The Uricosuric Effect of SGLT2 Inhibitors Is Maintained in the Long Term in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract
1. Introduction
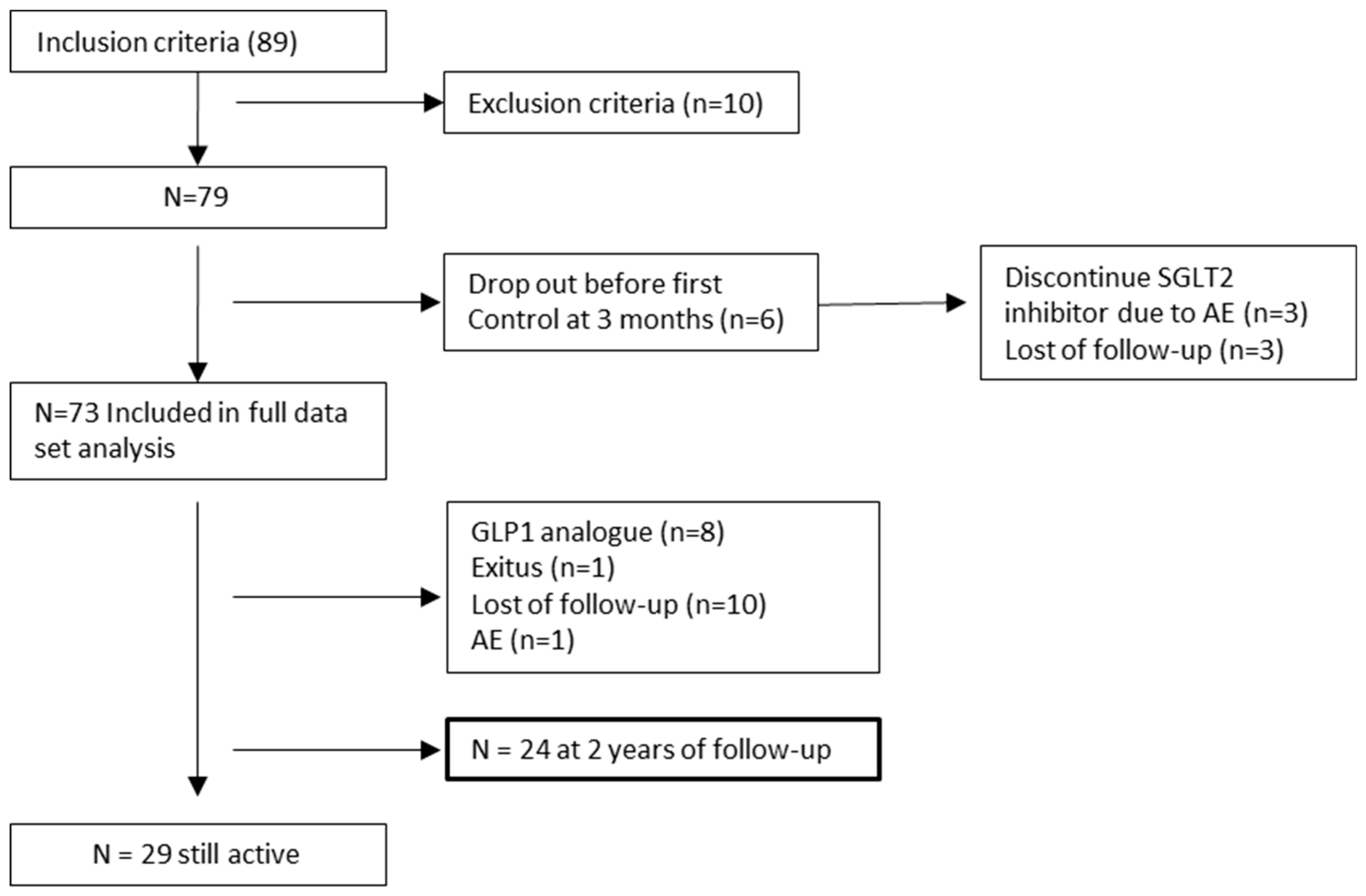
2. Materials and Methods
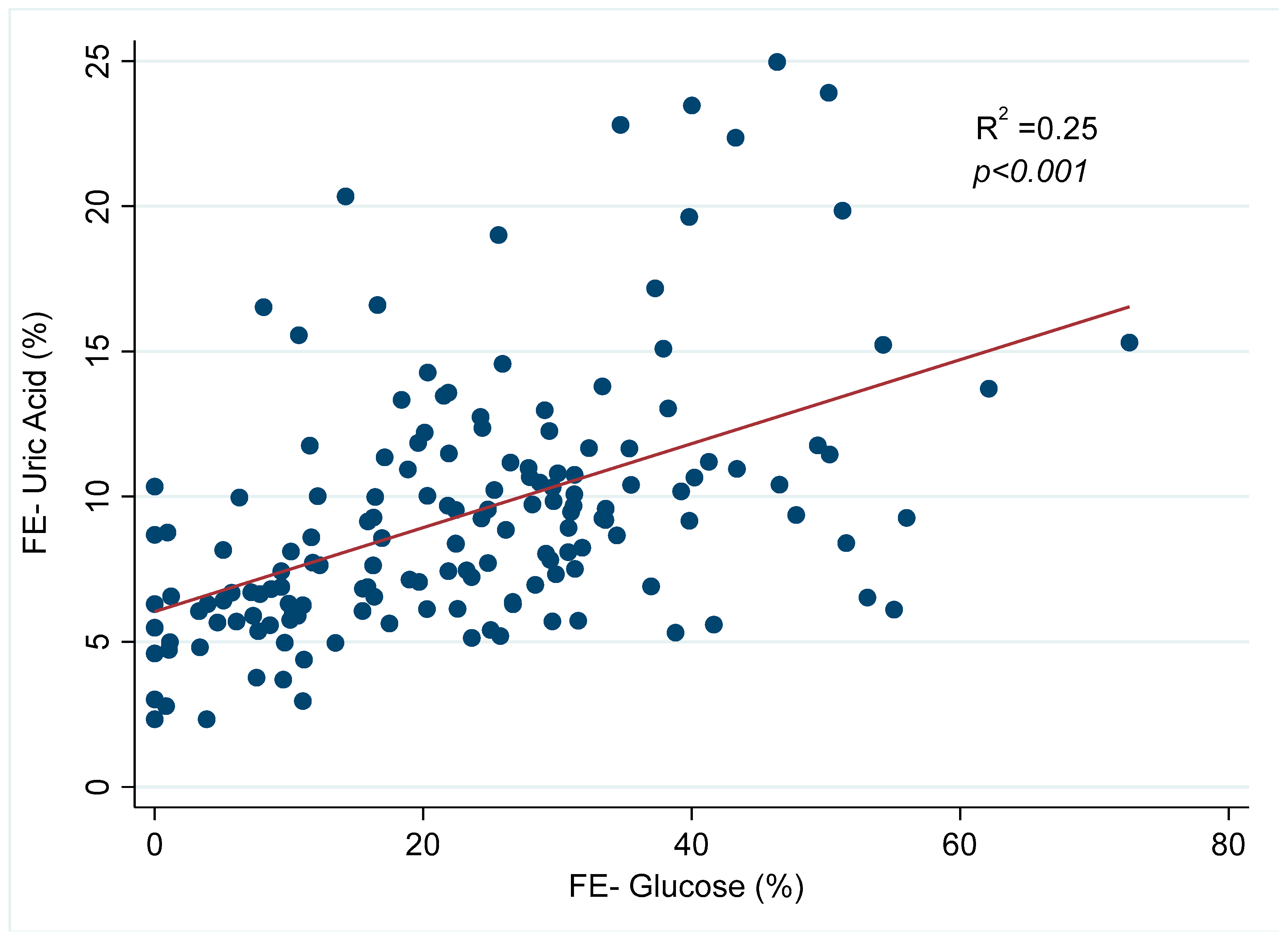
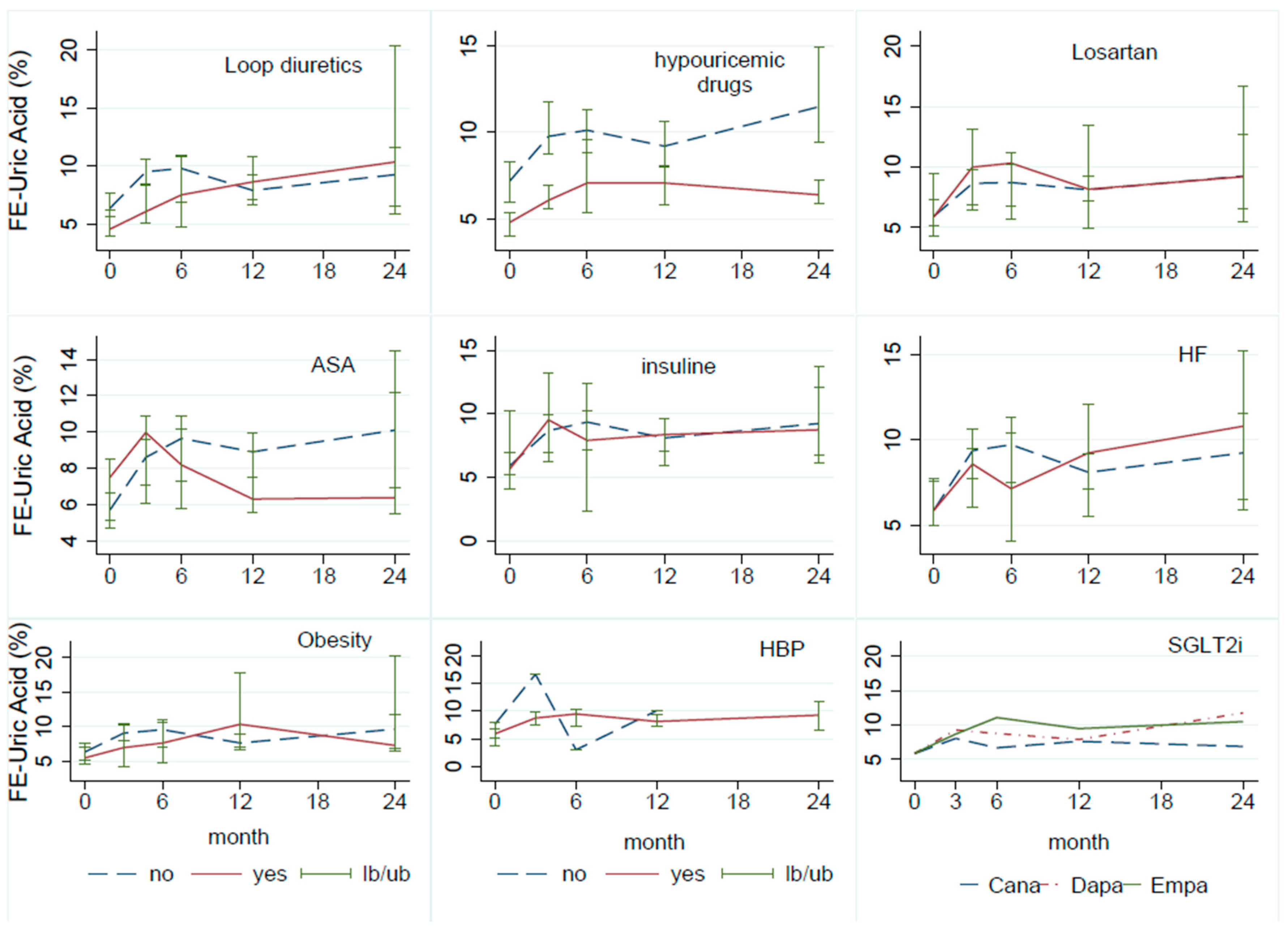
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goicoechea Diezandino, M. Ácido Úrico y Enfermedad Renal Crónica. Nefrol al Día [Internet]. 2021, pp. 1–25. Available online: https://www.nefrologiaaldia.org/200 (accessed on 15 November 2023).
- Takata, T.; Isomoto, H. Pleiotropic effects of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors: Renoprotective mechanisms beyond glycemic control. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belančić, A.; Klobučar, S. Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter 2 Inhibitors as a Powerful Cardioprotective and Renoprotective Tool: Overview of Clinical Trials and Mechanisms. Diabetology 2023, 4, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chino, Y.; Samukawa, Y.; Sakai, S.; Nakai, Y.; Yamaguchi, J.; Nakanishi, T.; Tamai, I. SGLT2 inhibitor lowers serum uric acid through alteration of uric acid transport activity in renal tubule by increased glycosuria. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 2014, 35, 391–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.; Liu, H.; Dong, P. Empagliflozin reduces blood pressure and uric acid in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2019, 33, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Xu, L.; Tian, D.; Xia, P.; Zheng, H.; Wang, L.; Chen, L. Effects of sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors on serum uric acid level: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2018, 20, 458–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chino, Y.; Kuwabara, M.; Hisatome, I. Factors Influencing Change in Serum Uric Acid After Administration of the Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitor Luseogliflozin in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2022, 62, 366–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yip, A.S.Y.; Leong, S.; Teo, Y.N.; Syn, N.L.X.; See, R.M.; Wee, C.F.; Chong, E.Y.; Lee, C.-H.; Chan, M.Y.; Yeo, T.-C.; et al. Effect of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors on serum urate levels in patients with and without diabetes: A systematic review and meta-regression of 43 randomized controlled trials. Ther. Adv. Chronic Dis. 2022, 13, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbari, A.; Rafiee, M.; Sathyapalan, T.; Sahebkar, A. Impacts of Sodium/Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors on Circulating Uric Acid Concentrations: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Diabetes Res. 2022, 2022, 7520632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suijk, D.L.; van Baar, M.J.; van Bommel, E.J.; Iqbal, Z.; Krebber, M.M.; Vallon, V.; Touw, D.; Hoorn, E.J.; Nieuwdorp, M.; Kramer, M.M.; et al. SGLT2 Inhibition and Uric Acid Excretion in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Normal Kidney Function. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2022, 17, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novikov, A.; Fu, Y.; Huang, W.; Freeman, B.; Patel, R.; van Ginkel, C.; Koepsell, H.; Busslinger, M.; Onishi, A.; Nespoux, J.; et al. SGLT2 inhibition and renal urate excretion: Role of luminal glucose, GLUT9, and URAT1. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2019, 316, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kannangara, D.R.; Ramasamy, S.N.; Indraratna, P.L.; Stocker, S.L.; Graham, G.G.; Jones, G.; Portek, I.; Williams, K.M.; O Day, R. Fractional clearance of urate: Validation of measurement in spot-urine samples in healthy subjects and gouty patients. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2012, 14, R189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levey, A.S.; Stevens, L.A.; Schmid, C.H.; Zhang, Y.L.; Castro, A.F., 3rd; Feldman, H.I.; Kusek, J.W.; Eggers, P.; Van Lente, F.; Greene, T.; et al. A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 150, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Q.; Xia, X.; Li, B.; Lin, Z.; Yu, X.; Huang, F. Serum uric acid and cardiovascular mortality in chronic kidney disease: A meta-analysis. BMC Nephrol. 2019, 20, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gherghina, M.E.; Peride, I.; Tiglis, M.; Neagu, T.P.; Niculae, A.; Checherita, I.A. Uric Acid and Oxidative Stress-Relationship with Cardiovascular, Metabolic, and Renal Impairment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doria, A.; Galecki, A.T.; Spino, C.; Pop-Busui, R.; Cherney, D.Z.; Lingvay, I.; Parsa, A.; Rossing, P.; Sigal, R.J.; Afkarian, M.; et al. Serum Urate Lowering with Allopurinol and Kidney Function in Type 1 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 2493–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, K.; Hosoya, T.; Uchida, S.; Inaba, M.; Makino, H.; Ito, S.; Yamamoto, T.; Tomino, Y.; Ohno, I.; Shibagaki, Y.; et al. Febuxostat Therapy for Patients With Stage 3 CKD and Asymptomatic Hyperuricemia: A Randomized Trial. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2018, 72, 798–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badve, S.V.; Pascoe, E.M.; Tiku, A.; Boudville, N.; Brown, F.G.; Cass, A.; Clarke, P.; Dalbeth, N.; Day, R.O.; de Zoysa, J.R.; et al. Effects of Allopurinol on the Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 2504–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prezelin-Reydit, M.; Combe, C.; Fouque, D.; Frimat, L.; Jacquelinet, C.; Laville, M.; Massy, Z.A.; Lange, C.; Ayav, C.; Pecoits-Filho, R.; et al. Longitudinal uric acid has nonlinear association with kidney failure and mortality in chronic kidney disease. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 3952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- KDIGO 2023 Clinical Practice Guideline for the Evaluation and Management of Chronic Kidney Disease. Public Review Draft. July 2023. Available online: https://kdigo.org/guidelines/ckd-evaluation-and-management/ (accessed on 30 June 2023).
- Assimacopoulos-Jeannet, F.; Cusin, I.; Greco-Perotto, R.; Terrettaz, J.; Rohner-Jeanrenaud, F.; Zarjevski, N.; Jeanrenaud, B. Glucose transporters: Structure, function, and regulation. Biochimie 1991, 73, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Patients (n) | 73 |
| Male (%) | 78.1 |
| Age (y; mean, SD) | 72.2 (8.7) |
| Caucasian (%) | 95.0 |
| Comorbidities (%) | |
| High blood pressure | 95.9 |
| Hyperuricemia | 74.0 |
| Heart failure | 26.0 |
| Obesity | 18.5 |
| Dyslipidemia | 68.4 |
| CKD etiology (%) | |
| Diabetes mellitus type 2 | 49.3 |
| Nephroangiosclerosis | 16.0 |
| Glomerulonephritis | 4.1 |
| Interstitial | 9.5 |
| Others | 20.4 |
| Drugs involved in uric acid metabolism (%) | |
| Losartan | 16.4 |
| Insulin | 19.1 |
| Loop diuretics | 27.4 |
| Tiazide | 38.4 |
| Acetylsalicylic acid | 27.4 |
| Alopurinol | 26.0 |
| Febuxostat | 8.2 |
| SGLT2 inhibitor drugs (%) | |
| Canagliflozina | 25.8 |
| Dapagliflozina | 61.3 |
| Empagliflozina | 9.7 |
| Time | Baseline | Month 3 | Month 6 | Month 12 | Month 24 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 73 | 61 | 45 | 45 | 24 |
| Uric acid FE (%) | 5.9 [4.4–8.3] | 8.7 [6.1–11.2] * | 9.1 [6.3–10.8] * | 8.2 [6.7–10.3] * | 9.6 [6.5–12.2] * |
| Glucose FE (%) | 0 | 20.1 [8.6–30.8] * | 25.3 [11.8–31.3] * | 21.9 [11.0–32.3] * | 24.3 [14.2–38.8] * |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 46 [40.0–55.0] | 39 [34.0–52.0] * | 37 [33.0–44.0] * | 38.5 [32.0–47.5] * | 40 [31.0–54.0] * |
| Serum uric acid (mg/dL) | 6.6 [5.6–7.8] | 6.4 [5.0–7.5] | 6.4 [4.8–7.5] | 6.2 [5.2–7.6] | 6.2 [5.2–7.0] |
| Serum glucose (mg/dL) | 131 [111.0–146.0] | 124 [113.0–141.0] | 126 [105.0–152.0] | 133 [115.0–155.0] | 120 [112.0–136.0] |
| Basal eGFR | Baseline | Month 3 | Month 6 | Month 12 | Month 24 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Uric acid FE (%) | 30–45 (n30) | 5.6 [4.3–7.9] | 9.3 [6.4–13.7] | 10.0 [6.7–11.4] | 7.6 [7.1–11.7] | 9.2 [5.9–20.3] |
| 45–60 (n32) | 6.8 [4.8–8.9] | 8.6 [6.1–12.2] | 8.8 [5.1–9.6] | 8.4 [6.5–9.6] | 7.8 [6.4–10.9] | |
| >60 (n11) | 5.6 [4.4–5.8] | 8.8 [6.3–10.0] | 7.7 [6.9–10.3] | 8.7 [7.1–11.8] | 11.5 [10.2–12.7] | |
| Glucose FE (%) | 30–45 (n30) | 0 [0.0–0.0] | 19.6 [8.1–31.8] | 28.1 [12.1–46.5] | 18.0 [9.7–32.3] | 12.9 [10.6–16.4] |
| 45–60 (n32) | 0 [0.0–0.0] | 21.2 [12.6–31.1] | 24.6 [16.9–30.0] | 26.2 [22.1–33.5] | 28.1 [20.2–41.1] | |
| >60 (n11) | 0 [0.0–0.0] | 13.2 [7.6–27.9] | 15.9 [11.8–29.6] | 19.3 [8.5–21.9] | 37.0 [24.3–37.3] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sánchez-Briales, P.; Marques Vidas, M.; López-Sánchez, P.; López-Illázquez, M.V.; Martín-Testillano, L.; Vedat-Ali, A.; Portolés, J. The Uricosuric Effect of SGLT2 Inhibitors Is Maintained in the Long Term in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 1360. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13051360
Sánchez-Briales P, Marques Vidas M, López-Sánchez P, López-Illázquez MV, Martín-Testillano L, Vedat-Ali A, Portolés J. The Uricosuric Effect of SGLT2 Inhibitors Is Maintained in the Long Term in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(5):1360. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13051360
Chicago/Turabian StyleSánchez-Briales, Paula, María Marques Vidas, Paula López-Sánchez, María Victoria López-Illázquez, Lucía Martín-Testillano, Aylin Vedat-Ali, and Jose Portolés. 2024. "The Uricosuric Effect of SGLT2 Inhibitors Is Maintained in the Long Term in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 5: 1360. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13051360
APA StyleSánchez-Briales, P., Marques Vidas, M., López-Sánchez, P., López-Illázquez, M. V., Martín-Testillano, L., Vedat-Ali, A., & Portolés, J. (2024). The Uricosuric Effect of SGLT2 Inhibitors Is Maintained in the Long Term in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(5), 1360. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13051360







