Combination Between Biomarkers and Echocardiographic Data for Prediction of Left Ventricular Reverse Remodelling in Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Biomarkers
2.2. Echocardiography
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Baseline Clinical and Echocardiographic Data of Responders vs. Non-Responders
3.3. Baseline Biomarker Levels
3.4. Biomarkers Trend at Follow-Up
3.5. Prediction of Response to Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy
3.6. Biomarkers Profile Considering Responder Status as Improvement in LVEF ≥ 10%
4. Discussion
4.1. Cardiac Biomarkers Associated with CRT Response
4.2. Echocardiographic Predictors of CRT Response
4.3. Researching Predictors of CRT Response: Still a Role in Clinical Practice?
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moulin, T.; Hamon, D.; Djouadi, K.; D’Humières, T.; Elbaz, N.; Boukantar, M.; Zerbib, C.; Rouffiac, S.; Dhanjal, T.S.; Ernande, L.; et al. Impact of cardiac resynchronization therapy optimization inside a heart failure programme: A real-world experience. ESC Heart Fail. 2022, 9, 3101–3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moss, A.J.; Hall, W.J.; Cannom, D.S.; Klein, H.; Brown, M.W.; Daubert, J.P.; Estes, N.A.M., III; Foster, E.; Greenberg, H.; Higgins, S.L.; et al. Cardiac-Resynchronization Therapy for the Prevention of Heart-Failure Events. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 1329–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, I.S.; Carson, P.; Galle, E.; Song, R.; Boehmer, J.; Ghali, J.K.; Jaski, B.; Lindenfeld, J.; O’Connor, C.; Steinberg, J.S.; et al. Cardiac resynchronization therapy reduces the risk of hospitalizations in patients with advanced heart failure results from the comparison of medical therapy, pacing and defibrillation in heart failure (COMPANION) trial. Circulation 2009, 119, 969–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullens, W.; Auricchio, A.; Martens, P.; Witte, K.; Cowie, M.R.; Delgado, V.; Dickstein, K.; Linde, C.; Vernooy, K.; Leyva, F.; et al. Optimized implementation of cardiac resynchronization therapy: A call for action for referral and optimization of care: A joint position statement from the Heart Failure Association (HFA), European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA), and European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging (EACVI) of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2020, 22, 2349–2369. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Palazzuoli, A.; Tramonte, F.; Beltrami, M. Laboratory and Metabolomic Fingerprint in Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction: From Clinical Classification to Biomarker Signature. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aimo, A.; Januzzi, J.L.; Vergaro, G.G.V.; Ripoli, A.; Latini, R.; Masson, S.; Magnoli, M.; Anand, I.S.; Cohn, J.N.; Tavazzi, L.; et al. Prognostic value of high-sensitivity troponin T in chronic heart failure an individual patient data meta-analysis. Circulation 2018, 137, 286–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dini, F.L.; Carluccio, E.; Ghio, S.; Pugliese, N.R.; Galeotti, G.; Correale, M.; Beltrami, M.; Tocchetti, C.G.; Mercurio, V.; Paolillo, S.; et al. Patient phenotype profiling using echocardiography and natriuretic peptides to personalise heart failure therapy. Heart Fail Rev. 2023, 29, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andre, C.; Piver, E.; Perault, R.; Bisson, A.; Pucheux, J.; Vermes, E.; Pierre, B.; Fauchier, L.; Babuty, D.; Clementy, N. Galectin-3 predicts response and outcomes after cardiac resynchronization therapy. J. Transl. Med. 2018, 16, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAloon, C.J.; Barwari, T.; Hu, J.; Hamborg, T.; Nevill, A.; Hyndman, S.; Ansell, V.; Musa, A.; Jones, J.; Goodby, J.; et al. Characterisation of circulating biomarkers before and after cardiac resynchronisation therapy and their role in predicting CRT response: The COVERT-HF study. Open Heart 2018, 5, e000899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltrami, M.; Galluzzo, A.; Brocci, R.T.; Paoletti Perini, A.; Pieragnoli, P.; Garofalo, M.; Halasz, G.; Milli, M.; Barilli, M.; Palazzuoli, A. The role of fibrosis, inflammation, and congestion biomarkers for outcome prediction in candidates to cardiac resynchronization therapy: Is “response” the right answer? Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 10, 1180960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltrami, M.; Ruocco, G.; Dastidar, A.G.; Franci, B.; Lucani, B.; Aloia, E.; Nuti, R.; Palazzuoli, A. Additional value of Galectin-3 to BNP in acute heart failure patients with preserved ejection fraction. Clin. Chim. Acta 2016, 457, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schimmel, K.; Ichimura, K.; Reddy, S.; Haddad, F.; Spiekerkoetter, E. Cardiac Fibrosis in the Pressure Overloaded Left and Right Ventricle as a Therapeutic Target. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 886553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgardoon, M.H.; Vasheghani-Farahani, A.; Sherafati, A. Usefulness of Biomarkers for Predicting Response to Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy. Curr. Cardiol. Rev. 2019, 16, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAloon, C.J.; Ali, D.; Hamborg, T.; Banerjee, P.; O’Hare, P.; Randeva, H.; Osman, F. Extracellular cardiac matrix biomarkers in patients with reduced ejection fraction heart failure as predictors of response to cardiac resynchronisation therapy: A systematic review. Open Heart 2017, 4, e000639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Andrés, N.; Rossignol, P.; Iraqi, W.; Fay, R.; Nuée, J.; Ghio, S.; Cleland, G.J.F.; Zannad, F.; Lacolley, P. Association of galectin-3 and fibrosis markers with long-term cardiovascular outcomes in patients with heart failure, left ventricular dysfunction, and dyssynchrony: Insights from the CARE-HF (Cardiac Resynchronization in Heart Failure) trial. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2012, 14, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lok, D.J.; Lok, S.I.; de la Porte, P.W.B.-A.; Badings, E.; Lipsic, E.; van Wijngaarden, J.; de Boer, R.A.; van Veldhuisen, D.J.; van der Meer, P. Galectin-3 is an independent marker for ventricular remodeling and mortality in patients with chronic heart failure. Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2013, 102, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karatolios, K.; Chatzis, G.; Holzendorf, V.; Störk, S.; Richter, A.; Binas, D.; Schieffer, B.; Pankuweit, S. Galectin-3 as a predictor of left ventricular reverse remodeling in recent-onset dilated cardiomyopathy. Dis. Markers 2018, 2018, 2958219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuern, C.S.; Floss, N.; Mueller, I.I.; Eick, C.; Duckheim, M.; Patzelt, J.; Gawaz, M.; May, A.E.; Mueller, K.A.L. Galectin-3 is associated with left ventricular reverse remodeling and outcome after percutaneous mitral valve repair. Int. J. Cardiol. 2018, 263, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaudoin, J.; Szymonifka, J.; Lavender, Z.; Deaño, R.C.; Zhou, Q.; Januzzi, J.L.; Singh, J.P.; Truong, Q.A. Relationship of soluble ST2 to pulmonary hypertension severity in patients undergoing cardiac resynchronization therapy. J. Thorac. Dis. 2019, 11, 5362–5371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohebi, R.; Liu, Y.; Felker, G.M.; Prescott, M.F.; Ward, J.H.; Piña, I.L.; Butler, J.; Solomon, S.D.; Januzzi, J.L. Heart Failure Duration and Mechanistic Efficacy of Sacubitril/Valsartan in Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction. J. Card. Fail. 2022, 28, 1673–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skali, H.; Gerwien, R.; Meyer, T.E.; Snider, J.V.; Solomon, S.D.; Stolen, C.M. Soluble ST2 and Risk of Arrhythmias, Heart Failure, or Death in Patients with Mildly Symptomatic Heart Failure: Results from MADIT-CRT. J. Cardiovasc. Transl. Res. 2016, 9, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaggin, H.K.; Szymonifka, J.; Bhardwaj, A.; Belcher, A.; De Berardinis, B.; Motiwala, S.; Wang, T.J.; Januzzi, J.L. Head-to-Head Comparison of Serial Soluble ST2, Growth Differentiation Factor-15, and Highly-Sensitive Troponin T Measurements in Patients with Chronic Heart Failure. JACC Heart Fail. 2014, 2, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Boer, R.A.; Lok, D.J.A.; Jaarsma, T.; van der Meer, P.; Voors, A.A.; Hillege, H.L.; van Veldhuisen, D.J. Predictive value of plasma galectin-3 levels in heart failure with reduced and preserved ejection fraction. Ann. Med. 2011, 43, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascual-Figal, D.A.; Ordoñez-Llanos, J.; Tornel, P.L.; Vázquez, R.; Puig, T.; Valdés, M.; Cinca, J.; de Luna, A.B.; Bayes-Genis, A.; Music Investigators. Soluble ST2 for Predicting Sudden Cardiac Death in Patients with Chronic Heart Failure and Left Ventricular Systolic Dysfunction. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009, 54, 2174–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ter Maaten, J.M.; Martens, P.; L’Hoyes, W.; Maass, A.H.; Damman, K.; Dupont, M.; Mullens, W. Response to Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy Across Chronic Kidney Disease Stages. J. Card. Fail. 2019, 25, 803–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, J.W.; Szeto, C.C.; Chan, J.Y.; Zhang, Q.; Chan, H.C.; Yip, G.W.; Yu, C.M. Prognostic value of renal function in patients with cardiac resynchronization therapy. Int. J. Cardiol. 2007, 122, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvier, L.; Martinez-Martinez, E.; Miana, M.; Cachofeiro, V.; Rousseau, E.; Sádaba, J.R.; Zannad, F.; Rossignol, P.; López-Andrés, N. The Impact of Galectin-3 Inhibition on Aldosterone-Induced Cardiac and Renal Injuries. JACC Heart Fail. 2015, 3, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waggoner, A.D.; Faddis, M.N.; Gleva, M.J.; Fuentes, L.d.L.; Osborn, J.; Heuerman, S.; Davila-Roman, V.G. Cardiac resynchronization therapy acutely improves diastolic function. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2005, 18, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Yip, G.; Yu, C.-M.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Tse, D.; Kong, S.-L.; Sanderson, J.E. Independent and incremental prognostic value of early mitral annulus velocity in patients with impaired left ventricular systolic function. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2005, 45, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjaergaard, J.; Ghio, S.; St John Sutton, M.; Hassager, C. Tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion and response to cardiac resynchronization therapy: Results from the Reverse trial. J. Card. Fail. 2011, 17, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghio, S.; Freemantle, N.; Scelsi, L.; Serio, A.; Magrini, G.; Pasotti, M.; Shankar, A.; Cleland, J.G.; Tavazzi, L. Long-term left ventricular reverse remodelling with cardiac resynchronization therapy: Results from the CARE-HF trial. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2009, 11, 480–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makaryus, A.N.; Arduini, A.D.; Mallin, J.; Chung, E.; Kort, S.; Shi, Q.; Jadonath, R.; Mangion, J. Echocardiographic features of patients with heart failure who may benefit from biventricular pacing. Echocardiography 2003, 20, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kjaergaard, J.; Petersen, C.L.; Kjaer, A.; Schaadt, B.K.; Oh, J.K.; Hassager, C. Evaluation of right ventricular volume and function by 2D and 3D echocardiography compared to MRI. Eur. J. Echocardiogr. 2006, 7, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bragança, B.; Trêpa, M.; Santos, R.; Silveira, I.; Fontes-Oliveira, M.; Sousa, M.J.; Reis, H.; Torres, S.; Santos, M. Echocardiographic assessment of right ventriculo-arterial coupling: Clinical correlates and prognostic impact in heart failure patients undergoing cardiac resynchronization therapy. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2020, 28, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalska-Kasiczak, M.; Bielecka-Dabrowa, A.; Von Haehling, S.; Anker, S.D.; Rysz, J.; Banach, M. Biomarkers, myocardial fibrosis and co-morbidities in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: An overview. Arch. Med. Sci. 2018, 14, 890–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, S.; Nielsen-Kudsk, J.E.; Vonk Noordegraaf, A.; De Man, F.S. Right Ventricular Fibrosis: A Pathophysiological Factor in Pulmonary Hypertension? Circulation 2019, 139, 269–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Non-Responder n = 35 | Responder n = 51 | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 71 ± 7 | 68 ± 10 | NS |
| Sex female (n,%) | 3(9) | 19(37) | 0.004 |
| BSA (mq) | 1.9 ± 0.1 | 1.8 ± 0.2 | 0.01 |
| Ischaemic aetiology | 19 (54) | 18 (22) | 0.03 |
| Diabetes | 15 (43) | 11 (21) | 0.03 |
| Smoke active | 10 (28) | 13 (25) | 0.003 |
| Former | 11 (31) | 6 (12) | 0.003 |
| Arterial hypertension | 20 (57) | 25 (49) | NS |
| Dyslipidaemia | 19 (54) | 22 (43) | NS |
| Atrial fibrillation | 15 (42) | 6 (11) | 0.004 |
| NYHA class | |||
| II (n,%) | 10 (28) | 13 (25) | NS |
| III (n,%) | 19 (54) | 34 (67) | NS |
| IV (n,%) | 6 (17) | 4 (8) | NS |
| Biomarkers | |||
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 1.2 [1.1;1,6] | 1.1 [1.0;1.5] | NS |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 54.5 [38.5;63.7] | 54.0 [44.5;69.5] | NS |
| NT-proBNP (pg/mL) | 1394 [671;2267] | 883 [554;2175] | NS |
| Gal-3 (ng/mL) | 30 [20;39.3] | 24.1 [16.8;32] | 0.03 |
| sST2 (ng/mL) | 34.5 [25;37.7] | 28.5 [20;36] | 0.03 |
| Echocardiographic data | |||
| LVEDV (mL) | 229 ± 65 | 197 ± 65 | 0.03 |
| LVESV (mL) | 169 ± 52 | 143 ± 53 | 0.02 |
| LVEF (%) | 25 [23;29] | 28 [22;32] | NS |
| LVDD (mm) | 71 ± 9 | 64 ± 8 | 0.001 |
| LVDS (mm) | 59 ± 9 | 51 ± 9 | <0.001 |
| E wave (cm/sec) | 85 ± 28 | 80 ± 24 | NS |
| E/A | 1.2 [0.7;1,7] | 0.9 [0.6;1.8] | NS |
| E/e’ | 18 [16;21] | 14 [10;17] | 0.001 |
| LA area (cm2) | 24 [21;27.5] | 23 [19;27] | NS |
| TAPSE (mm) | 15 [14;20] | 20 [17;21] | <0.001 |
| Treatment | |||
| B-blockers (n,%) | 32 (92) | 47 (94) | NS |
| ACEi/sacubitril–valsartan (n,%) | 30 (86) | 45 (88) | NS |
| MRA (n,%) | 28 (82) | 43 (84) | NS |
| Diuretic (n,%) | 33 (95) | 48 (95) | NS |
| Non-Responder n = 35 | Responder n = 51 | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Biomarkers | |||
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 1.57 ± 0.63 | 1.25 ± 0.45 | 0.008 |
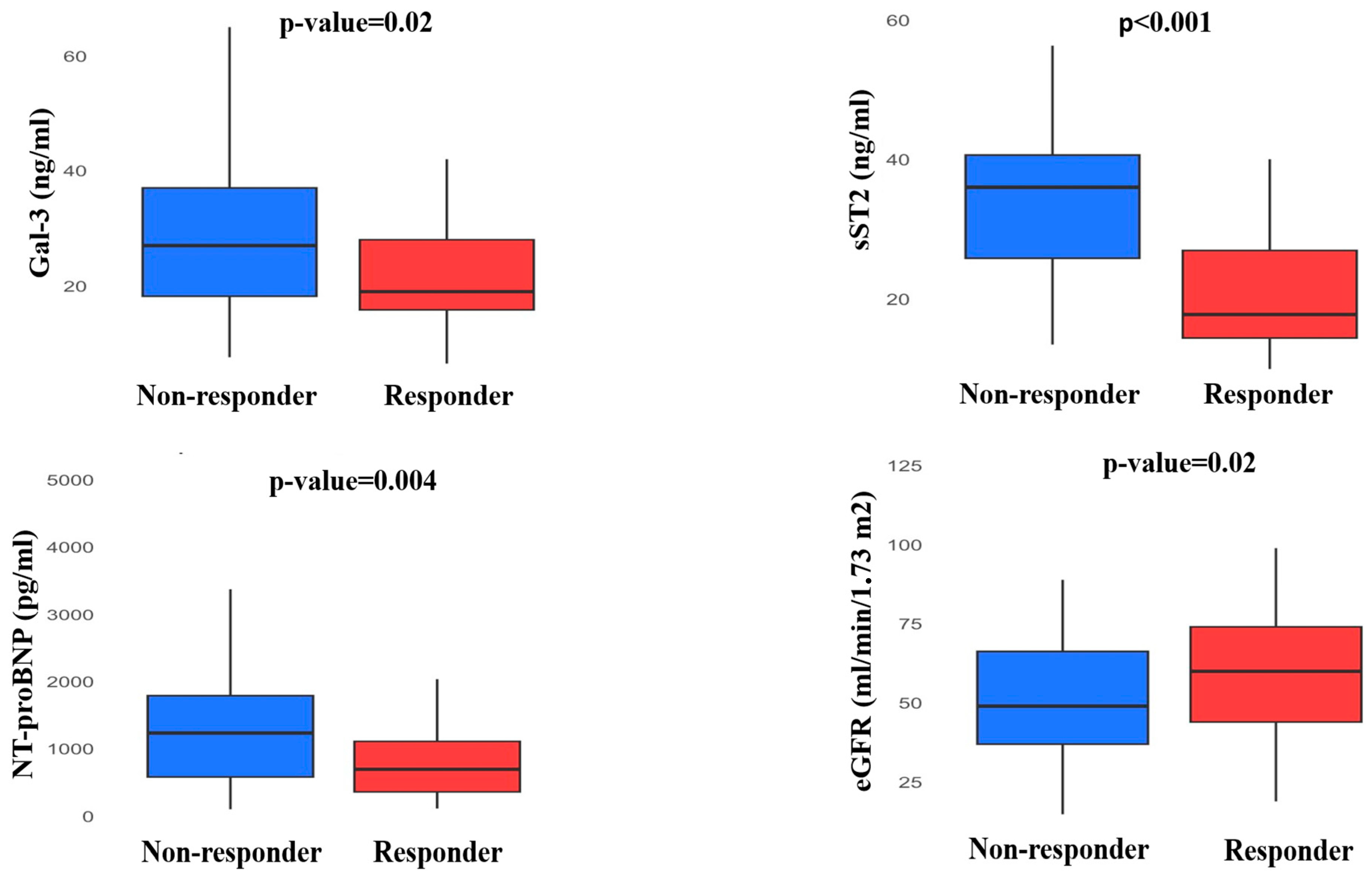
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 49 [37;66.2] | 60 [44;74] | 0.02 |
| ΔeGFR (%) | −6.3 ± 27.9 | 6.7 ± 24.3 | 0.03 |
| Gal-3 (ng/mL) | 27 [18.2;37] | 19 [15.8;28] | 0.02 |
| ΔGal-3 (%) | −2.5 [−19.2;2.3] | −12.1 [−23.4;3.5] | 0.04 |
| sST-2 (ng/mL) | 36 [25.8;40.6] | 17.8 [14.4;26.9] | <0.001 |
| ΔsST-2 (%) | 2.2 [−0.5;4.9] | −30.8 [−35.8;−20.2] | <0.001 |
| NT-proBNP (pg/mL) | 1483 [858;2833] | 749 [365;1182] | 0.004 |
| ΔNT-proBNP (%) | 5.2 [−27.5;53.3] | −16.4 [−48.1;25.5] | 0.04 |
| Echocardiographic data | |||
| LVEDV (mL) | 239 ± 72 | 140 ± 50 | <0.001 |
| LVESV (mL) | 175 ± 58 | 81 ± 40 | <0.001 |
| LVEF (%) | 26 [24;41.5] | 45 [38;50] | <0.001 |
| LVDD (mm) | 72 ± 9 | 59 ± 8 | <0.001 |
| LVDS (mm) | 60 [53;65] | 43 [39;52] | <0.001 |
| E wave (cm/sec) | 87 ± 28 | 69 ± 25 | 0.004 |
| E/A | 1.2 [0.6;2.0] | 0.77 [0.60;1.1] | 0.04 |
| E/e’ | 18 [12.7;22.7] | 11 [9.0;15.2] | <0.001 |
| E/e’ < 15 | 8(22) | 31(60) | 0.001 |
| LA area (cm2) | 27 ± 6 | 24 ± 6 | 0.01 |
| TAPSE (mm) | 14.5 [14;16.25] | 20 [18;22] | <0.001 |
| TAPSE > 17.5 | 9 (25) | 43 (84) | <0.001 |
| Odds Ratio [CI 95%] | p-Value | Log Likelihood = −37 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Biomarkers | |||
| Galectin-3 (pg/mL) ≤ 38.5 | 7.13 [1.12;45.41] | 0.03 | |
| E/e’ ≤ 15.5 | 1.98 [0.57;6.79] | 0.27 | |
| TAPSE (mm) > 17.5 | 10.86 [3.15;37.44] | <0.001 | |
| LVEF (%) | 1.01 [0.90;1.12] | 0.83 | |
| Ischemic etiology | 0.45 [0.14;1.47] | 0.18 |
| Odds Ratio [CI 95%] | p-Value | Log Likelihood = −35 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Biomarkers | |||
| Galectin-3 (pg/mL) ≤ 38.5 | 10.51 [1.42;77.73] | 0.02 | |
| E/e’ ≤ 15.5 | 1.82 [0.49;6.77] | 0.36 | |
| TAPSE (mm) > 17.5 | 8.91 [2.42;32.81] | 0.001 | |
| LVEF (%) | 1.0 [0.89;1.11] | 0.83 | |
| Sex (female) | 6.21 [0.97;39.63] | 0.05 |
| Odds Ratio [CI 95%] | p-Value | Log Likelihood = −33 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Biomarkers | |||
| ΔeGFR (ml/min/1.73 m2) | 1.06 [1.01;1.11] | 0.01 | |
| E/e’ ≤ 15.5 | 1.41 [0.35;6.34] | 0.62 | |
| TAPSE (mm) > 17.5 | 16.06 [3.84;67.09] | <0.001 | |
| LVEF (%) | 0.96 [0.85;1.09] | 0.56 | |
| Sex (female) | 5.91 [1.08;32.34] | 0.04 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Beltrami, M.; Galluzzo, A.; Bonacchi, G.; Checchi, L.; Ricciardi, G.; Perrotta, L.; Garofalo, M.; Paoletti Perini, A.; Mattesini, A.; Pieragnoli, P.; et al. Combination Between Biomarkers and Echocardiographic Data for Prediction of Left Ventricular Reverse Remodelling in Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3496. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103496
Beltrami M, Galluzzo A, Bonacchi G, Checchi L, Ricciardi G, Perrotta L, Garofalo M, Paoletti Perini A, Mattesini A, Pieragnoli P, et al. Combination Between Biomarkers and Echocardiographic Data for Prediction of Left Ventricular Reverse Remodelling in Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(10):3496. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103496
Chicago/Turabian StyleBeltrami, Matteo, Alessandro Galluzzo, Giacomo Bonacchi, Luca Checchi, Giuseppe Ricciardi, Laura Perrotta, Manuel Garofalo, Alessandro Paoletti Perini, Alessio Mattesini, Paolo Pieragnoli, and et al. 2025. "Combination Between Biomarkers and Echocardiographic Data for Prediction of Left Ventricular Reverse Remodelling in Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 10: 3496. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103496
APA StyleBeltrami, M., Galluzzo, A., Bonacchi, G., Checchi, L., Ricciardi, G., Perrotta, L., Garofalo, M., Paoletti Perini, A., Mattesini, A., Pieragnoli, P., & Palazzuoli, A. (2025). Combination Between Biomarkers and Echocardiographic Data for Prediction of Left Ventricular Reverse Remodelling in Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(10), 3496. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103496






