The Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Cardiomyopathies in the Light of New Guidelines: A Focus on Tissue Mapping
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. CMR-Based Sequences and Techniques
2.1. Morphology and Function
2.2. Tissue Characterization
3. Dilated Cardiomyopathy
4. Non-Dilated Left Ventricular Cardiomyopathy
5. Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
6. Cardiac Amyloidosis
7. Anderson–Fabry Disease
8. Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy
9. Cardiac Sarcoidosis
10. Iron Overload Cardiomyopathy
11. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACM | arrhytmogenic cardiomyopathy |
| AFD | Anderson–Fabry disease |
| AL | light chain amyloid |
| ARCV | arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy |
| ATTR | transthyretin amyloid |
| ATTRh | hereditable transthyretin amyloid |
| ATTRwt | wild-type transthyretin amyloid |
| b-SSFP | balanced steady-state free procession |
| CA | sardiac amyloidosis |
| CAD | coronary artery disease |
| CHD | congenital heart disease |
| CMR | cardiac magnetic resonance |
| CS | cardiac sarcoidosis |
| CT | computed tomography |
| CRT | cardiac resynchronization therapy |
| DCM | dilated cardiomyopathy |
| DSP | desmoplakin |
| EBM | endomyocardial biopsy |
| ECV | extracellular volume fraction |
| ESC | European Society of Cardiology |
| FLNC | filamin C |
| FT | feature-tracking |
| GBCA | gadolinium-based contrast agent |
| HCM | hypertrophic cardiomyopthy |
| HRS | Heart Rhythm Society |
| ICD | implantable cardioverter defibrillator |
| IO | iron overload |
| IOC | iron overload cardiomyopathy |
| ITF | International Task Force |
| JCS | Japanese Circulation Society |
| LGE | late gadolinium enhancement |
| LV | left ventricle |
| MACE | major adverse cardiac events |
| MRI | magnetic resonance imaging |
| n-T1 | native T1 mapping |
| NDLVC | non-dilated left ventricular cardiomyopathy |
| PET | positron emission tomography |
| QALE | query amyloid late enhancement |
| RV | right ventricle |
| STIR | short tau inversion recovery |
| T1-W | T1-weighted |
| T2-W | T2-weighted |
References
- Elliott, P.; Andersson, B.; Arbustini, E.; Bilinska, Z.; Cecchi, F.; Charron, P.; Dubourg, O.; Kuhl, U.; Maisch, B.; McKenna, W.J.; et al. Classification of the cardiomyopathies: A position statement from the European Society Of Cardiology Working Group on Myocardial and Pericardial Diseases. Eur. Heart J. 2008, 29, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbelo, E.; Protonotarios, A.; Gimeno, J.R.; Arbustini, E.; Barriales-Villa, R.; Basso, C.; Bezzina, C.R.; Biagini, E.; Blom, N.A.; de Boer, R.A.; et al. 2023 ESC Guidelines for the management of cardiomyopathies: Developed by the task force on the management of cardiomyopathies of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur. Heart J. 2023, 44, 3503–3626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlo, M.; Gagno, G.; Baritussio, A.; Bauce, B.; Biagini, E.; Canepa, M.; Cipriani, A.; Castelletti, S.; Dellegrottaglie, S.; Guaricci, A.I.; et al. Clinical application of CMR in cardiomyopathies: Evolving concepts and techniques: A position paper of myocardial and pericardial diseases and cardiac magnetic resonance working groups of Italian society of cardiology. Heart Fail. Rev. 2023, 28, 77–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forleo, C.; D‘Erchia, A.M.; Sorrentino, S.; Manzari, C.; Chiara, M.; Iacoviello, M.; Guaricci, A.I.; De Santis, D.; Musci, R.L.; La Spada, A.; et al. Targeted next-generation sequencing detects novel gene-phenotype associations and expands the mutational spectrum in cardiomyopathies. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guaricci, A.I.; Bulzis, G.; Pontone, G.; Scicchitano, P.; Carbonara, R.; Rabbat, M.; De Santis, D.; Ciccone, M.M. Current interpretation of myocardial stunning. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2018, 28, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neglia, D.; Liga, R.; Gimelli, A.; Podlesnikar, T.; Cvijić, M.; Pontone, G.; Miglioranza, M.H.; Guaricci, A.I.; Seitun, S.; Clemente, A.; et al. Use of cardiac imaging in chronic coronary syndromes: The EURECA Imaging registry. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 44, 142–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontone, G.; Di Bella, G.; Castelletti, S.; Maestrini, V.; Festa, P.; Ait-Ali, L.; Masci, P.G.; Monti, L.; di Giovine, G.; De Lazzari, M.; et al. Clinical recommendations of cardiac magnetic resonance, Part II: Inflammatory and congenital heart disease, cardiomyopathies and cardiac tumors: A position paper of the working group A‘pplicazioni della Risonanza Magnetica’ of the Italian Society of Cardiology. J. Cardiovasc. Med. 2017, 18, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baggiano, A.; Del Torto, A.; Guglielmo, M.; Muscogiuri, G.; Fusini, L.; Babbaro, M.; Collevecchio, A.; Mollace, R.; Scafuri, S.; Mushtaq, S.; et al. Role of CMR Mapping Techniques in Cardiac Hypertrophic Phenotype. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baggiano, A.; Conte, E.; Spiritigliozzi, L.; Mushtaq, S.; Annoni, A.; Carerj, M.L.; Cilia, F.; Fazzari, F.; Formenti, A.; Frappampina, A.; et al. Quantification of extracellular volume with cardiac computed tomography in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy. J. Cardiovasc. Comput. Tomogr. 2023, 17, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peretto, G.; Barison, A.; Forleo, C.; Di Resta, C.; Esposito, A.; Aquaro, G.D.; Scardapane, A.; Palmisano, A.; Emdin, M.; Resta, N.; et al. Late gadolinium enhancement role in arrhythmic risk stratification of patients with LMNA cardiomyopathy: Results from a long-term follow-up multicentre study. Europace 2020, 22, 1864–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontone, G.; Andreini, D.; Bertella, E.; Petullà, M.; Russo, E.; Innocenti, E.; Mushtaq, S.; Gripari, P.; Loguercio, M.; Segurini, C.; et al. Comparison of cardiac computed tomography versus cardiac magnetic resonance for characterization of left atrium anatomy before radiofrequency catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation. Int. J. Cardiol. 2015, 179, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscogiuri, G.; Martini, C.; Gatti, M.; Dell’Aversana, S.; Ricci, F.; Guglielmo, M.; Baggiano, A.; Fusini, L.; Bracciani, A.; Scafuri, S.; et al. Feasibility of late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) in ischemic cardiomyopathy using 2D-multisegment LGE combined with artificial intelligence reconstruction deep learning noise reduction algorithm. Int. J. Cardiol. 2021, 343, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Ferrari, V.A.; Han, Y. Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Heart Failure. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2021, 23, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aquaro, G.D.; Camastra, G.; Monti, L.; Lombardi, M.; Pepe, A.; Castelletti, S.; Maestrini, V.; Todiere, G.; Masci, P.; di Giovine, G.; et al. Reference values of cardiac volumes, dimensions, and new functional parameters by MR: A multicenter, multivendor study. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2017, 45, 1055–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramer, C.M.; Barkhausen, J.; Bucciarelli-Ducci, C.; Flamm, S.D.; Kim, R.J.; Nagel, E. Standardized cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging (CMR) protocols: 2020 update. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 2020, 22, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontone, G.; Guaricci, A.I.; Fusini, L.; Baggiano, A.; Guglielmo, M.; Muscogiuri, G.; Volpe, A.; Abete, R.; Aquaro, G.; Barison, A.; et al. Cardiac Magnetic Resonance for Prophylactic Implantable-Cardioverter Defibrillator Therapy in Ischemic Cardiomyopathy: The DERIVATE-ICM International Registry. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2023, 16, 1387–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedrizzetti, G.; Claus, P.; Kilner, P.J.; Nagel, E. Principles of cardiovascular magnetic resonance feature tracking and echocardiographic speckle tracking for informed clinical use. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 2016, 18, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, T.; Schuster, A. Quantification of Myocardial Deformation Applying CMR-Feature-Tracking-All About the Left Ventricle? Curr. Heart Fail. Rep. 2021, 18, 225–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markousis-Mavrogenis, G.; Giannakopoulou, A.; Belegrinos, A.; Pons, M.R.; Bonou, M.; Vartela, V.; Papavasiliou, A.; Christidi, A.; Kourtidou, S.; Kolovou, G.; et al. Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Imaging Patterns in Rare Cardiovascular Diseases. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guglielmo, M.; Fusini, L.; Muscogiuri, G.; Baessato, F.; Loffreno, A.; Cavaliere, A.; Rizzon, G.; Baggiano, A.; Rabbat, M.G.; Muratori, M.; et al. T1 mapping and cardiac magnetic resonance feature tracking in mitral valve prolapse. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 1100–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messroghli, D.R.; Moon, J.C.; Ferreira, V.M.; Grosse-Wortmann, L.; He, T.; Kellman, P.; Mascherbauer, J.; Nezafat, R.; Salerno, M.; Schelbert, E.B.; et al. Clinical recommendations for cardiovascular magnetic resonance mapping of T1, T2, T2* and extracellular volume: A consensus statement by the Society for Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance (SCMR) endorsed by the European Association for Cardiovascular Imaging (EACVI). J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 2017, 19, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heymans, S.; Lakdawala, N.K.; Tschope, C.; Klingel, K. Dilated cardiomyopathy: Causes, mechanisms, and current and future treatment approaches. Lancet 2023, 402, 998–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghanbari, F.; Joyce, T.; Lorenzoni, V.; Guaricci, A.I.; Pavon, A.G.; Fusini, L.; Andreini, D.; Rabbat, M.G.; Aquaro, G.D.; Abete, R.; et al. AI Cardiac MRI Scar Analysis Aids Prediction of Major Arrhythmic Events in the Multicenter DERIVATE Registry. Radiology 2023, 307, e222239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iles, L.M.; Ellims, A.H.; Llewellyn, H.; Hare, J.L.; Kaye, D.M.; McLean, C.A.; Taylor, A.J. Histological validation of cardiac magnetic resonance analysis of regional and diffuse interstitial myocardial fibrosis. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2015, 16, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todiere, G.; Barison, A.; Baritussio, A.; Cipriani, A.; Guaricci, A.I.; Pica, S.; Indolfi, C.; Pontone, G.; Dellegrottaglie, S. Acute clinical presentation of nonischemic cardiomyopathies: Early detection by cardiovascular magnetic resonance. J. Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 24, e36–e46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puntmann, V.O.; Carr-White, G.; Jabbour, A.; Yu, C.Y.; Gebker, R.; Kelle, S.; Hinojar, R.; Doltra, A.; Varma, N.; Child, N.; et al. T1-Mapping and Outcome in Nonischemic Cardiomyopathy: All-Cause Mortality and Heart Failure. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2016, 9, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vita, T.; Grani, C.; Abbasi, S.A.; Neilan, T.G.; Rowin, E.; Kaneko, K.; Coelho-Filho, O.; Watanabe, E.; Mongeon, F.P.; Farhad, H.; et al. Comparing CMR Mapping Methods and Myocardial Patterns Toward Heart Failure Outcomes in Nonischemic Dilated Cardiomyopathy. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2019, 12, 1659–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadour, F.; Quemeneur, M.; Biere, L.; Donal, E.; Bentatou, Z.; Eicher, J.C.; Roubille, F.; Lalande, A.; Giorgi, R.; Rapacchi, S.; et al. Prognostic value of cardiovascular magnetic resonance T1 mapping and extracellular volume fraction in nonischemic dilated cardiomyopathy. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 2023, 25, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrabba, N.; Amico, M.A.; Guaricci, A.I.; Carella, M.C.; Maestrini, V.; Monosilio, S.; Pedrotti, P.; Ricci, F.; Monti, L.; Figliozzi, S.; et al. CMR Mapping: The 4th-Era Revolution in Cardiac Imaging. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mordi, I.; Carrick, D.; Bezerra, H.; Tzemos, N. T1 and T2 mapping for early diagnosis of dilated non-ischaemic cardiomyopathy in middle-aged patients and differentiation from normal physiological adaptation. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2016, 17, 797–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, M.G. Myocardial edema—A new clinical entity? Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2010, 7, 292–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Li, W.; Wan, K.; Liang, Y.; Jiang, X.; Wang, J.; Mui, D.; Li, Y.; Tang, S.; Guo, J.; et al. Myocardial Tissue Reverse Remodeling after Guideline-Directed Medical Therapy in Idiopathic Dilated Cardiomyopathy. Circ. Heart Fail. 2021, 14, e007944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guaricci, A.I.; Masci, P.G.; Muscogiuri, G.; Guglielmo, M.; Baggiano, A.; Fusini, L.; Lorenzoni, V.; Martini, C.; Andreini, D.; Pavon, A.G.; et al. CarDiac magnEtic Resonance for prophylactic Implantable-cardioVerter defibrillAtor ThErapy in Non-Ischaemic dilated CardioMyopathy: An international Registry. Europace 2021, 23, 1072–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gigli, M.; Stolfo, D.; Merlo, M.; Barbati, G.; Ramani, F.; Brun, F.; Pinamonti, B.; Sinagra, G. Insights into mildly dilated cardiomyopathy: Temporal evolution and long-term prognosis. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2017, 19, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Li, Z.; Guo, L.; Yu, S.; Li, T.; Zheng, L.; Pan, G.; Yang, J.; Sun, Y.; Hui, R.; et al. Prevalence of hypokinetic non-dilated cardiomyopathy in a large general Chinese population. Int. J. Cardiol. 2016, 223, 708–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitaoka, H.; Matsumura, Y.; Yamasaki, N.; Kondo, F.; Furuno, T.; Doi, Y. Long-term prognosis of patients with mildly dilated cardiomyopathy. Circ. J. 2002, 66, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eda, Y.; Nabeta, T.; Iikura, S.; Takigami, Y.; Fujita, T.; Iida, Y.; Ikeda, Y.; Ishii, S.; Ako, J. Non-dilated left ventricular cardiomyopathy vs. dilated cardiomyopathy: Clinical background and outcomes. ESC Heart Fail. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donal, E.; Delgado, V.; Bucciarelli-Ducci, C.; Galli, E.; Haugaa, K.H.; Charron, P.; Voigt, J.U.; Cardim, N.; Masci, P.G.; Galderisi, M.; et al. Multimodality imaging in the diagnosis, risk stratification, and management of patients with dilated cardiomyopathies: An expert consensus document from the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2019, 20, 1075–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dass, S.; Suttie, J.J.; Piechnik, S.K.; Ferreira, V.M.; Holloway, C.J.; Banerjee, R.; Mahmod, M.; Cochlin, L.; Karamitsos, T.D.; Robson, M.D.; et al. Myocardial tissue characterization using magnetic resonance noncontrast t1 mapping in hypertrophic and dilated cardiomyopathy. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2012, 5, 726–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhuang, B.; Sirajuddin, A.; Li, S.; Huang, J.; Yin, G.; Song, L.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, S.; Lu, M. MRI T1 Mapping in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy: Evaluation in Patients without Late Gadolinium Enhancement and Hemodynamic Obstruction. Radiology 2020, 294, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.Y.; Abbasi, S.A.; Neilan, T.G.; Shah, R.V.; Chen, Y.; Heydari, B.; Cirino, A.L.; Lakdawala, N.K.; Orav, E.J.; Gonzalez, A.; et al. T1 measurements identify extracellular volume expansion in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy sarcomere mutation carriers with and without left ventricular hypertrophy. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2013, 6, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Ran, L.; Zhao, P.; Tang, D.; Han, R.; Ai, T.; Xia, L.; Tao, Q. MRI native T1 and T2 mapping of myocardial segments in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: Tissue remodeling manifested prior to structure changes. Br. J. Radiol. 2019, 92, 20190634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gastl, M.; Lachmann, V.; Christidi, A.; Janzarik, N.; Veulemans, V.; Haberkorn, S.; Holzbach, L.; Jacoby, C.; Schnackenburg, B.; Berrisch-Rahmel, S.; et al. Cardiac magnetic resonance T2 mapping and feature tracking in athlete’s heart and HCM. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 2768–2777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razvi, Y.; Patel, R.K.; Fontana, M.; Gillmore, J.D. Cardiac Amyloidosis: A Review of Current Imaging Techniques. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 751293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tore, D.; Faletti, R.; Gaetani, C.; Bozzo, E.; Biondo, A.; Carisio, A.; Menchini, F.; Miccolis, M.; Papa, F.P.; Trovato, M.; et al. Cardiac magnetic resonance of hypertrophic heart phenotype: A review. Heliyon 2023, 9, e17336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagura, L.; Porcari, A.; Cameli, M.; Biagini, E.; Canepa, M.; Crotti, L.; Imazio, M.; Forleo, C.; Pavasini, R.; Limongelli, G.; et al. ECG/echo indexes in the diagnostic approach to amyloid cardiomyopathy: A head-to-head comparison from the AC-TIVE study. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2023, 122, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Naharro, A.; Treibel, T.A.; Abdel-Gadir, A.; Bulluck, H.; Zumbo, G.; Knight, D.S.; Kotecha, T.; Francis, R.; Hutt, D.F.; Rezk, T.; et al. Magnetic Resonance in Transthyretin Cardiac Amyloidosis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 70, 466–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Naharro, A.; Kotecha, T.; Norrington, K.; Boldrini, M.; Rezk, T.; Quarta, C.; Treibel, T.A.; Whelan, C.J.; Knight, D.S.; Kellman, P.; et al. Native T1 and Extracellular Volume in Transthyretin Amyloidosis. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2019, 12, 810–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nativi-Nicolau, J.N.; Karam, C.; Khella, S.; Maurer, M.S. Screening for ATTR amyloidosis in the clinic: Overlapping disorders, misdiagnosis, and multiorgan awareness. Heart Fail. Rev. 2022, 27, 785–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, L.K.; Forero, J.F.; Popovic, Z.B.; Phelan, D.; Delgado, D.; Rakowski, H.; Wintersperger, B.J.; Thavendiranathan, P. Patterns of CMR measured longitudinal strain and its association with late gadolinium enhancement in patients with cardiac amyloidosis and its mimics. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 2017, 19, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dungu, J.N.; Valencia, O.; Pinney, J.H.; Gibbs, S.D.; Rowczenio, D.; Gilbertson, J.A.; Lachmann, H.J.; Wechalekar, A.; Gillmore, J.D.; Whelan, C.J.; et al. CMR-based differentiation of AL and ATTR cardiac amyloidosis. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2014, 7, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontana, M.; Pica, S.; Reant, P.; Abdel-Gadir, A.; Treibel, T.A.; Banypersad, S.M.; Maestrini, V.; Barcella, W.; Rosmini, S.; Bulluck, H.; et al. Prognostic Value of Late Gadolinium Enhancement Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance in Cardiac Amyloidosis. Circulation 2015, 132, 1570–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briasoulis, A.; Bampatsias, D.; Papamichail, A.; Kuno, T.; Skoularigis, J.; Xanthopoulos, A.; Triposkiadis, F. Invasive and Non-Invasive Diagnostic Pathways in the Diagnosis of Cardiac Amyloidosis. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2023, 10, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baggiano, A.; Boldrini, M.; Martinez-Naharro, A.; Kotecha, T.; Petrie, A.; Rezk, T.; Gritti, M.; Quarta, C.; Knight, D.S.; Wechalekar, A.D.; et al. Noncontrast Magnetic Resonance for the Diagnosis of Cardiac Amyloidosis. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2020, 13, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ioannou, A.; Patel, R.K.; Martinez-Naharro, A.; Razvi, Y.; Porcari, A.; Rauf, M.U.; Bolhuis, R.E.; Fernando-Sayers, J.; Virsinskaite, R.; Bandera, F.; et al. Tracking Treatment Response in Cardiac Light-Chain Amyloidosis with Native T1 Mapping. JAMA Cardiol. 2023, 8, 848–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Pavia, P.; Rapezzi, C.; Adler, Y.; Arad, M.; Basso, C.; Brucato, A.; Burazor, I.; Caforio, A.L.P.; Damy, T.; Eriksson, U.; et al. Diagnosis and treatment of cardiac amyloidosis: A position statement of the ESC Working Group on Myocardial and Pericardial Diseases. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 1554–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gama, F.; Rosmini, S.; Bandula, S.; Patel, K.P.; Massa, P.; Tobon-Gomez, C.; Ecke, K.; Stroud, T.; Condron, M.; Thornton, G.D.; et al. Extracellular Volume Fraction by Computed Tomography Predicts Long-Term Prognosis among Patients with Cardiac Amyloidosis. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2022, 15, 2082–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponsiglione, A.; De Giorgi, M.; Ascione, R.; Nappi, C.; Sanduzzi, L.; Pisani, A.; Dell’Aversana, S.; Cuocolo, A.; Imbriaco, M. Advanced CMR Techniques in Anderson-Fabry Disease: State of the Art. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linhart, A.; Kampmann, C.; Zamorano, J.L.; Sunder-Plassmann, G.; Beck, M.; Mehta, A.; Elliott, P.M. Cardiac manifestations of Anderson-Fabry disease: Results from the international Fabry outcome survey. Eur. Heart J. 2007, 28, 1228–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frustaci, A.; Morgante, E.; Russo, M.A.; Scopelliti, F.; Grande, C.; Verardo, R.; Franciosa, P.; Chimenti, C. Pathology and function of conduction tissue in Fabry disease cardiomyopathy. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2015, 8, 799–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Militaru, S.; Ginghina, C.; Popescu, B.A.; Saftoiu, A.; Linhart, A.; Jurcut, R. Multimodality imaging in Fabry cardiomyopathy: From early diagnosis to therapeutic targets. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2018, 19, 1313–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozor, R.; Callaghan, F.; Tchan, M.; Hamilton-Craig, C.; Figtree, G.A.; Grieve, S.M. A disproportionate contribution of papillary muscles and trabeculations to total left ventricular mass makes choice of cardiovascular magnetic resonance analysis technique critical in Fabry disease. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 2015, 17, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merlo, M.; Porcari, A.; Pagura, L.; Cameli, M.; Vergaro, G.; Musumeci, B.; Biagini, E.; Canepa, M.; Crotti, L.; Imazio, M.; et al. A national survey on prevalence of possible echocardiographic red flags of amyloid cardiomyopathy in consecutive patients undergoing routine echocardiography: Study design and patients characterization-the first insight from the AC-TIVE Study. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2021, 29, e173–e177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordin, S.; Kozor, R.; Baig, S.; Abdel-Gadir, A.; Medina-Menacho, K.; Rosmini, S.; Captur, G.; Tchan, M.; Geberhiwot, T.; Murphy, E.; et al. Cardiac Phenotype of Prehypertrophic Fabry Disease. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2018, 11, e007168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, R.; Shah, R.; Saiedi, M.; Patil, S.; Ganesan, A.; Linhart, A.; Selvanayagam, J.B. The Role of Cardiac Imaging in the Diagnosis and Management of Anderson-Fabry Disease. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2019, 12, 1230–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordin, S.; Kozor, R.; Medina-Menacho, K.; Abdel-Gadir, A.; Baig, S.; Sado, D.M.; Lobascio, I.; Murphy, E.; Lachmann, R.H.; Mehta, A.; et al. Proposed Stages of Myocardial Phenotype Development in Fabry Disease. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2019, 12, 1673–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pieroni, M.; Moon, J.C.; Arbustini, E.; Barriales-Villa, R.; Camporeale, A.; Vujkovac, A.C.; Elliott, P.M.; Hagege, A.; Kuusisto, J.; Linhart, A.; et al. Cardiac Involvement in Fabry Disease: JACC Review Topic of the Week. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2021, 77, 922–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Augusto, J.B.; Nordin, S.; Vijapurapu, R.; Baig, S.; Bulluck, H.; Castelletti, S.; Alfarih, M.; Knott, K.; Captur, G.; Kotecha, T.; et al. Myocardial Edema, Myocyte Injury, and Disease Severity in Fabry Disease. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2020, 13, e010171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frustaci, A.; Verardo, R.; Grande, C.; Galea, N.; Piselli, P.; Carbone, I.; Alfarano, M.; Russo, M.A.; Chimenti, C. Immune-Mediated Myocarditis in Fabry Disease Cardiomyopathy. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2018, 7, e009052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcus, F.I.; McKenna, W.J.; Sherrill, D.; Basso, C.; Bauce, B.; Bluemke, D.A.; Calkins, H.; Corrado, D.; Cox, M.G.; Daubert, J.P.; et al. Diagnosis of arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy/dysplasia: Proposed modification of the task force criteria. Circulation 2010, 121, 1533–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrado, D.; Perazzolo Marra, M.; Zorzi, A.; Beffagna, G.; Cipriani, A.; Lazzari, M.; Migliore, F.; Pilichou, K.; Rampazzo, A.; Rigato, I.; et al. Diagnosis of arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy: The Padua criteria. Int. J. Cardiol. 2020, 319, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borgquist, R.; Haugaa, K.H.; Gilljam, T.; Bundgaard, H.; Hansen, J.; Eschen, O.; Jensen, H.K.; Holst, A.G.; Edvardsen, T.; Svendsen, J.H.; et al. The diagnostic performance of imaging methods in ARVC using the 2010 Task Force criteria. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2014, 15, 1219–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalal, D.; Tandri, H.; Judge, D.P.; Amat, N.; Macedo, R.; Jain, R.; Tichnell, C.; Daly, A.; James, C.; Russell, S.D.; et al. Morphologic variants of familial arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia/cardiomyopathy a genetics-magnetic resonance imaging correlation study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009, 53, 1289–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muscogiuri, G.; Fusini, L.; Ricci, F.; Sicuso, R.; Guglielmo, M.; Baggiano, A.; Gasperetti, A.; Casella, M.; Mushtaq, S.; Conte, E.; et al. Additional diagnostic value of cardiac magnetic resonance feature tracking in patients with biopsy-proven arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy. Int. J. Cardiol. 2021, 339, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quarta, G.; Husain, S.I.; Flett, A.S.; Sado, D.M.; Chao, C.Y.; Tome Esteban, M.T.; McKenna, W.J.; Pantazis, A.; Moon, J.C. Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy mimics: Role of cardiovascular magnetic resonance. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 2013, 15, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heermann, P.; Fritsch, H.; Koopmann, M.; Sporns, P.; Paul, M.; Heindel, W.; Schulze-Bahr, E.; Schülke, C. Biventricular myocardial strain analysis using cardiac magnetic resonance feature tracking (CMR-FT) in patients with distinct types of right ventricular diseases comparing arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC), right ventricular outflow-tract tachycardia (RVOT-VT), and Brugada syndrome (BrS). Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2019, 108, 1147–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zghaib, T.; Ghasabeh, M.A.; Assis, F.R.; Chrispin, J.; Keramati, A.; Misra, S.; Berger, R.; Calkins, H.; Kamel, I.; Nazarian, S.; et al. Regional Strain by Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging Improves Detection of Right Ventricular Scar Compared with Late Gadolinium Enhancement on a Multimodality Scar Evaluation in Patients with Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2018, 11, e007546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rastegar, N.; Burt, J.R.; Corona-Villalobos, C.P.; Te Riele, A.S.; James, C.A.; Murray, B.; Calkins, H.; Tandri, H.; Bluemke, D.A.; Zimmerman, S.L.; et al. Cardiac MR findings and potential diagnostic pitfalls in patients evaluated for arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy. Radiographics 2014, 34, 1553–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aquaro, G.D.; Barison, A.; Todiere, G.; Grigoratos, C.; Ait Ali, L.; Di Bella, G.; Emdin, M.; Festa, P. Usefulness of Combined Functional Assessment by Cardiac Magnetic Resonance and Tissue Characterization Versus Task Force Criteria for Diagnosis of Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy. Am. J. Cardiol. 2016, 118, 1730–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al’Aref, S.J.; Altibi, A.M.; Malkawi, A.; Mansour, M.; Baskaran, L.; Masri, A.; Rahmouni, H.; Abete, R.; Andreini, D.; Aquaro, G.; et al. Cardiac magnetic resonance for prophylactic implantable-cardioverter defibrillator therapy international study: Prognostic value of cardiac magnetic resonance-derived right ventricular parameters substudy. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2022, 24, 472–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cipriani, A.; Mattesi, G.; Bariani, R.; Cecere, A.; Martini, N.; De Michieli, L.; Da Pozzo, S.; Corradin, S.; De Conti, G.; Zorzi, A.; et al. Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging of arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy: Evolving diagnostic perspectives. Eur. Radiol. 2023, 33, 270–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casella, M.; Gasperetti, A.; Sicuso, R.; Conte, E.; Catto, V.; Sommariva, E.; Bergonti, M.; Vettor, G.; Rizzo, S.; Pompilio, G.; et al. Characteristics of Patients with Arrhythmogenic Left Ventricular Cardiomyopathy: Combining Genetic and Histopathologic Findings. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2020, 13, e009005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourfiss, M.; Prakken, N.H.J.; van der Heijden, J.F.; Kamel, I.; Zimmerman, S.L.; Asselbergs, F.W.; Leiner, T.; Velthuis, B.K.; Te Riele, A. Diagnostic Value of Native T(1) Mapping in Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2019, 12, 1580–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwai, K.; Tachibana, T.; Takemura, T.; Matsui, Y.; Kitaichi, M.; Kawabata, Y. Pathological studies on sarcoidosis autopsy. I. Epidemiological features of 320 cases in Japan. Acta Pathol. Jpn. 1993, 43, 372–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drent, M.; Crouser, E.D.; Grunewald, J. Challenges of Sarcoidosis and Its Management. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1018–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terasaki, F.; Azuma, A.; Anzai, T.; Ishizaka, N.; Ishida, Y.; Isobe, M.; Inomata, T.; Ishibashi-Ueda, H.; Eishi, Y.; Kitakaze, M.; et al. JCS 2016 Guideline on Diagnosis and Treatment of Cardiac Sarcoidosis—Digest version. Circ. J. 2019, 83, 2329–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birnie, D.H.; Sauer, W.H.; Bogun, F.; Cooper, J.M.; Culver, D.A.; Duvernoy, C.S.; Judson, M.A.; Kron, J.; Mehta, D.; Cosedis Nielsen, J.; et al. HRS expert consensus statement on the diagnosis and management of arrhythmias associated with cardiac sarcoidosis. Heart Rhythm. 2014, 11, 1305–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slart, R.; Glaudemans, A.; Lancellotti, P.; Hyafil, F.; Blankstein, R.; Schwartz, R.G.; Jaber, W.A.; Russell, R.; Gimelli, A.; Rouzet, F.; et al. A joint procedural position statement on imaging in cardiac sarcoidosis: From the Cardiovascular and Inflammation & Infection Committees of the European Association of Nuclear Medicine, the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging, and the American Society of Nuclear Cardiology. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 2018, 25, 298–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Xu, Q.; Xu, B.; Wang, H. Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Diagnosis of Cardiac Sarcoidosis: A Meta-Analysis. Can. Respir. J. 2018, 2018, 7457369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.L.; Fong, H.K.; Birati, E.Y.; Han, Y. Cardiac Sarcoidosis. Am. J. Cardiol. 2019, 123, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velangi, P.S.; Chen, K.A.; Kazmirczak, F.; Okasha, O.; von Wald, L.; Roukoz, H.; Farzaneh-Far, A.; Markowitz, J.; Nijjar, P.S.; Bhargava, M.; et al. Right Ventricular Abnormalities on Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Patients with Sarcoidosis. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2020, 13, 1395–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orii, M.; Hirata, K.; Tanimoto, T.; Ota, S.; Shiono, Y.; Yamano, T.; Matsuo, Y.; Ino, Y.; Yamaguchi, T.; Kubo, T.; et al. Comparison of cardiac MRI and 18F-FDG positron emission tomography manifestations and regional response to corticosteroid therapy in newly diagnosed cardiac sarcoidosis with complet heart block. Heart Rhythm 2015, 12, 2477–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabir, D.; Meyer, D.; Kuetting, D.; Luetkens, J.; Homsi, R.; Pizarro, C.; Nadal, J.; Thomas, D. Diagnostic Value of Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Strain Analysis for Detection of Cardiac Sarcoidosis. Rofo 2018, 190, 712–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puntmann, V.O.; Isted, A.; Hinojar, R.; Foote, L.; Carr-White, G.; Nagel, E. T1 and T2 Mapping in Recognition of Early Cardiac Involvement in Systemic Sarcoidosis. Radiology 2017, 285, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okasha, O.; Kazmirczak, F.; Chen, K.A.; Farzaneh-Far, A.; Shenoy, C. Myocardial Involvement in Patients with Histologically Diagnosed Cardiac Sarcoidosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Gross Pathological Images From Autopsy or Cardiac Transplantation Cases. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2019, 8, e011253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hulten, E.; Agarwal, V.; Cahill, M.; Cole, G.; Vita, T.; Parrish, S.; Bittencourt, M.S.; Murthy, V.L.; Kwong, R.; Di Carli, M.F.; et al. Presence of Late Gadolinium Enhancement by Cardiac Magnetic Resonance among Patients with Suspected Cardiac Sarcoidosis Is Associated with Adverse Cardiovascular Prognosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2016, 9, e005001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabir, D.; Luetkens, J.; Kuetting, D.; Nadal, J.; Schild, H.H.; Thomas, D. Myocardial Mapping in Systemic Sarcoidosis: A Comparison of Two Measurement Approaches. Rofo 2021, 193, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greulich, S.; Kitterer, D.; Latus, J.; Aguor, E.; Steubing, H.; Kaesemann, P.; Patrascu, A.; Greiser, A.; Groeninger, S.; Mayr, A.; et al. Comprehensive Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Assessment in Patients with Sarcoidosis and Preserved Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2016, 9, e005022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brissot, P.; Troadec, M.B.; Loréal, O.; Brissot, E. Pathophysiology and classification of iron overload diseases; update 2018. Transfus. Clin. Biol. 2019, 26, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girelli, D.; Busti, F.; Brissot, P.; Cabantchik, I.; Muckenthaler, M.U.; Porto, G. Hemochromatosis classification: Update and recommendations by the BIOIRON Society. Blood 2022, 139, 3018–3029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gujja, P.; Rosing, D.R.; Tripodi, D.J.; Shizukuda, Y. Iron overload cardiomyopathy: Better understanding of an increasing disorder. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2010, 56, 1001–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kremastinos, D.T.; Farmakis, D. Iron overload cardiomyopathy in clinical practice. Circulation 2011, 124, 2253–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, J.C. Magnetic resonance imaging measurement of iron overload. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2007, 14, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, J.C.; Otto-Duessel, M.; Aguilar, M.; Nick, H.; Nelson, M.D.; Coates, T.D.; Pollack, H.; Moats, R. Cardiac iron determines cardiac T2*, T2, and T1 in the gerbil model of iron cardiomyopathy. Circulation 2005, 112, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triadyaksa, P.; Oudkerk, M.; Sijens, P.E. Cardiac T2* mapping: Techniques and clinical applications. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2020, 52, 1340–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, L.J.; Holden, S.; Davis, B.; Prescott, E.; Charrier, C.C.; Bunce, N.H.; Firmin, D.N.; Wonke, B.; Porter, J.; Walker, J.M.; et al. Cardiovascular T2-star (T2*) magnetic resonance for the early diagnosis of myocardial iron overload. Eur. Heart J. 2001, 22, 2171–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casale, M.; Filosa, A.; Ragozzino, A.; Amendola, G.; Roberti, D.; Tartaglione, I.; De Michele, E.; Cozzolino, D.; Rispoli, G.; Palmieri, F.; et al. Long-term improvement in cardiac magnetic resonance in β-thalassemia major patients treated with deferasirox extends to patients with abnormal baseline cardiac function. Am. J. Hematol. 2019, 94, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torlasco, C.; Cassinerio, E.; Roghi, A.; Faini, A.; Capecchi, M.; Abdel-Gadir, A.; Giannattasio, C.; Parati, G.; Moon, J.C.; Cappellini, M.D.; et al. Role of T1 mapping as a complementary tool to T2* for non-invasive cardiac iron overload assessment. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krittayaphong, R.; Zhang, S.; Saiviroonporn, P.; Viprakasit, V.; Tanapibunpon, P.; Komoltri, C.; Wangworatrakul, W. Detection of cardiac iron overload with native magnetic resonance T1 and T2 mapping in patients with thalassemia. Int. J. Cardiol. 2017, 248, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepe, A.; Meloni, A.; Rossi, G.; Midiri, M.; Missere, M.; Valeri, G.; Sorrentino, F.; D‘Ascola, D.G.; Spasiano, A.; Filosa, A.; et al. Prediction of cardiac complications for thalassemia major in the widespread cardiac magnetic resonance era: A prospective multicentre study by a multi-parametric approach. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2018, 19, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanneman, K.; Nguyen, E.T.; Thavendiranathan, P.; Ward, R.; Greiser, A.; Jolly, M.P.; Butany, J.; Yang, I.Y.; Sussman, M.S.; Wintersperger, B.J. Quantification of Myocardial Extracellular Volume Fraction with Cardiac MR Imaging in Thalassemia Major. Radiology 2016, 279, 720–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahir, E.; Fischer, R.; Grosse, R.; Tavrovski, P.; Yamamura, J.; Starekova, J.; Lund, G.K.; Bannas, P.; Graessner, J.; Radunski, U.K.; et al. Strain Analysis Using Feature-Tracking CMR to Detect LV Systolic Dysfunction in Myocardial Iron Overload Disease. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2020, 13, 2267–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


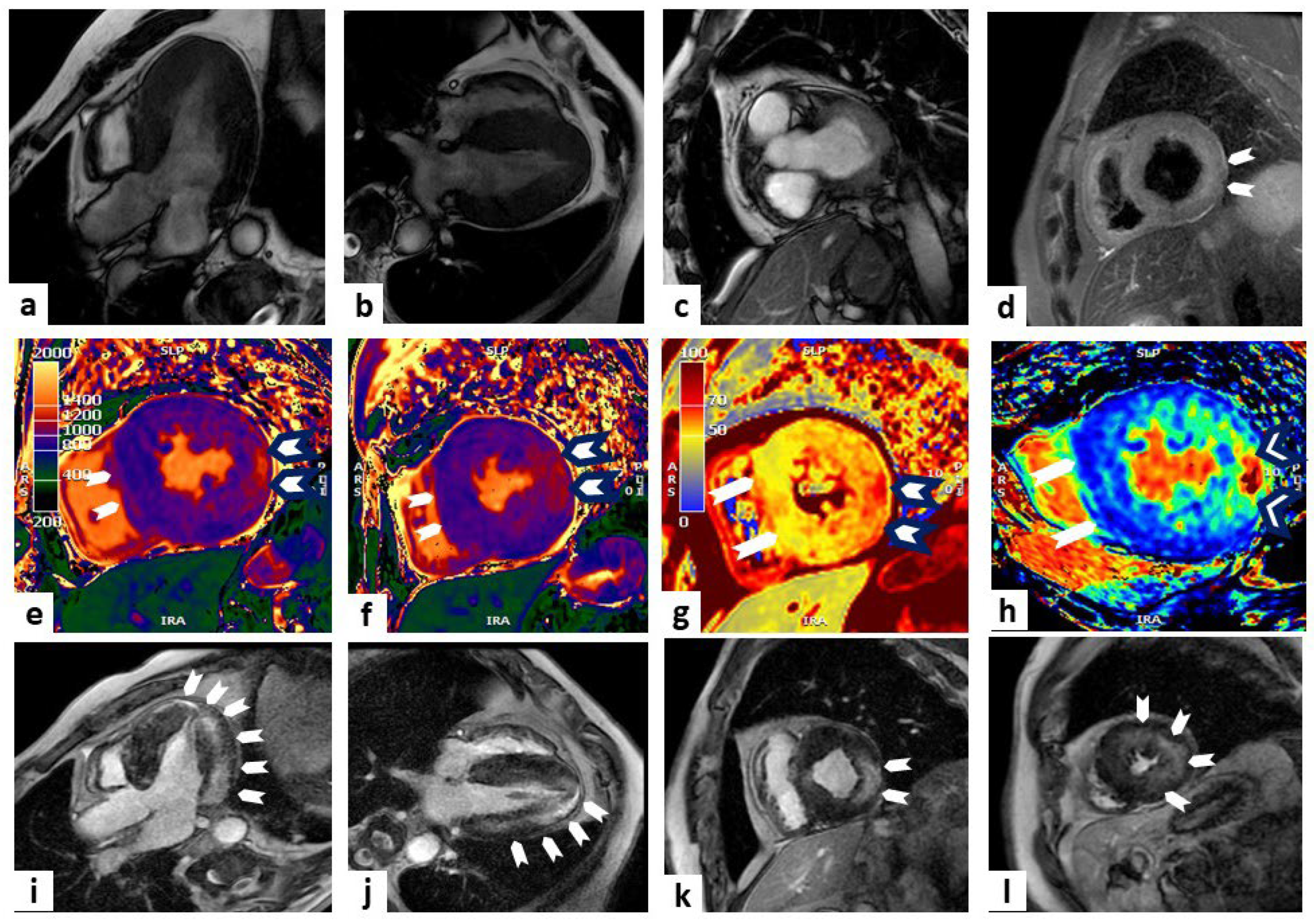
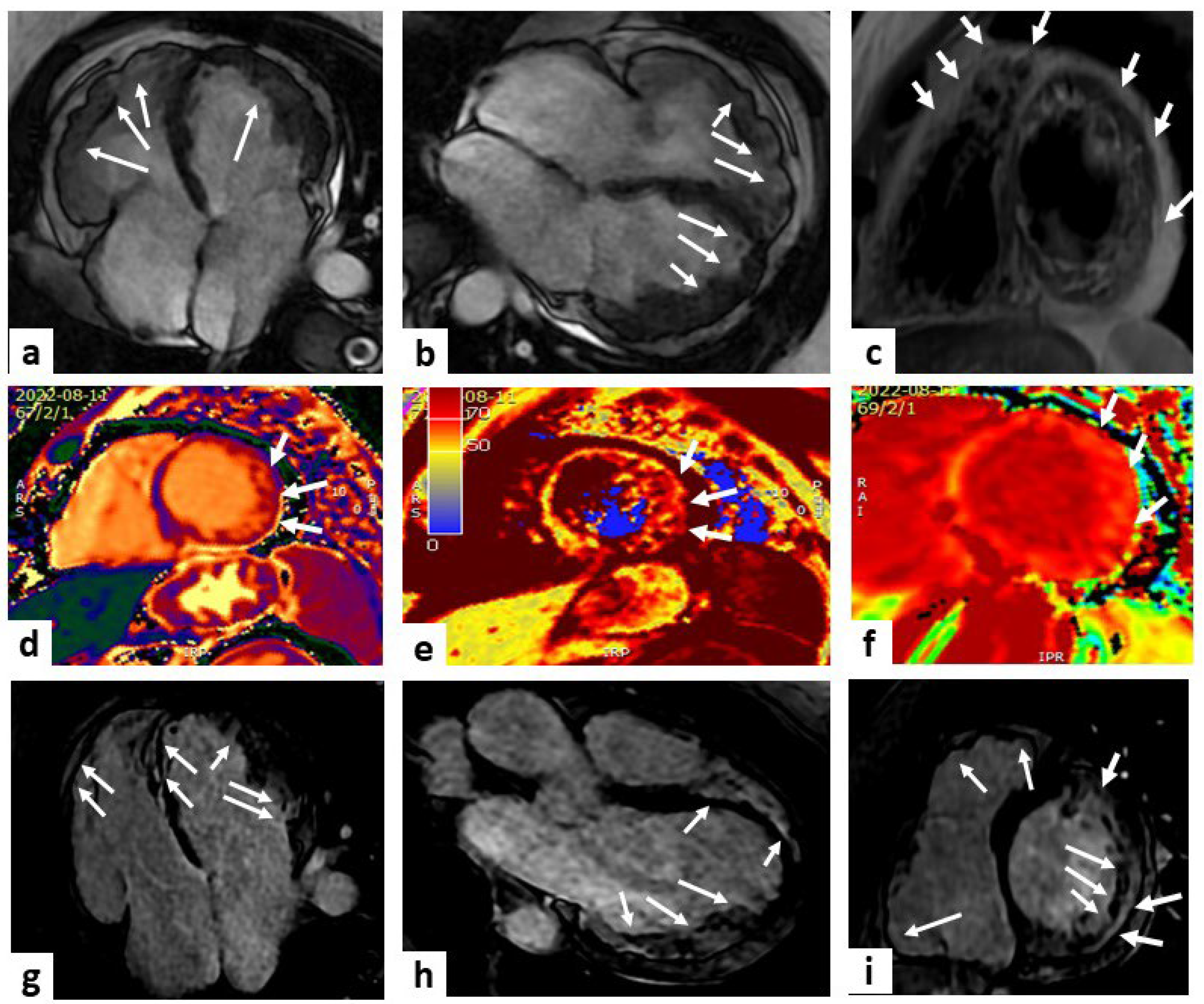
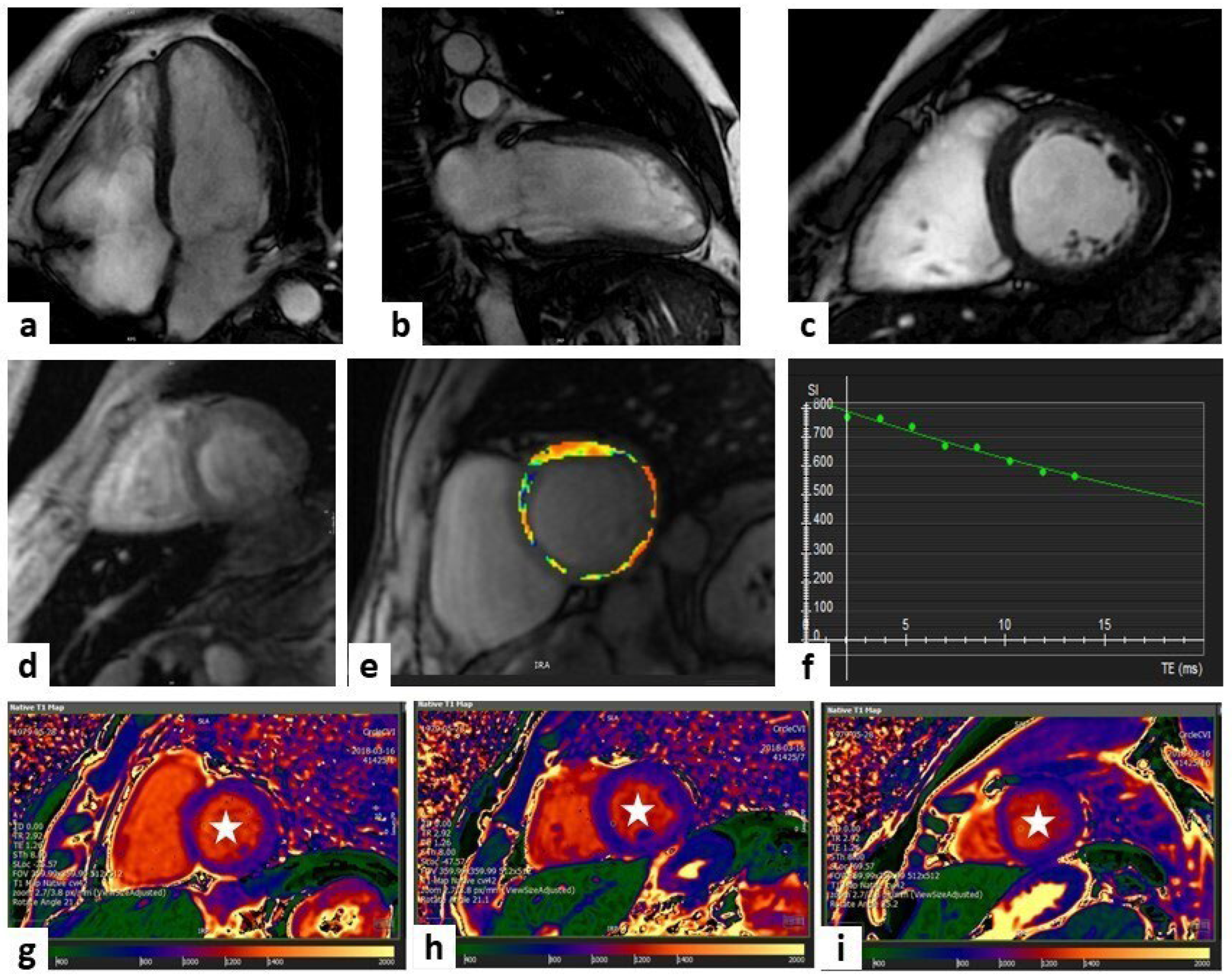
| Sequence | Characteristics | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Cine | b-SSFP sequences, cine images with high spatial and temporal resolution | Quantification of cardiac chamber size, volume, mass, and function |
| Black-blood imaging | T1- or PD- weighted FSE | Fatty infiltration |
| LGE T1-W | IR-SSFP/IR-GRE sequences, acquired after GBCA infusion | Extracellular GBCA deposition (necrosis, fibrosis, amyloid deposition) |
| STIR T2-W | IR-FSE sequences | Water accumulation due to inflammatory extracellular edema |
| Native T1-mapping | MOLLI/ShMOLLI IR-SSPF sequences | Increased in amyloid deposition, inflammatory edema, ischemia, necrosis, diffuse fibrosis; decreased in iron overload, AFD |
| Native T2-mapping | T2-prepared bSSFP, GraSE, FSE sequences | Increased in necrosis, ischemia, inflammatory edema; decreased in iron overload |
| Native T2*-mapping | GRE sequences | Decreased in iron overload |
| ECV-mapping | MOLLI/ShMOLLI IR- SSFP sequences, acquired after GBCA infusion | Increased in amyloid deposition, necrosis, fibrosis |
| FT-GLS | post-processing analysis of b-SSFP sequences with strain and strain rate deformation assessments | Assess early changes in myocardial mechanics and function |
| ITF Criteria (2010) | Padua Criteria (2020) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Global or regional dysfunction and structural alterations | Major: Regional RV akinesia or dyskinesia or dyssynchronous RV contraction and 1 of the following:
Regional RV akinesia or dyskinesia or dyssynchronous RV contraction and 1 of the following:
| Morpho-functional ventricular abnormalities | Major: Regional RV akinesia, dyskinesia, or bulging plus one of the following:
Regional RV akinesia, dyskinesia, or aneurysm of the RV free wall |
| Structural myocardial abnormalities | Transmural LGE (stria pattern) of ≥1 RV region(s) (inlet, outlet, and apex in 2 orthogonal views) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Forleo, C.; Carella, M.C.; Basile, P.; Mandunzio, D.; Greco, G.; Napoli, G.; Carulli, E.; Dicorato, M.M.; Dentamaro, I.; Santobuono, V.E.; et al. The Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Cardiomyopathies in the Light of New Guidelines: A Focus on Tissue Mapping. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 2621. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13092621
Forleo C, Carella MC, Basile P, Mandunzio D, Greco G, Napoli G, Carulli E, Dicorato MM, Dentamaro I, Santobuono VE, et al. The Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Cardiomyopathies in the Light of New Guidelines: A Focus on Tissue Mapping. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(9):2621. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13092621
Chicago/Turabian StyleForleo, Cinzia, Maria Cristina Carella, Paolo Basile, Donato Mandunzio, Giulia Greco, Gianluigi Napoli, Eugenio Carulli, Marco Maria Dicorato, Ilaria Dentamaro, Vincenzo Ezio Santobuono, and et al. 2024. "The Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Cardiomyopathies in the Light of New Guidelines: A Focus on Tissue Mapping" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 9: 2621. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13092621
APA StyleForleo, C., Carella, M. C., Basile, P., Mandunzio, D., Greco, G., Napoli, G., Carulli, E., Dicorato, M. M., Dentamaro, I., Santobuono, V. E., Memeo, R., Latorre, M. D., Baggiano, A., Mushtaq, S., Ciccone, M. M., Pontone, G., & Guaricci, A. I. (2024). The Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Cardiomyopathies in the Light of New Guidelines: A Focus on Tissue Mapping. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(9), 2621. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13092621












