Multimodal Physiotherapist Intervention Program for Physical and Psychological Functioning in Children with Chronic Pain: Guiding Physiotherapy Intervention with the Pediatric Pain Screening Tool with Recommendations for Clinical Practice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Participants
2.3. Recruitment
2.4. Procedure
2.5. Intervention
2.6. Initial Phase
2.7. Intermediate Phase
2.8. Final Phase
2.9. Outcomes
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Clinical Recommendations for Multimodal Physiotherapy Interventions According to Risk Stratification
6. Limitations and Future Directions
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chambers, C.T.; Dol, J.; Tutelman, P.R.; Langley, C.L.; Parker, J.A.; Cormier, B.T.; Macfarlane, G.J.; Jones, G.T.; Chapman, D.; Proudfoot, N.; et al. The prevalence of chronic pain in children and adolescents: A systematic review update and meta-analysis. Pain 2024, 165, 2215–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapos, F.P.; Vandeleur, D.M.; Tham, S.W.; Palermo, T.M.; Groenewald, C.B. Comparing the prevalence of chronic pain in school-aged children in the United States from 2019 to 2020: A nationally representative study examining differences associated with the COVID-19 pandemic. Pain 2024, 165, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miró, J.; Roman-Juan, J.; Sánchez-Rodríguez, E.; Solé, E.; Castarlenas, E.; Jensen, M. Chronic Pain and High Impact Chronic Pain in Children and Adolescents: A Cross-Sectional Study. J. Pain 2023, 24, 812–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faltyn, M.; Cresswell, L.; Van Lieshout, R. Psychological problems in parents of children and adolescents with chronic pain: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychol. Health Med. 2021, 26, 298–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandelli, Y.N.; Chambers, C.T.; Mackinnon, S.P.; Parker, J.A.; Huber, A.M.; Stinson, J.N.; Wildeboer, E.M.; Wilson, J.P.; Piccolo, O. A systematic review of the psychosocial factors associated with pain in children with juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Pediatr. Rheumatol. Online J. 2023, 21, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solé, E.; Sharma, S.; Ferreira-Valente, A.; Pathak, A.; Sánchez-Rodríguez, E.; Jensen, M.P.; Miró, J. The Associations Between Sleep Disturbance, Psychological Dysfunction, Pain Intensity, and Pain Interference in Children with Chronic Pain. Pain Med. 2022, 23, 1106–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solé, E.; Tomé-Pires, C.; de la Vega, R.; Racine, M.; Castarlenas, E.; Jensen, M.P.; Miró, J. Cognitive Fusion and Pain Experience in Young People. Clin. J. Pain 2016, 32, 602–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahrer, N.E.; Montaño, Z.; Gold, J.I. Relations between anxiety sensitivity, somatization, and health-related quality of life in children with chronic pain. J. Pediatr. Psychol. 2012, 37, 808–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zernikow, B.; Wager, J.; Hechler, T.; Hasan, C.; Rohr, U.; Dobe, M.; Meyer, A.; Hübner-Möhler, B.; Wamsler, C.; Blankenburg, M. Characteristics of highly impaired children with severe chronic pain: A 5-year retrospective study on 2249 pediatric pain patients. BMC Pediatr. 2012, 12, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, J.C.; Meldrum, M.; Kim, S.C.; Zeltzer, L.K. Anxiety sensitivity and health-related quality of life in children with chronic pain. J. Pain 2007, 8, 814–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashikar-Zuck, S.; Goldschneider, K.R.; Powers, S.W.; Vaught, M.H.; Hershey, A.D. Depression and functional disability in chronic pediatric pain. Clin. J. Pain 2001, 17, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Alboom, M.; Elmer, T.; Boersma, K.; Forgeron, P.; Baert, F.; Bracke, P.; Goubert, L. Social integration of adolescents with chronic pain: A social network analysis. Pain 2022, 163, 2232–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solé, E.; Roman-Juan, J.; Sánchez-Rodríguez, E.; Castarlenas, E.; Jensen, M.P.; Miró, J. School bullying and peer relationships in children with chronic pain. Pain 2024, 165, 1169–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmer, Z.; Fraser, K.; Grol-Prokopczyk, H.; Zajacova, A. A global study of pain prevalence across 52 countries: Examining the role of country-level contextual factors. Pain 2022, 163, 1740–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forgeron, P.A.; King, S.; Stinson, J.N.; McGrath, P.J.; MacDonald, A.J.; Chambers, C.T. Social functioning and peer relationships in children and adolescents with chronic pain: A systematic review. Pain Res. Manag. 2010, 15, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palermo, T.M.; Holley, A.L. The importance of the family environment in pediatric chronic pain. JAMA Pediatr. 2013, 167, 93–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitschen, A.; Wahidie, D.; Meyer, D.; Rau, L.M.; Ruhe, A.K.; Wager, J.; Zernikow, B.; Sauerland, D. Cost-of-illness and Economic Evaluation of Interventions in Children and Adolescents With Chronic Pain: A Systematic Review. Clin. J. Pain 2024, 40, 306–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruhe, A.-K.; Wager, J.; Linder, R.; Meusch, A.; Pfenning, I.; Zernikow, B. Chronic pain in children and adolescents: An economic perspective. Schmerz 2020, 34, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, E.F.; Palermo, T.M.; Zhou, C.; Groenewald, C.B. Economic Impact of Headache and Psychiatric Comorbidities on Healthcare Expenditures Among Children in the United States: A Retrospective Cross-Sectional Study. Headache 2019, 59, 1504–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Luo, M.; Xi, C.; Lei, Y.; Pan, S.; Gao, X.; Xu, Y.; Huang, G.; Deng, X.; Guo, L.; et al. Cross-sectional study on influence of the family environment on the lifetime non-medical use of prescription drugs among Chinese adolescents in Guangdong: An analysis of sex differences. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e026758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberg, D.; Stevens, G.; Bucksch, J.; Inchley, J.; de Looze, M. Do country-level environmental factors explain cross-national variation in adolescent physical activity? A multilevel study in 29 European countries. BMC Public Health 2019, 19, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Law, E.F.; Groenewald, C.B.; Zhou, C.; Palermo, T.M. Effect on Health Care Costs for Adolescents Receiving Adjunctive Internet-Delivered Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy: Results of a Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Pain 2018, 19, 910–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groenewald, C.B.; Palermo, T.M. The price of pain: The economics of chronic adolescent pain. Pain Manag. 2015, 5, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groenewald, C.B.; Essner, B.S.; Wright, D.; Fesinmeyer, M.D.; Palermo, T.M. The economic costs of chronic pain among a cohort of treatment-seeking adolescents in the United States. J. Pain 2014, 15, 925–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hechler, T.; Ruhe, A.K.; Schmidt, P.; Hirsch, J.; Wager, J.; Dobe, M.; Krummenauer, F.; Boris, Z. Inpatient-based intensive interdisciplinary pain treatment for highly impaired children with severe chronic pain: Randomized controlled trial of efficacy and economic effects. Pain 2014, 155, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamin, J.Z.; Harbeck-Weber, C.; Sim, L. Pain is a family matter: Quality of life in mothers and fathers of youth with chronic pain. Child. Care Health Dev. 2019, 45, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huestis, S.; Kao, G.; Dunn, A.; Hilliard, A.; Yoon, I.A.; Golianu, B.; Bhandari, R.P. Multi-Family Pediatric Pain Group Therapy: Capturing Acceptance and Cultivating Change. Children 2017, 4, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczynski, K.; Gambhir, R.; Caruso, A.; Lebel, A. Depression as a mediator of the relation between family functioning and functional disability in youth with chronic headaches. Headache 2016, 56, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palermo, T.M.; Valrie, C.R.; Karlson, C.W. Family and parent influences on pediatric chronic pain: A developmental perspective. Am. Psychol. 2014, 69, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palermo, T. Impact of recurrent and chronic pain on child and family daily functioning: A critical review of the literature. J. Dev. Behav. Pediatr. 2000, 21, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, C.B.; Li, R.; Kashikar-Zuck, S.; Zhou, C.; Palermo, T.M. Adolescent predictors of young adult pain and health outcomes: Results from a 6-year prospective follow-up study. Pain 2025, 166, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, C.B.; Murphy, L.K.; Jordan, A.; Owens, M.T.; McLeod, D.; Palermo, T.M. Healthcare Transition Among Young Adults With Childhood-Onset Chronic Pain: A Mixed Methods Study and Proposed Framework. J. Pain 2022, 23, 1358–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, C.B.; Groenewald, C.B.; de la Vega, R.; Palermo, T.M. Long-term impact of adolescent chronic pain on young adult educational, vocational, and social outcomes. Pain 2020, 161, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hestbaek, L.; Leboeuf-Yde, C.; Kyvik, K.O.; Manniche, C. The course of low back pain from adolescence to adulthood: Eight-year follow-up of 9600 twins. Spine 2006, 31, 468–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, L.E.; Pate, J.W.; Richardson, P.A.; Ickmans, K.; Wicksell, R.K.; Simon, L.E. Best-Evidence for the Rehabilitation of Chronic Pain Part 1: Pediatric Pain. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 21, 1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley-Wallace, A.; Nowotny, E.; Schoth, D.; Liossi, C. Online multidisciplinary interventions for paediatric chronic pain: A content analysis. Eur. J. Pain 2021, 25, 2140–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, P.; Stinson, J.; Choiniere, M.; Dion, D.; Intrater, H.; LeFort, S.; Lynch, M.; Ong, M.; Rashiq, S.; Tkachuk, G.; et al. Dedicated multidisciplinary pain management centres for children in Canada: The current status. Can. J. Anesth. 2007, 54, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raja, S.N.; Carr, D.B.; Cohen, M.; Finnerup, N.B.; Flor, H.; Gibson, S.; Keefe, F.J.; Mogil, J.S.; Ringkamp, M.; Sluka, K.A.; et al. The revised International Association for the Study of Pain definition of pain: Concepts, challenges, and compromises. Pain 2020, 161, 1976–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simons, L.E.; Logan, D.E.; Chastain, L.; Cerullo, M. Engagement in multidisciplinary interventions for pediatric chronic pain: Parental expectations, barriers, and child outcomes. Clin. J. Pain 2010, 26, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, L.; Roofigari, N.; Faraz, M.; Popov, J.; Moshkovich, M.; Figueiredo, M.; Hartung, E.; Talbo, M.; Lalanne-Mistrih, M.L.; Sherlock, M.; et al. Physical Activity in Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Scoping Review. Pediatr. Exerc. Sci. 2024, 36, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andias, R.; Neto, M.; Silva, A. The effects of pain neuroscience education and exercise on pain, muscle endurance, catastrophizing and anxiety in adolescents with chronic idiopathic neck pain: A school-based pilot, randomized and controlled study. Physiother. Theory Pract. 2018, 34, 682–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neto, M.; Andias, R.; Silva, A. Pain Neuroscience Education and Exercise for Neck Pain: A Focus Group Study on Adolescents’ Views. Pediatr. Phys. Ther. 2018, 30, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdemir, B.C.; Savci, S.; Tanriverdi, A.; Ozcan Kahraman, B.; Isguder, R.; Makay, B.; Unsal, E. Determinants of physical activity level in children and adolescents with juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Z. Rheumatol. 2024, 84, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lodovica, L.M.F.; Francesca, M.; Paolo, P.; Gabriele, T.; Anselmo, C.; Caleb, D.; Cristina, D.; Irene, M.; Alessandro, P. The effects of different levels of sports activity on health-related quality of life and lifestyle habits in high school Italian students. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2024, 183, 4041–4048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento Leite, M.; Kamper, S.J.; O’Connell, N.E.; Michaleff, Z.A.; Fisher, E.; Viana Silva, P.; Williams, C.M.; Yamato, T.P. Physical activity and education about physical activity for chronic musculoskeletal pain in children and adolescents. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2023, 7, Cd013527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, K.M.; Campbell, P.; Lewis, M.; Hill, J.C.; van der Windt, D.A.; Afolabi, E.; Protheroe, J.; Wathall, S.; Jowett, S.; Oppong, R.; et al. Refinement and validation of a tool for stratifying patients with musculoskeletal pain. Eur. J. Pain 2021, 25, 2081–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogbeivor, C.; Elsabbagh, L. Management approach combining prognostic screening and targeted treatment for patients with low back pain compared with standard physiotherapy: A systematic review & meta-analysis. Musculoskelet. Care 2021, 19, 436–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanaway, F.F.; Bell, K.J.L. Challenges of a stratified care approach to musculoskeletal pain. Lancet Rheumatol. 2022, 4, e578–e579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croft, P.; Hill, J.C.; Foster, N.E.; Dunn, K.M.; van der Windt, D.A. Stratified health care for low back pain using the STarT Back approach: Holy grail or doomed to fail? Pain 2024, 165, 2679–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohjankoski, H.; Hietanen, M.; Leppänen, L.; Vilen, H.; Kautiainen, H.; Mikkelsson, M.; Vuorimaa, H. Prolonged, widespread, disabling musculoskeletal pain of adolescents among referrals to the Pediatric Rheumatology Outpatient Clinic from the Päijät-Häme Hospital District in southern Finland. Scand. J. Pain 2018, 18, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuorimaa, H.; Leppänen, L.; Kautiainen, H.; Mikkelsson, M.; Hietanen, M.; Vilen, H.; Pohjankoski, H. Risk severity moderated effectiveness of pain treatment in adolescents. Scand. J. Pain 2019, 19, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holley, A.; Gaultney, W.; Turner, H.; Wilson, A. The Pediatric Pain Screening Tool (PPST) can Rapidly Identify Elevated Pain and Psychosocial Symptomatology in Treatment-Seeking Youth with Acute Musculoskeletal Pain. J. Pain 2022, 23, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamon, K.; Carlson, M.; Hildenbrand, A. Who Gets Referred? A Pilot Study of Risk Stratification and Treatment Referral in Pediatric Headache Using the Pediatric Pain Screening Tool. J. Pediatr. Psychol. 2022, 47, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vroom, D.C.; Rodgers-Melnick, S.N.; Brown, T.; Owusu-Ansah, A.; Dusek, J.A. Pain screening in youth with sickle cell disease: A quality improvement study. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2024, 71, e30912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palermo, T.; Walco, G.; Roy Paladhi, U.; Birnie, K.; Crombez, G.; Vega, R.; Eccleston, C.; Kashikar-Zuck, S.; Stone, A. Core outcome set for pediatric chronic pain clinical trials: Results from a Delphi poll and consensus meeting. Pain 2021, 162, 2539–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbero, F.R.; Miró, J.; Solé, E.; Bordallo, G.C.; Castarlenas, E.; de la Calle García, B.; de la Vega, R.; García, E.M.; Sánchez-Rodríguez, E.; Andrés, A.S. Clinical assessment of chronic pain in children and adolesecents: Recommendations of the working group on pediatric pain of the spanish pain society/Valoración clínica de la población infanto-juvenil con dolor crónico: Recomendaciones del grupo de trabajo de dolor infantil de la sociedad española del dolor. Rev. Soc. Española Dolor 2025, 31, 2–11. [Google Scholar]
- Simons, L.; Smith, A.; Ibagon, C.; Coakley, R.; Logan, D.; Schechter, N.; Borsook, D.; Hill, J. Pediatric Pain Screening Tool rapid identification of risk in youth with pain complaints. Pain 2015, 156, 1511–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heathcote, L.; Rabner, J.; Lebel, A.; Hernandez, J.; Simons, L. Rapid Screening of Risk in Pediatric Headache: Application of the Pediatric Pain Screening Tool. J. Pediatr. Psychol. 2018, 43, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sil, S.; Cohen, L.; Dampier, C. Pediatric pain screening identifies youth at risk of chronic pain in sickle cell disease. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2019, 66, e27538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanasamy, S.; Yang, F.; Ding, L.; Geisler, K.; Glynn, S.; Ganesh, A.; Sathyamoorthy, M.; Garcia, V.; Sturm, P.; Chidambaran, V. Pediatric Pain Screening Tool: A Simple 9-Item Questionnaire Predicts Functional and Chronic Postsurgical Pain Outcomes After Major Musculoskeletal Surgeries. J. Pain 2022, 23, 98–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Gibler, R.; Rheel, E.; Slack, K.; Palermo, T. Recommendations for Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System pediatric measures in youth with chronic pain: A COnsensus-based Standards for the selection of health Measurement INstruments systematic review of measurement properties. Pain 2023, 165, 258–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palermo, T.; Li, R.; Birnie, K.; Crombez, G.; Eccleston, C.; Kashikar-Zuck, S.; Stone, A.; Walco, G. Updated recommendations on measures for clinical trials in pediatric chronic pain: A multiphase approach from the Core Outcomes in Pediatric Persistent Pain (Core-OPPP) Workgroup. Pain 2024, 165, 1086–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, R.R.; Schreiber, K.L.; Dworkin, R.H.; Turk, D.C.; Baron, R.; Freeman, R.; Jensen, T.S.; Latremoliere, A.; Markman, J.D.; Rice, A.S.C.; et al. Optimizing and Accelerating the Development of Precision Pain Treatments for Chronic Pain: IMMPACT Review and Recommendations. J. Pain 2023, 24, 204–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, M.J.L.; Tripp, D.A. Pain Catastrophizing: Controversies, Misconceptions and Future Directions. J. Pain 2024, 25, 575–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crombez, G.; Scott, W.; De Paepe, A.L. Knowing What We Are Talking About: The Case of Pain Catastrophizing. J. Pain 2024, 25, 591–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagnier, J.J.; Kienle, G.; Altman, D.G.; Moher, D.; Sox, H.; Riley, D. The CARE Guidelines: Consensus-based Clinical Case Reporting Guideline Development. Glob. Adv. Health Med. 2013, 2, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, B. Revisions to the IASP definition of pain-What does this mean for children? Paediatr. Neonatal. Pain 2021, 3, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, S.; Wang, S.; Porfyris, S.; Kamasinski-Sol, R.; Steinhorn, D.M. Massage therapy in outpatient pediatric chronic pain patients: Do they facilitate significant reductions in levels of distress, pain, tension, discomfort, and mood alterations? Paediatr. Anaesth. 2008, 18, 884–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceniza-Bordallo, G.; González-Ordi, H.; Varela-Donoso, E. The placebo effect in the treatment of musculoskeletal neck pain: A randomized clinical trial. Clin. Salud 2019, 30, 155–161. [Google Scholar]
- Basson, A.; Olivier, B.; Ellis, R.; Coppieters, M.; Stewart, A.; Mudzi, W. The Effectiveness of Neural Mobilization for Neuromusculoskeletal Conditions: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2017, 47, 593–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Ortega, F.; Lomas-Vega, R.; Hita-Contreras, F.; Plaza Manzano, G.; Achalandabaso, A.; Ramos-Morcillo, A.J.; Martínez-Amat, A. Immediate effects of spinal manipulation on nitric oxide, substance P and pain perception. Man. Ther. 2014, 19, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andias, R.; Sa-Couto, P.; Silva, A. Blended-Learning Pain Neuroscience Education and Exercise in High School Students With Chronic Neck Pain: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Phys. Ther. 2022, 102, pzac048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pas, R.; Rheel, E.; Van Oosterwijck, S.; Foubert, A.; De Pauw, R.; Leysen, L.; Roete, A.; Nijs, J.; Meeus, M.; Ickmans, K. Pain Neuroscience Education for Children with Functional Abdominal Pain Disorders: A Randomized Comparative Pilot Study. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacey, V.; Tofts, L.; Adams, R.; Munns, C.; Nicholson, L. Exercise in children with joint hypermobility syndrome and knee pain: A randomised controlled trial comparing exercise into hypermobile versus neutral knee extension. Pediatr. Rheumatol. Online J. 2013, 11, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rathleff, M.; Rathleff, C.; Holden, S.; Thorborg, K.; Olesen, J. Exercise therapy, patient education, and patellar taping in the treatment of adolescents with patellofemoral pain: A prospective pilot study with 6 months follow-up. Pilot. Feasibility Stud. 2018, 4, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathleff, M.; Roos, E.; Olesen, J.; Rasmussen, S. Exercise during school hours when added to patient education improves outcome for 2 years in adolescent patellofemoral pain: A cluster randomised trial. Br. J. Sports Med. 2015, 49, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Baets, L.; Matheve, T.; Timmermans, A. The Association Between Fear of Movement, Pain Catastrophizing, Pain Anxiety, and Protective Motor Behavior in Persons With Peripheral Joint Conditions of a Musculoskeletal Origin: A Systematic Review. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2020, 99, 941–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashikar-Zuck, S.; Thomas, S.; Bonnette, S.; Gibler, R.C.; DiCesare, C.; Schille, A.; Hulburt, T.; Briggs, M.S.; Ounpuu, S.; Myer, G.D. Comparison of Pain Characteristics, Strength, and Movement Patterns in Adolescents With Juvenile Fibromyalgia and High Versus Low Fear of Movement. J. Pain 2024, 25, 104586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolnough, L.U.; Lentini, L.; Sharififar, S.; Chen, C.; Vincent, H.K. The relationships of kinesiophobia and physical function and physical activity level in juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Pediatr. Rheumatol. Online J. 2022, 20, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandstedt, E.; Fasth, A.; Eek, M.N.; Beckung, E. Muscle strength, physical fitness and well-being in children and adolescents with juvenile idiopathic arthritis and the effect of an exercise programme: A randomized controlled trial. Pediatr. Rheumatol. Online J. 2013, 11, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shear, D.; Harrison, L.E.; O’Brien, S.; Khazendar, Z.; Lyons, S.; Morgan, J.J.; Chan, S.K.; Feinstein, A.B.; Simons, L.E. Rapid Transition to Virtual Assessment and Treatment in an Interdisciplinary Randomized Clinical Trial for Youth With Chronic Pain: Adaptations and Implications for Future Trials. Clin. J. Pain 2022, 38, 459–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuntze, G.; Nesbitt, C.; Whittaker, J.L.; Nettel-Aguirre, A.; Toomey, C.; Esau, S.; Doyle-Baker, P.K.; Shank, J.; Brooks, J.; Benseler, S.; et al. Exercise Therapy in Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2018, 99, 178–193.e171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klepper, S.; Mano Khong, T.; Klotz, R.; Gregorek, A.; Chan, Y.; Sawade, S. Effects of Structured Exercise Training in Children and Adolescents With Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis. Pediatr. Phys. Ther. 2019, 31, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pack, R.; Gilliland, R.; Mecham, A. The treatment of central sensitization in an adolescent using pain neuroscience education and graded exposure to activity: A case report. Physiother. Theory Pract. 2020, 36, 1164–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castarlenas, E.; Jensen, M.P.; von Baeyer, C.L.; Miró, J. Psychometric Properties of the Numerical Rating Scale to Assess Self-Reported Pain Intensity in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review. Clin. J. Pain 2017, 33, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleagle, T.R.; Post, A.A.; Dailey, D.L.; Vance, C.G.T.; Zimmerman, M.B.; Bayman, E.O.; Crofford, L.J.; Sluka, K.A.; Chimenti, R.L. Minimal Clinically Important Change of Movement Pain in Musculoskeletal Pain Conditions. J. Pain 2024, 25, 104507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceniza-Bordallo, G.; Fraile, A.; Martín-Casas, P.; López-de-Uralde-Villanueva, I. Validity and reliability of Spanish PROMIS pediatric pain interference short form. J. Pediatr. Nurs. 2022, 6, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Pérez, L.; López-Martínez, A.E.; Ruiz-Párraga, G.T. Psychometric Properties of the Spanish Version of the Tampa Scale for Kinesiophobia (TSK). J. Pain 2011, 12, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenbloom, B.N.; Pagé, M.G.; Isaac, L.; Campbell, F.; Stinson, J.N.; Cribbie, R.; Katz, J. Fear of movement in children and adolescents undergoing major surgery: A psychometric evaluation of the Tampa Scale for Kinesiophobia. Eur. J. Pain 2020, 24, 1999–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupuis, F.; Cherif, A.; Batcho, C.; Massé-Alarie, H.; Roy, J.S. The Tampa Scale of Kinesiophobia: A Systematic Review of Its Psychometric Properties in People With Musculoskeletal Pain. Clin. J. Pain 2023, 39, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceniza-Bordallo, G.; Gómez Fraile, A.; Martín-Casas, P.; López-de-Uralde-Villanueva, I. Cross-cultural adaptation and psychometric properties of Spanish Child Pain AnxietySymptoms Scale (CPASS). An. Pediatr. 2023, 99, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceniza-Bordallo, G.; Gómez-Fraile, A.; Martín-Casas, P.; López-de-Uralde-Villanueva, I. Validation of Spanish Pain Catastrophizing Scale- Children (PCS-C). An. Pediatr. 2023, 99, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, L.; Sieberg, C.; Carpino, E.; Logan, D.; Berde, C. The Fear of Pain Questionnaire (FOPQ): Assessment of pain-related fear among children and adolescents with chronic pain. J. Pain 2011, 12, 677–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varni, J.; Seid, M.; Rode, C. The PedsQL: Measurement model for the pediatric quality of life inventory. Med. Care 1999, 37, 126–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurst, H.; Bolton, J. Assessing the clinical significance of change scores recorded on subjective outcome measures. J. Manip. Physiol. Ther. 2004, 27, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrar, J.; Young, J.; LaMoreaux, L.; Werth, J.; Poole, M. Clinical importance of changes in chronic pain intensity measured on an 11-point numerical pain rating scale. Pain 2001, 94, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceniza-Bordallo, G.; Li, R.; de-la-vega, R.; Palermo, T.M. Patient Global Impression of Change in Pediatric Chronic Pain Clinical Trials. In Proceedings of the World Congress on Pain (IASP) 2024, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 5–9 August 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences, 2nd ed.; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Publishers: Mahwah, NJ, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- SPSS, Inc. IBM® SPSS® Statistics 28; SPSS: Chicago, IL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Roman-Juan, J.; Ceniza-Bordallo, G.; Sánchez-Rodríguez, E.; Jensen, M.P.; Miró, J. Fatigue, sleep disturbance, and pain interference in children and adolescents with chronic pain: A longitudinal study. Pain 2025, 166, 927–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liossi, C.; Johnstone, L.; Lilley, S.; Caes, L.; Williams, G.; Schoth, D.E. Effectiveness of interdisciplinary interventions in paediatric chronic pain management: A systematic review and subset meta-analysis. Br. J. Anaesth. 2019, 123, e359–e371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trottier, E.D.; Ali, S.; Doré-Bergeron, M.J.; Chauvin-Kimoff, L. Best practices in pain assessment and management for children. Paediatr. Child Health 2022, 27, 429–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahin, R.L. Use of Multimodal Multidisciplinary Pain Management in the US. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2240620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parnell Prevost, C.; Gleberzon, B.; Carleo, B.; Anderson, K.; Cark, M.; Pohlman, K. Manual therapy for the pediatric population: A systematic review. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 19, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Wei, X.; Wang, S. Does cervical spine manipulation reduce pain in people with degenerative cervical radiculopathy? A systematic review of the evidence, and a meta-analysis. Clin. Rehabil. 2016, 30, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dekker, C.; van Haastregt, J.C.M.; Verbunt, J.A.M.C.F.; de Jong, J.R.; van Meulenbroek, T.; Pernot, H.F.M.; van Velzen, A.D.; Bastiaenen, C.H.G.; Goossens, M.E.J.B. Pain-related fear in adolescents with chronic musculoskeletal pain: Process evaluation of an interdisciplinary graded exposure program. Health Serv. Res. 2020, 20, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simons, L.; Kaczynski, K. The Fear Avoidance model of chronic pain: Examination for pediatric application. J. Pain 2012, 13, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danilov, A.; Badaeva, A.; Kosareva, A.; Popovskaya, K.; Novikov, V. State-of-the-Art Personalized Therapy Approaches for Chronic Non-Specific Low Back Pain: Understanding the Mechanisms and Drivers. Pain Ther. 2025, 14, 479–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coronado, R.A.; Brintz, C.E.; McKernan, L.C.; Master, H.; Motzny, N.; Silva, F.M.; Goyal, P.M.; Wegener, S.T.; Archer, K.R. Psychologically informed physical therapy for musculoskeletal pain: Current approaches, implications, and future directions from recent randomized trials. Pain Rep. 2020, 5, e847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcos-Martín, F.; González-Ferrero, L.; Martín-Alcocer, N.; Paris-Alemany, A.; La Touche, R. Multimodal physiotherapy treatment based on a biobehavioral approach for patients with chronic cervico-craniofacial pain: A prospective case series. Physiother. Theory Pract. 2018, 34, 671–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, U.; Treede, R.D.; Sabatowski, R. Multimodal pain therapy in chronic noncancer pain-gold standard or need for further clarification? Pain 2017, 158, 1853–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-de-Las-Peñas, C.; Nijs, J.; Giordano, R.; Arendt-Nielsen, L. Precision management of post-COVID pain: An evidence and clinical-based approach. Eur. J. Pain 2023, 27, 1107–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCracken, L.M. Personalized pain management: Is it time for process-based therapy for particular people with chronic pain? Eur. J. Pain 2023, 27, 1044–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, S.C.; Hofmann, S.G.; Stanton, C.E.; Carpenter, J.K.; Sanford, B.T.; Curtiss, J.E.; Ciarrochi, J. The role of the individual in the coming era of process-based therapy. Behav. Res. Ther. 2019, 117, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickson, C.; de Zoete, R.M.J.; Berryman, C.; Weinstein, P.; Chen, K.K.; Rothmore, P. Patient-related barriers and enablers to the implementation of high-value physiotherapy for chronic pain: A systematic review. Pain Med. 2024, 25, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrosyan, H.; Leonardi, C.; Thakral, A.; Roth, J.; Russoniello, N.; Goldin, Y.; Parikh, S. Barriers and factors associated with adherence to a home exercise program of adults with musculoskeletal pain. J. Back. Musculoskelet. Rehabil. 2024, 37, 473–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joslin, R.; Donovan-Hall, M.; Roberts, L. Meaningful Clinical Outcomes for Young People and Parents When Treated for Chronic Musculoskeletal Pain in the UK: Q Set Development. J. Pain 2024, 25, 104482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caneiro, J.P.; Smith, A.; Bunzli, S.; Linton, S.; Moseley, G.L.; O’Sullivan, P. From Fear to Safety: A Roadmap to Recovery From Musculoskeletal Pain. Phys. Ther. 2022, 102, pzab271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra-Armas, J.; Flores-Cortes, M.; Ceniza-Bordallo, G.; Matamala-Gomez, M. User Experience in Immersive Virtual Reality-Induced Hypoalgesia in Adults and Children Suffering from Pain Conditions. Multimodal Technol. Interact. 2024, 8, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanious, R.; Onghena, P. Randomized Single-Case Experimental Designs in Healthcare Research: What, Why, and How? Healthcare 2019, 7, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundström, F.T.A.; Lavefjord, A.; Buhrman, M.; McCracken, L.M. Are people with chronic pain more diverse than we think? An investigation of ergodicity. Pain 2025. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasny-Pacini, A.; Evans, J. Single-case experimental designs to assess intervention effectiveness in rehabilitation: A practical guide. Ann. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2018, 61, 164–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Armijo-Olivo, S.; Gross, D.P. Single-Case Experimental Design in Rehabilitation: Basic Concepts, Advantages, and Challenges. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2023, 102, 454–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceniza-Bordallo, G.; Gómez Fraile, A.; Martín-Casas, P.; Rabbitts, J.; Li, R.; Palermo, T.; López-de-Uralde-Villanueva, I. Prevalence, pain trajectories, and presurgical predictors for chronic postsurgical pain in a pediatric sample in Spain with a 24-month follow-up. Pain 2025, 166, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

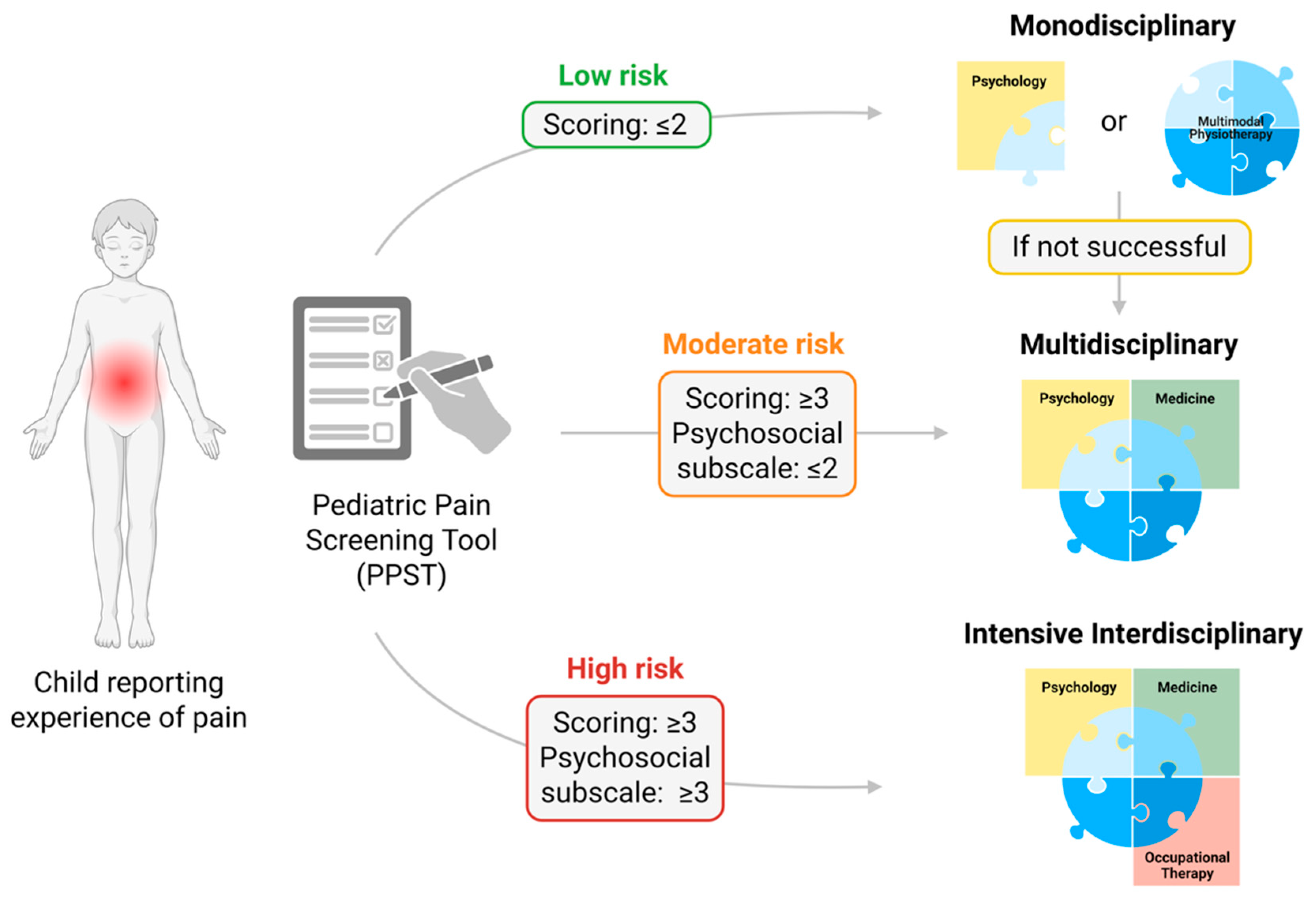

| Phase | Subjective Report | Treatment |
|---|---|---|
|
| |
| Initial phase |
|
|
| Intermediate phase |
|
|
| Final phase |
|
|
| Variables | n (%)/Mean (SD) |
|---|---|
| Age | 13.5 (2.4) |
| Sex | |
| Male | 4 (40%) |
| Female | 6 (60%) |
| Gender | |
| Boy | 4 (40%) |
| Girl | 6 (60%) |
| Race/Ethnicity | |
| White (Caucasian) | 10 (100%) |
| Black (African American) | 0 (0%) |
| Other | 0 (0%) |
| Household income | |
| >100,000 | 0 (0%) |
| 99,999–60,000 | 1 (10%) |
| 59,999–40,000 | 6 (60%) |
| 39,999–29,000 | 3 (30%) |
| <28,999 | 0 (0%) |
| Type of chronic pain | |
| Musculoskeletal chronic pain | 7 (70%) |
| Low back pain | 5 |
| Knee | 2 |
| Chronic headache | 2 (20%) |
| Chronic postsurgical pain | 1 (10%) |
| Variables | All Samples (n = 10) Mean/(SD) | High-Risk Group (n = 6) mean/(SD) | Medium-Risk Group (n = 3) Mean/(SD) | Low-Risk Group (n = 1) Mean/(SD) | Mean Differences * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type of chronic pain | |||||
| Low back pain | 5 | 3 | 2 | 1 | – |
| Knee | 2 | 1 | 1 | – | |
| Chronic headache | 1 | 1 | – | ||
| Chronic postsurgical pain | 1 | 1 | – | ||
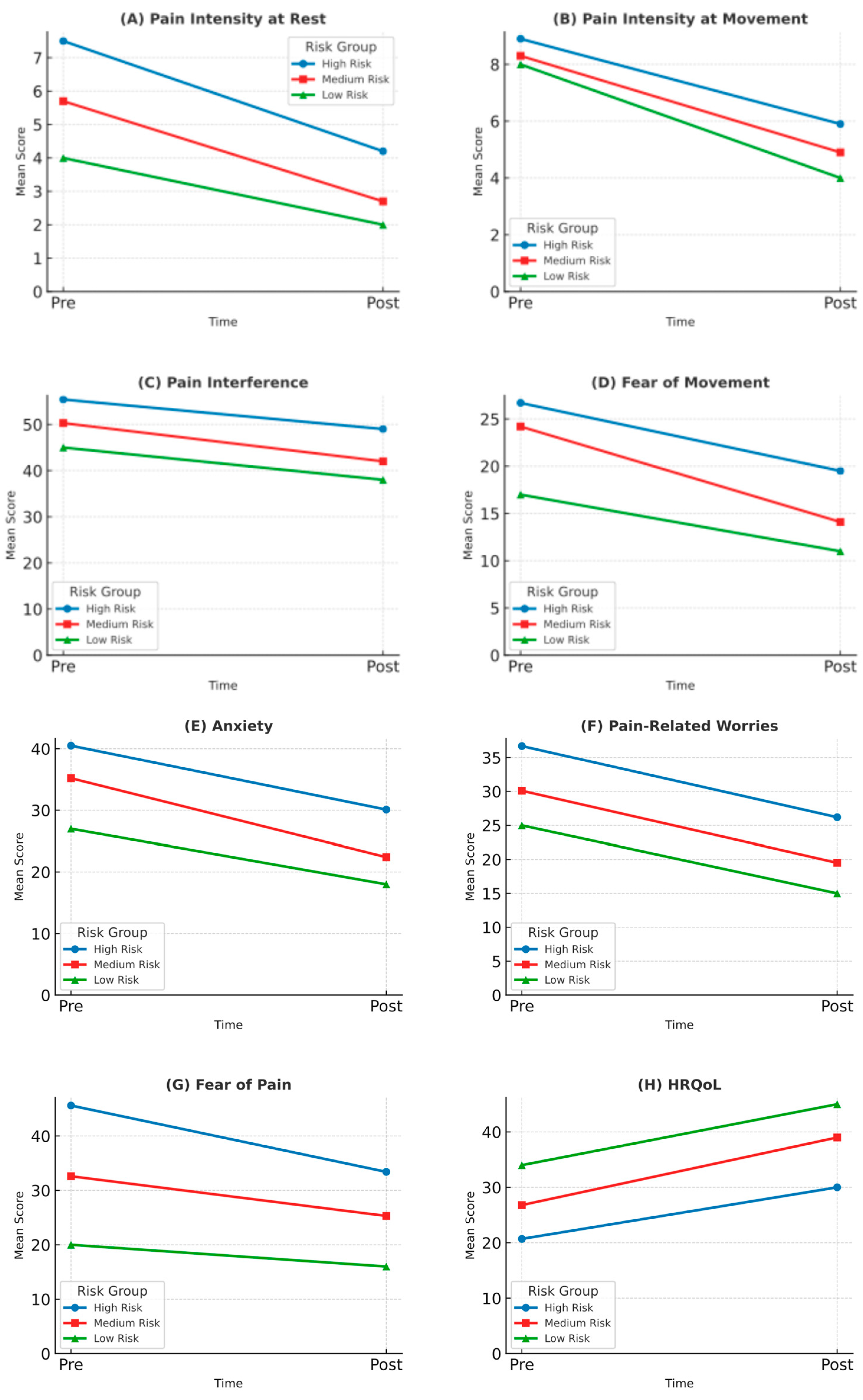
| Pain intensity at rest (NRS) | 6.3 (3.5) | 7.5 (1.3) | 5.7 (2.3) | 4.0 | a–b |
| Pain intensity at movement (NRS-M) | 8.2 (0.5) | 8.9 (1.0) | 8.3 (0.2) | 8.0 | none |
| Pain interference (PROMIS-PPI) | 53.5 (10.3) | 55.4 (7.8) | 50.3 (15.3) | 45.0 | a–b, b–c, a–c |
| Fear of movement (TSK-11) | 20.5 (5.2) | 26.7 (5.2) | 24.2 (5.2) | 17.0 | a–c |
| Anxiety (CPASS) | 34.2 (8.5) | 40.5 (4.3) | 35.2 (4.1) | 27.0 | a–b, b–c, a–c |
| Pain-related worries (PCS-C) | 30.5 (6.5) | 36.7 (2.4) | 30.1 (4.5) | 25.0 | a–b, b–c, a–c |
| Fear of pain (FOPQ-C) | 37.5 (7.9) | 45.6 (3.2) | 32.6 (3.2) | 20.0 | a–b, b–c, a–c |
| HRQoL (PedsQL) | 28.9 (5.6) | 20.7 (5.7) | 26.8 (4.6) | 34.0 | a–c |
| Variables | All Samples (n = 10) Mean/(SD) | High-Risk Group (n = 6) Mean/(SD) | Medium-Risk Group (n = 3) Mean/(SD) | Low-Risk Group (n = 1) Mean/(SD) | Mean Differences * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pain intensity at rest (NRS) | 3.2 (1.8) | 4.2 (1.0) | 2.7 (1.0) | 2.0 | a–b, b–c, a–c |
| Pain intensity at movement (NRS-M) | 5.2 (0.8) | 5.9 (0.7) | 4.9 (0.5) | 4.0 | a–c |
| Pain interference (PROMIS-PPI) | 46.0 (8.2) | 49.0 (6.5) | 42.0 (9.4) | 38.0 | a–b, b–c, a–c |
| Fear of movement (TSK-11) | 16.2 (4.0) | 19.5 (3.5) | 14.1 (3.1) | 11.00 | a–c |
| Anxiety (CPASS) | 25.6 (6.2) | 30.1 (4.5) | 22.4 (3.5) | 18.0 | a–b, b–c, a–c |
| Pain-related worries (PCS-C) | 22.0 (5.3) | 26.2 (3.1) | 19.5 (3.5) | 15.0 | a–b, b–c, a–c |
| Fear of pain (FOPQ-C) | 28.1 (6.7) | 33.4 (4.0) | 25.3 (3.5) | 16.0 | a–b, b–c, a–c |
| HRQoL (PedsQL) | 36.2 (6.0) | 30.0 (5.5) | 39.0 (4.0) | 45.0 | a–c |
| Variables | All Samples (n = 10) Mean Differences (p Value/Cohen d) | High-Risk Group (n = 6) Mean Differences (p Value/Cohen d) | Medium-Risk Group (n = 3) Mean Differences (p Value/Cohen d) | Low-Risk Group (n = 1) Mean Differences | Mean Differences ¶ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pain intensity at rest (NRS) | −3.1 * (p = 0.002 d = 2.60) | −3.3 * (p = 0.003 d = 2.85) | −3.0 * (p = 0.006 d = 2.50) | −2.0 * | none |
| Pain intensity at movement (NRS-M) | −3.0 * (p = 0.004 d = 2.55) | −3.0 * (p = 0.006 d = 2.50) | −3.4 * (p = 0.001 d = 2.90) | −4.0 * | none |
| Pain interference (PROMIS-PPI) | −7.5 * (p = 0.040 d = 1.69) | −6.4 (p = 0.058 d = 0.89) | −8.3 * (p = 0.038 d = 1.09) | −7.0 * | none |
| Fear of movement (TSK-11) | −4.3 (p = 0.091 d = 0.26) | −7.2 * (p = 0.015 d = 1.62) | −10.1 * (p = 0.005 d = 1.95) | −6.0 | b–c |
| Anxiety (CPASS) | −8.6 (p = 0.059 d = 0.48) | −10.4 * (p = 0.006 d = 2.36) | −12.8 * (p = 0.002 d = 2.76) | −9.0 * | b–c |
| Pain-related worries (PCS-C) | −8.5 (p = 0.061 d = 0.40) | −10.5 * (p = 0.001 d = 3.79) | −10.6 * (p = 0.001 d = 3.89) | −10.0 * | none |
| Fear of pain (FOPQ-C) | −9.4 * (p = 0.018 d = 2.89) | −12.2 * (p = 0.002 d = 3.37) | −7.3 (p = 0.068 d = 0.80) | −4.0 | a–b, b–c, a–c |
| HRQoL (PedsQL) | 7.3 (p = 0.077 d = 1.06) | 9.3 (p = 0.167 d = 1.66) | 12.2 * (p = 0.039 d = 2.66) | 11.0 * | a–b, a–c |
| Patient Global Impression of Change (PGIC) | All Samples (n = 10) N/Percentage | High-Risk Group (n = 6) N/Percentage | Medium-Risk Group (n = 3) N/Percentage | Low-Risk Group (n = 1) N/Percentage | – |
| A great deal better | 8 (80%) | 6 (100%) | 2 (66%) | 0 (0%) | – |
| Better | 1 (10%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (33%) | 0 (0%) | – |
| Moderately better | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | – |
| Somewhat better | 1 (10%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (100%) | – |
| A little better | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | – |
| Almost the same | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | – |
| No change | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | – |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ceniza-Bordallo, G.; Guerra-Armas, J.; Flores-Cortes, M.; Bermúdez-Ramirez, S. Multimodal Physiotherapist Intervention Program for Physical and Psychological Functioning in Children with Chronic Pain: Guiding Physiotherapy Intervention with the Pediatric Pain Screening Tool with Recommendations for Clinical Practice. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3629. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113629
Ceniza-Bordallo G, Guerra-Armas J, Flores-Cortes M, Bermúdez-Ramirez S. Multimodal Physiotherapist Intervention Program for Physical and Psychological Functioning in Children with Chronic Pain: Guiding Physiotherapy Intervention with the Pediatric Pain Screening Tool with Recommendations for Clinical Practice. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(11):3629. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113629
Chicago/Turabian StyleCeniza-Bordallo, Guillermo, Javi Guerra-Armas, Mar Flores-Cortes, and Sara Bermúdez-Ramirez. 2025. "Multimodal Physiotherapist Intervention Program for Physical and Psychological Functioning in Children with Chronic Pain: Guiding Physiotherapy Intervention with the Pediatric Pain Screening Tool with Recommendations for Clinical Practice" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 11: 3629. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113629
APA StyleCeniza-Bordallo, G., Guerra-Armas, J., Flores-Cortes, M., & Bermúdez-Ramirez, S. (2025). Multimodal Physiotherapist Intervention Program for Physical and Psychological Functioning in Children with Chronic Pain: Guiding Physiotherapy Intervention with the Pediatric Pain Screening Tool with Recommendations for Clinical Practice. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(11), 3629. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14113629






