Abstract
Background: Diabetes mellitus is a heterogeneous metabolic disorder that poses substantial challenges in the management of patients with diabetes. Emerging research underscores the potential of unsupervised cluster analysis as a promising methodological approach for unraveling the complex heterogeneity of diabetes mellitus. This systematic review evaluated the effectiveness of unsupervised cluster analysis in identifying diabetes phenotypes, elucidating the risks of diabetes-related complications, and distinguishing treatment responses. Methods: We searched MEDLINE Complete, PubMed, and Web of Science and reviewed forty-one relevant studies. Additionally, we conducted a cross-sectional study using K-means cluster analysis of real-world clinical data from 558 patients with diabetes. Results: A key finding was the consistent reproducibility of the five clusters across diverse populations, encompassing various patient origins and ethnic backgrounds. MOD and MARD were the most prevalent clusters, while SAID was the least prevalent. Subgroup analysis stratified by ethnic group indicated a higher prevalence of SIDD among individuals of Asian descent than among other ethnic groups. These clusters shared similar phenotypic traits and risk profiles for complications, with some variations in their distribution and key clinical variables. Notably, the SIRD subtype was associated with a wide spectrum of kidney-related clinical presentations. Alternative clustering techniques may reveal additional clinically relevant diabetes subtypes. Our cross-sectional study identified five subgroups, each with distinct profiles of glycemic control, lipid metabolism, blood pressure, and renal function. Conclusions: Overall, the results suggest that unsupervised cluster analysis holds promise for revealing clinically meaningful subgroups with distinct characteristics, complication risks, and treatment responses that may remain undetected using conventional approaches.
1. Introduction
Diabetes mellitus has become one of the fastest-growing healthcare challenges of the 21st century [1]. According to recent statistics from the International Diabetes Federation (IDF), the prevalence of diabetes has increased sharply worldwide, with 537 million adults affected in 2021 [1]. Given the heterogeneity in the clinical manifestations, trajectories, and outcomes of diabetes [2], the conventional classification of diabetes into primarily type 1 (T1D) and type 2 diabetes (T2D) is widely considered insufficient to capture the complexity of the disease [3]. Subdividing diabetes into more homogeneous subgroups may enhance risk stratification for complications and refine therapeutic approaches, potentially improving treatment efficacy and patient prognosis [2].
Recently, Ahlqvist et al. [4] made an unprecedented contribution to the identification of distinct diabetes phenotypes using data-driven cluster analysis. The ANDIS (All New Diabetics in Scania) cohort, which consisted of individuals with newly diagnosed diabetes, was assigned to clusters based on phenotypic similarity, as defined by six variables. The included model variables reflect important risk factors, illuminate key pathophysiological features, and can be relatively easily determined in routine clinical practice: glutamic acid decarboxylase antibodies (GADA), age at onset of diabetes, body mass index (BMI), hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c), homeostasis model assessment (HOMA) 2 estimates of β-cell function (HOMA2-B), and insulin resistance (HOMA2-IR). Using K-means and hierarchical clustering, five phenotypic diabetes subtypes were identified and named based on their distinctive features: Severe Autoimmune Diabetes (SAID), Severe Insulin-Deficient Diabetes (SIDD), Severe Insulin-Resistant Diabetes (SIRD), Mild Obesity-Related Diabetes (MOD), and Mild Age-Related Diabetes (MARD).
This innovative clustering strategy for diabetes subphenotyping has generated enormous scientific interest. Over the past few years, the clustering technique has been applied to various populations of people with diabetes using either a similar method as in the original study [4] or diverse clustering algorithms and model variables. Overall, five subtypes have been widely replicated across studies involving participants of different ethnic backgrounds [5]. These clusters differ in clinical presentation: SAID and SIDD are characterized by early onset, low BMI, insulin deficiency, and poor glycemic control, with SAID defined by GADA positivity; SIRD features severe insulin resistance and high BMI; MOD includes younger individuals with obesity and moderate insulin resistance; and MARD comprises older participants with relatively mild metabolic disturbances [5]. A prior systematic review indicated that some studies were able to reproduce the same clusters with similar traits, while other research revealed notable discrepancies in both the distribution of clusters and the central tendencies of the variables utilized in the algorithmic models [5]. Research that applied other clustering techniques and/or variables yielded notable distinctions [5]. It remains uncertain whether the noted discrepancy is linked to variations in the dominant pathophysiological features of diabetes among different populations or arises from the selection of a particular clustering approach.
A recent whole-genome sequencing study of healthy ethnic Kazakhs confirmed that this population has a unique genetic profile characterized by substantial admixture from both European and Asian ancestral lineages [6]. This high level of admixture is typical of Central Asian populations and reflects the region’s historical role as a crossroads for migration and trade [6]. The study also identified genetic variants associated with metabolic traits, including T2D and hypertension [6]. These findings underscore the importance of investigating disease patterns in this region, particularly in the context of metabolic disorders common in Central Asia.
Building on this background, this systematic review aimed to extend previous research efforts [5] and evaluate whether unsupervised cluster analysis could interpret complex interactions within data and identify distinct subgroups with clinically significant differences in disease trajectories, risk of diabetes-related complications, and treatment response. To support this aim, we performed a cross-sectional study using real-world clinical data from Kazakhstan, a Central Asian country with a unique genetic profile and environmental background, to further assess the efficacy of unsupervised cluster analysis in identifying distinct diabetes phenotypes.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Systematic Review
We conducted a systematic review following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines [7] and the pre-established PROSPERO research protocol (CRD42024609962).
2.1.1. Search Strategy
Three English electronic bibliographic databases, namely MEDLINE Complete, PubMed, and Web of Science, were searched to retrieve potentially relevant publications that reported the results of subclassification of diabetes using an unsupervised clustering approach. The comprehensive search strategies included the terms «diabetes mellitus» and «cluster analysis» using various combinations of medical subject heading (MeSH) terms and free text words. The full database search strategies are detailed in Table 1. To supplement the electronic database search, the reference lists of the included studies and relevant review articles were screened to identify other potentially eligible publications. Following a previous systematic review [5], the literature search strategy included searching for English-language studies published between August 2020 and August 2024. The retrieved publications were organized and managed using Zotero reference management software (version 6.0.37).

Table 1.
Search strategies for electronic bibliographic databases.
2.1.2. Selection Criteria and Data Extraction
The inclusion criteria were as follows: (1) studies that included patients diagnosed with diabetes, regardless of type; (2) implementation of a subclassification of diabetes using an unsupervised clustering approach; and (3) full-text articles that included research participants without age restrictions. Non-original works, including reviews and meeting abstracts, were excluded. Studies that involved research participants with diabetes and certain comorbidities, such as established cardiovascular disease, or those with specific diabetes-related complications or on a particular treatment, were excluded to preserve comparability and consistency within clusters.
After removing duplicate records, the remaining studies were independently reviewed and extracted by two investigators (B.T. and A.A.). All discrepancies were resolved through discussion to achieve consensus. In cases where consensus was not reached, a senior reviewer (A.S.-S.) was consulted and intervened to resolve inconsistencies. The following information was extracted from each eligible study: first author’s name, year of publication, ethnicity/geographic region, study design, data source, sample size and its characteristics, diabetes diagnostic criteria, clustering methods and dimensionality reduction techniques, methods for determining the number of clusters, variables for cluster analysis, and identified clusters and their characteristics.
2.1.3. Statistical Analysis
Data analysis was conducted using STATA software (version MP17.0). The pooled prevalence of clusters was estimated along with the corresponding 95% confidence interval (95% CI) after Freeman-Tukey Double Arcsine Transformation. Heterogeneity and inconsistency were measured using the chi-square test (Cochrane Q statistic) and inconsistency index (I2). Given the significant heterogeneity between studies, a random-effects model (REM) was employed to calculate the overall prevalence. Subgroup analyses were conducted based on ethnic groups to investigate potential sources of heterogeneity and variations in prevalence. Studies involving participants of multiple ethnicities were excluded from the subgroup analysis to maintain comparability across groups.
2.1.4. Quality Assessment
The methodological quality of each study included in this systematic review was independently evaluated by two researchers (B.T. and R.S.) using the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) tool for cohorts [8] and the Joanna Briggs Institute (JBI) Critical Appraisal Tool for cross-sectional studies [9]. Any disagreements between the two reviewers were resolved by a senior reviewer (A.S.-S.). Additionally, we examined the methodological quality of the randomized controlled trials (RCTs) used as data sources for several studies. These studies not only performed cluster analyses but also assessed the intervention effects within the clusters. The evaluation was performed using the Revised Cochrane Risk-of-Bias Tool for RCTs (RoB 2) [10].
2.2. Cross-Sectional Study
2.2.1. Study Population and Design
Following the decision of the Nazarbayev University School of Medicine Institutional Research Ethics Committee on 14 December 2022, the cross-sectional study (NUSOM-IREC 2022DEC#06) was exempted from the Research Ethics Review.
This cross-sectional study was conducted between December 2022 and January 2023. Data were collected from four outpatient clinics in Astana, Kazakhstan. We analyzed de-identified electronic health record (EHR) data from 558 patients aged 18 years and older, diagnosed with T2D or T1D between 2019 and 2022. A total of 77.5% of the study participants self-identified as ethnic Kazakhs and 20.6% as Russian. The remaining participants were Korean, German, Chinese, Ingush, Armenian, and Tatar. Women comprised 56.5% of the study population.
Diabetes diagnosis was defined using the International Classification of Diseases (ICD) codes. The age at diagnosis refers to the age of the patients when they were first diagnosed with diabetes, as documented in the EHR. All other relevant EHR data were extracted at the time closest to the diabetes diagnosis.
The inclusion criteria were a documented diagnosis of diabetes (T1D or T2D) and the availability of complete clinical or laboratory data required for cluster assignment. The exclusion criteria included secondary forms of diabetes (e.g., steroid-induced or due to pancreatic disorders), gestational diabetes, and age under 18 years.
2.2.2. Cluster Analysis
We employed K-means cluster analysis to identify subgroups of diabetes based on a set of variables. Specifically, nine distinct variables were selected for clustering: age at diagnosis, BMI, systolic blood pressure (SBP), diastolic blood pressure (DBP), HbA1c, fasting plasma glucose (FPG), total cholesterol (TC), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR). The eGFR was calculated using the Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration (CKD-EPI) creatinine equation. The values were scaled to a range between 0 and 1 using the MinMaxScaler function from the scikit-learn Python machine learning library (version 3.10.8). This process ensures that all variables are normalized and contribute equally to the clustering process without introducing any bias. We applied the Elbow method to determine the optimal number of clusters by assessing the values of k ranging from 2 to 20. The within-cluster sum of squares (WCSS) was computed and plotted against the corresponding k values. The optimal number of clusters was identified at the point where increasing k no longer led to improvements in WCSS, with five clusters being determined as optimal. To validate this, the Silhouette width method was used, as it measures how well each data point fits within its assigned cluster (cohesion) compared to its closest alternative cluster (separation). The findings are visually represented by a graph created using Flourish Studio (version 18.8.0) [11].
3. Results
3.1. Systematic Review
Figure 1 presents a comprehensive overview of the steps undertaken in our literature search. The initial search strategy yielded 1873 potentially relevant articles from electronic databases. After removing duplicates, 884 articles remained. Following title and abstract screening, 826 studies were deemed irrelevant and excluded. The remaining 58 studies underwent full-text evaluation of their full text to determine eligibility. After full-text screening, 17 articles were eliminated for several reasons, as detailed in Figure 1. A total of 41 studies fulfilled the inclusion criteria and were subsequently incorporated into the systematic review.
Figure 1.
PRISMA flow diagram presenting the results of the literature search and study selection process.
3.1.1. Characteristics of Included Studies
The characteristics of the selected articles are summarized in Table S1. Forty-one studies fulfilled the eligibility criteria, with 270,067 research participants in total. Among this study population, 237,543 (87.96%) individuals were diagnosed with T2D, 15,173 (5.62%) with T1D, 140 (0.05%) with latent autoimmune diabetes in adults (LADA), and 17,211 (6.37%) with undifferentiated diabetes. The analyzed studies were sourced from multiple countries, including China [12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26], Germany [27], Japan [28,29], India [30,31,32], the United States of America (USA) [33,34,35,36], Ghana [37], Denmark [38], the Republic of Singapore [39], the USA/Qatar [40], Thailand [41], the Netherlands [42], the Republic of Korea [43], the United Arab Emirates [44], the Netherlands/Scotland [45], Sweden [46], Montenegro [47,48], Germany/Austria [49], and Spain [50].
The sample size varied considerably across studies, ranging from 95 to 114,231 patients. The largest sample size, consisting of data from 114,231 people with newly diagnosed T2D from the National Diabetes Register of Sweden, was incorporated into the research conducted by Lugner et al. [46]. The study conducted at the Primary Health Care Centre in Podgorica, Montenegro, had the smallest sample size, with only 95 participants [47]. The disease duration ranged from less than one year [22,27] to thirty-eight years or more [36]. In most studies, the diagnosis of diabetes was established based on the criteria of the World Health Organization (WHO) [51,52] and the American Diabetes Association (ADA) [53,54,55,56,57]. In some studies, diabetes was diagnosed using certain laboratory parameters [13,15,19,20] and assessment of specific health conditions and/or administration of hypoglycemic pharmacotherapy [26,28,30,36,37,45], as well as on the basis of the ICD codes [29,33,46,48,50]. One study relied on self-reported information to ascertain the presence of diabetes [34].
Data were obtained from multiple healthcare facilities and other sources, including university hospitals, tertiary care centers, outpatient clinics, primary care medical facility databases, national research centers, disease or clinical registries, EHR, and surveys. The study designs of the reviewed publications were as follows: twenty-two cohort studies, 14 cross-sectional studies, and five studies utilizing data from RCTs. The follow-up duration in cohort studies varied from approximately two [41,49] to fourteen years [43].
3.1.2. Methods for Clustering and Dimensionality Reduction Techniques
The cluster analysis methodologies employed in the selected studies are presented in Table S2. K-means clustering was the most commonly utilized method for clustering in the reviewed publications [12,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,28,29,30,31,32,34,36,38,39,40,41,42,45,46]. The next most prevalent clustering techniques were hierarchical cluster analysis [33,47,49] and two-step clustering [13,14,15,26,37,48]. Several studies have employed a combination of techniques for performing cluster analysis [43,44,50,58]. K-prototype clustering is the least commonly used cluster analysis method [35]. Five studies emphasized the use of dimensionality reduction techniques as a preparatory step before conducting cluster analysis [12,16,19,21,23]. Table S3 lists the variables used in the cluster analysis.
3.1.3. Quality Assessment Results
Overall, all cohort studies achieved scores above 70%, indicating moderate-to-high quality of evidence. The cross-sectional studies were assessed as having a risk of bias ranging from low to moderate. The RCTs were rated as having a low risk of bias or as research efforts with some concerns. The findings of the quality control assessment are summarized in Tables S4–S6.
3.1.4. Prevalence of Clusters
The reviewed studies identified three [13,32,39,40], four [16,17,18,19,21,22,23,31,34,38,43,58], and five [12,14,15,27,28,29,33,37,59] distinct subtypes in their approach to generating clusters similar to those initially observed in the Scandinavian population [4].
Table 2 presents the pooled prevalence estimates for clusters derived from studies that identified five clusters [12,14,15,27,28,29,33,37,59] under the REM. The studies showed significant between-study heterogeneity (I2 > 90%, Ph < 0.001). The SAID cluster had the lowest pooled prevalence (8%; 95% CI: 6.0–11%), while the MOD (31%; 95% CI: 23–39%) and MARD (27%; 95% CI: 21–34%) clusters had the highest prevalence. Subgroup analysis stratified by ethnic group indicated a higher prevalence of SIDD (25%; 95% CI: 16–34% vs. 11%; 95% CI: 1.0–23%), SIRD (14%; 95% CI: 10–19% vs. 10%; 95% CI: 4.0–15%), and MARD (29%; 95% CI: 23–34% vs. 22%; 95% CI: 10–33%) among individuals of Asian descent than among individuals of other ethnic groups.

Table 2.
The pooled prevalence of clusters in studies identified five clusters.
Table 3 presents both the overall and subgroup analyses under the REM, providing estimates for the pooled prevalence of the four clusters identified in studies on T2D [16,17,18,19,21,22,23,31,32,38,40,43,58]. There was strong evidence of heterogeneity among the studies (I2 > 88%, Ph < 0.001). In the overall analysis, SIRD had the lowest pooled prevalence (17%; 95% CI: 14–19%), whereas MARD was the most frequently observed cluster (37%; 95% CI: 34–40%). The pooled prevalence of SIDD (22%; 95% CI: 18–26% vs. 9%; 95% CI: 8.0–10%) and MOD (30%; 95% CI: 25–35% vs. 26%; 95% CI: 25–28%) was notably higher in Asian populations than in individuals from other ethnicities. In contrast, SIRD and MARD were more predominant in the non-Asian groups.

Table 3.
The pooled prevalence of clusters in studies on type 2 diabetes (T2D) identified up to four clusters.
3.1.5. Characteristics of Clusters
Table S7 provides a summary of the key characteristics of the clusters, which align either fully or partially with those identified by Ahlqvist et al. [4]. Numerous studies have replicated the same major diabetes subtypes, which share largely similar features and phenotypic characteristics. Individuals assigned to SAID exhibited positive GADA status, relatively early onset of the disease, low or depleted insulin secretory capacity, comparatively low BMI, and poor long-term glycemic control based on HbA1c. The key distinguishing characteristic of SIDD was GADA negativity; otherwise, its clinical profile closely resembled that of SAID. The SIRD cluster was characterized by high BMI, severe insulin resistance, and elevated β-cell function. Glycemic control was relatively well managed. Individuals in the MOD cluster were distinguished by a relatively young age, high BMI, and less pronounced insulin resistance than those in the SIRD cluster. Participants with MARD differed by having older-age-onset diabetes and mild to moderate metabolic abnormalities, with no further extreme characteristics noted.
Beyond the variations in clinical characteristics across clusters, there was a notable divergence in complications, highlighting a heterogeneous risk profile among the diabetes population. A higher prevalence and risk of diabetic retinopathy (DR) were predominantly observed in the SIDD subtype [12,13,17,28,30,31,59]. Zhang et al. reported that participants assigned to the SAID cluster had a higher incidence of both DR and diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) [15]. Christensen et al. noted that the MARD cluster had a higher prevalence of diabetic eye disease [38].
The SIRD subtype is associated with a wide spectrum of clinical presentations of kidney involvement. Individuals classified into the SIRD cluster were most likely to develop diabetic kidney disease (DKD) [12,14,19]. The SIRD subtype is linked to a lower median eGFR at baseline [58] and a higher risk and prevalence of chronic kidney disease (CKD) [13,17,22,39,59], macroalbuminuria [59], microalbuminuria [28], and renal dysfunction [29,38]. Notably, Song et al. found no statistically significant difference in the risk of DKD between subgroups after adjusting for HOMA2-IR [14]. In the GoDARTS cohort, patients assigned to SIRD had nearly a two-fold higher risk of developing CKD and end-stage renal disease (ESRD), while patients with MOD faced an approximately five-fold higher risk of ESRD relative to those in the mild diabetes with high high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (MDH) subgroup [45]. Individuals in the SIDD cluster also have a higher prevalence of albuminuria [17] and risk of CKD [24]. Hwang et al. found that individuals in the MARD and SIDD clusters were more likely to develop CKD, defined as at least stage 3A, than those in the SIRD subgroup [43].
Song et al. found that individuals in the MOD were at a higher risk of developing non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), even after adjusting for BMI and HOMA2-IR [14]. However, Wang et al. reported that participants assigned to the severe obesity-related and insulin-resistant diabetes (SOIRD) cluster were more likely to have incident metabolic-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD), followed by those in the MOD cluster compared to the MARD subtype [20]. In a study by Hwang et al., the SIRD cluster demonstrated the highest prevalence of MAFLD, with 97% of patients affected [43]. Li and Chen observed consistent results, with the greatest prevalence of NAFLD identified among individuals with SIRD (74.5%), followed by those in MOD (72.1%) [22].
Lu et al. reported that the risk of diabetic neuropathy was overall higher in SIDD than in other clusters [33]. Xiong et al. revealed that individuals in the SIDD cluster were more prone to diabetic foot, while patients in the SIRD faced a greater risk of DPN [13].
An unfavorable cardiovascular risk profile was evident across all clusters, with no distinct patterns (SAID [15], SIDD [33,43], SIRD [12,28,39,45,59], MOD [22], MARD [24,43], SOIRD [24], and uric acid-related diabetes (UARD) [13].
Several studies have examined the therapeutic response to antidiabetic agents, suggesting that certain clusters exhibit unique patterns of treatment efficacy. Huang et al. observed that within the MARD cluster, telomere lengths (TLs) were significantly longer in the group receiving metformin than in the metformin-free group, even after adjusting for age and sex [16]. According to Pigeyre et al., glargine decreased hyperglycemia by 19%, 13%, and 9% in the SAID, SIDD, and MOD clusters, respectively, compared to standard care, with MARD serving as the reference group [59]. In a study by Zou et al., canagliflozin demonstrated the strongest glucose-lowering effect in the MOD cluster over 52–104 weeks, outperforming both sitagliptin and glimepiride [58]. In addition, the highest proportion of participants achieving the HbA1c target (<7.0%) in the MARD were those treated with sitagliptin [58]. Abdul-Ghani et al. found that Group 1, which was comparable to the SIDD, demonstrated a more favorable reduction in HbA1c over three years when treated with combination therapy, including pioglitazone and exenatide, compared to insulin therapy or the conventional treatment regimen of metformin, followed sequentially by glipizide, and glargine insulin [40].
Table S8 presents the clusters identified using alternative clustering methodologies that do not directly correspond to those described by Ahlqvist et al. [4].
Lugner et al. identified four clusters in T2D patients [46]. Individuals with a high BMI (Cluster 1) exhibited worse glycemic control and less favorable lipid profiles. Patients diagnosed at an older age (Cluster 3) tended to have more controlled blood glucose levels. Younger individuals with a high BMI (Cluster 4) were more likely to maintain close-to-target glycemic control.
Cojic et al. identified four distinct phenotypes among individuals with T2D using a clustering approach that integrated various parameters, including the vitamin D status [47]. Notably, the cluster with the highest vitamin D levels exhibited significantly lower insulin resistance than those with vitamin D deficiency or insufficiency. Additionally, this cluster demonstrated superior glycemic control compared to the clusters with vitamin D insufficiency.
Grimsmann et al. identified eight data-driven clusters of adults with T2D and T1D [49]. Four of these clusters were characterized by early onset diabetes, with a median age at diagnosis of between 40 and 50 years. Despite the shared age range, these clusters exhibited significant heterogeneity in key clinical variables, including BMI, HbA1c levels, prevalence of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), and β-cell antibody positivity. Two clusters were composed of individuals diagnosed in their early 60s, who generally achieved target HbA1c levels but showed notable differences in BMI and sex distribution within the clusters. The remaining two clusters represented late-onset diabetes, diagnosed in the late 60s and beyond, but were distinguished by substantial variability in the HbA1c levels.
Wang et al. stratified participants with T2D into four distinct clusters [25]. The clusters were ranked from low to high risk based on the likelihood of developing complications. Individuals in Cluster 1, labeled as low-risk, had better glycemic control, more favorable lipid metabolism control, and moderate insulin resistance that was less pronounced than in other clusters. In contrast, those in Cluster 4, designated as high-risk, exhibited very poor glycemic control, worse lipid profiles, and the greatest risk of microangiopathy, diabetic nephropathy, and DR.
In 2024, Cojic et al. revealed four unique clusters among individuals with T2D [48]. Their study specifically examined the inflammatory markers associated with each cluster, providing further insights into the role of inflammation in the pathophysiology of disease. Notably, Cluster 3, which comprised older patients with longer disease duration, suboptimal glycemic control, and the greatest prevalence of hypertension and nephropathy, exhibited the highest levels of inflammation-related markers.
Somolinos-Simon et al. identified five distinct subgroups within the T1D study population and analyzed their key differences, as well as the associated risks for diabetes-related complications over a five-year follow-up period [36]. The complications evaluated included DR, coronary artery disease (CAD), autonomic neuropathy, albuminuria, hypertension, severe hypoglycemia, DKA, and depression.
The potential for individuals with diabetes to shift between different diabetes clusters over time remains an intriguing research question. Li et al. revealed that over 28% of individuals shifted to different subgroups after just two years [45]. In the GoDARTS cohort, the Risk Assessment and Progression of Diabetes project (RHAPSODY) SIRD (RHAP-SIRD) subgroup exhibited the highest stability, with 77% of individuals remaining in the same cluster over an eight-year study period. In contrast, the RHAPSODY SIDD (RHAP-SIDD) subgroup showed the least stability, with only 8% of individuals remaining in the same cluster. There was no significant difference in the risk of macrovascular disease between individuals who transitioned from the mild subgroups (RHAPSODY mild diabetes (RHAP-MD), RHAP-MOD, and RHAP-MDH) to the severe subgroups (RHAP-SIDD and RHAP-SIRD) and those who remained in the severe subgroups over a two-year period. However, among individuals initially classified in the severe subgroup, those who remained in this category over the two years demonstrated a significantly higher risk of developing CKD than individuals who transitioned to the mild subgroups. In contrast, individuals initially classified in the mild subgroup who progressed to the severe subgroup during the two-year follow-up demonstrated an increased risk of acute myocardial infarction (AMI) and congestive heart failure (CHF) relative to those who remained in the mild subgroup.
3.2. Cross-Sectional Study
The research participants had a median age at diagnosis of 57.9 years (interquartile range (IQR), 48.8–64.3) and a median BMI of 30.5 kg/m2 (IQR, 27.5–34.0). Blood pressure measurements revealed a median SBP of 120 mm Hg (IQR, 120–130) and a median DBP of 80 mm Hg (IQR, 80–80). The median HbA1c level, an indicator of long-term glycemic control, was 7.7% (IQR, 6.8–9.5). The median TC and LDL-C, lipid metabolism markers, were 5.3 mmol/L (IQR, 4.5–6.2) and 3.4 mmol/L (IQR, 2.7–4.0), respectively. The median eGFR was 96.7 mL/min/1.73 m2 (IQR, 79.3–106.9). Women comprised 56.5% of the participants.
In our study based on Kazakhstani data, the participants were categorized into five distinct clusters. The characteristics of each cluster are summarized in Table 4 and Figure 2. Cluster 1 comprised 176 (31.5%) older individuals who exhibited suboptimal glycemic control and a relatively favorable lipid profile with borderline optimal TC and LDL-C levels. Cluster 2 included 83 (14.9%) individuals characterized by late-onset diabetes, higher BMI corresponding to Obesity Class I, elevated SBP and DBP, suboptimal glycemic control, mild lipid abnormalities with TC and LDL-C in the borderline-high range, and lower eGFR. Cluster 3 consisted of 98 (17.6%) individuals who were diagnosed at a younger age and demonstrated a lower BMI within the overweight range, suboptimal glycemic control, and better lipid metabolism control, with lower levels of TC and LDL-C. In Cluster 4, 110 (19.7%) individuals presented with high BMI levels consistent with Obesity Class I and suboptimal glycemic control, along with a more unfavorable lipid profile, marked by higher TC and LDL-C levels. Finally, Cluster 5, comprising 91 (16.3%) individuals, featured overweight status, very poor glycemic control, and mild dyslipidemia with borderline-high levels of TC and LDL-C.

Table 4.
Cluster profiling based on Kazakhstani data.
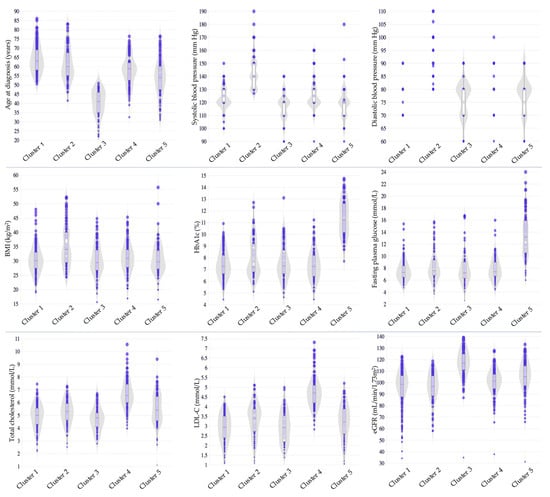
Figure 2.
Cluster profiling based on the Kazakhstani data. BMI, body mass index; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; HbA1c, hemoglobin A1c; LDL-C, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol.
4. Discussion
Our systematic review demonstrates that unsupervised cluster analysis holds significant potential for effectively capturing the complex heterogeneity within the diabetes population and identifying distinct and homogeneous clusters characterized by pathophysiologically feasible factors and unique clinical profiles. Another key observation was the remarkable reproducibility of the five clusters across a diverse range of participants, encompassing various patient origins and ethnic backgrounds. Although the clusters shared similar phenotypic characteristics and a common risk profile for complications, there was substantial variability in the distribution of these clusters and the central tendencies of the key variables. Studies utilizing alternative clustering techniques and algorithmic model variables have revealed additional clinically relevant clusters. In general, cluster analysis can be employed to empirically explore phenotypic traits and diagnostic differences across homogenous and clinically meaningful diabetes subtypes, although it is subject to certain limitations.
A distinct issue to consider is the potential influence of participants’ ethnic backgrounds on the distribution and composition of the clusters. Conflicting evidence exists regarding the differences in the prevalence of SIDD between individuals of European and Asian origin [60]. Our systematic review highlights substantial variability in the prevalence of SIDD across different populations. Notably, Asian groups, particularly East Asians, who were represented in 16 of the twenty-two studies, exhibited higher SIDD prevalence rates compared to their non-Asian counterparts. The present findings comply with the conclusions drawn in the previously published research conducted by Varghese and Narayan [61]. East Asians generally demonstrate a lower endogenous capacity for insulin secretion [62,63,64,65], and T2D tends to develop at a lower average BMI than that of individuals of European ancestry [66]. Overall, in lean individuals with T2D who do not have severely impaired insulin sensitivity, β-cell exhaustion is thought to progress with age and prolonged exposure to glycemic stress, often exacerbated by poor dietary habits [60]. Over several decades, this ongoing metabolic strain gradually reduces the pancreas’s intrinsic ability to secrete insulin, eventually leading to the onset of T2D [60,67].
Based on our findings, the prevalence of SIRD across Asian and other demographic groups appears inconsistent, leading to uncertainty regarding its ethnic-specific prevalence. Studies have consistently shown that individuals of South Asian heritage exhibit a greater predisposition to insulin resistance than their White counterparts [68,69,70,71,72]. A recent study further revealed that non-Hispanic Whites and African Americans experience lower insulin resistance levels than South and East Asian individuals [73]. One possible explanation for this disparity is that individuals of South Asian descent may have a greater biological propensity to accumulate fat, predominantly in the abdominal region, with a lower overall BMI [2,62]. Generally, individuals with ectopic fat accumulation in the liver and skeletal muscles, resulting from a diminished lipogenic capacity of subcutaneous fat, are more prone to developing insulin resistance, which is a key factor underlying the onset of T2D [60,74]. Indeed, recent research has demonstrated that the South Asian-American population has lower β-cell function, increased insulin resistance, and less favorable body composition, characterized by higher levels of liver and intermuscular fat and lower muscle mass, compared to four other racial and ethnic groups in the United States [75]. However, contrary to the prevailing belief, Narayan et al. argued that South Asians exhibit lower levels of insulin resistance and greater insulin deficiency relative to both U.S. Black and White populations [76]. Further research is crucial to elucidate the predominant pathophysiological mechanisms driving the high prevalence of T2D in different ethnic groups.
In addition to the observed differences in clinical characteristics among the identified clusters, cluster analysis also revealed distinct cluster-specific risk profiles for complications. The higher prevalence and increased risk of DKD are predominantly associated with the SIRD subtype. Insulin resistance is a key pathogenic driver of various metabolic diseases, including T2D [77,78]. A potential pathogenetic pathway linking insulin resistance to renal dysfunction involves a multifactorial interplay between metabolic syndrome, adipocytokine dysregulation, hyperinsulinemia, and chronic low-grade inflammation [79]. These interconnected factors collectively promote renal injury by disrupting various biochemical and molecular pathways, particularly the insulin-signaling pathway in the kidneys [79], which plays a pivotal role in the pathophysiology of renal dysfunction [80,81]. Insulin signaling is crucial for several key renal processes, including the maintenance of glomerular function [80,82], renal gluconeogenesis [83], tubular transport [84,85], and vascular regulation [80]. Disruption of insulin action may impair renal hemodynamics [86,87], compromise podocyte viability [88,89,90] and negatively affect tubular function [80,91,92].
SIDD is a high-risk group for the development of DR, potentially resulting from sustained and inadequate glycemic control, which accelerates microvascular damage in the retinal tissue. Multiple lines of evidence have consistently demonstrated that the development and progression of DR are strongly correlated with prolonged hyperglycemia [93,94,95,96]. Moreover, a growing body of research has established a significant relationship between long-term variability in HbA1c levels and both the onset [97] and progression of DR [98,99], underscoring the importance of glycemic stability in mitigating the risk of retinal damage.
Cluster analysis indicated that individuals within the SIRD cluster are at a significantly higher risk of developing NAFLD, now termed MAFLD, with a similar trend observed in the SOIRD and MOD clusters. T2D and NAFLD share a complex bi-directional relationship, with each driving the onset and progression of the other [100,101]. Beyond the well-established relationship between insulin resistance and an increased incidence of CVD [102,103], NAFLD has been independently associated with a heightened long-term risk of both fatal and non-fatal CVD events [104,105] and an increased risk of CKD [105,106].
The SAID, SIDD, and SIRD clusters exhibited a notably high risk of diabetic neuropathy, driven by overlapping pathophysiological mechanisms. Chronic hyperglycemia, insulin resistance, and dyslipidemia activate several key metabolic pathways, including the polyol, hexosamine, and protein kinase C (PKC) pathways [107,108]. Together, these processes ultimately foster mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, inflammation, and alterations in gene expression, leading to intracellular damage, nerve dysfunction, and neuronal cell death [107,108].
It remains uncertain whether clustering can detect subgroups of individuals who would experience greater therapeutic benefits from specific classes of medications used to manage hyperglycemia. Pigeyre et al. demonstrated that insulin glargine exhibited superior efficacy in reducing elevated blood glucose levels in the SIDD cluster when compared to standard care [59]. This finding underscores the benefit of initiating insulin therapy early in this specific patient cohort, suggesting that early insulin intervention may provide enhanced control of hyperglycemia in individuals with SIDD. Canagliflozin, a sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor, demonstrated superior glucose-lowering efficacy compared with sitagliptin, a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor, and glimepiride, a sulfonylurea, in the MOD cluster [58]. The enhanced efficacy of canagliflozin is likely attributable to its distinct mechanism of action, which involves the inhibition of renal glucose reabsorption, thereby enhancing urinary glucose excretion [109]. Additionally, canagliflozin promotes weight loss and exerts beneficial effects on both cardiovascular and renal outcomes [110]. Zou et al. further demonstrated that participants in the MARD cluster treated with sitagliptin had the highest proportion of individuals achieving the target HbA1c level [58]. This may be attributed to the drug’s mechanism of action, which enhances insulin secretion and thereby improves glucose homeostasis [111]. Moreover, its favorable safety profile, characterized by a neutral effect on body weight and a lack of increased risk of hypoglycemia, distinguishes sitagliptin from other antidiabetic therapies [112]. Abdul-Ghani et al. demonstrated that patients in a subgroup comparable to the SIDD cluster experienced a more favorable reduction in HbA1c when treated with combination therapy, including pioglitazone and exenatide, compared to those receiving insulin therapy or the conventional regimen of metformin, glipizide, and glargine insulin [40]. In addition to augmenting insulin sensitivity through the activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPAR-γ) [113], pioglitazone also contributes to the improvement of β-cell function [114,115,116,117]. Exenatide, a glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1 RA), exerts its effects through the direct stimulation of insulin secretion, suppression of glucagon release [118,119], and promotion of β-cell proliferation [120]. The results of this study indicated that, in specific patient subsets, agents that preserve β-cell function may offer superior efficacy in enhancing insulin sensitivity compared to insulin replacement therapy. These findings partially contradict those reported by Pigeyre et al. [59] and underscore the necessity for further research to evaluate the therapeutic response of diabetes clusters to glucose-lowering treatment.
Other studies employing alternative methodologies have identified distinct diabetes clusters that only partially align with those proposed by Ahlqvist et al. [4]. These variations indicate the complexity of diabetes as a heterogeneous disease and underscore the need for further refinement in subgroup identification. Future research is required to explore whether these alternative clusters represent truly distinct pathophysiological mechanisms or reflect methodological differences in clustering approaches.
Diabetes encompasses a broad spectrum of heterogeneity, with individuals falling into distinct subgroups that may be driven by underlying genetic factors and molecular signatures. However, pharmacological treatments, lifestyle interventions, and personalized care plans may shift individuals from one subgroup to another. This dynamic movement may be further influenced by the patient’s response to treatment and disease progression, highlighting the need for continuous monitoring and reassessment of diabetes subtypes to optimize management strategies.
The findings of our cross-sectional study based on Kazakhstani data highlighted distinct subgroups of individuals with diabetes, each with unique characteristics in terms of glycemic control, lipid metabolism, blood pressure regulation, renal function, and weight status. Notably, certain subgroups demonstrated moderate-to-severe metabolic disturbances, higher blood pressure, and pronounced renal impairment. In contrast, the other subgroups exhibited a relatively favorable clinical profile. Clusters characterized by more adverse indicators likely represent high-risk populations. The clustering approach used in this study has several critical clinical and research implications. The variation in HbA1c levels suggests that different clusters may benefit from personalized treatment strategies rather than standardized approaches. Differences in eGFR across clusters reinforce the importance of routine kidney function monitoring to detect renal impairment and initiate nephroprotective strategies. Cardiovascular risk assessment should be prioritized in clusters with dyslipidemia, hypertension, and kidney dysfunction. Clusters with higher BMI require targeted weight-loss strategies, while those with lower BMI may require alternative metabolic interventions to optimize insulin sensitivity. In essence, the identified variations in health markers point to key areas that require targeted interventions to improve patient outcomes.
Speculatively, among the five distinct clusters identified in our study, several showed partial similarities to those originally described by Ahlqvist et al. [4]. Cluster 1, comprising older individuals with suboptimal glycemic control and a relatively favorable lipid profile, shared features with the MARD cluster. Cluster 2 included individuals characterized by late-onset diabetes, higher BMI, elevated blood pressure, suboptimal glycemic control, and lower eGFR, partially aligning with the SIRD and, to a lesser extent, with the MOD cluster. Cluster 5, composed of individuals with relatively lower BMI and very poor glycemic control, could correspond to the SIDD cluster. However, these similarities should be interpreted with caution, as our cluster analysis did not include variables reflecting insulin secretion capacity or insulin resistance.
Since fasting insulin, C-peptide, and GADA levels are not routinely measured in our clinical settings, our clustering approach may be more applicable to real-world healthcare environments. However, given the cross-sectional design of our study, the identified clusters reflect phenotypic patterns observed at a single point in time, limiting our ability to assess longitudinal changes, disease progression, or the causality between clinical features and outcomes. Despite this limitation, the use of real-world clinical data provides valuable insights into the heterogeneity of diabetes within the studied population. To build on these findings, longitudinal follow-up studies are essential to identify the development of diabetes-related complications specific to each cluster and evaluate the impact of diabetes progression on patient clustering. Future research may also offer valuable insights into how different treatment strategies affect distinct patient subgroups.
This systematic review has several limitations. First, there was diversity in the methodologies used across the included studies. The inclusion of studies employing various diabetes clustering techniques introduces significant methodological heterogeneity, limiting the ability to draw consistent conclusions and affecting the generalizability of the results. Second, the inclusion of studies using different datasets with varying sample sizes, demographics, and clinical settings may introduce bias, as the identified clusters may be context-dependent. Studies also vary in terms of study design, follow-up duration, population characteristics, and diagnostic criteria, which further complicates the synthesis. Finally, the observed high between-study heterogeneity could potentially obscure the true prevalence of the clusters.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, unsupervised cluster analysis offers substantial promise for identifying distinct subgroups of individuals with diabetes, providing valuable insights into disease progression and varying risks of diabetes-related complications. This technique has the potential to enhance personalized treatment strategies by distinguishing differential treatment responses, ultimately paving the way for more targeted and proactive interventions. Nevertheless, further research is needed to determine the most effective clustering algorithms and variable selection criteria, which remain key challenges in this field. Integrating these approaches with clinical data is essential to enhance their applicability in real-world healthcare settings and ultimately improve patient outcomes.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/jcm14103588/s1, Table S1: Characteristics of selected studies; Table S2: Cluster analysis methodologies used in the selected studies; Table S3: Variables used in cluster analysis; Table S4: JBI critical appraisal tool for cross-sectional studies; Table S5: Risk-of-bias evaluation of included randomized controlled trials using the RoB 2 tool; Table S6: Evaluation of quality of cohort studies using the NHLBI tool; Table S7: Characteristics of clusters aligned with a previously described diabetes classification (SAID, SIDD, SIRD, MOD, MARD); Table S8: Characteristics of clusters identified using alternative clustering methods; Table S9: Prisma 2020 Checklist.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.S.-S. and B.T.; systematic review—data analysis and interpretation, B.T., A.S. and A.A.; cross-sectional study—execution of the clustering technique, R.S. and S.F.; writing—original draft preparation, B.T.; writing—review and editing, B.T., M.M.Y., K.A., Y.S. and A.S.-S.; supervision, M.M.Y., K.A., Y.S. and A.S.-S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Science Committee of the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Republic of Kazakhstan, grant number AP19676488.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, and ethical review and approval were waived by the Nazarbayev University School of Medicine Institutional Research Ethics Committee, as the cross-sectional study was deemed eligible for exemption from Research Ethics Review (NUSOM-IREC 2022DEC#06, 14 December 2022).
Informed Consent Statement
Patient consent was waived because the cross-sectional study analyzed de-identified electronic health record data.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article and the Supplementary Materials. Further inquiries should be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| ADA | American Diabetes Association |
| AMI | Acute myocardial infarction |
| ANDIS | All New Diabetics in Scania |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| BP | Blood pressure |
| CAD | Coronary artery disease |
| CHF | Congestive heart failure |
| CKD | Chronic kidney disease |
| CKD-EPI | Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration |
| CVD | Cardiovascular disease |
| DBP | Diastolic blood pressure |
| DKA | Diabetic ketoacidosis |
| DKD | Diabetic kidney disease |
| DPN | Diabetic peripheral neuropathy |
| DPP-4 | Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 |
| DR | Diabetic retinopathy |
| eGFR | Estimated glomerular filtration rate |
| EHR | Electronic health record |
| ESRD | End-stage renal disease |
| FPG | Fasting plasma glucose |
| GADA | Glutamic acid decarboxylase antibodies |
| GFR | Glomerular filtration rate |
| GLP-1 RA | Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist |
| HbA1c | Hemoglobin A1c |
| HDL-C | High-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| HOMA | homeostasis model assessment |
| HOMA2-B | Homeostasis model assessment 2 of β-cell function |
| HOMA2-IR | Homeostasis model assessment 2 of insulin resistance |
| HOMA-B | Homeostasis model assessment of β-cell function |
| HOMA-IR | Homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance |
| ICD | International Classification of Diseases |
| IDF | International Diabetes Federation |
| LADA | Latent autoimmune diabetes in adults |
| LDL-C | Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| MAFLD | Metabolic-associated fatty liver disease |
| MARD | Mild age-related diabetes |
| MD | Mild diabetes |
| MDH | Mild diabetes with high high-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| MeSH | Medical subject heading |
| MOD | Mild obesity-related diabetes |
| NAFLD | Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease |
| PKC | Protein kinase C |
| PPAR-γ | Proliferator-activated receptor gamma |
| PRISMA | Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses |
| RCT | Randomized controlled trial |
| REM | Random-effects model |
| RHAPSODY | Risk Assessment and Progression of Diabetes project |
| SAID | Severe autoimmune diabetes |
| SBP | Systolic blood pressure |
| SGLT2 | Sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 |
| SIDD | Severe insulin-deficient diabetes |
| SIRD | Severe insulin-resistant diabetes |
| SOIRD | Severe obesity-related and insulin-resistant diabetes |
| T1D | Type 1 diabetes |
| T2D | Type 2 diabetes |
| TC | Total cholesterol |
| TG | Triglycerides |
| TL | Telomere lengths |
| UARD | Uric acid-related diabetes |
| WCSS | Within-cluster sum of squares |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
References
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas, 10th ed.; International Diabetes Federation: Brussels, Belgium, 2021; Available online: https://www.diabetesatlas.org (accessed on 21 November 2024).
- Ahlqvist, E.; Prasad, R.B.; Groop, L. Subtypes of type 2 diabetes determined from clinical parameters. Diabetes 2020, 69, 2086–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deutsch, A.J.; Ahlqvist, E.; Udler, M.S. Phenotypic and genetic classification of diabetes. Diabetologia 2022, 65, 1758–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahlqvist, E.; Storm, P.; Käräjämäki, A.; Martinell, M.; Dorkhan, M.; Carlsson, A.; Vikman, P.; Prasad, R.B.; Aly, D.M.; Almgren, P.; et al. Novel subgroups of adult-onset diabetes and their association with outcomes: A data-driven cluster analysis of six variables. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018, 6, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarría-Santamera, A.; Orazumbekova, B.; Maulenkul, T.; Gaipov, A.; Atageldiyeva, K. The Identification of Diabetes Mellitus Subtypes Applying Cluster Analysis Techniques: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 9523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kairov, U.; Molkenov, A.; Sharip, A.; Rakhimova, S.; Seidualy, M.; Rhie, A.; Kozhamkulov, U.; Zhabagin, M.; Kim, J.I.; Lee, J.H.; et al. Whole-Genome Sequencing and genomic variant analysis of Kazakh individuals. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 902804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Quality Assessment Tool for Observational Cohort and Cross-Sectional Studies. National Institutes of Health. Available online: https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-pro/guidelines/in-develop/cardiovascular-risk-reduction/tools/cohort (accessed on 27 November 2024).
- Moola, S.; Munn, Z.; Tufanaru, C.; Aromataris, E.; Sears, K.; Sfetcu, R.; Currie, M.; Qureshi, R.; Mattis, P.; Lisy, K.; et al. Chapter 7: Systematic reviews of etiology and risk. In JBI Manual for Evidence Synthesis; Aromataris, E., Munn, Z., Eds.; JBI: Adelaide, Australia, 2020; Available online: https://synthesismanual.jbi.global (accessed on 27 November 2024).
- Sterne, J.A.C.; Savović, J.; Page, M.J.; Elbers, R.G.; Blencowe, N.S.; Boutron, I.; Cates, C.J.; Cheng, H.-Y.; Corbett, M.S.; Eldridge, S.M.; et al. RoB 2: A revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 2019, 366, l4898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flourish Studio. Canva UK Operations Ltd. Available online: https://flourish.studio (accessed on 9 March 2023).
- Wang, W.; Pei, X.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Z.; Lin, D.; Duan, X.; Fan, J.; Pan, Q.; Guo, L. Application of new international classification of adult-onset diabetes in Chinese inpatients with diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2021, 37, e3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.F.; Yang, Y.; Wei, L.; Xiao, Y.; Li, L.; Sun, L. Identification of two novel subgroups in patients with diabetes mellitus and their association with clinical outcomes: A two-step cluster analysis. J. Diabetes Investig. 2021, 12, 1346–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Lv, Y.; Huang, N.; Sun, J.; Yang, T.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, Z.; Gao, H.; Li, J.; et al. Clinical characteristics of inpatients with new-onset diabetes mellitus in Eastern China: Based on novel clustering analysis. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 927661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Deng, Y.; Wan, Y.; Wang, J.; Xu, J. Diabetes duration and types of diabetes treatment in data-driven clusters of patients with diabetes. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 994836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Peng, X.; Dong, K.; Tao, J.; Yang, Y. The association between antidiabetic agents and leukocyte telomere length in the novel classification of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Gerontology 2021, 67, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Peng, F.; Liang, Q.; Dai, X.; Ren, J.; Wu, H.; Yang, S.; Zhu, Y.; Jia, L.; Zhao, S. Clinical characteristics and risk of diabetic complications in data-driven clusters among type 2 diabetes. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 617628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Wang, K.; Zhao, W.; Zhuang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Q.; Ahmadizar, F. Cardiorenal risk profiles among data-driven type 2 diabetes sub-phenotypes: A post-hoc analysis of the China Health and Nutrition Survey. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 828403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Huang, J.; Zou, H.; Peng, B.; Xia, S.; Dong, K.; Sun, N.; Tao, J.; Yang, Y. Roles of plasma leptin and resistin in novel subgroups of type 2 diabetes driven by cluster analysis. Lipids Health Dis. 2022, 21, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zheng, R.; Li, L.; Xu, M.; Lu, J.; Zhao, Z.; Li, M.; Wang, T.; Wang, S.; Bi, Y.; et al. Novel subgroups and chronic complications of diabetes in middle-aged and elderly Chinese: A prospective cohort study. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 12, 802114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Jia, T.; Liu, Y.; Deng, H.; Chen, Z.; Wang, J.; Geng, Z.; Wei, R.; Qiao, J.; Ma, Y.; et al. Data-driven subgroups of newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes and the relationship with cardiovascular diseases at genetic and clinical levels in Chinese adults. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2023, 17, 102850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, H. Characteristics of glucolipid metabolism and complications in novel cluster-based diabetes subgroups: A retrospective study. Lipids Health Dis. 2023, 22, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, X.; Chen, F.; Wei, R.; Chen, Z.; Li, J.; Qiao, J.; Pan, Q.; Yang, W.; Guo, L. Secondary analysis of newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes subgroups and treatment responses in the MARCH cohort. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2024, 18, 102936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Yang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Wang, W.; Gao, Z.; Yan, L.; Qin, G.; Tang, X.; Wan, Q.; et al. Clinical characteristics and complication risks in data-driven clusters among Chinese community diabetes populations. J. Diabetes 2024, 16, e13596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Dong, K.; Li, C.; Wang, G.; Lin, X.; Zhao, H. Unsupervised cluster analysis of clinical and metabolite characteristics in patients with chronic complications of T2DM: An observational study of real data. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1230921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Xie, Y.; Xia, Y.; Xie, Z.; Huang, G.; Fan, L.; Zhou, Z.; Li, X. Type 2 diabetes family history as a significant index on the clinical heterogeneity differentiation in type 1 diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 108, e1633–e1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herder, C.; Maalmi, H.; Strassburger, K.; Zaharia, O.P.; Ratter, J.M.; Karusheva, Y.; Elhadad, M.A.; Bódis, K.; Bongaerts, B.W.C.; Rathmann, W.; et al. Differences in biomarkers of inflammation between novel subgroups of recent-onset diabetes. Diabetes 2021, 70, 1198–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanabe, H.; Hirai, H.; Saito, H.; Tanaka, K.; Masuzaki, H.; Kazama, J.J.; Shimabukuro, M. Detecting sarcopenia risk by diabetes clustering: A Japanese prospective cohort study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 107, 2729–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, K.; Inoue, T.; Ariyasu, H.; Shimada, T.; Itoh, H.; Tanaka, I.; Terao, C. Usefulness of subclassification of adult diabetes mellitus among inpatients in Japan. J. Diabetes Investig. 2022, 13, 706–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjana, R.M.; Baskar, V.; Nair, A.T.N.; Jebarani, S.; Siddiqui, M.K.; Pradeepa, R.; Unnikrishnan, R.; Palmer, C.; Pearson, E.; Mohan, V. Novel subgroups of type 2 diabetes and their association with microvascular outcomes in an Asian Indian population: A data-driven cluster analysis: The INSPIRED study. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2020, 8, e001506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, I.; Raizada, N.; Aslam, M.; Madhu, S. Phenotypic clusters of type 2 diabetes mellitus among North Indians reveal higher levels of insulin deficiency along with insulin resistance. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2024, 18, 102993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, P.; Vyawahare, A.; Kadam, N.; Tiwari, D.; Biswas, M.D.; Kathrikolly, T.; Sharma, B.; Vijayakumar, V.; Kuppusamy, M. Comparison of clustering and phenotyping approaches for subclassification of type 2 diabetes and its association with remission in Indian population. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 20260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Li, P.; Crouse, A.B.; Grimes, T.; Might, M.; Ovalle, F.; Shalev, A. Data-driven cluster analysis reveals increased risk for severe insulin-deficient diabetes in Black/African Americans. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 110, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.; Jones-Antwi, R.; Ali, M.K.; Patel, S.A. Do diabetes phenotypes in US women differ by race/ethnicity? A population-based cluster analysis. Metabol. Open 2022, 17, 100225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, M.; Tosur, M.; Astudillo, M.; Refaey, A.; Sabharwal, A.; Redondo, M.J. Clinical characterization of data-driven diabetes clusters of pediatric type 2 diabetes. Pediatr. Diabetes 2023, 2023, 6955723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Somolinos-Simón, F.J.; García-Sáez, G.; Tapia-Galisteo, J.; Corcoy, R.; Elena Hernando, M. Cluster analysis of adult individuals with type 1 diabetes: Treatment pathways and complications over a five-year follow-up period. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2024, 215, 111803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danquah, I.; Mank, I.; Hampe, C.S.; Meeks, K.A.C.; Agyemang, C.; Owusu-Dabo, E.; Smeeth, L.; Klipstein-Grobusch, K.; Bahendeka, S.; Spranger, J.; et al. Subgroups of adult-onset diabetes: A data-driven cluster analysis in a Ghanaian population. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 10756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, D.H.; Nicolaisen, S.K.; Ahlqvist, E.; Stidsen, J.V.; Nielsen, J.S.; Hojlund, K.; Olsen, M.H.; García-Calzón, S.; Ling, C.; Rungby, J.; et al. Type 2 diabetes classification: A data-driven cluster study of the Danish Centre for Strategic Research in Type 2 Diabetes (DD2) cohort. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2022, 10, e002731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, J.J.; Gurung, R.L.; Liu, S.; Lee, J.; M, Y.; Ang, K.; Shao, Y.M.; Tang, J.I.; Benke, P.I.; et al. Clinical variable-based cluster analysis identifies novel subgroups with a distinct genetic signature, lipidomic pattern and cardio-renal risks in Asian patients with recent-onset type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2022, 65, 2146–2156, Erratum in Diabetologia 2022, 65, 2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Ghani, T.; Puckett, C.; Migahid, O.; Abdelgani, S.; Migahed, A.; Adams, J.; Triplitt, C.; DeFronzo, R.; Jayyousi, A.; Abdul-Ghani, M. Type 2 diabetes subgroups and response to glucose-lowering therapy: Results from the EDICT and Qatar studies. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2022, 24, 1810–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preechasuk, L.; Khaedon, N.; Lapinee, V.; Tangjittipokin, W.; Srivanichakorn, W.; Sriwijitkamol, A.; Plengvidhya, N.; Likitmaskul, S.; Thongtang, N. Cluster analysis of Thai patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus to predict disease progression and treatment outcomes: A prospective cohort study. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2022, 10, e003145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; van Giessen, A.; Altunkaya, J.; Slieker, R.C.; Beulens, J.W.J.; ‘t Hart, L.M.; Pearson, E.R.; Elders, P.J.M.; Feenstra, T.L.; Leal, J. Potential value of identifying type 2 diabetes subgroups for guiding intensive treatment: A comparison of novel data-driven clustering with risk-driven subgroups. Diabetes Care 2023, 46, 1395–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, Y.C.; Ahn, H.Y.; Jun, J.E.; Jeong, I.K.; Ahn, K.J.; Chung, H.Y. Subtypes of type 2 diabetes and their association with outcomes in Korean adults—A cluster analysis of community-based prospective cohort. Metabolism 2023, 141, 155514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayoumi, R.; Farooqi, M.; Alawadi, F.; Hassanein, M.; Osama, A.; Mukhopadhyay, D.; Abdul, F.; Sulaiman, F.; Dsouza, S.; Mulla, F.; et al. Etiologies underlying subtypes of long-standing type 2 diabetes. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0304036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Donnelly, L.A.; Slieker, R.C.; Beulens, J.W.J.; ‘t Hart, L.M.; Elders, P.J.M.; Pearson, E.R.; van Giessen, A.; Leal, J.; Feenstra, T. Trajectories of clinical characteristics, complications and treatment choices in data-driven subgroups of type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2024, 67, 1343–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lugner, M.; Gudbjörnsdottir, S.; Sattar, N.; Svensson, A.M.; Miftaraj, M.; Eeg-Olofsson, K.; Eliasson, B.; Franzén, S. Comparison between data-driven clusters and models based on clinical features to predict outcomes in type 2 diabetes: Nationwide observational study. Diabetologia 2021, 64, 1973–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cojic, M.M.; Klisic, A.; Kocic, R.; Veljkovic, A.; Kocic, G. Data-driven cluster analysis of oxidative stress indexes in relation to vitamin D level, age, and metabolic control in patients with type 2 diabetes on metformin therapy. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 7942716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cojic, M.; Klisic, A.; Sahmanovic, A.; Petrovic, N.; Kocic, G. Cluster analysis of patient characteristics, treatment modalities, renal impairments, and inflammatory markers in diabetes mellitus. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 5994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimsmann, J.M.; Tittel, S.R.; Bramlage, P.; Mayer, B.; Fritsche, A.; Seufert, J.; Laimer, M.; Zimny, S.; Meyhoefer, S.M.; Hummel, M.; et al. Disease heterogeneity of adult diabetes based on routine clinical variables at diagnosis: Results from the German/Austrian Diabetes Follow-up Registry. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2022, 24, 2253–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzini, E.; Vlacho, B.; Franch-Nadal, J.; Escudero, J.; Génova, A.; Reixach, E.; Andrés, E.; Pizarro, I.; Portero, J.L.; Mauricio, D.; et al. Longitudinal deep learning clustering of type 2 diabetes mellitus trajectories using routinely collected health records. J. Biomed. Inform. 2022, 135, 104218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, K.G.; Zimmet, P.Z. Definition, diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its complications. Part 1: Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus provisional report of a WHO consultation. Diabet. Med. 1998, 15, 539–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Classification of Diabetes Mellitus; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019; Available online: https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/325182/9789241515702-eng.pdf (accessed on 21 November 2024).
- American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes—2010. Diabetes Care 2010, 33 (Suppl. S1), S11–S61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes—2011. Diabetes Care 2011, 34 (Suppl. S1), S11–S61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes—2018 abridged for primary care providers. Clin. Diabetes 2018, 36, 14–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association. 2. Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: Standards of medical care in diabetes-2020. Diabetes Care 2020, 43 (Suppl. S1), S14–S31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 2. Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: Standards of medical care in diabetes-2022. Diabetes Care 2022, 45 (Suppl. S1), S17–S38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, X.; Huang, Q.; Luo, Y.; Ren, Q.; Han, X.; Zhou, X.; Ji, L. The efficacy of canagliflozin in diabetes subgroups stratified by data-driven clustering or a supervised machine learning method: A post hoc analysis of canagliflozin clinical trial data. Diabetologia 2022, 65, 1424–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pigeyre, M.; Hess, S.; Gomez, M.F.; Asplund, O.; Groop, L.; Paré, G.; Gerstein, H. Validation of the classification for type 2 diabetes into five subgroups: A report from the ORIGIN trial. Diabetologia 2022, 65, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanabe, H.; Masuzaki, H.; Shimabukuro, M. Novel strategies for glycaemic control and preventing diabetic complications applying the clustering-based classification of adult-onset diabetes mellitus: A perspective. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2021, 180, 109067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, J.S.; Narayan, K.M.V. Ethnic differences between Asians and non-Asians in clustering-based phenotype classification of adult-onset diabetes mellitus: A systematic narrative review. Prim. Care Diabetes 2022, 16, 853–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K. Incretin response in Asian type 2 diabetes: Are Indians different? Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 19, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabe, D.; Seino, Y.; Fukushima, M.; Seino, S. β cell dysfunction versus insulin resistance in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes in East Asians. Curr. Diab Rep. 2015, 15, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodama, K.; Tojjar, D.; Yamada, S.; Toda, K.; Patel, C.J.; Butte, A.J. Ethnic differences in the relationship between insulin sensitivity and insulin response: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 1789–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zou, X.; Huang, Q.; Han, X.; Zhou, X.; Ji, L. Do East Asians with normal glucose tolerance have worse β-cell function? A meta-analysis of epidemiological studies. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 780557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.C.; Chan, J.C. Type 2 diabetes in East Asians: Similarities and differences with populations in Europe and the United States. Ann. N. Y Acad. Sci. 2013, 1281, 64–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wysham, C.; Shubrook, J. Beta-cell failure in type 2 diabetes: Mechanisms, markers, and clinical implications. Postgrad. Med. 2020, 132, 676–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, K.S.; Bigelow, M.L.; Asmann, Y.W.; Chow, L.S.; Coenen-Schimke, J.M.; Klaus, K.A.; Guo, Z.K.; Sreekumar, R.; Irving, B.A. Asian Indians have enhanced skeletal muscle mitochondrial capacity to produce ATP in association with severe insulin resistance. Diabetes 2008, 57, 1166–1175, Erratum in Diabetes 2009, 58, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raji, A.; Seely, E.W.; Arky, R.A.; Simonson, D.C. Body fat distribution and insulin resistance in healthy Asian Indians and Caucasians. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 5366–5371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yajnik, C.S. The insulin resistance epidemic in India: Fetal origins, later lifestyle, or both? Nutr. Rev. 2001, 59 Pt 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandalia, M.; Abate, N.; Garg, A.; Stray-Gundersen, J.; Grundy, S.M. Relationship between generalized and upper body obesity to insulin resistance in Asian Indian men. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1999, 84, 2329–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulman, A.; Simmons, R.K.; Brunner, E.J.; Witte, D.R.; Færch, K.; Vistisen, D.; Ikehara, S.; Kivimaki, M.; Tabák, A.G. Trajectories of glycaemia, insulin sensitivity and insulin secretion in South Asian and white individuals before diagnosis of type 2 diabetes: A longitudinal analysis from the Whitehall II cohort study. Diabetologia 2017, 60, 1252–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raygor, V.; Abbasi, F.; Lazzeroni, L.C.; Kim, S.; Ingelsson, E.; Reaven, G.M.; Knowles, J.W. Impact of race/ethnicity on insulin resistance and hypertriglyceridaemia. Diab Vasc. Dis. Res. 2019, 16, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grepper, D.; Tabasso, C.; Aguettaz, A.K.F.; Martinotti, A.; Ebrahimi, A.; Lagarrigue, S.; Amati, F. Methodological advancements in organ-specific ectopic lipid quantitative characterization: Effects of high fat diet on muscle and liver intracellular lipids. Mol. Metab. 2023, 68, 101669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanaya, A.M. Diabetes in South Asians: Uncovering novel risk factors with longitudinal epidemiologic data: Kelly West Award Lecture 2023. Diabetes Care 2024, 47, 7–16, Erratum in Diabetes Care 2024, 47, 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayan, K.M.V.; Kondal, D.; Daya, N.; Gujral, U.P.; Mohan, D.; Patel, S.A.; Shivashankar, R.; Anjana, R.M.; Staimez, L.R.; Ali, M.K.; et al. Incidence and pathophysiology of diabetes in South Asian adults living in India and Pakistan compared with US blacks and whites. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2021, 9, e001927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Park, S.Y.; Choi, C.S. Insulin resistance: From mechanisms to therapeutic strategies. Diabetes Metab. J. 2022, 46, 15–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parvanova, A.I.; Trevisan, R.; Iliev, I.P.; Dimitrov, B.D.; Vedovato, M.; Tiengo, A.; Remuzzi, G.; Ruggenenti, P. Insulin resistance and microalbuminuria: A cross-sectional, case-control study of 158 patients with type 2 diabetes and different degrees of urinary albumin excretion. Diabetes 2006, 55, 1456–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Cosmo, S.; Menzaghi, C.; Prudente, S.; Trischitta, V. Role of insulin resistance in kidney dysfunction: Insights into the mechanism and epidemiological evidence. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2013, 28, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artunc, F.; Schleicher, E.; Weigert, C.; Fritsche, A.; Stefan, N.; Häring, H.U. The impact of insulin resistance on the kidney and vasculature. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2016, 12, 721–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lay, A.C.; Tran, V.D.T.; Nair, V.; Betin, V.; Hurcombe, J.A.; Barrington, A.F.; Pope, R.J.; Burdet, F.; Mehl, F.; Kryvokhyzha, D.; et al. Profiling of insulin-resistant kidney models and human biopsies reveals common and cell-type-specific mechanisms underpinning Diabetic Kidney Disease. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 10018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daza-Arnedo, R.; Rico-Fontalvo, J.; Aroca-Martínez, G.; Rodríguez-Yanez, T.; Martínez-Ávila, M.C.; Almanza-Hurtado, A.; Cardona-Blanco, M.; Henao-Velásquez, C.; Fernández-Franco, J.; Unigarro-Palacios, M.; et al. Insulin and the kidneys: A contemporary view on the molecular basis. Front. Nephrol. 2023, 3, 1133352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, C.; Stumvoll, M.; Nadkarni, V.; Dostou, J.; Mitrakou, A.; Gerich, J. Abnormal renal and hepatic glucose metabolism in type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Clin. Investig. 1998, 102, 619–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeFronzo, R.A.; Goldberg, M.; Agus, Z.S. The effects of glucose and insulin on renal electrolyte transport. J. Clin. Investig. 1976, 58, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, N.; Nakamura, M.; Suzuki, M.; Suzuki, A.; Seki, G.; Horita, S. Roles of Akt and SGK1 in the regulation of renal tubular transport. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 971697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, K.; Fujiwara, K.; Oka, K.; Nagahama, T.; Matsuda, H.; Saruta, T. Effects of insulin on rat renal microvessels: Studies in the isolated perfused hydronephrotic kidney. Kidney Int. 1997, 51, 1507–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmetterer, L.; Müller, M.; Fasching, P.; Diepolder, C.; Gallenkamp, A.; Zanaschka, G.; Findl, O.; Strenn, K.; Mensik, C.; Tschernko, E.; et al. Renal and ocular hemodynamic effects of insulin. Diabetes 1997, 46, 1868–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welsh, G.I.; Hale, L.J.; Eremina, V.; Jeansson, M.; Maezawa, Y.; Lennon, R.; Pons, D.A.; Owen, R.J.; Satchell, S.C.; Miles, M.J.; et al. Insulin signaling to the glomerular podocyte is critical for normal kidney function. Cell Metab. 2010, 12, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhusudhan, T.; Wang, H.; Dong, W.; Ghosh, S.; Bock, F.; Thangapandi, V.R.; Ranjan, S.; Wolter, J.; Kohli, S.; Shahzad, K.; et al. Defective podocyte insulin signalling through p85-XBP1 promotes ATF6-dependent maladaptive ER-stress response in diabetic nephropathy. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejada, T.; Catanuto, P.; Ijaz, A.; Santos, J.V.; Xia, X.; Sanchez, P.; Sanabria, N.; Lenz, O.; Elliot, S.J.; Fornoni, A. Failure to phosphorylate AKT in podocytes from mice with early diabetic nephropathy promotes cell death. Kidney Int. 2008, 73, 1385–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, N.; Ito, O.; Abe, K. Tubular effects of insulin. Hypertens. Res. 1996, 19 (Suppl. S1), S41–S45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuczkowski, A.; Brinkkoetter, P.T. Metabolism and homeostasis in the kidney: Metabolic regulation through insulin signaling in the kidney. Cell Tissue Res. 2017, 369, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yau, J.W.; Rogers, S.L.; Kawasaki, R.; Lamoureux, E.L.; Kowalski, J.W.; Bek, T.; Chen, S.J.; Dekker, J.M.; Fletcher, A.; Grauslund, J.; et al. Meta-Analysis for Eye Disease (META-EYE) Study Group. Global prevalence and major risk factors of diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hainsworth, D.P.; Bebu, I.; Aiello, L.P.; Sivitz, W.; Gubitosi-Klug, R.; Malone, J.; White, N.H.; Danis, R.; Wallia, A.; Gao, X.; et al. Diabetes Control and Complications Trial (DCCT)/Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications (EDIC) Research Group. Risk Factors for Retinopathy in Type 1 Diabetes: The DCCT/EDIC Study. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, 875–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.H.; Jeong, J.S.; Kim, M.K.; Kwon, H.S.; Baek, K.H.; Ko, S.H.; Ahn, Y.B. Discordance in risk factors for the progression of diabetic retinopathy and diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Diabetes Investig. 2019, 10, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarasewicz, D.; Conell, C.; Gilliam, L.K.; Melles, R.B. Quantification of risk factors for diabetic retinopathy progression. Acta Diabetol. 2023, 60, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.U.; Park, S.P.; Kim, Y.K. Long-term HbA1c variability and the development and progression of diabetic retinopathy in subjects with type 2 diabetes. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hietala, K.; Wadén, J.; Forsblom, C.; Harjutsalo, V.; Kytö, J.; Summanen, P.; Groop, P.H.; FinnDiane Study Group. HbA1c variability is associated with an increased risk of retinopathy requiring laser treatment in type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia 2013, 56, 737–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermann, J.M.; Hammes, H.P.; Rami-Merhar, B.; Rosenbauer, J.; Schütt, M.; Siegel, E.; Holl, R.W.; DPV Initiative the German BMBF Competence Network Diabetes Mellitus. HbA1c variability as an independent risk factor for diabetic retinopathy in type 1 diabetes: A German/Austrian multicenter analysis on 35,891 patients. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonardo, A.; Lugari, S.; Ballestri, S.; Nascimbeni, F.; Baldelli, E.; Maurantonio, M. A round trip from nonalcoholic fatty liver disease to diabetes: Molecular targets to the rescue? Acta Diabetol. 2019, 56, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cernea, S. NAFLD fibrosis progression and type 2 diabetes: The hepatic-metabolic interplay. Life 2024, 14, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmas, C.E.; Bousvarou, M.D.; Kostara, C.E.; Papakonstantinou, E.J.; Salamou, E.; Guzman, E. Insulin resistance and cardiovascular disease. J. Int. Med. Res. 2023, 51, 3000605231164548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Jaramillo, P.; Gomez-Arbelaez, D.; Martinez-Bello, D.; Abat, M.E.M.; Alhabib, K.F.; Avezum, Á.; Barbarash, O.; Chifamba, J.; Diaz, M.L.; Gulec, S.; et al. Association of the triglyceride glucose index as a measure of insulin resistance with mortality and cardiovascular disease in populations from five continents (PURE study): A prospective cohort study. Lancet Healthy Longev. 2023, 4, e23–e33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, A.; Csermely, A.; Petracca, G.; Beatrice, G.; Corey, K.E.; Simon, T.G.; Byrne, C.D.; Targher, G. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and risk of fatal and non-fatal cardiovascular events: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 6, 903–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Targher, G.; Lonardo, A.; Byrne, C. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and chronic vascular complications of diabetes mellitus. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, A.; Petracca, G.; Beatrice, G.; Csermely, A.; Lonardo, A.; Schattenberg, J.M.; Tilg, H.; Byrne, C.D.; Targher, G. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and risk of incident chronic kidney disease: An updated meta-analysis. Gut 2022, 71, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cernea, S.; Raz, I. Management of diabetic neuropathy. Metabolism 2021, 123, 154867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Hu, Z.; Luo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Luo, W.; Du, X.; Luo, Z.; Hu, J.; Peng, S. Diabetic peripheral neuropathy: Pathogenetic mechanisms and treatment. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 14, 1265372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simes, B.C.; MacGregor, G.G. Sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors: A clinician’s guide. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2019, 12, 2125–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reed, J.W. Impact of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors on blood pressure. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2016, 12, 393–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Peralta, F.; Abreu, C.; Gomez-Rodriguez, S.; Barranco, R.J.; Umpierrez, G.E. Safety and efficacy of DPP4 inhibitor and basal insulin in type 2 diabetes: An updated review and challenging clinical scenarios. Diabetes Ther. 2018, 9, 1775–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florentin, M.; Kostapanos, M.S.; Papazafiropoulou, A.K. Role of dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors in the new era of antidiabetic treatment. World J. Diabetes 2022, 13, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, F.; Islam, M.A.; Mohamed, M.; Ahmad, I.; Kamal, M.A.; Donnelly, R.; Idris, I.; Gan, S.H. Efficacy and safety of pioglitazone monotherapy in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Wang, H.; Yang, G.; Gao, Z.; Luo, Y.; Dong, A.; Zhang, F.; Xu, M.; Liu, S.; Yang, X.; et al. Pioglitazone improved insulin sensitivity and first phase insulin secretion among obese and lean people with diabetes: A multicenter clamp study. Diabetes Ther. 2018, 9, 815–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gastaldelli, A.; Ferrannini, E.; Miyazaki, Y.; Matsuda, M.; Mari, A.; DeFronzo, R.A. Thiazolidinediones improve beta-cell function in type 2 diabetic patients. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 292, E871–E883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldor, R.; DeFronzo, R.A.; Abdul-Ghani, M. In vivo actions of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors: Glycemic control, insulin sensitivity, and insulin secretion. Diabetes Care 2013, 36 (Suppl. S2), S162–S174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, A.H.; Peters, R.K.; Kjos, S.L.; Marroquin, A.; Goico, J.; Ochoa, C.; Kawakubo, M.; Buchanan, T.A. Effect of pioglitazone on pancreatic beta-cell function and diabetes risk in Hispanic women with prior gestational diabetes. Diabetes 2006, 55, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, K.V.; Raskin, P. Exenatide extended-release: A once weekly treatment for patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2014, 7, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Mariam, Z.; Niazi, S.K. Glucagon-like peptide agonists: A prospective review. Endocrinol. Diabetes Metab. 2024, 7, e462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, L. GLP-1 receptor agonists: A review of glycemic benefits and beyond. JAAPA 2024, 37, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).