Comparative Clinical Outcomes and Safety of Generic Versus Original Imatinib in the Treatment of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: A Real-World Cohort Study from Thailand
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Treatment Response and Depth of Response
3.3. Event-Free and Overall Survival
3.4. Adverse Events
4. Discussion
4.1. Baseline Characteristics
4.2. Response Outcomes
4.3. Event-Free Survival (EFS) and Overall Survival (OS)
4.4. Limitations
4.5. Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACAs | Additional cytogenetic abnormalities |
| AEs | Adverse events |
| AP | Accelerated phase |
| BP | Blastic phase |
| CCyR | Complete cytogenetic response |
| CHR | Complete hematologic response |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| CML | Chronic myeloid leukemia |
| CSMBS | Civil Servant Medical Benefit Scheme |
| ECOG | Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group |
| EFS | Event-free survival |
| ELN | European LeukemiaNet |
| ELTS | EUTOS Long-Term Survival |
| FISH | Fluorescence in situ hybridization |
| GIST | Gastrointestinal stromal tumor |
| HR | Hazard ratio |
| IQR | Interquartile range |
| MMR | Major molecular response |
| OS | Overall survival |
| PCR | Polymerase chain reaction |
| Ph | Philadelphia chromosome |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| SSS | Social Security Scheme |
| TKI | Tyrosine kinase inhibitor |
| UCS | Universal Coverage Scheme |
| WBC | White blood cell |
References
- Thompson, P.A.; Kantarjian, H.M.; Cortes, J.E. Diagnosis and Treatment of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia in 2015. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2015, 90, 1440–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O'Brien, S.G.; Guilhot, F.; Larson, R.A.; Gathmann, I.; Baccarani, M.; Cervantes, F.; Cornelissen, J.J.; Fischer, T.; Hochhaus, A.; Hughes, T.; et al. Imatinib compared with interferon and low-dose cytarabine for newly diagnosed chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 994–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hochhaus, A.; Larson, R.A.; Guilhot, F.; Radich, J.P.; Branford, S.; Hughes, T.P.; Baccarani, M.; Deininger, M.W.; Cervantes, F.; Fujihara, S.; et al. Long-Term Outcomes of Imatinib Treatment for Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 917–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eskazan, A.E.; Elverdi, T.; Yalniz, F.F.; Salihoglu, A.; Ar, M.C.; Aydin, S.O.; Baslar, Z.; Aydin, Y.; Tuzuner, N.; Ozbek, U.; et al. The efficacy of generic formulations of imatinib mesylate in the treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia. Leuk. Lymphoma 2014, 55, 2935–2937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.X.; Qin, Y.Z.; Lai, Y.Y.; Huang, X.J.; Jiang, Q. A comparison of efficacy and safety between Chinese generic imatinib versus branded imatinib in patients with newly-diagnosed chronic myeloid leukemia in the chronic phase: A single-center prospective cohort study. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi 2016, 55, 922–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danthala, M.; Gundeti, S.; Kuruva, S.P.; Puligundla, K.C.; Adusumilli, P.; Karnam, A.P.; Bala, S.; Konatam, M.L.; Maddali, L.S.; Digumarti, R.R. Generic Imatinib in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: Survival of the Cheapest. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2017, 17, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Zhi, L.T.; Hou, M.; Wang, J.X.; Wu, D.P.; Huang, X.J. Comparison of generic and original imatinib in the treatment of newly diagnosed patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia in chronic phase: A multicenter retrospective clinical study. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi 2017, 38, 566–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lejniece, S.; Udre, I.; Rivkina, A. Generic imatinib in the treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia: Two years’ experience in Latvia. Exp Oncol. 2017, 39, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou Dalle, I.; Kantarjian, H.; Burger, J.; Estrov, Z.; Ohanian, M.; Verstovsek, S.; Ravandi, F.; Borthakur, G.; Garcia-Manero, G.; Jabbour, E.; et al. Efficacy and safety of generic imatinib after switching from original imatinib in patients treated for chronic myeloid leukemia in the United States. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 6559–6565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalzulli, E.; Colafigli, G.; Latagliata, R.; Pepe, S.; Diverio, D.; Stocchi, F.; Di Prima, A.; Efficace, F.; Martelli, M.; Foà, R.; et al. Switch from branded to generic imatinib: Impact on molecular responses and safety in chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia patients. Ann Hematol. 2020, 99, 2773–2777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erçalışkan, A.; Seyhan Erdoğan, D.; Eşkazan, A.E. Current evidence on the efficacy and safety of generic imatinib in CML and the impact of generics on health care costs. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 3344–3353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phukan, A.; Mandal, P.K.; Dolai, T.K. Efficacy and safety profile of generic imatinib in patients with newly diagnosed chronic myeloid leukemia-chronic phase: Sharing experience of a hemato-oncology center from eastern India. Ann Hematol. 2021, 100, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dou, X.L.; Yu, L.; Qin, Y.Z.; Shi, H.X.; Lai, Y.Y.; Hou, Y.; Huang, X.J.; Jiang, Q. Comparison of the efficacy and safety of Chinese generic imatinib and branded imatinib in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia in consideration of demographic characteristics. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi 2019, 40, 924–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, X.; Qin, Y.; Lai, Y.; Shi, H.; Huang, X.; Jiang, Q. Comparable Efficacy and Safety of Generic Imatinib and Branded Imatinib in Patients With Newly Diagnosed Chronic Myeloid Leukemia With a Consideration of Socioeconomic Characteristics: A Retrospective Study From a Single Center. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2020, 20, e304–e315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suttorp, M.; Metzler, M.; Millot, F.; Shimada, H.; Bansal, D.; Günes, A.M.; Kalwak, K.; Sedlacek, P.; Baruchel, A.; Biondi, A.; et al. Generic formulations of imatinib for treatment of Philadelphia chromosome-positive leukemia in pediatric patients. Pediatr. Blood Cancer. 2018, 65, e27431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagnano, K.B.; Fava, C.; Miranda, E.C.; Bendit, I.; Seguro, F.S.; Magalhaes, G.H.; Clementino, N.D.; Conchon, M.; Gonçalves, N.N.; Gaidano, G.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Generic Imatinib Compared to Glivec in Chronic Phase—Chronic Myeloid Leukemia—A Multicenter, Observational Study. Blood 2018, 132, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baccarani, M.; Deininger, M.W.; Rosti, G.; Hochhaus, A.; Soverini, S.; Apperley, J.F.; Cervantes, F.; Clark, R.E.; Cortes, J.E.; Guilhot, F.; et al. European LeukemiaNet recommendations for the management of chronic myeloid leukemia: 2013. Blood 2013, 122, 872–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochhaus, A.; Baccarani, M.; Silver, R.T.; Schiffer, C.; Apperley, J.F.; Cervantes, F.; Clark, R.E.; Cortes, J.E.; Deininger, M.W.; Guilhot, F.; et al. European LeukemiaNet 2020 recommendations for treating chronic myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2020, 34, 966–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tantiworawit, A.; Kongjarern, S.; Rattarittamrong, E.; Lekawanvijit, S.; Bumroongkit, K.; Boonma, N.; Rattanathammethee, T.; Hantrakool, S.; Chai-Adisaksopha, C.; Norasetthada, L.; et al. Diagnosis and Monitoring of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: Chiang Mai University Experience. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2016, 17, 2159–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fucharoen, S.; Winichagoon, P. Haemoglobinopathies in southeast Asia. Indian J. Med. Res. 2011, 134, 498–506. [Google Scholar]
- Fabarius, A.; Leitner, A.; Hochhaus, A.; Müller, M.C.; Hanfstein, B.; Haferlach, C.; Göhring, G.; Schlegelberger, B.; Jotterand, M.; Reiter, A.; et al. Impact of additional cytogenetic aberrations at diagnosis on prognosis of CML: Long-term observation of 1151 patients from the randomized CML Study IV. Blood 2011, 118, 6760–6768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, E.; de Kraa, R.; Louw, A.; Cooney, J.P. High incidence of minor and micro breakpoints in Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia with additional cytogenetic abnormalities at diagnosis—The Western Australian series. Leuk Res Rep. 2022, 18, 100344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tashfeen, S.; Mahmood, R.; Khan, S.A.; Khadim, T. Additional chromosomal abnormalities in Philadelphia positive chronic myeloid leukemia. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2020, 36, 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hehlmann, R.; Lauseker, M.; Voskanyan, A.; Fabarius, A.; Haferlach, C.; Hochhaus, A.; Saußele, S. Impact of emerging ACA on survival in chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). Leukemia 2022, 36, 2544–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, R.E.; Apperley, J.F.; Copland, M.; Cicconi, S. Additional chromosomal abnormalities at chronic myeloid leukemia diagnosis predict an increased risk of progression. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 1102–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Baseline Characteristics | Total (n = 71) | Original Imatinib (n = 46) | Generic Imatinib (n = 25) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex, n (%) Male Female | 39 (54.9) 32 (45.1) | 25 (54.4) 21 (45.6) | 14 (56.0) 11 (44.0) | 0.894 |
| Age, years (median (IQR)) | 40 (33–54) | 38.5 (33–49) | 50 (33–66) | 0.061 |
| ECOG Performance Status, n (%) 0 1 | 46 (64.8) 25 (35.2) | 33 (71.7) 13 (28.3) | 13 (52.0) 12 (48.0) | 0.096 |
| Hemoglobin at diagnosis, g/dL (mean ± SD) | 9.7 ± 2.6 | 9.9 ± 2.5 | 9.3 ± 2.6 | 0.404 |
| Initial white blood cell count, ×109/L (median (IQR)) | 165.1 (90.4–336.1) | 137.4 (90.4–284.4) | 209.5 (105.7–350.2) | 0.354 |
| Platelet, ×109/L (median (IQR)) | 527 (257–784) | 542 (268–997) | 495 (257–650) | 0.204 |
| Sokal Score, n (%) Low Intermediate High | 20 (28.2) 17 (23.9) 34 (47.9) | 17 (37.0) 10 (21.7) 19 (41.3) | 3 (12.0) 7 (28.0) 15 (60.0) | 0.086 |
| ELTS Score, n (%) Low Intermediate High | 30 (42.2) 20 (28.2) 21 (29.6) | 23 (50.0) 12 (26.1) 11 (23.9) | 7 (28.0) 8 (32.0) 10 (40.0) | 0.176 |
| BCR::ABL1 fusion gene (n = 60) e13a2 (b2a2) e14a2 (b3a2) Others | 21 (35.0) 37 (61.7) 2 (3.3) | 16 (41.0) 23 (59.0) 0 (0.0) | 5 (23.8) 14 (66.7) 2 (9.5) | 0.103 |
| ACA, n (%) Major route abnormality, n (%) | 9 (12.7) 4 (5.6) | 4 (8.7) 3 (6.5) | 5 (20.0) 1 (4.0) | 0.160 0.559 |
| Healthcare Scheme, n (%) CSMBS UCS SSS | 8 (11.3) 49 (69.0) 14 (19.7) | 6 (13.1) 30 (65.2) 10 (21.7) | 2 (8.0) 19 (76.0) 4 (16.0) | 0.686 |
| Follow-up Period, months (median (IQR)) | 80.3 (52.0–106.4) | 97.9 (81.7–115.4) | 44.6 (29.9–54.5) | <0.001 |
| Outcome Category | Timepoint | Original Imatinib (n = 46) | Generic Imatinib (n = 25) | p-Value Compare at Each Timepoint | Repeated Measure p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CHR, n (%) | 3 months | 45 (97.8) | 24 (96.0) | >0.999 | 0.487 |
| 6 months | 46 (100.0) | 25 (100.0) | >0.999 | ||
| 12 months | 45 (100.0) | 25 (100.0) | >0.999 | ||
| CCyR, n (%) | 3 months | 11 (23.9) | 8 (32.0) | 0.462 | <0.001 |
| 6 months | 23 (50.0) | 12 (48.0) | 0.872 | ||
| 12 months | 33 (73.3) | 17 (70.8) | 0.825 | ||
| MMR, n (%) | 3 months | 0 (0.0) | 1 (4.0) | 0.352 | <0.001 |
| 6 months | 5 (10.9) | 2 (8.0) | >0.999 | ||
| 12 months | 16 (35.6) | 10 (41.7) | 0.618 | ||
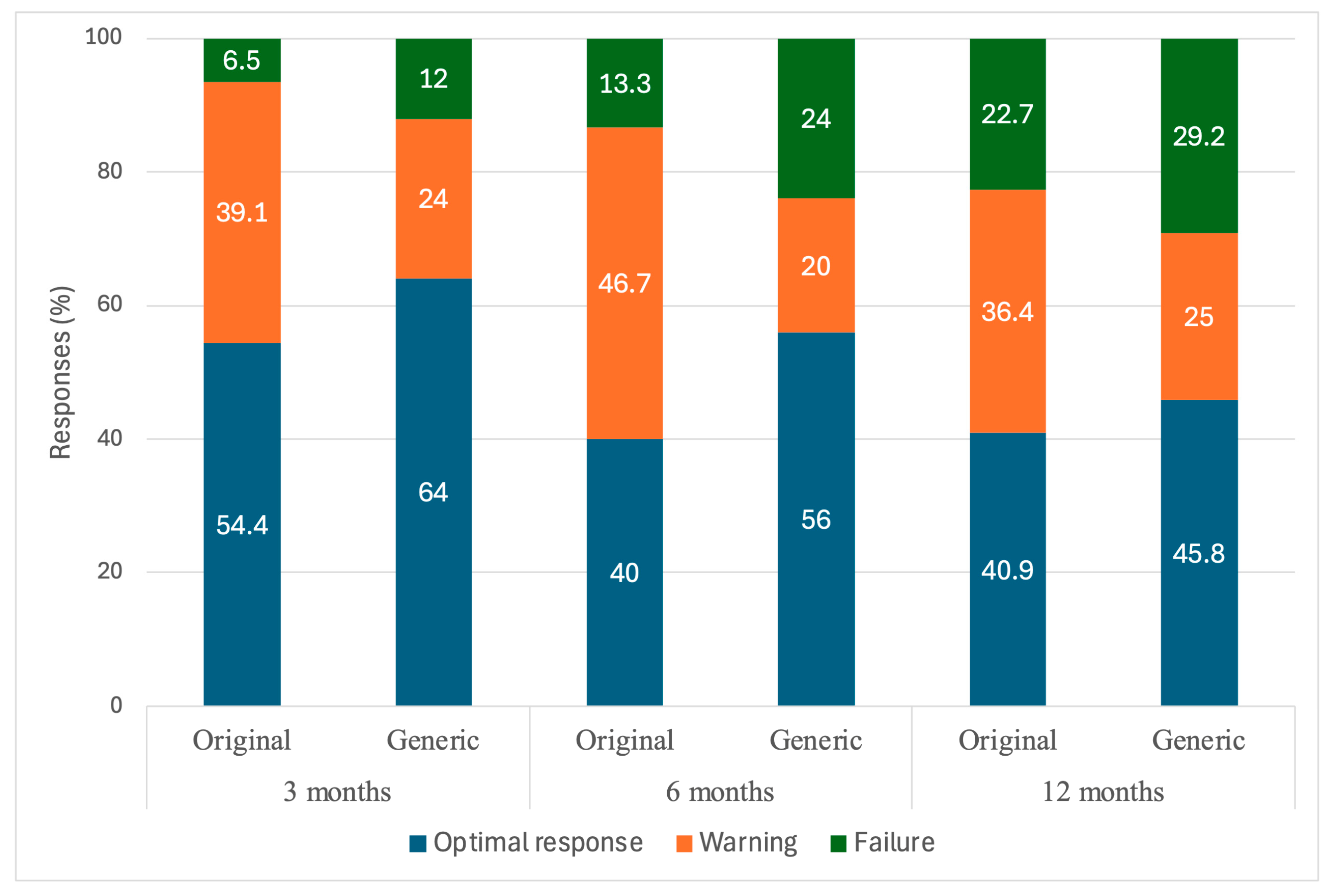
| ELN 2013 Response Outcomes, n (%) | |||||
| 3 months | 25 (54.4) | 16 (64.0) | 0.352 | 0.249 |
| 18 (39.1) | 6 (24.0) | ||||
| 3 (6.5) | 3 (12.0) | ||||
| 6 months | 18 (40.0) | 14 (56.0) | 0.080 | |
| 21 (46.7) | 5 (20.0) | ||||
| 6 (13.3) | 6 (24.0) | ||||
| 12 months | 18 (40.9) | 11 (45.8) | 0.617 | |
| 16 (36.4) | 6 (25.0) | ||||
| 10 (22.7) | 7 (29.2) | ||||
| Switched to 2nd generation TKI, n (%) | 3 months | 2 (4.4) | 1 (4.0) | >0.999 | 0.009 |
| 6 months | 7 (15.0) | 7 (28.0) | 0.196 | ||
| 12 months | 11 (24.4) | 7 (29.2) | 0.670 | ||
| Variables | Total n = 71 | Total Event n = 23 | Event, n (%) | Total Death n = 7 | Death, n (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR | 95% CI | p-Value | HR | 95% CI | p-Value | ||||
| Sex Male Female | 39 32 | 12 (30.8) 11 (34.4) | Ref 1.09 | 0.48–2.47 | 0.834 | 3 (7.5) 4 (12.5) | Ref 1.95 | 0.43–8.89 | 0.390 |
| Age at diagnosis, years (median (IQR)) | 40 (33–54) | 47 (30–57) | 1.02 | 0.99–1.05 | 0.190 | 49 (33–75) | 1.07 | 1.01–1.13 | 0.019 |
| ECOG 0 1 | 46 25 | 13 (28.3) 10 (40.0) | Ref 1.76 | 0.77–4.03 | 0.178 | 3 (6.5) 4 (16.0) | Ref 3.44 | 0.75–15.73 | 0.110 |
| Sokal Score Low Intermediate High | 20 17 34 | 7 (35.0) 7 (41.2) 9 (26.5) | Ref 1.35 0.78 | 0.47–3.85 0.29–2.09 | 0.577 0.620 | 1 (5.0) 3 (17.7) 3 (8.8) | Ref 4.09 2.16 | 0.42–39.66 0.22–20.83 | 0.224 0.505 |
| ELTS Score Low Intermediate High | 30 20 21 | 9 (30.0) 8 (40.0) 6 (28.6) | Ref 1.57 0.86 | 0.61–4.09 0.36–2.84 | 0.351 0.986 | 1 (3.3) 4 (20.0) 2 (9.5) | Ref 6.38 3.43 | 0.71–57.71 0.31–37.94 | 0.099 0.314 |
| ACAs Major route abnormality | 9 (12.7) 4 (5.6) | 7 (30.4) 2 (8.7) | 7.13 2.14 | 2.87–17.74 0.50–9.18 | <0.001 0.304 | 4 (57.1) 2 (28.6) | 11.92 6.49 | 2.65–53.68 1.25–33.63 | 0.001 0.026 |
| Healthcare scheme CSMBS UCS SSS | 8 49 14 | 2 (25.0) 17 (34.7) 4 (28.6) | Ref 1.44 1.18 | 0.33–6.22 0.22–6.42 | 0.629 0.852 | 1 (12.5) 5 (10.2) 1 (7.1) | Ref 0.66 0.46 | 0.07–5.80 0.03–7.60 | 0.706 0.590 |
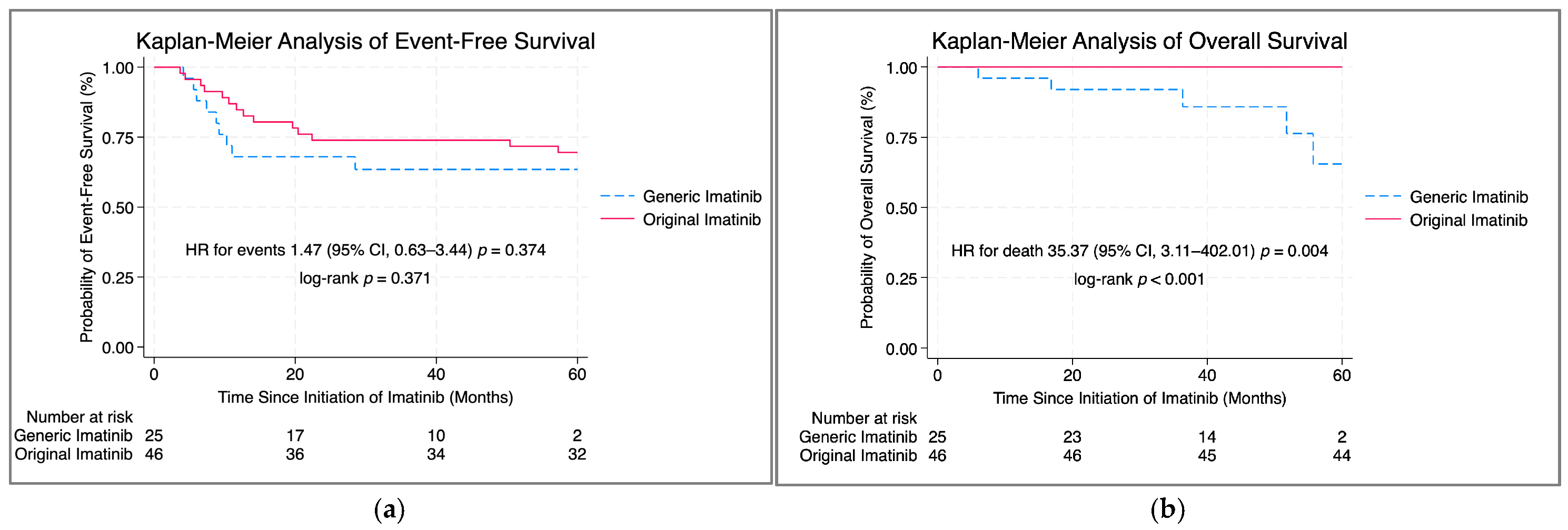
| Imatinib Treatment Original Generic | 46 25 | 14 (30.4) 9 (36.0) | Ref 1.47 | 0.63–3.44 | 0.374 | 2 (4.4) 5 (20.0) | Ref 35.37 | 3.11–402.01 | 0.004 |
| Time to achieve CCyR ≤12 months >12 months | 48 23 | 6 (12.5) 17 (73.9) | Ref 9.36 | 3.63–24.1 | <0.001 | 1 (2.1) 6 (26.1) | Ref 12.99 | 1.56–108.05 | 0.018 |
| Time to achieve MMR ≤12 months >12 months | 16 55 | 2 (12.5) 21 (38.2) | Ref 3.54 | 0.83–15.1 | 0.088 | 1 (6.3) 6 (10.9) | Ref 1.60 | 0.19–13.34 | 0.662 |
| Adverse Event | Total (n = 71) | Original Imatinib (n = 46) | Generic Imatinib (n = 25) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-hematologic events | ||||
| Muscle cramp | 7 (9.9%) | 7 (15.2) | 0 (0.0) | 0.047 |
| Edema | 10 (14.1%) | 5 (10.9) | 5 (20.0) | 0.307 |
| Nausea | 8 (11.3%) | 7 (15.2) | 1 (4.0) | 0.246 |
| Rash | 3 (4.2%) | 2 (4.4) | 1 (4.0) | >0.999 |
| Hematologic events | ||||
| Anemia | 11 (15.5) | 4 (8.7) | 7 (28.0) | 0.043 |
| Thrombocytopenia | 18 (25.4) | 10 (21.7) | 8 (32.0) | 0.342 |
| Leukopenia | 18 (25.4) | 9 (19.6) | 9 (36.0) | 0.128 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tangkitchot, J.; Tantiworawit, A.; Niprapan, P.; Wongsarikan, N.; Srichairatanakool, S.; Punnachet, T.; Hantrakun, N.; Piriyakhuntorn, P.; Rattanathammethee, T.; Chai-Adisaksopha, C.; et al. Comparative Clinical Outcomes and Safety of Generic Versus Original Imatinib in the Treatment of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: A Real-World Cohort Study from Thailand. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3695. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113695
Tangkitchot J, Tantiworawit A, Niprapan P, Wongsarikan N, Srichairatanakool S, Punnachet T, Hantrakun N, Piriyakhuntorn P, Rattanathammethee T, Chai-Adisaksopha C, et al. Comparative Clinical Outcomes and Safety of Generic Versus Original Imatinib in the Treatment of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: A Real-World Cohort Study from Thailand. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(11):3695. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113695
Chicago/Turabian StyleTangkitchot, Jirapath, Adisak Tantiworawit, Piangrawee Niprapan, Nuttanun Wongsarikan, Sirichai Srichairatanakool, Teerachat Punnachet, Nonthakorn Hantrakun, Pokpong Piriyakhuntorn, Thanawat Rattanathammethee, Chatree Chai-Adisaksopha, and et al. 2025. "Comparative Clinical Outcomes and Safety of Generic Versus Original Imatinib in the Treatment of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: A Real-World Cohort Study from Thailand" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 11: 3695. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113695
APA StyleTangkitchot, J., Tantiworawit, A., Niprapan, P., Wongsarikan, N., Srichairatanakool, S., Punnachet, T., Hantrakun, N., Piriyakhuntorn, P., Rattanathammethee, T., Chai-Adisaksopha, C., Rattarittamrong, E., Norasetthada, L., & Hantrakool, S. (2025). Comparative Clinical Outcomes and Safety of Generic Versus Original Imatinib in the Treatment of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: A Real-World Cohort Study from Thailand. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(11), 3695. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113695






