Extremely Rare Complications in Uniportal Spinal Endoscopy: A Systematic Review with Unique Case Analyses
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Complication Rates
3.2. Common Complications
3.3. Rare Complications
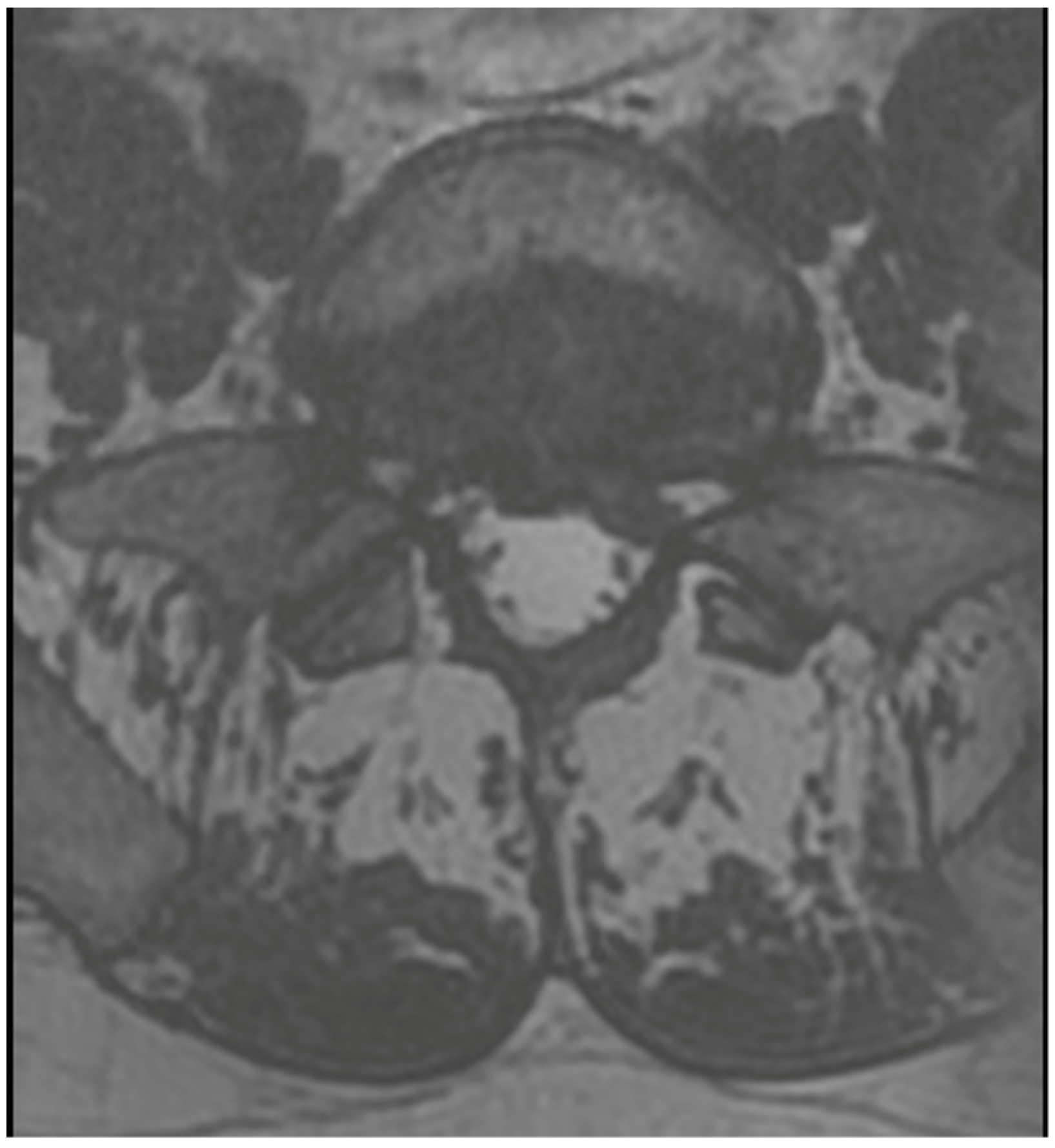
3.4. Case 1: Transient Cauda Equina Syndrome Due to Subdural Hematoma
3.5. Case 2: Sudden Cardiac Arrest Due to Air Embolism
3.6. Case 3: Transient Paraparesis following Iatrogenic Vascular Fistula of the Dural Sac
4. Discussion
4.1. Learning Curve Consideration
4.2. Case Report Reflection
- Case 1: Incidents of postoperative cauda equina syndrome are documented in the context of traditional surgical approaches. In our literature review, we identified a singular case of postoperative cauda equina syndrome, which, however, pertained to a patient following endoscopic intervertebral stabilization. This incident was associated with the migration of bone material into the dural sac [43]. Our case suggests that previous surgery, leading to scarring and adhesions, and anatomical challenges such as steep and large facet joints, might have contributed to the complication by complicating root mobilization and endoscope trajectory.
- Case 2: Air embolism during spinal surgeries is noted primarily in extensive procedures like scoliosis correction [48], according to our literature search. However, we also found a single case description from the 1970s following a discectomy operation [49]. This indicates that while the complication is more commonly linked to major surgeries, it can also occur in less extensive, traditional procedures. No endoscopic cases were found in our literature search. Nevertheless, the use of irrigation pumps instead of gravity flow in endoscopic surgeries can introduce air, potentially leading to embolism. Observations of air bubbles in the endoscopic view underscore the risk, highlighting the need for careful fluid management during these procedures.
- Case 3: Our review did not uncover any literature on intradural hematomas following endoscopic surgery. While there are isolated reports of such hematomas in other contexts [50,51], the dramatic progression and conservative management decision in our case are unique and underscore the need for cautious postoperative monitoring and possibly early intervention in similar future cases.
5. Conclusions
6. Limitations and Strengths
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahn, Y.; Lee, S.G.; Son, S.; Keum, H.J. Transforaminal endoscopic lumbar discectomy versus open lumbar microdiscectomy: A comparative cohort study with a 5-year follow-up. Pain Physician 2019, 22, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarebi, M.; Awaf, A.; Lefranc, M.; Peltier, J. A matched comparison of outcomes between percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy and open lumbar microdiscectomy for the treatment of lumbar disc herniation: A 2-year retrospective cohort study. Spine J. 2021, 21, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.H.; Chung, C.K.; Choi, Y.; Kim, M.J.; Yim, D.; Yang, S.H.; Lee, C.H.; Jung, J.M.; Hwang, S.H.; Kim, D.H.; et al. The Long-term Reoperation Rate Following Surgery for Lumbar Herniated Intervertebral Disc Disease: A Nationwide Sample Cohort Study with a 10-year Follow-up. Spine 2019, 44, 1382–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu, P.G.P.; Lourenço, J.A.; Romero, C.; D’almeida, G.N.; Pappamikail, L.; Lopes, M.F.; Brito, M.; Teles, P.; Correia, J.P. Endoscopic treatment of spondylodiscitis: Systematic review. Eur. Spine J. 2022, 31, 1765–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latka, K.; Kolodziej, W.; Pawlak, K.; Sobolewski, T.; Rajski, R.; Chowaniec, J.; Olbrycht, T.; Tanaka, M.; Latka, D. Fully Endoscopic Spine Separation Surgery in Metastatic Disease-Case Series, Technical Notes, and Preliminary Findings. Medicina 2023, 59, 993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.C.; Lee, C.H.; Wei, L.; Lui, T.N.; Lin, T.J. Comparison of percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy and open lumbar surgery for adjacent segment degeneration and recurrent disc hernation. Neurol. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 791943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.C.; Kim, J.-S.; Park, C.-K. Percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy as an alternative to openlumbar microdiscectomy for Large lumbar disc herniation. Pain Physician 2016, 19, E291–E300. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jing, Z.; Li, L.; Song, J. Percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy versus microendoscopic discectomy for upper lumbar disc herniation: A retrospective comparative study. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2021, 13, 3111–3119. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, W.S.; Yan, Q.; Cong, L. Comparison of Endoscopic Discectomy Versus Non-Endoscopic Discectomy for Symptomatic Lumbar Disc Herniation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Glob. Spine J. 2022, 12, 1012–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.C.; Chen, C.M.; Lin, M.H.; Huang, W.C.; Lee, M.H.; Kim, J.S.; Chen, K.T. Complications of Full-Endoscopic Lumbar Discectomy versus Open Lumbar Microdiscectomy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2022, 168, 333–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Chamoli, U.; Vargas Castillo, J.; Ramakrishna, V.A.S.; Diwan, A.D. Complication rates of different discectomy techniques for symptomatic lumbar disc herniation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Spine J. 2020, 29, 1752–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latka, K.; Kolodziej, W.; Domisiewicz, K.; Pawus, D.; Olbrycht, T.; Niedzwiecki, M.; Zaczynski, A.; Latka, D. Outpatient Spine Procedures in Poland: Clinical Outcomes, Safety, Complications, and Technical Insights into an Ambulatory Spine Surgery Center. Healthcare 2023, 11, 2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Compagnone, D.; Mandelli, F.; Ponzo, M.; Langella, F.; Cecchinato, R.; Damilano, M.; Redaelli, A.; Peretti, G.M.; Vanni, D.; Berjano, P. Complications in endoscopic spine surgery: A systematic review. Eur. Spine J. 2023, 16, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.M.; Chen, A.F.; Lou, X.X.; Zhang, Y.G. Comparison of Three Common Intervertebral Disc Discectomies in the Treatment of Lumbar Disc Herniation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Based on Multiple Data. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, B.; Li, H.; Hou, X.; Yin, L. Comparison of percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy and open lumbar discectomy for lumbar disc herniations: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Surg. 2022, 9, 984868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Lian, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, M.; Zhang, H.; Pei, B.; Hu, C.; Yang, Q. Percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy compared with other surgeries for lumbar disc herniation: A meta-analysis. Medicine 2021, 100, e24747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, R.; Wang, F.; Hong, X.; Wang, Y.T.; Bao, J.P.; Liu, L.; Wang, X.H.; Xie, Z.Y.; Wu, X.T. Comparison of percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy versus microendoscopic discectomy for the treatment of lumbar disc herniation: A meta-analysis. Int. Orthop. 2019, 43, 923–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Lee, S.; Kim, H.S.; Park, S.; Shim, S.Y.; Lim, D.J. A Comparison of Percutaneous Endoscopic Lumbar Discectomy and Open Lumbar Microdiscectomy for Lumbar Disc Herniation in the Korean: A Meta-Analysis. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 9073460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, R.; Liu, B.; Hao, J.; Zhou, P.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, F.; Chen, X. Percutaneous Endoscopic Lumbar Discectomy Versus Posterior Open Lumbar Microdiscectomy for the Treatment of Symptomatic Lumbar Disc Herniation: A Systemic Review and Meta-Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2018, 120, 352–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, W.; Feng, F.; Liu, Z.; Xie, J.; Cai, L.; Ping, A. Comparison of percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy versus open lumbar microdiscectomy for lumbar disc herniation: A meta-analysis. Int. J. Surg. 2016, 31, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruetten, S.; Komp, M.; Merk, H.; Godolias, G. Full-endoscopic interlaminar and transforaminal lumbar discectomy versus conventional microsurgical technique: A prospective, randomized, controlled study. Spine 2008, 33, 931–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.M.; Ahn, S.S.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, Y.D.; Cho, J.H.; Kim, D.H. Comparative Study of the Outcomes of Percutaneous Endoscopic Lumbar Discectomy and Microscopic Lumbar Discectomy Using the Tubular Retractor System Based on the VAS, ODI, and SF-36. Korean J. Spine 2012, 9, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Zhang, P.; Yin, Q. Comparison of tissue damages caused by endoscopic lumbar discectomy and traditional lumbar discectomy: A randomised controlled trial. Int. J. Surg. 2014, 12, 534–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Ha, Y.; Yi, S.; Cao, K. Efficacy of Transforaminal Endoscopic Spine System (TESSYS) Technique in Treating Lumbar Disc Herniation. Med. Sci. Monit. 2016, 22, 530–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, J.N.A.; Subramanian, A.S.; Scott, C.E.H. A randomised controlled trial of transforaminal endoscopic discectomy vs microdiscectomy. Eur. Spine J. 2017, 26, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yuan, S.; Tian, Y.; Wang, L.; Gong, L.; Zheng, Y.; Li, J. Comparison of percutaneous endoscopic transforaminal discectomy, microendoscopic discectomy, and microdiscectomy for symptomatic lumbar disc herniation: Minimum 2-year follow-up results. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2018, 28, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, L.; Dong, J.; Xie, P.; Liu, B.; Wang, Q.; Chen, R.; Feng, F.; Yang, B.; Shu, T.; et al. Percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy compared with microendoscopic discectomy for lumbar disc herniation: 1-year results of an ongoing randomized controlled trial. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2018, 28, 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, L.; Dong, J.; Xie, P.; Liu, B.; Wang, Q.; Chen, R.; Shu, T.; Li, S.; Feng, F.; et al. Percutaneous Transforaminal Endoscopic Discectomy Versus Microendoscopic Discectomy for Lumbar Disc Herniation: Two-Year Results of a Randomized Controlled Trial. Spine 2020, 45, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, G.; DA Rocha, I.D.; Cristante, A.F.; Marcon, R.M.; Coutinho, T.P.; Torelli, A.G.; Petersen, P.A.; Letaif, O.B.; de Barros Filho, T.E.P. Percutaneous Endoscopic Lumbar Discectomy Versus Microdiscectomy for the Treatment of Lumbar Disc Herniation: Pain, Disability, and Complication Rate-A Randomized Clinical Trial. Int. J. Spine Surg. 2020, 14, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, L.; Dong, J.; Xie, P.; Liu, B.; Chen, R.; Li, S.; Liu, Z.; Yang, B.; Feng, F.; et al. Percutaneous Transforaminal Endoscopic Discectomy Versus Microendoscopic Discectomy for Lumbar Disk Herniation: Five-year Results of a Randomized Controlled Trial. Spine 2023, 48, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadjradj, P.S.; Rubinstein, S.M.; Peul, W.C.; Depauw, P.R.; Vleggeert-Lankamp, C.L.; Seiger, A.; van Susante, J.L.; de Boer, M.R.; van Tulder, M.W.; Harhangi, B.S. Full endoscopic versus open discectomy for sciatica: Randomised controlled non-inferiority trial. BMJ 2022, 376, e065846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Li, H.; Qin, W.; Liu, Z.; Liu, H.; Zhang, J.; Mao, H.; Zhang, K.; Chen, K. Comparison of percutaneous endoscopic interlaminar discectomy and conventional open lumbar discectomy for L4/5 and L5/S1 double-segmental lumbar disk herniation. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2023, 18, 950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Chhawra, S.; Jain, R.; Singh, G. Full transforaminal endoscopic discectomy versus microlumbar discectomy for lumbar disc herniation: 2-year results. Indian Spine J. 2024, 7, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, Y.; Kim, J.U.; Lee, B.H.; Lee, S.H.; Park, J.D.; Hong, D.H.; Lee, J.H. Postoperative retroperitoneal hematoma following transforaminal percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2009, 10, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Zhang, G.; Panchal, R.R.; Ren, X.; Xiang, H.; Xuexiao, M.; Chen, X.; Tongtong, G.; Hong, W.; Dixson, A.D. Unique Complications of Percutaneous Endoscopic Lumbar Discectomy and Percutaneous Endoscopic Interlaminar Discectomy. Pain Physician 2018, 21, E105–E112. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, B.; Jiang, Y.; Shang, L.; Yan, M.; Ma, H.J.; Ren, D.J.; Liu, X.G. Complications of Percutaneous Endoscopic Lumbar Discectomy: Experiences and Literature Review. J. Spine 2017, 6, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ai, P.; Zhan, G.; Shen, B. Lumbar artery injury during transforaminal percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy: Successful treatment by emergent transcatheter arterial embolization. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2018, 53, 267.e11–267.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Wang, X.-D.; Nie, H.-F.; Yang, Z.-Q.; Chen, K.; Li, Z.-H.; Song, Y.-M.; Pei, F.-X.; Zeng, J.-C. Negative pressure pulmonary edema after percutaneous endoscopic interlaminar lumbar discectomy—A case report. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2018, 19, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, W.; Wang, H.; Zhu, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Lu, G.; Ni, B. Nerve root entrapment with pseudomeningocele after percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy: A case report. J. Spinal Cord. Med. 2020, 43, 552–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liang, S.; Xie, W.; Luo, J.; Tang, J.; Liu, L.; Li, Y.; Wu, C.; Li, X. Symptomatic postoperative discal pseudocyst following percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy: A case report and review of the literature. Medicine 2021, 100, e24026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, X.; Chen, P.; Shen, J.; Chen, J.; Ge, Y.; Ji, W. Why does such a cyst appear after unilateral biportal endoscopy surgery: A case report and literature review. Medicine 2023, 102, e36665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, J.; Qin, Z.; Deng, Y.; Li, M.; Li, Y. Clinical Features and Management of Seizure after Percutaneous Endoscopic Spine Surgery: A Retrospective Case Series Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2022, 167, e891–e903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Li, Q.; Liu, Y.; Gu, D.; Qi, J.; Xu, K.; Ming, H.; Fan, X.; Chen, R. Cauda Equina Syndrome Caused by Intradural Bone Graft Materials after Endoscopic Lumbar Fusion. Orthopedics 2023, 46, e384–e386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, J.N.; Cowie, J.G.; Iprenburg, M. Transforaminal endoscopic spinal surgery: The future ‘gold standard’ for discectomy?—A review. Surgeon 2012, 10, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golan, J.D.; Elkaim, L.M.; Alrashidi, Q.; Georgiopoulos, M.; Lasry, O. Economic comparisons of endoscopic spine surgery: A systematic review. Eur. Spine J. 2023, 32, 2627–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erken, H.Y.; Yilmaz, O. Collimation Reduces Radiation Exposure to the Surgeon in Endoscopic Spine Surgery: A Prospective Study. J. Neurol. Surg. A Cent. Eur. Neurosurg. 2022, 83, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotheeranurak, V.; Liawrungrueang, W.; Quillo-Olvera, J.; Siepe, C.J.; Li, Z.Z.; Lokhande, P.V.; Choi, G.; Ahn, Y.; Chen, C.M.; Choi, K.C.; et al. Full-Endoscopic Lumbar Discectomy Approach Selection: A Systematic Review and Proposed Algorithm. Spine 2023, 48, 534–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haji Mohd Amin, M.Z.; Beng, J.T.B.; Young, B.T.Y.; Faruk Seman, N.A.; Ching, T.S.; Chek, W.C. A case of cardiac arrest due to air embolism during scoliosis surgery. J. Orthop. Surg. 2019, 27, 2309499019840083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albin, M.S. Venous air embolism and lumbar disk surgery. JAMA 1978, 240, 1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymaekers, V.; Beck, T.; Goebel, S.; Janssens, F.; Van den Branden, L.; Menovsky, T.; Plazier, M. An Acute Spinal Intradural Hematoma after an Extraforaminal Wiltse Approach: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. J. Neurol. Surg. A Cent. Eur. Neurosurg. 2021, 82, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcinek, M.; Tkocz, M.; Marczewski, K.; Partyka, R.; Kukulski, L.; Młynarek-Śnieżek, K.; Sędziak-Marcinek, B.; Rajwa, P.; Berezowski, A.; Kokocińska, D. Evaluation of Parameters Affecting the Occurrence of Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome in Patients Operated on Due to Kidney Tumors. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| Author | Journal | TELD | IELD | MLD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compagnone et al. (2023) [13] | European Spine Journal | 5.2 | 3.1 | N/A |
| Li et al. (2022) [9] | Global Spine Journal | 4.3 | 14.6 | |
| Zhao et al. (2022) [14] | Journal of Clinical Medicine | No significant differences | ||
| Yang et al. (2022) [10] | World Neurosurgery | 5.5 (RCT meta-analysis) 6.4 (Cohort meta-analysis) | 10.4 (RCT meta-analysis) 4.0 (Cohort meta-analysis) | |
| Zhang et al. (2022) [15] | Frontiers in surgery | No significant differences | ||
| Bai et al. (2021) [16] | Medicine | 6.79 | 6.36 | |
| Chen et al. (2020) [11] | European Spine Journal | 5.8 | 16.8 | |
| Shi et al. (2019) [17] | International Orthopaedics | 6.8 (54/778) | 7.61 (57/749) | |
| Kim et al. (2018) [18] | Hindawi BioMed Research International | No significant differences | ||
| Qin et al. (2018) [19] | World Neurosurgery | 3.6 | 3.53 | |
| Ruan et al. (2016) [20] | International Journal of Surgery | 4.69 | 2.33 | |
| Pooled Risk | 5.34 ± 1.32 | 8.2 ± 3.95 | ||
| Compagnone et al. (2023) [13] | Shi et al. (2019) [17] | Qin et al. (2018) [19] | Yang et al. (2022) [10] | Zhou et al. (2018) [14] | Pooled Risk | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IELD | TELD | RCT | COHORT | |||||
| hematoma | 0.06 | 0.04 | N/A | 0 | 0 | 0.1 | N/A | 0.05 ± 0.03 |
| residual disc | 0.3 | 1.0 | 4.25 | N/A | 0.7 | 3.1 | 1.4 | 1.79 ± 1.49 |
| neurologic deficit | 0.3 | 0.3 | N/A | N/A | 0 | 0.1 | N/A | 0.23 ± 0.2 |
| dysesthesia | 1.3 | 1.5 | 1.7 | 4.1 | 2.6 | N/A | 2.24 ± 0.94 | |
| dural tear | 0.9 | 0.7 | 0.68 | 0.76 | 1.0 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 0.81 ± 0.11 |
| nerve root injury | N/A | N/A | N/A | 0.38 | 0 | 0.6 | 1.2 | 0.55 ± 0.53 |
| discitis | N/A | N/A | N/A | 0.38 | 0 | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| instability | 0.1 | 0.2 | N/A | N/A | N/A | 0 | N/A | N/A |
| infection | N/A | N/A | N/A | 0 | 0 | 0 | N/A | N/A |
| reoperation | N/A | N/A | 4.03 | N/A | 4.8 | 7.6 | N/A | 5.48 ± 2.08 |
| Author | Type | Age | Quantity (n) | Dural Tear | Neural Injury | Transient Dysesthesia | Persisted Pain | Hematoma | Motor Weakness | Post Operative Urinary Retention | Wound Heeling/INFECTION | Residue/Recurrence | Total No. of Complications | Reoperation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rueten et al. (2008) [21] | TELD | 43 | 41 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 4 | 3 |
| IELD | 43 | 59 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 6 | 4 | |
| MLD | 43 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 3 | 2 | 5 | 17 | 5 | |
| Yoon et al. (2012) [22] | PELD | 45.88 | 37 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 0 |
| MLD | 56.46 | 35 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 0 | |
| Lei Pan et al. (2014) [23] | PELD | N/A | 10 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MLD | N/A | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Gibson et al. (2016) [24] | TELD | 42 ± 9 | 70 | 2 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 9 | 5 |
| MLD | 39 ± 9 | 70 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | |
| Zhimin Pan et al. (2016) [25] | TELD | 39.5 | 48 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 |
| MLD | 42.8 | 58 | 2 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 13 | 0 | |
| Liu et al. (2018) [26] | TELD | 36.2 ± 5.9 | 60 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 5 | 0 |
| MED | 33.1 ± 6.2 | 89 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 6 | 0 | |
| MLD | 34.0 ± 3.8 | 105 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 5 | 0 | |
| Chen et al. (2018) [27] | TELD | 40.9 ± 11.9 | 80 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 11 | 5 |
| MED | 41.0 ± 10.8 | 73 | 1 | 0 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 12 | 3 | |
| Chen et al. (2019) [28] | TELD | 40.9 ± 11.9 | 119 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6/4 | 16 | 10 |
| MLD | 41.0 ± 10.8 | 122 | 3 | 1 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0/5 | 19 | 5 | |
| Meyer et al. (2020) [29] | PELD | 47.2 ± 10.6 | 23 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| MLD | 45.2 ± 10.6 | 24 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 3 | |
| Chen et al. (2022) [30] | TELD | 40.9 ± 11.9 | 97 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | 7 | N/A | 5 |
| MLD | 41.0 ± 10.8 | 97 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | 7 | N/A | 7 | |
| Gadjradj et al. (2022) [31] | TELD | 45.3 (12.4) | 179 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | N/A | 2 | 9 |
| MLD | 45.7 (11.3) | 249 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 3 | N/A | 7 | 14 | |
| Tang et al. (2023) [32] | PELD | 40.44 ± 8.23 | 25 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 |
| MLD | 37.80 ± 9.35 | 25 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 1 | |
| Sharma et al. (2024) [33] | TELD | 35 ± 15.78 | 220 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 10 | 4 |
| MLD | 38 ± 17.49 | 220 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 1 | 14 | 2 | |
| Total (%) | TELD | 914 | 0.55 | 0.88 | 1.75 | 0.33 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.11 | 3.72 | 7.33 | 4.49 | |
| IELD | 59 | 0 | 0 | 3.39 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6.78 | 10.17 | 6.77 | ||
| PELD | 1009 | 0.50 | 0.79 | 1.78 | 0.30 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.10 | 3.77 | 7.23 | 4.52 | ||
| MLD | 1115 | 1.17 | 0.27 | 1.7 | 0.18 | 0.36 | 0.45 | 0.72 | 1.35 | 2.15 | 8.34 | 3.5 |
| Procedures | p Value | Risk Ratio (RR) | Statistical Significance |
|---|---|---|---|
| TELD vs. IELD | p < 0.0001 | RR = 0.72 | TELD safer |
| TELD vs. MLD | p = 0.18 | RR = 0.98 | no difference |
| IELD vs. MLD | p = 0.04 | RR = 1.27 | MLD safer |
| MLD vs. PELD | p = 0.0092 | RR = 1.06 | PELD safer |
| Procedures | p Value | Risk Ratio (RR) | Statistical Significance |
|---|---|---|---|
| TELD vs. IELD | p < 0.0001 | RR = 0.66 | TELD less reoperations |
| TELD vs. MLD | p < 0.0001 | RR = 1.28 | MLD less reoperations |
| IELD vs. MLD | p < 0.0001 | RR = 1.93 | MLD less reoperations |
| MLD vs. PELD | p < 0.0001 | RR = 0.77 | MLD less reoperations |
| Rare Complication Type | Author |
|---|---|
| psoas muscle hematoma | Ahn et al. (2009) [34] |
| working channel malposition | Zhou et al. (2018) [35] |
| instrument entrapment | Zhou et al. (2018) [35] Zhu et al. (2017) [36] |
| radicular artery injury | Zhou et al. (2018) [35] Wang Y. et al. (2018) [37] |
| negative pressure pulmonary oedema | Chen G. et al. (2018) [38] |
| pseudomeningocele with nerve root entrapment | Shu W. et al. (2020) [39] |
| discal pseudocyst | Li J et al. (2020) [40] |
| arachnoid cyst | Lou X et al. (2023) [41] |
| seizure | Zhang et al. (2022) [42] |
| cauda equina syndrome | Yang et al. [43] |
| bowel injury | Yoon et al. [22] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Łątka, K.; Kołodziej, W.; Pawuś, D.; Waligóra, M.; Trompeta, J.; Klepinowski, T.; Lasowy, P.; Tanaka, M.; Łabuz-Roszak, B.; Łątka, D. Extremely Rare Complications in Uniportal Spinal Endoscopy: A Systematic Review with Unique Case Analyses. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 1765. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13061765
Łątka K, Kołodziej W, Pawuś D, Waligóra M, Trompeta J, Klepinowski T, Lasowy P, Tanaka M, Łabuz-Roszak B, Łątka D. Extremely Rare Complications in Uniportal Spinal Endoscopy: A Systematic Review with Unique Case Analyses. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(6):1765. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13061765
Chicago/Turabian StyleŁątka, Kajetan, Waldemar Kołodziej, Dawid Pawuś, Marek Waligóra, Jacek Trompeta, Tomasz Klepinowski, Piotr Lasowy, Masato Tanaka, Beata Łabuz-Roszak, and Dariusz Łątka. 2024. "Extremely Rare Complications in Uniportal Spinal Endoscopy: A Systematic Review with Unique Case Analyses" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 6: 1765. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13061765
APA StyleŁątka, K., Kołodziej, W., Pawuś, D., Waligóra, M., Trompeta, J., Klepinowski, T., Lasowy, P., Tanaka, M., Łabuz-Roszak, B., & Łątka, D. (2024). Extremely Rare Complications in Uniportal Spinal Endoscopy: A Systematic Review with Unique Case Analyses. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(6), 1765. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13061765









