Abstract
Background: Treatment of oropharyngolaryngeal venous malformations (VMs) remains challenging. This study evaluated the effectiveness and safety of fluoroscopy- and endoscopy-guided transoral sclerotherapy for oropharyngolaryngeal VMs in a hybrid operation room (OR). Methods: Patients with oropharyngolaryngeal VMs who underwent transoral sclerotherapy in a hybrid OR were enrolled. Results: Fourteen patients (six females, eight males; median age of 26 years; range, 4–71 years) were analyzed. The symptoms observed were breathing difficulties (n = 3), snoring (n = 2), sleep apnea (n = 1), and swallowing difficulties (n = 1). Lesions were extensive in the face and neck (n = 9) and limited in the oropharyngolarynx (n = 5). A permanent tracheostomy was performed on two patients, while a temporary tracheostomy was performed on five patients. The treated regions were the soft palate (n = 8), pharynx (n = 7), base of the tongue (n = 4), and epiglottis (n = 1). The median number of sclerotherapy sessions was 2.5 (range, 1–9). The median follow-up duration was 81 months (range, 6–141). Treatment outcomes were graded as excellent (n = 2), good (n = 7), or fair (n = 5). The post-treatment complication was bleeding (n = 1), resulting in an urgent tracheostomy. Conclusions: Fluoroscopy- and endoscopy-guided transoral sclerotherapy in a hybrid OR can be effective and safe for oropharyngolaryngeal VMs.
1. Introduction
Hybrid operation rooms (ORs) have been commonly used in fields such as neurovascular and cardiovascular medicine since the 2010s [1,2]. Improvements in image quality and the ability to perform intraoperative three-dimensional computed tomography (3D-CT) are among the advantages provided by a hybrid OR, allowing for safe and minimally invasive interventions. In hybrid ORs, the imaging device is directly connected to the operating table and navigation system, and all devices are directly controlled by the attending surgeon or radiological technologist [3].
Venous malformations (VMs) are the most frequent type of congenital vascular malformation, developing in the head and neck region more often than in the trunk or extremities [4]. Oropharyngolaryngeal VMs often interfere with swallowing and respiration [5,6]. Sclerotherapy has become a common and less invasive therapeutic option for VMs [4]. However, due to their anatomical location, sclerotherapy and the subsequent airway management of oropharyngolaryngeal VMs remains challenging. Therefore, multimodality-guided sclerotherapy is the preferred approach to ensure safety and reproducibility [7,8,9]. Thus, we used a hybrid OR to provide high-resolution DSA and 3D-CT for the sclerotherapy of oropharyngolaryngeal VMs.
This study aims to evaluate the effectiveness and safety of fluoroscopy- and endoscopy-guided transoral sclerotherapy for oropharyngolaryngeal VMs in a hybrid OR. To our knowledge, this is the first study using a hybrid OR for the sclerotherapy of vascular malformations.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Hybrid Operation Room and the Endoscopy
The hybrid OR was installed with the Allura Xper FD20 X-ray system (Phillips, Best, The Netherlands) in combination with the radiolucent carbon-fiber operating table (Maquet Magnus, Phillips) at Tonan Hospital in 2016 (Figure 1). Digital subtraction angiography (DSA) was performed using this system. Endoscopy was performed using rigid telescopes of 0° or 70° connected to a camera head (OTV-S7ProH-HD-12E), a video processor (OTV-S190), a xenon light source (CLV-S190), and a monitor (OEV261H) (Visera Elite system; all from Olympus Medical Systems, Tokyo, Japan).
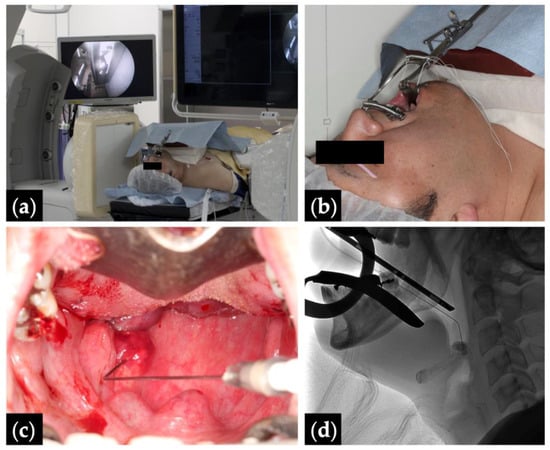
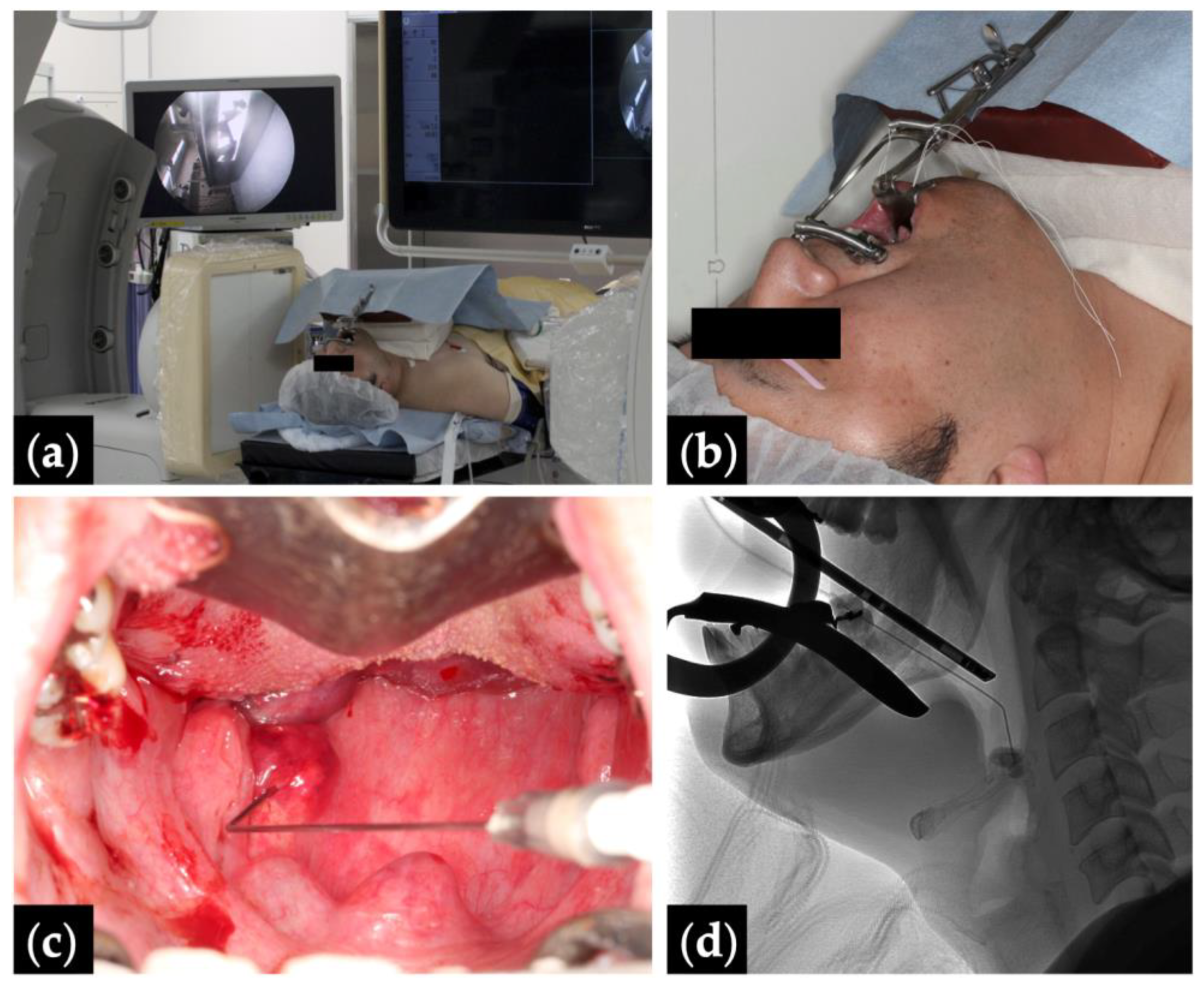
Figure 1.
Fluoroscopy- and endoscopy-guided transoral sclerotherapy: (a) treatment position with monitors depicting the fluoroscopy (right) and the endoscopy (left); (b) Patient 10 positioned head tilt–chin lift with a Dott mouth gag and a tongue blade, and intubated via a tracheostomy; (c) endoscopic view with the pharyngeal lesion punctured by an angled angiocatheter; and (d) intraoperative fluoroscopic view.
2.2. Patients and Treatment Indications
The electronic medical charts of all patients with VMs treated between 2016 and 2023 at Tonan Hospital were retrospectively reviewed. Patients with oropharyngolaryngeal VMs who underwent transoral sclerotherapy in the hybrid OR with at least 6 months’ follow-up were enrolled in this study. Data were assessed for age at presentation, sex, symptoms, presence or absence of tracheostomy and its duration, and radiological studies during the follow-up period. Data are presented as median (range) or as numbers.
Symptoms included breathing difficulties, snoring, sleep apnea, and swallowing difficulties. Breathing difficulties were defined as any difficulties or discomfort during breathing, and swallowing difficulties were defined as any difficulties or discomfort during the swallowing of food or drink based on the patients’ report. Indications of the treatment were decided on the basis of symptoms or to reduce considerable risk of future airway obstruction due to the enlargement of the lesions for the patients without symptoms [8]. Patients whose main target lesion was the soft palate were treated without a tracheostomy.
Before the sclerotherapy, all patients underwent magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to assess the distribution of the lesions. Diagnosis of VM was based on their clinical history and findings on physical examination, ultrasonography, and MRI. All lesions included in this study met the MRI criteria for VMs [10,11,12]. Lesions were categorized as limited in the oropharyngolarynx without cutaneous involvement or extensive in the face and neck with cutaneous involvement. The relationship of categorized lesions with the presence of symptoms was assessed using Fisher’s exact test. Statistical significance was set at p < 0.05.
2.3. Sclerotherapy Procedures
All patients received intravenous hydration before and after sclerotherapy. All sclerotherapy sessions were conducted under general anesthesia by two surgeons (either S.S. or K.I.). An endotracheal tube was inserted through a tracheostomy or nasal route. The patients were positioned head tilt–chin lift with the tongue pulled forward using a silk suture, and a Dott mouth gag and tongue blade were used to keep the mouth open [13]. To visualize needle placement and facilitate direct cannulation of the lesion, the lesion was punctured with a 22-G angiocatheter under fluoroscopic and endoscopic guidance. Nonionic contrast material (iopamidol 300 mgI/mL, Iopamiron 300; Bayer Schering Pharma, Osaka, Japan) was injected under fluoroscopic guidance to confirm the absence of any dangerous venous drainage.
The sclerosant used was 3% polidocanol (Polidocasklerol 3% injection, 30 mg/mL; Kaigen Pharma, Osaka, Japan). The foamed sclerosing solution was obtained by the mixture of 2 mL of 3% polidocanol, 2 mL of contrast material, and 6 mL of atmospheric air (polidocanol, 6 mg/mL) in two syringes attached using a three-way stopcock [14]. The foamed sclerosing solution was subsequently injected into the lesion until adequate filling of the vascular lesion on DSA or upon reaching our maximum dose of the foamed sclerosing solution (1 mL/kg; polidocanol, 6 mg/kg; off-label use) [15,16]. Generally, the maximum dose of polidocanol is 2 mg/kg of body weight for the sclerotherapy of varicose veins [17]. Three-dimensional computed tomography was performed, and the reconstructed images were obtained immediately in the hybrid OR (Supplemental Video S1).
The interval between each sclerotherapy session was scheduled as 3–12 months to allow the swelling to subside and for the clinical status to be accurately assessed. The number of sclerotherapy sessions, doses of foamed sclerosing solution, and post-treatment complications were reviewed. Subsequent swelling of the treated lesions and exacerbations in pain after sclerotherapy were not considered to be complications [18].
2.4. Airway Management after Sclerotherapy
After the sclerotherapy, patients with the tracheostomy had their endotracheal tubes replaced with tracheostomy tubes, and patients without a tracheostomy were extubated in the OR, then transferred to the intensive care unit overnight. Methylprednisolone was administered intravenously to reduce swelling of the treated lesions in patients without a tracheostomy. All patients were on intravenous nutrition on the day of the sclerotherapy and started oral intake from a mixer diet the next day onward.
2.5. Evaluation of Outcomes
All patients were examined with MRI before the first sclerotherapy session and at least 6 months after the final sclerotherapy session to compare the volume of the targeted lesion on the axial images. The volume reduction rate was defined as multiplication of the longest diameter by the greatest perpendicular diameter of the largest lesion [19,20]. Treatment outcomes were retrospectively graded by two surgeons who had not performed the treatment, using MRI before and after treatments, as follows: excellent (>50% decrease), good (>25% decrease), fair (<25% decrease), and poor (increase in size). Improvement in symptoms was assessed by reviewing patients’ medical charts documented based on the patients’ report at a later follow-up.
3. Results
3.1. Patients’ Characteristics
Fourteen consecutive patients (six female and eight male) with oropharyngolaryngeal VMs were included in this study. Their median patient age at presentation was 26 years (range, 4–71). Their symptoms were breathing difficulties (n = 3), snoring (n = 2), sleep apnea (n = 1), and swallowing difficulties (n = 1). Lesions were extensive in the face and neck (n = 9) and limited in the oropharyngolarynx (n = 5). Patients with extensive lesions had more symptoms than patients with limited lesions, although this difference was not statistically significant. (56% vs. 20%; p = 0.3).
A permanent tracheostomy was performed in two patients at presentation, while a temporary tracheostomy was performed in five patients, which closed spontaneously in four patients after the end of treatment, after the removal of the tracheostomy tube in three patients (duration, 2–28 months), and operatively in one patient (duration, 55 months). Eight patients are receiving ongoing treatment for oropharyngolaryngeal VMs with further sclerotherapy sessions. Table 1 summarizes the clinical characteristics of the patients.

Table 1.
Clinical characteristics of the patients.
3.2. Treatment Outcomes
The treated regions included the soft palate (n = 8), pharynx (n = 7), base of the tongue (n = 4), and epiglottis (n = 1). The median number of sclerotherapy sessions per patient was 2.5 (range, 1–9). The median dose of foamed sclerosing solution per session was 18 mL (range, 3.5–60; polidocanol, 114 mg, range, 21–360). The median follow-up duration after the first sclerotherapy session was 81 months (range, 6–141). Treatment outcomes were graded as excellent (n = 2), good (n = 7), or fair (n = 5). All symptoms were improved at later follow-up.
The only post-treatment complication was bleeding (n = 1). At the end of the first sclerotherapy session for the lesion of the tongue, persistent oozing bleeding from the base of the tongue was noted. Since packing with gauze did not stop the bleeding, an urgent tracheostomy was performed, and the patient was transferred to the intensive care unit with gauze packing overnight. The next morning, the bleeding had stopped spontaneously. Table 2 summarizes the treatment outcomes of the patients. Representative cases are shown in Figure 2, Figure 3 and Figure 4 (Patients 1, 2, and 10).

Table 2.
Treatment outcomes of the patients.
4. Discussion
Vascular malformations are vascular structural abnormalities that do not present neoplastic proliferation of the vascular endothelial cells, in contrast to hemangiomas [21]. They are classified by the International Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies (ISSVA) based on their affected vascular components (i.e., capillary, lymphatic, venous, arteriovenous, or combined) [22]. VMs are the most common slow-flow congenital vascular malformations, characterized by dilated venous channels of different sizes and shapes with abnormal smooth muscles [4]. Common symptoms of VMs include pain [23], swelling, bleeding, disfigurement, and functional impairment based on the distribution of lesions [24]. In patients with oropharyngolaryngeal VMs, specific symptoms include breathing, speech, and swallowing difficulties [5,6,25]. As VMs enlarge through expansion stimulated by hormonal changes, trauma, infection, or thrombosis [4,26], asymptomatic oropharyngolaryngeal VMs may pose a potential risk of airway obstruction throughout life.
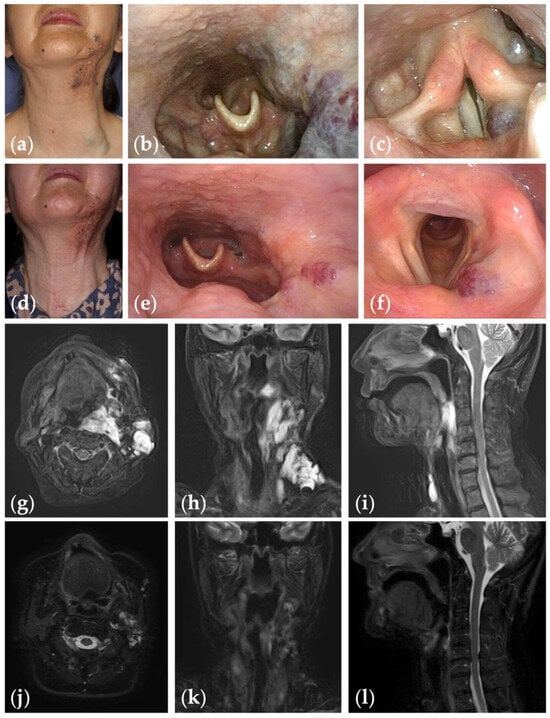
Figure 2.
Patient 1 graded “excellent” for treatment outcomes after nine sessions of fluoroscopy- and endoscopy-guided transoral sclerotherapy: (a) initial clinical photograph, (b) endoscopic photographs of the pharynx; and (c) the glottis of a 67-year-old woman with oropharyngolaryngeal venous malformation; (d) clinical photograph; (e) endoscopic photographs of the pharynx; and (f) the glottis six months after the final sclerotherapy session at the age of 75 years; (g–i) fat-suppressed T2-weighted magnetic resonance images before treatment; (j–l) short tau inversion recovery T2-weighted magnetic resonance images six months after the final sclerotherapy session.
Figure 2.
Patient 1 graded “excellent” for treatment outcomes after nine sessions of fluoroscopy- and endoscopy-guided transoral sclerotherapy: (a) initial clinical photograph, (b) endoscopic photographs of the pharynx; and (c) the glottis of a 67-year-old woman with oropharyngolaryngeal venous malformation; (d) clinical photograph; (e) endoscopic photographs of the pharynx; and (f) the glottis six months after the final sclerotherapy session at the age of 75 years; (g–i) fat-suppressed T2-weighted magnetic resonance images before treatment; (j–l) short tau inversion recovery T2-weighted magnetic resonance images six months after the final sclerotherapy session.
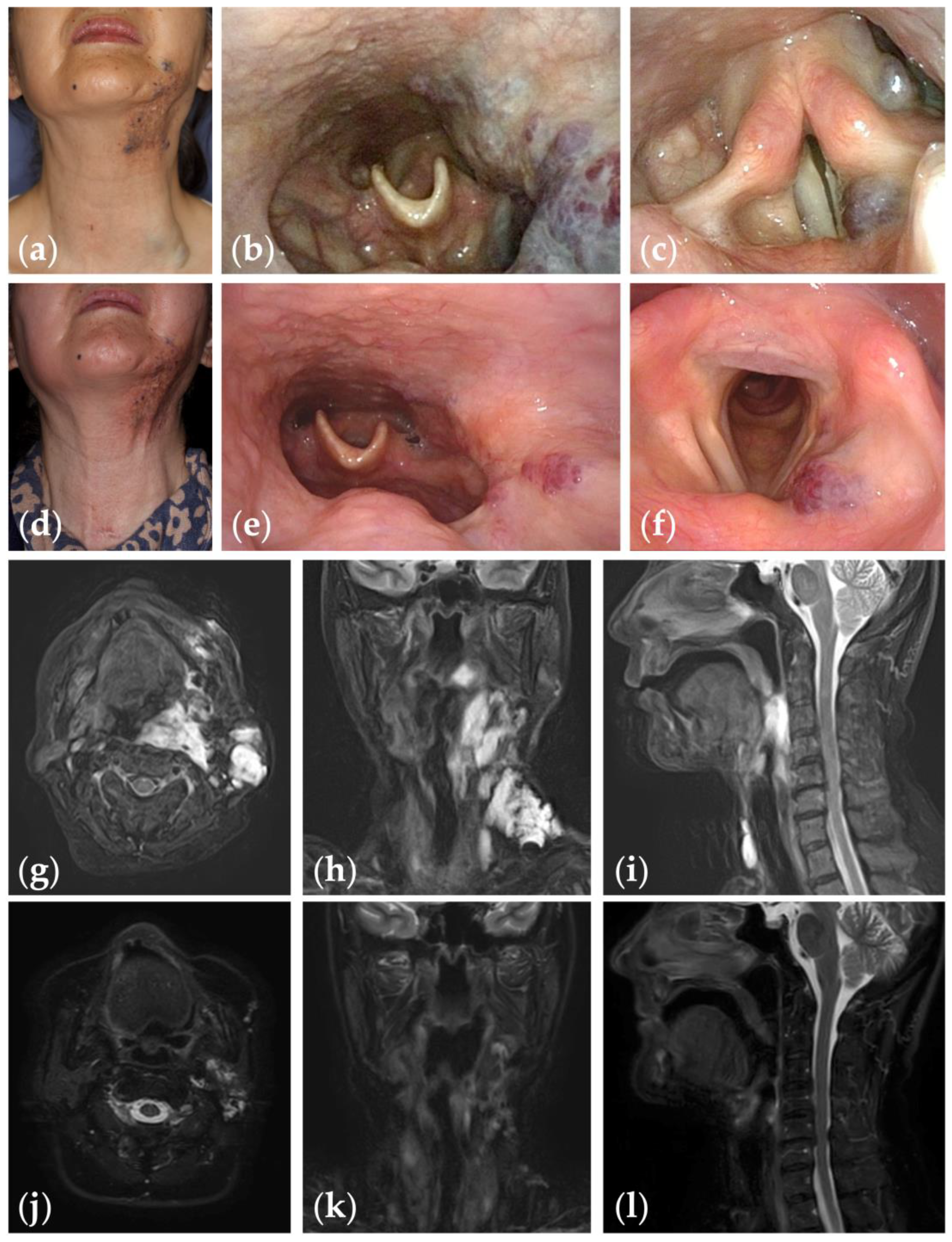
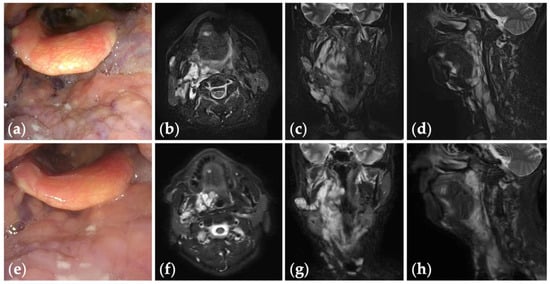
Figure 3.
Patient 2 graded “good” for treatment outcomes after seven sessions of fluoroscopy- and endoscopy-guided transoral sclerotherapy: (a) an initial endoscopic photograph of the pharynx of a 71-year-old man with oropharyngolaryngeal venous malformation, and (e) the latest endoscopic photograph six months after the fifth sclerotherapy session at the age of 73 years; (b–d) short tau inversion recovery T2-weighted magnetic resonance images before treatment, and (f–h) three years after the final sclerotherapy session at the age of 78 years.
Figure 3.
Patient 2 graded “good” for treatment outcomes after seven sessions of fluoroscopy- and endoscopy-guided transoral sclerotherapy: (a) an initial endoscopic photograph of the pharynx of a 71-year-old man with oropharyngolaryngeal venous malformation, and (e) the latest endoscopic photograph six months after the fifth sclerotherapy session at the age of 73 years; (b–d) short tau inversion recovery T2-weighted magnetic resonance images before treatment, and (f–h) three years after the final sclerotherapy session at the age of 78 years.
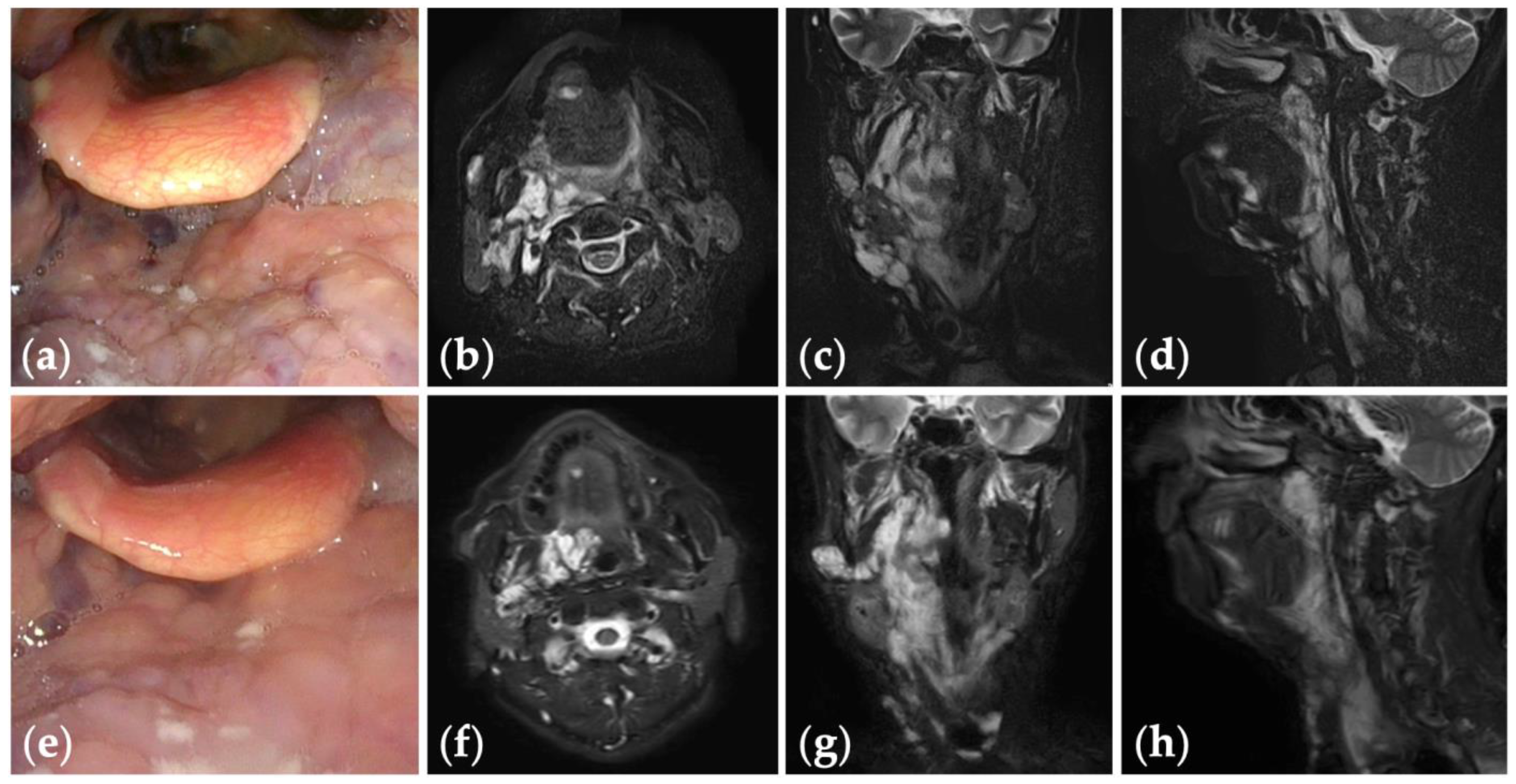
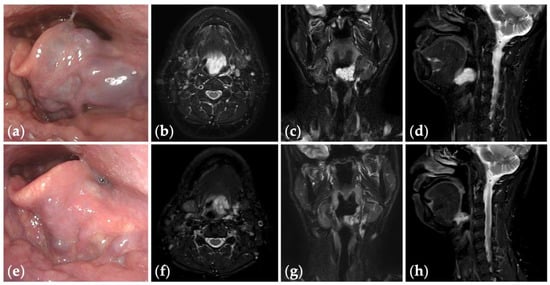
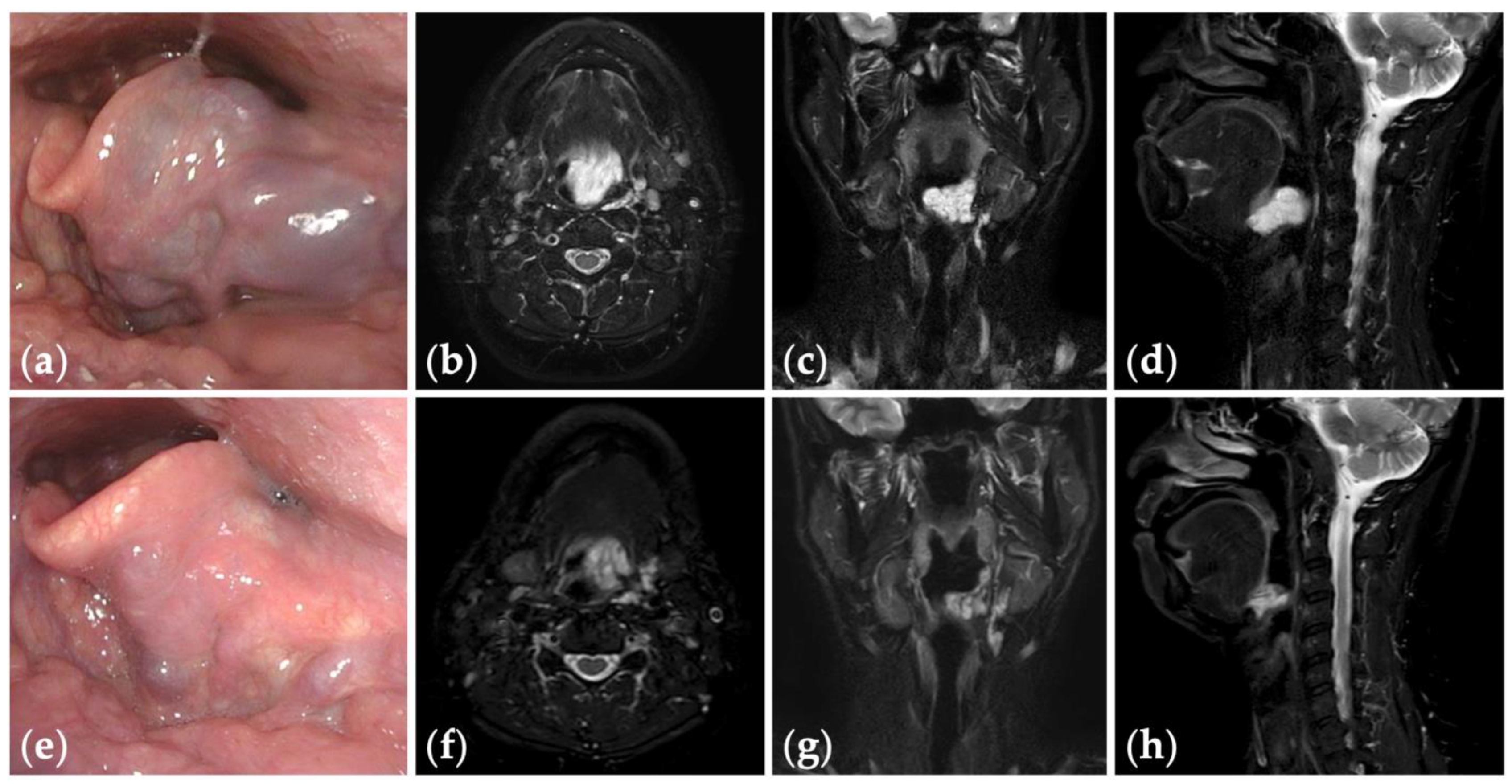
Figure 4.
Patient 10 graded “excellent” for treatment outcomes after three sessions of fluoroscopy- and endoscopy-guided transoral sclerotherapy: (a) an initial endoscopic photograph of the epiglottis of a 43-year-old man with pharyngeal venous malformation, and (e) the latest endoscopic photograph six months after the final sclerotherapy session at the age of 45 years; (b–d) short tau inversion recovery T2-weighted magnetic resonance images before treatment, and (f–h) three years after the final sclerotherapy session at the age of 47 years.
Figure 4.
Patient 10 graded “excellent” for treatment outcomes after three sessions of fluoroscopy- and endoscopy-guided transoral sclerotherapy: (a) an initial endoscopic photograph of the epiglottis of a 43-year-old man with pharyngeal venous malformation, and (e) the latest endoscopic photograph six months after the final sclerotherapy session at the age of 45 years; (b–d) short tau inversion recovery T2-weighted magnetic resonance images before treatment, and (f–h) three years after the final sclerotherapy session at the age of 47 years.
Imaging is critically important in the diagnosis and treatment planning of vascular malformations [12]. Although ultrasound can provide real-time information of vascularity (fast-flow or slow-flow), MRI provides high-contrast resolution and assessment of anatomical structures without radiation exposure [27]. The standard contrast-enhanced MRI protocol includes pre-contrast axial T1-weighted imaging (WI), multiplanar T2WI, and post-gadolinium multiplanar T1WI sequences [27].
MRIs of VMs show multilocular and lobulated masses that are hypointense or isointense to the muscle on T1WI and hyperintense on T2WI [12]. A more heterogenous appearance can be observed within the setting of hemorrhage or thrombosis in the lesions [11]. These lesions frequently infiltrate into adjacent muscles, joints, nerves, ligaments, and organs [28]. VMs can be confirmed with late enhancement (later than 6 sec after arterial enhancement), absence of flow voids, and the presence of dilated venous spaces [29]. Lower signal areas may represent phleboliths on all imaging sequences [11].
Sclerotherapy is an established minimally invasive treatment option for VMs [4], involving direct cannulation of the lesion and injection of sclerosants [30]. The sclerosants damage the vascular endothelial cells, causing thrombosis and subsequent fibrosis [30]. Absolute ethanol [31], polidocanol [32], ethanolamine oleate [33], bleomycin [34], and sodium tetradecyl sulfate [7] are frequently used sclerosants for VMs of the head and neck [35]. Absolute ethanol is the most effective sclerosant; however, it causes potential side effects such as local tissue necrosis and permanent nerve damage [4]. Polidocanol is a non-ionic detergent and less potent sclerosant with fewer side effects than absolute ethanol [36]. Foamed polidocanol can cause more severe damage to the intima of the veins, compared with the liquid form [14]. We previously preferred to use absolute ethanol and foamed polidocanol for the sclerotherapy of VMs [15,16,37,38], while we used only foamed polidocanol for oropharyngolaryngeal VMs.
Due to their anatomical location, sclerotherapy of oropharyngolaryngeal VMs poses formidable challenges in terms of needle access difficulties, the risk of local side effects, and subsequent airway management. Sclerosants cause swelling, with a considerable risk of airway obstruction [8]. A temporary tracheostomy was necessary before sclerotherapy of the pharynx and the base of the tongue for subsequent airway management [8,26]. Multimodality-guided sclerotherapy is the preferred treatment strategy for oropharyngolaryngeal VMs, allowing for optimal exposure of the targeted lesion [7,8,9]. The combination of fluoroscopy and endoscopy can make it safe and reproducible, especially in a hybrid OR providing high-resolution DSA and 3D-CT.
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study applying a hybrid OR for the sclerotherapy of vascular malformations. DSA was smoothly performed using the imaging system linked to the radiolucent operating table, controlled by a radiological technologist according to the surgeon’s directions. Finally, the distribution of sclerosant mixed with contrast material could be visualized from the 3D-CT imagery obtained in the hybrid OR.
We demonstrated that fluoroscopy- and endoscopy-guided transoral sclerotherapy can be an effective and safe treatment for oropharyngolaryngeal VMs. Treatment outcomes graded as excellent or good were achieved in 64% of patients. Eight patients had undergone transoral sclerotherapy three or fewer times, with treatment outcomes graded as excellent (n = 1), good (n = 4), or fair (n = 3), although half of them were under ongoing treatment. Patients with extensive lesions required more sclerotherapy sessions than patients with limited lesions (mean number of sclerotherapy sessions per patient, 3.9 vs. 2.6 times, respectively), but 67% of patients with extensive lesions had outcomes graded as excellent or good.
The limitations of this study were its small patient population, a wide range of patients’ ages (4–71 years), and the lack of a control group. Further study is necessary to clarify the effectiveness and safety of fluoroscopy- and endoscopy-guided transoral sclerotherapy in hybrid ORs. Radiation exposure during the procedure is also a concern for patients and medical staff.
5. Conclusions
Fluoroscopy- and endoscopy-guided transoral sclerotherapy in a hybrid OR can be effective and safe for oropharyngolaryngeal VMs, enabling intraoperative assessment of the distribution of sclerosant.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/jcm13082369/s1: Video S1: Fluoroscopy- and endoscopy-guided transoral sclerotherapy in the hybrid operation room (Patient 10).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.I., Y.Y. and S.S.; methodology, K.I., N.M., S.M., S.O. and S.S.; validation, K.I., T.M. (Takahiro Miura) and E.F.; formal analysis, K.I. and T.M. (Takahiro Miura); investigation, K.I., N.M., Y.S., D.S. and S.S.; resources, K.I., Y.S., D.S., S.M., S.O. and S.S.; data curation, K.I. and E.F.; writing—original draft preparation, K.I.; writing—review and editing, T.M. (Taku Maeda) and Y.Y.; visualization, K.I.; supervision, S.S. and Y.Y.; project administration, K.I. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and was approved on 14 November 2023 by the Ethics Committee of Tonan Hospital (protocol code 15-2-1).
Informed Consent Statement
Patient consent was waived due to the retrospective nature of this study.
Data Availability Statement
The data supporting this study’s findings are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
| CT | computed tomography |
| DSA | digital subtraction angiography |
| MRI | magnetic resonance imaging |
| OR | operation room |
| VM | venous malformation |
| WI | weighted imaging |
References
- Iihara, K.; Satow, T.; Matsushige, T.; Kataoka, H.; Nakajima, N.; Fukuda, K.; Isozaki, M.; Maruyama, D.; Nakae, T.; Hashimoto, N. Hybrid operating room for the treatment of complex neurovascular and brachiocephalic lesions. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2013, 22, e277–e285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneko, T.; Davidson, M.J. Use of the hybrid operating room in cardiovascular medicine. Circulation 2014, 130, 910–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuetze, K.; Rau, B.; Dehner, C.; Schultheiss, M.; Richter, P.; Cintean, R.; Gebhard, F.; Eickhoff, A. Spine surgery in a state-of-the-art hybrid operating room: An experience of 1745 implanted pedicle screws in the thoracolumbar spine. J. Robot. Surg. 2023, 17, 1365–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berenguer, B.; Burrows, P.E.; Zurakowski, D.; Mulliken, J.B. Sclerotherapy of craniofacial venous malformations: Complications and results. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1999, 104, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamijo, A.; Hatsushika, K.; Kanemaru, S.; Moriyama, M.; Kase, Y.; Masuyama, K. Five adult laryngeal venous malformation cases treated effectively with sclerotherapy. Laryngoscope 2013, 123, 2766–2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourgouin, P.; Thomas-Chausse, F.; Gilbert, P.; Giroux, M.F.; Perigny, S.; Guertin, L.; Dubois, J.; Soulez, G. Effectiveness and safety of sclerotherapy for treatment of low-flow vascular malformations of the oropharyngeal region. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2018, 29, 809–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stimpson, P.; Hewitt, R.; Barnacle, A.; Roebuck, D.J.; Hartley, B. Sodium tetradecyl sulphate sclerotherapy for treating venous malformations of the oral and pharyngeal regions in children. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2012, 76, 569–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oomen, K.P.; Paramasivam, S.; Waner, M.; Niimi, Y.; Fifi, J.T.; Berenstein, A.; Teresa, M.O. Endoscopic transmucosal direct puncture sclerotherapy for management of airway vascular malformations. Laryngoscope 2016, 126, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azene, E.; Mitchell, S.; Radvany, M.; Agrawal, N.; Eisele, D.; Weiss, C. Foamed bleomycin sclerosis of airway venous malformations: The role of interspecialty collaboration. Laryngoscope 2016, 126, 2726–2732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, J.S.; Hoffer, F.A.; Barnes, P.D.; Mulliken, J.B. Biological classification of soft-tissue vascular anomalies: MR correlation. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 1991, 157, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Legiehn, G.M.; Heran, M.K. Venous malformations: Classification, development, diagnosis, and interventional radiologic management. Radiol. Clin. N. Am. 2008, 46, 545–597, vi. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, R.; Chaudry, G. Diagnostic imaging of vascular anomalies. Clin. Plast. Surg. 2011, 38, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ameer, F.; Singh, A.K.; Kumar, S. The story of mouth gags. J. Cleft Lip Palate Craniofacial Anom. 2014, 1, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessari, L.; Cavezzi, A.; Frullini, A. Preliminary experience with a new sclerosing foam in the treatment of varicose veins. Dermatol. Surg. 2001, 27, 58–60. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ishikawa, K.; Sasaki, S.; Furukawa, H.; Nagao, M.; Iwasaki, D.; Saito, N.; Yamamoto, Y. Preliminary experience with intraoperative near-infrared fluorescence imaging in percutaneous sclerotherapy of soft-tissue venous malformations. Dermatol. Surg. 2013, 39, 907–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishikawa, K.; Sasaki, S.; Furukawa, H.; Maeda, T.; Miura, T.; Sasaki, Y.; Yamamoto, Y.; Funayama, E. Effectiveness and safety of percutaneous sclerotherapy using absolute ethanol and/or polidocanol for maxillofacial venous malformations involving the masticatory muscles: A case series. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2023, 135, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabe, E.; Pannier, F. Sclerotherapy of varicose veins with polidocanol based on the guidelines of the German Society of Phlebology. Dermatol. Surg. 2010, 36 (Suppl. S2), 968–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Lin, X.; Chen, H.; Li, W.; Hu, X.; Ma, G.; Zhu, L.; Sun, M.; Yang, C.; Wang, W. Craniofacial venous malformations: Magnetic resonance imaging features that predict treatment outcome. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2009, 67, 2388–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, A.B.; Hoogstraten, B.; Staquet, M.; Winkler, A. Reporting results of cancer treatment. Cancer 1981, 47, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwashina, Y.; Ozaki, M.; Wong, M.; Ihara, A.; Fujiki, M.; Takushima, A.; Harii, K. Sclerotherapy for venous malformations of the pharynx or the tongue base without tracheostomy: Treatment protocol with intubation and outcomes. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2020, 31, 702–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulliken, J.B.; Glowacki, J. Hemangiomas and vascular malformations in infants and children: A classification based on endothelial characteristics. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1982, 69, 412–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISSVA Classification of Vascular Anomalies ©2018 International Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies. Available online: https://www.issva.org/classification (accessed on 29 January 2024).
- Rikihisa, N.; Akita, S.; Osuga, K.; Mimura, H.; Yuzuriha, S.; Sasaki, S. Evaluation of pain incidence due to venous malformation based on data from 85 institutions in Japan. J. Vasc. Surg. Venous Lymphat. Disord. 2020, 8, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, V.F.; Masthoff, M.; Czihal, M.; Cucuruz, B.; Haberle, B.; Brill, R.; Wohlgemuth, W.A.; Wildgruber, M. Imaging of peripheral vascular malformations—Current concepts and future perspectives. Mol. Cell Pediatr. 2021, 8, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, P.L.; Eckard, D.A.; Brecheisen, M.A.; Girod, D.A.; Tsue, T.T. Percutaneous ethanol sclerotherapy of venous malformations of the tongue. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2002, 23, 779–782. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Araslanova, R.; Min-Jung, O.T.; Waner, M. Endoscopic multimodal approach to the treatment of airway venous malformations. Laryngoscope 2021, 131, E521–E524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, L.J.; Koshy, J.; Mitchell, S.E.; Weiss, C.R.; Carson, K.A.; Huisman, T.A.; Tekes, A. Time-resolved contrast-enhanced MRA (TWIST) with gadofosveset trisodium in the classification of soft-tissue vascular anomalies in the head and neck in children following updated 2014 ISSVA classification: First report on systematic evaluation of MRI and TWIST in a cohort of 47 children. Clin. Radiol. 2016, 71, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moukaddam, H.; Pollak, J.; Haims, A.H. MRI characteristics and classification of peripheral vascular malformations and tumors. Skelet. Radiol. 2009, 38, 535–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Rijswijk, C.S.; van der Linden, E.; van der Woude, H.J.; van Baalen, J.M.; Bloem, J.L. Value of dynamic contrast-enhanced MR imaging in diagnosing and classifying peripheral vascular malformations. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2002, 178, 1181–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hein, K.D.; Mulliken, J.B.; Kozakewich, H.P.; Upton, J.; Burrows, P.E. Venous malformations of skeletal muscle. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2002, 110, 1625–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamba, S.; Keshava, S.K.N.; Moses, V.; Surendrababu, N.; Gupta, A.K. Ethanol sclerotherapy for treatment of venous malformations of face and neck— a single centre experience. Eur. J. Plast. Surg. 2012, 35, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaise, S.; Charavin-Cocuzza, M.; Riom, H.; Brix, M.; Seinturier, C.; Diamand, J.M.; Gachet, G.; Carpentier, P.H. Treatment of low-flow vascular malformations by ultrasound-guided sclerotherapy with polidocanol foam: 24 cases and literature review. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2011, 41, 412–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, M.D.; McTaggart, R.A.; Choudhri, O.A.; Marcellus, M.L.; Do, H.M. Percutaneous sclerotherapy with ethanolamine oleate for venous malformations of the head and neck. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2014, 6, 695–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spence, J.; Krings, T.; TerBrugge, K.G.; Agid, R. Percutaneous treatment of facial venous malformations: A matched comparison of alcohol and bleomycin sclerotherapy. Head Neck 2011, 33, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horbach, S.E.; Lokhorst, M.M.; Saeed, P.; de Gouyon Matignon de Pontouraude, C.M.; Rothova, A.; van der Horst, C.M. Sclerotherapy for low-flow vascular malformations of the head and neck: A systematic review of sclerosing agents. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2016, 69, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, B.; Yang, B.; Nie, Q.Q.; Zhang, J.B.; Chen, J.; Liu, P.; Fan, X.Q.; Ye, Z.D. Comparison of polidocanol foam versus bleomycin polidocanol foam for treatment of venous malformations. J. Vasc. Surg. Venous Lymphat. Disord. 2023, 11, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furukawa, H.; Sasaki, S.; Oyama, A.; Funayama, E.; Hayashi, T.; Saito, N.; Nagao, M.; Mol, W.; Yamamoto, Y. Efficacy of percutaneous ethanol sclerotherapy for venous malformation in lower extremities: A retrospective review of 21 cases. Eur. J. Plast. Surg. 2013, 36, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, K.; Sasaki, S.; Furukawa, H.; Nagao, M.; Iwasaki, D.; Fujita, M.; Saito, N.; Oyama, A.; Yamamoto, Y. A case of combined soft tissue and intraosseous venous malformation of the thumb treated with sclerotherapy using a bone marrow aspiration needle. Cas. Rep. Plast. Surg. Hand Surg. 2015, 2, 37–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).