Neutrophil Extracellular Traps in Anti-Neutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-Associated Vasculitis: Diagnostic and Clinical Significance—A Review of the Current Literature
Abstract
1. AAV—Classification, Symptoms, Pathophysiology
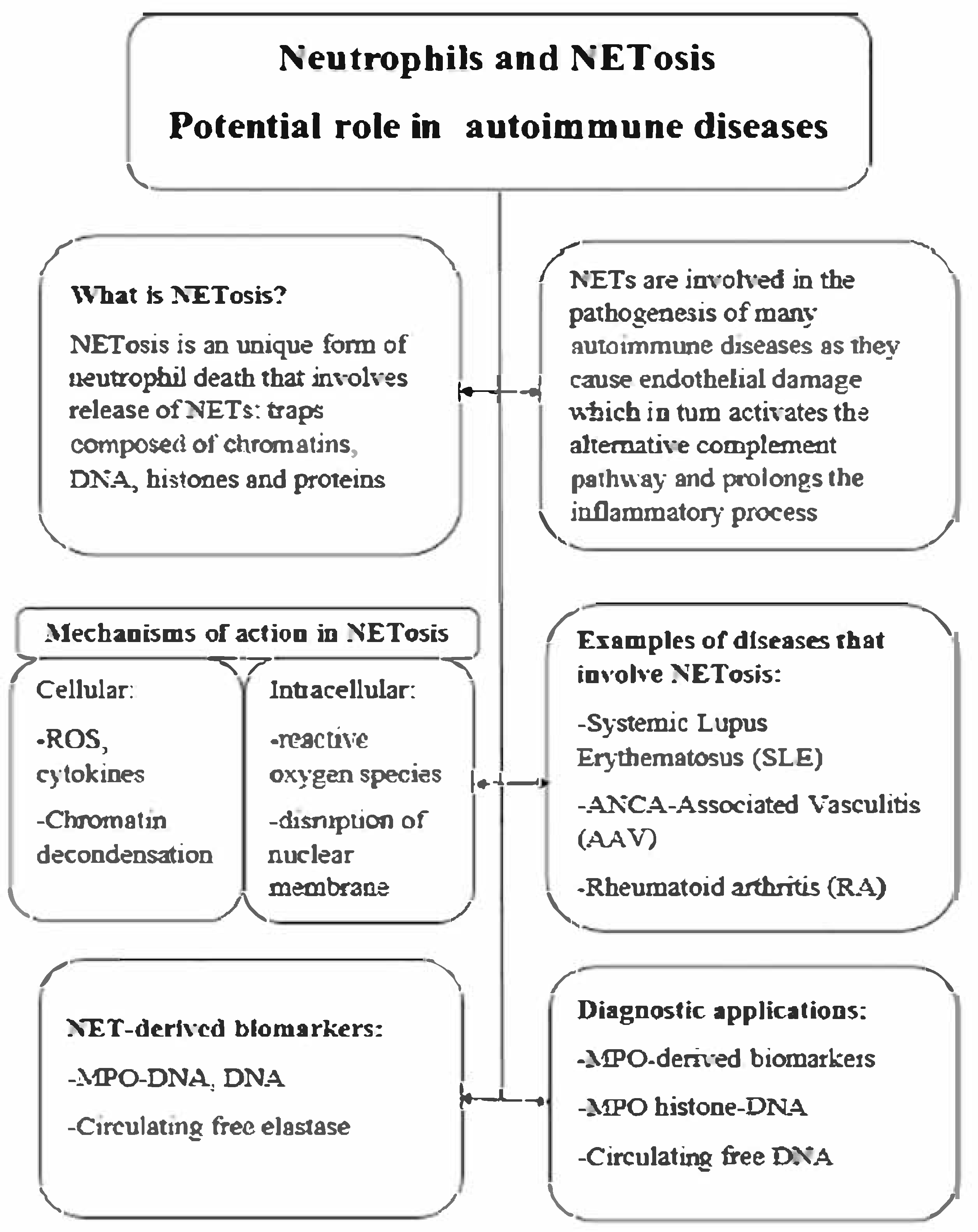
2. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps (NETs)
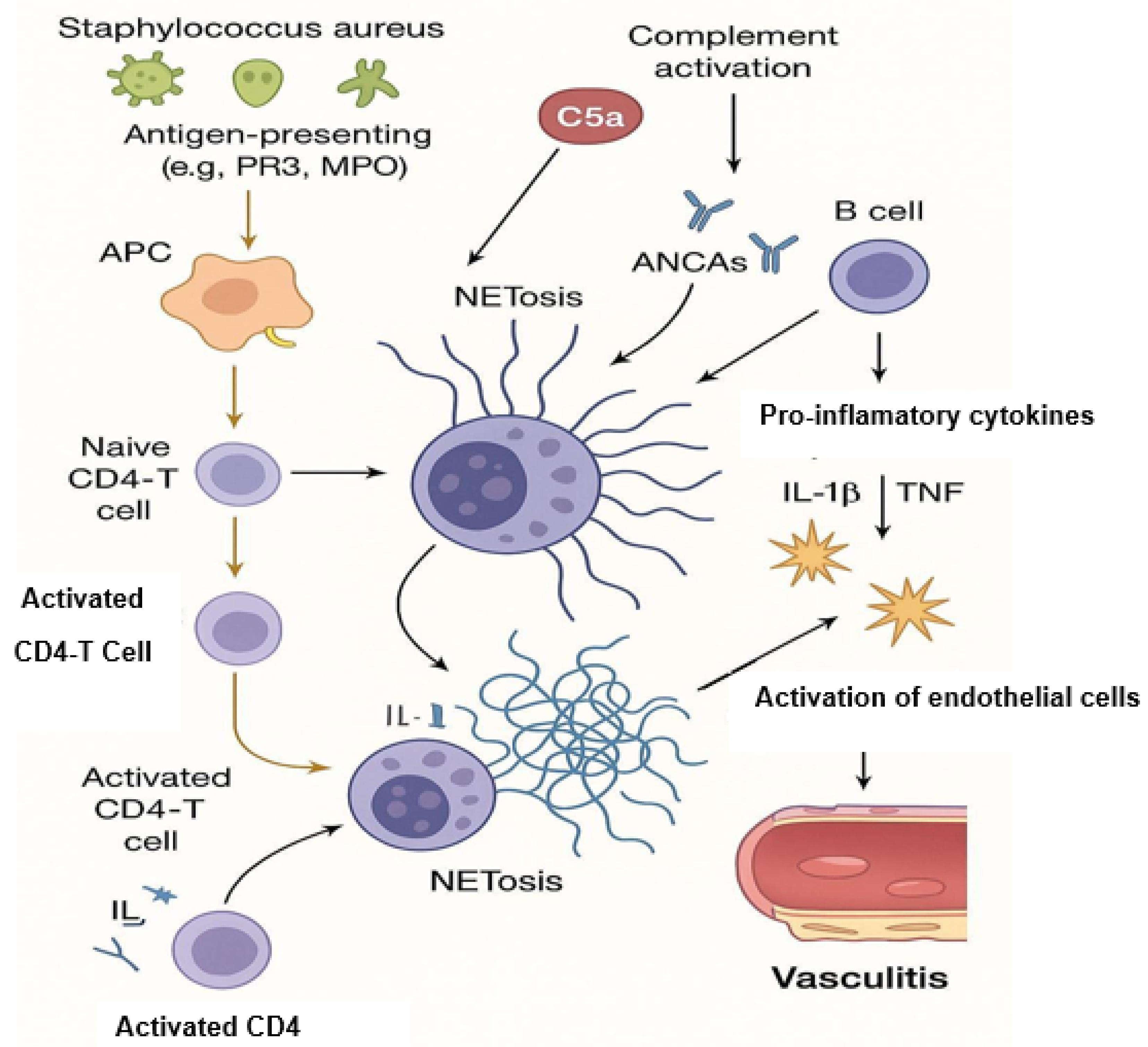
3. NETosis and Its Contribution to AAV Pathogenesis
4. Detection of NETosis—Methods Overview
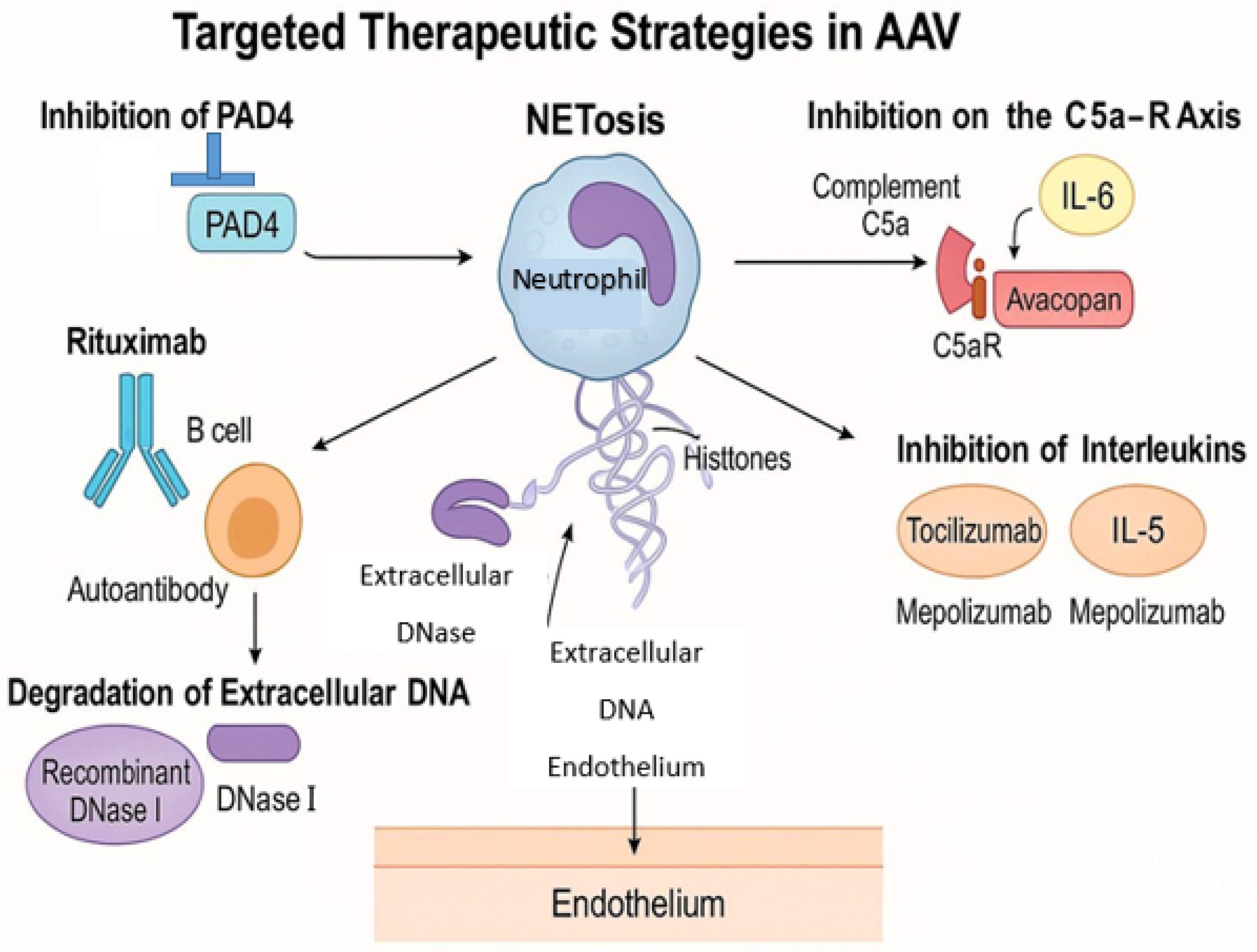
5. Therapeutic Implications and Future Directions
6. Summary
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Watts, R.A.; Mahr, A.; Mohammad, A.J.; Gatenby, P.; Basu, N.; Flores-Suárez, L.F. Classification, epidemiology and clinical subgrouping of antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)-associated vasculitis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2015, 30 (Suppl. S1), i14–i22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitching, A.R.; Anders, H.-J.; Basu, N.; Brouwer, E.; Gordon, J.; Jayne, D.R.; Kullman, J.; Lyons, P.A.; Merkel, P.A.; Savage, C.O.S.; et al. ANCA-associated vasculitis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2020, 6, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boud’Hors, C.; Copin, M.C.; Wacrenier, S.; Piccoli, G.B.; Croue, A.; Augusto, J.-F.; Brilland, B. Histopathological prognostic factors in ANCA-associated glomerulonephritis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2022, 21, 103139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rathmann, J.; Mohammad, A.J. Classification Criteria for ANCA Associated Vasculitis—Ready for Prime Time? Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2024, 26, 332–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berti, A.; Cornec, D.; Crowson, C.S.; Specks, U.; Matteson, E.L. The Epidemiology of Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Autoantibody-Associated Vasculitis in Olmsted County, Minnesota: A Twenty-Year US Population-Based Study. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017, 69, 2338–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Shen, C.; Meng, T.; Lin, W.; Hu, X.; Tang, R.; Xiong, Q.; Ooi, J.D.; Eggenhuizen, P.J.; Chen, J.; et al. Clinical features and prognosis of ANCA-associated vasculitis patients who were double-seropositive for myeloperoxidase-ANCA and proteinase 3-ANCA. Clin. Exp. Med. 2024, 24, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alahmari, H.; Daajani HAl Alsayed, F.; Alrashid, A. ANCA-Associated Vasculitis Clinical Presentation and Clinical Predictors of Relapse in Saudi Arabia. Open Access Rheumatol Res Rev. 2021, 13, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaseen, K.; Mandell, B.F. ANCA associated vasculitis (AAV): A review for internists. Postgrad Med. 2023, 135 (Suppl. S1), 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hruskova, Z.; Stel, V.S.; Jayne, D.; Aasarød, K.; De Meester, J.; Ekstrand, A.; Eller, K.; Heaf, J.G.; Hoitsma, A.; Jimenéz, C.M.; et al. Characteristics and Outcomes of Granulomatosis With Polyangiitis (Wegener) and Microscopic Polyangiitis Requiring Renal Replacement Therapy: Results From the European Renal Association-European Dialysis and Transplant Association Registry. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2015, 66, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrera, C.; Fadeel, B. Macrophage clearance of neutrophil extracellular traps is a silent process. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 2647–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, T.A.; Brill, A.; Duerschmied, D.; Schatzberg, D.; Monestier, M.; Myers, D.D., Jr.; Wrobleski, S.K.; Wakefield, T.W.; Hartwig, J.H.; Wagner, D.D. Extracellular DNA traps promote thrombosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 15880–15885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutton, H.L.; Holdsworth, S.R.; Kitching, A.R. ANCA-Associated Vasculitis: Pathogenesis, Models, and Preclinical Testing. Semin. Nephrol. 2017, 37, 418–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scurt, F.G.; Hirschfeld, V.; Schubert, L.; Mertens, P.R.; Chatzikyrkou, C. Monitoring disease activity in antineutrophil antibody-associated vasculitis. Scand. J. Immunol. 2023, 98, e13284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkmann, V.; Reichard, U.; Goosmann, C.; Fauler, B.; Uhlemann, Y.; Weiss, D.S.; Weinrauch, Y.; Zychlinsky, A. Neutrophil extracellular traps kill bacteria. Science 2004, 303, 1532–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, T.A.; Abed, U.; Goosmann, C.; Hurwitz, R.; Schulze, I.; Wahn, V.; Weinrauch, Y.; Brinkmann, V.; Zychlinsky, A. Novel cell death program leads to neutrophil extracellular traps. J. Cell Biol. 2007, 176, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, S.R.; Ma, A.C.; Tavener, S.A.; McDonald, B.; Goodarzi, Z.; Kelly, M.M.; Patel, K.D.; Chakrabarti, S.; McAvoy, E.; Sinclair, G.D.; et al. Platelet TLR4 activates neutrophil extracellular traps to ensnare bacteria in septic blood. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leffler, J.; Gullstrand, B.; Jönsen, A.; Nilsson, J.; Martin, M.; Blom, A.M.; Bengtsson, A. Degradation of neutrophil extracellular traps co-varies with disease activity in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2013, 15, R84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhns, D.B.; Alvord, W.G.; Heller, T.; Feld, J.J.; Pike, K.M.; Marciano, B.E.; Uzel, G.; DeRavin, S.S.; Priel, D.A.L.; Soule, B.P.; et al. Residual NADPH Oxidase and Survival in Chronic Granulomatous Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 2600–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, M.; Hakkim, A.; Brinkmann, V.; Siler, U.; Seger, R.A.; Zychlinsky, A.; Reichenbach, J. Restoration of NET formation by gene therapy in CGD controls aspergillosis. Blood 2009, 114, 2619–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakkim, A.; Fürnrohr, B.G.; Amann, K.; Laube, B.; Abed, U.A.; Brinkmann, V.; Herrmann, M.; Voll, R.E.; Zychlinsky, A. Impairment of neutrophil extracellular trap degradation is associated with lupus nephritis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 9813–9818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodero, M.P.; Decalf, J.; Bondet, V.; Hunt, D.; Rice, G.I.; Werneke, S.; McGlasson, S.L.; Alyanakian, M.A.; Bader-Meunier, B.; Barneria, C.; et al. Detection of interferon alpha protein reveals differential levels and cellular sources in disease. J. Exp. Med. 2017, 214, 1547–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartl, J.; Serpas, L.; Wang, Y.; Rashidfarrokhi, A.; Perez, O.A.; Sally, B.; Sisirak, V.; Soni, C.; Khodadadi-Jamayran, A.; Tsirigos, A.; et al. Autoantibody-mediated impairment of DNASE1L3 activity in sporadic systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Exp. Med. 2021, 218, e20201138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Yang, P.; Gao, M.; Yu, T.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, M.; Yao, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X. NLRP3 activation induced by neutrophil extracellular traps sustains inflammatory response in the diabetic wound. Clin. Sci. 2019, 133, 565–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, J.; Steiger, S.; Anders, H.-J. Molecular Pathophysiology of Gout. Trends Mol. Med. 2017, 23, 756–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Xie, B.; Yuan, S.; Zhang, J. The “Self-Sacrifice” of ImmuneCells in Sepsis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 833479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, T.; Ueki, S.; Kamide, Y.; Miyabe, Y.; Fukuchi, M.; Yokoyama, Y.; Furukawa, T.; Azuma, N.; Oka, N.; Takeuchi, H.; et al. Increased Circulating Cell-Free DNA in Eosinophilic Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis: Implications for Eosinophil Extracellular Traps and Immunothrombosis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 801897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe-Kusunoki, K.; Nakazawa, D.; Kusunoki, Y.; Kudo, T.; Hattanda, F.; Nishio, S.; Masuda, S.; Tomaru, U.; Kondo, T.; Atsumi, T.; et al. Recombinant thrombomodulin ameliorates autoimmune vasculitis via immune response regulation and tissue injury protection. J. Autoimmun. 2020, 108, 102390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakazawa, D.; Masuda, S.; Tomaru, U.; Ishizu, A. Pathogenesis and therapeutic interventions for ANCA-associated vasculitis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2019, 15, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakazawa, D.; Shida, H.; Tomaru, U.; Yoshida, M.; Nishio, S.; Atsumi, T.; Ishizu, A. Enhanced formation and disordered regulation of NETs in myeloperoxidase-ANCA-associated microscopic polyangiitis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 25, 990–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkmann, V.; Zychlinsky, A. Neutrophil extracellular traps: Is immunity the second function of chromatin? J. Cell Biol. 2012, 198, 773–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.; He, Y.; Li, L.; Li, Y.; Liao, W.; Nie, H.; Gao, P. Identification and validation of immune-associated NETosis subtypes and biomarkers in anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody associated glomerulonephritis. Front Immunol. 2023, 14, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, A.; Rousselle, A.; Becker, J.U.; von Mässenhausen, A.; Linkermann, A.; Kettritz, R. Necroptosis controls NET generation and mediates complement activation, endothelial damage, and autoimmune vasculitis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E9618–E9625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiratori-Aso, S.; Nakazawa, D. The involvement of NETs in ANCA-associated vasculitis. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1261151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heeringa, P.; Rutgers, A.; Kallenberg, C.G.M. The net effect of ANCA on neutrophil extracellular trap formation. Kidney Int. 2018, 94, 14–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dam, L.S.; Kraaij, T.; Kamerling, S.W.A.; Bakker, J.A.; Scherer, U.H.; Rabelink, T.J.; van Kooten, C.; Teng, Y.K.O. Intrinsically Distinct Role of Neutrophil Extracellular Trap Formation in Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody–Associated Vasculitis Compared to Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 2047–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dam, L.S.; Rabelink, T.J.; van Kooten, C.; Teng, Y.K.O. Clinical Implications of Excessive Neutrophil Extracellular Trap Formation in Renal Autoimmune Diseases. Kidney Int. Rep. 2019, 4, 196–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Sha, L.-L.; Ma, T.-T.; Zhang, L.-X.; Chen, M.; Zhao, M.-H. Circulating Level of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Is Not a Useful Biomarker for Assessing Disease Activity in Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-Associated Vasculitis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0148197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Schreiber, A.; Heeringa, P.; Falk, R.J.; Jennette, J.C. Alternative complement pathway in the pathogenesis of disease mediated by anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibodies. Am. J. Pathol. 2007, 170, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konwar, S.; Schroda, S.; Rogg, M.; Kleindienst, J.; Decker, E.L.; Pohl, M.; Zieger, B.; Panse, J.P.; Wang, H.; Grosse, R.; et al. Thrombospondin-1 inhibits alternative complement pathway activation in antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis. J. Clin. Investig. 2025, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Linden, M.; Kumari, S.; van Dalen, S.; Kip, A.; Zwiers, E.; Waaijenberg, K.; Reinieren-Beeren, I.; van Es, H.; Meldrum, E.; Chirivi, R.G.S. Real-Time, High-Throughput Microscopic Quantification of Human Neutrophil Extracellular Trap Release and Assessing the Pharmacology of Antagonists. J. Vis. Exp. 2024, 18, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Linden, M.; Kumari, S.; Montizaan, D.; van Dalen, S.; Kip, A.; Foster, M.; Reinieren-Beeren, I.; Neubert, E.; Erpenbeck, L.; Waaijenberg, K.; et al. Anti-citrullinated histone monoclonal antibody CIT-013, a dual action therapeutic for neutrophil extracellular trap-associated autoimmune diseases. mAbs 2023, 15, 2281763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, S.; Shimizu, S.; Matsuo, J.; Nishibata, Y.; Kusunoki, Y.; Hattanda, F.; Shida, H.; Nakazawa, D.; Tomaru, U.; Atsumi, T.; et al. Measurement of NET formation in vitro and in vivo by flow cytometry. Cytom. Part A J. Int. Soc. Anal. Cytol. 2017, 91, 822–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zharkova, O.; Tay, S.H.; Lee, H.Y.; Shubhita, T.; Ong, W.Y.; Lateef, A.; MacAry, P.A.; Lim, L.H.K.; Connolly, J.E.; Fairhurst, A. A Flow Cytometry-Based Assay for High-Throughput Detection and Quantification of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps in Mixed Cell Populations. Cytom. Part A J. Int. Soc. Anal. Cytol. 2019, 95, 268–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona-Rivera, C.; Kaplan, M.J. Induction and Quantification of NETosis. Curr. Protoc. Immunol. 2016, 115, 14–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozaki, Y. New Insights into Novel Therapeutic Targets in ANCA-Associated Vasculitis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 631055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayne, D.R.W.; Merkel, P.A.; Schall, T.J.; Bekker, P. Avacopan for the Treatment of ANCA-Associated Vasculitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 599–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, J.H.; Merkel, P.A.; Spiera, R.; Seo, P.; Langford, C.A.; Hoffman, G.S.; Kallenberg, C.G.; Clair, E.W.S.; Turkiewicz, A.; Tchao, N.K.; et al. Rituximab versus cyclophosphamide for ANCA-associated vasculitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraaij, T.; Kamerling, S.W.; Bakker, J.; Huizinga, T.W.; Rabelink, T.J.; Kooten, C.; Teng, Y. OP0302 Significant reductions of pathogenic autoantibodies by synergetic rituximab and belimumab treatment effectively inhibits neutrophil extracellular traps in severe, refractory sle—The synbiose study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, J.S.; Carmona-Rivera, C.; Kaplan, M.J. Proteins derived from neutrophil extracellular traps may serve as self-antigens and mediate organ damage in autoimmune diseases. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Chen, Z.; Ruan, F.; Jiang, Y.; Bao, W.; Wu, D.; Chao, L.; Wu, R.; Le, K. Inhibition of PAD4-mediated neutrophil extracellular traps formation attenuates hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in neonatal mice. Exp. Neurol. 2025, 384, 115065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoimenou, M.; Tzoros, G.; Skendros, P.; Chrysanthopoulou, A. Methods for the Assessment of NET Formation: From Neutrophil Biology to Translational Research. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Huang, J.; Zhong, H.; Shen, N.; Faggioni, R.; Fung, M.; Yao, Y. Targeting interleukin-6 in inflammatory autoimmune diseases and cancers. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 141, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wechsler, M.E.; Akuthota, P.; Jayne, D.; Khoury, P.; Klion, A.; Langford, C.A.; Merkel, P.A.; Moosig, F.; Specks, U.; Cid, M.C.; et al. Mepolizumab or Placebo for Eosinophilic Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 1921–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rada, B. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1982, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Peng, J.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, L.; Jin, L.; Han, M.; Su, B.; Li, Y. Emerging therapeutic strategies targeting extracellular histones for critical and inflammatory diseases: An updated narrative review. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1438984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Subtype | ANCA Specificity | Key Clinical Features | Histopathology | Commonly Affected Organs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis (GPA) | PR3-ANCA (c-ANCA); occasionally MPO-ANCA | - Necrotizing granulomatous inflammation - Upper and lower respiratory tract involvement - Necrotizing glomerulonephritis - Nasal crusting, sinusitis, pulmonary nodules | - Necrotizing granulomatous inflammation - Pauci-immune necrotizing vasculitis | Upper/lower respiratory tract, kidneys, eyes, skin, peripheral nerves |
| Microscopic Polyangiitis (MPA) | MPO-ANCA (p-ANCA); occasionally PR3-ANCA | - Rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis - Pulmonary capillaritis - Purpura, mononeuritis multiplex - No granulomatous inflammation | - Pauci-immune necrotizing vasculitis - Necrotizing glomerulonephritis - No granulomas | Kidneys, lungs, skin, peripheral nerves |
| Eosinophilic Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis (EGPA) | MPO-ANCA (p-ANCA) in ~30–40%; often ANCA-negative | - Asthma, allergic rhinitis - Eosinophilia - Pulmonary infiltrates - Cardiac and nerve involvement | - Eosinophil-rich necrotizing granulomas - Necrotizing vasculitis | Lungs, nerves, heart, skin, GI tract |
| ANCA-Negative Vasculitis | None detected | - Similar to other AAV subtypes - Diagnosis based on clinical and histopathological findings | - Findings similar to AAV - ANCA absent | Varies depending on clinical features |
| Method | Principle | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Immunofluorescence Microscopy | Visualization of NETs using fluorescent antibodies targeting NET components (e.g., CitH3, MPO) | High specificity; allows morphological assessment; can be semi-quantitative | Time-consuming; requires specialized equipment and expertise |
| ELISA (e.g., MPO-DNA, CitH3-DNA) | Quantification of NET components in plasma/serum using antibody-based detection | Quantitative; suitable for high-throughput analysis; relatively simple to perform | Potential cross-reactivity; may not distinguish NETs from other sources of cell-free DNA |
| Sytox Green Assay | Detection of extracellular DNA by fluorescence upon binding to DNA | Rapid; cost-effective; suitable for live-cell imaging | Not specific to NETs; cannot differentiate between NETosis and other forms of cell death |
| Flow Cytometry | Measurement of NET-associated markers on neutrophils using fluorescent antibodies | Quantitative; allows analysis of large cell populations; can assess multiple markers simultaneously | Requires cell suspension; may not detect NET structures effectively |
| Confocal Microscopy | High-resolution imaging of NETs in three dimensions | Detailed structural analysis; can confirm co-localization of NET components | Expensive equipment; lower throughput compared to other methods |
| Machine Learning-Based Analysis | Automated identification and quantification of NETs using trained algorithms on imaging data | High-throughput; reduces observer bias; can handle large datasets | Requires computational resources and expertise; dependent on quality of training data |
| Phase | Study Design | Population | Key Findings | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phase I | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled | Healthy volunteers | CIT-013 was well-tolerated up to 0.3 mg/kg IV and 0.9 mg/kg with premedication. Subcutaneous administration showed good bioavailability (~66%) and was well-tolerated. Near-complete inhibition of LPS-induced NETs observed at 0.3 and 0.9 mg/kg doses. | https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/early-clinical-development-of-cit-013-a-first-in-class-netosis-inhibitor-in-a-randomized-phase-i-dose-escalation-study-in-healthy-volunteers-demonstrating-potent-inhibition-of-lps-induced-neutrophil/ (accessed on 27 April 2025) |
| Phase IIa (Planned) | Proof-of-concept | RA and HS patients | Phase IIa studies are planned to commence in 2025 to evaluate efficacy in RA and HS. | https://citryll.com/cit-013-clinical-development/ (accessed on 27 April 2025) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Drożdżal, S.; Gomółka, A.; Opara-Bajerowicz, M.; Lisak, M.; Sielicka, U.; Bąk, K.; Przybyciński, J.; Feret-Adrabińska, W. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps in Anti-Neutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-Associated Vasculitis: Diagnostic and Clinical Significance—A Review of the Current Literature. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3639. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113639
Drożdżal S, Gomółka A, Opara-Bajerowicz M, Lisak M, Sielicka U, Bąk K, Przybyciński J, Feret-Adrabińska W. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps in Anti-Neutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-Associated Vasculitis: Diagnostic and Clinical Significance—A Review of the Current Literature. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(11):3639. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113639
Chicago/Turabian StyleDrożdżal, Sylwester, Aleksandra Gomółka, Martyna Opara-Bajerowicz, Marcin Lisak, Urszula Sielicka, Katarzyna Bąk, Jarosław Przybyciński, and Wiktoria Feret-Adrabińska. 2025. "Neutrophil Extracellular Traps in Anti-Neutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-Associated Vasculitis: Diagnostic and Clinical Significance—A Review of the Current Literature" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 11: 3639. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113639
APA StyleDrożdżal, S., Gomółka, A., Opara-Bajerowicz, M., Lisak, M., Sielicka, U., Bąk, K., Przybyciński, J., & Feret-Adrabińska, W. (2025). Neutrophil Extracellular Traps in Anti-Neutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-Associated Vasculitis: Diagnostic and Clinical Significance—A Review of the Current Literature. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(11), 3639. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113639






