The Relationship Between Health Parameters, Body Size, Elements of Lifestyle, and Hand Grip Strength in a Group of Patients with Type 2 Diabetes, Aged 40–98, from Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design, Setting, Participants, and Questionnaire
2.2. Measurement of Handgrip Strength
2.3. Statistical Analyses
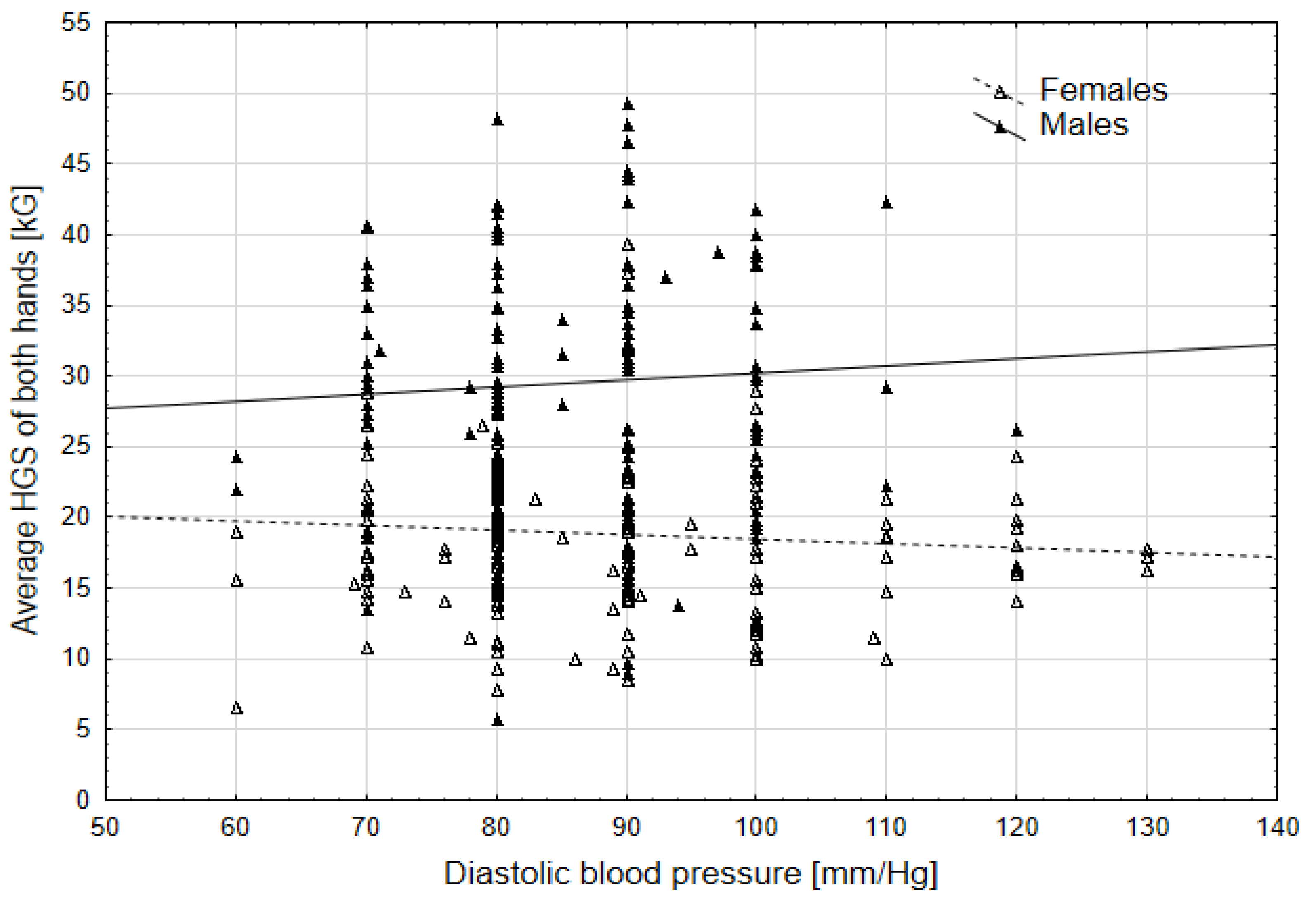
3. Results
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wild, S.; Roglic, G.; Green, A.; Sicree, R.; King, H. Global Prevalence of Diabetes: Estimates for the year 2000 and projections for 2030. Diabetes Care 2004, 27, 1047–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobson, A.M.; Braffett, B.H.; Cleary, P.A.; Gubitosi-Klug, R.A.; Larkin, M.E.; DCCT/EDIC Research Group. The Long-Term Effects of Type 1 Diabetes Treatment and Complications on Health-Related Quality of Life: A 23-year follow-up of the Diabetes Control and Complications/Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications cohort. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 3131–3138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Diabetes. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/diabetes#tab=tab_1 (accessed on 22 December 2024).
- Lewis, M.; Herron, L.M.; Chatfield, M.D.; Tan, R.C.; Dale, A.; Nash, S.; Lee, A.J. Healthy Food Prices Increased More Than the Prices of Unhealthy Options during the COVID-19 Pandemic and Concurrent Challenges to the Food System. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 3146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, R.B.; Rauber, F.; Chang, K.; da Costa Louzada, M.L.; Monteiro, C.A.; Millett, C.; Vamos, E.P. Ultra-processed food consumption and type 2 diabetes incidence: A prospective cohort study. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 3608–3614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, M.-J.; Vinke, P.C.; Navis, G.; Corpeleijn, E.; Dekker, L.H. Ultra-processed food and incident type 2 diabetes: Studying the underlying consumption patterns to unravel the health effects of this heterogeneous food category in the prospective Lifelines cohort. BMC Med. 2022, 20, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.; Usman, K.; Reddy, H.; Gutch, M.; Jain, N.; Qidwai, S. Prevalence of hand disorders in type 2 diabetes mellitus and its correlation with microvascular complications. Ann. Med. Health Sci. Res. 2013, 3, 349–354. [Google Scholar]
- Persad-Paisley, E.M.; Lee, C.; Bhatt, R.A. Understanding diabetic cheiroarthropathy: A focus on clinical presentation. J. Surg. Case Rep. 2024, 2024, rjae123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohannon, R.W.; Magasi, S.R.; Bubela, D.J.; Wang, Y.-C.; Gershon, R.C. Grip and knee extension muscle strength reflect a common construct among adults. Muscle Nerve 2012, 46, 555–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, H.J.; Yule, V.; Syddall, H.E.; Dennison, E.M.; Cooper, C.; Aihie Sayer, A. Is hand-held dynamometry useful for the measurement of quadriceps strength in older people? A comparison with the gold standard Bodex dynamometry. Gerontology 2006, 52, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, M.; Deeg, D.J.; Lips, P.; Harris, T.B.; Bouter, L.M. Skeletal muscle mass and muscle strength in relation to lower-extremity performance in older men and women. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2000, 48, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer, M.S.; Burcham, J.; Cheng, H. Diabetes mellitus is associated with an increased risk of falls in elderly residents of a long-term care facility. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2005, 60, 1157–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orlando, G.; Balducci, S.; Bazzucchi, I.; Pugliese, G.; Sacchetti, M. Neuromuscular dysfunction in type 2 diabetes: Underlying mechanisms and effect of resistance training. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2016, 32, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacDonald, T.L.; Pattamaprapanont, P.; Pathak, P.; Fernandez, N.; Freitas, E.C.; Hafida, S.; Mitri, J.; Britton, S.L.; Koch, L.G.; Lessard, S.J. Hyperglycaemia is associated with impaired muscle signalling and aerobic adaptation to exercise. Nat. Metab. 2020, 2, 902–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, R.; Pan, G.; Zheng, L.; Li, C. Handgrip strength is associated with insulin resistance and glucose metabolism in adolescents: Evidence from National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2011 to 2014. Pediatr. Diabetes 2018, 19, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grøntved, A.; Ried-Larsen, M.; Ekelund, U.; Froberg, K.; Brage, S.; Andersen, L.B. Independent and combined association of muscle strength and cardiorespiratory fitness in youth with insulin resistance and β-cell function in young adulthood: The European Youth Heart Study. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 2575–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.J.; Wittert, G.A.; Vincent, A.; Atlantis, E.; Shi, Z.; Appleton, S.L.; Hill, C.L.; Jenkins, A.J.; Januszewski, A.S.; Adams, R.J. Muscle grip strength predicts incident type 2 diabetes: Population-based cohort study. Metabolism 2016, 65, 883–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaishya, R.; Misra, A.; Vaish, A.; Ursino, N.; D’Ambrosi, R. Hand grip strength as a proposed new vital sign of health: A narrative review of evidences. J. Health Popul. Nutr. 2024, 43, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Kim, T.; Park, J.-C.; Kim, Y.H. Usefulness of hand grip strength to estimate other physical fitness parameters in older adults. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 17496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, J.; Yoo, H.J. Effects of Handgrip Strength on 10-Year Cardiovascular Risk among the Korean Middle-Aged Population: The Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2014. Healthcare 2020, 8, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayan, A.; Erkhembayar, R.; Luvsandavaajav, O.; Mukhtar, Y.; Enkhtuvshin, B.; Tumenbayar, B. Prevalence of Type 2 Diabetes in Mongolia: Results from Population-Based Survey Compared with 1999 Study. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2023, 16, 1833–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanditha, A.; Ma, R.C.; Ramachandran, A.; Snehalatha, C.; Chan, J.C.; Chia, K.S.; Shaw, J.E.; Zimmet, P.Z. Diabetes in Asia and the Pacific: Implications for the Global Epidemic. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 472–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.-K.; Woo, J.; Assantachai, P.; Auyeung, T.-W.; Chou, M.-Y.; Iijima, K.; Jang, H.C.; Kang, L.; Kim, M.; Kim, S.; et al. Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia: 2019 Consensus Update on Sarcopenia Diagnosis and Treatment. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2020, 21, 300–307.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dell Statistica (Data Analysis Software System); Dell Inc.: Round Rock, TX, USA, 2016.
- Ramalho, D.; Silva, L.; Almeida, C.; Rocha, L.; Rocha, G.; Veríssimo, R. Hand grip strength: A reliable assessment tool of frailty status on the person with type 2 diabetes mellitus | La force de prehension: Un outil d’évaluation fiable de la fragilité chez la personne atteinte de diabète de type 2. Nutr. Clin. Metab. 2023, 37, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-H.; Sung, W.-H.; Chiang, S.-L.; Lee, S.-C.; Wang, P.-C.; Wang, X.-M. Influence of aging and visual feedback on the stability of hand grip control in elderly adults. Exp. Gerontol. 2019, 119, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-H.; Chou, L.-W.; Wei, S.-H.; Lieu, F.-K.; Chiang, S.-L.; Sung, W.-H. Influence of aging on bimanual coordination control. Exp. Gerontol. 2014, 53, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carson, R.G. Get a grip: Individual variations in grip strength are a marker of brain health. Neurobiol. Aging 2018, 71, 189–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardo, A.; Kivell, T.L.; Town, K.; Donati, G.; Ballieux, H.; Stamate, C.; Edginton, T.; Forrester, G.S. Get a grip: Variation in human hand grip strength and implications for human evolution. Symmetry 2021, 13, 1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huebner, M.; Lawrence, F.; Lusa, L. Sex Differences in Age-Associated Rate of Decline in Grip Strength When Engaging in Vigorous Physical Activity. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 11009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byambaa, A.; Altankhuyag, I.; Damdinbazar, O.; Jadamba, T.; Byambasukh, O. Anthropometric and Body Circumference Determinants for Hand Grip Strength: A Population-Based Mon-Timeline Study. J. Aging Res. 2023, 2023, 6272743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khader, A.; Almashaqbeh, S. Handgrip Strength and its Association with Anthropometric Measurements at Different Anatomical Positions of Arm among Young Individuals. J. Biomim. Biomater. Biomed. Eng. 2023, 60, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wey, A.K.X.; Caszo, B.A.; Ikram, M.A.; Gnanou, J.V. Effect of hand anthropometry indices on the measurement of hand grip strength using a handheld dynamometer in young asian males. Eur. J. Phys. Educ. Sport Sci. 2023, 9, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nivethapriya, P.; Neelambikai, N.; Shanmugavadivu, R. Hand grip strength in athletes of different sports. Biomedicine 2018, 38, 36–39. [Google Scholar]
- Rajesh, M.; Adithi, H.; Prathik, P.; Panth, S.J. Statistical Study of the Influence of Anthropometric Parameters on the Hand Grip Strength of an Individual. In Intelligent Manufacturing Systems in Industry 4.0. IPDIMS 2022; Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering; Deepak, B.B.V.L., Bahubalendruni, M.V.A.R., Parhi, D.R.K., Biswal, B.B., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Li, X.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yan, J.; Jiang, J.; Liu, W.; Chen, J. Hand grip strength should be normalized by weight not height for eliminating the influence of individual differences: Findings from a cross-sectional study of 1511 healthy undergraduates. Front. Nutr. 2023, 9, 1063939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salim, S.; Rose Davy, C. Correlation of body mass index with handgrip strength and blood pressure indices among young adults. Indian J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2023, 67, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Andrade Fernandes, A.; Natali, A.J.; Vieira, B.C.; Do Valle, M.A.A.N.; Moreira, D.G.; Massy-Westropp, N.; Marins, J.C.B.M. The relationship between hand grip strength and anthropometric parameters in men. Arch. Med. Del Deport. 2014, 31, 160–164. [Google Scholar]
- Soraya, N.; Parwanto, E. The Controversial Relationship between Body Mass Index and Handgrip Strength in the Elderly: An Overview. Malays. J. Med. Sci. 2023, 30, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Gu, Y.; Wang, X.; Meng, G.; Rayamajhi, S.; Thapa, A.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, L.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, T.; et al. Association Between Handgrip Strength and Type 2 Diabetes: A Prospective Cohort Study and Systematic Review with Meta-analysis. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2023, 78, 1383–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Gu, Y.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, L.; Meng, G.; Yao, Z.; Wu, H.; Bao, X.; Chi, V.T.Q.; et al. Relationship Between Grip Strength and Prediabetes in a Large-Scale Adult Population. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2019, 56, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, C.; Merovci, A.; Tripathy, D.; Abdul-Ghani, M.; Norton, L.; Defronzo, R.A. Effects of Hyperglycemia on Skeletal Muscle Glucose Metabolism in Healthy Subjects. Diabetes 2018, 67 (Suppl. S1), 1920-P. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badu-Mensah, A.; Valinski, P.; Parsaud, H.; Hickman, J.J.; Guo, X. Hyperglycemia Negatively Affects IPSC-Derived Myoblast Proliferation and Skeletal Muscle Regeneration and Function. Cells 2022, 11, 3674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, T.; Miyatake, N.; Sakano, N.; Oda, K.; Katayama, A.; Nishii, K.; Numata, T. Relationship between cigarette smoking and muscle strength in Japanese men. J. Prev. Med. Public Health 2012, 45, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szulc, P.; Duboeuf, F.; Marchand, F.; Delmas, P.D. Hormonal and lifestyle determinants of appendicular skeletal muscle mass in men: The MINOS study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 80, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, H.; Choi, Y.E.; Kong, J.Y.; Park, J.H.; Yoo, H.J.; Byeon, J.H.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, S.H. Association of hand grip strength and cardiometabolic markers in Korean adult population: The Korea national health and nutrition examination survey 2015–2016. Korean J. Fam. Med. 2020, 41, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, C.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, R.; Wu, Q.; Zhao, Y. Handgrip strength is positively related to blood pressure and hypertension risk: Results from the National Health and nutrition examination survey. Lipids Health Dis. 2018, 17, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anjakumar, J.M.; Shashikala, L. Association between blood pressure and hand grip strength among adult population visiting a tertiary care centre—a cross-sectional study. Indian J. Appl. Res. 2023, 13, 37–41. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, M.J.; Khang, A.R.; Yi, D.; Kang, Y.H. Low relative hand grip strength is associated with a higher risk for diabetes and impaired fasting glucose among the Korean population. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0275746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.J.; Park, J.H.; Oh, Y.; Kim, H.; Kong, M.; Moon, J. Association of decreased grip strength with lower urinary tract symptoms in women: A cross-sectional study from Korea. BMC Womens Health 2021, 21, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.Y.; Rho, J.W.; Kim, E.; Kim, Y.S. Comparison of Absolute and Relative Grip Strength to Predict Incidence of Diabetes Mellitus in Korea: A Prospective Cohort Study. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 2024, 22, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Wang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Mo, Y.; Ma, X.; Hu, G.; Zhou, J. Potential modifying effect of grip strength on the association between glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) and all-cause mortality in older adults with type 2 diabetes: Evidence from UK Biobank. Chin. Med. J. 2024, 137, 1501–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Zeng, J.; Fan, M.; Chen, B.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Xu, S. Associations between handgrip strength and skeletal muscle mass with all-cause mortality and cardiovascular mortality in people with type 2 diabetes: A prospective cohort study of the UK Biobank. J. Diabetes 2024, 16, e13464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, S.; Shimoda, M.; Kimura, T.; Katakura, Y.; Sanada, J.; Fushimi, Y.; Iwamoto, Y.; Iwamoto, H.; Mune, T.; Kaku, K.; et al. The impact of grip strength, waist circumference, and body mass index on Hemoglobin A1c value: Cross-sectional study using outpatient clinical data in Japanese elderly patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2024, 24, 410–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boonpor, J.; Parra-Soto, S.; Petermann-Rocha, F.; Ferrari, G.; Welsh, P.; Pell, J.P.; Sattar, N.; Gill, J.M.; Ho, F.K.; Gray, S.R.; et al. Associations between grip strength and incident type 2 diabetes: Findings from the UK Biobank prospective cohort study. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2021, 9, e001865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Kooi, A.L.; Snijder, M.B.; Peters, R.J.; Van Valkengoed, I.G. The association of handgrip strength and type 2 diabetes mellitus in six ethnic groups: An analysis of the HELIUS study. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0137739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Males | Females | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | N | Mean | SD | N | Mean | SD | t |
| Age [years] | 139 | 58.55 | 7.96 | 208 | 60.75 | 9.45 | 2.26 * |
| High glucose [mmol/L] | 139 | 18.14 | 8.07 | 208 | 18.32 | 6.61 | ns |
| Low glucose [mmol/L] | 139 | 7.46 | 3.72 | 208 | 7.98 | 3.17 | ns |
| SBP [mm/Hg] | 139 | 133.09 | 17.07 | 208 | 134.65 | 18.68 | ns |
| DBP [mm/Hg] | 139 | 85.15 | 10.71 | 208 | 87.35 | 13.73 | ns |
| Years of diabetes | 139 | 1.98 | 0.84 | 208 | 1.79 | 0.82 | 2.06 * |
| Height [cm] | 139 | 168.96 | 6.36 | 208 | 160.65 | 5.92 | 12.43 ** |
| BMI [kg/m2] | 139 | 28.79 | 4.37 | 208 | 28.74 | 5.06 | ns |
| Height-to-waist ratio | 139 | 0.59 | 0.07 | 208 | 0.59 | 0.09 | ns |
| Variables | N | % |
|---|---|---|
| Sex | ||
| Male | 139 | 40.06 |
| Female | 208 | 59.94 |
| Current (every day) smoking | ||
| Yes | 93 | 26.80 |
| No | 254 | 73.20 |
| Average of Both Hands | Right Hand | Left Hand | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wald’s X2 | p | Wald’s X2 | p | Wald’s X2 | p | |
| Sex | 0.08 | ns | 0.03 | ns | 0.15 | ns |
| Current smoking | 6.38 | <0.05 | 5.24 | <0.05 | 3.75 | ns |
| Height | 19.60 | <0.001 | 12.19 | <0.001 | 23.57 | <0.001 |
| BMI | 0.50 | ns | 0.27 | ns | 0.66 | ns |
| Waist-to-height ratio | 2.69 | ns | 3.06 | ns | 1.89 | ns |
| DBP | 3.86 | <0.05 | 1.65 | ns | 6.06 | <0.05 |
| SBP | 8.11 | 5.26 | <0.05 | 9.68 | <0.01 | |
| High glucose | 0.40 | ns | 0.19 | ns | 0.56 | ns |
| Low glucose | 10.11 | <0.01 | 13.09 | <0.001 | 5.58 | <0.05 |
| Years of diabetes | 5.47 | <0.05 | 5.30 | <0.05 | 4.36 | <0.05 |
| Age | 8.79 | <0.05 | 6.61 | <0.05 | 8.92 | <0.01 |
| Interactions with sex | ||||||
| DBP | 4.96 | <0.05 | 1.50 | ns | 9.15 | <0.01 |
| SBP | 1.63 | ns | 0.30 | ns | 3.65 | ns |
| High glucose | 0.50 | ns | 1.14 | ns | 0.06 | ns |
| Low glucose | 0.06 | ns | 0.01 | ns | 0.30 | ns |
| Years of diabetes | 3.36 | ns | 2.42 | ns | 3.70 | ns |
| Age | 0.01 | ns | 0.00 | ns | 0.02 | ns |
| Current smoking | 0.01 | ns | 0.19 | ns | 0.39 | ns |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jaalkhorol, M.; Cieślik, A.; Dashtseren, M.; Khairat, A.; Damdinbazar, O.; Ochirdorj, G.; Khurelbaatar, T.; Batmunkh, G.; Ganzorig, U.; Kozieł, S. The Relationship Between Health Parameters, Body Size, Elements of Lifestyle, and Hand Grip Strength in a Group of Patients with Type 2 Diabetes, Aged 40–98, from Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14010102
Jaalkhorol M, Cieślik A, Dashtseren M, Khairat A, Damdinbazar O, Ochirdorj G, Khurelbaatar T, Batmunkh G, Ganzorig U, Kozieł S. The Relationship Between Health Parameters, Body Size, Elements of Lifestyle, and Hand Grip Strength in a Group of Patients with Type 2 Diabetes, Aged 40–98, from Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(1):102. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14010102
Chicago/Turabian StyleJaalkhorol, Myadagmaa, Agata Cieślik, Myagmartseren Dashtseren, Anya Khairat, Otgonbayar Damdinbazar, Gerelmaa Ochirdorj, Tsetsegsuren Khurelbaatar, Ganbayar Batmunkh, Ulemjjargal Ganzorig, and Sławomir Kozieł. 2025. "The Relationship Between Health Parameters, Body Size, Elements of Lifestyle, and Hand Grip Strength in a Group of Patients with Type 2 Diabetes, Aged 40–98, from Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 1: 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14010102
APA StyleJaalkhorol, M., Cieślik, A., Dashtseren, M., Khairat, A., Damdinbazar, O., Ochirdorj, G., Khurelbaatar, T., Batmunkh, G., Ganzorig, U., & Kozieł, S. (2025). The Relationship Between Health Parameters, Body Size, Elements of Lifestyle, and Hand Grip Strength in a Group of Patients with Type 2 Diabetes, Aged 40–98, from Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(1), 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14010102









