Frequency, Severity, Risk Factors, and Outcome of Hemorrhagic Transformation in Anterior and Posterior Stroke
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Inclusion/Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Demographic and Basic Clinical Parameters
2.4. Imaging
2.5. Definition of HT
2.6. Outcome Measures
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rethemiotaki, I. Global prevalence of cardiovascular diseases by gender and age during 2010–2019. Arch. Med. Sci. Atheroscler. Dis. 2023, 8, e196–e205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Havenon, A.; Zhou, L.W.; Johnston, K.C.; Dangayach, N.S.; Ney, J.; Yaghi, S.; Sharma, R.; Abbasi, M.; Delic, A.; Majersik, J.J.; et al. Twenty-Year Disparity Trends in United States Stroke Death Rate by Age, Race/Ethnicity, Geography, and Socioeconomic Status. Neurology 2023, 101, e464–e474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzik, A.; Bushnell, C. Stroke Epidemiology and Risk Factor Management. Continuum 2017, 23, 15–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamson, J.; Beswick, A.; Ebrahim, S. Is stroke the most common cause of disability? J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2004, 13, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takashima, N.; Arima, H.; Kita, Y.; Fujii, T.; Miyamatsu, N.; Komori, M.; Sugimoto, Y.; Nagata, S.; Miura, K.; Nozaki, K. Incidence, Management and Short-Term Outcome of Stroke in a General Population of 1.4 Million Japanese- Shiga Stroke Registry. Circ. J. 2017, 81, 1636–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hacke, W.; Kaste, M.; Fieschi, C.; von Kummer, R.; Davalos, A.; Meier, D.; Larrue, V.; Bluhmki, E.; Davis, S.; Donnan, G.; et al. Randomised double-blind placebo-controlled trial of thrombolytic therapy with intravenous alteplase in acute ischaemic stroke (ECASS II). Lancet 1998, 352, 1245–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, K.; An, X.; Kong, Y.; Chen, Z. Predictive model for the risk of hemorrhagic transformation after rt-PA intravenous thrombolysis in patients with acute ischemic stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2024, 239, 108225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Gu, Y.; Zhang, D.Z. Cerebral circulation time on DSA after thrombectomy associated with hemorrhagic transformation in acute ischemic stroke. Acta Neurochir. 2024, 166, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, H.; Wang, N.; Lv, M.; Yang, Y.; Liu, H. The early predictive value of platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio to hemorrhagic transformation of young acute ischemic stroke. Asian Biomed. 2023, 17, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.; Wei, M.; Feng, X.; Luo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xia, J. Hemorrhagic transformation in patients with large-artery atherosclerotic stroke is associated with the gut microbiota and lipopolysaccharide. Neural Regen. Res. 2024, 19, 1532–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirtas, B.S.; Ocek, L.; Zorlu, Y.; Oztekin, O. Factors Associated with Hemorrhagic Transformation in Infarctions Involving the Posterior Circulation System. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2019, 28, 2193–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagola, J.; Ribo, M.; Alvarez-Sabin, J.; Rubiera, M.; Santamarina, E.; Maisterra, O.; Delgado-Mederos, R.; Ortega, G.; Quintana, M.; Molina, C.A. Thrombolysis in anterior versus posterior circulation strokes: Timing of recanalization, ischemic tolerance, and other differences. J. Neuroimaging 2011, 21, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Kummer, R.; Broderick, J.P.; Campbell, B.C.; Demchuk, A.; Goyal, M.; Hill, M.D.; Treurniet, K.M.; Majoie, C.B.; Marquering, H.A.; Mazya, M.V.; et al. The Heidelberg Bleeding Classification: Classification of Bleeding Events After Ischemic Stroke and Reperfusion Therapy. Stroke 2015, 46, 2981–2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valentino, F.; Gentile, L.; Terruso, V.; Mastrilli, S.; Aridon, P.; Ragonese, P.; Sarno, C.; Savettieri, G.; D’Amelio, M. Frequency and determinants for hemorrhagic transformation of posterior cerebral stroke: Posterior ischemic stroke and hemorrhagic transformation. BMC Res. Notes 2017, 10, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costru-Tasnic, E.; Gavriliuc, M.; Manole, E. Serum biomarkers to predict hemorrhagic transformation and ischemic stroke outcomes in a prospective cohort study. J. Med. Life 2023, 16, 908–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, L.; Zhang, S.; Wan, K.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X. Risk factors of haemorrhagic transformation for acute ischaemic stroke in Chinese patients receiving intravenous thrombolysis: A meta-analysis. Medicine 2020, 99, e18995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Wang, D.; Wang, F.; Norton, C.; Liu, X.; Selim, M. The Risk of Hemorrhagic Transformation After Thrombolysis for Acute Ischemic Stroke in Chinese Versus North Americans: A Comparative Study. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2018, 27, 2381–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, F.; Labreuche, J.; Haussen, D.C.; Piotin, M.; Steglich-Arnholm, H.; Taschner, C.; Papanagiotou, P.; Lapergue, B.; Dorn, F.; Cognard, C.; et al. Hemorrhagic Transformation After Thrombectomy for Tandem Occlusions. Stroke 2019, 50, 516–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dar, N.Z.; Ain, Q.U.; Nazir, R.; Ahmad, A. Cerebral Microbleeds in an Acute Ischemic Stroke as a Predictor of Hemorrhagic Transformation. Cureus 2018, 10, e3308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagaraja, N.; Tasneem, N.; Shaban, A.; Dandapat, S.; Ahmed, U.; Policeni, B.; Olalde, H.; Shim, H.; Samaniego, E.A.; Pieper, C.; et al. Cerebral Microbleeds are an Independent Predictor of Hemorrhagic Transformation Following Intravenous Alteplase Administration in Acute Ischemic Stroke. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2018, 27, 1403–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terao, T.; Mishina, M.; Takumi, I.; Komaba, Y.; Mizunari, T.; Kobayashi, S.; Yoshida, D.; Teramoto, A. Early computed tomography signs as early predictors of hemorrhagic transformation under heparinization in patients with cardiogenic embolism. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2012, 12, 418–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Zeng, J.; Wang, F.; Zhuang, X.; Chen, X.; Miao, J. Risk factors of hemorrhagic transformation after intravenous thrombolysis with rt-PA in acute cerebral infarction. QJM 2019, 112, 323–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Wang, D.; Li, J.; Lin, J.; Xiong, Y.; Liu, B.; Wei, C.; Wu, B.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, S.; et al. Cerebral Microbleeds Do Not Predict Hemorrhagic Transformation in Acute Ischemic Stroke Patients with Atrial Fibrillation and/or Rheumatic Heart Disease. Curr. Neurovasc. Res. 2017, 14, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darabont, R.O.; Stoicescu, C.; Tiu, C. Therapeutic Challenges in Patients with Noncardioembolic Acute Ischemic Stroke in Need of Double Antiplatelet Therapy for Coronary Artery Disease. Am. J. Ther. 2019, 26, e213–e221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakimi, R.; Garg, A. Imaging of Hemorrhagic Stroke. Continuum 2016, 22, 1424–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lip, G.Y. Stroke in atrial fibrillation: Epidemiology and thromboprophylaxis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2011, 9 (Suppl. S1), 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoppellaro, G.; Granziera, S.; Padayattil Jose, S.; Denas, G.; Bracco, A.; Iliceto, S.; Pengo, V. Minimizing the risk of hemorrhagic stroke during anticoagulant therapy for atrial fibrillation. Expert. Opin. Drug Saf. 2015, 14, 683–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masjuan, J.; De Felipe, A. Secondary prevention in non-valvular atrial fibrillation patients: A practical approach with edoxaban. Int. J. Neurosci. 2017, 127, 716–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fierini, F.; Poggesi, A.; Pantoni, L. Leukoaraiosis as an outcome predictor in the acute and subacute phases of stroke. Expert. Rev. Neurother. 2017, 17, 963–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nighoghossian, N.; Abbas, F.; Cho, T.H.; Geraldo, A.F.; Cottaz, V.; Janecek, E.; Mechtouff, L.; Bischoff, M.; El Khoury, C.; Schott, A.M.; et al. Impact of leukoaraiosis on parenchymal hemorrhage in elderly patients treated with thrombolysis. Neuroradiology 2016, 58, 961–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ancelet, C.; Neveü, S.; Venditti, L.; Cortese, J.; Chassin, O.; Pelissou, C.; Berthou, E.T.; Babin, M.; Nasser, G.; Benoudiba, F.; et al. Pre-treatment risk markers for hemorrhagic transformation in posterior circulation acute ischemic stroke treated with reperfusion therapy. J. Neurol. 2023, 270, 5493–5501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panni, P.; Gory, B.; Xie, Y.; Consoli, A.; Desilles, J.P.; Mazighi, M.; Labreuche, J.; Piotin, M.; Turjman, F.; Eker, O.F.; et al. Acute Stroke with Large Ischemic Core Treated by Thrombectomy. Stroke 2019, 50, 1164–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salehi Omran, S.; Boddu, S.R.; Gusdon, A.M.; Kummer, B.; Baradaran, H.; Patel, P.; Díaz, I.; Navi, B.B.; Gupta, A.; Kamel, H.; et al. Angiographic Blush after Mechanical Thrombectomy is Associated with Hemorrhagic Transformation of Ischemic Stroke. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2018, 27, 3124–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexandre, A.M.; Scarcia, L.; Brunetti, V.; Scala, I.; Kalsoum, E.; Valente, I.; Camilli, A.; De Leoni, D.; Colò, F.; Frisullo, G.; et al. Predictors of parenchymal hematoma and clinical outcome after mechanical thrombectomy in patients with large ischemic core due to large vessel occlusion: A retrospective multicenter study. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2023, jnis-2023-021146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappellari, M.; Pracucci, G.; Saia, V.; Sallustio, F.; Casetta, I.; Fainardi, E.; Capasso, F.; Nencini, P.; Vallone, S.; Bigliardi, G.; et al. Predictors for hemorrhagic transformation and cerebral edema in stroke patients with first-pass complete recanalization. Int. J. Stroke 2023, 18, 1238–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alawieh, A.; Vargas, J.; Turner, R.D.; Turk, A.S.; Chaudry, M.I.; Lena, J.; Spiotta, A. Equivalent favorable outcomes possible after thrombectomy for posterior circulation large vessel occlusion compared with the anterior circulation: The MUSC experience. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2018, 10, 735–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marchis, G.M.; Kohler, A.; Renz, N.; Arnold, M.; Mono, M.L.; Jung, S.; Fischer, U.; Karameshev, A.I.; Brekenfeld, C.; Gralla, J.; et al. Posterior versus anterior circulation strokes: Comparison of clinical, radiological and outcome characteristics. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2011, 82, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorňák, T.; Král, M.; Hazlinger, M.; Herzig, R.; Veverka, T.; Buřval, S.; Šaňák, D.; Zapletalová, J.; Antalíková, K.; Kaňovský, P. Posterior vs. anterior circulation infarction: Demography, outcomes, and frequency of hemorrhage after thrombolysis. Int. J. Stroke 2015, 10, 1224–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, H.; Lee, D.; Lee, D.H.; Suh, D.C.; Kwon, S.U.; Kang, D.W.; Kim, J.S. Etiology-Related Outcome of Endovascular Therapy in Posterior Circulation Stroke Compared to Anterior Circulation Stroke. J. Stroke 2022, 24, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessin, M.S.; Del Zoppo, G.J.; Estol, C.J. Thrombolytic agents in the treatment of stroke. Clin. Neuropharmacol. 1990, 13, 271–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, C.; Fiorelli, M.; Steiner, T.; Schäbitz, W.R.; Bozzao, L.; Bluhmki, E.; Hacke, W.; von Kummer, R. Hemorrhagic transformation of ischemic brain tissue: Asymptomatic or symptomatic? Stroke 2001, 32, 1330–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Parameter | All (n = 253) | ACS (n = 186) | PCS (n = 67) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patient data | ||||
| Age, y (IQR) | 77 (66,83) | 77.5 (68,84) | 72 (58,80) | 0.003 |
| Females, n (%) | 102 (40.3) | 78 (41.9) | 24 (35.8) | 0.128 |
| Arterial hypertension, n (%) | 193 (76.3) | 145 (78) | 48 (71.6) | 0.297 |
| Diabetes mellitus, n (%) | 84 (33.2) | 60 (32.3) | 24 (35.8) | 0.595 |
| LDL, mmol/L (IQR) | 110 (84,139) | 111(87,136) | 106 (78.5,140.5) | 0.729 |
| Previous medications | ||||
| No medications. n (%) | 155 (61.3) | 109 (58.6) | 46 (68.7) | 0.148 |
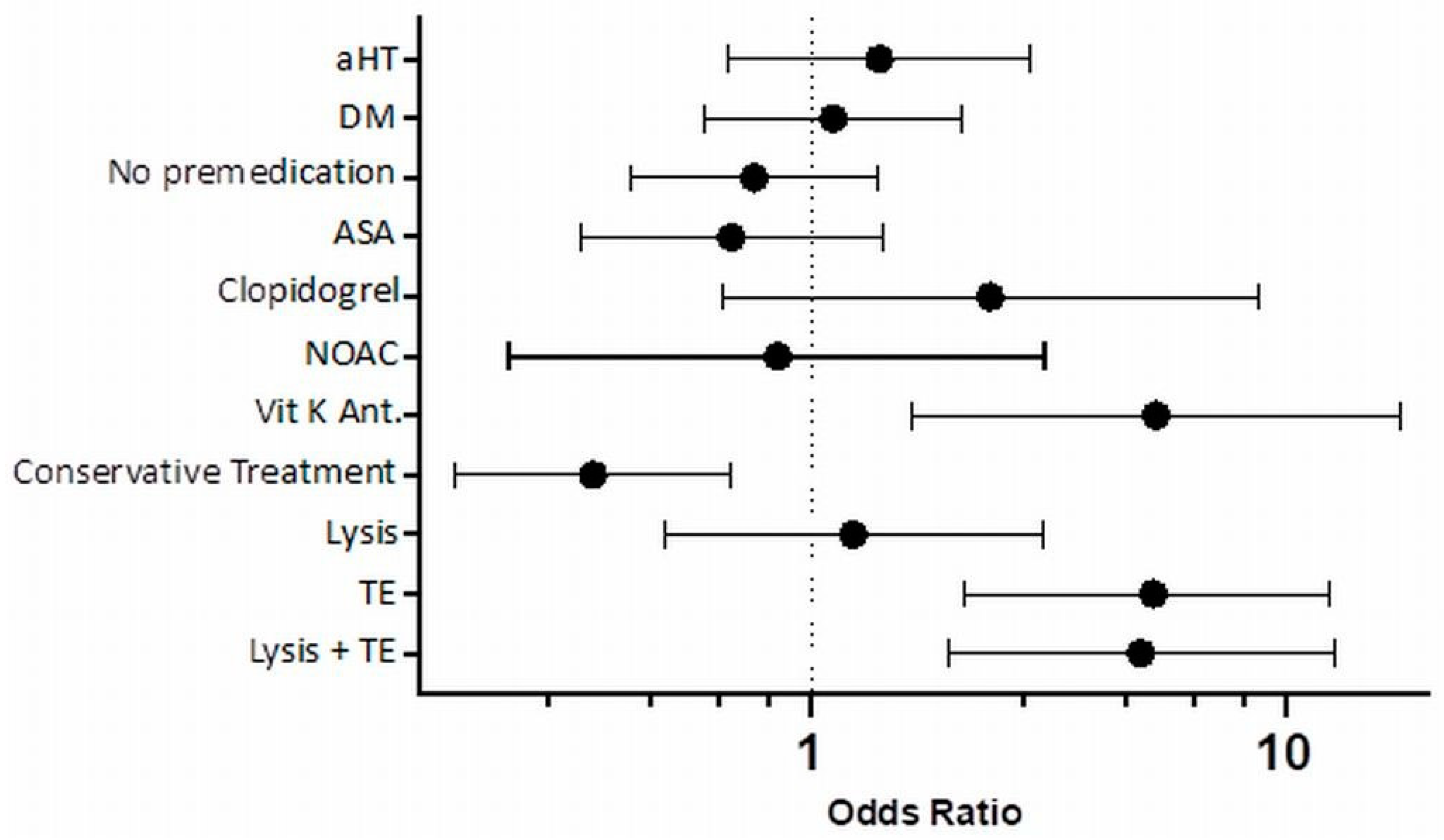
| ASA. n (%) | 62 (24.5) | 52 (28) | 10 (14.9) | 0.034 |
| Clopidogrel. n (%) | 10 (4) | 6 (3.2) | 4 (6) | 0.323 |
| NOAC. n (%) | 15 (5.9) | 12 (6.5) | 3 (4.5) | 0.765 |
| Dabigatran. n (%) | 3 (1.2) | 3 (1.6) | 0 (0) | N/A |
| Rivaroxaban. n (%) | 4 (1.6) | 3 (1.6) | 1 (1.5) | N/A |
| Apixaban. n (%) | 4 (1.6) | 3 (1.6) | 1 (1.5) | N/A |
| Edoxaban. n (%) | 4 (1.6) | 3 (1.6) | 1 (1.5) | N/A |
| Vitamin K antagonist. n (%) | 12 (4.7) | 8 (4.3) | 4 (6) | 0.523 |
| Imaging | ||||
| MRI, n (%) | 182 (71.9) | 126 (67.7) | 56 (83.6) | 0.013 |
| MRI with HS, n (%) | 154 (60.9) | 104 (55.9) | 50 (74.6) | 0.007 |
| Microbleeds, n (%) | ||||
| <10, n (%) | 44 (17.4) | 32 (17.2) | 12 (17.9) | 0.853 |
| >10, n (%) | 7 (2.8) | 5 (2.7) | 2 (3) | >0.999 |
| WML, n (%) | ||||
| Mild, n (%) | 83 (32.8) | 62 (33.3) | 21 (31.3) | 0.184 |
| Moderate–severe, n (%) | 153 (60.5) | 114 (61.3) | 39 (58.2) | 0.167 |
| Therapy-Modality | ||||
| Conservative (antiplatelet) treatment, n (%) | 202 (79.8) | 143 (76.9) | 59 (88.1) | 0.051 |
| Thrombolysis, n (%) | 27 (10.7) | 21 (11.3) | 6 (9) | 0.818 |
| Thrombectomy, n (%) | 4 (1.6) | 3 (1.6) | 1 (1.5) | >0.999 |
| Thrombolysis and thrombectomy, n (%) | 20 (7.9) | 19 (10.2) | 1 (1.5) | 0.031 |
| Parameter | ||||
| NIHSS at hd1 (IQR) | 4 (2,9) | 5 (2,10) | 2 (1,5) | <0.001 |
| NIHSS at hd7 (IQR) | 2 (0.5,7) | 3 (1,8) | 1 (0,3) | 0.006 |
| Parameter | All (n = 253) | ACS (n = 186) | PCS (n = 67) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
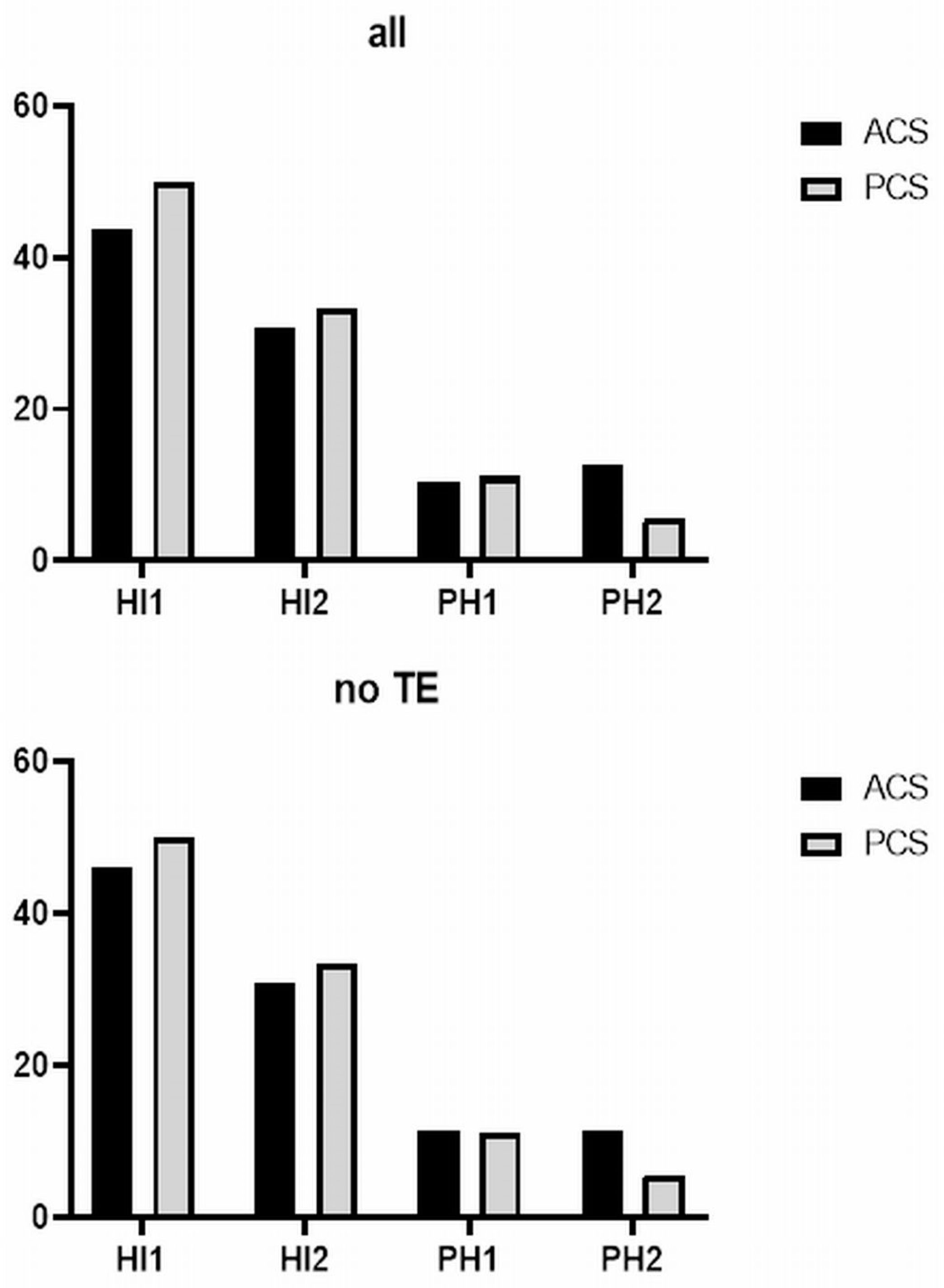
| HT (total), n (%) | 57 (22.5) | 39 (21.0) | 18 (26.9) | 0.322 |
| HI type 1, n (%) | 26 (10.3) | 17 (9.1) | 9 (13.4) | 0.294 |
| HI type 2, n (%) | 18 (7.1) | 12 (6.5) | 6 (9.0) | 0.439 |
| PH type 1, n (%) | 6 (2.4) | 4 (2.2) | 2 (3.0) | 0.644 |
| PH type 2 *, n (%) | 9 (3.6) | 8 (4.3) | 1 (1.5) | 0.691 |
| Treatment type | ||||
| Antiplatelet | 37 (18.3) | 22 (15.4) | 15 (25.4) | 0.094 |
| i.v. thrombolysis only | 7 (25.9) | 4 (19.0) | 3 (50.0) | 0.290 |
| TE only | 2 (50.0) | 2 (66.7) | 0 (0) | N/A |
| Thrombolysis + TE | 11 (55.0) | 11 (57.9) | 0 (0) | N/A |
| Antiplatelet + i.v. thrombolysis (without TE) | 44 (19.2) | 26 (15.9) | 18 (27.7) | 0.040 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ayub, T.; Barwari, A.; Finsterer, J. Frequency, Severity, Risk Factors, and Outcome of Hemorrhagic Transformation in Anterior and Posterior Stroke. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 2010. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13072010
Ayub T, Barwari A, Finsterer J. Frequency, Severity, Risk Factors, and Outcome of Hemorrhagic Transformation in Anterior and Posterior Stroke. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(7):2010. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13072010
Chicago/Turabian StyleAyub, Tanya, Awini Barwari, and Josef Finsterer. 2024. "Frequency, Severity, Risk Factors, and Outcome of Hemorrhagic Transformation in Anterior and Posterior Stroke" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 7: 2010. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13072010
APA StyleAyub, T., Barwari, A., & Finsterer, J. (2024). Frequency, Severity, Risk Factors, and Outcome of Hemorrhagic Transformation in Anterior and Posterior Stroke. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(7), 2010. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13072010






