Transfusion Thresholds and Neurological Functional Outcome After Acute Brain Injury: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.3. Intervention
2.4. Outcome Measures
2.5. Data Sources
2.6. Data Collection and Analysis
2.7. Subgroup Analysis
2.8. Risk-of-Bias Assessment
2.9. Statistical Analysis
2.10. Sensitivity Analyses
3. Results
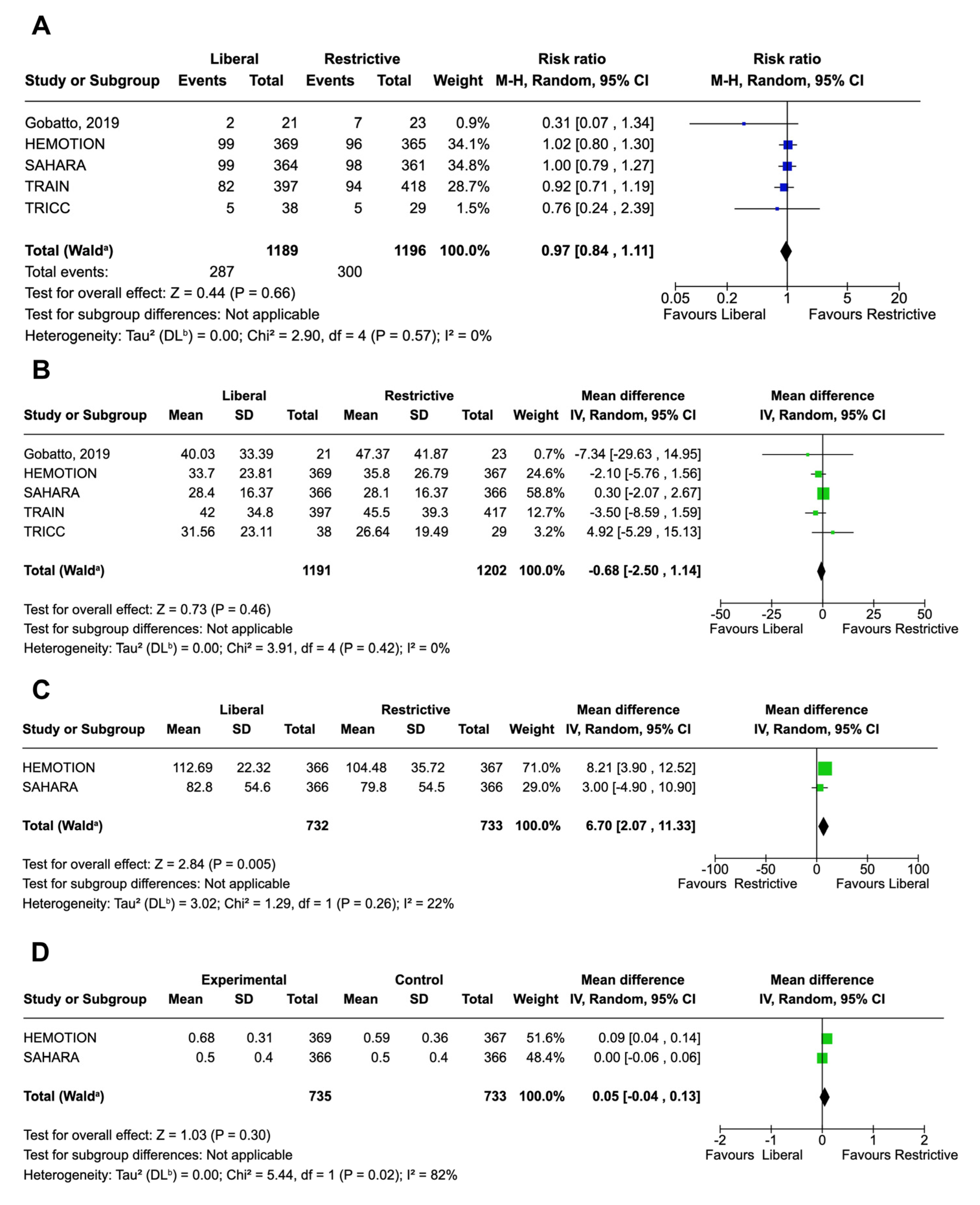
3.1. Primary Outcome
3.2. Sensitivity Analyses of the Primary Outcome
3.3. Subgroup Analyses of the Primary Outcome
3.4. Secondary Outcomes
3.5. Safety Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABI | acute brain injury |
| EQ-5D-5L | EuroQol Five-Dimension, Five-Level Instrument |
| FIM | functional independence measure |
| GOS | Glasgow Outcome Scale |
| GOS-E | Glasgow Outcome Scale-Extended |
| GRADE | Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation framework |
| ICH | intracerebral hemorrhage |
| ICU | intensive care unit |
| IQR | interquartile range |
| LOS | length of stay |
| MD | mean difference |
| NCC | neurocritical care |
| QOL | quality of life |
| RCT | randomized control trial |
| ROB | risk of bias |
| SAH | subarachnoid hemorrhage |
| SD | standard deviation |
| TBI | traumatic brain injury |
References
- Lelubre, C.; Bouzat, P.; Crippa, I.A.; Taccone, F.S. Anemia management after acute brain injury. Crit. Care 2016, 20, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrett, L.A.; McIntyre, L.; Turgeon, A.F.; English, S.W. Anemia and Red Blood Cell Transfusion in Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Neurocrit. Care 2023, 39, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, D.H.; Raines, D.A. The Risks Associated with Red Blood Cell Transfusion: Implications for Critical Care Practice. Crit. Care Nurs. Clin. N. Am. 2017, 29, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, E.Y.; Barrie, U.; Kenfack, Y.J.; Edukugho, D.; Caruso, J.P.; Rail, B.; Hicks, W.H.; Oduguwa, E.; Pernik, M.N.; Tao, J.; et al. Transfusion Guidelines in Traumatic Brain Injury: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Currently Available Evidence. Neurotrauma Rep. 2022, 3, 554–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, C.S.; Hannay, H.J.; Yamal, J.-M.; Gopinath, S.; Goodman, J.C.; Tilley, B.C.; Baldwin, A.; Lara, L.R.; Saucedo-Crespo, H.; the Epo Severe TBI Trial Investigators; et al. Effect of Erythropoietin and Transfusion Threshold on Neurological Recovery After Traumatic Brain Injury: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2014, 312, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gobatto, A.L.N.; Link, M.A.; Solla, D.J.; Bassi, E.; Tierno, P.F.; Paiva, W.; Taccone, F.S.; Malbouisson, L.M. Transfusion requirements after head trauma: A randomized feasibility controlled trial. Crit. Care 2019, 23, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taccone, F.S.; Rynkowski, C.B.; Møller, K.; Lormans, P.; Quintana-Díaz, M.; Caricato, A.; Ferreira, M.A.C.; Badenes, R.; Kurtz, P.; Søndergaard, C.B.; et al. Restrictive vs Liberal Transfusion Strategy in Patients with Acute Brain Injury: The TRAIN Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2024, 332, 1623–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turgeon, A.F.; Fergusson, D.A.; Clayton, L.; Patton, M.-P.; Neveu, X.; Walsh, T.S.; Docherty, A.; Malbouisson, L.M.; Pili-Floury, S.; English, S.W.; et al. Liberal or Restrictive Transfusion Strategy in Patients with Traumatic Brain Injury. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 391, 722–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- English, S.W.; Delaney, A.; Fergusson, D.A.; Chassé, M.; Turgeon, A.F.; Lauzier, F.; Tuttle, A.; Sadan, O.; Griesdale, D.E.; Redekop, G.; et al. Liberal or Restrictive Transfusion Strategy in Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 392, 1079–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutin, A.; Chassé, M.; Shemilt, M.; Lauzier, F.; Moore, L.; Zarychanski, R.; Griesdale, D.; Desjardins, P.; Lacroix, J.; Fergusson, D.; et al. Red Blood Cell Transfusion in Patients with Traumatic Brain Injury: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Transfus. Med. Rev. 2016, 30, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florez-Perdomo, W.A.; García-Ballestas, E.; Martinez-Perez, R.; Agrawal, A.; Deora, H.; Joaquim, A.F.; Quiñones-Ossa, G.A.; Moscote-Salazar, L.R. Hemoglobin levels as a transfusion criterion in moderate to severe traumatic brain injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Neurosurg. 2021, 37, 1473–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Fu, Y.; Li, W.; Sun, T.; Cheng, C.; Chong, Y.; Han, R.; Cui, W. Red blood cell transfusion in neurocritical patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Anesthesiol. 2024, 24, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, X.; Zhang, S.; Wan, J.; Chen, C.; Wang, P.; Fan, S.; Liu, Y.; Yang, J.; Hou, J.; You, Q.; et al. Efficacy of restrictive versus liberal transfusion strategies in patients with traumatic brain injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Ann. Intensiv. Care 2024, 14, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Wan, X.; Liu, J.; Tong, T. Optimally estimating the sample mean from the sample size, median, mid-range, and/or mid-quartile range. Stat. Methods Med. Res. 2018, 27, 1785–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Luo, D.; Weng, H.; Zeng, X.; Lin, L.; Chu, H.; Tong, T. Optimally estimating the sample standard deviation from the five-number summary. Res. Synth. Methods 2020, 11, 641–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouzzani, M.; Hammady, H.; Fedorowicz, Z.; Elmagarmid, A. Rayyan—A web and mobile app for systematic reviews. Syst. Rev. 2016, 5, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterne, J.A.C.; Savović, J.; Page, M.J.; Elbers, R.G.; Blencowe, N.S.; Boutron, I.; Cates, C.J.; Cheng, H.Y.; Corbett, M.S.; Eldridge, S.M.; et al. RoB 2: A revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 2019, 366, l4898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moro, P.; Lattanzi, S.; Beier, C.P.; Di Bonaventura, C.; Irelli, E.C. Cognitive behavioral therapy in adults with functional seizures: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Epilepsy Behav. 2024, 159, 109981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Review Manager (RevMan) [Computer Program], Version 7.2.0; The Cochrane Collaboration: London, UK, 2024. Available online: https://revman.cochrane.org/info/trial (accessed on 8 May 2025).
- Guyatt, G.H.; Oxman, A.D.; Vist, G.E.; Kunz, R.; Falck-Ytter, Y.; Alonso-Coello, P.; Schünemann, H.J. GRADE: An emerging consensus on rating quality of evidence and strength of recommendations. BMJ 2008, 336, 924–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntyre, L.A.; Fergusson, D.A.; Hutchison, J.S.; Pagliarello, G.; Marshall, J.C.; Yetisir, E.; Hare, G.M.T.; Hébert, P.C.; Canadian Critical Care Trials Group. Effect of a Liberal Versus Restrictive Transfusion Strategy on Mortality in Patients with Moderate to Severe Head Injury. Neurocrit. Care 2006, 5, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hébert, P.C.; Wells, G.; Blajchman, M.A.; Marshall, J.; Martin, C.; Pagliarello, G.; Tweeddale, M.; Schweitzer, I.; Yetisir, E. A multicenter, randomized, controlled clinical trial of transfusion requirements in critical care. Transfusion Requirements in Critical Care Investigators, Canadian Critical Care Trials Group. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 340, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- English, S.W.; McIntyre, L. Is hemoglobin good for cerebral oxygenation and clinical outcome in acute brain injury? Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2018, 24, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prisco, L.; Iscra, F.; Ganau, M.; Berlot, G. Early predictive factors on mortality in head injured patients: A retrospective analysis of 112 traumatic brain injured patients. J. Neurosurg. Sci. 2012, 56, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mamman, R.; Grewal, J.; Garrone, J.N.; Schmidt, J. Biopsychosocial factors of quality of life in individuals with moderate to severe traumatic brain injury: A scoping review. Qual. Life Res. 2024, 33, 877–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonesson, B.; Kronvall, E.; Säveland, H.; Brandt, L.; Nilsson, O.G. Long-term reintegration and quality of life in patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage and a good neurological outcome: Findings after more than 20 years. J. Neurosurg. 2018, 128, 785–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.B.; Wilson, L.D.; Bregman, J.A.; Leath, T.C.; Humble, S.S.; Davidson, M.A.; de Riesthal, M.R.; Guillamondegui, O.D. Neurologic Functional and Quality of Life Outcomes after TBI: Clinic Attendees versus Non-Attendees. J. Neurotrauma 2015, 32, 984–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmrich, I.R.A.R.; van Klaveren, D.; Andelic, N.; Lingsma, H.; Maas, A.; Menon, D.; Polinder, S.; Røe, C.; Steyerberg, E.W.; Van Veen, E.; et al. Discrepancy between disability and reported well-being after traumatic brain injury. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2022, 93, 785–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Dong, Y.; Liao, P.; Yin, X.; He, J.; Guo, L. Prognostic value of hemoglobin in patients with sepsis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Heart Lung 2023, 64, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Su, Y.; Luo, J.; Ding, N. Association between admission hemoglobin level and prognosis in sepsis patients based on a critical care database. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 5212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, D.; Peng, M. Early Hemoglobin Status as a Predictor of Long-Term Mortality for Sepsis Patients in Intensive Care Units. Shock 2021, 55, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristof, K.; Büttner, B.; Grimm, A.; Mewes, C.; Schmack, B.; Popov, A.F.; Ghadimi, M.; Beissbarth, T.; Hinz, J.; Bergmann, I.; et al. Anaemia requiring red blood cell transfusion is associated with unfavourable 90-day survival in surgical patients with sepsis. BMC Res. Notes 2018, 11, 879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaastra, B.; Ren, D.; Alexander, S.; Awad, I.A.; Blackburn, S.; Doré, S.; Hanley, D.; Nyquist, P.; Bulters, D.; Galea, I. Evidence-based interconversion of the Glasgow Outcome a.nd modified Rankin scales: Pitfalls and best practices. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2022, 31, 106845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Study | Restrictive(R) Threshold | Liberal (L) Threshold | Unfavorable Neurological Outcome (Definition) | FU, mo | Patients n°R/L | Male, % R/L | Age †, y R/L | GCS † at Admission R/L | Injury Severity Score at Admission † R/L | Hb † at Admission R/L | Time Injury to Randomization | Patients Transfused Before Randomization R/L | Surgical or Interventional Radiological Procedure R/L |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gobatto 2019 [6] | <7 g/dL | <9 g/dL | GOS ≤3 | 6 | 23/21 | 87/95 | 36/33 | 5/4 | 31/28 | 12.5/12 | 65/75 § | 15/9 | 19/21 |
| TRAIN 2024 [7] | ≤7 g/dL | ≤9 g/dL | GOS-E ≤5 | 6 | 423/397 | 53.4/54.9 | 51/52 | 6/7 | NA | 11.9/11.8 | NA | NA | 135/110 |
| HEMOTION 2024 [8] | ≤7 g/dL | ≤10 g/dL | GOS-E ≤4 | 6 | 367/369 | 69.5/75.9 | 48.4/48.9 | 4/4 | 32/30 | 13.1/13.3 | 56/55 § | 67/57 | 226/255 |
| TRICC 1999 [22] | <7 g/dL | <10 g/dL | NA | 2 | 29/38 | 90/74 | 41.7/39.8 | 7.3/7.5 | 29.8/31.3 | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| SAHARA 2024 [9] | ≤8 g/dL | ≤10 g/dL | mRS ≥4 | 12 | 366/366 | 18.3/18.3 | 59.5/59.3 | NA | NA | 9.3/9.4 | 3.8/3.6 ‡ | 28/40 | NA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moro, P.; Andrighetti, M.; Siconolfi, G.; Borioni, M.S.; Di Bonaventura, C.; Toni, D.; Cerulli Irelli, E. Transfusion Thresholds and Neurological Functional Outcome After Acute Brain Injury: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3487. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103487
Moro P, Andrighetti M, Siconolfi G, Borioni MS, Di Bonaventura C, Toni D, Cerulli Irelli E. Transfusion Thresholds and Neurological Functional Outcome After Acute Brain Injury: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(10):3487. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103487
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoro, Pierludovico, Marco Andrighetti, Giovanni Siconolfi, Maria Sole Borioni, Carlo Di Bonaventura, Danilo Toni, and Emanuele Cerulli Irelli. 2025. "Transfusion Thresholds and Neurological Functional Outcome After Acute Brain Injury: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 10: 3487. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103487
APA StyleMoro, P., Andrighetti, M., Siconolfi, G., Borioni, M. S., Di Bonaventura, C., Toni, D., & Cerulli Irelli, E. (2025). Transfusion Thresholds and Neurological Functional Outcome After Acute Brain Injury: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(10), 3487. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103487





