Profile of Cytokines Associated with SARS-CoV2 Seropositivity in Multiple Sclerosis Patients and Its Persistence over Six Months
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Patients
2.2. Blood Samples for Antibodies and Cytokine Analysis
2.3. Statistical Analysis
2.4. Ethics
2.5. Use of IA
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| COVID-19 | Coronavirus Disease 2019 |
| DMT(s) | Disease-Modifying Therapy(ies) |
| EDSS | Expanded Disability Status Scale |
| ELISA | Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay |
| FACS | Fluorescence-Activated Cell Sorting |
| GLMM | Generalized Linear Mixed Models |
| IQR | Interquartile Range |
| IFN | Interferon (including IFN-α and IFN-γ) |
| IL | Interleukin (e.g., IL-1, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, IL-12, IL-17, IL-18, IL-23, IL-33) |
| Ig | Immunoglobulin (e.g., IgG, IgM, IgA) |
| MCP-1 | Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 |
| MS | Multiple Sclerosis |
| NK | Natural Killer (cells) |
| OR | Odds Ratio |
| pwMS | Patients with Multiple Sclerosis |
| RRMS | Relapsing–Remitting Multiple Sclerosis |
| SPMS | Secondary Progressive Multiple Sclerosis |
| TNF-α | Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha |
| S1/S2 | Spike protein subunit 1 and Spike protein subunit 2 |
| 5PL | Five-Parameter Logistic curve |
References
- Lei, Y. Synthetic Strategies in Molecular Imprinting. Adv. Biochem. Eng. Biotechnol. 2015, 123, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Chu, D.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; George, J.; Young, H.A.; Liu, G. Cytokines: From Clinical Significance to Quantification. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2004433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sprague, A.H.; Khalil, R.A. Inflammatory cytokines in vascular dysfunction and vascular disease. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2009, 78, 539–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.W.; Farooq, M.; Hwang, M.J.; Haseeb, M.; Choi, S. Autoimmune Neuroinflammatory Diseases: Role of Interleukins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Wu, P.F.; Zhang, W.; Liao, X. Circulating Interleukins and Risk of Multiple Sclerosis: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 647588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, D.S.; Lucchinetti, C.F.; Calabresi, P.A. Multiple Sclerosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Song, F.; Fernandez-Escobar, A.; Luo, G.; Wang, J.H.; Sun, Y. The Properties of Cytokines in Multiple Sclerosis: Pros and Cons. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 356, 552–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Huang, S.; Yin, L. The cytokine storm and COVID-19. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Ling, Y.; Bai, T.; Xie, Y.; Huang, J.; Li, J.; Xiong, W.; Yang, D.; Chen, R.; Lu, F.; et al. COVID-19 with different severities: A multicenter study of clinical features. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 201, 1380–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussman, J.P. Cellular and Molecular Pathways of COVID-19 and Potential Points of Therapeutic Intervention. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiemi Enokida Mori, M.; Name Colado Simão, A.; Danelli, T.; Rangel Oliveira, S.; Luis Candido de Souza Cassela, P.; Lerner Trigo, G.; Morais Cardoso, K.; Mestre Tejo, A.; Naomi Tano, Z.; Regina Delicato de Almeida, E.; et al. Protective effects of IL18-105G>A and IL18-137C> Ggenetic variants on severity of COVID-19. Cytokine 2024, 174, 156476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prosperini, L.; Arrambide, G.; Celius, E.G.; Goletti, D.; Killestein, J.; Kos, D.; Lavorgna, L.; Louapre, C.; Sormani, M.P.; Stastna, D.; et al. COVID-19 and multiple sclerosis: Challenges and lessons for patient care. Lancet Reg. Health-Eur. 2024, 44, 100979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinheiro, J.C.; Bates, D.M. Mixed-Effects Models in S and S-PLUS; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Bates, D.; Mächler, M.; Bolker, B.; Walker, S. Fitting Linear Mixed-Effects Models Using lme4. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 67, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Lan, Z.; Ye, J.; Pang, L.; Liu, Y.; Wu, W.; Qin, X.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, P. Cytokine Storm: The Primary Determinant for the Pathophysiological Evolution of COVID-19 Deterioration. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 589095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, L.; Chen, Z.; Lui, G.; Wong, C.K.; Wong, W.T.; Ng, R.W.; Tso, E.Y.; Fung, K.S.; Chan, V.; Yeung, A.C.; et al. Longitudinal Cytokine Profile in Patients with Mild to Critical COVID-19. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 763292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.S.; Shu, T.; Kang, L.; Wu, D.; Zhou, X.; Liao, B.W.; Sun, X.L.; Zhou, X.; Wang, Y.Y. Temporal profiling of plasma cytokines, chemokines and growth factors from mild, severe and fatal COVID-19 patients. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 6–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, Y.H.; Fong, S.W.; Poh, C.M.; Carissimo, G.; Yeo, N.K.W.; Amrun, S.N.; Goh, Y.S.; Lim, J.; Xu, W.; Chee, R.S.L.; et al. Asymptomatic COVID-19: Disease tolerance with efficient anti-viral immunity against SARS-CoV-2. EMBO Mol. Med. 2021, 13, e14045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahgat, M.M.; Nadeem, R.; Nasraa, M.H.; Amer, K.; Hassan, W.A.; ELGarhy, F.M.; Reda, S.A.-E.D. Proinflammatory Cytokine Profiles in Both Mild Symptomatic and Asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2-Infected Egyptian Individuals and a Proposed Relationship to Post-COVID-19 Sequela. Viral Immunol. 2023, 36, 600–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindarajan, V.; De Rivero Vaccari, J.P.; Keane, R.W. Role of inflammasomes in multiple sclerosis and their potential as therapeutic targets. J. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 17, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.J.; Truong, A.K. COVID-19 infection on IL-23 inhibition. Dermatol. Ther. 2020, 33, 33–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porro, C.; Cianciulli, A.; Panaro, M.A. The regulatory role of IL-10 in neurodegenerative diseases. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlini, V.; Noonan, D.M.; Abdalalem, E.; Goletti, D.; Sansone, C.; Calabrone, L.; Albini, A. The multifaceted nature of IL-10: Regulation, role in immunological homeostasis and its relevance to cancer, COVID-19 and post-COVID conditions. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1161067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smail, S.W.; Babaei, E.; Amin, K.; Abdulahad, W.H. Serum IL-23, IL-10, and TNF-α predict in-hospital mortality in COVID-19 patients. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1145840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.H.; Salloum, S.; Wang, J.Y.; Wong, L.P.; Regan, J.; Lefteri, K.; Manickas-Hill, Z.; Gao, C.; Li, J.Z.; Sadreyev, R.I.; et al. Type I, II, and III Interferon Signatures Correspond to Coronavirus Disease 2019 Severity. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 224, 777–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primorac, D.; Vrdoljak, K.; Brlek, P.; Pavelić, E.; Molnar, V.; Matišić, V.; Erceg Ivkošić, I.; Parčina, M. Adaptive Immune Responses and Immunity to SARS-CoV-2. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 848582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, A.; Iwasaki, A. Type I and Type III Interferons—Induction, Signaling, Evasion, and Application to Combat COVID-19. Cell Host Microbe. 2020, 27, 870–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartung, H.P.; Cree, B.A.C.; Barnett, M.; Meuth, S.G.; Bar-Or, A.; Steinman, L. Bioavailable central nervous system disease-modifying therapies for multiple sclerosis. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1290666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halenova, T.I.; Raksha, N.H.; Vovk, T.B.; Karbovskyy, V.L.; Sholomon, S.M.; Melnyk, V.S.; Savchuk, O.M. Cytokine profile in multiple sclerosis patients with and without COVID-19. Wiad. Lek. 2024, 77, 640–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihim, S.A.; Abubakar, S.D.; Zian, Z.; Sasaki, T.; Saffarioun, M.; Maleknia, S.; Azizi, G. Interleukin-18 cytokine in immunity, inflammation, and autoimmunity: Biological role in induction, regulation, and treatment. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 919973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasser, S.M.T.; Rana, A.A.; Doffinger, R.; Kafizas, A.; Khan, T.A.; Nasser, S. Elevated free interleukin-18 associated with severity and mortality in prospective cohort study of 206 hospitalised COVID-19 patients. Intensive Care Med. Exp. 2023, 11, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Bao, C.; Yang, Z.; Liu, S.; Sun, Y.; Cao, W.; Wang, T.; Schwantes-An, T.H.; Choy, J.S.; Naidu, S.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 spike protein induces IL-18-mediated cardiopulmonary inflammation via reduced mitophagy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degen, W.G.J.; Van Zuilekom, H.I.; Scholtes, N.C.; Van Daal, N.; Schijns, V.E.J.C. Potentiation of humoral immune responses to vaccine antigens by recombinant chicken IL-18 (rChIL-18). Vaccine 2005, 23, 4212–4218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakano, H.; Tsutsui, H.; Terada, M.; Yasuda, K.; Matsui, K.; Yumikura-Futatsugi, S.; Yamanaka, K.I.; Mizutani, H.; Yamamura, T.; Nakanishi, K. Persistent secretion of IL-18 in the skin contributes to IgE response in mice. Int. Immunol. 2003, 15, 611–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| n = 90 | |
|---|---|
| Sex | |
| Female | 67 (74.44%) |
| Male | 23 (25.56%) |
| Age (years) | |
| Median [IQR] | 47.00 [43.00; 53.00] |
| MS type | |
| Relapsing remitting MS (RRMS) | 78 (86.67%) |
| Secondary progressive MS (SPMS) | 12 (13.33%) |
| EDSS | |
| Median [IQR] | 1.50 [0.00; 3.88] |
| Time since symtomps onset | |
| Median [IQR] | 13.00 [8.00, 20.00] |
| Time since MS diagnosis | |
| Median [IQR] | 11.50 [6.00, 19.00] |
| First-line DMT | 46 (51.11%) |
| Interferon | 20 (22.22%) |
| Copaxone | 0 (0.0%) |
| Teriflonomide | 6 (6.67%) |
| Dimethyl fumarate | 20 (22.22%) |
| Second-line DMT | 44 (48.89%) |
| Cladribine | 5 (5.56%) |
| Fingolimod | 6 (6.67%) |
| Alemtuzumab | 7 (7.78%) |
| Natalizumab | 8 (8.89%) |
| Ocrelizumab | 11 (12.22%) |
| Rituximab | 7 (7.78%) |
| Cytokines | Seropositive (Median Levels) | Seronegative (Median Levels) | p | Rank Biserial Correlation (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL-1 | 18.29 | 17.95 | 0.659 | −0.078 (−0.395, 0.255) |
| IFN-α | 8.69 | 8.25 | 0.659 | −0.254 (−0.536, 0.08) |
| IL-6 | 12.82 | 13.89 | 0.061 | −0.325 (−0.589, 0.002) |
| IFN-γ | 3.92 | 4.56 | 0.231 | −0.208 (−0.501, 0.127) |
| TNF-α | 5.19 | 6.96 | 0.359 | −0.16 (−0.462, 0.176) |
| MCP-1 | 352.21 | 432.53 | 0.091 | −0.293 (−0.566, 0.038) |
| IL-8 | 41.03 | 41.57 | 0.384 | −0.152 (−0.456, 0.184) |
| IL-10 | 5.51 | 6.85 | 0.049 | −0.34 (−0.6, −0.015) |
| IL-12 | 3.31 | 3.78 | 0.174 | −0.236 (−0.523, 0.098) |
| IL-17 | 1.35 | 1.58 | 0.183 | −0.231 (−0.531, 0.12) |
| IL-18 | 200.22 | 252.45 | 0.372 | −0.156 (−0.459, 0.18) |
| IL-23 | 3.77 | 7.88 | 0.025 | −0.393 (−0.638, −0.076) |
| IL-33 | 21.46 | 29.67 | 0.838 | −0.036 (−0.362, 0.298) |
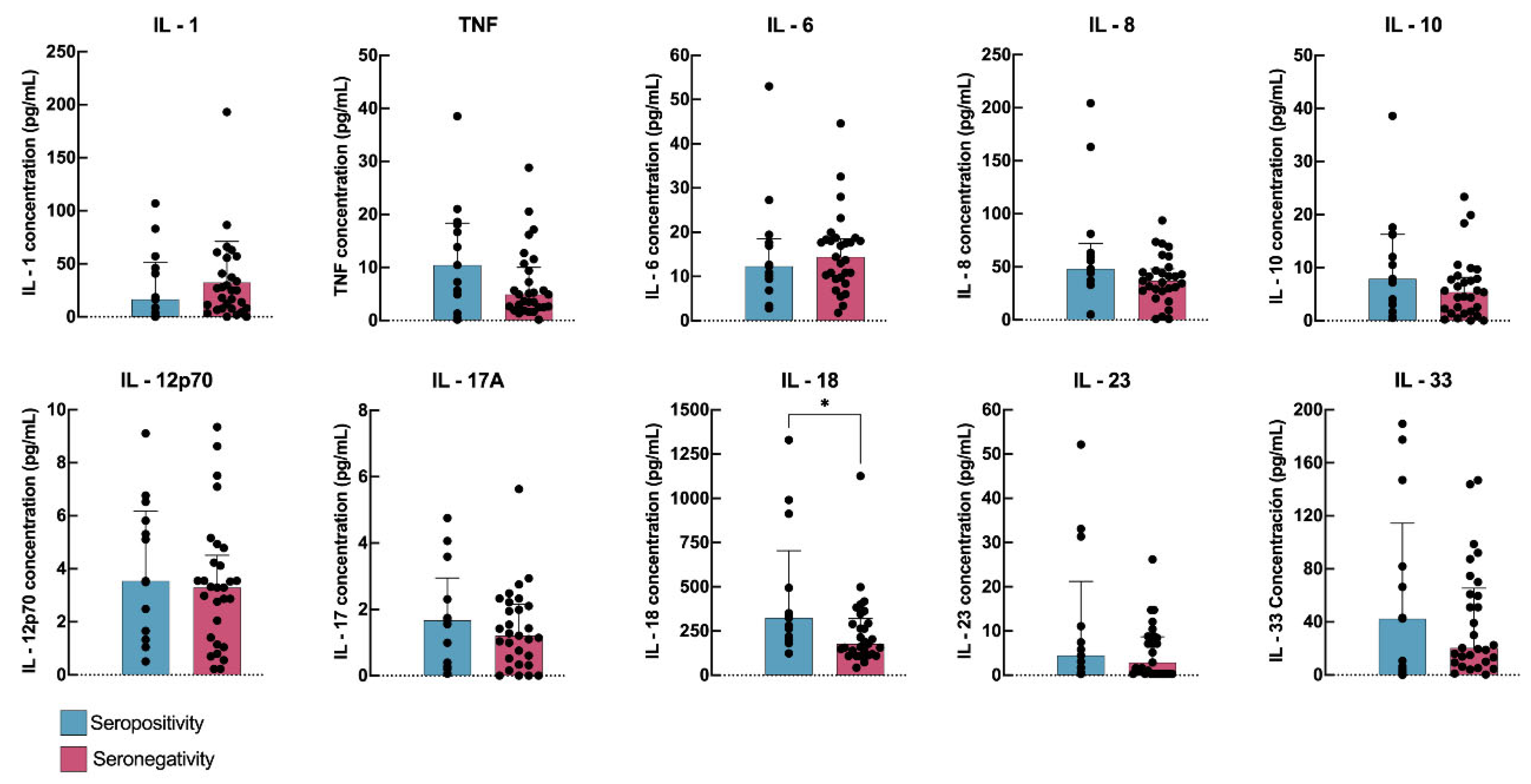
| Cytokines Median (IQR) | Seropositive | Seronegative | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| IL-1 | 16.39 (1.15–51.58) | 24.91 (7.64–48.25) | 0.5495 |
| IFN-α | 6.656 (1.429–21.75) | 8.391 (3.476–15.54) | 0.8561 |
| IL-6 | 12.28 (8.15–18.53) | 14.43 (9.62–18.55) | 0.5585 |
| IFN-γ | 5.5 (0.955–9.8) | 3.8 (2.125–9.81) | 0.783 |
| TNF-α | 10.45 (3.12–18.34) | 4.90 (2.49–10.01) | 0.1609 |
| MCP-1 | 326 (206.3–871) | 390.6 (270.5–498.1) | 0.5724 |
| IL-8 | 48.23 (35.21–72.33) | 36.89 (27.30–48.12) | 0.0759 |
| IL-10 | 7.88 (2.37–16.27) | 5.37 (1.55–8.18) | 0.2062 |
| IL-12 | 3.54 (1.50–6.17) | 3.29 (1.28–4.51) | 0.455 |
| IL-17 | 2.95 (1.67–4.76) | 2.16 (1.21–5.63) | 0.4884 |
| IL-18 | 324.60 (208.10–703.70) | 177.60 (116.00–320.30) | 0.0193 ** |
| IL-23 | 4.45 (1.13–21.24) | 2.90 (0.30–8.71) | 0.3222 |
| IL-33 | 42.41 (3.31–114.40) | 20.36 (9.68–65.46) | 0.9946 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sancho-Saldaña, A.; Gil-Sánchez, A.; Quirant-Sánchez, B.; Boigues, M.; Canudes, M.; Peralta, S.; Solana, M.J.; González-Mingot, C.; Quibus, L.; Martínez-Cáceres, E.; et al. Profile of Cytokines Associated with SARS-CoV2 Seropositivity in Multiple Sclerosis Patients and Its Persistence over Six Months. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3736. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113736
Sancho-Saldaña A, Gil-Sánchez A, Quirant-Sánchez B, Boigues M, Canudes M, Peralta S, Solana MJ, González-Mingot C, Quibus L, Martínez-Cáceres E, et al. Profile of Cytokines Associated with SARS-CoV2 Seropositivity in Multiple Sclerosis Patients and Its Persistence over Six Months. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(11):3736. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113736
Chicago/Turabian StyleSancho-Saldaña, Agustín, Anna Gil-Sánchez, Bibiana Quirant-Sánchez, Marc Boigues, Marc Canudes, Silvia Peralta, María José Solana, Cristina González-Mingot, Laura Quibus, Eva Martínez-Cáceres, and et al. 2025. "Profile of Cytokines Associated with SARS-CoV2 Seropositivity in Multiple Sclerosis Patients and Its Persistence over Six Months" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 11: 3736. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113736
APA StyleSancho-Saldaña, A., Gil-Sánchez, A., Quirant-Sánchez, B., Boigues, M., Canudes, M., Peralta, S., Solana, M. J., González-Mingot, C., Quibus, L., Martínez-Cáceres, E., Torres, P., Hervás, J. V., Moreno-Magallon, J., & Brieva, L. (2025). Profile of Cytokines Associated with SARS-CoV2 Seropositivity in Multiple Sclerosis Patients and Its Persistence over Six Months. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(11), 3736. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113736






