Identification of Novel and Recurrent Variants in BTD, GBE1, AGL and ASL Genes in Families with Metabolic Disorders in Saudi Arabia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Approval and Family Selection
2.2. Whole Exome Sequencing
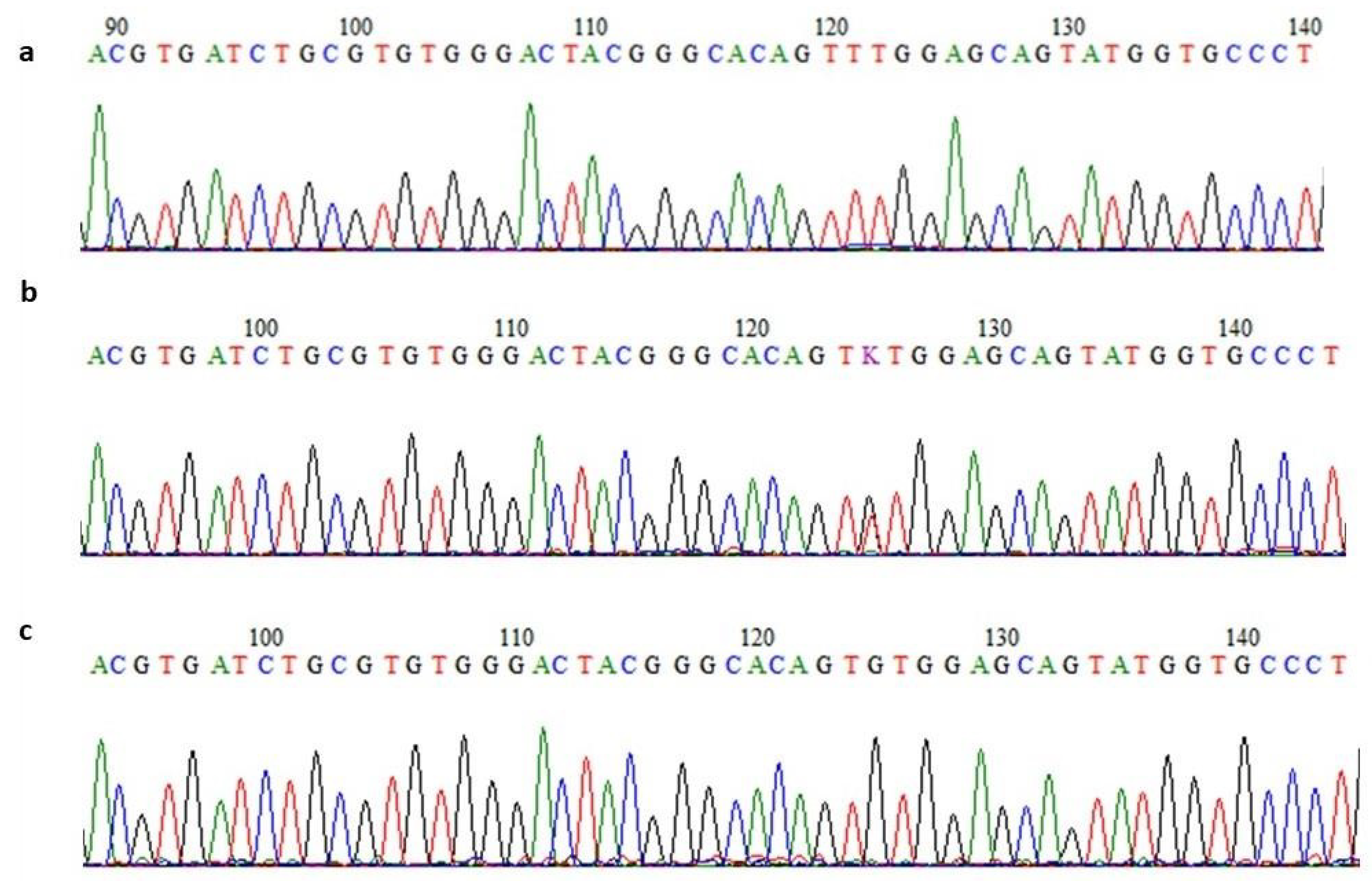
2.3. Confirmation of Genomic Variant by Sanger Sequencing
2.4. In Silico Analysis of Protein Sequences
3. Results
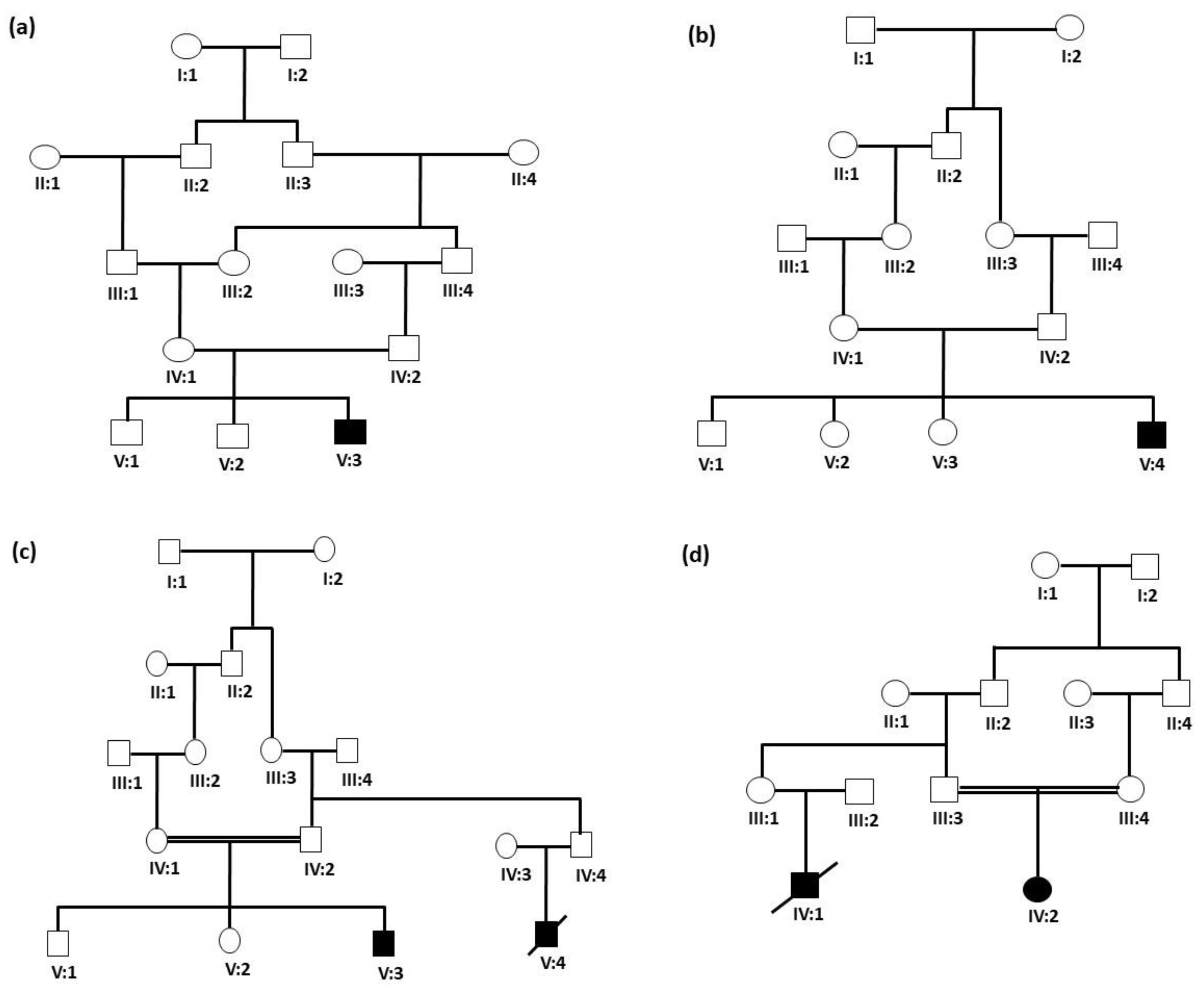
3.1. Clinical Features of Patients
3.2. WES Identified Genetic Defects in Each Family
3.2.1. Identification of Homozygous Variant in the BTD Gene
3.2.2. Identification of Homozygous Missense Variant in the ASL Gene
3.2.3. Identification of Homozygous Variant in the GBE1 Gene
3.2.4. Identification of Homozygous Missense Variant in the AGL Gene
3.2.5. Confirmation of Variants’ Segregation
3.3. In Silico Gene Co-Expression and Functional Interpretations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ben-Rebeh, I.; Hertecant, J.L.; Al-Jasmi, F.A.; Aburawi, H.E.; Al-Yahyaee, S.A.; Al-Gazali, L.; Ali, B.R. Identification of mutations underlying 20 inborn errors of metabolism in the United Arab Emirates population. Genet. Test. Mol. Biomark. 2012, 16, 366–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendrieckx, C.; Ivory, N.; Singh, H.; Frier, B.M.; Speight, J. Impact of severe hypoglycaemia on psychological outcomes in adults with Type 2 diabetes: A systematic review. Diabet. Med. A J. Br. Diabet. Assoc. 2019, 36, 1082–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Du, A.; Liu, H.; Wang, Z.; Hu, J. Systematic Analysis of the Global, Regional and National Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases from 1990 to 2017. J. Epidemiol. Glob. Health 2022, 12, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, K.F.; Yong, W.T.L.; Bhuiyan, M.S.A.; Siddiquee, S.; Shah, M.D.; Venmathi Maran, B.A. Current Understanding on the Genetic Basis of Key Metabolic Disorders: A Review. Biology 2022, 11, 1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennick, K.; Sturt, J.; Speight, J. What is diabetes distress and how can we measure it? A narrative review and conceptual model. J. Diabetes Its Complicat. 2017, 31, 898–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzymski, J.J.; Elhanan, G.; Morales Rosado, J.A.; Smith, E.; Schlauch, K.A.; Read, R.; Rowan, C.; Slotnick, N.; Dabe, S.; Metcalf, W.J.; et al. Population genetic screening efficiently identifies carriers of autosomal dominant diseases. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1235–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhawal, R.; Fu, Q.; Anderson, E.T.; Gibson, G.E.; Zhang, S. Serum Metabolomic and Lipidomic Profiling Reveals Novel Biomarkers of Efficacy for Benfotiamine in Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manivannan, M.; Jogalekar, M.P.; Kavitha, M.S.; Maran, B.A.V.; Gangadaran, P. A mini-review on the effects of COVID-19 on younger individuals. Exp. Biol. Med. Maywood N. J. 2021, 246, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, B.L.; Graham, B.; Delorey, M.J.; Pegalajar-Jurado, A.; Islam, M.N.; Wormser, G.P.; Aucott, J.N.; Rebman, A.W.; Soloski, M.J.; Belisle, J.T.; et al. Metabolic Response in Patients With Post-treatment Lyme Disease Symptoms/Syndrome. Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2021, 73, e2342–e2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molares-Vila, A.; Corbalán-Rivas, A.; Carnero-Gregorio, M.; González-Cespón, J.L.; Rodríguez-Cerdeira, C. Biomarkers in Glycogen Storage Diseases: An Update. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoytema van Konijnenburg, E.M.M.; Wortmann, S.B.; Koelewijn, M.J.; Tseng, L.A.; Houben, R.; Stöckler-Ipsiroglu, S.; Ferreira, C.R.; van Karnebeek, C.D.M. Treatable inherited metabolic disorders causing intellectual disability: 2021 review and digital app. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2021, 16, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franceschini, N.; Frick, A.; Kopp, J.B. Genetic Testing in Clinical Settings. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2018, 72, 569–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://www.rx-genes.com/about/ (accessed on 7 November 2023).
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. Off. J. Am. Coll. Med. Genet. 2015, 17, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greene, D.; Richardson, S.; Turro, E. Phenotype Similarity Regression for Identifying the Genetic Determinants of Rare Diseases. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2016, 98, 490–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köhler, S.; Schulz, M.H.; Krawitz, P.; Bauer, S.; Dölken, S.; Ott, C.E.; Mundlos, C.; Horn, D.; Mundlos, S.; Robinson, P.N. Clinical diagnostics in human genetics with semantic similarity searches in ontologies. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2009, 85, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashmi, J.A.; Albarry, M.A.; Almatrafi, A.M.; Albalawi, A.M.; Mahmood, A.; Basit, S. Whole exome sequencing identified a novel single base pair insertion mutation in the EYS gene in a six generation family with retinitis pigmentosa. Congenit. Anom. 2018, 58, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coudert, E.; Gehant, S.; de Castro, E.; Pozzato, M.; Baratin, D.; Neto, T.; Sigrist, C.J.A.; Redaschi, N.; Bridge, A. Annotation of biologically relevant ligands in UniProtKB using ChEBI. Bioinform. Oxf. Engl. 2023, 39, btac793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Gable, A.L.; Lyon, D.; Junge, A.; Wyder, S.; Huerta-Cepas, J.; Simonovic, M.; Doncheva, N.T.; Morris, J.H.; Bork, P.; et al. STRING v11: Protein-protein association networks with increased coverage, supporting functional discovery in genome-wide experimental datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D607–D613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M. Toward pathway engineering: A new database of genetic and molecular pathways. Sci. Technol. Jpn. 1996, 59, 34–38. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, S.H.; Bylstra, Y.; Teo, J.X.; Kuan, J.L.; Bertin, N.; Gonzalez-Porta, M.; Hebrard, M.; Tirado-Magallanes, R.; Tan, J.H.J.; Jeyakani, J.; et al. Analysis of clinically relevant variants from ancestrally diverse Asian genomes. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsatto, T.; Sperb-Ludwig, F.; Pinto, L.L.; Luca, G.R.; Carvalho, F.L.; Souza, C.F.; Medeiros, P.F.; Lourenço, C.M.; Lo Filho, R.; Neto, E.C.; et al. Biotinidase deficiency: Clinical and genetic studies of 38 Brazilian patients. BMC Med. Genet. 2014, 15, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semeraro, D.; Verrocchio, S.; Di Dalmazi, G.; Rossi, C.; Pieragostino, D.; Cicalini, I.; Ferrante, R.; Di Michele, S.; Stuppia, L.; Rizzo, C.; et al. High Incidence of Partial Biotinidase Deficiency in the First 3 Years of a Regional Newborn Screening Program in Italy. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 8141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naseer, M.I.; Pushparaj, P.N.; Abdulkareem, A.A.; Muthaffar, O.Y. Whole-Exome Sequencing Reveals a Missense Variant c.1612C>T (p.Arg538Cys) in the BTD Gene Leading to Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder in Saudi Families. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 829251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, S.; Pérez-Palma, E.; Jespersen, J.B.; May, P.; Hoksza, D.; Heyne, H.O.; Ahmed, S.S.; Rifat, Z.T.; Rahman, M.S.; Lage, K.; et al. Comprehensive characterization of amino acid positions in protein structures reveals molecular effect of missense variants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 28201–28211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, P.V.S.; Badia, B.M.L.; Farias, I.B.; Pinto, W.; Oliveira, A.S.B.; Akman, H.O.; DiMauro, S. GBE1-related disorders: Adult polyglucosan body disease and its neuromuscular phenotypes. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2021, 44, 534–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smit, G.P.A.; Rake, J.P.; Akman, H.O.; DiMauro, S. The Glycogen Storage Diseases and Related Disorders. In Inborn Metabolic Diseases: Diagnosis and Treatment; Fernandes, J., Saudubray, J.-M., van den Berghe, G., Walter, J.H., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 101–119. [Google Scholar]
- Froese, D.S.; Michaeli, A.; McCorvie, T.J.; Krojer, T.; Sasi, M.; Melaev, E.; Goldblum, A.; Zatsepin, M.; Lossos, A.; Álvarez, R.; et al. Structural basis of glycogen branching enzyme deficiency and pharmacologic rescue by rational peptide design. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2015, 24, 5667–5676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, K.C.; Kwitek, A.E. Multi-Omic Approaches to Identify Genetic Factors in Metabolic Syndrome. Compr. Physiol. 2021, 12, 3045–3084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durairaj, T.; Alagappan, C.; Suresh, S.S.R.; Ramasamy, V. An Introductory Chapter: Secondary Metabolites. In Secondary Metabolites; Ramasamy, V., Suresh, S.S.R., Eds.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2018; p. Ch. 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennis, M.; Bowen, W.; Cho, L. Mechanisms of Clinical Signs, 1st ed.; Churchill Livingstone: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Canda, E.; Kalkan Uçar, S.; Çoker, M. Biotinidase Deficiency: Prevalence, Impact And Management Strategies. Pediatr. Health Med. Ther. 2020, 11, 127–133. [Google Scholar]
- Wolf, B.; Grier, R.E.; Allen, R.J.; Goodman, S.I.; Kien, C.L. Biotinidase deficiency: The enzymatic defect in late-onset multiple carboxylase deficiency. Clin. Chim. Acta Int. J. Clin. Chem. 1983, 131, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, B. Biotinidase deficiency: “If you have to have an inherited metabolic disease, this is the one to have”. Genet. Med. Off. J. Am. Coll. Med. Genet. 2012, 14, 565–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kho, J.; Tian, X.; Wong, W.T.; Bertin, T.; Jiang, M.M.; Chen, S.; Jin, Z.; Shchelochkov, O.A.; Burrage, L.C.; Reddy, A.K.; et al. Argininosuccinate Lyase Deficiency Causes an Endothelial-Dependent Form of Hypertension. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2018, 103, 276–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagamani, S.C.S.; Erez, A.; Lee, B. Argininosuccinate Lyase Deficiency. In GeneReviews(®); Adam, M.P., Mirzaa, G.M., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Bean, L.J.H., Gripp, K.W., Amemiya, A., Eds.; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ozben, T. Expanded newborn screening and confirmatory follow-up testing for inborn errors of metabolism detected by tandem mass spectrometry. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2013, 51, 157–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leuger, L.; Dieu, X.; Chao de la Barca, J.M.; Moriconi, M.; Halley, G.; Donin de Rosière, X.; Reynier, P.; Mirebeau-Prunier, D.; Homedan, C. Late-onset argininosuccinic aciduria in a 72-year-old man presenting with fatal hyperammonemia. JIMD Rep. 2021, 62, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erez, A. Argininosuccinic aciduria: From a monogenic to a complex disorder. Genet. Med. Off. J. Am. Coll. Med. Genet. 2013, 15, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.Y.; Kang, B.; Choe, J.Y.; Lee, Y.; Jang, H.J.; Park, H.D.; Lee, S.K.; Choe, Y.H. A Case of Glycogen Storage Disease IV with Rare Homozygous Mutations in the Glycogen Branching Enzyme Gene. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Nutr. 2018, 21, 365–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, J.S.; Moon, J.S.; Seo, J.K.; Yang, H.R.; Chang, J.Y.; Park, S.S. A mutation analysis of the AGL gene in Korean patients with glycogen storage disease type III. J. Hum. Genet. 2014, 59, 42–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basit, S.; Malibari, O.; Al Balwi, A.M.; Abdusamad, F.; Abu Ismail, F. A founder splice site mutation underlies glycogen storage disease type 3 in consanguineous Saudi families. Ann. Saudi Med. 2014, 34, 390–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.; Qiu, Z.; Sun, M.; Wang, W.; Wei, M.; Zhang, X. Spectrum of AGL mutations in Chinese patients with glycogen storage disease type III: Identification of 31 novel mutations. J. Hum. Genet. 2016, 61, 641–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, R.; Wei, X.; Zhang, K.; Song, F.; Lv, Y.; Gao, M.; Wang, D.; Ma, J.; Gai, Z.; Liu, Y. Genotypic and phenotypic characteristics of 12 chinese children with glycogen storage diseases. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 932760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousseau-Nepton, I.; Okubo, M.; Grabs, R.; Mitchell, J.; Polychronakos, C.; Rodd, C. A founder AGL mutation causing glycogen storage disease type IIIa in Inuit identified through whole-exome sequencing: A case series. CMAJ Can. Med. Assoc. J. 2015, 187, E68–E73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, G.; Choi, M. Application of whole exome sequencing to identify disease-causing variants in inherited human diseases. Genom. Inform. 2012, 10, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meienberg, J.; Bruggmann, R.; Oexle, K.; Matyas, G. Clinical sequencing: Is WGS the better WES? Hum. Genet. 2016, 135, 359–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Name of Gene | Protein Family | Domain | Pathways |
|---|---|---|---|
| Biotinidase (BTD) | Biotinidase-like, eukaryotic, Biotinidase/VNN family | Carbon-nitrogen hydrolase, Vanin, C-terminal | Biotin metabolism. Metabolic pathways. Vitamin digestion and absorption. |
| Arginosuccinate lyase (ASL) | Fumarate lyase family Argininosuccinate lyase | Fumerate_Lyase_N/Argininosuccinate Lyase | Arginine biosynthesis. Alanine, aspartate, and glutamate metabolism. Metabolic pathways. Biosynthesis of secondary metabolites. Biosynthesis of amino acids. |
| Glucan-branching enzyme (GBE1) | GlgB 1,4-alpha-glucan-branching enzyme | Glycoside hydrolase, family 13, N-terminal Alpha-amylase | Starch and sucrose metabolism. Metabolic pathways. Biosynthesis of secondary metabolites. |
| Glycogen Debranching Enzyme (AGL) | Glycogen debranching enzyme, metazoa | Glucanotransferase, Glycogen debranching enzyme, C-terminal | Starch and sucrose metabolism. Metabolic pathways. Biosynthesis of secondary metabolites. |
| Variant Predictions | BTD (c.1270G > C) | ASL (c.1300G > T) | GBE1 (c.985T > G) | AGL (c.113C > G) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Protein change | p. Asp424His | p. Val434Leu | p.Tyr329Cys | p.Thr38Ser |
| ACMG classification | Pathogenic | Likely Pathogenic | Pathogenic | Likely Benign |
| PhyloP score | 3.238 | 8.539 | 8.803 | 4.125 |
| REVEL | Pathogenic | Pathogenic | Pathogenic | Benign |
| SIFT | Uncertain | Uncertain | Pathogenic | Benign |
| MutationTaster | Benign | Uncertain | Uncertain | Benign |
| MutationAssesor | Pathogenic | Benign | Pathogenic | Benign |
| Provean | Pathogenic | Uncertain | Pathogenic | Benign |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Latif, M.; Hashmi, J.A.; Alayoubi, A.M.; Ayub, A.; Basit, S. Identification of Novel and Recurrent Variants in BTD, GBE1, AGL and ASL Genes in Families with Metabolic Disorders in Saudi Arabia. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 1193. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13051193
Latif M, Hashmi JA, Alayoubi AM, Ayub A, Basit S. Identification of Novel and Recurrent Variants in BTD, GBE1, AGL and ASL Genes in Families with Metabolic Disorders in Saudi Arabia. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(5):1193. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13051193
Chicago/Turabian StyleLatif, Muhammad, Jamil Amjad Hashmi, Abdulfatah M. Alayoubi, Arusha Ayub, and Sulman Basit. 2024. "Identification of Novel and Recurrent Variants in BTD, GBE1, AGL and ASL Genes in Families with Metabolic Disorders in Saudi Arabia" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 5: 1193. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13051193
APA StyleLatif, M., Hashmi, J. A., Alayoubi, A. M., Ayub, A., & Basit, S. (2024). Identification of Novel and Recurrent Variants in BTD, GBE1, AGL and ASL Genes in Families with Metabolic Disorders in Saudi Arabia. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(5), 1193. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13051193







