Evidence for the Necessity of Objective Hearing Tests in Cochlear Implantation Assessment: Excluding Functional Hearing Loss Cases
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Subjective Audiological Methods
2.3. Objective Audiological Methods
2.4. Imaging
2.5. Data Processing
3. Results
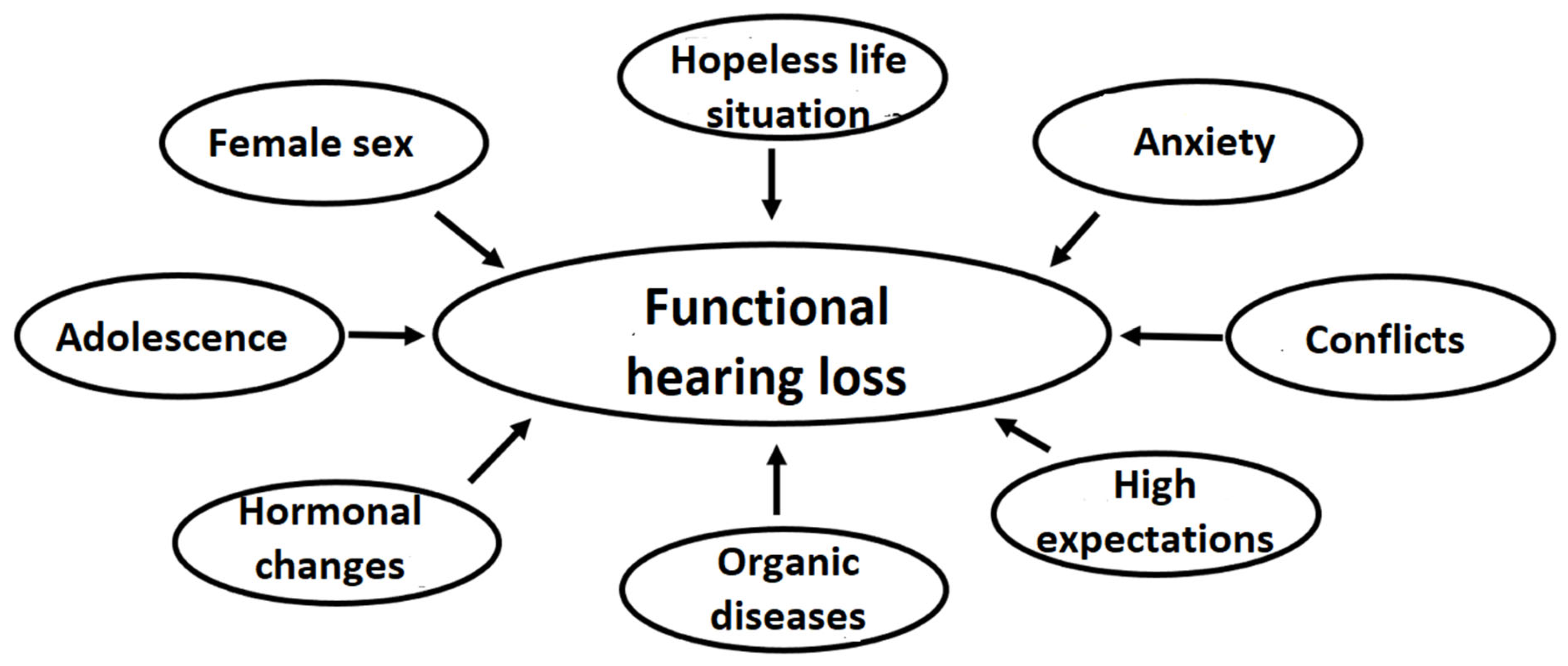
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABR | auditory brainstem response |
| ADHD | attention deficit hyperactivity disorder |
| ASSR | auditory steady-state response |
| CI | cochlear implantation |
| cPTSD | complex post-traumatic stress disorder |
| FHL | functional hearing loss |
| HRCT | high-resolution computed tomography |
| MRI | magnetic resonance imaging |
| OAE | otoacoustic emission |
| PCCT | photon counting computed tomography |
| PTA | pure-tone audiometry |
References
- Van de Heyning, P.; Gavilán, J.; Godey, B.; Hagen, R.; Hagr, A.; Kameswaran, M.; Li, Y.; Manoj, M.; Mlynski, R.; O’Driscoll, M.; et al. Worldwide Variation in Cochlear Implant Candidacy. J. Int. Adv. Otol. 2022, 18, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Szyfter, W.; Karlik, M.; Sekula, A.; Harris, S.; Gawęcki, W. Current indications for cochlear implantation in adults and children. Otolaryngol. Pol. 2019, 73, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeitler, D.M.; Prentiss, S.M.; Sydlowski, S.A.; Dunn, C.C. American Cochlear Implant Alliance Task Force: Recommendations for Determining Cochlear Implant Candidacy in Adults. Laryngoscope 2024, 134 (Suppl. S3), S1–S14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hamed, N.; Alajmi, N.; Alkoblan, F.I.; Alghtani, Y.A.; Abdelsamad, Y.; Alhussien, A.; Alhajress, R.I.; Alhabib, S.F. The Chronological Evolution of Cochlear Implant Contraindications: A Comprehensive Review. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- American Academy of Audiology. Clinical Practice Guideline: Cochlear Implants. 2019. Available online: https://www.audiology.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/05/CochlearImplantPracticeGuidelines.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2019).
- American Academy of Otolaryngology—Head and Neck Surgery. Position Statement: Cochlear Implantation for Children with Bilateral Sensorineural Hearing Loss; American Academy of Otolaryngology—Head and Neck Surgery: Alexandria, VA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- American Academy of Otolaryngology—Head and Neck Surgery. Position Statement: Cochlear Implantation for Single-Sided Deafness in Adults; American Academy of Otolaryngology—Head and Neck Surgery: Alexandria, VA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- American Academy of Otolaryngology—Head and Neck Surgery. Position Statement: Cochlear Implantation for Children with Unilateral Sensorineural Hearing Loss; American Academy of Otolaryngology—Head and Neck Surgery: Alexandria, VA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Wesarg, T.; Aschendorff, A.; Baumgaertel, R.; Böttcher, J.; De Coninck, L.; Dhooge, I.; Dierckx, A.; Klenzner, T.; Schörg, P.; Sprinzl, G.; et al. Cochlear Implantation in Single-Sided Deafness and Asymmetric Hearing Loss: 12 Months Follow-Up Results of a European Multicenter Evaluation. J. Int. Adv. Otol. 2024, 20, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Schmidt, C.M.; am Zehnhoff-Dinnesen, A.; Matulat, P.; Knief, A.; Rosslau, K.; Deuster, D. Nonorganic hearing loss in children: Audiometry, clinical characteristics, biographical history and recovery of hearing thresholds. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2013, 77, 1190–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Staecker, H. Nonorganic hearing loss. Semin. Neurol. 2006, 26, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austen, S.; Lynch, C. Non-organic hearing loss redefined: Understanding, categorizing and managing non-organic behaviour. Int. J. Audiol. 2004, 43, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peck, J. The terminology of false and exaggerated hearing loss. Audiol. Today 2019, 31, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, S.A.S.; Hohman, M.H. Nonorganic Functional Hearing Loss. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed.; American Psychiatric Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palermo, T.M.; Krell, H.; Janosy, N.; Zeltzer, L.K. Pain somatoform disorders. In Developmental-Behavioral Pediatrics: Evidence and Practice; Wolraich, M.L., Dworkin, P.H., Drotar, D.D., Perrin, E.C., Eds.; Mosby: Maryland Heights, MO, USA, 2008; pp. 711–741. [Google Scholar]
- Varley, D.V. The Clinical Management of Functional Neurological Disorder in UK Health Services: A Mixed-Methods Study of Diagnostic Assessments and Treatments, Experiences, and Perspectives. Ph.D. Thesis, University of York, York, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Ban, J.H.; Jin, S.M. A clinical analysis of psychogenic sudden deafness. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2006, 134, 970–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, I.M.; Greenberg, D.B.; Smith, F.A.; Cassem, N.D. Functional somatic symptoms, deception syndromes, and somatoform disorders. In Massachusetts General Hospital Handbook of General Hospital Psychiatry; Stern, T.A., Fricchione, T.L., Cassem, N.D., Jellinek, M., Rosenbaum, J.F., Eds.; Saunders/Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2010; pp. 173–187. [Google Scholar]
- Prekopp, P.; Kondé, M.; Szigeti, F.J.; Baranyi, I.; Küstel, M.; Tamás, L.; Gáborján, A. A funkcionális halláscsökkenés felismerése és komplex diagnosztikája [Recognition and complex diagnostics of functional hearing loss]. Orv. Hetil. 2023, 164, 283–292. (In Hungarian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aimoni, C.; Crema, L.; Savini, S.; Negossi, L.; Rosignoli, M.; Sacchetto, L.; Bianchini, C.; Ciorba, A. Hearing threshold estimation by auditory steady state responses (ASSR) in children. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2018, 38, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Vasileiou, A.; Pavlos, M.; Antonios, T.; Ioannis, X.; Vlastarakos, P.V.; Nikolopoulos, T.P. Correlation of ASSR hearing thresholds with ABR hearing thresholds in children. J. Hear. Sci. 2018, 8, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.H.; Lee, H.S.; Kim, Y.J.; Yoon, T.H.; Chung, J.W. Comparing pure-tone audiometry and auditory steady state response for the measurement of hearing loss. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2007, 136, 966–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Stadio, A.; Sossamon, J.; De Luca, P.; Indovina, I.; Motta, G.; Ralli, M.; Brenner, M.J.; Frohman, E.M.; Plant, G.T. “Do You Hear What I Hear?” Speech and Voice Alterations in Hearing Loss: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Komazec, Z.; Lemajić-Komazec, S.; Jović, R.; Nadj, C.; Jovancević, L.; Savović, S. Comparison between auditory steady-state responses and pure-tone audiometry. Vojnosanit. Pregl. 2010, 67, 761–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarawneh, H.Y.; Sohrabi, H.R.; Mulders, W.H.A.M.; Martins, R.N.; Jayakody, D.M.P. Comparison of Auditory Steady-State Responses with Conventional Audiometry in Older Adults. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 924096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ozdek, A.; Karacay, M.; Saylam, G.; Tatar, E.; Aygener, N.; Korkmaz, M.H. Comparison of pure tone audiometry and auditory steady-state responses in subjects with normal hearing and hearing loss. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2010, 267, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseinabadi, R.; Jafarzadeh, S. Auditory steady-state response thresholds in adults with conductive and mild to moderate sensorineural hearing loss. Iran Red. Crescent Med. J. 2014, 17, e18029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Swami, H.; Kumar, S. Comparison of Frequency-Specific Hearing Thresholds Between Pure-Tone Audiometry and Auditory Steady-State Response. Indian J. Otol. 2019, 25, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leigh, J.; Farrell, R.; Courtenay, D.; Dowell, R.; Briggs, R. Relationship Between Objective and Behavioral Audiology for Young Children Being Assessed for Cochlear Implantation: Implications for CI Candidacy Assessment. Otol. Neurotol. 2019, 40, e252–e259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.H.; Chen, P.R.; Hsu, C.J.; Wu, H.P. Validation of multi-channel auditory steady-state response in adults with sensorineural hearing loss. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2009, 123, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plioutas, J.; Vlastarakos, P.V.; Delidis, A.; Vasileiou, A.; Nikolopoulos, T.P.; Maragoudakis, P. Is Auditory Steady-State Response Testing the Key for Diagnosing Non-Organic Hearing Disorders? Implications for Current Audiological Practice. J. Audiol. Otol. 2022, 26, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kemp, D.T. Otoacoustic emissions, their origin in cochlear function, and use. Br. Med. Bull. 2002, 63, 223–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portugal, N.; Poling, G.L.; Dreisbach, L. Rethinking the clinical utility of distortion-product otoacoustic emission (DPOAE) signal-to-noise ratio. Int. J. Audiol. 2023, 63, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morsy, S.K.; Aybek, S.; Carson, A.; Nicholson, T.R.; Stone, J.; Kamal, A.M.; Abdel-Fadeel, N.A.; Hassan, M.A.; Kanaan, R.A.A. The relationship between types of life events and the onset of functional neurological (conversion) disorder in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychol. Med. 2022, 52, 401–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigel, A.; Maehder, K.; Witt, M.; Löwe, B. Psychotherapists’ perspective on the treatment of patients with somatic symptom disorders. J. Psychosom. Res. 2020, 138, 110228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aplin, D.Y.; Rowson, V.J. Psychological characteristics of children with functional hearing loss. Br. J. Audiol. 1990, 24, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oishi, N.; Kanzaki, S.; Kataoka, C.; Tazoe, M.; Takei, Y.; Nagai, K.; Kohno, N.; Ogawa, K. Acute-onset unilateral psychogenic hearing loss in adults: Report of six cases and diagnostic pitfalls. ORL J. Otorhinolaryngol. Relat. Spec. 2009, 71, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topuz, M.F.; Ozel, H.E.; Onen, S. A simple supportive evaluation way for the diagnosis of psychogenic hearing loss. Ann. Med. Res. 2021, 27, 1008–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistry, S.G.; Carr, S.D.; Tapper, L.; Meredith, B.; Strachan, D.R.; Raine, C.H. Inside implant criteria or not?—Detection of non-organic hearing loss during cochlear implant assessment. Cochlear Implants Int. 2016, 17, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kompis, M.; Senn, P.; Mantokoudis, G.; Caversaccio, M. Cochlear implant candidates with psychogenic hearing loss. Acta Otolaryngol. 2015, 135, 376–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamazaki, M.; Kawase, T.; Hino-Fukuyo, N.; Morimoto, T.; Metoki, H.; Takahashi, H.; Fukuchi, N.; Takanashi, Y.; Ohta, N. Functional hearing loss and developmental imbalances. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2023, 173, 111700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pflug, C.; Kiehn, S.; Koseki, J.C.; Pinnschmidt, H.; Müller, F.; Nienstedt, J.C.; Flügel, T.; Niessen, A. Prognostic factors in non-organic hearing loss in children. Int. J. Audiol. 2022, 61, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timmer, B.; Bleichhardt, G.; Rief, W. Importance of psychotherapy motivation in patients with somatization syndrome. Psychother. Res. 2006, 16, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajluni, V. Integrating psychiatry and family medicine in the management of somatic symptom disorders: Diagnosis, collaboration, and communication strategies. J. Gen. Fam. Med. 2024, 26, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

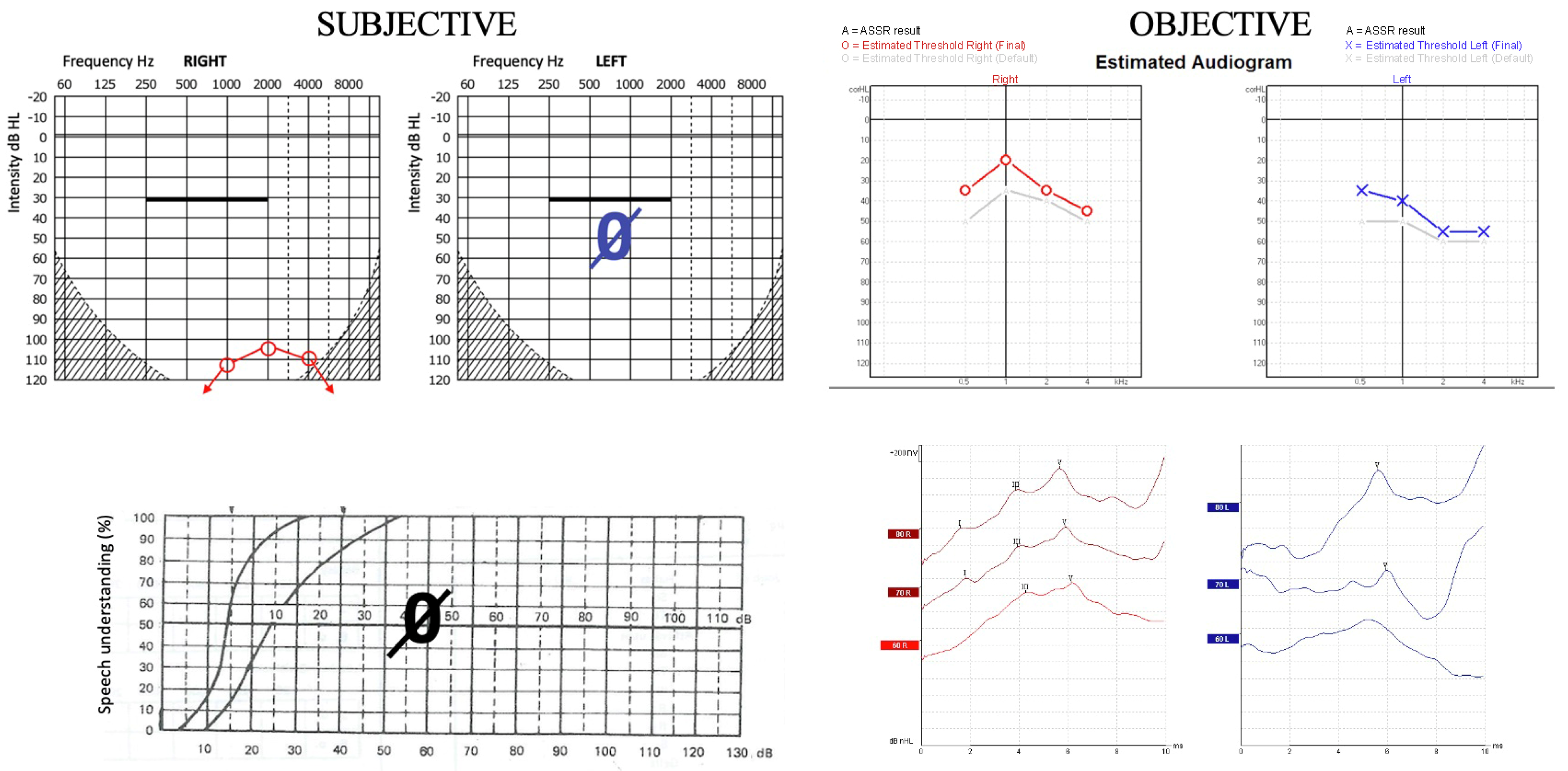
| Patient | Age (Years) Female/Male | PTA (dB) | ASSR (dB) | FHL (dB) | DPOAEs | Organic Background | Communication During Examination | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Right Ear | Left Ear | Right Ear | Left Ear | Right Ear | Left Ear | R/L | ||||
| P1 | 32 M | 110 | 120 | 34 | 46 | 76 | 74 | −/− | yes (inner ear) | no communication |
| P2 | 37 F | 120 | * 75 | 52.5 | 45 | 67.5 | 30 * | −/− | yes (otosclerosis) | minimal difficulty |
| P3 | 13 F | 97.5 | 100 | 36 | 44 | 61.5 | 56 | −/− | yes (middle ear) | minimal difficulty |
| P4 | 41 F | 106 | 90 | 46 | 52.5 | 60 | 37.5 | −/− | yes (inner ear) | minimal difficulty |
| P5 | 17 F | 77.5 | 77.5 | 19 | 11 | 58.5 | 66.5 | +/+ | no | proper communication |
| P6 | 22 F | 100 | 100 | 26 | 24 | 74 | 76 | +/+ | no | minimal difficulty |
| P7 | 15 F | 120 | 120 | 37.5 | 25 | 82.5 | 95 | intolerance | no | minimal difficulty |
| P8 | 64 F | * 71 | 91 | 37.5 | 59 | 33.5 * | 32 | −/− | yes (inner ear) | difficulty |
| P9 | 54 F | 109 | 92.5 | 39 | 50 | 70 | 42.5 | +/+ | yes (inner ear) | difficulty |
| P10 | 15 F | 95 | 95 | 26 | 25 | 69 | 70 | +/+ | no | no communication |
| P11 | 33 F | 95 | * 76 | 47.5 | 72.5 | 47.5 | 3.5 * | +/+ | yes (inner ear) | proper communication |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gáborján, A.; Kondé, M.; Küstel, M.; Kecskeméti, N.; Tamás, L.; Baranyi, I.; Polony, G.; Szigeti, J.F. Evidence for the Necessity of Objective Hearing Tests in Cochlear Implantation Assessment: Excluding Functional Hearing Loss Cases. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3585. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103585
Gáborján A, Kondé M, Küstel M, Kecskeméti N, Tamás L, Baranyi I, Polony G, Szigeti JF. Evidence for the Necessity of Objective Hearing Tests in Cochlear Implantation Assessment: Excluding Functional Hearing Loss Cases. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(10):3585. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103585
Chicago/Turabian StyleGáborján, Anita, Márton Kondé, Marianna Küstel, Nóra Kecskeméti, László Tamás, Ildikó Baranyi, Gábor Polony, and Judit F. Szigeti. 2025. "Evidence for the Necessity of Objective Hearing Tests in Cochlear Implantation Assessment: Excluding Functional Hearing Loss Cases" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 10: 3585. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103585
APA StyleGáborján, A., Kondé, M., Küstel, M., Kecskeméti, N., Tamás, L., Baranyi, I., Polony, G., & Szigeti, J. F. (2025). Evidence for the Necessity of Objective Hearing Tests in Cochlear Implantation Assessment: Excluding Functional Hearing Loss Cases. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(10), 3585. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103585






