Exploring Pulmonary Dysfunction in Parkinson’s Disease: The Role of Impulse Oscillometry—A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.3. Data Extraction
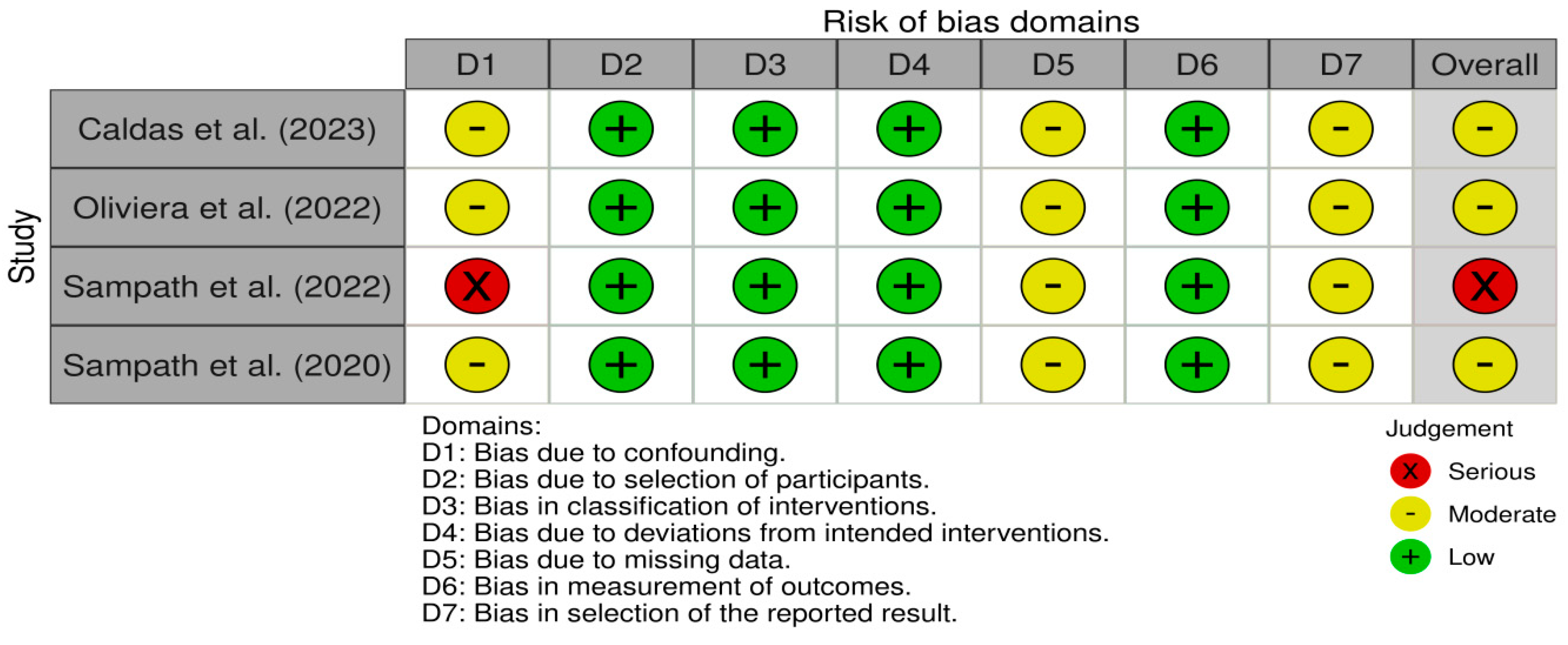
2.4. Risk of Bias
3. Results
3.1. Search
3.2. Description of Selected Studies
3.3. Risk of Bias Assessment
4. Discussions
4.1. Overview of Respiratory Dysfunction in PD
4.2. Spirometry and the Challenge of Effort-Dependent Testing
4.3. IOS as an Alternative Tool in PD Respiratory Assessment
4.4. Evidence from IOS Studies in PD
4.5. Limitations of the Studies
4.6. Implications for Future Research
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zafar, S.; Yaddanapudi, S.S. Parkinson Disease [Internet]; Nih.gov; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Kouli, A.; Torsney, K.M.; Kuan, W.-L. Parkinson’s Disease: Etiology, Neuropathology, and Pathogenesis. In Parkinson’s Disease: Pathogenesis and Clinical Aspects, [Internet]; Stoker, T.B., Greenland, J.C., Eds.; Codon Publication: Brisbane, Australia, 2018; Chapter 1; pp. 3–26. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK536722/ (accessed on 26 March 2025).
- World Health Organization. Parkinson Disease [Internet]; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023; Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/parkinson-disease (accessed on 27 March 2025).
- Gupta, S.; Shukla, S. Non-motor symptoms in Parkinson’s disease: Opening new avenues in treatment. Curr. Res. Behav. Sci. 2021, 2, 100049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, M.B.; Lang, A.; Poewe, W. Toward a redefinition of Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2012, 27, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGeer, P.L.; McGeer, E.G. Glial reactions in Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2008, 23, 474–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alster, P.; Madetko-Alster, N.; Otto-Ślusarczyk, D.; Migda, A.; Migda, B.; Struga, M.; Friedman, A. Role of Orexin in Pathogenesis of Neurodegenerative Parkinsonisms. Neurol. Neurochir. Polska 2023, 57, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkinson, J. An essay on the shaking palsy. J. Neuropsychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2002, 14, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabaté, M.; González, I.; Ruperez, F.; Rodríguez, M. Obstructive and restrictive pulmonary dysfunctions in Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurol. Sci. 1996, 138, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Arrigo, A.; Floro, S.; Bartesaghi, F.; Casellato, C.; Papa, G.F.S.; Centanni, S.; Priori, A.; Bocci, T. Respiratory Dysfunction in Parkinson’s Disease: A Narrative Review. ERJ Open Res. 2020, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owolabi, L.F.; Nagoda, M.; Babashani, M. Pulmonary function tests in patients with Parkinson’s disease: A case-control study. Niger. J. Clin. Pract. 2016, 19, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polatli, M.; Akyol, A.; Çildaǧ, O.; Bayülkem, K. Pulmonary Function Tests in Parkinson’s Disease. Eur. J. Neurol. 2001, 8, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldas, B.T.; Ribeiro, F.C.V.; Pereira, J.S.; Souza, W.C.; Lopes, A.J.; de Melo, P.L. Oscillometry of the respiratory system in Parkinson’s disease: Physiological changes and diagnostic use. BMC Pulm. Med. 2023, 23, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, H.; Reinhold, P.; Goldman, M. Forced oscillation technique and impulse oscillometry. Eur. Respir. Monogr. 2005, 31, 72–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desiraju, K.; Agrawal, A. Impulse oscillometry: The state-of-art for lung function testing. Lung India 2016, 33, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gartman, E.J. Pulmonary Function Testing in Neuromuscular and Chest Wall Disorders. Clin. Chest Med. 2018, 39, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira, R.T.; dos Santos, F.M.; Ramos, A.G.; Seki, K.L.M.; Müller, P.d.T.; Christofoletti, G. Pulmonary function and medication effect in mild-stage subjects with Parkinson’s disease. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2022, 80, 1233–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sampath, M.; Bade, G.; Goyal, V.; Srivastava, A.K.; Jaryal, A.K.; Deepak, K.K.; Talwar, A. Respiratory Dysfunction in Parkinson’s Disease: Relation with Dysautonomia. Ann. Indian Acad. Neurol. 2022, 25, 683–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sampath, M.; Srivastava, A.K.; Goyal, V.; Jaryal, A.K.; Deepak, K.K.; Talwar, A. Effect of Disease Severity on Respiratory Impedance in Parkinson’s Disease. Ann. Neurosci. 2020, 27, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Dugger, B.N.; Dickson, D.W. Pathology of Neurodegenerative Diseases. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2017, 9, a028035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Aquino, Y.C.; Cabral, L.M.; Miranda, N.C.; Naccarato, M.C.; Falquetto, B.; Moreira, T.S.; Takakura, A.C. Respiratory Disorders of Parkinson’s Disease. J. Neurophysiol. 2022, 127, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrino, R.; Viegi, G.; Brusasco, V.; Crapo, R.O.; Burgos, F.; Casaburi, R.; Coates, A.; Van Der Grinten, C.P.M.; Gustafsson, P.; Hankinson, J.; et al. Interpretative Strategies for Lung Function Tests. Eur. Respir. J. 2005, 26, 948–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.R.; Hankinson, J.; Brusasco, V.; Burgos, F.; Casaburi, R.; Coates, A.; Crapo, R.; Enright, P.; Van Der Grinten, C.P.M.; Gustafsson, P.; et al. Standardisation of Spirometry. Eur. Respir. J. 2005, 26, 319–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falsetti, L.; Viticchi, G.; Zaccone, V.; Tarquinio, N.; Nobili, L.; Nitti, C.; Salvi, A.; Moroncini, G.; Silvestrini, M. Chronic Respiratory Diseases and Neurodegenerative Disorders: A Primer for the Practicing Clinician. Med. Princ. Pract. 2021, 30, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Palma, J.; Kaufmann, H. Treatment of autonomic dysfunction in Parkinson disease and other synucleinopathies. Mov. Disord. 2018, 33, 372–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bogaard, J.M.; Hovestadt, A.; Meerwaldt, J.; Meché, F.G.A.V.D.; Stigt, J. Maximal Expiratory and Inspiratory Flow-Volume Curves in Parkinson’s Disease. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1989, 139, 610–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fromageot, C.; Lofaso, F.; Annane, D.; Falaize, L.; Lejaille, M.; Clair, B.; Gajdos, P.; Raphaël, J.C. Supine Fall in Lung Volumes in the Assessment of Diaphragmatic Weakness in Neuromuscular Disorders. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2001, 82, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Noord, J.A.; Demedts, M.; Clement, J.; Cauberghs, M.; Van de Woestijne, K.P. Effect of Rib Cage and Abdominal Restriction on Total Respiratory Resistance and Reactance. J. Appl. Physiol. 1986, 61, 1736–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Mehta, A.; Xiao, B.; Chaudhuri, K.R.; Tan, E.-K.; Tan, L.C.S. Parkinson’s disease subtypes: Approaches and clinical implications. Park. Relat. Disord. 2024, 130, 107208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
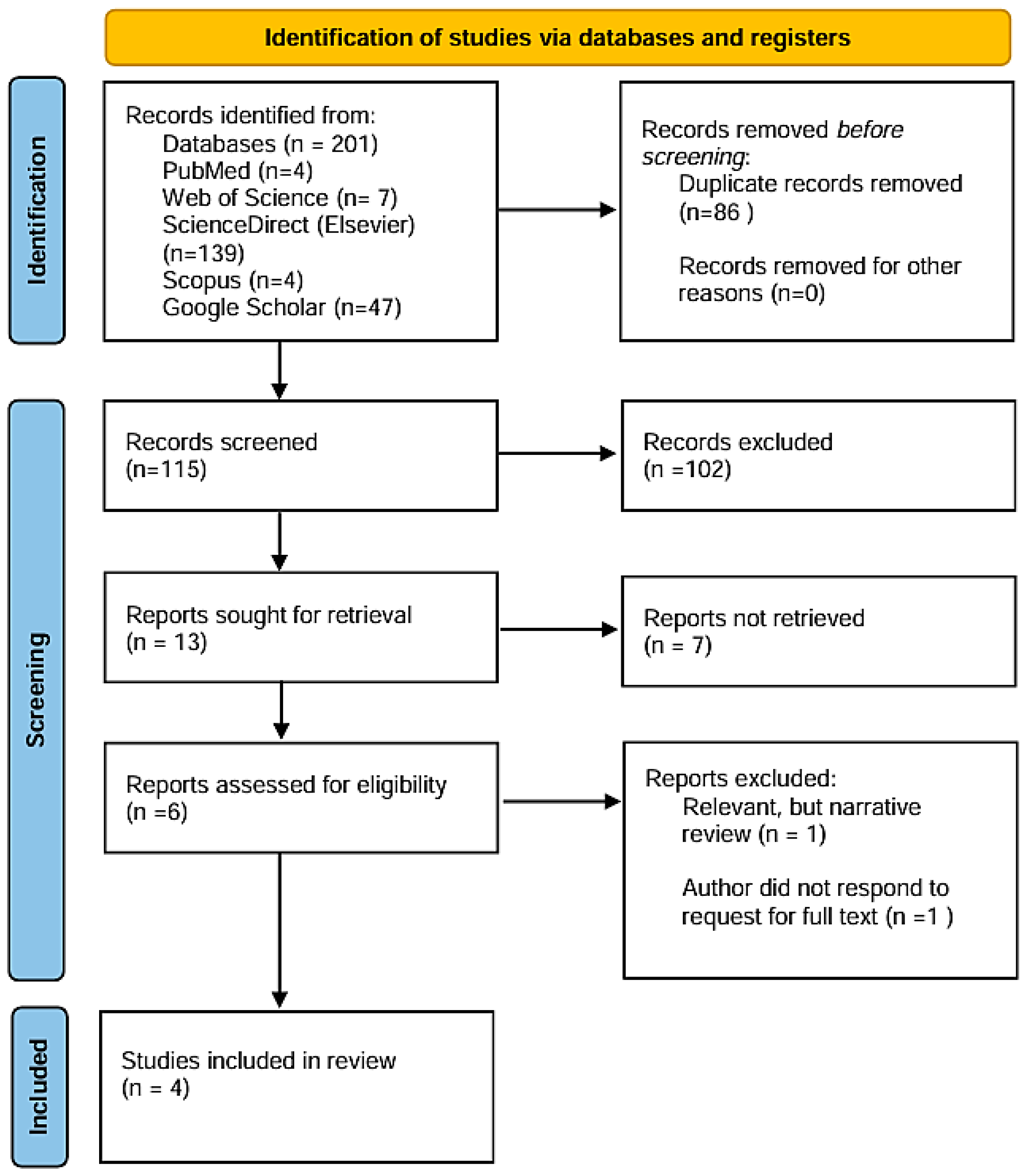
| Database | Search String Used | Articles Retrieved |
|---|---|---|
| PubMed | (“Parkinson” AND “oscillometry” AND “pulmonary function”) OR (“Parkinson” AND “impedance” AND “lung function”) | 4 |
| Web of Science | 7 | |
| Scopus | 4 | |
| ScienceDirect (Elsevier) | 139 | |
| Google Scholar | 47 |
| Authors | Year | Study Designs | Population | PD Stage | Technique | Main Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Caldas et al. [13] | 2023 | Observational, Cross-sectional | 47 patients with PD, 20 controls | I–III H&Y | IOS, Spirometry, Manovacuometry | IOS detects early peripheral airway changes in PD; correlates with muscle weakness and has high diagnostic accuracy (AUC > 0.85) |
| Oliviera et al. [18] | 2022 | Observational, Cross-sectional | 21 patients with PD, 20 controls | I–II H&Y | IOS, Spirometry | IOS values were within normal range in mild-stage PD; spirometry showed signs of incipient obstructive disorder; levodopa had minimal effect on pulmonary function |
| Sampath et al. [19] | 2022 | Observational, Cross-sectional | 30 PD patients | I–II HY | IOS, Spirometry, HRV * | Increased R20 correlated with HRV indices, indicating autonomic dysfunction; IOS detected changes between disease stages |
| Sampath et al. [20] | 2020 | Observational, Cross-sectional | 30 PD patients | I–II H&Y | IOS, Spirometry | R5 and R20 increased with disease severity; negative correlation with FEV1 and PEF, suggesting IOS is more sensitive than spirometry |
| Feature | Spirometry | IOS |
|---|---|---|
| Measurement Type | Effort-dependent; requires maximal inspiration/expiration | Effort-independent; measured during tidal breathing |
| Main Parameters | FEV1, FVC, FEV1/FVC, PEFR | R5, R20, R5–R20, X5, AX, Fres |
| Assesses | Global ventilatory capacity, obstruction, restriction | Airway resistance and reactance (central and peripheral) |
| Sensitivity to Early Dysfunction | Limited, especially in early or subclinical stages | High; detects subtle peripheral airway impairment |
| Motor Requirement | High; affected by tremor, rigidity and fatigue | Low; suitable for patients with motor impairments |
| Use in Autonomic Assessment | Not applicable | Correlates with heart rate variability in PD |
| Interpretive Complexity | Widely familiar across clinical disciplines | Requires specialized understanding of impedance metrics |
| Clinical Pattern in PD (Study) | Expected Spirometry Findings | Expected IOS Changes | IOS Superior? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mild to moderate PD and smokers—Caldas et al., 2023 [13] | ↓ FVC, ↓ PEF with disease progression | ↑ Rp in early PD, ↑Fr in moderate PD; ↓ Cdyn | Yes—identifies progressive dysfunction and stratifies by stage |
| Mild PD (“on/off” Levodopa)—Oliveira et al., 2022 [18] | Incipient obstructive changes (↓ FEV1/FVC, ↓ PEF) | No significant IOS changes between groups | Partial—spirometry more sensitive in this context |
| Autonomic dysfunction (HRV correlation)—Sampath et al., 2022 [19] | Not reported in detail; focused on HRV | ↑ R20 positively correlated with HRV indices; ↓ X5 in some cases | Yes—reveals autonomic modulation of airway resistance |
| Early vs. Mild PD (H&Y I vs. II)—Sampath et al., 2020 [20] | Often normal; no significant change across stages | ↑ R5, ↑ R20 in stage II; R5 negatively correlated with FEV1, PEF | Yes—detects subclinical changes before spirometry |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gache, A.-C.; Danteș, E.; Mocanu, E.; Postu, A.-C.; Opariuc-Dan, C.; Axelerad, A. Exploring Pulmonary Dysfunction in Parkinson’s Disease: The Role of Impulse Oscillometry—A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3730. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113730
Gache A-C, Danteș E, Mocanu E, Postu A-C, Opariuc-Dan C, Axelerad A. Exploring Pulmonary Dysfunction in Parkinson’s Disease: The Role of Impulse Oscillometry—A Systematic Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(11):3730. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113730
Chicago/Turabian StyleGache, Alexandra-Cristiana, Elena Danteș, Elena Mocanu, Andreea-Cristina Postu, Cristian Opariuc-Dan, and Any Axelerad. 2025. "Exploring Pulmonary Dysfunction in Parkinson’s Disease: The Role of Impulse Oscillometry—A Systematic Review" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 11: 3730. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113730
APA StyleGache, A.-C., Danteș, E., Mocanu, E., Postu, A.-C., Opariuc-Dan, C., & Axelerad, A. (2025). Exploring Pulmonary Dysfunction in Parkinson’s Disease: The Role of Impulse Oscillometry—A Systematic Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(11), 3730. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113730