribeiro, Ivone Rodrigues, Bruno Paiva, Isa Nzwalo, Deise Catamo, Jamal Baco, Helena Buque, and et al. 2025. "An Integrative Review of Potential Diagnostic Biomarkers for Complex Regional Pain Syndrome" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 11: 3751. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113751
APA StyleLopes, R., Santos, A., Gomes, T., Ribeiro, J., Rodrigues, I., Paiva, B., Nzwalo, I., Catamo, D., Baco, J., Buque, H., Botelho, M., Pais, S., & Nzwalo, H. (2025). An Integrative Review of Potential Diagnostic Biomarkers for Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(11), 3751. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113751








