Do Onodi Cells Influence the Onset of Sphenoiditis? A Multicentric Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Setting
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Characteristics
3.2. Onodi Cells and Sphenoiditis
3.3. Predictors Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| OC | Onodi Cell |
| CT | Computed Tomography |
| OR | Odd Ratio |
| ONC | Optic Nerve Canal |
| ICA | Internal carotid artery |
| ESS | Endoscopic sinus surgery |
| PNS | Paranasal sinus |
References
- Onodi, A. The optic nerve and the accessory sinuses of the nose. In Der Sehnerv and Die NebenOhlen der Nase; Alfred Holder: Wien, Germany, 1907; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Fadda, G.L.; Petrelli, A.; Urbanelli, A.; Castelnuovo, P.; Bignami, M.; Crosetti, E.; Succo, G.; Cavallo, G. Risky anatomical variations of sphenoid sinus and surrounding structures in endoscopic sinus surgery. Head Face Med. 2022, 18, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Özdemir, A.; Bayar Muluk, N.; Asal, N.; Şahan, M.H.; Inal, M. Is there a relationship between Onodi cell and optic canal? Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2019, 276, 1057–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, I.K.; Sansare, K.; Karjodkar, F.; Saalim, M. Imaging Analysis of Onodi Cells on Cone-Beam Computed Tomography. Int. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2020, 24, e319–e322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chipczyńska, B.; Kosowski, H.; Skrzat, J. Sphenoid sinus and sphenoid bone fractures in patients with isolated orbital injuries. Med. Sci. Monit. 2016, 22, 4327–4332. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Chung, I.H. Clinical significance of the Onodi cell in sphenoiditis. Laryngoscope 2016, 126, 1673–1677. [Google Scholar]
- Tomovic, S.; Esmaeili, A.; Chan, N.J.; Choudhry, O.J.; Shukla, P.A.; Liu, J.K.; Eloy, J.A. High-resolution computed tomography analysis of the prevalence of Onodi cells. Laryngoscope 2012, 122, 1470–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, C.C.; Dillon, W.P.; McDermott, M.W. Mucocele involving the anterior clinoid process: MR and CT findings. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 1999, 20, 287–290. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wang, Z.M.; Kanoh, N.; Dai, C.F.; Kutler, D.I.; Xu, R.; Chi, F.L.; Tian, X. Isolated sphenoid sinus disease: An analysis of 122 cases. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2002, 111, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fadda, G.L.; Gisolo, M.; Crosetti, E.; Fulcheri, A.; Succo, G. Intracranial complication of rhinosinusitis from actinomycosis of the paranasal sinuses: A rare case of abducens nerve palsy. Case Rep. Otolaryngol. 2014, 2014, 601671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Batra, P.S.; Citardi, M.J.; Lanza, D.C. Sphenoid sinusitis: Current concepts. Curr. Opin. Otolaryngol. Head. Neck Surg. 2004, 12, 30–35. [Google Scholar]
- Driben, J.S.; Bolger, W.E.; Robles, H.A.; Cable, B.; Zinreich, S.J. The reliability of computerized tomographic detection of the Onodi (Sphenoethmoid) cell. Am. J. Rhinol. 1998, 12, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thanaviratananich, S.; Chaisiwamongkol, K.; Kraitrakul, S.; Tangsawad, W. The prevalence of an Onodi cell in adult Thai cadavers. Ear Nose Throat J. 2003, 82, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeoh, K.H.; Tan, K.K. The optic nerve in the posterior ethmoid in Asians. Acta Otolaryngol. 1994, 114, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wada, K.; Moriyama, H.; Edamatsu, H.; Hama, T.; Arai, C.; Kojima, H.; Otori, N.; Yanagi, K. Identification of Onodi cell and new classification of sphenoid sinus for endoscopic sinus surgery. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2015, 5, 1068–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chmielik, L.P.; Chmielik, A. The prevalence of the Onodi cell—Most suitable method of CT evaluation in its detection. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2017, 97, 202–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, E.I.; Kuo, C.L.; Lee, L.W. A 16-Year Study on Incidence and Progression of Diseased Sphenoethmoidal (Onodi) Cell. Biomed. Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 2410415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Doubi, A.; Albathi, A.; Sukyte-Raube, D.; Castelnuovo, P.; Alfawwaz, F.; AlQahtani, A. Location of the Sphenoid Sinus Ostium in Relation to Adjacent Anatomical Landmarks. Ear Nose Throat J. 2021, 100 (Suppl. S10), 961S–968S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Yan, Z.; Yang, Y. Anatomical identification of supraseptal posterior ethmoid cells and its significance for endoscopic sinus surgery. Folia Morphol. 2023, 82, 696–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kainz, J.; Stammberger, H. Danger areas of the posterior rhinobasis. An endoscopic and anatomical-surgical study. Acta Otolaryngol. 1992, 112, 852–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, K.; Nakayama, T.; Asaka, D. Etiology and pathophysiology of chronic rhinosinusitis: The role of Onodi cells. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2018, 32, 180–185. [Google Scholar]
- Merritt, R.M.; Bent, J.P.; Kuhn, F.A. The intersinus septal cell: Anatomic, radiologic, and clinical correlation. Am. J. Rhinol. 1996, 10, 299–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awadalla, A.M.; Hussein, Y.; Mahmoud, E.M. Impact of onodi cells on management of antrochoanal polyp transnasal endoscopic approach. Int. J. Otorhinolaryngol. Clin. 2015, 7, 25–28. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, S.S.; Tabaee, A.; Salman, S.D. The Onodi cell: A reason for failure of endoscopic sphenoidal surgery. Laryngoscope 2008, 118, 176–178. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, H.K.K.; Ong, Y.K.; Teo, M.S.K. The Onodi cell: An important anatomical variation in sinus surgery. Otolaryngol. Head. Neck Surg. 2003, 128, 154–155. [Google Scholar]
- Christmas, D.A.; Mirante, J.P.; Yanagisawa, E. A possible case of two Onodi cells in a single patient. Ear Nose Throat J. 2003, 82, 873–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.U.; Kim, S.S.; Kang, S.S.; Chung, I.H.; Lee, J.G.; Yoon, J.H. Surgical anatomy of the natural ostium of the sphenoid sinus. Laryngoscope 2001, 111, 1599–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P. STROBE Initiative. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: Guidelines for reporting observational studies. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2008, 61, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thimmaiah, V.T.; Anupama, C. Pneumatization patterns of Onodi cell on multidetector computed tomography. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Radiol. 2017, 5, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadda, G.L.; Urbanelli, A.; Petrelli, A.; Trossarello, M.; Nitro, L.; Saibene, A.M.; De Corso, E.; Gned, D.; Panfili, M.; Cavallo, G. Type IV optic nerve and Onodi cell: Is there a risk of injury during sphenoid sinus surgery? Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2024, 44, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liu, J.; Yuan, J.; Dai, J.; Wang, N. The Whole Lateral Type of the Sphenoethmoidal Cell and Its Relevance to Endoscopic Sinus Surgery. Ear Nose Throat J. 2021, 100, NP416–NP423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Piñas, I.; Sabaté, J.; Carmona, A.; Catalina-Herrera, C.J.; Jiménez-Castellanos, J. Anatomical variations in the human paranasal sinus region studied by CT. J. Anat. 2000, 197 Pt 2, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ozturan, O.; Yenigun, A.; Degirmenci, N.; Aksoy, F.; Veyseller, B. Co-existence of the Onodi cell with the variation of perisphenoidal structures. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2013, 270, 2057–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.J.; Lee, I.H.; Kim, S.W.; Kim, D.H. Surgical and Radiological Differences in Intersphenoid Sinus Septation and the Prevalence of Onodi Cells with the Endoscopic Endonasal Transsphenoidal Approach. Medicina 2022, 58, 1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shin, J.H.; Kim, S.W.; Hong, Y.K.; Jeun, S.S.; Kang, S.G.; Kim, S.W.; Cho, J.H.; Park, Y.J. The Onodi cell: An obstacle to sellar lesions with a transsphenoidal approach. Otolaryngol. Head. Neck Surg. 2011, 145, 1040–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, Y.J.; Kim, G.T.; Park, M.J. Sudden Unilateral Visual Loss Due to an Onodi Cell Mucocele. Ear Nose Throat J. 2023, 1455613231214705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaikh, N.; Nguyen, J.; Bailey, C.E.; Patel, A.; Ellis, B.; Makary, C.A. Rhinogenic Optic Neuropathy with No Light Perception Secondary to Onodi Cell Mucocele with Visual Recovery after Optic Nerve Decompression. Ear Nose Throat J. 2023, 1455613231170600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, K.W.; Oh, J.S.; Kim, J.W.; Yoo, R.E.; Kang, J.G. Onodi cell mucocele causing isolated trochlear nerve palsy: A case report. Medicine 2019, 98, e15475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Geng, C.; Tong, Q.; Wang, Y.; Huang, S.; Wang, M.; Xing, Z.; Sun, K. Onodi cell mucocele with cholesterol granuloma is more likely to cause serious optic neuropathy, compared with simple Onodi cell mucocele. Ear Nose Throat J. 2024, 103, 724–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, X.; Guo, T. Optic nerve canal in the sphenoid sinus: Assessment with computed tomography and its impact on surgical approach to the sella and pituitary. J. Craniofac Surg. 2018, 29, 1583–1586. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, T.; Aggarwal, A.; Sahni, D. Anatomical landmarks for locating the sphenoid ostium during endoscopic endonasal approach: A cadaveric study. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2013, 35, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senturk, M.; Guler, I.; Azgin, I.; Sakarya, E.U.; Ovet, G.; Alatas, N.; Tolu, I.; Erdur, O. The role of Onodi cells in sphenoiditis: Results of multiplanar reconstruction of computed tomography scanning. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2017, 83, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
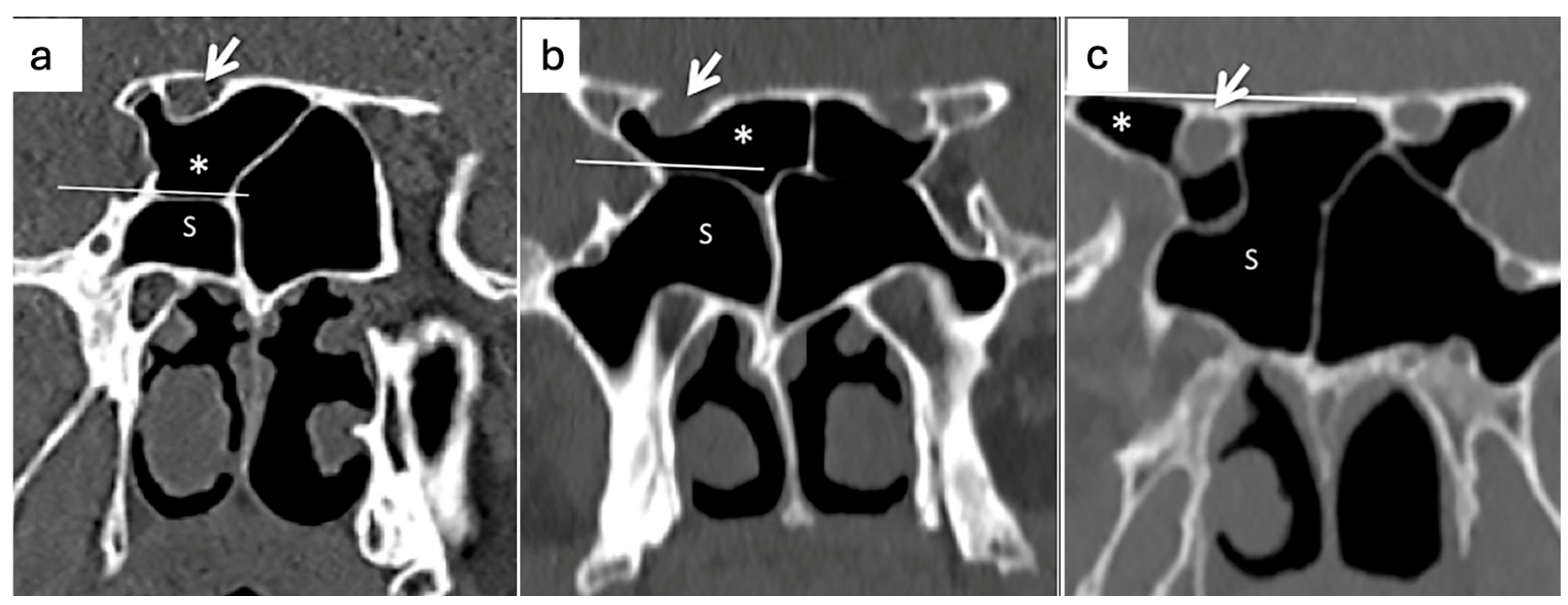
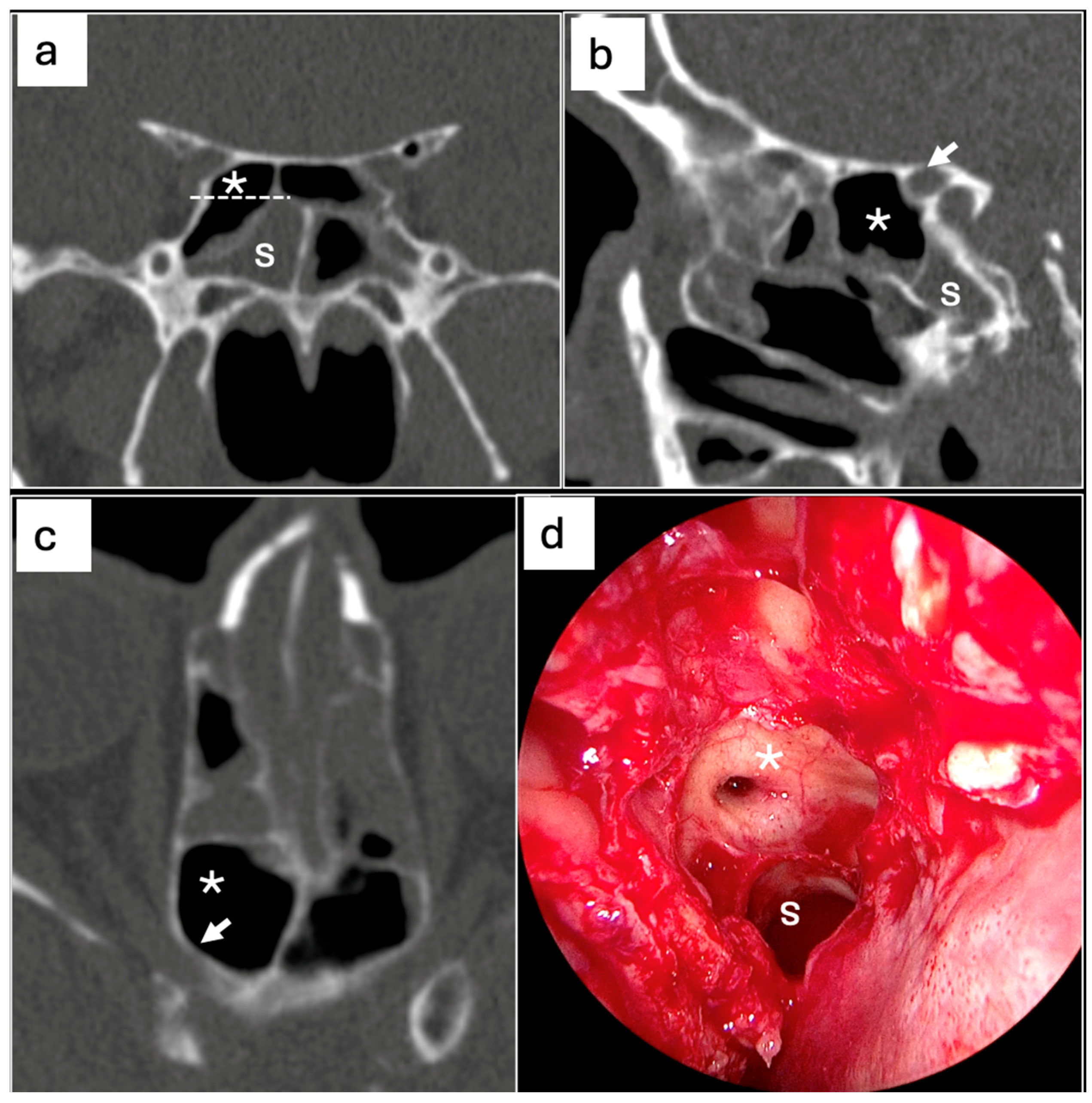
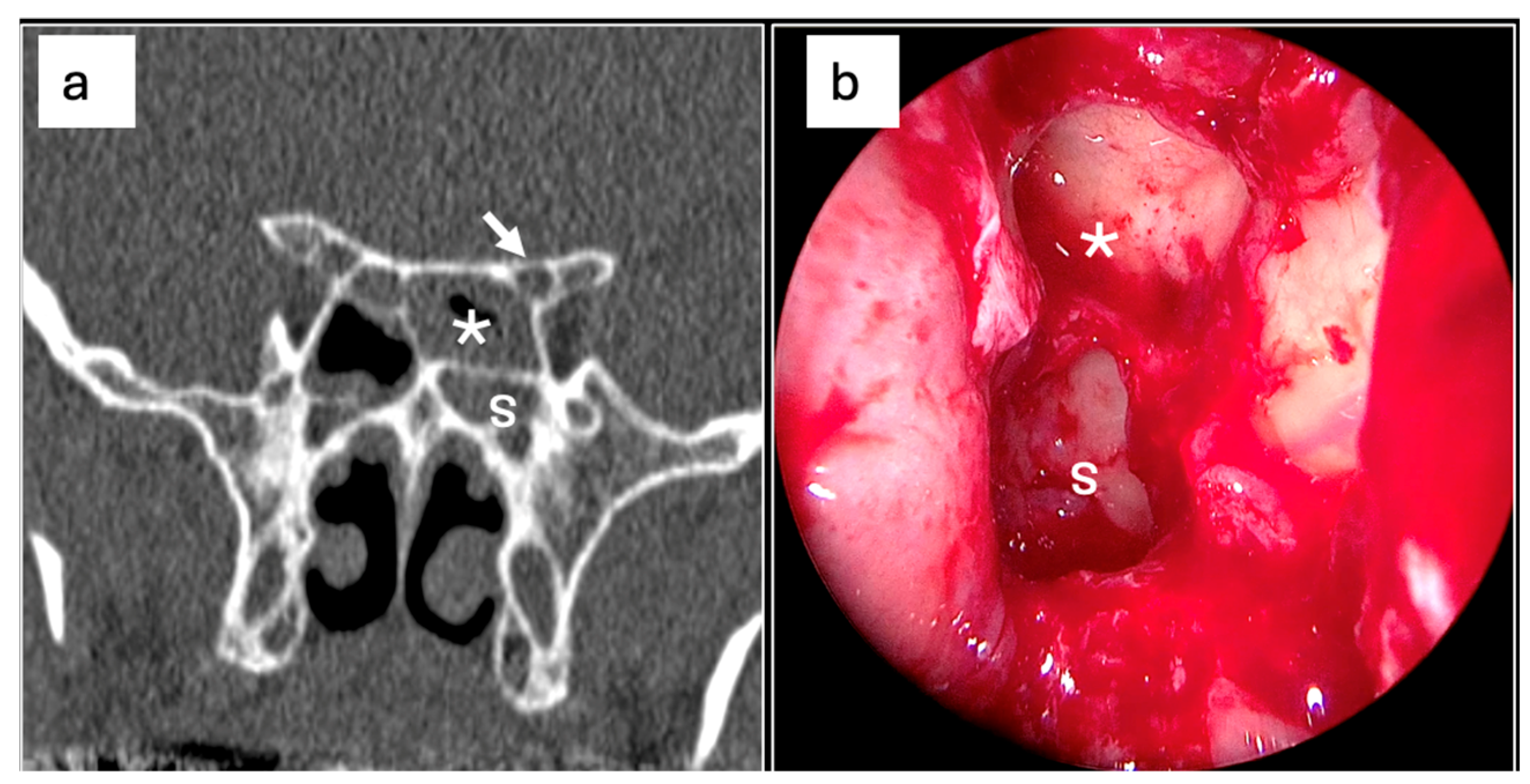
| N° (%) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|
| Age | 52, 9 ± 18 y | |
| Sex | 550 (100%) | |
| Female | 237 (43.1%) | |
| Male | 313 (56.9%) | |
| OC | 178 (32.4%) | |
| No | 372 (67.6%) | <0.001 |
| Right | 101 (18.4%) | |
| Left | 46 (8.4%) | |
| Bilateral | 31 (5.6%) | |
| OC type I | 65 (11.8%) | |
| No | 485 (88.2%) | <0.001 |
| Right | 47 (8.5%) | |
| Left | 18 (3.3%) | |
| OC type II | 39 (7.1%) | |
| No | 511 (92.9%) | <0.001 |
| Right | 35 (6.4%) | |
| Left | 4 (0.7%) | |
| OC type III | 24 (4.4%) | |
| No | 526 (95.6%) | <0.001 |
| Right | 22 (4%) | |
| Left | 2 (0.4%) | |
| ONC protrusion | 24 (4.3%) | |
| No | 529 (96.2%) | <0.001 |
| Right | 18 (3.3%) | |
| Left | 3 (0.5%) | |
| Bilateral Protrusion | 3 (0.5%) | |
| Sphenoiditis | 70 (12.7%) | |
| No | 480 (87.3%) | <0.001 |
| Right | 25 (4.5%) | |
| Left | 26 (4.7%) | |
| Bilateral | 19 (3.5%) |
| Sphenoiditis | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No (%) | Right | Left | Bilateral | Total | p-Value | ||
| OC | No | 328 (88.2%) | 15 (4.0%) | 19 (5.1%) | 10 (2.7%) | 372 | 0.344 |
| Right | 87 (86.1%) | 4 (4%) | 6 (5.9%) | 4 (4%) | 101 | ||
| Left | 37 (80.4%) | 5 (10.9%) | 1 (2.2%) | 3 (6.5%) | 46 | ||
| Bilateral | 28 (90.3%) | 1 (3.2%) | 0 | 2 (6.5%) | 31 | ||
| OC type I | No | 427 (88%) | 20 (4.1%) | 24 (4.9%) | 14 (3%) | 485 | 0.069 |
| Right | 37 (79%) | 3 (6.3%) | 2 (4.2%) | 5 (10.5%) | 47 | ||
| Left | 16 (88.9%) | 2 (11.1%) | 0 | 0 | 18 | ||
| OC type II | No | 448 (87.7%) | 23 (4.5%) | 24 (4.7%) | 16 (3.1) | 511 | 0.705 |
| Right | 28 (80%) | 2 (5.7%) | 2 (5.7%) | 3 (8.6%) | 35 | ||
| Left | 4 (100%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | ||
| OC type III | No | 459 (87.3%) | 23 (4.4%) | 26 (4.9%) | 18 (3.4%) | 526 | 0.869 |
| Right | 19 (86.4%) | 2 (9.1%) | 0 | 1 (4.5%) | 22 | ||
| Left | 2 (100%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | ||
| ONC protrusion | No | 462 (87%) | 25 (4.7%) | 23 (4.3%) | 19 (4%) | 529 | 0.272 |
| Right | 15 (83.3%) | 0 | 3 (16.7%) | 0 | 18 | ||
| Left | 3 (100%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | ||
| ONC bilateral protrusion | Yes | 477 (87.2%) | 25 (4.6%) | 26 (4.7%) | 19 (3.5%) | 547 | 0.932 |
| No | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | ||
| Right-Side Sphenoiditis | No | Yes | OR (Univariable) | OR (Multivariable) | Left-Side Sphenoiditis | No | Yes | OR (Univariable) | OR (Multivariable) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | Female | 217 (91.6%) | 20 (8.4%) | - | - | Sex | Female | 219 (92.4%) | 18 (7.6%) | - | - |
| Male | 288 (92%) | 25 (8%) | 0.94 (0.51–1.76, p = 0.848) | 0.93 (0.50–1.74, p = 0.808) | Male | 287 (91.7%) | 26 (8.3%) | 1.10 (0.59–2.09, p = 0.761) | 1.00 (0.53–1.92, p = 0.999) | ||
| OC | No | 449 (91.8%) | 40 (8.2%) | - | - | OC | No | 454 (92.8%) | 35 (7.2%) | - | - |
| Yes | 56 (91.8%) | 5 (8.2%) | 1.00 (0.34–2.43, p = 0.996) | 0.32 (0.06–1.70, p = 0.186) | Yes | 52 (85.2%) | 9 (14.8%) | 2.25 (0.97–4.75, p = 0.044) | 1.33 (0.31–6.46, p = 0.712) | ||
| Bilateral OC | No | 476 (91.7%) | 43 (8.3%) | - | - | Bilateral OC | No | 478 (92.1%) | 41 (7.9%) | - | - |
| Yes | 29 (93.5%) | 2 (6.5%) | 0.76 (0.12–2.66, p = 0.718) | 0.30 (0.03–1.82, p = 0.221) | Yes | 28 (90.3%) | 3 (9.7%) | 1.25 (0.29–3.72, p = 0.724) | 0.27 (0.04–1.41, p = 0.145) | ||
| OC type I | No | 463 (91.9%) | 41 (8.1%) | - | - | OC type I | No | 476 (92.8%) | 37 (7.2%) | - | - |
| Yes | 42 (91.3%) | 4 (8.7%) | 1.08 (0.31–2.83, p = 0.894) | 3.73 (0.57–19.35, p = 0.134) | Yes | 30 (81.1%) | 7 (18.9%) | 3.00 (1.15–6.96, p = 0.015) | 2.98 (0.57–12.21, p = 0.157) | ||
| OC type II | No | 485 (92.2%) | 41 (7.8%) | - | - | OC type II | No | 489 (92.1%) | 42 (7.9%) | - | - |
| Yes | 20 (83.3%) | 4 (16.7%) | 2.37 (0.66–6.62, p = 0.132) | 6.81 (1.14–38.97, p = 0.029) | Yes | 17 (89.5%) | 2 (10.5%) | 1.37 (0.21–5.00, p = 0.681) | 1.49 (0.18–7.25, p = 0.661) | ||
| OC type III | No | 497 (91.7%) | 45 (8.3%) | - | - | OC type III | No | 490 (92.1%) | 42 (7.9%) | - | - |
| Yes | 8 (100%) | 0 (0%) | 0.00 (NA, p = 0.987) | 0.00 (NA, p = 0.986) | Yes | 16 (88.9%) | 2 (11.1%) | 1.46 (0.23–5.36, p = 0.623) | 1.40 (0.15–8.45, p = 0.739) | ||
| ONC protrusion | No | 495 (91.8%) | 44 (8.2%) | - | - | ONC protrusion | No | 493 (91.8%) | 44 (8.2%) | - | - |
| Yes | 10 (90.9%) | 1 (9.1%) | 1.12 (0.06–6.08, p = 0.912) | 1.50 (0.07–10.67, p = 0.725) | Yes | 13 (100%) | 0 (0%) | 0.00 (NA, p = 0.983) | 0.00 (NA, p = 0.988) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fadda, G.L.; Saibene, A.M.; Rustichelli, C.; Nitro, L.; Lentini, M.; Parisi, F.M.; Cocuzza, S.; Cavallo, G.; De Corso, E.; Maniaci, A. Do Onodi Cells Influence the Onset of Sphenoiditis? A Multicentric Cross-Sectional Study. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3508. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103508
Fadda GL, Saibene AM, Rustichelli C, Nitro L, Lentini M, Parisi FM, Cocuzza S, Cavallo G, De Corso E, Maniaci A. Do Onodi Cells Influence the Onset of Sphenoiditis? A Multicentric Cross-Sectional Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(10):3508. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103508
Chicago/Turabian StyleFadda, Gian Luca, Alberto Maria Saibene, Chiara Rustichelli, Letizia Nitro, Mario Lentini, Federica Maria Parisi, Salvatore Cocuzza, Giovanni Cavallo, Eugenio De Corso, and Antonino Maniaci. 2025. "Do Onodi Cells Influence the Onset of Sphenoiditis? A Multicentric Cross-Sectional Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 10: 3508. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103508
APA StyleFadda, G. L., Saibene, A. M., Rustichelli, C., Nitro, L., Lentini, M., Parisi, F. M., Cocuzza, S., Cavallo, G., De Corso, E., & Maniaci, A. (2025). Do Onodi Cells Influence the Onset of Sphenoiditis? A Multicentric Cross-Sectional Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(10), 3508. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103508











