Perspective on Renal Involvement in Antiphospholipid Syndrome: Implications for Diagnosis, Pathogenesis, and Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Epidemiology of Renal Involvement in APS
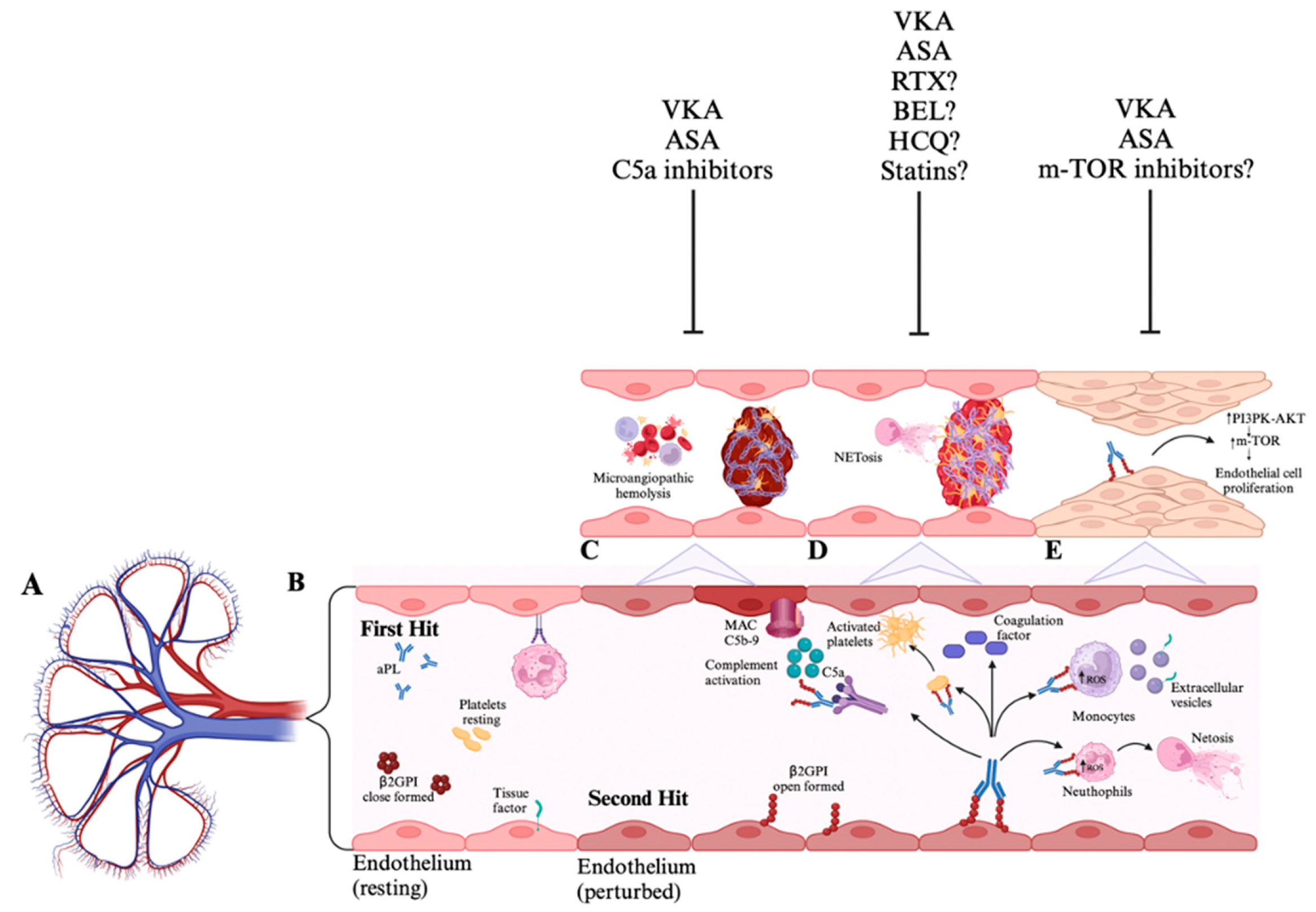
3. Pathophysiology of Renal Involvement in APS
4. Kidney Involvement in APS
4.1. Macrovascular Involvement
4.1.1. Renal Arterial Stenosis
4.1.2. Renal Vein Thrombosis
4.2. Microvascular Involvement
4.2.1. APL-Nephropathy
4.2.2. Glomerular Lesions
5. Renal Transplantation in APS
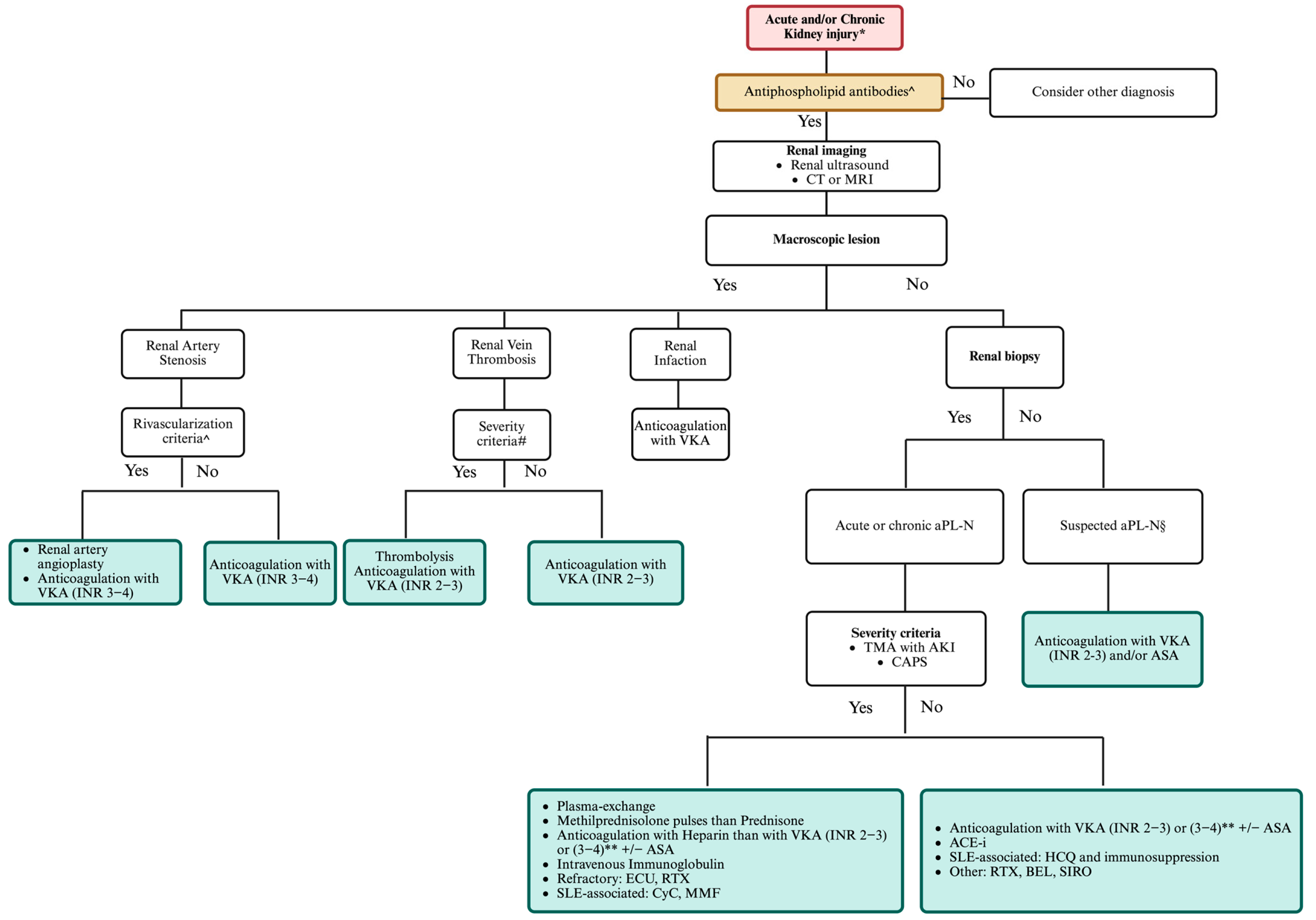
6. Management of Renal Involvement in APS
7. Unmet Needs and Future Strategies in Antiphospholipid Antibody Nephropathy
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barbhaiya, M.; Zuily, S.; Naden, R.; Hendry, A.; Manneville, F.; Amigo, M.C.; Amoura, Z.; Andrade, D.; Andreoli, L.; Artim-Esen, B.; et al. 2023 ACR/EULAR antiphospholipid syndrome classification criteria. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2023, 82, 1258–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knight, J.S.; Branch, D.W.; Ortel, T.L. Antiphospholipid syndrome: Advances in diagnosis, pathogenesis, and management. BMJ 2023, 380, e069717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, K.; Sciascia, S.; de Groot, P.G.; Devreese, K.; Jacobsen, S.; Ruiz-Irastorza, G.; Salmon, J.E.; Shoenfeld, Y.; Shovman, O.; Hunt, B.J. Antiphospholipid syndrome. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2018, 11, 17103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyakis, S.; Lockshin, M.D.; Atsumi, T.; Branch, D.W.; Brey, R.L.; Cervera, R.; Derksen, R.H.; DEGroot, P.G.; Koike, T.; Meroni, P.L.; et al. International consensus statement on an update of the classification criteria for definite antiphospholipid syndrome (APS). J. Thromb. Haemost. 2006, 4, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asherson, R.A. The catastrophic antiphospholipid (Asherson’s) syndrome. Autoimmun. Rev. 2006, 6, 64–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pengo, V.; Ruffatti, A.; Legnani, C.; Gresele, P.; Barcellona, D.; Erba, N.; Testa, S.; Marongiu, F.; Bison, E.; Denas, G.; et al. Clinical course of high-risk patients diagnosed with antiphospholipid syndrome. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2010, 8, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoxha, A.; Perin, N.; Lovisotto, M.; Calligaro, A.; Del Ross, T.; Favaro, M.; Tonello, M.; Doria, A.; Simioni, P. Risk factors for damage accrual in primary antiphospholipid syndrome: A retrospective single-center cohort study. J. Autoimmun. 2024, 144, 103180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoxha, A.; Lovisotto, M.; Perin, N.; Nalesso, F.; Del Prete, D.; Simioni, P. Antiphospholipid antibodies nephropathy is associated with an increased risk of kidney failure: A systematic literature review and meta-analysis. Clin. Kidney. J. 2024, 17, sfae302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheen, M.; Adedjouma, A.; Esteve, E.; Buob, D.; Abisror, N.; Planche, V.; Fain, O.; Boffa, J.J.; De Seigneux, S.; Mekinian, A.; et al. Kidney disease in antiphospholipid antibody syndrome: Risk factors, pathophysiology and management. Autoimmun. Rev. 2022, 21, 103072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvariño, R.; Sant, F.; Espinosa GPons-Estel, G.; Solé, M.; Cervera, R.; Arrizabalaga, P. Nephropathy associated with antiphospholipid antibodies in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 2011, 20, 721–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruffatti, A.; Tonello, M.; Calligaro, A.; Del Ross, T.; Favaro, M.; Zen, M.; Hoxha, A.; Alaibac, M. Prevalence and adverse consequences of delayed diagnosis and misdiagnosis in thrombotic antiphospholipid syndrome. An observational cohort study and a review of the literature. Clin. Rheumatol. 2023, 42, 3007–3019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cervera, R.; Piette, J.-C.; Font, J.; Khamashta, M.A.; Shoenfeld, Y.; Camps, M.T.; Jacobsen, S.; Lakos, G.; Tincani, A.; Kontopoulou-Griva, I.; et al. Antiphospholipid syndrome: Clinical and immunologic manifestations and patterns of disease expression in a cohort of 1,000 patients: Clinical and immunologic manifestations of APS. Arthritis. Rheum. 2002, 46, 1019–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinico, R.A.; Cavazzana, I.; Nuzzo MVianelli, M.; Napodano, P.; Scaini, P.; Tincani, A. Renal involvement in primary antiphospholipid syndrome: Retrospective analysis of 160 patients. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 5, 1211–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sciascia, S.; Yazdany, J.; Moroni, G.; Becker, J.U.; Seshan, S.V.; Andrade, D.; Emmi, G.; Cuadrado, M.J.; Radin, M.; Cecchi, I.; et al. Clinical-pathological characteristics of renal injuries identify different clusters in patients with antiphospholipid antibodies. Kidney. Int. Rep. 2023, 8, 754–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervera, R.; Bucciarelli, S.; Plasín, M.A.; Gómez-Puerta, J.A.; Plaza, J.; Pons-Estel, G.; Shoenfeld, Y.; Ingelmo, M.; Espinos, G.; Catastrophic Antiphospholipid Syndrome (CAPS) Registry Project Group (European Forum On Antiphospholipid Antibodies). Catastrophic antiphospholipid syndrome (CAPS): Descriptive analysis of a series of 280 patients from the “CAPSregistry”. J. Autoimmun. 2009, 32, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller-Calleja, N.; Hollerbach, A.; Ritter, S.; Pedrosa, D.G.; Strand, D.; Graf, C.; Reinhardt, C.; Strand, S.; Poncelet, P.; Griffin, J.H.; et al. Tissue factor pathway inhibitor primes monocytes for antiphospholipid antibody-induced thrombosis. Blood 2019, 134, 1119–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romay-Penabad, Z.; Aguilar-Valenzuela, R.; Urbanus, R.T.; Derksen, R.H.; Pennings, M.T.; Papalardo, E.; Shilagard, T.; Vargas, G.; Hwang, Y.; de Groot, P.G.; et al. Apolipoprotein E receptor 2 is involved in the thrombotic complications in a murine model of the antiphospholipid syndrome. Blood 2011, 117, 1408–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritis, K.; Doumas, M.; Mastellos, D.; Micheli, A.; Giaglis, S.; Magotti, P.; Rafail, S.; Kartalis, G.; Sideras, P.; Lambris, J.D. A novel C5a receptor-tissue factor cross-talk in neutrophils links innate immunity to coagulation pathways. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 4794–4802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierangeli, S.S.; Girardi, G.; Vega-Ostertag, M.; Liu, X.; Espinola, R.G.; Salmon, J. Requirement of activation of complement C3 and C5 for antiphospholipid antibody-mediated thrombophilia. Arthritis. Rheum. 2005, 52, 2120–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romay-Penabad, Z.; Liu, X.X.; Montiel-Manzano, G.; Papalardo De Martínez, E.; Pierangeli, S.S. C5a receptor-deficient mice are protected from thrombophilia and endothelial cell activation induced by some antiphospholipid antibodies. Ann. New York Acad. Sci. 2007, 1108, 554–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, S.; Braunstein, E.M.; Yuan, X.; Yu, J.; Alexander, A.; Chen, H.; Gavriilaki, E.; Alluri, R.; Streiff, M.B.; Petri, M.; et al. Complement activity and complement regulatory gene mutations are associated with thrombosis in APS and CAPS. Blood 2020, 135, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seshan, S.V.; Franzke, C.W.; Redecha, P.; Monestier, M.; Mackman, N.; Girardi, G. Role of tissue factor in a mouse model of thrombotic microangiopathy induced by antiphospholipid antibodies. Blood 2009, 114, 1675–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nangaku, M.; Alpers, C.E.; Pippin, J.; Shankland, S.J.; Kurokawa, K.; Adler, S.; Morgan, B.P.; Johnson, R.J.; Couser, W.G. CD59 protects glomerular endothelial cells from immune-mediated thrombotic microangiopathy in rats. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1998, 9, 590–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chua, J.S.; Baelde, H.J.; Zandbergen, M.; Wilhelmus, S.; van Es, L.A.; de Fijter, J.W.; Bruijn, J.A.; Bajema, I.M.; Cohen, D. Complement Factor C4d Is a Common Denominator in Thrombotic Microangiopathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 26, 2239–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Chen, X.W.; Sun, C.Y.; Dai, M.; Yan, Y.C.; Yang, C.D. Association between anti-beta2 glycoprotein I antibodies and renal glomerular C4d deposition in lupus nephritis patients with glomerular microthrombosis: A prospective study of 155 cases. Lupus 2010, 19, 1195–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canaud, G.; Bienaimé, F.; Tabarin, F.; Bataillon, G.; Seilhean, D.; Noël, L.H.; Dragon-Durey, M.A.; Snanoudj, R.; Friedlander, G.; Halbwachs-Mecarelli, L.; et al. Inhibition of the mTORC pathway in the antiphospholipid syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, W.A.; Gharavi, A.E.; Koike, T.; Lockshin, M.D.; Branch, D.W.; Piette, J.C.; Brey, R.; Derksen, R.; Harris, E.N.; Hughes, G.R.; et al. International consensus statement on preliminary classification criteria for definite antiphospholipid syndrome: Report of an international workshop. Arthritis. Rheum. 1999, 42, 1309–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostuni, P.A.; Lazzarin, P.; Pengo, V.; Ruffatti, A.; Schiavon, F.; Gambari, P. Renal-artery thrombosis and hypertension in a 13-year-old girl with antiphospholipid syndrome. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1990, 49, 184–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tektonidou, M.G. Antiphospholipid Syndrome Nephropathy: From Pathogenesis to Treatment. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amigo, M.C.; Garcia-Torres, R.; Robles, M.; Bochicchio, T.; Reyes, P.A. Renal involvement in primary antiphospholipid syndrome. J. Rheumatol. 1992, 19, 1181–1185. [Google Scholar]
- Ames, P.R.; Cianciaruso, B.; Bellizzi, V.; Balletta, M.; Lubrano, E.; Scarpa, R.; Brancaccio, V. Bilateral renal artery occlusion in a patient with primary antiphospholipid antibody syndrome: Thrombosis, vasculitis or both? J. Rheumatol. 1992, 19, 1802–1806. [Google Scholar]
- Sangle, S.R.; D’Cruz, D.P.; Jan, W.; Karim, M.Y.; Khamashta, M.A.; Abbs, I.C.; Hughes, G.R. Renal artery stenosis in the antiphospholipid (Hughes) syndrome and hypertension. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2003, 62, 999–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, W.C.; Bardelli, M.; Yevzlin, A.S. Imaging for renovascular disease. Semin. Nephrol. 2011, 31, 272–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girometti, R.; Stocca, T.; Serena, E.; Granata, A.; Bertolotto, M. Impact of contrast-enhanced ultrasound in patients with renal function impairment. World J. Radiol. 2017, 9, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, W.S.; Lim, P.S.; Sung, Y.P. Renal vein thrombosis as first clinical manifestation of the primary antiphospholipid syndrome. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 1995, 10, 1929–1931. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Morgan, R.J.; Feneley, R.C. Renal vein thrombosis caused by primary antiphospholipid syndrome. Br. J. Urol. 1994, 74, 807–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaturvedi, S.; Brandao, L.; Geary, D.; Licht, C. Primary antiphospholipid syndrome presenting as renal vein thrombosis and membranous nephropathy. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2011, 26, 979–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, C.S.; d Oliveira, I.; Bacchiega, A.B.S.; Klumb, E.M.; Albuquerque, E.M.; Souza, E.; Suassuna, J.H.; Ribeiro, F.M. Renal transplantation in lupus nephritis: A Brazilian cohort. Lupus 2012, 21, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glazer, G.; Francis, I.; Gross, B.; Amendola MGlazer, G.M.; Francis, I.R.; Gross, B.H.; Amendola, M.A. Computed tomography of renal vein thrombosis. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 1984, 8, 288–293. [Google Scholar]
- Nochy, D.; Daugas, E.; Droz, D.; Beaufils, H.; Grünfeld, J.P.; Piette, J.C.; Bariety, J.; Hill, G. The intrarenal vascular lesions associated with primary antiphospholipid syndrome. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1999, 10, 507–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tektonidou, M.G.; Sotsiou, F.; Moutsopoulos, H.M. Antiphospholipid Syndrome (APS) nephropathy in catastrophic, primary and systemic lupus erythematosus-related APS. J. Rheumatol. 2008, 35, 1983–1988. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Daugas, E.; Nochy, D.; Huong, D.L.T.; Duhaut, P.; Beaufils, H.; Caudwell, V.; Bariety, J.; Piette, J.C.; Hill, G. Antiphospholipid syndrome nephropathy in systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2002, 13, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tektonidou, M.G.; Sotsiou, F.; Nakopoulou, L.; Vlachoyiannopoulos, P.G.; Moutsopoulos, H.M. Antiphospholipid syndrome nephropathy in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and antiphospholipid antibodies: Prevalence, clinical associations, and long-term outcome. Arthritis. Rheum. 2004, 50, 2569–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejìa-Vilet, J.M.; Córdova-Sánchez, B.M.; Uribe-Uribe, N.O.; Correa-Rotter, R.; Morales-Buenrostro, L.E. Prognostic significance of renal vascular pathology in lupus nephritis. Lupus 2017, 26, 1042–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strufaldi, F.L.; Menezes Neves, P.D.M.M.; Dias, C.B.; Dias, C.B.; Yu, L.; Woronik, V.; Cavalcante, L.B.; Malheiros, D.M.A.C.; Jorge, L.B. Renal thrombotic microangiopathy associated to worse renal prognosis in Lupus Nephritis. J. Nephrol. 2021, 34, 1147–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moroni, G.; Ventura, D.; Riva, P.; Panzeri, P.; Quaglini, S.; Banfi, G.; Simonini, P.; Bader, R.; Meroni, P.L.; Ponticelli, C. Antiphospholipid antibodies are associated with an increased risk for chronic renal insufficiency in patients with lupus nephritis. Am. J. Kidney. Dis. 2004, 43, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbhaiya, M.; Taghavi, M.; Zuily, S.; Domingues, V.; Chock, E.Y.; Tektonidou, M.G.; Erkan, D.; Seshan, S.V.; New APS Classification Criteria Steering Committee and APS ACTION Collaborators. Efforts to Better Characterize “Antiphospholipid Antibody Nephropathy” for the 2023 ACR/EULAR Antiphospholipid Syndrome Classification Criteria: Renal Pathology Subcommittee Report. J. Rheumatol. 2024, 51, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, P.; Yuan, G.; Li, S.; Peng, Y.; Xu, C.; Benkert, T.; Hu, D.; Han, M.; Li, Z. Noninvasive Assessment of the Renal Function, Oxford Classification and Prognostic Risk Stratification of IgAN by Using Intravoxel Incoherent Motion Diffusion-Weighted Imaging and Blood Oxygenation Level-Dependent MRI. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2023, 58, 879–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhouri, F.; Noël, L.H.; Zuber, J.; Beaufils, H.; Martinez, F.; Lebon, P.; Papo, T.; Chauveau, D.; Bletry, O.; Grünfeld, J.P.; et al. The expanding spectrum of renal diseases associated with antiphospholipid syndrome. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2003, 41, 1205–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, J.H.; Amend, W.J.C.; Criswell, L.A. Antiphospholipid antibody syndrome in renal transplantation: Occurrence of clinical events in 96 consecutive patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 1999, 34, 1040–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canaud, G.; Bienaimé, F.; Noël, L.H.; Royal, V.; Alyanakian, M.A.; Dautzenberg, M.D.; Rabant, M.; Posson, J.; Thervet, E.; Anglicheau, D.; et al. Severe vascular lesions and poor functional outcome in kidney transplant recipients with lupus anticoagulant antibodies. Am. J. Transplant. 2010, 10, 2051–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gauthier, M.; Canoui-Poitrine, F.; Guéry, E.; Desvaux, D.; Hue, S.; Canaud, G.; Stehle, T.; Lang, P.; Kofman, T.; Grimbert, P.; et al. Anti-cardiolipin antibodies and 12-month graft function in kidney transplant recipients: A prognosis cohort survey. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2018, 33, 709–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaidya, S. Ten-yr renal allograft survival of patients with antiphospholipid antibody syndrome. Clin. Transpl. 2012, 26, 853–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagenknecht, D.R.; Fastenau, D.R.; Torry, R.J.; Carter, C.B.; Haag, B.W.; McIntyre, J.A. Antiphospholipid antibodies are a risk factor for early renal allograft failure: Isolation of antiphospholipid antibodies from a thrombosed renal allograft. Transplant. Proc. 1999, 31, 285–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furmańczyk-Zawiska, A.; Bułło-Piontecka, B.; Komorniczak, M.; Dębska-Ślizień, A.; Augustyniak-Bartosik, H.; Durlik, M. Antiphospholipid Syndrome in Renal Allograft Recipients-A Long-Term Multicenter Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, M.; Martínez-Flores, J.A.; Pérez, D.; García, F.; Cabrera-Marante, O.; Pleguezuelo, D.; Paz-Artal, E.; Morales, J.M.; González, E.; Serrano, A. β2-Glycoprotein I/IgA Immune Complexes: A Marker to Predict Thrombosis After Renal Transplantation in Patients With Antiphospholipid Antibodies. Circulation 2017, 135, 1922–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoxha, A.; Ruffatti, A.; Mattia, E.; Meneghel, L.; Tonello, M.; Salvan, E.; Pengo, V.; Punzi, L. Relationship between antiphosphatidylserine/prothrombin and conventional antiphospholipid antibodies in primary antiphospholipid syndrome. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2015, 53, 1265–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoxha, A.; Ruffatti, A.; Tonello, M.; Bontadi, A.; Salvan, E.; Banzato, A.; Pengo, V.; Punzi, L. Antiphosphatidylserine/prothrombin antibodies in primary antiphospholipid syndrome. Lupus 2012, 21, 787–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangle, S.R.; D’Cruz, D.P.; Abbs, I.C.; Khamashta, M.A.; Hughes, G.R. Renal artery stenosis in hypertensive patients with antiphospholipid (Hughes) syndrome: Outcome following anticoagulation. Rheumatology 2005, 44, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tektonidou, M.G.; Andreoli, L.; Limper, M.; Amoura, Z.; Cervera, R.; Costedoat-Chalumeau, N.; Cuadrado, M.J.; Dörner, T.; Ferrer-Oliveras, R.; Hambly, K.; et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of antiphospholipid syndrome in adults. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 1296–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tektonidou, M.G. Identification and treatment of APS renal involvement. Lupus 2014, 23, 1276–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korkmaz, C.; Kabukcuoğlu, S.; Isiksoy, S.; Yalçin, A.U. Renal involvement in primary antiphospholipid syndrome and its response to immunosuppressive therapy. Lupus 2003, 12, 760–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pengo, V.; Denas, G.; Zoppellaro, G.; Jose, S.P.; Hoxha, A.; Ruffatti, A.; Andreoli, L.; Tincani, A.; Cenci, C.; Prisco, D.; et al. Rivaroxaban vs warfarin in high-risk patients with antiphospholipid syndrome. Blood 2018, 132, 1365–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pengo, V.; Hoxha, A.; Andreoli, L.; Tincani, A.; Silvestri, E.; Prisco, D.; Fierro, T.; Gresele, P.; Cafolla, A.; De Micheli, V.; et al. Trial of Rivaroxaban in AntiPhospholipid Syndrome (TRAPS): Two-year outcomes after the study closure. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2021, 19, 531–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khairani, C.D.; Bejjani, A.; Piazza, G.; Jimenez, D.; Monreal, M.; Chatterjee, S.; Pengo, V.; Woller, S.C.; Cortes-Hernandez, J.; Connors, J.M.; et al. Direct Oral Anticoagulants vs Vitamin K Antagonists in Patients With Antiphospholipid Syndromes: Meta-Analysis of Randomized Trials. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2023, 81, 16–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kronbichler, A.; Brezina, B.; Quintana, L.F.; Jayne, D.R. Efficacy of plasma exchange and immunoadsorption in systemic lupus erythematosus and antiphospholipid syndrome: A systematic review. Autoimmun. Rev. 2016, 15, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruffatti, A.; De Silvestro, G.; Marson, P.; Tonello, M.; Calligaro, A.; Favaro, M.; Del Ross, T.; Hoxha, A.; Mattia, E.; Pengo, V. Catastrophic antiphospholipid syndrome: Lessons from 14 cases successfully treated in a single center. A narrative report. J. Autoimmun. 2018, 93, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erkan, D.; Vega, J.; Ramón, G.; Kozora, E.; Lockshin, M.D. A pilot open-label phase II trial of rituximab for non-criteria manifestations of antiphospholipid syndrome. Arthritis. Rheum. 2013, 65, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sciascia, S.; Naretto, C.; Rossi, D.; Bazzan, M.; Roccatello, D. Treatment-induced downregulation of antiphospholipid antibodies: Effect of rituximab alone on clinical and laboratory features of antiphospholipid syndrome. Lupus 2011, 20, 1106–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsagalis, G.; Psimenou, E.; Nakopoulou, L.; Laggouranis, A. Effective treatment of antiphospholipid syndrome with plasmapheresis and rituximab. Hippokratia 2010, 14, 215–216. [Google Scholar]
- Yazici, A.; Yazirli, B.; Erkan, D. Belimumab in primary antiphospholipid syndrome. Lupus 2017, 26, 1123–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sciascia, S.; Radin, M.; Cecchi, I.; Barinotti, A.; Rubini, E.; Rossi, D.; Fenoglio, R.; Vaccarino, A.; Menegatti, E.; Roccatello, D. Open-label, prospective, phase II descriptive pilot trial of belimumab therapy for refractory and/or non-criteria manifestations of antiphospholipid syndrome: Study protocol. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2022, 41, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kronbichler, A.; Frank, R.; Kirschfink, M.; Szilágyi, Á.; Csuka, D.; Prohászka, Z.; Schratzberger, P.; Lhotta, K.; Mayer, G. Efficacy of eculizumab in a patient with immunoadsorption-dependent catastrophic antiphospholipid syndrome: A case report. Medicine 2014, 93, e143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lonze, B.E.; Zachary, A.A.; Magro, C.M.; Desai, N.M.; Orandi, B.J.; Dagher, N.N.; Singer, A.L.; Carter-Monroe, N.; Nazarian, S.M.; Segev, D.L.; et al. Eculizumab prevents recurrent antiphospholipid antibody syndrome and enables successful renal transplantation. Am. J. Transplant. 2014, 14, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ávila, A.; Gavela, E.; Sancho, A. Thrombotic Microangiopathy After Kidney Transplantation: An Underdiagnosed and Potentially Reversible Entity. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 642864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciascia, S.; Radin, M.; Yazdany, J.; Tektonidou, M.; Cecchi, I.; Roccatello, D.; Dall’Era, M. Expanding the therapeutic options for renal involvement in lupus: Eculizumab, available evidence. Rheumatol. Int. 2017, 37, 1249–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Benjume, B.; Rodríguez-Pintó, I.; Amigo, M.C.; Erkan, D.; Shoenfeld, Y.; Cervera, R.; Espinosa, G.; on behalf the CAPS Registry Project Group/European Forum on Antiphospholipid Antibodies. Eculizumab use in catastrophic antiphospholipid syndrome (CAPS): Descriptive analysis from the “CAPS Registry”. Autoimmun. Rev. 2022, 21, 103055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grenn, R.C.; Yalavarthi, S.; Gandhi, A.A.; Kazzaz, N.M.; Núñez-Álvarez, C.; Hernández-Ramírez, D.; Cabral, A.R.; McCune, W.J.; Bockenstedt, P.L.; Knight, J.S. Endothelial progenitor dysfunction associates with a type I interferon signature in primary antiphospholipid syndrome. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecchi, I.; Radin, M.; Barinotti, A.; Foddai, S.G.; Menegatti, E.; Roccatello, D.; Suárez, A.; Sciascia, S.; Rodríguez-Carrio, J. Type I interferon pathway activation across the antiphospholipid syndrome spectrum: Associations with disease subsets and systemic antiphospholipid syndrome presentation. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1351446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verrou, K.M.; Sfikakis, P.P.; Tektonidou, M.G. Whole blood transcriptome identifies interferon-regulated genes as key drivers in thrombotic primary antiphospholipid syndrome. J. Autoimmun. 2023, 134, 102978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.T.; Chen, Y.S.; Chen, T.T.; Chao, Y.H.; Kung, S.P.; Chen, D.Y.; Lin, C.C. Inhibiting Tyrosine Kinase 2 Ameliorates Antiphospholipid Syndrome Nephropathy. Mediators. Inflamm. 2024, 2024, 5568822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heerspink, H.J.L.; Stef’ansson, B.V.; Correa-Rotter, R.; Chertow, G.M.; Greene, T.; Hou, F.F.; Mann, J.F.E.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Lindberg, M.; Rossing, P.; et al. Dapagliflozin in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1436–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrington, W.G.; Staplin, N.; Wanner, C.; Green, J.B.; Hauske, S.J.; Emberson, J.R.; Preiss, D.; Judge, P.; Mayne, K.J.; Ng, S.Y.A.; et al. Empagliflozin in patients with chronic kidney disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, L.H., Jr.; Ayoub, I.; Caster, D.; Choi, M.J.; Cobb, J.; Geetha, D.; Rheault, M.N.; Wadhwani, S.; Yau, T.; Whittier, W.L. KDOQI US Commentary on the 2021 KDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Glomerular Diseases. Am. J. Kidney. Dis. 2023, 82, 121–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floege, J.; Jayne, D.R.W.; Sanders, J.F.; Tesar, V.; Balk, E.M.; Gordon, C.E.; Adam, G.; Tonelli, M.A.; Cheung, M.; Earley, A.; et al. Executive summary of the KDIGO 2024 Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of ANCA-Associated Vasculitis. Kidney. Int. 2024, 105, 447–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Middeldorp, S.; Nieuwlaat, R.; Baumann Kreuziger, L.; Coppens, M.; Houghton, D.; James, A.H.; Lang, E.; Moll, S.; Myers, T.; Bhatt, M.; et al. American Society of Hematology 2023 guidelines for management of venous thromboembolism: Thrombophilia testing. Blood. Adv. 2023, 7, 7101–7138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Chen, A.; Gao, J.; Zou, M.; Du, J.; Wu, P.Y.; Zhang, J.; Mao, Y.; Song, Y.; Chen, M. Diffusion-weighted, intravoxel incoherent motion, and diffusion kurtosis tensor MR imaging in chronic kidney diseases: Correlations with histology. Magn. Reson. Imaging. 2024, 106, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sułkowska, K.; Palczewski, P.; Furmańczyk-Zawiska, A.; Perkowska-Ptasińska, A.; Wójcik, D.; Szeszkowski, W.; Durlik, M.; Gołębiowski, M.; Małkowski, P. Diffusion Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging in the Assessment of Renal Function and Parenchymal Changes in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Preliminary Study. Ann. Transplant. 2020, 25, e920232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tektonidou, M.G.; Verrou, K.M.; Gakiopoulou, H.; Manoloukos, M.; Lembessis, P.; Hatzis, P.; Sfikakis, P.P. Kidney whole-transcriptome profiling in primary antiphospholipid syndrome reveals complement, interferons and NETs-related gene expression. Rheumatology 2024, 63, 3184–3190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raschi, E.; Borghi, M.O.; Tedesco, F.; Meroni, P.L. Antiphospholipid syndrome pathogenesis in 2023: An update of new mechanisms or just a reconsideration of the old ones? Rheumatology 2024, 63, SI4–SI13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruffatti, A.; Tonello, M.; Calligaro, A.; Del Ross, T.; Favaro, M.; Zen, M.; Carletto, A.; Lotti, V.; Bertoldo, E.; Tedesco, F.; et al. High plasma C5a and C5b-9 levels during quiescent phases are associated to severe antiphospholipid syndrome subsets. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2022, 40, 2088–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruffatti, A.; Tonello, M.; Macor, P.; Calligaro, A.; Del Ross, T.; Favaro, M.; Lotti, V.; Carletto, A.; Hoxha, A.; Biasi, D. Markers of complement activation in plasma during quiescent phases in patients with catastrophic antiphospholipid syndrome. Blood 2021, 137, 2989–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazetto, B.M.; Hounkpe, B.W.; da Silva Saraiva, S.; Vieira-Damiani, G.; dos Santos, A.P.R.; Jacinto, B.C.; Vaz, C.d.O.; Mesquita, G.T.V.; Annichino-Bizzacchi, J.M.; De Paula, E.V.; et al. Association between neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) and thrombosis in antiphospholipid syndrome. Thromb. Res. 2022, 214, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Entry Criteria | ||
|---|---|---|
| ≥1 Clinical Criterion Plus ≥ 1 aPL Test | ||
| (aPL Positive Within Three Years from the Clinical Criterion) | ||
| Clinical Domain | Score | |
| Domain 1 | Venous Thromboembolism | |
| with VTE high-risk profile | 1 | |
| without VTE high-risk profile | 3 | |
| Domain 2 | Arterial Thrombosis | |
| with AT high-risk profile | 2 | |
| without AT high-risk profile | 4 | |
| Domain 3 | Microvascular | |
| Suspected * | 2 | |
| Livedo racemose | ||
| Livedoid vasculopathy | ||
| Acute/chronic aPL-N | ||
| Pulmonary hemorrhage | ||
| Established § | 5 | |
| Livedoid vasculopathy | ||
| Acute/chronic aPL-N | ||
| Pulmonary hemorrhage | ||
| Myocardial disease | ||
| Adrenal hemorrhage | ||
| Domain 4 | Obstetric | |
| ≥ 3 consecutive pre-fetal (<10 WG) and/or early fetal (<16 WG) | 1 | |
| Fetal death (≥16 WG) without PEC/PI | 1 | |
| Severe PEC or Severe PI (<34 WG) | 3 | |
| Severe PEC and Severe PI (<34 WG) | 4 | |
| Domain 5 | Cardiac Valve | |
| Thickening | 2 | |
| Vegetation | 4 | |
| Domain 6 | Hematology | |
| Thrombocytopenia (20–130 × 109/L) | 2 | |
| Laboratory Domain | ||
| Domain 7 | Lupus anticoagulant test | |
| One-time positive | 1 | |
| Persistent positive | 5 | |
| Domain 8 | Anti-cardiolipin and anti-β2-glycoprotein I ^ | |
| Moderate–high positive IgM aCL and/or anti-β2GPI | 1 | |
| Moderate positive IgG aCL and/or anti-β2GPI | 4 | |
| High positive IgG aCL or anti-β2GPI | 5 | |
| High positive IgG aCL and anti-β-2GPI | 7 | |
| aPL-N | Definition |
|---|---|
| Suspected aPL-N * | New-onset hypertension or deterioration of previously well-controlled hypertension |
| Proteinuria ≥ 0.5 g in 24 h urine specimen or protein/creatinine ratio ≥0.5 mg/mg (50 mg/mmol) | |
| Acute renal failure | |
| Glomerular microscopic hematuria | |
| Established aPL-N ^ | Acute renal vascular or glomerular thrombotic microangiopathy |
| Chronic renal vascular or glomerular lesions |
| Type of Lesion | Definition |
|---|---|
| Acute aPL-N | Fibrin thrombi in arterioles or glomeruli without inflammatory cells or immune complexes |
| Chronic aPL-N | Organized arterial or arteriolar microthrombi with or without recanalization |
| Fibrous and fibrocellular arterial or arteriolar occlusions | |
| Cortical atrophy with or without thyroidization | |
| Fibrous intimal hyperplasia | |
| Organized glomerular thrombi |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hoxha, A.; Del Prete, D.; Condonato, I.; Martino, F.K.; Lovisotto, M.; Nalesso, F.; Simioni, P. Perspective on Renal Involvement in Antiphospholipid Syndrome: Implications for Diagnosis, Pathogenesis, and Treatment. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3326. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103326
Hoxha A, Del Prete D, Condonato I, Martino FK, Lovisotto M, Nalesso F, Simioni P. Perspective on Renal Involvement in Antiphospholipid Syndrome: Implications for Diagnosis, Pathogenesis, and Treatment. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(10):3326. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103326
Chicago/Turabian StyleHoxha, Ariela, Dorella Del Prete, Irene Condonato, Francesca K. Martino, Marco Lovisotto, Federico Nalesso, and Paolo Simioni. 2025. "Perspective on Renal Involvement in Antiphospholipid Syndrome: Implications for Diagnosis, Pathogenesis, and Treatment" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 10: 3326. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103326
APA StyleHoxha, A., Del Prete, D., Condonato, I., Martino, F. K., Lovisotto, M., Nalesso, F., & Simioni, P. (2025). Perspective on Renal Involvement in Antiphospholipid Syndrome: Implications for Diagnosis, Pathogenesis, and Treatment. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(10), 3326. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14103326









