Real-Time Measurement of Intrarenal Pressure Using LithoVue™ Elite: Focus on Small Ureteral Access Sheaths and Appropriate Irrigation Settings
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
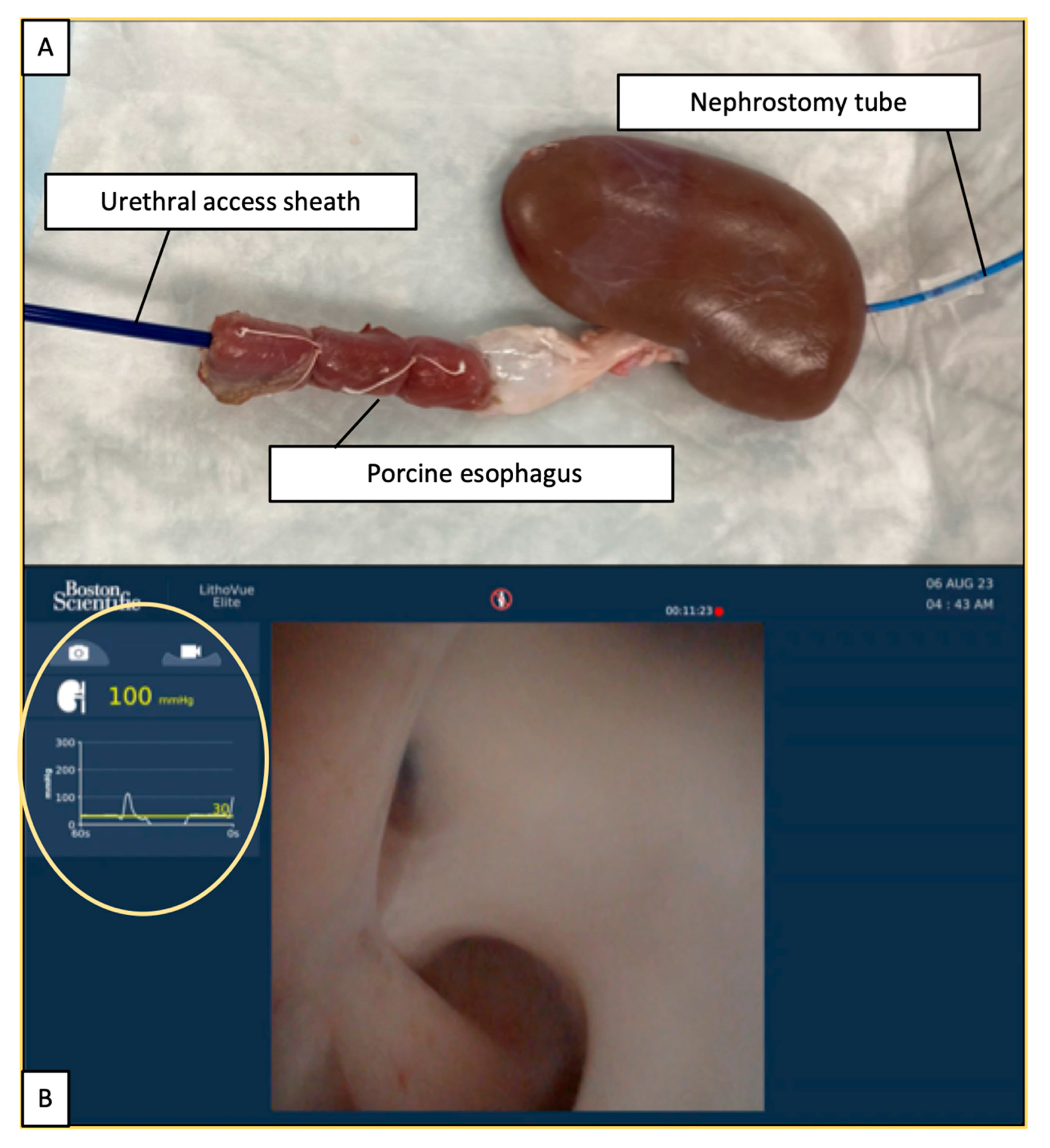
2.1. Experimental Setting
2.2. Ureteroscope and IRP Measurements
2.3. Statistical Analyses
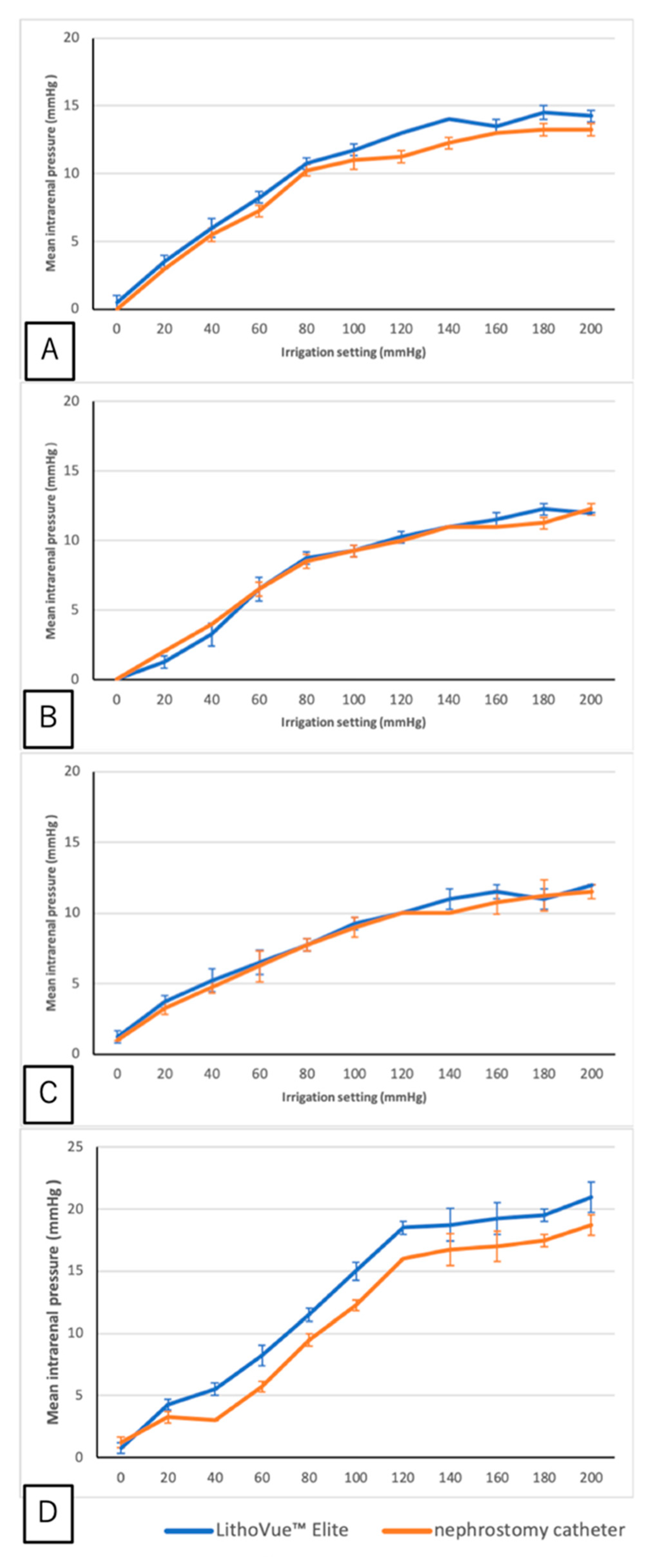
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jiang, P.; Xie, L.; Arada, R.; Patel, R.M.; Landman, J.; Clayman, R.V. Qualitative review of clinical guidelines for medical and surgical management of urolithiasis: Consensus and controversy 2020. J. Urol. 2021, 205, 999–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zumstein, V.; Betschart, P.; Abt, D.; Schmid, H.P.; Panje, C.M.; Putora, P.M. Surgical management of urolithiasis—A systematic analysis of available guidelines. BMC Urol. 2018, 18, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, A.G.; Lipkin, M.E.; Scales, C.D., Jr.; Preminger, G.M. Use of ureteral access sheaths in ureteroscopy. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2016, 13, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- York, N. Routine use of ureteral access sheaths for ureteroscopy: Yay or nay? J. Endourol. 2022, 36, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokas, T.; Herrmann, T.R.W.; Skolarikos, A.; Nagele, U. Pressure matters: Intrarenal pressures during normal and pathological conditions, and impact of increased values to renal physiology. World J. Urol. 2019, 37, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.; Leto, G.; Wang, L.; Zeng, G. Systemic inflammatory response syndrome after flexible ureteroscopic lithotripsy: A study of risk factors. J. Endourol. 2015, 29, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzelburc, V.; Balasar, M.; Colakogullari, M.; Guven, S.; Kandemir, A.; Ozturk, A.; Karaaslan, P.; Erkurt, B.; Albayrak, S. Comparison of absorbed irrigation fluid volumes during retrograde intrarenal surgery and percutaneous nephrolithotomy for the treatment of kidney stones larger than 2 cm. Springerplus 2016, 5, 1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwalb, D.M.; Eshghi, M.; Davidian, M.; Franco, I. Morphological and physiological changes in the urinary tract associated with ureteral dilation and ureteropyeloscopy: An experimental study. J. Urol. 1993, 149, 1576–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.S.; Connors, B.A.; Agarwal, D.K.; Assmus, M.A.; Williams, J.C., Jr.; Large, T.; Krambeck, A.E. Determining the threshold of acute renal parenchymal damage for intrarenal pressure during flexible ureteroscopy using an in vivo pig model. World J. Urol. 2022, 40, 2675–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinman, F.; Redewill, F.H. Pyelovenous back flow. JAMA 1926, 87, 1287–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boccafoschi, C.; Lugnani, F. Intra-renal reflux. Urol. Res. 1985, 13, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croghan, S.M.; Skolarikos, A.; Jack, G.S.; Manecksha, R.P.; Walsh, M.T.; O′Brien, F.J.; Davis, N.F. Upper urinary tract pressures in endourology: A systematic review of range, variables and implications. BJU Int. 2023, 131, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Huang, T.; Song, B.; Liu, W.; Cheng, Y.; Fang, L. The optimal ratio of endoscope-sheath diameter with negative-pressure ureteral access sheath: An in vitro research. World J. Urol. 2024, 42, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergamini, L.B.; Molina, W.R.; Ito, W.; Tverye, A.; Walcott, Q.; Du, H.E.; Sardiu, M.E.; Valadon, C.; Hanna, D.R.; Neff, D.; et al. Intrarenal pressure and flow rate profile using LithoVue™ elite: Impact of different irrigation systems and working channel instruments. World J. Urol. 2024, 42, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, B.H.; Shalabi, N.; Herout, R.; Reicherz, A.; Wong, K.F.V.; Searles, K.; Bhojani, N. Intrarenal pressure measured using a novel flexible ureteroscope with pressure sensing capabilities: A study of the effects of ureteral access sheath, irrigation, and working channel accessories. J. Endourol. 2023, 37, 1200–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhojani, N.; Koo, K.C.; Bensaadi, K.; Halawani, A.; Wong, V.K.; Chew, B.H. Retrospective first-in-human use of the LithoVue™ Elite ureteroscope to measure intrarenal pressure. BJU Int. 2023, 132, 678–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Chi, Y.; Shangguan, T.; Lin, J.; Ye, Y.; Huang, J.; Wen, Y.; Liu, R.; Chen, R.; Cai, W.; et al. Intrarenal pressure detection during flexible ureteroscopy with fiber optic pressure sensor system in porcine model. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 9446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, T.; Tsuruoka, N.; Haga, Y.; Kinoshita, H.; Lee, S.S.; Matsunaga, T. Automatic irrigation system with a fiber-optic pressure sensor regulating intrapelvic pressure for flexible ureteroscopy. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 22853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sener, T.E.; Cloutier, J.; Villa, L.; Marson, F.; Butticè, S.; Doizi, S.; Traxer, O. Can we provide low intrarenal pressures with good irrigation flow by decreasing the size of ureteral access sheaths? J. Endourol. 2016, 30, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauhar, V.; Traxer, O.; Castellani, D.; Sietz, C.; Chew, B.H.; Fong, K.Y.; Hamri, S.B.; Gökce, M.I.; Gadzhiev, N.; Galosi, A.B.; et al. Could use of a flexible and navigable suction ureteral access sheath be a potential game-changer in retrograde intrarenal surgery? Outcomes at 30 days from a large, prospective, multicenter, real-world study by the European Association of Urology Urolithiasis Section. Eur. Urol. Focus 2024, 10, 975–982. [Google Scholar]
- Pauchard, F.; Bhojani, N.; Chew, B.; Ventimiglia, E. How to measure intra-renal pressure during flexible URS: Historical background, technological innovations and future perspectives. Actas Urol. Esp. 2024, 48, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, L.; Xie, G.; Zheng, Z.; Liu, W.; Zhu, J.; Huang, T.; Lu, Y.; Cheng, Y. The effect of ratio of endoscope-sheath diameter on intrapelvic pressure during flexible ureteroscopic lasertripsy. J. Endourol. 2019, 33, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traxer, O.; Thomas, A. Prospective evaluation and classification of ureteral wall injuries resulting from insertion of a ureteral access sheath during retrograde intrarenal surgery. J. Urol. 2013, 189, 580–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, W.T.; Preminger, G.M. Intrarenal pressures generated during flexible deflectable ureterorenoscopy. J. Endourol. 1990, 4, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierra, A.; Corrales, M.; Kolvatzis, M.; Doizi, S.; Traxer, O. Real time intrarenal pressure control during flexible ureterorrenscopy using a vascular pressureWire: Pilot study. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 12, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, R.M.; Jefferson, F.A.; Owyong, M.; Hofmann, M.; Ayad, M.L.; Osann, K.; Okhunov, Z.; Landman, J.; Clayman, R.V. Characterization of intracalyceal pressure during ureteroscopy. World J. Urol. 2021, 39, 883–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, W.; Liang, J.; Wang, D.; Lin, H.; Xie, S.; Chen, S.; He, J.; Xu, A. The effect of irrigation rate on intrarenal pressure in an ex vivo porcine kidney model—Preliminary study with different flexible ureteroscopes and ureteral access sheaths. World J. Urol. 2023, 41, 865–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, G.; Kho, Y.; Park, J.S.; Yuk, H.D.; Ryang, S.H.; Cho, S.Y. Surgical parameters related to excessive intrarenal pressure during minimally invasive percutaneous nephrolithotomy in the supine position: A prospective observational clinical study. Biomed. Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 1199052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

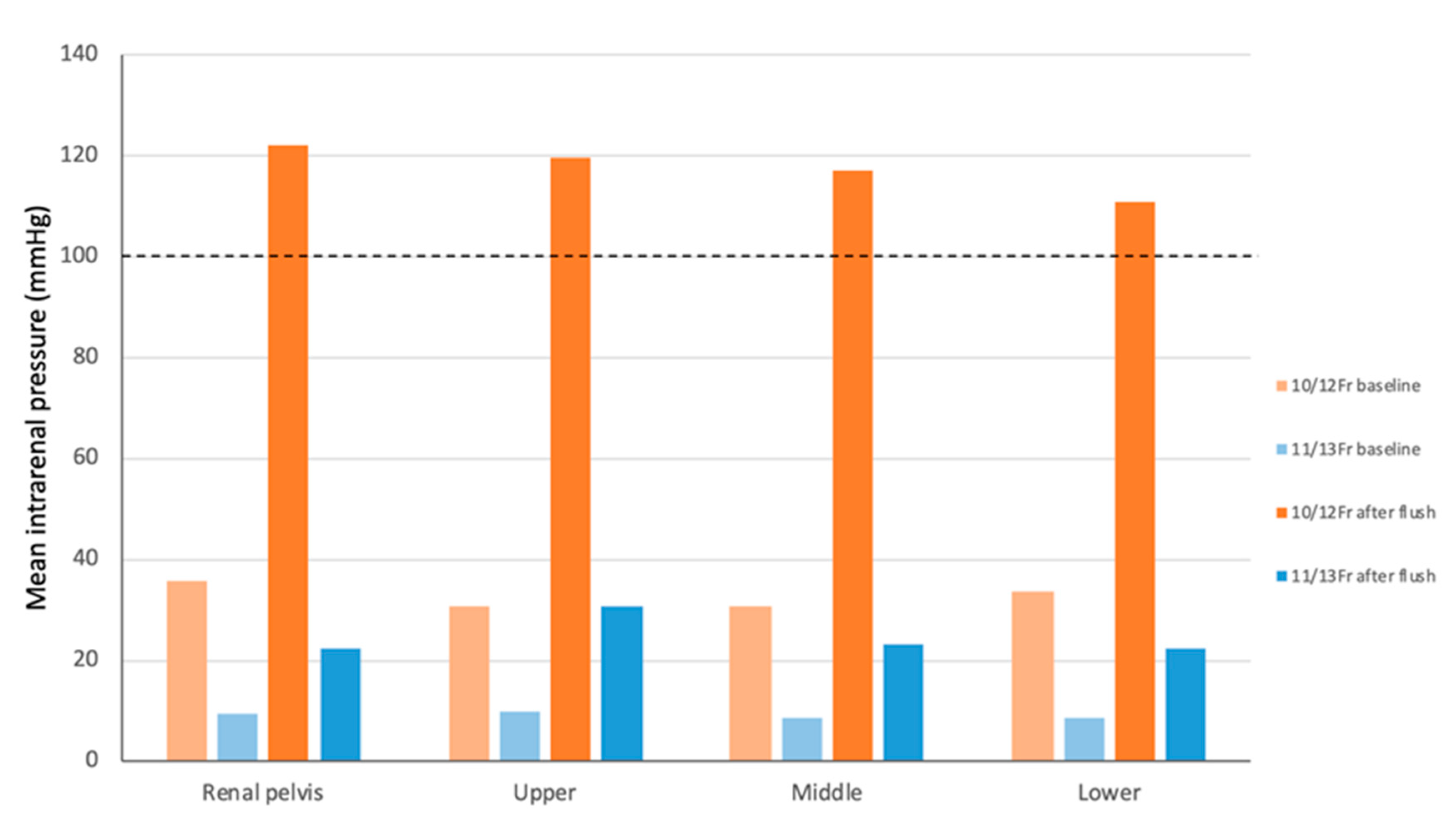
| Summary of Intrarenal Pressure (Mean ± SD, mmHg) | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Irrigation setting | Automatic irrigation pump | Hand pumping | ||||||||||||
| 0 mmHg | 20 mmHg | 40 mmHg | 60 mmHg | 80 mmHg | 100 mmHg | 120 mmHg | 140 mmHg | 160 mmHg | 180 mmHg | 200 mmHg | Baseline | After flush | ||
| 11/13-Fr | Upper pole | 0.5 ± 0.50 | 3.5 ± 0.50 | 6 ± 0.70 | 8.25 ± 0.43 | 10.75 ± 0.43 | 11.75 ± 0.43 | 13 ± 0 | 14 ± 0 | 13.5 ± 0.50 | 14.5 ± 0.50 | 14.25 ± 0.43 | 9.75 ± 0.43 | 30.75 ± 2.49 |
| Middle pole | 0 ± 0 | 1.25 ± 0.43 | 3.25 ± 0.83 | 6.5 ± 0.87 | 8.75 ± 0.43 | 9.25 ± 0.43 | 10.25 ± 0.43 | 11 ± 0 | 11.5 ± 0.50 | 12.25 ± 0.43 | 12 ± 0 | 8.75 ± 0.43 | 23.25 ± 0.43 | |
| Lower pole | 1.25 ± 0.43 | 3.75 ± 0.43 | 5.25 ± 0.83 | 6.5 ± 0.87 | 7.75 ± 0.43 | 9.25 ± 0.43 | 10 ± 0 | 11 ± 0.71 | 11.5 ± 0.50 | 11 ± 0.71 | 12 ± 0 | 8.75 ± 0.43 | 22.5 ± 0.50 | |
| Renal pelvis | 0.75 ± 0.43 | 4.25 ± 0.43 | 5.5 ± 0.50 | 8.25 ± 0.83 | 11.5 ± 0.50 | 15 ± 0.71 | 18.5 ± 0.50 | 18.75 ± 1.30 | 19.25 ± 1.30 | 19.5 ± 0.50 | 21 ± 1.22 | 9.5 ± 0.87 | 22.5 ± 0.87 | |
| 10/12-Fr | Upper pole | 5.75 ± 0.43 | 11 ± 0.71 | 18.75 ± 1.92 | 29.5 ± 1.11 | 34 ± 0.71 | 41.25 ± 1.64 | 47 ± 1.22 | 52 ± 0.71 | 56.75 ± 1.09 | 59.25 ± 0.83 | 64 ± 1.87 | 30.75 ± 0.83 | 119.75 ± 1.79 |
| Middle pole | 3 ± 0.71 | 9 ± 0 | 18.25 ± 0.43 | 27 ± 0 | 35.25 ± 0.43 | 41.5 ± 0.50 | 46.5 ± 1.12 | 52.25 ± 0.83 | 54.25 ± 1.30 | 60 ± 0 | 64 ± 0.71 | 30.75 ± 0.43 | 117.25 ± 7.89 | |
| Lower pole | 4 ± 1.00 | 9.25 ± 0.43 | 18.25 ± 0.43 | 27.25 ± 1.09 | 35.75 ± 0.83 | 43.75 ± 0.43 | 47.75 ± 0.83 | 53.75 ± 1.09 | 59.75 ± 1.48 | 62.75 ± 0.83 | 67.75 ± 0.83 | 33.75 ± 0.83 | 110.75 ± 3.11 | |
| Renal pelvis | 7.25 ± 1.09 | 16 ± 0.71 | 29 ± 0 | 39.75 ± 1.09 | 46.25 ± 1.64 | 51.25 ± 0.83 | 54 ± 1.22 | 57.75 ± 1.48 | 55 ± 0.71 | 60 ± 0 | 63.25 ± 1.92 | 35.75 ± 0.83 | 122.25 ± 7.01 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tanaka, N.; Elises, J.C.; Yamamichi, F.; Kaku, Y.; Fukiishi, Y.; Fujita, M.; Inoue, T. Real-Time Measurement of Intrarenal Pressure Using LithoVue™ Elite: Focus on Small Ureteral Access Sheaths and Appropriate Irrigation Settings. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3573. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103573
Tanaka N, Elises JC, Yamamichi F, Kaku Y, Fukiishi Y, Fujita M, Inoue T. Real-Time Measurement of Intrarenal Pressure Using LithoVue™ Elite: Focus on Small Ureteral Access Sheaths and Appropriate Irrigation Settings. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(10):3573. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103573
Chicago/Turabian StyleTanaka, Naoto, Jose Carlo Elises, Fukashi Yamamichi, Yasuhiro Kaku, Yosuke Fukiishi, Masaichiro Fujita, and Takaaki Inoue. 2025. "Real-Time Measurement of Intrarenal Pressure Using LithoVue™ Elite: Focus on Small Ureteral Access Sheaths and Appropriate Irrigation Settings" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 10: 3573. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103573
APA StyleTanaka, N., Elises, J. C., Yamamichi, F., Kaku, Y., Fukiishi, Y., Fujita, M., & Inoue, T. (2025). Real-Time Measurement of Intrarenal Pressure Using LithoVue™ Elite: Focus on Small Ureteral Access Sheaths and Appropriate Irrigation Settings. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(10), 3573. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103573








