Postoperative Refractory Diarrhea After Margin Accentuation of the Superior Mesenteric Artery with Irreversible Electroporation in Pancreaticoduodenectomy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Selection
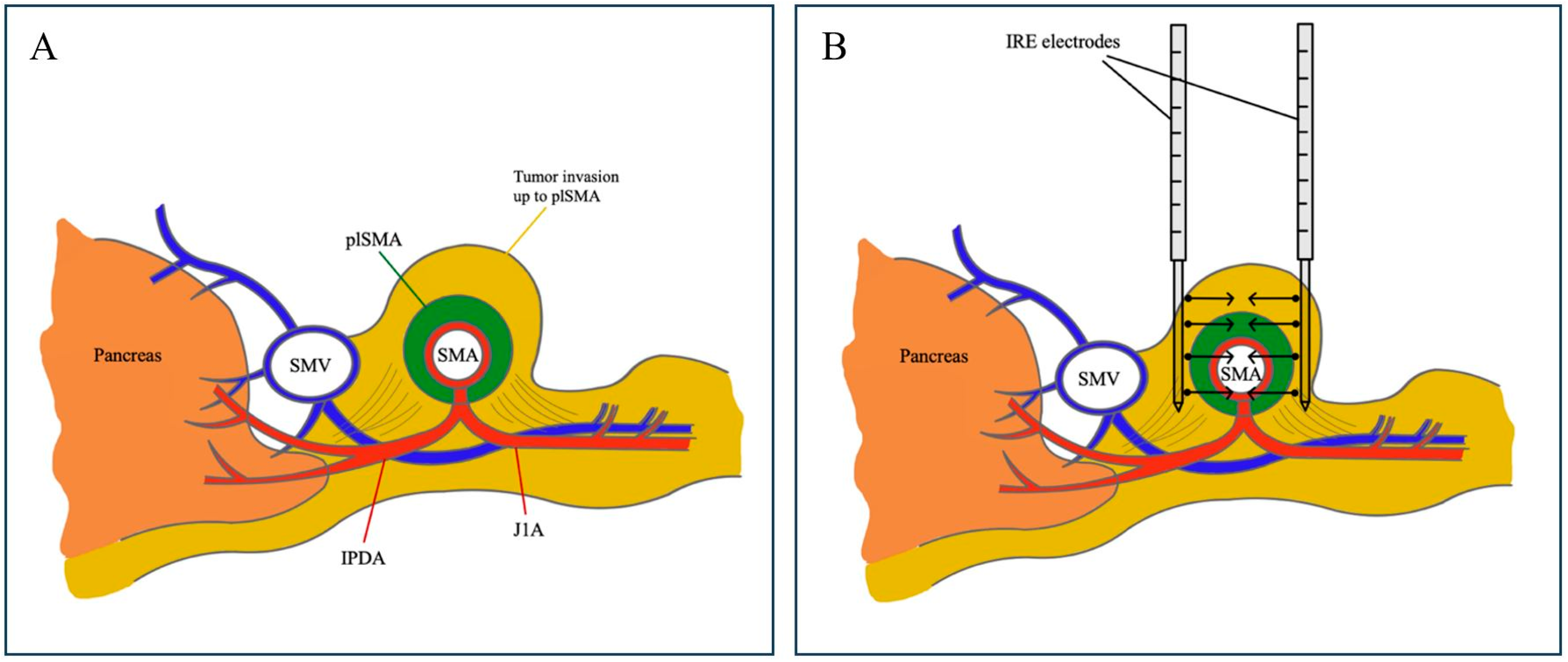
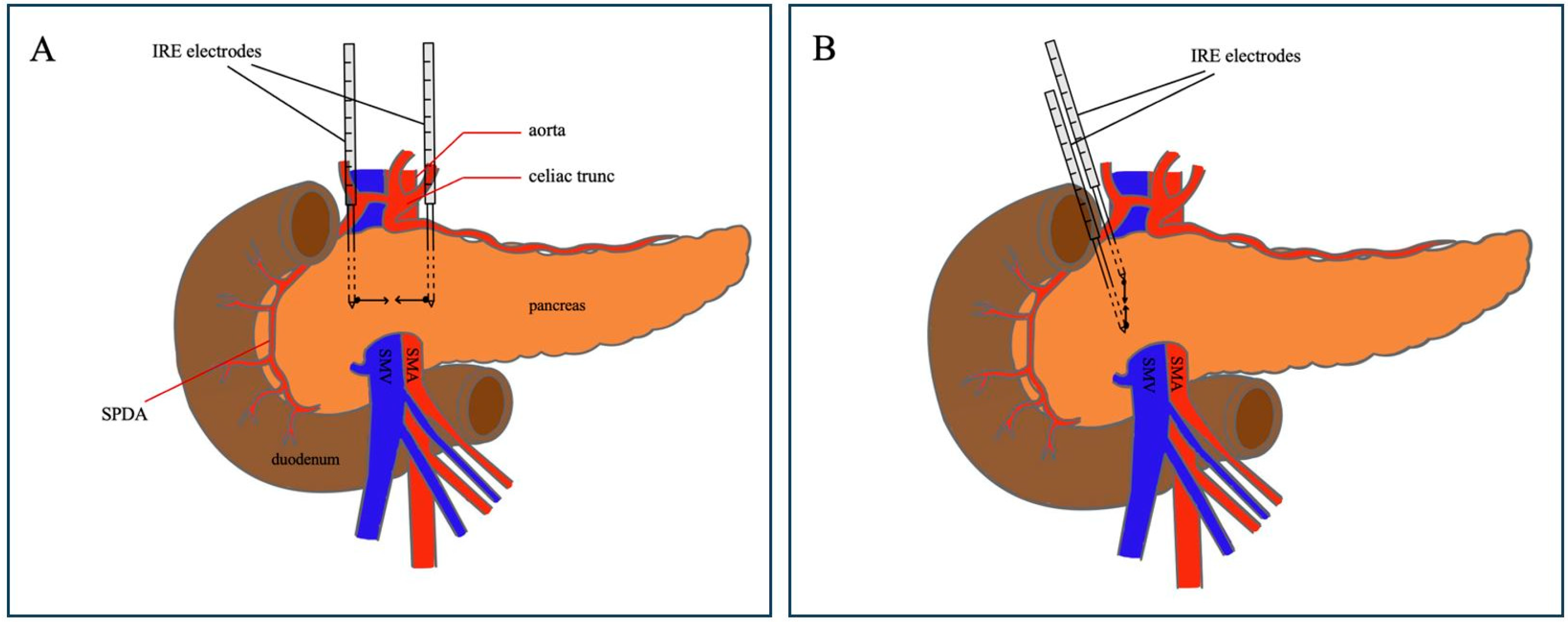
2.2. Operative Procedure: Margin Accentuation with IRE
2.3. Ethical Approval
2.4. Statistics
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PDAC | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma |
| IRE | Irreversible electroporation |
| PD | Pancreaticoduodenectomy |
| SMA | Superior mesenteric artery |
| R | Residual tumor |
| BRPC | Borderline resectable pancreatic cancer |
| LAPC | Locally advanced pancreatic cancer |
| IQR | Interquartile range |
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizrahi, J.D.; Surana, R.; Valle, J.W.; Shroff, R.T. Pancreatic cancer. Lancet 2020, 395, 2008–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, G.F.; Kersting, S.; Haller, F.; Grützmann, R. R1 resection for pancreatic carcinoma. Chirurg 2017, 88, 764–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermanek, P.; Wittekind, C. Residual tumor (R) classification and prognosis. Semin. Surg. Oncol. 1994, 10, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbeke, C.S. Resection margins in pancreatic cancer. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2013, 93, 647–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xue, W.; Yan, W.; Yin, L.; Dong, B.; He, B.; Yu, Y.; Shi, W.; Zhou, Z.; Lin, H.; et al. Extended Focal Ablation of Localized Prostate Cancer With High-Frequency Irreversible Electroporation: A Nonrandomized Controlled Trial. JAMA Surg. 2022, 157, 693–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsanic, P.; Mellano, A.; Sottile, A.; De Simone, M. Irreversible electroporation as treatment of locally advanced and as margin accentuation in borderline resectable pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2017, 55, 1123–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, D.; McFarland, K.; Velanovich, V.; Martin, R.C., 2nd. Borderline and locally advanced pancreatic adenocarcinoma margin accentuation with intraoperative irreversible electroporation. Surgery 2014, 156, 910–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnayake, B.; Al-Leswas, D.; Mohammadi-Zaniani, G.; Littler, P.; Sen, G.; Manas, D.; Pandanaboyana, S. Margin Accentuation Irreversible Electroporation in Stage III Pancreatic Cancer: A Systematic Review. Cancers 2021, 13, 3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, R.C., 2nd; McFarland, K.; Ellis, S.; Velanovich, V. Irreversible electroporation therapy in the management of locally advanced pancreatic adenocarcinoma. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2012, 215, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, R.C., 2nd; Durham, A.N.; Besselink, M.G.; Iannitti, D.; Weiss, M.J.; Wolfgang, C.L.; Huang, K.W. Irreversible electroporation in locally advanced pancreatic cancer: A call for standardization of energy delivery. J. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 114, 865–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kundalia, K.; Hakeem, A.; Papoulas, M.; McPhail, M.; Reddy, S.; Peddu, P.; Kibriya, N.; Atkinson, S.; Prachalias, A.; Srinivasan, P.; et al. Margin ACcentuation for resectable Pancreatic cancer using Irreversible Electroporation—Results from the MACPIE-I study. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2021, 47, 2571–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, R.C.G., 2nd; Schoen, E.C.; Philips, P.; Egger, M.E.; McMasters, K.M.; Scoggins, C.R. Impact of margin accentuation with intraoperative irreversible electroporation on local recurrence in resected pancreatic cancer. Surgery 2023, 173, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papoulas, M.; Abdul-Hamid, S.; Peddu, P.; Cotoi, C.; Heaton, N.; Menon, K. Irreversible electroporation in borderline resectable pancreatic adenocarcinoma for margin accentuation. J. Surg. Case Rep. 2018, 2018, rjy127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Liang, B.; Feng, J.; Zhang, H.Y.; Chang, H.S.; Liu, B.; Chen, Y.L. Safety and feasibility of irreversible electroporation for the pancreatic head in a porcine model. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2022, 14, 1499–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.W.; Shahrouki, P.; Peterson, S.; Tafti, B.A.; Ding, P.X.; Kee, S.T. Safety of Irreversible Electroporation Ablation of the Pancreas. Pancreas 2021, 50, 1281–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackert, T.; Strobel, O.; Michalski, C.W.; Mihaljevic, A.L.; Mehrabi, A.; Müller-Stich, B.; Berchtold, C.; Ulrich, A.; Büchler, M.W. The TRIANGLE operation—Radical surgery after neoadjuvant treatment for advanced pancreatic cancer: A single arm observational study. HPB 2017, 19, 1001–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diener, M.K.; Mihaljevic, A.L.; Strobel, O.; Loos, M.; Schmidt, T.; Schneider, M.; Berchtold, C.; Mehrabi, A.; Müller-Stich, B.P.; Jiang, K.; et al. Periarterial divestment in pancreatic cancer surgery. Surgery 2021, 169, 1019–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limbu, Y.; Regmee, S.; Ghimire, R.; Maharjan, D.K.; Thapa, P.B. Arterial Divestment and Resection in Post-neoadjuvant Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. Cureus 2021, 13, e20275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroki, N.; Ono, Y.; Sato, T.; Inoue, Y.; Oba, A.; Ito, H.; Mise, Y.; Saiura, A.; Takahashi, Y. Long-Term Outcome of Patients with Postoperative Refractory Diarrhea After Tailored Nerve Plexus Dissection Around the Major Visceral Arteries During Pancreatoduodenectomy for Pancreatic Cancer. World J. Surg. 2022, 46, 1172–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, S.; Satoi, S.; Takami, H.; Yamamoto, T.; Yoshioka, I.; Sonohara, F.; Yamaki, S.; Shibuya, K.; Hayashi, M.; Hashimoto, D.; et al. Multicenter randomized phase II trial of prophylactic right-half dissection of superior mesenteric artery nerve plexus in pancreatoduodenectomy for pancreatic head cancer. Ann. Gastroenterol. Surg. 2021, 5, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiozaki, H.; Shirai, Y.; Suka, M.; Hamura, R.; Horiuchi, T.; Yasuda, J.; Furukawa, K.; Onda, S.; Gocho, T.; Ikegami, T. Practical significance of pancreatectomy with lymphadenectomy around the superior mesenteric artery for pancreatic cancer: Comparison of prognosis after adjusting for major prognostic factors. Langenbecks Arch. Surg. 2021, 406, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurosaki, I.; Minagawa, M.; Takano, K.; Takizawa, K.; Hatakeyama, K. Left posterior approach to the superior mesenteric vascular pedicle in pancreaticoduodenectomy for cancer of the pancreatic head. Jop 2011, 12, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Inoue, Y.; Saiura, A.; Oba, A.; Kawakatsu, S.; Ono, Y.; Sato, T.; Mise, Y.; Ishizawa, T.; Takahashi, Y.; Ito, H. Optimal Extent of Superior Mesenteric Artery Dissection during Pancreaticoduodenectomy for Pancreatic Cancer: Balancing Surgical and Oncological Safety. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2019, 23, 1373–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klotz, R.; Hackert, T.; Heger, P.; Probst, P.; Hinz, U.; Loos, M.; Berchtold, C.; Mehrabi, A.; Schneider, M.; Müller-Stich, B.P.; et al. The TRIANGLE operation for pancreatic head and body cancers: Early postoperative outcomes. HPB 2022, 24, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlitter, A.M.; Esposito, I. Definition of microscopic tumor clearance (r0) in pancreatic cancer resections. Cancers 2010, 2, 2001–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | Patients (n = 5) n (%) Median (IQR) |
|---|---|
| Preoperative | |
| Sex | |
| Female | 4 (80%) |
| Male | 1 (20%) |
| Age, years | 70 (64–71) |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 22.7 (21–25.1) |
| Tumor size, cm | 2.5 (2.2–4.3) |
| Resectability | |
| LAPC | 4 (80%) |
| BRPC | 1 (20%) |
| Intra-operative | |
| Margin accentuation of SMA with IRE | |
| Administration frequency | 2 (1–2.5) |
| Additional SMA dissection? | |
| Yes | 1 (20%) |
| No | 4 (80%) |
| Residual tumor status R | |
| R0 resection | 1 (20%) |
| R1 indirect resection | 3 (60%) |
| R1 direct resection | 1 (20%) |
| R2 resection | 0 |
| ypTNM classification | |
| ypT4NxM0 | 2 (40%) |
| ypT2NxM0 | 2 (40%) |
| ypT2N0M0 | 1 (20%) |
| Postoperative | |
| Length of in hospital stay, days | 14 (11.5–18.5) |
| 30-day mortality | 0 |
| Reoperation | 2 (40%) |
| Reason: bleeding after anticoagulation | 2 |
| Local recurrence | 0 |
| Development of metastases | 2 (40%) |
| Time between IRE and metastases, months | 8 (6.9–9.2) |
| Status at 24-month follow-up | |
| Dead | 4 (80%) |
| Alive | 1 (20%) |
| Cause of death | |
| Progressive clinical decline | 2 (40%) |
| Distant metastatic disease | 2 (40%) |
| Time between IRE and death, months | 15.2 (10.2–19.6) |
| Characteristics | Patients (n = 5) n (%) Median (Range) |
|---|---|
| Stool | |
| Secretory | 5 (100%) |
| Steatorrhea | 1 (20%) |
| Coproculture | |
| Positive | 0 |
| Negative | 5 (100%) |
| Frequency per day | 5 (5–6.5) |
| Body weight loss a, kg | 9 (7.5–12) |
| Duration after surgery, months | 6 (5–6.5) |
| Characteristics | Patients (n = 6) n (%) Median (Range) |
|---|---|
| R-status | |
| R0 | 4 (66.6%) |
| R1 indirect | 2 (33.3%) |
| R1 direct | 0 |
| R2 | 0 |
| Duration of postoperative diarrhea, days | 8 (6–10) |
| Local recurrence | 1 (16.7%) |
| Time between IRE and recurrence, months | 7.6 (7.6–7.6) |
| Development of metastases | 2 (33.3%) |
| Time between IRE and metastases, months | 9.5 (7.1–11.8) |
| Status at 12-month follow-up | |
| Dead | 1 (16.7%) |
| Alive | 5 (83.3%) |
| Cause of death | |
| Local recurrence | 1 (16.7%) |
| Time between IRE and death, months | 8 (8–8) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brys, E.-A.; Gryspeerdt, F.; Rashidian, N.; Lerut, A.V.; Dries, P.; Abreu de Carvalho, L.; Berrevoet, F. Postoperative Refractory Diarrhea After Margin Accentuation of the Superior Mesenteric Artery with Irreversible Electroporation in Pancreaticoduodenectomy. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3568. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103568
Brys E-A, Gryspeerdt F, Rashidian N, Lerut AV, Dries P, Abreu de Carvalho L, Berrevoet F. Postoperative Refractory Diarrhea After Margin Accentuation of the Superior Mesenteric Artery with Irreversible Electroporation in Pancreaticoduodenectomy. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(10):3568. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103568
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrys, Eline-Alice, Filip Gryspeerdt, Nikdokht Rashidian, An Verena Lerut, Pieter Dries, Luís Abreu de Carvalho, and Frederik Berrevoet. 2025. "Postoperative Refractory Diarrhea After Margin Accentuation of the Superior Mesenteric Artery with Irreversible Electroporation in Pancreaticoduodenectomy" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 10: 3568. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103568
APA StyleBrys, E.-A., Gryspeerdt, F., Rashidian, N., Lerut, A. V., Dries, P., Abreu de Carvalho, L., & Berrevoet, F. (2025). Postoperative Refractory Diarrhea After Margin Accentuation of the Superior Mesenteric Artery with Irreversible Electroporation in Pancreaticoduodenectomy. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(10), 3568. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103568






