High Prevalence of Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease (MAFLD) in Children and Adolescents with Severe Obesity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
- Inclusion criteria:
- 1.
- Age 3–18 years.
- 2.
- The presence of severe obesity defined as a BMI > 30 kg/m2 in children aged 3–6 years, BMI > 35 kg/m2 in children aged 6–14 years and BMI > 40 kg/m2 in children aged > 14 years [9].
- 3.
- Hyperphagia and food-seeking behaviours.
- 4.
- Written informed consent of the patient’s parent/guardian and patient above the age of 13 years to participate in the study.
- Exclusion criteria:
- 1.
- Lack of written informed consent from the patient’s parent/guardian or patient above the age of 13 years.
- 2.
- Secondary cause of obesity: previously diagnosed genetic syndrome coexisting with obesity, treatment with medicine with known effect on weight gain (glucocorticoids, valproic acid, risperidone, and others), Cushing’s syndrome, and other secondary causes of obesity.
2.2. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Limitations of the Present Study
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. WHO European Childhood Obesity Surveillance Initiative (COSI): Report on the Fourth Round of Data Collection. 2015–2017; WHO Regional Office for Europe: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2021; Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/341189 (accessed on 2 May 2024).
- Spinelli, A.; Buoncristiano, M.; Kovacs, V.A.; Yngve, A.; Spiroski, I.; Obreja, G.; Starc, G.; Pérez, N.; Rito, A.I.; Kunešová, M.; et al. Prevalence of Severe Obesity among Primary School Children in 21 European Countries. Obes. Facts 2019, 12, 244–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eslam, M.; Alkhouri, N.; Vajro, P.; Baumann, U.; Weiss, R.; Socha, P.; Marcus, C.; Lee, W.S.; Kelly, D.; Porta, G.; et al. Defining paediatric metabolic (dysfunction)-associated fatty liver disease: An international expert consensus statement. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 6, 864–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eslam, M.; Newsome, P.N.; Sarin, S.K.; Anstee, Q.M.; Targher, G.; Romero-Gomez, M.; Zelber-Sagi, S.; Wong, V.W.-S.; Dufour, J.-F.; Schattenberg, J.M.; et al. A new definition for metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: An international expert consensus statement. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vajro, P.; Lenta, S.; Socha, P.; Dhawan, A.; McKiernan, P.; Baumann, U.; Durmaz, O.; Lacaille, F.; McLin, V.; Nobili, V. Diagnosis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in children and adolescents: Position paper of the ESPGHAN Hepatology Committee. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2012, 54, 700–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Garf, S.; Nègre, V.; Anty, R.; Gual, P. Metabolic Fatty Liver Disease in Children: A Growing Public Health Problem. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaunak, M.; Byrne, C.D.; Davis, N.; Afolabi, P.; Faust, S.N. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and childhood obesity. Arch. Dis. Child. 2021, 106, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mierzwa, M.; Bik-Multanowski, M.; Ranke, M.B.; Brandt, S.; Flehmig, B.; Małecka-Tendera, E.; Mazur, A.; Petriczko, E.; Wabitsch, M.; Wójcik, M.; et al. Clinical, genetic, and epidemiological survey of Polish children and adolescents with severe obesity: A study protocol of the Polish-German study project on severe early-onset obesity. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 21, 972174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Schnurbein, J.; Wabitsch, M. Monogene Adipositas: Pathophysiologie—Diagnostik—Therapieoptionen. Med. Genet. 2017, 29, 348–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Marshall, W.A.; Tanner, J.M. Variations in the pattern of pubertal changes in boys. Arch. Dis. Child. 1970, 45, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, W.A.; Tanner, J.M. Variations in pattern of pubertal changes in girls. Arch. Dis. Child. 1969, 44, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lurbe, E.; Agabiti-Rosei, E.; Cruickshank, J.K.; Dominiczak, A.; Erdine, S.; Hirth, A.; Invitti, C.; Litwin, M.; Mancia, G.; Pall, D.; et al. 2016 European Society of Hypertension guidelines for the management of high blood pressure in children and adolescents. J. Hypertens. 2016, 34, 1887–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organisation. Growth Reference Data. Available online: https://www.who.int/tools/growth-reference-data-for-5to19-years/indicators/bmi-for-age (accessed on 9 September 2023).
- 2023 Guidelines on the Management of Patients with Diabetes—A Position of Diabetes Poland. Available online: https://ptdiab.pl/zalecenia-ptd/zalecania-aktywni-czlonkowie-2023 (accessed on 9 September 2023).
- Nobili, V.; Alisi, A.; Vania, A.; Tiribelli, C.; Pietrobattista, A.; Bedogni, G. The pediatric NAFLD fibrosis index: A predictor of liver fibrosis in children with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. BMC Med. 2009, 1, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmet, P.; Alberti, K.G.; Kaufman, F.; Tiribelli, C.; Pietrobattista, A.; Bedogni, G. IDF Consensus Group. The metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents—An IDF consensus report. Pediatr. Diabetes 2007, 8, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Świąder-Leśniak, A.; Kułaga, Z.; Grajda, A.; Gurzkowska, B.; Góźdź, M.; Wojtyło, M.; Różdżyńska-Świątkowska, A.; Litwin, M. References for waist and hip circumferences in Polish children and adolescents 3-18 year of age. Stand. Med. Pediatr. 2015, 1, 137–150. [Google Scholar]
- Ahrens, W.; Moreno, L.A.; Mårild, S.; Molnár, D.; Siani, A.; De Henauw, S.; Böhmann, J.; Günther, K.; Hadjigeorgiou, C.; Iacoviello, L.; et al. IDEFICS consortium. Metabolic syndrome in young children: Definitions and results of the IDEFICS study. Int. J. Obes. 2014, 38, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzyżaniak, A.; Krzywińska-Wiewiorowska, M.; Stawińska-Witoszyńska, B.; Kaczmarek, M.; Krzych, L.; Kowalska, M.; Szilágyi-Pągowska, I.; Palczewska, I.; Karch, A.; Jośko, J.; et al. Blood pressure references for Polish children and adolescents. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2009, 168, 1335–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shashaj, B.; Luciano, R.; Contoli, B.; Morino, G.S.; Spreghini, M.R.; Rustico, C.; Sforza, R.W.; Dallapiccola, B.; Manco, M. Reference ranges of HOMA-IR in normal-weight and obese young caucasians. Acta Diabetol. 2016, 53, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, E.L.; Howe, L.D.; Jones, H.E.; Higgins, J.P.T.; Lawlor, D.A.; Fraser, A. The Prevalence of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, J.; Gomez, R.; Rodriguez, G.; Moran, S. P0223 Prevalence of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) in mexican children of an elementary school. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2004, 39, S143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Mu, C.; Li, K.; Luo, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z. Estimating global prevalence of metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease in overweight or obese children and adolescents: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Public Health 2021, 66, 1604371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.C.; Wu, C.C.; Ni, Y.H. New Perspectives on Genetic Prediction for Pediatric Metabolic Associated Fatty Liver Disease. Front. Pediatr. 2020, 9, 603654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loomba, R.; Sanyal, A.J. The global NAFLD epidemic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 10, 686–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Adamo, E.; Castorani, V.; Nobili, V. The Liver in Children with Metabolic Syndrome. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 2, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basarir, G.; Ozcabi, B.; Aksu, S.; Akay, H.O.; Yildiz, F.M. Evaluation of clinical, endocrine and metabolic findings in obese children with and without hepatosteatosis. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 34, 1081–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denzer, C.; Thiere, D.; Muche, R.; Koenig, W.; Mayer, H.; Kratzer, W.; Wabitsch, M. Gender-specific prevalences of fatty liver in obese children and adolescents: Roles of body fat distribution, sex steroids, and insulin resistance. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 94, 3872–3881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Adamo, E.; Cali, A.M.; Weiss, R.; Santoro, N.; Pierpont, B.; Northrup, V.; Caprio, S. Central role of fatty liver in the pathogenesis of insulin resistance in obese adolescents. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 1817–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.; Giannini, C.; Pierpont, B.; Feldstein, A.E.; Santoro, N.; Kursawe, R.; Shaw, M.; Duran, E.; Goldberg, R.; Dziura, J.; et al. Longitudinal effects of MRI-measured hepatic steatosis on biomarkers of glucose homeostasis and hepatic apoptosis in obese youth. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simental-Mendía, L.E.; Ortega-Pacheco, C.J.; García-Guerrero, E.; Sicsik-Aragón, M.A.; Guerrero-Romero, F.; Martínez-Aguilar, G. The triglycerides and glucose index is strongly associated with hepatic steatosis in children with overweight or obesity. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2021, 180, 1755–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faure, S.; Benjamin, R.; Ramos, J.; Medhi, S.; David, N.; Anne, L.; Galtier, F.; Pageaux, G.-P. The triglycerides and glucose (TyG) index: A new marker associated with Non Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) and fibrosis in obese patients? J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, S835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Park, G.; Lee, H.S.; Lee, M.; Lee, H.I.; Choi, H.S.; Suh, J.; Kwon, A.; Kim, H.S.; Chae, H.W. Comparison of the triglyceride glucose index and modified triglyceride glucose indices to predict nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in youths. J. Pediatr. 2022, 242, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furdela, V.; Pavlyshyn, H.; Shulhai, A.-M.; Kozak, K.; Furdela, M. Triglyceride glucose index, pediatric NAFLD fibrosis index, and triglyceride-to-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio are the most predictive markers of the metabolically unhealthy phenotype in overweight/obese adolescent boys. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 10, 1124019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cigri, E.; Inan, F.C.; Er, E.; Yildiz, E. The Relationship Between Lipid Profile and Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Children and Adolescents with Obesity. J. Coll. Physicians Surg. Pak. 2022, 32, 591–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bălănescu, A.; Bălănescu, P.; Comănici, V.; Stan, I.; Acs, B.; Prisăcariu, L.; Brezan, F.; Ciomârtan, T.; Gherghina, I. Lipid profile pattern in pediatric overweight population with or without NAFLD in relation to IDF criteria for metabolic syndrome: A preliminary study. Rom. J. Intern. Med. 2018, 56, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez-Rivera, C.; Hadjiyannakis, S.; Davila, J.; Hurteau, J.; Aglipay, M.; Barrowman, N.; Adamo, K.B. Prevalence and risk factors for non-alcoholic fatty liver in children and youth with obesity. BMC Pediatr. 2017, 26, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atabek, M.E.; Selver Eklioglu, B.; Akyürek, N. Which metabolic syndrome criteria best predict non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in children? Eat. Weight Disord. 2014, 19, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigam, P.; Bhatt, S.P.; Misra, A.; Vaidya, M.; Dasgupta, J.; Chadha, D.S. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is closely associated with sub-clinical inflammation: A case-control study on Asian Indians in North India. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e49286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Springwald, A.; Różana-Kowalska, P.; Gibała, P.; Zajdel-Cwynar, O.; Małecka-Tendera, E.; Matusik, P. Usefulness of the metabolic syndrome diagnosis in obese children in clinical practice. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Diabetes Metab. 2019, 25, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslan, A.; Erdemli, S.; Günaydın, G.D.; Aslan, M.; Yazar, R.Ö.; Kabaalioğlu, A.; Ağırbaşlı, M.A. Cardiometabolic risk factors in Turkish children with hepatosteatosis. Turk. J. Pediatr. 2019, 61, 714–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.F.; Shi, H.B.; Liu, L.R.; Jiang, P.; Liang, L.; Wang, C.L.; Liu, X.Y. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: An early mediator predicting metabolic syndrome in obese children? World J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 17, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, M.; Ogawa, S.; Tayama, J.; Sagara, I.; Takeoka, A.; Bernick, P.; Kawano, T.; Abiru, N.; Hayashida, M.; Shirabe, S. Intra-abdominal fat accumulation is an important predictor of metabolic syndrome in young adults. Med. Baltim. 2020, 99, e22202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holterman, A.L.; Guzman, G.; Fantuzzi, G.; Wang, H.; Aigner, K.; Browne, A.; Holterman, M. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in severely obese adolescent and adult patients. Obesity 2013, 21, 591–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, E.L.; Schwimmer, J.B. Epidemiology of Pediatric Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Clin. Liver Dis. 2021, 17, 196–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosca, A.; Della Volpe, L.; Alisi, A.; Veraldi, S.; Francalanci, P.; Maggiore, G. Non-Invasive Diagnostic Test for Advanced Fibrosis in Adolescents with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 26, 885576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkhouri, N.; Sedki, E.; Alisi, A.; Lopez, R.; Pinzani, M.; Feldstein, A.E.; Nobili, V. Combined paediatric NAFLD fibrosis index and transient elastography to predict clinically significant fibrosis in children with fatty liver disease. Liver Int. 2013, 33, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gülcü Taşkın, D.; Kayadibi, Y.; Baş, A.; Civan, H.A.; Beser, O.F.; Adaletli, I.; Cokugras, F.C.; Erkan, T.; Kutlu, T. Accuracy Rate of Shear Wave Elastography in Detecting the Liver Fibrosis in Overweight and Obese Children with Hepatosteatosis. Turk. Arch. Pediatr. 2023, 58, 436–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
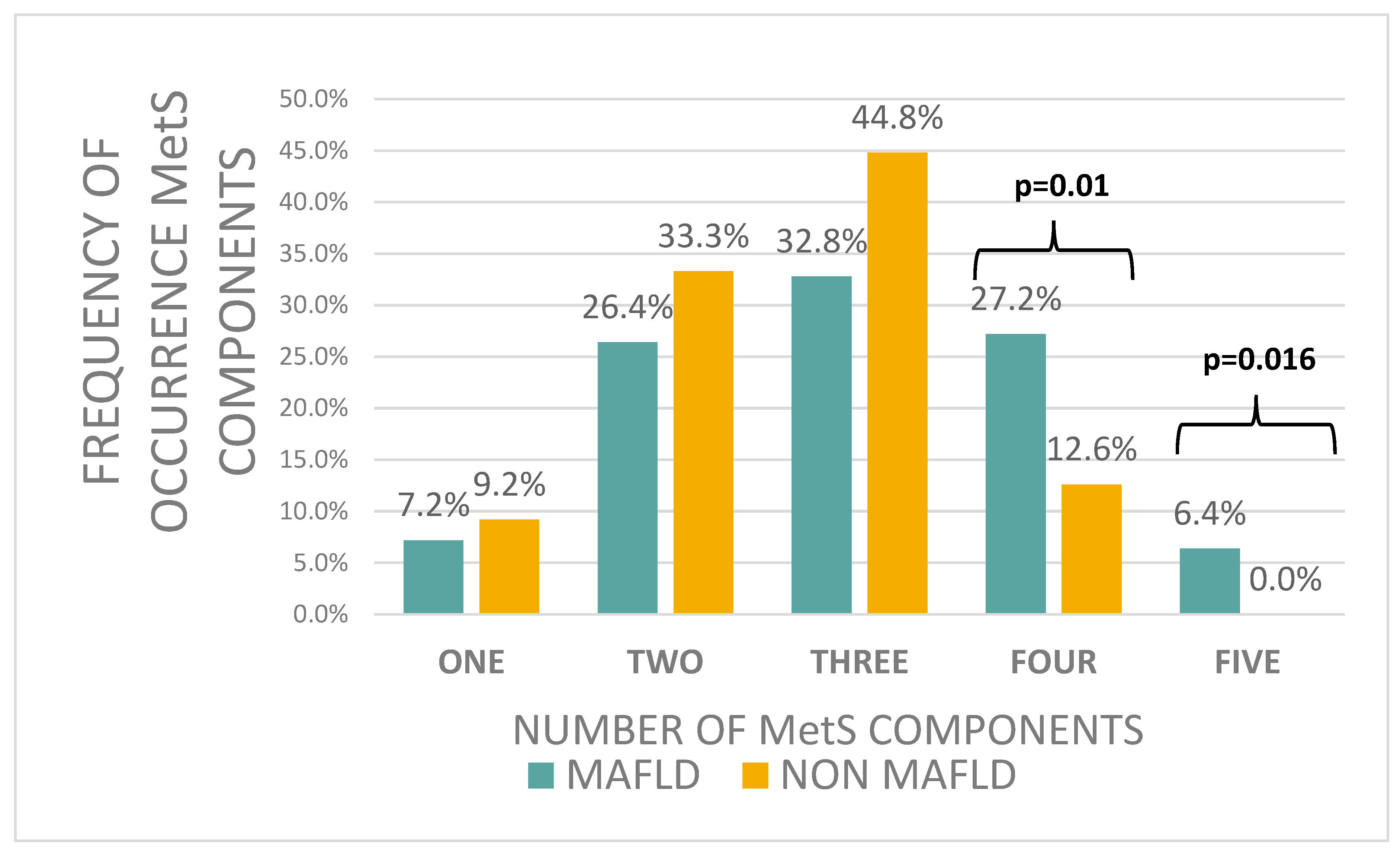
| Patients with MAFLD | Patients Without MAFLD | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age [years] | 14.0 ± 3.0 | 13 ± 3.4 | 0.2 ** |
| Age of obesity onset [years] | 4.5 ± 6.5 | 3.0 ± 8.0 | 0.52 ** |
| Obesity duration time [years] | 8.0 ± 7.0 | 8.0 ± 7.5 | 0.36 ** |
| Birth weight [g] | 3468.4 ± 508.5 | 3342.7 ± 612.7 | 0.06 * |
| BMI Z-SCORE | 3.7 ± 0.5 | 3.6 ± 0.5 | 0.25 ** |
| Waist circumference [cm] | 115.2 ± 12.6 | 109.6 ± 15.2 | 0.004 * 0.07 # |
| Fat mass [%] | 46.1 ± 9.1 | 46.9 ± 8.1 | 0.71 ** |
| Free fat mass [%] | 53.8 ± 9.2 | 53.4 ± 9.0 | 0.93 ** |
| Muscle mass [kg] | 53.9 ± 17.6 | 49.7 ± 12.2 | 0.32 * |
| Patients with MAFLD | Patients Without MAFLD | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Liver AP midclavicular diameter [mm] | 149.4 ± 17.9 | 135.1 ± 17.5 | <0.0001 * 0.001 # |
| Alanine aminotransferase [μU/mL] | 31.3 ± 23.6 | 24.0 ± 10.0 | <0.0001 ** |
| Aspartate aminotransferase [μU/mL] | 26.4 ± 13.0 | 21.0 ± 13.0 | <0.0001 ** |
| ALT/AST ratio | 1.2 ± 0.6 | 1.1 ± 0.4 | 0.007 ** |
| Gamma-glutamyl transferase [μU/mL] | 23.0 ± 14.0 | 18.0 ± 11.0 | <0.0001 ** |
| Alkaline fosfatase [μU/mL] | 118.0 ± 123.8 | 141 ± 147 | 0.74 ** |
| PNFI | 9.87 ± 0.33 | 9.62 ± 0.74 | 0.016 ** |
| Patients with MAFLD | Patients Without MAFLD | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glucose 0 [mg/dL] | 89 ± 13.0 | 87.0 ± 11.2 | 0.08 ** |
| Glucose 120 [mg/dL] | 118 ± 31.6 | 105.0 ± 30.0 | 0.0006 ** |
| Insulin 0 [IU/mL] | 27.9 ± 16.8 | 22.5 ± 16.3 | 0.0008 ** |
| Insulin 120 [IU/mL] | 135.1 ± 115.4 | 85.0 ± 92.1 | 0.004 ** |
| HOMA-IR | 6.1 ± 4.1 | 4.7 ± 4.2 | 0.0005 ** |
| QUICKY | 0.4 ± 0.1 | 0.4 ± 0.1 | 0.0006 ** |
| TyG | 8.7 ± 0.7 | 8.4 ± 0.5 | 0.002 ** |
| Total cholesterol [mg/dL] | 161.0 ± 47.8 | 159.1 ± 33.0 | 0.3 ** |
| LDL cholesterol [mg/dL] | 94.0 ± 40.0 | 93.0 ± 33.3 | 0.99 ** |
| HDL cholesterol [mg/dL] | 40.6 ± 7.6 | 42.2 ± 9.1 | 0.16 * |
| Triglycerides [mg/dL] | 125.0 ± 81.9 | 107.5 ± 60.4 | 0.008 ** |
| TG/HDL-C ratio | 3.3 ± 2.3 | 2.6 ± 1.7 | 0.006 ** |
| Uric Acid [umol/L] | 404.5 ± 111.0 | 362.8 ± 93.8 | 0.0016 ** |
| CRP [mg/L] | 4.4 ± 3.9 | 5.0 ± 5.0 | 0.4 ** |
| COMPONENT OF METABOLIC SYNDROME | Patients with MAFLD, n (%) | Patients Without MAFLD, n (%) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| ABDOMINAL OBESITY Waist Circumference ≥ 90th percentile | 125 (100%) | 87 (100%) | 1.0 |
| HIGH BLOOD PRESSURE ≥90th percentile <10 years; >10 years: Systolic BP ≥ 130 or diastolic BP ≥ 85 mmHg or treatment of previously diagnosed hypertension | 105 (86.7%) | 67 (80.7%) | 0.24 |
| HIGH FASTING GLUCOSE FPG ≥ 100 mg/dL or known T2DM | 17 (13.8%) | 3 (3.4%) | 0.017 |
| HYPERTRIGLICERYDEMIA ≥130 mg/dL below the age 10, ≥150 mg/dL above the age 10, or specific treatment for high Triglycerides | 41 (32.8%) | 19 (21.8%) | 0.08 |
| LOW HDL CHOLESTEROL <10th percentile for age and sex below age of 10 <40 mg/dL in males and females 10–16 years and <50 mg/dL in females ≥ 16 years, or specific treatment for low HDL cholesterol | 70 (56.0%) | 41 (47.1%) | 0.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mierzwa, M.; Malczyk, Ż.; Bik-Multanowski, M.; Brandt-Heunemann, S.; Flehmig, B.; Małecka-Tendera, E.; Mazur, A.; Petriczko, E.; Ranke, M.B.; Wabitsch, M.; et al. High Prevalence of Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease (MAFLD) in Children and Adolescents with Severe Obesity. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3565. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103565
Mierzwa M, Malczyk Ż, Bik-Multanowski M, Brandt-Heunemann S, Flehmig B, Małecka-Tendera E, Mazur A, Petriczko E, Ranke MB, Wabitsch M, et al. High Prevalence of Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease (MAFLD) in Children and Adolescents with Severe Obesity. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(10):3565. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103565
Chicago/Turabian StyleMierzwa, Magdalena, Żaneta Malczyk, Mirosław Bik-Multanowski, Stephanie Brandt-Heunemann, Bertram Flehmig, Ewa Małecka-Tendera, Artur Mazur, Elżbieta Petriczko, Michael B. Ranke, Martin Wabitsch, and et al. 2025. "High Prevalence of Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease (MAFLD) in Children and Adolescents with Severe Obesity" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 10: 3565. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103565
APA StyleMierzwa, M., Malczyk, Ż., Bik-Multanowski, M., Brandt-Heunemann, S., Flehmig, B., Małecka-Tendera, E., Mazur, A., Petriczko, E., Ranke, M. B., Wabitsch, M., Wójcik, M., Domżol, A., & Zachurzok, A. (2025). High Prevalence of Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease (MAFLD) in Children and Adolescents with Severe Obesity. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(10), 3565. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103565








