Risk Factors and Outcomes of Surgical Site Infections of the Spine: A Retrospective Multi-Center Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Statistical Analysis
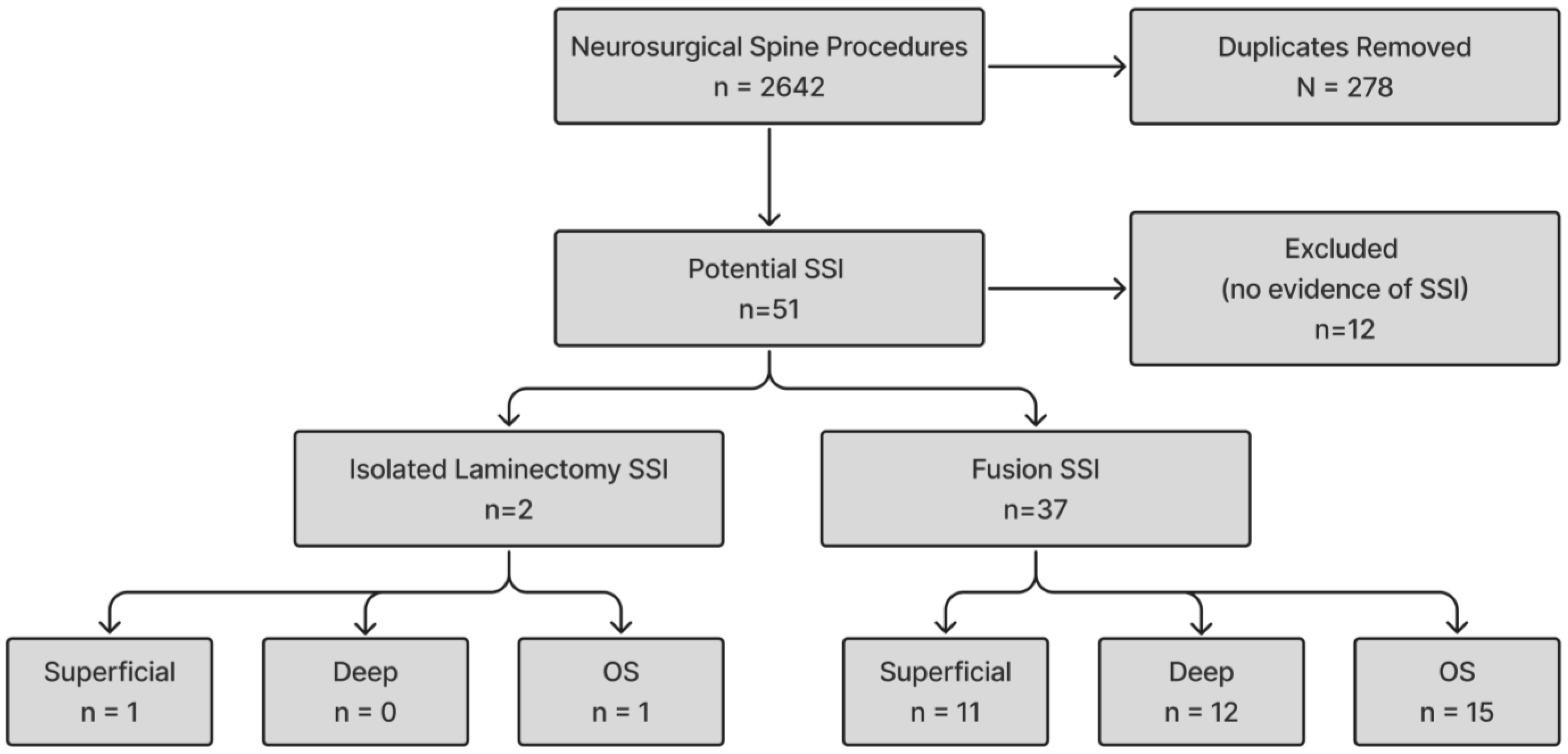
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Overall Infection Rate
4.2. Risk Factors
4.3. Surgery Characteristics
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SSI | Surgical Site Infection |
| OS | Organ/Space |
| CHG | Chlorhexidine Gluconate |
| IVDU | Intravenous Drug Use |
| SEA | Spinal Epidural Abscess |
| EHR | Electronic Health Record |
| NHSN | National Healthcare Safety Network |
| ICD-10 | International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision |
| aOR | Adjusted Odds Ratio |
| HLD | Hyperlipidemia |
| GERD | Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease |
| COPD | Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease |
| NSQIP | National Surgical Quality Improvement Program |
| CAD | Coronary Artery Disease |
| OR | Odds Ratio |
| CoNS | Coagulase Negative Staphylococcus |
| DM | Diabetes Mellitus |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
References
- Zhou, J.; Wang, R.; Huo, X.; Xiong, W.; Kang, L.; Xue, Y. Incidence of Surgical Site Infection After Spine Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Spine 2020, 45, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeramaneni, S.; Robinson, C.; Hostin, R. Impact of Spine Surgery Complications on Costs Associated with Management of Adult Spinal Deformity. Curr. Rev. Musculoskelet Med. 2016, 9, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pennington, Z.; Sundar, S.J.; Lubelski, D.; Alvin, M.D.; Benzel, E.C.; Mroz, T.E. Cost and Quality of Life Outcome Analysis of Postoperative Infections after Posterior Lumbar Decompression and Fusion. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2019, 68, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, K.; Ando, K.; Nishida, Y.; Ishiguro, N.; Imagama, S. Epidemiological Trends in Spine Surgery over 10 Years in a Multicenter Database. Eur. Spine J. 2018, 27, 1698–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, J.R.; Peterson, K.D.; Mu, Y.; Banerjee, S.; Allen-Bridson, K.; Morrell, G.; Dudeck, M.A.; Pollock, D.A.; Horan, T.C. National Healthcare Safety Network (NHSN) Report: Data Summary for 2006 through 2008, Issued December 2009. Am. J. Infect. Control 2009, 37, 783–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NHSN SSI. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/nhsn/pdfs/pscmanual/9pscssicurrent.pdf (accessed on 16 March 2025).
- Akhondi, H.; Baker, M.B. Epidural Abscess. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Chow, F. Brain and Spinal Epidural Abscess. Contin. Lifelong Learn. Neurol. 2018, 24, 1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, W.A.; Graeber, A.; Cecava, N.D. Vertebral Osteomyelitis. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Sharfman, Z.T.; Gelfand, Y.; Shah, P.; Holtzman, A.J.; Mendelis, J.R.; Kinon, M.D.; Krystal, J.D.; Brook, A.; Yassari, R.; Kramer, D.C. Spinal Epidural Abscess: A Review of Presentation, Management, and Medicolegal Implications. Asian Spine J. 2020, 14, 742–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ee, W.W.G.; Lau, W.L.J.; Yeo, W.; Von Bing, Y.; Yue, W.M. Does Minimally Invasive Surgery Have a Lower Risk of Surgical Site Infections Compared With Open Spinal Surgery? Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2014, 472, 1718–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruo, K.; Berven, S.H. Outcome and Treatment of Postoperative Spine Surgical Site Infections: Predictors of Treatment Success and Failure. J. Orthop. Sci. 2014, 19, 398–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M.; Sakai, D.; Matsuyama, D.; Yamamoto, Y.; Sato, M.; Mochida, J. Risk Factors for Surgical Site Infection Following Spine Surgery: Efficacy of Intraoperative Saline Irrigation. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2010, 12, 540–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tominaga, H.; Setoguchi, T.; Ishidou, Y.; Nagano, S.; Yamamoto, T.; Komiya, S. Risk Factors for Surgical Site Infection and Urinary Tract Infection after Spine Surgery. Eur. Spine J. 2016, 25, 3908–3915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, M.A.; Mayfield, J.; Lauryssen, C.; Polish, L.B.; Jones, M.; Vest, J.; Fraser, V.J. Risk Factors for Surgical Site Infection in Spinal Surgery. J. Neurosurg. 2003, 98, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, I.; Wilson-MacDonald, J.; Chami, G.; Burgoyne, W.; Vinayakam, P.; Berendt, T.; Fairbank, J. The Diagnosis and Management of Infection Following Instrumented Spinal Fusion. Eur. Spine J. 2008, 17, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsamadicy, A.A.; Adogwa, O.; Lydon, E.; Sergesketter, A.; Kaakati, R.; Mehta, A.I.; Vasquez, R.A.; Cheng, J.; Bagley, C.A.; Karikari, I.O. Depression as an Independent Predictor of Postoperative Delirium in Spine Deformity Patients Undergoing Elective Spine Surgery. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2017, 27, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsamadicy, A.A.; Serrato, P.; Sadeghzadeh, S.; Dietz, N.; Lo, S.-F.L.; Sciubba, D.M. Implications of Surgical Infection on Surgical and Hospital Outcomes after Spine Surgery: A NSQIP Study of 410,930 Patients. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2024, 245, 108505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pull ter Gunne, A.F.; Skolasky, R.L.; Cohen, D.B. Fracture Characteristics Predict Patient Mortality after Blunt Force Cervical Trauma. Eur. J. Emerg. Med. 2010, 17, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piper, K.F.; Tomlinson, S.B.; Santangelo, G.; Van Galen, J.; DeAndrea-Lazarus, I.; Towner, J.; Kimmell, K.T.; Silberstein, H.; Vates, G.E. Risk Factors for Wound Complications Following Spine Surgery. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2017, 8, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmiston, C.E.; Leaper, D.J.; Chitnis, A.S.; Holy, C.E.; Chen, B.P.-H. Risk and Economic Burden of Surgical Site Infection Following Spinal Fusion in Adults. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2023, 44, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Sheng, Q.; Guo, K.; Xu, G.; Chen, X.; Luo, D.; Liu, S.; Wu, Z.-A. Development of an Evaluation System for the Prophylactic Use of Antimicrobial Drugs in the Perioperative Period of Class I Surgical Incisions in Neurosurgery. World Neurosurg. 2024, 184, e468–e485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire-Archer, M.; Sarraj, M.; Koziarz, A.; Thornley, P.; Alshaalan, F.; Alnemari, H.; Kachur, E.; Bhandari, M.; Oitment, C. Incidence and Recurrence of Deep Spine Surgical Site Infections: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Spine 2023, 48, E269–E285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Garza-Ramos, R.; Abt, N.B.; Kerezoudis, P.; McCutcheon, B.A.; Bydon, A.; Gokaslan, Z.; Bydon, M. Deep-Wound and Organ-Space Infection after Surgery for Degenerative Spine Disease: An Analysis from 2006 to 2012. Neurol. Res. 2016, 38, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López Pereira, P.; Díaz-Agero Pérez, C.; Fresneña, N.; Las Heras Mosteiro, J.; Palancar Cabrera, A.; Rincón Carlavilla, Á.L.; Aranaz Andrés, J.M. ‘Epidemiology of Surgical Site Infection in a Neurosurgery Department. Br. J. Neurosurg. 2017, 31, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haleem, A.; Chiang, H.-Y.; Vodela, R.; Behan, A.; Pottinger, J.M.; Smucker, J.; Greenlee, J.D.; Clark, C.; Herwaldt, L.A. Risk Factors for Surgical Site Infections Following Adult Spine Operations. Infect. Control. Hosp. Epidemiol. 2016, 37, 1458–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, A.; Hu, S.S.; Endres, N.; Bradford, D.S. Risk Factors for Infection after Spinal Surgery. Spine 2005, 30, 1460–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connor, D.E.; Chittiboina, P.; Caldito, G.; Nanda, A. Comparison of Operative and Nonoperative Management of Spinal Epidural Abscess: A Retrospective Review of Clinical and Laboratory Predictors of Neurological Outcome. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2013, 19, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, D.; Wang, J.; Song, D.; Xu, W.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Y.; Ma, J.; Ma, X. Predictors for Mortality in Elderly Patients with Cervical Spine Injury: A Systematic Methodological Review. Spine 2013, 38, 770–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Pan, Y.; Zhao, L.; Niu, Z.; Guo, Q.; Zhao, B. A Machine Learning-Based Approach to Predict Prognosis and Length of Hospital Stay in Adults and Children With Traumatic Brain Injury: Retrospective Cohort Study. J. Med. Internet Res. 2022, 24, e41819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.K.; Prasad, B.C.M.; Chandra, V.R.; Kumar, M.J.; Jayachandar, V. Cervical Pseudomeningocoele Following Posterior Cervical Spine Surgery: An Uncommon Cause of Neurologic Deterioration. J. Clin. Sci. Res. 2014, 3, 274–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adindu, E.; Singh, D.; Geck, M.; Stokes, J.; Truumees, E. How Minimal Clinically Important Difference and Patient Acceptable Symptom State Relate to Patient Expectations and Satisfaction in Spine Surgery: A Review. Clin. Spine Surg. 2024, 37, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Teng, Y.; Fan, Z.; Khan, S.; Xia, Y. Does Obesity Affect the Surgical Outcome and Complication Rates of Spinal Surgery? A Meta-Analysis. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res.® 2014, 472, 968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghajanian, S.; Shafiee, A.; Teymouri Athar, M.M.; Mohammadifard, F.; Goodarzi, S.; Esmailpur, F.; Elsamadicy, A.A. Impact of Depression on Postoperative Medical and Surgical Outcomes in Spine Surgeries: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, R.G.; Svendsen, M.B.S.; Tolsgaard, M.G.; Konge, L.; Røder, A.; Bjerrum, F. Automated Performance Metrics and Surgical Gestures: Two Methods for Assessment of Technical Skills in Robotic Surgery. J. Robot. Surg. 2024, 18, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, N.; Akosman, I.; Mortenson, R.; Kumar, A.; Xu, G.; Lathrop, C.; Bakhmat, K.; Amen, T.B.; Hussain, I. Gender Disparities in Postoperative Outcomes Following Elective Spine Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2023, 40, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, H.; Chan, A.K.; Ammanuel, S.G.; Chan, A.Y.; Oh, T.; Skrehot, H.C.; Edwards, C.S.; Kondapavulur, S.; Nichols, A.D.; Liu, C.; et al. Risk Factors for Deep Surgical Site Infection Following Thoracolumbar Spinal Surgery. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2019, 32, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, M.A.; Nepple, J.J.; Riew, K.D.; Lenke, L.G.; Bridwell, K.H.; Mayfield, J.; Fraser, V.J. Risk Factors for Surgical Site Infection Following Orthopaedic Spinal Operations. JBJS 2008, 90, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zheng, Q.-J.; Wang, S.; Zeng, S.-X.; Zhang, Y.-P.; Bai, X.-J.; Hou, T.-Y. Diabetes Mellitus Is Associated with Increased Risk of Surgical Site Infections: A Meta-Analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies. Am. J. Infect. Control 2015, 43, 810–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaichana, K.L.; Bydon, M.; Santiago-Dieppa, D.R.; Hwang, L.; McLoughlin, G.; Sciubba, D.M.; Wolinsky, J.-P.; Bydon, A.; Gokaslan, Z.L.; Witham, T. Risk of Infection Following Posterior Instrumented Lumbar Fusion for Degenerative Spine Disease in 817 Consecutive Cases. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2014, 20, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijs, A.; de Greeff, S.; Vos, M.; Geerlings, S.; Koek, M. The Effect of Body Mass Index on the Risk of Surgical Site Infection. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect Control 2015, 4, O29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, D.; Ma, J.-X.; Ma, X.-L.; Song, D.-H.; Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, S.-W.; Ma, B.-Y.; Feng, R. A Methodological, Systematic Review of Evidence-Based Independent Risk Factors for Surgical Site Infections after Spinal Surgery. Eur. Spine J. 2013, 22, 605–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, A.I.; Babu, R.; Karikari, I.O.; Grunch, B.; Agarwal, V.J.; Owens, T.R.; Friedman, A.H.; Bagley, C.A.; Gottfried, O.N. 2012 Young Investigator Award Winner: The Distribution of Body Mass as a Significant Risk Factor for Lumbar Spinal Fusion Postoperative Infections. Spine 2012, 37, 1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adindu, E.; Singh, D.; Geck, M.; Stokes, J. Eeric Truumees The Impact of Obesity on Postoperative and Perioperative Outcomes in Lumbar Spine Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Spine J. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benavidez, G.A.; Zahnd, W.E.; Hung, P.; Eberth, J.M. Chronic Disease Prevalence in the US: Sociodemographic and Geographic Variations by Zip Code Tabulation Area. Prev. Chronic Dis. 2024, 21, E14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schimmel, J.J.P.; Horsting, P.P.; de Kleuver, M.; Wonders, G.; van Limbeek, J. Risk Factors for Deep Surgical Site Infections after Spinal Fusion. Eur. Spine J. 2010, 19, 1711–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Comorbidity | All pts (%) | No SSI (%) | SSI (%) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patients | 2363 | 2324 | 39 | |
| Age | 55.6 ± 15.7 | 55.7 ± 15.7 | 55.2 ± 14.0 | 0.768 |
| BMI | 30.4 ± 7.7 | 30.2 ± 7.6 | 30.4 ± 10.8 | 0.903 |
| Male | 1399 (59.2%) | 1379 (59.3%) | 20 (51.3%) | 0.310 |
| COPD | 473 (20.0%) | 459 (19.7%) | 14 (35.9%) | 0.012 |
| Depression | 499 (21.1%) | 490 (21.0%) | 9 (23.1%) | 0.762 |
| Diabetes Mellitus | 1111 (47.0%) | 1091 (46.9%) | 20 (51.3%) | 0.591 |
| GERD | 858 (36.3%) | 844 (36.3%) | 14 (35.9%) | 0.957 |
| CVD | 582 (24.6%) | 566 (24.4%) | 16 (41.0%) | 0.017 |
| Hyperlipidemia | 896 (37.8%) | 880 (37.9%) | 16 (41.0%) | 0.687 |
| Hypertension | 1993 (84.3%) | 1958 (84.2%) | 35 (89.7%) | 0.349 |
| Drug Abuse | 21 (0.89%) | 20 (0.86%) | 1 (2.5%) | 0.296 |
| Ever Smoker | 941 (39.8%) | 921 (39.6%) | 20 (51.3%) | 0.239 |
| Hardware | 2124 (89.9%) | 2087 (89.8%) | 37 (94.9%) | 0.424 |
| Risk Factor | Adjusted OR (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| COPD | 2.072 (1.034–3.992) | 0.041 |
| Cardiovascular Disease | 1.97 (1.009–3.762) | 0.033 |
| Age | BMI | Sex | COPD | Depression | DM | GERD | CVD | HLD | HTN | Drug Abuse | Ever Smoker | Level | Surgical Tissue Culture |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 23 | 23.57 | F | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | T1–T6 | Serratia marcescens and Morganella morgani |
| 45 | 41.4 | M | Yes | No | No | Yes | No | No | Yes | No | Yes | L4–S1 | Proteus mirabilis, CRO Klebsiella pneumoniae |
| 64 | 32.23 | M | Yes | No | No | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | no | C2–C7 | Rare Staphylococcus aureus and Acinetobacter baumanni complex/hemolyticus |
| 42 | 38.1 | M | Yes | No | No | Yes | No | No | No | No | no | T12–L4 | No growth |
| 51 | 23.81 | F | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | no | L3–L5 | Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus |
| 69 | 26.63 | F | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | no | T8–T11 | No growth |
| 48 | 26.59 | M | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | No | no | L4–5 | Staphylococcus epidermidis |
| 68 | 41.81 | M | No | No | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | No | Yes | L2–S1 | Staphylococcus epidermidis |
| 62 | 29.53 | M | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | L1–L5 | Staphylococcus aureus |
| 36 | 38.92 | M | No | Yes | No | No | No | No | Yes | No | No | L4–S1 | Staphylococcus aureus |
| 64 | 27.11 | F | No | No | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | No | No | C2–T2 | Klebsiella oxytoca |
| 61 | 51.54 | M | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | T5–T11 | Staphylococcus aureus |
| 57 | 18.52 | F | No | No | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | L3–L5 | Enterococcus faecalis |
| 67 | 20.98 | M | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | L2–S1 | No growth |
| 72 | 38.52 | M | No | No | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | C1–C5 | Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lupo, B.D.; Jameson, W.P.; Quinones, C.J.; Malek, A.E.; Kumbhare, D.; Guthikonda, B.; Hoang, S. Risk Factors and Outcomes of Surgical Site Infections of the Spine: A Retrospective Multi-Center Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3520. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103520
Lupo BD, Jameson WP, Quinones CJ, Malek AE, Kumbhare D, Guthikonda B, Hoang S. Risk Factors and Outcomes of Surgical Site Infections of the Spine: A Retrospective Multi-Center Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(10):3520. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103520
Chicago/Turabian StyleLupo, Bailey D., Wesley P. Jameson, Christian J. Quinones, Alexandre E. Malek, Deepak Kumbhare, Bharat Guthikonda, and Stanley Hoang. 2025. "Risk Factors and Outcomes of Surgical Site Infections of the Spine: A Retrospective Multi-Center Analysis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 10: 3520. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103520
APA StyleLupo, B. D., Jameson, W. P., Quinones, C. J., Malek, A. E., Kumbhare, D., Guthikonda, B., & Hoang, S. (2025). Risk Factors and Outcomes of Surgical Site Infections of the Spine: A Retrospective Multi-Center Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(10), 3520. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103520





