Enhancing Cochlear Implant Outcomes across Age Groups: The Interplay of Forward Focus and Advanced Combination Encoder Coding Strategies in Noisy Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Neal, K.; McMahon, C.M.; Hughes, S.E.; Boisvert, I. Listening-Based Communication Ability in Adults With Hearing Loss: A Scoping Review of Existing Measures. Front. Psychol. 2022, 13, 786347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McRackan, T.R.; Bauschard, M.; Hatch, J.L.; Franko-Tobin, E.; Droghini, H.R.; Nguyen, S.A.; Dubno, J.R. Meta-analysis of quality-of-life improvement after cochlear implantation and associations with speech recognition abilities. Laryngoscope 2018, 128, 982–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.R.; Yaffe, K.; Xia, J.; Xue, Q.-L.; Harris, T.B.; Purchase-Helzner, E.; Satterfield, S.; Ayonayon, H.N.; Ferrucci, L.; Simonsick, E.M.; et al. Hearing loss and cognitive decline in older adults. JAMA Intern. Med. 2013, 173, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livingston, G.; Huntley, J.; Sommerlad, A.; Ames, D.; Ballard, C.; Banerjee, S.; Brayne, C.; Burns, A.; Cohen-Mansfield, J.; Cooper, C.; et al. Dementia prevention, intervention, and care: 2020 report of the Lancet Commission. Lancet 2020, 396, 413–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.R.; Albert, M. Hearing loss and dementia—Who is listening? Aging Ment. Health 2014, 18, 671–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Li, A.; Xu, Y.; Qian, X.; Gao, X. Hearing Loss and Dementia: A Meta-Analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 695117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weißgerber, T.; Stöver, T.; Baumann, U. Speech perception in modulated noise assessed in bimodal CI users. HNO 2023, 72, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutter, E.; Grapp, M.; Argstatter, H. Music therapy in adults with cochlear implants: Effects on music perception and subjective sound quality. HNO 2016, 64, 880–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Latif, K.H.A.; Meister, H. Speech Recognition and Listening Effort in Cochlear Implant Recipients and Normal-Hearing Listeners. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 725412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, E.M.H.; Strong, D.; Anderson, M.; Kaizer, A.M.; Gubbels, S. Do Patients Benefit from a Cochlear Implant When They Qualify Only in the Presence of Background Noise? Otol. Neurotol. 2021, 42, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamzavi, J.; Franz, P.; Baumgartner, W.D.; Gstöettner, W. Hearing performance in noise of cochlear implant patients versus severely-profoundly hearing-impaired patients with hearing aids. Audiology 2001, 40, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudery, J.A.; Francis, R.; McCrary, H.; Jacob, A. Older Individuals Meeting Medicare Cochlear Implant Candidacy Criteria in Noise but Not in Quiet: Are These Patients Improved by Surgery? Otol. Neurotol. 2017, 38, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hey, M.; Hocke, T.; Mauger, S.; Müller-Deile, J. A clinical assessment of cochlear implant recipient performance: Implications for individualized map settings in specific environments. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2016, 273, 4011–4020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hey, M.; Hocke, T.; Böhnke, B.; Mauger, S.J. ForwardFocus with cochlear implant recipients in spatially separated and fluctuating competing signals—Introduction of a reference metric. Int. J. Audiol. 2019, 58, 869–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawson, P.W.; Mauger, S.J.; Hersbach, A.A. Clinical evaluation of signal-to-noise ratio–based noise reduction in Nucleus® cochlear implant recipients. Ear Hear. 2011, 32, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauger, S.J.; Arora, K.; Dawson, P.W. Cochlear implant optimized noise reduction. J. Neural Eng. 2012, 9, 065007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauger, S.J.; Warren, C.D.; Knight, M.R.; Goorevich, M.; Nel, E. Clinical evaluation of the Nucleus®6 cochlear implant system: Performance improvements with SmartSound iQ. Int. J. Audiol. 2014, 53, 564–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollack, I.; Pickett, J.M. Cocktail Party Effect. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1957, 29, 1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wimmer, W.; Weder, S.; Caversaccio, M.; Kompis, M. Speech Intelligibility in Noise with a Pinna Effect Imitating Cochlear Implant Processor. Otol. Neurotol. 2016, 37, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steffens, T. The systematic selection of speech audiometric procedures. HNO 2017, 65, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keidser, G.; Naylor, G.; Brungart, D.S.; Caduff, A.; Campos, J.; Carlile, S.; Carpenter, M.G.; Grimm, G.; Hohmann, V.; Holube, I.; et al. The Quest for Ecological Validity in Hearing Science: What It Is, Why It Matters, and How to Advance It. Ear Hear. 2020, 41, 5S–19S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francart, T.; van Wieringen, A.; Wouters, J. Comparison of fluctuating maskers for speech recognition tests. Int. J. Audiol. 2011, 50, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qazi, O.U.R.; van Dijk, B.; Moonen, M.; Wouters, J. Understanding the effect of noise on electrical stimulation sequences in cochlear implants and its impact on speech intelligibility. Hear. Res. 2013, 299, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, K.A.; Noble, J.H.; Dawant, B.M.; Dwyer, R.T.; Labadie, R.F.; Gifford, R.H. Speech recognition as a function of the number of channels in perimodiolar electrode recipients. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2019, 145, 1556–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shew, M.A.; Herzog, J.A.; Kallogjeri, D.; Chen, S.; Wick, C.; Durakovic, N.; McJunkin, J.; Buchman, C.A. The Impact of Age on Noise Sensitivity in Cochlear Implant Recipients. Otol. Neurotol. 2022, 43, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Füllgrabe, C. Age-dependent changes in temporal-fine-structure processing in the absence of peripheral hearing loss. Am. J. Audiol. 2013, 22, 313–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppe, U.; Hocke, T.; Iro, H. Age-Related Decline of Speech Perception. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 891202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peelle, J.E. Listening Effort: How the Cognitive Consequences of Acoustic Challenge Are Reflected in Brain and Behavior. Ear Hear. 2018, 39, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philips, C.; Jacquemin, L.; Lammers, M.J.W.; Mertens, G.; Gilles, A.; Vanderveken, O.M.; Van Rompaey, V. Listening effort and fatigue among cochlear implant users: A scoping review. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1278508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenbäck, V.; Marsja, E.; Hällgren, M.; Lyxell, B.; Larsby, B. The Contribution of Age, Working Memory Capacity, and Inhibitory Control on Speech Recognition in Noise in Young and Older Adult Listeners. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2021, 64, 4513–4523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perreau, A.E.; Wu, Y.-H.; Tatge, B.; Irwin, D.; Corts, D. Listening Effort Measured in Adults with Normal Hearing and Cochlear Implants. J. Am. Acad. Audiol. 2017, 28, 685–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahne, T.; Wagner, T.M.; Kopsch, A.C.; Plontke, S.K.; Wagner, L. Influence of Age on Speech Recognition in Noise and Hearing Effort in Listeners with Age-Related Hearing Loss. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 6133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagener, K.; Brand, T.; Kollmeier, B. Entwicklung und Evaluation eines Satztests für die deutsche Sprache Teil III: Evaluation des Oldenburger Satztests - Development and evaluation of a German sentence test Part III: Evaluation of the Oldenburg sentence test. Z. Audiol. 1999, 38, 86–95. [Google Scholar]
- Kollmeier, B.; Warzybok, A.; Hochmuth, S.; Zokoll, M.A.; Uslar, V.; Brand, T.; Wagener, K.C. The multilingual matrix test: Principles, applications, and comparison across languages: A review. Int. J. Audiol. 2015, 54, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krüger, M.; Schulte, M.; Holube, I. Entwicklung einer Adaptiven Skalierungsmethode zur Ermittlung der Subjektiven Höranstrengung Conference Paper, 18. Jahrestagung der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Audiologie 2015, pp. 1–6. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/277010703_Entwicklung_einer_adaptiven_Skalierungsmethode_zur_Ermittlung_der_subjektiven_Horanstrengung (accessed on 11 January 2024).
- Rahne, T.; Fröhlich, L.; Wagner, L.; Kropp, M.H.; Müller, A. Speech perception and hearing effort using a new active middle ear implant audio processor. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2022, 279, 4667–4675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hey, M.; Böhnke, B.; Mewes, A.; Munder, P.; Mauger, S.J.; Hocke, T. Speech comprehension across multiple CI processor generations: Scene dependent signal processing. Laryngoscope Investig. Otolaryngol. 2021, 6, 807–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowell, R.C. The case for earlier cochlear implantation in postlingually deaf adults. Int. J. Audiol. 2016, 55, S51–S56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dazert, S.; Thomas, J.P.; Loth, A.; Zahnert, T.; Stöver, T. Cochlea-Implantation. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2020, 117, 690–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badajoz-Davila, J.; Buchholz, J.M. Effect of Test Realism on Speech-in-noise Outcomes in Bilateral Cochlear Implant Users. Ear Hear. 2021, 42, 1687–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hey, M.; Mewes, A.; Hocke, T. Speech comprehension in noise—Considerations for ecologically valid assessment of communication skills ability with cochlear implants. HNO 2023, 71, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rader, T.; Fastl, H.; Baumann, U. Speech perception with combined electric-acoustic stimulation and bilateral cochlear implants in a multisource noise field. Ear Hear. 2013, 34, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, M. A glimpsing model of speech perception in noise. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2006, 119, 1562–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rader, T.; Adel, Y.; Fastl, H.; Baumann, U. Speech Perception with Combined Electric-Acoustic Stimulation: A Simulation and Model Comparison. Ear Hear. 2015, 36, e314–e325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meister, H. Speech comprehension and cognitive performance in acoustically difficult situations. HNO 2020, 68, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissgerber, T.; Stöver, T.; Baumann, U. Speech perception in noise: Impact of directional microphones in users of combined electric-acoustic stimulation. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0213251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreschler, W.A.; Verschuure, H.; Ludvigsen, C.; Westermann, S. ICRA noises: Artificial noise signals with speech-like spectral and temporal properties for hearing instrument assessment. Int. J. Audiol. 2001, 40, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichora-Fuller, M.K.; Kramer, S.E.; Eckert, M.A.; Edwards, B.; Hornsby, B.W.; Humes, L.E.; Lemke, U.; Lunner, T.; Matthen, M.; Mackersie, C.L.; et al. Hearing impairment and cognitive energy: The framework for understanding effortful listening (FUEL). Ear Hear. 2016, 37, 5S–27S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, C.; Han, W. Age-Related Difficulty of Listening Effort in Elderly. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlyon, R.P.; Goehring, T. Cochlear Implant Research and Development in the Twenty-first Century: A Critical Update. J. Assoc. Res. Otolaryngol. 2021, 22, 481–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
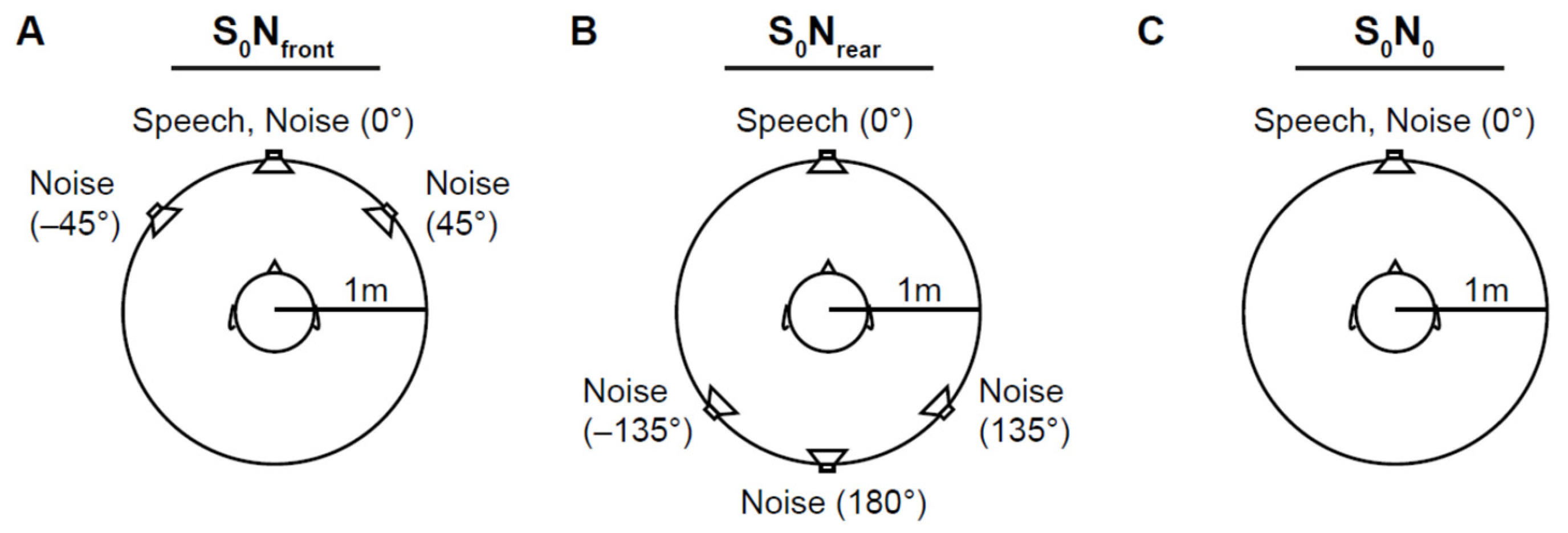
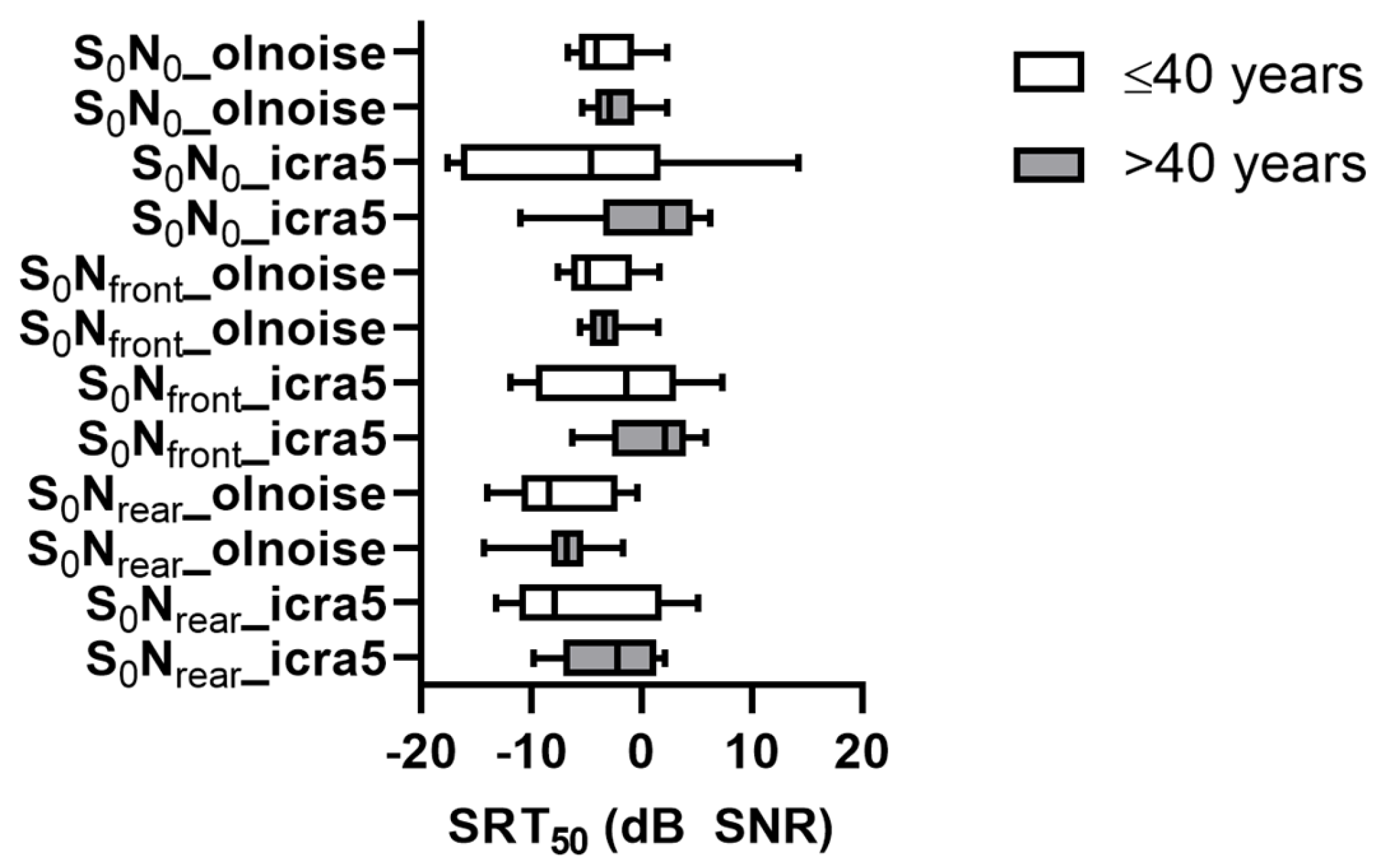
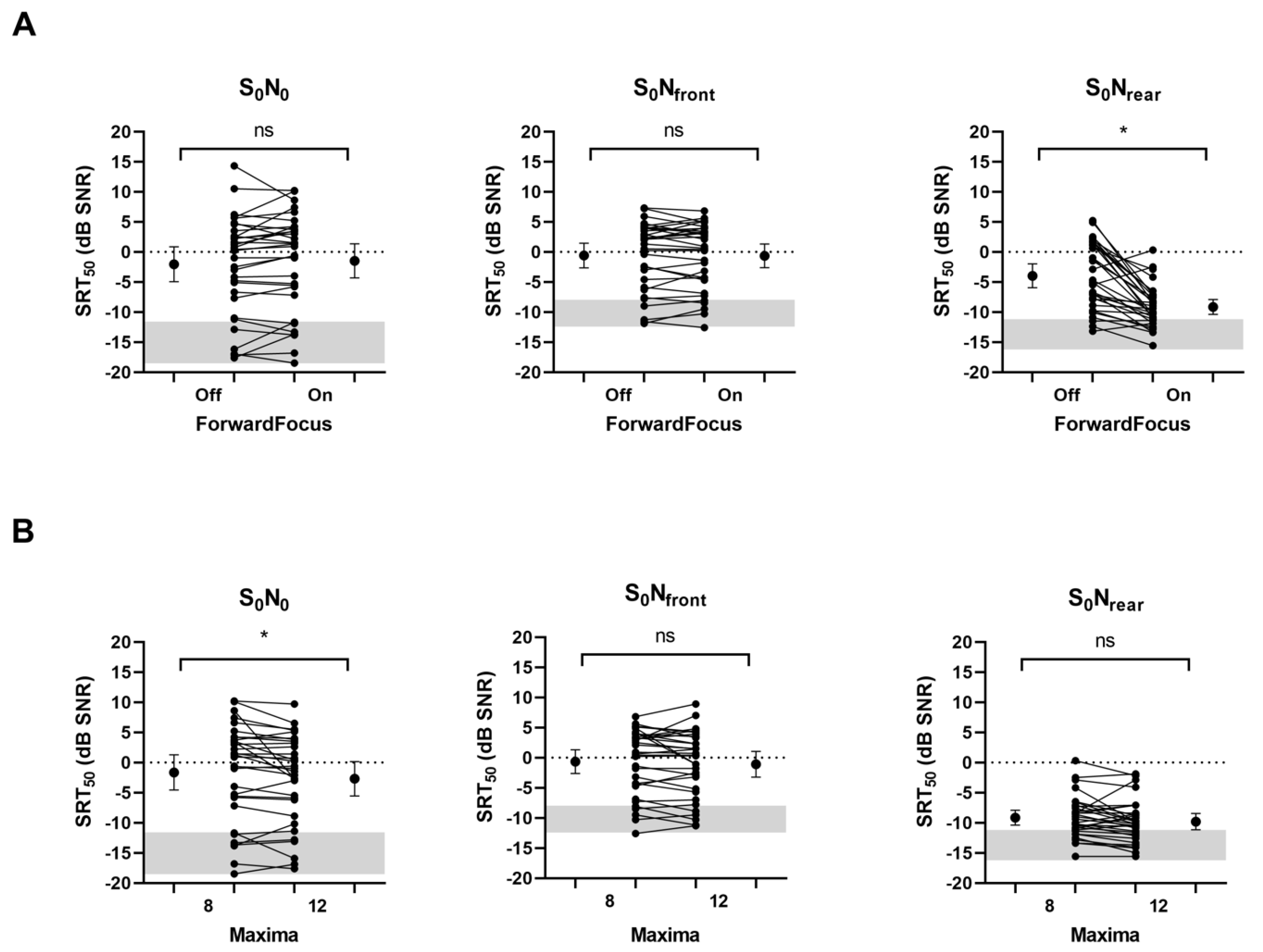
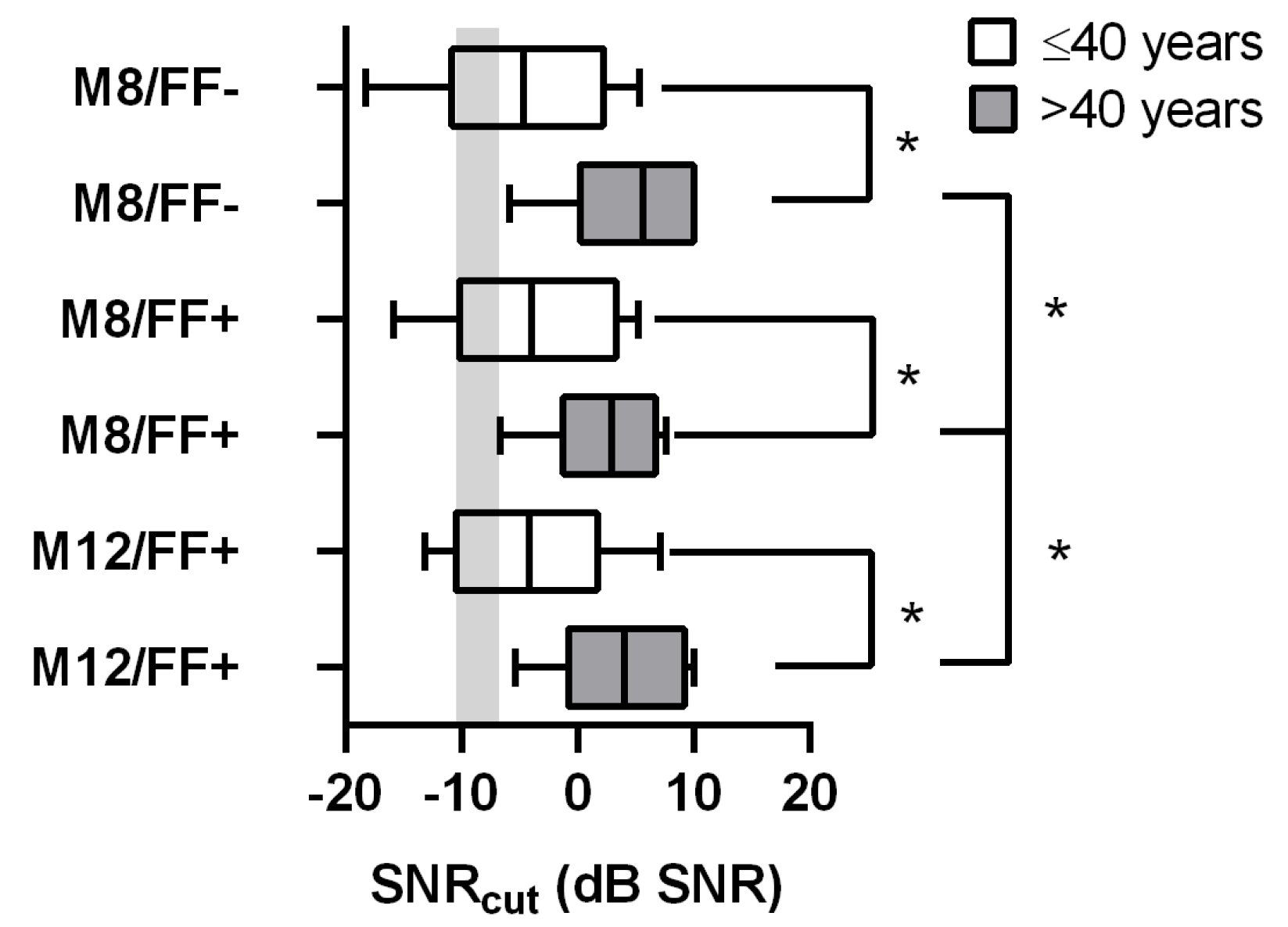
| Age Groups | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristics | ≤40 Years | >40 Years | All |
| Number | 14 | 18 | 32 |
| Age, mean (SD), years | 28.6 (7.9) | 70.0 (7.2) | 51.9 (22.1) |
| Median [25th, 75th percentiles] | 27.0 [20.0, 36.3] | 69.5 [62.8, 76.3] | 61.0 [29.5, 71.5] |
| Men/women, N | 9/5 | 13/5 | 22/10 |
| Right/left CI, N | 5/9 | 8/10 | 13/19 |
| Word recognition, mean (SD), % correct at 65 dB SPL | |||
| Ipsilateral | 71 (17) | 73 (15) | 72 (15) |
| Median [25th, 75th percentiles] | 73 [58, 85] | 75 [60, 85] | 75 [60, 85] |
| Contralateral | 65 (40) | 59 (23) | 62 (31) |
| Median [25th, 75th percentiles] | 78 [34, 100] | 65 [53, 75] | 68 [48, 84] |
| Active electrodes, mean (SD), n | 21.8 (0.8) | 21.8 (0.5) | 21.8 (0.6) |
| Median [25th, 75th percentiles] | 22.0 [22.0, 22.0] | 22.0 [22.0, 22.0] | 22.0 [22.0, 22.0] |
| Pulse width, mean (SD), ms | 35.5 (13.7) | 29.7 (7.5) | 32.3 (10.9) |
| Median [25th, 75th percentiles] | 37.0 [25.0, 37.0] | 25.0 [25.0, 37.0] | 25.0 [25.0, 37.0] |
| Stimulation rate, mean (SD), Hz | 921.4 (80.2) | 977.8 (186.5) | 953.1 (150.2) |
| Median [25th, 75th percentiles] | 900.0 [900.0, 900.0] | 900.0 [900.0, 1200.0] | 900.0 [900.0, 900.0] |
| CI usage per day, mean (SD), hours | 11.5 (5.5) | 13.7 (2.3) | 12.8 (4.1) |
| Median [25th, 75th percentiles] | 13.0 [8.8, 15.3] | 14.0 [12.0, 15.2] | 14.0 [11.3, 15.0] |
| CI experience, mean (SD), years | 5.9 (4.9) | 5.1 (3.2) | 5.4 (4.0) |
| Median [25th, 75th percentiles] | 4.5 [1.7, 9.5] | 4.0 [2.8, 7.0] | 4.0 [2.0, 9.0] |
| Age Group, Years | Age Group, Years | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Outcome | ≤40 | >40 | Total | ||
| Speech recognition in noise | |||||
| SRT50 in dB SNR, mean (SD) | |||||
| olnoise M8/FF− | S0N0 | −3.2 (2.9) | −2.3 (2.4) | −2.7 (2.6) | |
| S0Nfront | −3.9 (3.0) | −3.1 (1.9) | −3.5 (2.4) | ||
| S0Nrear | −7.5 (4.4) | −7.0 (2.8) | −7.2 (3.5) | ||
| icra5 M8/FF− | S0N0 | −5.1 (10.6) | 0.1 (5.1) | −2.2 (8.2) | |
| S0Nfront | −2.6 (7.1) | 1.0 (3.8) | −0.6 (5.7) | ||
| S0Nrear | −5.3 (6.8) | −2.9 (4.1) | −4.0 (5.5) | ||
| icra5 M8/FF+ | S0N0 | −4.7 (9.9) | 0.7 (5.5) | −1.6 (8.1) | |
| S0Nfront | −2.8 (6.6) | 1.0 (3.7) | −0.7 (5.4) | ||
| S0Nrear | −9.7 (4.0) | −8.7 (2.9) | −9.1 (3.4) | ||
| icra5 M12/FF+ | S0N0 | −5.9 (8.8) | −0.2 (5.0) | −2.7 (7.4) | |
| S0Nfront | −3.1 (6.6) | 0.5 (4.1) | −1.1 (5.5) | ||
| S0Nrear | −10.3 (4.6) | −9.5 (2.4) | −9.8 (3.5) | ||
| Listening effort in noise | |||||
| SNRcut in dB SNR (SD) | |||||
| icra5 M8/FF− | S0N0 | −4.8 (7.8) | 4.7 (5.7) | 0.1 (8.2) | |
| icra5 M8/FF+ | S0N0 | −4.3 (7.4) | 2.3 (4.8) | −0.9 (6.9) | |
| icra5 M12/FF+ | S0N0 | −3.7 (7.0) | 3.5 (5.4) | 0.1 (7.1) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wagner, T.M.; Wagner, L.; Plontke, S.K.; Rahne, T. Enhancing Cochlear Implant Outcomes across Age Groups: The Interplay of Forward Focus and Advanced Combination Encoder Coding Strategies in Noisy Conditions. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 1399. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13051399
Wagner TM, Wagner L, Plontke SK, Rahne T. Enhancing Cochlear Implant Outcomes across Age Groups: The Interplay of Forward Focus and Advanced Combination Encoder Coding Strategies in Noisy Conditions. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(5):1399. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13051399
Chicago/Turabian StyleWagner, Telse M., Luise Wagner, Stefan K. Plontke, and Torsten Rahne. 2024. "Enhancing Cochlear Implant Outcomes across Age Groups: The Interplay of Forward Focus and Advanced Combination Encoder Coding Strategies in Noisy Conditions" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 5: 1399. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13051399
APA StyleWagner, T. M., Wagner, L., Plontke, S. K., & Rahne, T. (2024). Enhancing Cochlear Implant Outcomes across Age Groups: The Interplay of Forward Focus and Advanced Combination Encoder Coding Strategies in Noisy Conditions. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(5), 1399. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13051399








